The 2β Splice Variation Alters the Structure and Function of the Stromal Interaction Molecule Coiled-Coil Domains
Abstract
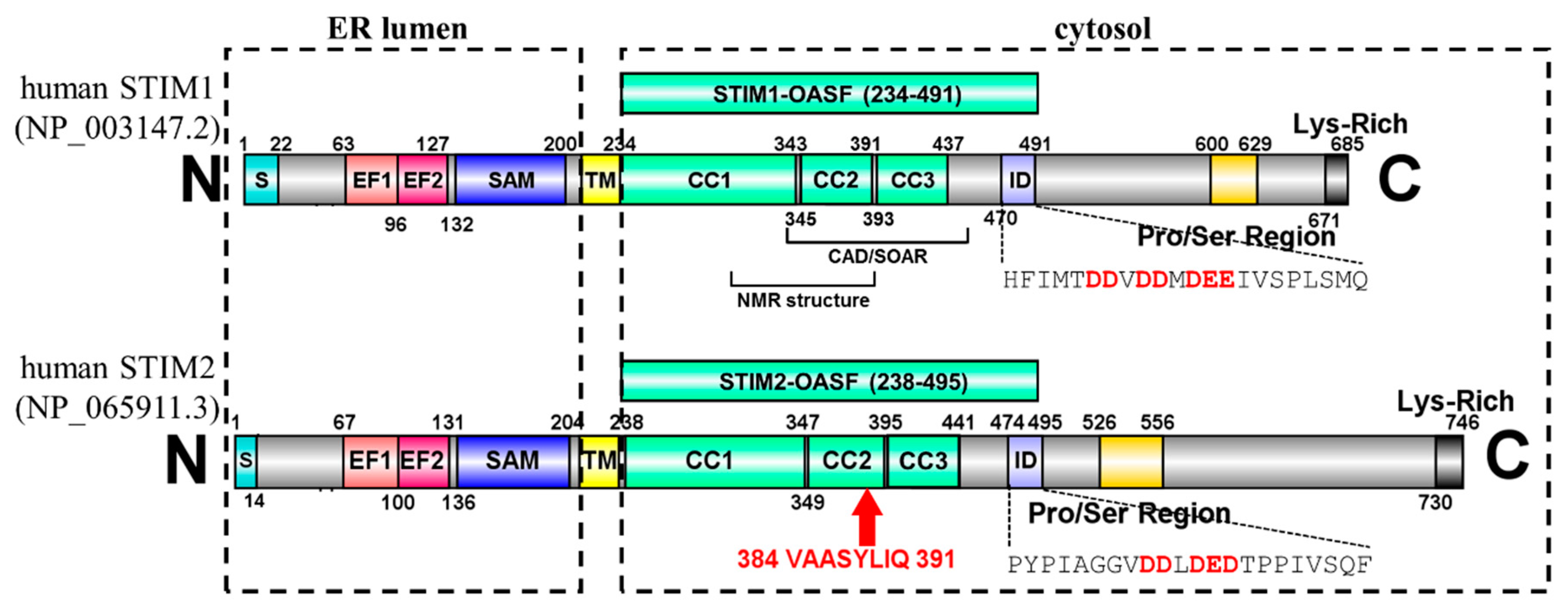
1. Introduction
2. Results
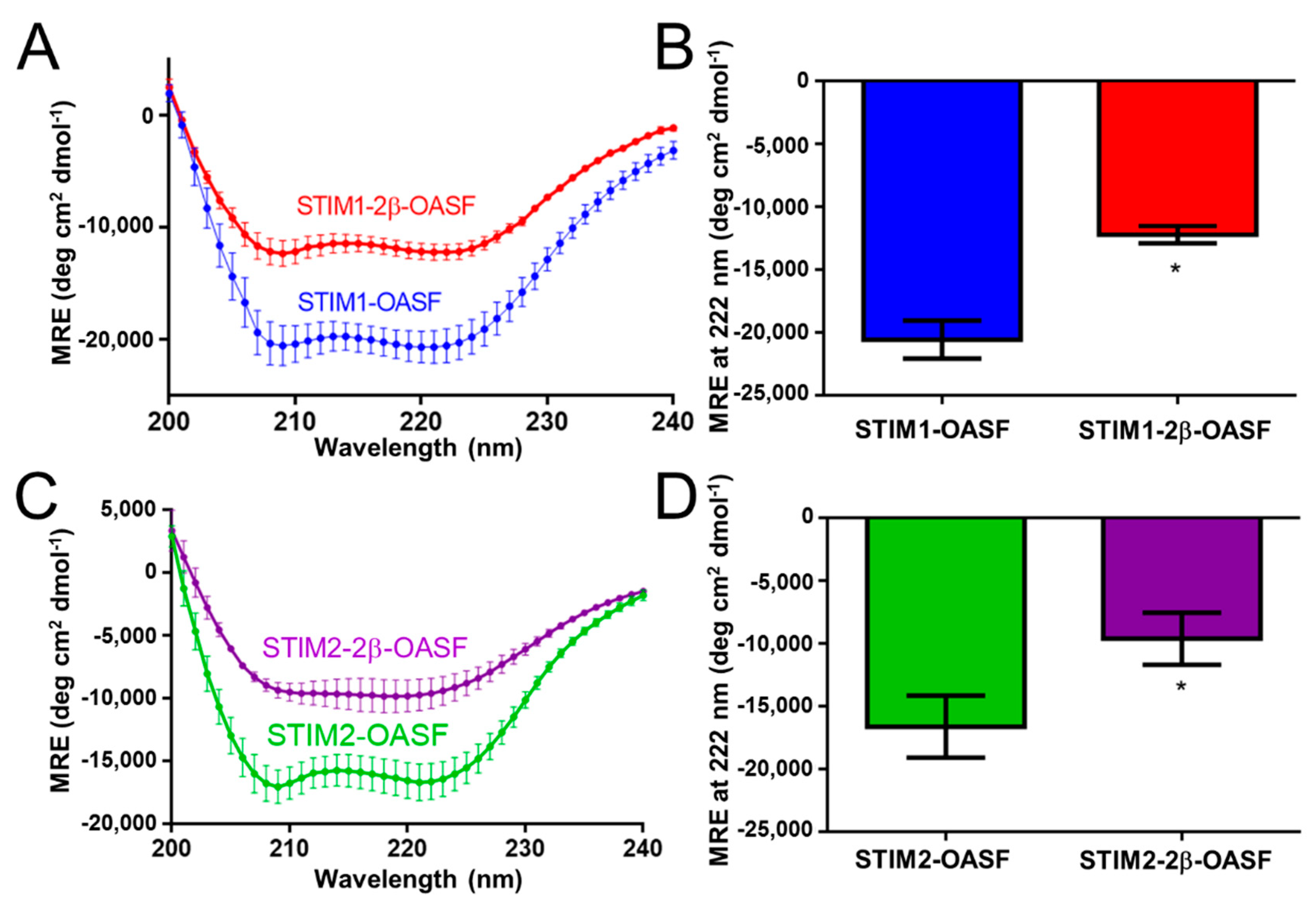
2.1. The 2β Insertion Decreases the α-Helicity of OASF
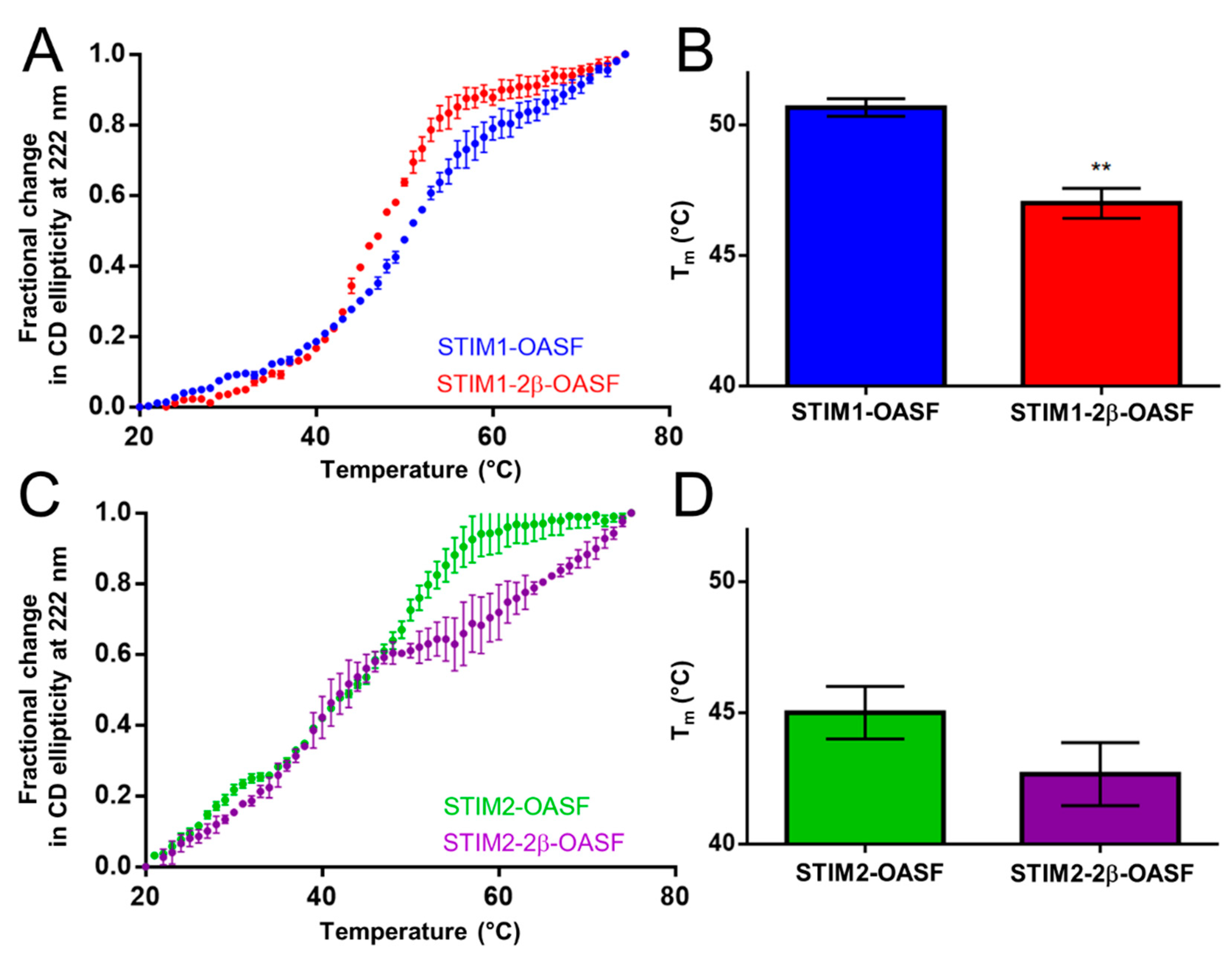
2.2. The 2β Insert Reduces the Thermal Stability of STIM1-OASF
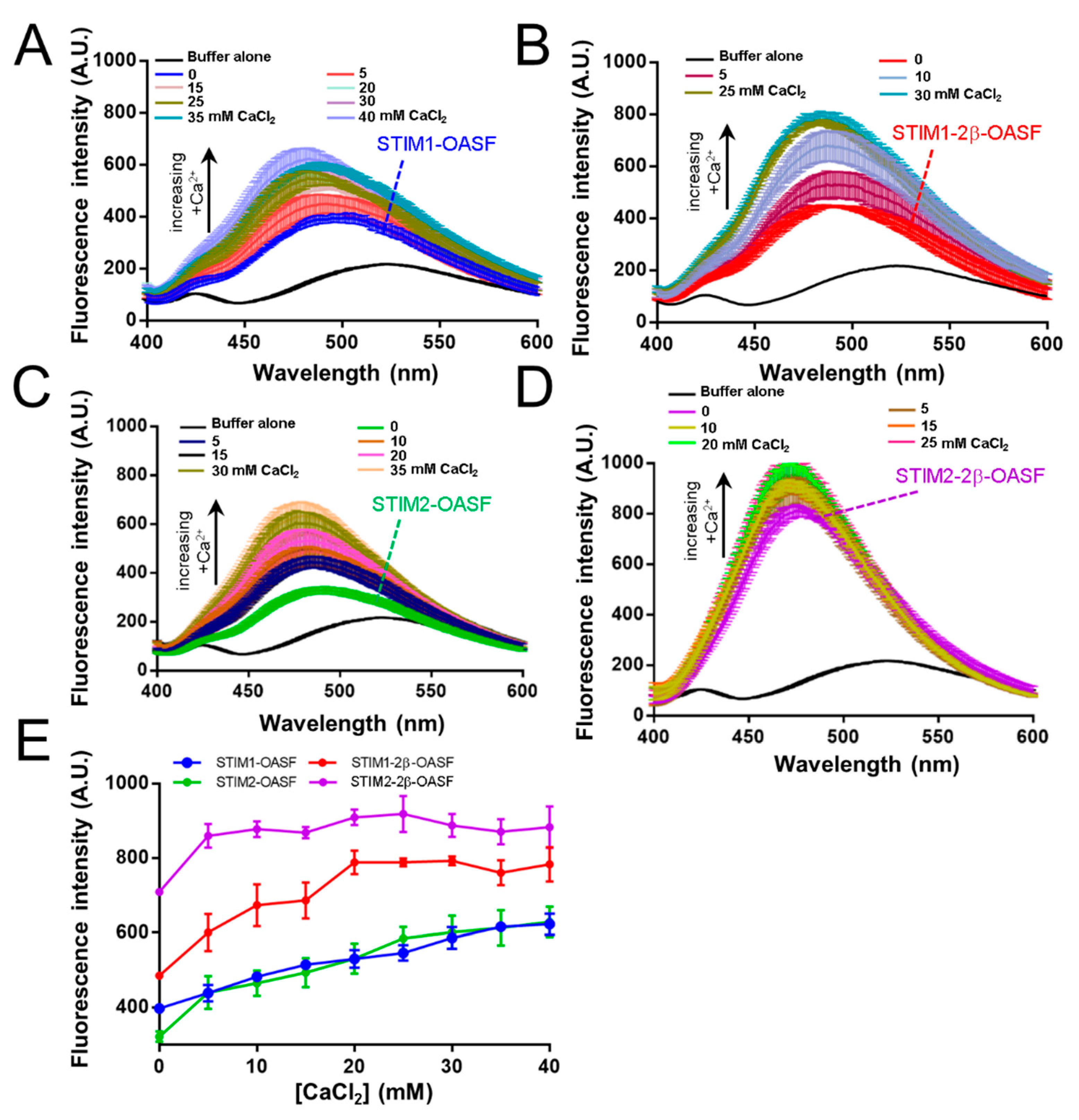
2.3. The 2β Insert Exacerbates Ca2+-Induced Hydrophobic Exposure of OASF
2.4. Ca2+ Minimally Affects the α-Helicity of the OASF Domains with or without 2β
2.5. Ca2+ Thermally Destabilizes STIM1-OASF and STIM1-2β-OASF
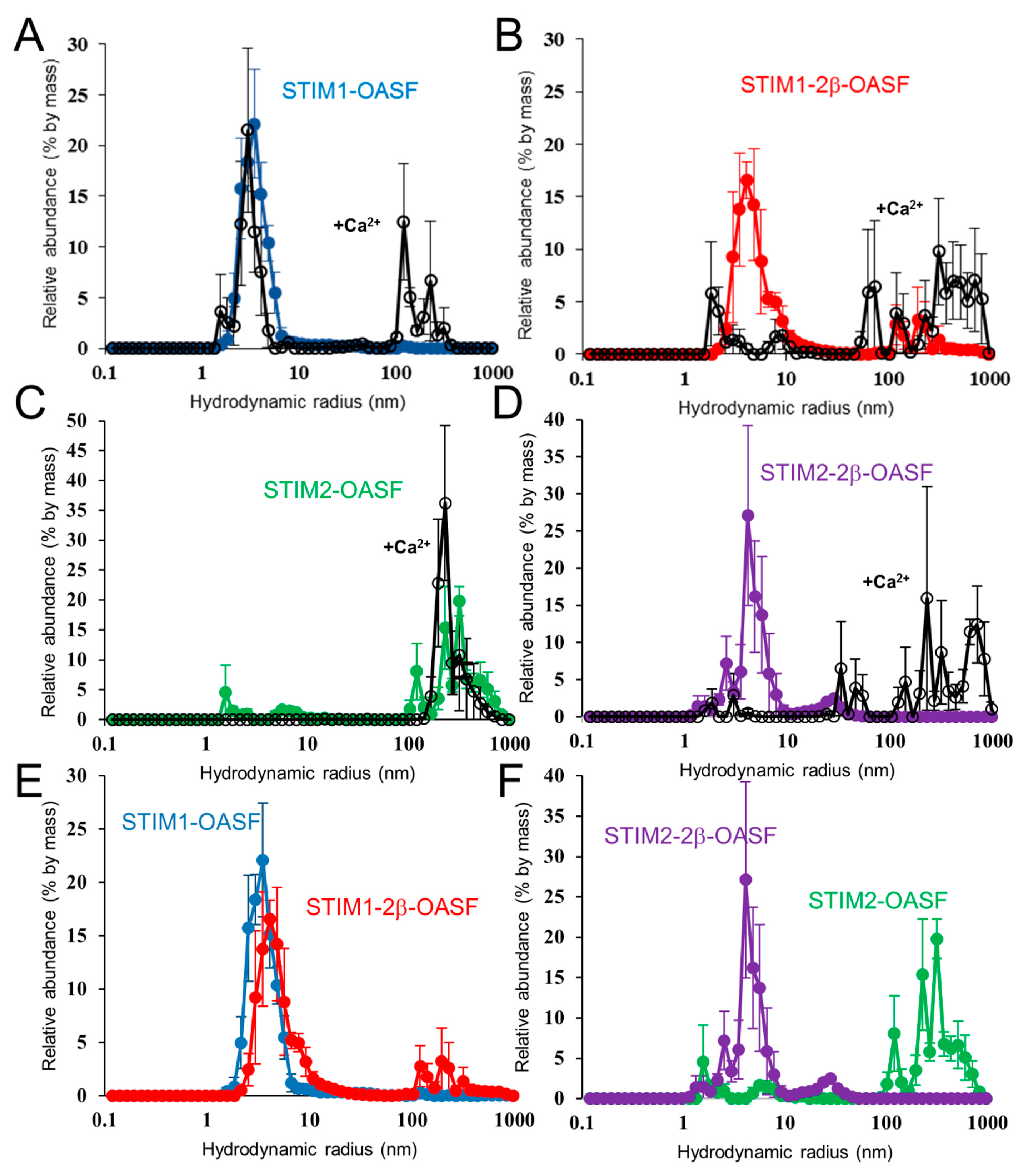
2.6. Ca2+ Increases the Aggregation Propensity of OASF
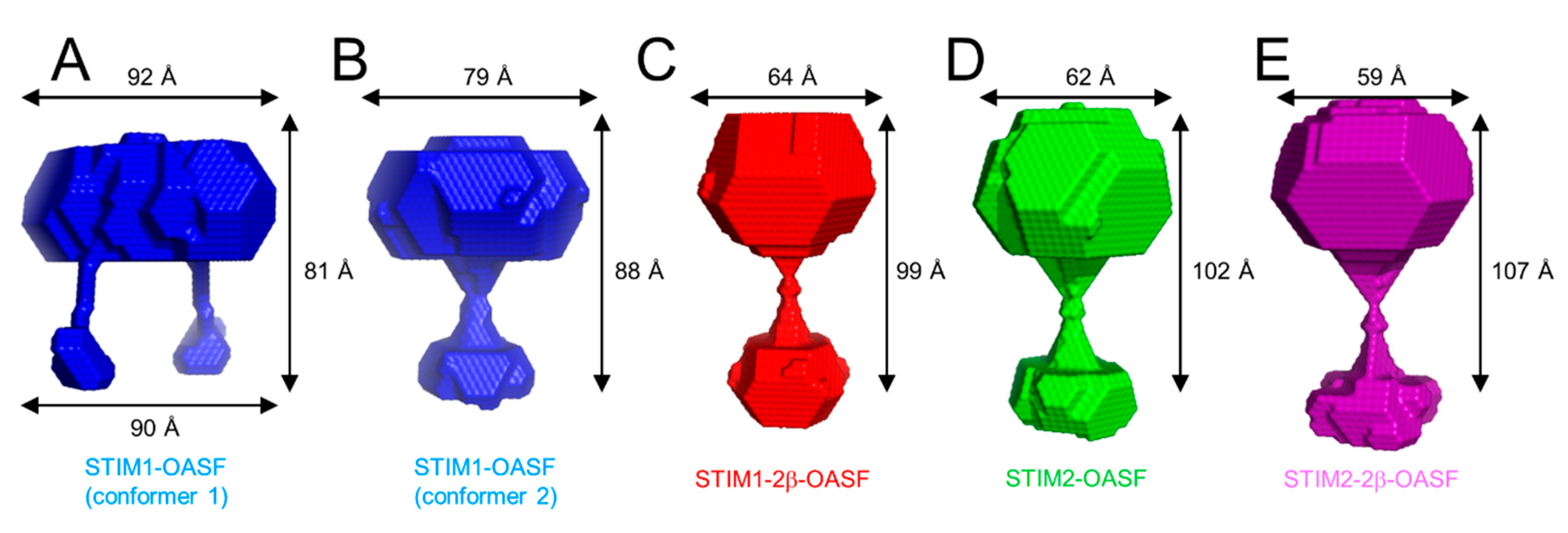
2.7. The 2β Insertion Does Not Alter OASF Dimer Quaternary Structure
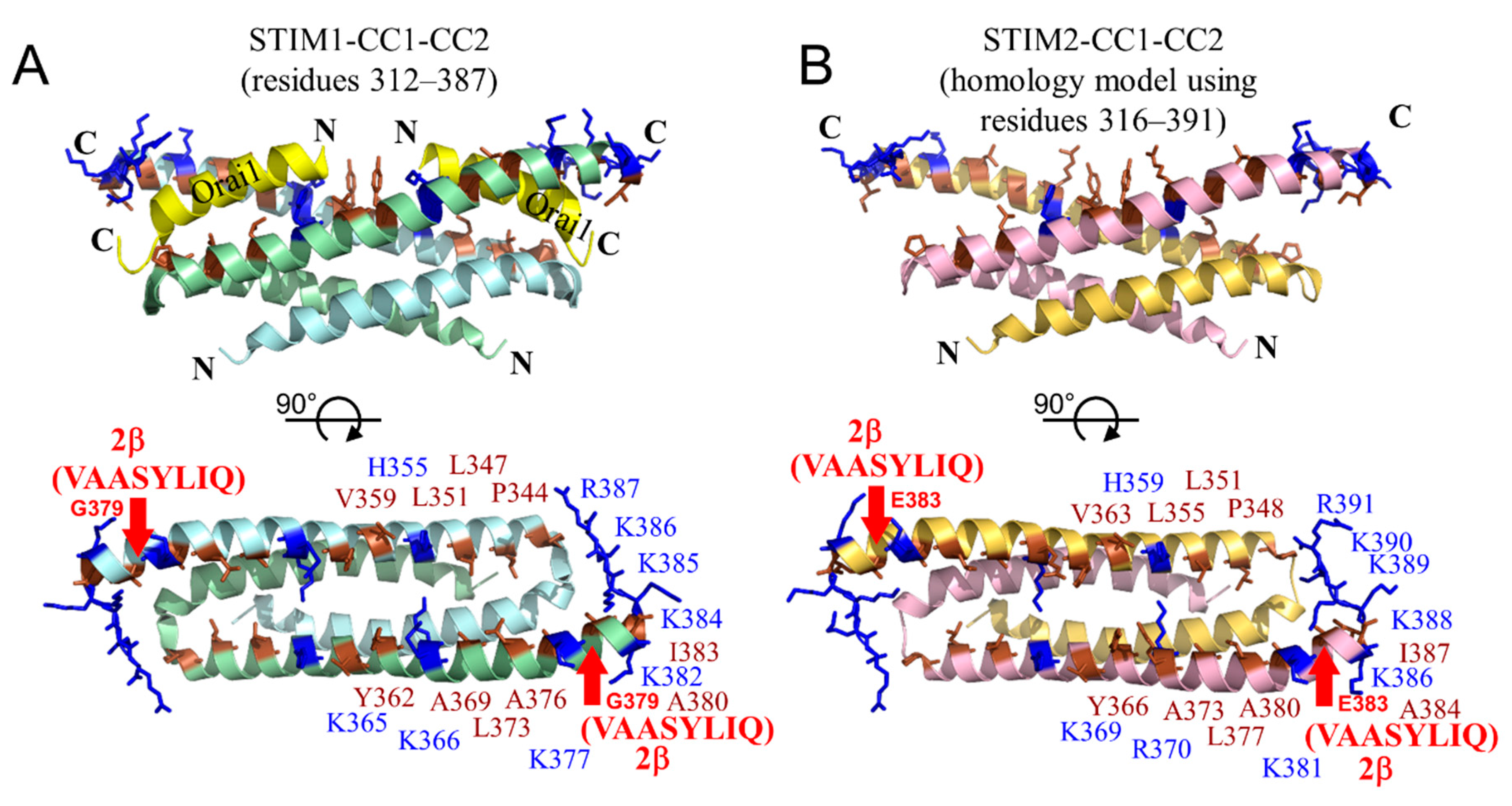
2.8. The 2β Insertion Causes Local Changes in OASF Structure
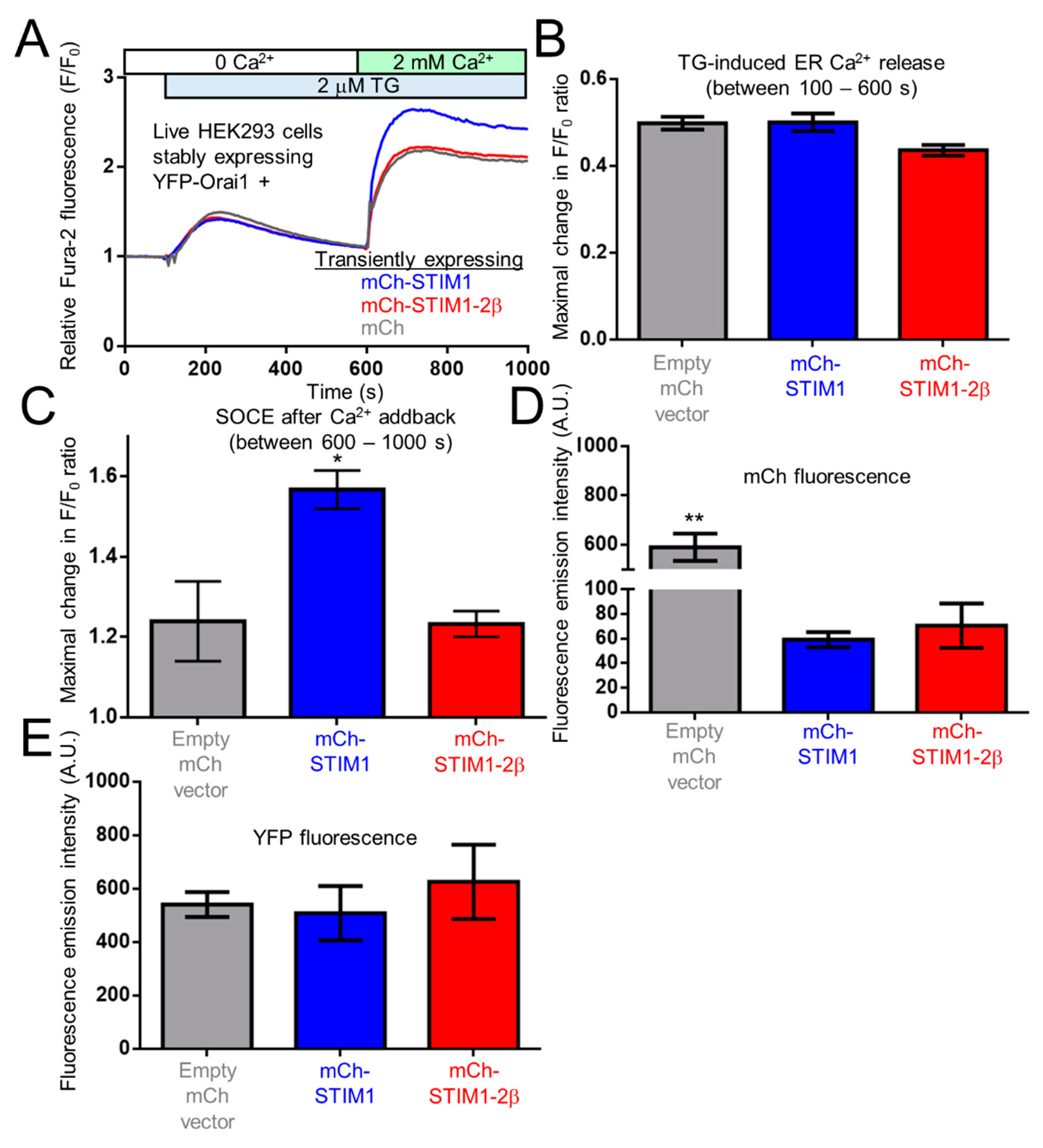
2.9. The 2β Insertion Inhibits OASF Function Independent of the STIM2 Context
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. STIM OASF Expression and Purification
4.2. Far UV CD Spectroscopy
4.3. ANS Fluorescence Spectroscopy
4.4. SEC-MALS
4.5. DLS
4.6. SAXS
4.7. Fura-2 Fluorimetry
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Putney, J.W.J. A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium 1986, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J.; Bootman, M.D.; Roderick, H.L. Calcium signalling: Dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, J.; Kim, M.L.; Heo, W.D.; Jones, J.T.; Myers, J.W.; Ferrell, J.E.J.; Meyer, T. STIM is a Ca2+ sensor essential for Ca2+-store-depletion-triggered Ca2+ influx. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, J.; DiGregorio, P.J.; Yeromin, A.V.; Ohlsen, K.; Lioudyno, M.; Zhang, S.; Safrina, O.; Kozak, J.A.; Wagner, S.L.; Cahalan, M.D.; et al. STIM1, an essential and conserved component of store-operated Ca2+ channel function. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.L.; Yu, Y.; Roos, J.; Kozak, J.A.; Deerinck, T.J.; Ellisman, M.H.; Stauderman, K.A.; Cahalan, M.D. STIM1 is a Ca2+ sensor that activates CRAC channels and migrates from the Ca2+ store to the plasma membrane. Nature 2005, 437, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feske, S.; Gwack, Y.; Prakriya, M.; Srikanth, S.; Puppel, S.H.; Tanasa, B.; Hogan, P.G.; Lewis, R.S.; Daly, M.; Rao, A. A mutation in Orai1 causes immune deficiency by abrogating CRAC channel function. Nature 2006, 441, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakriya, M.; Feske, S.; Gwack, Y.; Srikanth, S.; Rao, A.; Hogan, P.G. Orai1 is an essential pore subunit of the CRAC channel. Nature 2006, 443, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vig, M.; Beck, A.; Billingsley, J.M.; Lis, A.; Parvez, S.; Peinelt, C.; Koomoa, D.L.; Soboloff, J.; Gill, D.L.; Fleig, A.; et al. CRACM1 multimers form the ion-selective pore of the CRAC channel. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vig, M.; Peinelt, C.; Beck, A.; Koomoa, D.L.; Rabah, D.; Koblan-Huberson, M.; Kraft, S.; Turner, H.; Fleig, A.; Penner, R.; et al. CRACM1 is a plasma membrane protein essential for store-operated Ca2+ entry. Science 2006, 312, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeromin, A.V.; Zhang, S.L.; Jiang, W.; Yu, Y.; Safrina, O.; Cahalan, M.D. Molecular identification of the CRAC channel by altered ion selectivity in a mutant of Orai. Nature 2006, 443, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Fujii, Y.; Mizushima, A.; Watarai, H.; Wakamori, M.; Numaga, T.; Mori, Y.; Iino, M.; Hikida, M.; et al. Coupling of STIM1 to store-operated Ca2+ entry through its constitutive and inducible movement in the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16704–16709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, J.; Fivaz, M.; Inoue, T.; Meyer, T. Live-cell imaging reveals sequential oligomerization and local plasma membrane targeting of stromal interaction molecule 1 after Ca2+ store depletion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9301–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luik, R.M.; Wu, M.M.; Buchanan, J.; Lewis, R.S. The elementary unit of store-operated Ca2+ entry: Local activation of CRAC channels by STIM1 at ER-plasma membrane junctions. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 174, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.M.; Buchanan, J.; Luik, R.M.; Lewis, R.S. Ca2+ store depletion causes STIM1 to accumulate in ER regions closely associated with the plasma membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 174, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.N.; Zeng, W.; Kim, J.Y.; Yuan, J.P.; Han, L.; Muallem, S.; Worley, P.F. STIM1 carboxyl-terminus activates native SOC, I(crac) and TRPC1 channels. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Lange, I.; Feske, S. A minimal regulatory domain in the C terminus of STIM1 binds to and activates ORAI1 CRAC channels. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 385, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muik, M.; Frischauf, I.; Derler, I.; Fahrner, M.; Bergsmann, J.; Eder, P.; Schindl, R.; Hesch, C.; Polzinger, B.; Fritsch, R.; et al. Dynamic coupling of the putative coiled-coil domain of ORAI1 with STIM1 mediates ORAI1 channel activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 8014–8022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.Y.; Hoover, P.J.; Mullins, F.M.; Bachhawat, P.; Covington, E.D.; Raunser, S.; Walz, T.; Garcia, K.C.; Dolmetsch, R.E.; Lewis, R.S. STIM1 clusters and activates CRAC channels via direct binding of a cytosolic domain to Orai1. Cell 2009, 136, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.P.; Zeng, W.; Dorwart, M.R.; Choi, Y.J.; Worley, P.F.; Muallem, S. SOAR and the polybasic STIM1 domains gate and regulate Orai channels. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X. Molecular evolution and functional divergence of the Ca2+ sensor protein in store-operated Ca2+ entry: Stromal interaction molecule. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.T.; Manji, S.S.; Parker, N.J.; Hancock, M.S.; Van Stekelenburg, L.; Eid, J.P.; Senior, P.V.; Kazenwadel, J.S.; Shandala, T.; Saint, R.; et al. Identification and characterization of the STIM (stromal interaction molecule) gene family: Coding for a novel class of transmembrane proteins. Biochem. J. 2001, 357, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stathopulos, P.B.; Li, G.Y.; Plevin, M.J.; Ames, J.B.; Ikura, M. Stored Ca2+ depletion-induced oligomerization of stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) via the EF-SAM region: An initiation mechanism for capacitive Ca2+ entry. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35855–35862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stathopulos, P.B.; Zheng, L.; Li, G.Y.; Plevin, M.J.; Ikura, M. Structural and mechanistic insights into STIM1-mediated initiation of store-operated calcium entry. Cell 2008, 135, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, B.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Dong, C.; Shen, Y. The inhibitory helix controls the intramolecular conformational switching of the C-terminus of STIM1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derler, I.; Fahrner, M.; Muik, M.; Lackner, B.; Schindl, R.; Groschner, K.; Romanin, C. A CRAC modulatory domain (CMD) within STIM1 mediates fast Ca2+-dependent inactivation of ORAI1 channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 24933–24938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.P.; Yuan, J.P.; Zeng, W.; So, I.; Worley, P.F.; Muallem, S. Molecular determinants of fast Ca2+-dependent inactivation and gating of the Orai channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14687–14692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muik, M.; Fahrner, M.; Schindl, R.; Stathopulos, P.; Frischauf, I.; Derler, I.; Plenk, P.; Lackner, B.; Groschner, K.; Ikura, M.; et al. STIM1 couples to ORAI1 via an intramolecular transition into an extended conformation. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1678–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novello, M.J.; Zhu, J.; Feng, Q.; Ikura, M.; Stathopulos, P.B. Structural elements of stromal interaction molecule function. Cell Calcium 2018, 73, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandman, O.; Liou, J.; Park, W.S.; Meyer, T. STIM2 is a feedback regulator that stabilizes basal cytosolic and endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ levels. Cell 2007, 131, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Stathopulos, P.B.; Schindl, R.; Li, G.Y.; Romanin, C.; Ikura, M. Auto-inhibitory role of the EF-SAM domain of STIM proteins in store-operated calcium entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Lu, X.; Feng, Q.; Stathopulos, P.B. A charge-sensing region in the stromal interaction molecule 1 luminal domain confers stabilization-mediated inhibition of SOCE in response to S-nitrosylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 8900–8911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Srinivasan, P.; Razavi, S.; Seymour, S.; Meraner, P.; Gudlur, A.; Stathopulos, P.B.; Ikura, M.; Rao, A.; Hogan, P.G. Initial activation of STIM1, the regulator of store-operated calcium entry. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covington, E.D.; Wu, M.M.; Lewis, R.S. Essential role for the CRAC activation domain in store-dependent oligomerization of STIM1. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muik, M.; Fahrner, M.; Derler, I.; Schindl, R.; Bergsmann, J.; Frischauf, I.; Groschner, K.; Romanin, C. A cytosolic homomerization and a modulatory domain within STIM1 C terminus determine coupling to ORAI1 channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 8421–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korzeniowski, M.K.; Popovic, M.A.; Szentpetery, Z.; Varnai, P.; Stojilkovic, S.S.; Balla, T. Dependence of STIM1/Orai1-mediated calcium entry on plasma membrane phosphoinositides. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 21027–21035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, C.M.; Chvanov, M.; Haynes, L.P.; Petersen, O.H.; Tepikin, A.V.; Burgoyne, R.D. Role of phosphoinositides in STIM1 dynamics and store-operated calcium entry. Biochem. J. 2010, 425, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calloway, N.; Owens, T.; Corwith, K.; Rodgers, W.; Holowka, D.; Baird, B. Stimulated association of STIM1 and Orai1 is regulated by the balance of PtdIns(4,5)P(2) between distinct membrane pools. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 2602–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, B.A.; Somasundaram, A.; Jairaman, A.; Yamashita, M.; Prakriya, M. The C- and N-terminal STIM1 binding sites on Orai1 are required for both trapping and gating CRAC channels. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 2833–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miederer, A.M.; Alansary, D.; Schwar, G.; Lee, P.H.; Jung, M.; Helms, V.; Niemeyer, B.A. A STIM2 splice variant negatively regulates store-operated calcium entry. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; Yen, M.; Sadaghiani, A.M.; Malmersjo, S.; Park, C.Y.; Dolmetsch, R.E.; Lewis, R.S. Alternative splicing converts STIM2 from an activator to an inhibitor of store-operated calcium channels. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 209, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hendron, E.; Mancarella, S.; Andrake, M.D.; Rothberg, B.S.; Soboloff, J.; Gill, D.L. Distinct Orai-coupling domains in STIM1 and STIM2 define the Orai-activating site. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Mancarella, S.; Wang, Y.; Yue, C.; Ritchie, M.; Gill, D.L.; Soboloff, J. The short N-terminal domains of STIM1 and STIM2 control the activation kinetics of Orai1 channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19164–19168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, D.; Svergun, D.I. DAMMIF, a program for rapid ab-initio shape determination in small-angle scattering. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misceo, D.; Holmgren, A.; Louch, W.E.; Holme, P.A.; Mizobuchi, M.; Morales, R.J.; de Paula, A.M.; Stray-Pedersen, A.; Lyle, R.; Dalhus, B.; et al. A dominant STIM1 mutation causes Stormorken syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, G.; Bruechle, N.O.; Singh, A.R.; Knopp, C.; Jedraszak, G.; Elbracht, M.; Bremond-Gignac, D.; Hartmann, K.; Sevestre, H.; Deutz, P.; et al. Gain-of-function mutation in STIM1 (P.R304W) is associated with stormorken syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahrner, M.; Stadlbauer, M.; Muik, M.; Rathner, P.; Stathopulos, P.; Ikura, M.; Muller, N.; Romanin, C. A dual mechanism promotes switching of the Stormorken STIM1 R304W mutant into the activated state. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, S.; Rensing-Ehl, A.; Speckmann, C.; Bengsch, B.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Bondzio, I.; Maul-Pavicic, A.; Bass, T.; Vraetz, T.; Strahm, B.; et al. Antiviral and regulatory T cell immunity in a patient with stromal interaction molecule 1 deficiency. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maus, M.; Jairaman, A.; Stathopulos, P.B.; Muik, M.; Fahrner, M.; Weidinger, C.; Benson, M.; Fuchs, S.; Ehl, S.; Romanin, C.; et al. Missense mutation in immunodeficient patients shows the multifunctional roles of coiled-coil domain 3 (CC3) in STIM1 activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6206–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.L.; Shuttleworth, T.J. Anchoring protein AKAP79-mediated PKA phosphorylation of STIM1 determines selective activation of the ARC channel, a store-independent Orai channel. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.L.; Zhao, Y.; Stathopulos, P.B.; Grossfield, A.; Shuttleworth, T.J. Phosphorylation-mediated structural changes within the SOAR domain of stromal interaction molecule 1 enable specific activation of distinct Orai channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 3145–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Nwokonko, R.M.; Cai, X.; Loktionova, N.A.; Abdulqadir, R.; Xin, P.; Niemeyer, B.A.; Wang, Y.; Trebak, M.; Gill, D.L. Cross-linking of orai1 channels by STIM proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3398–E3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, M.; Head, J.F.; Persechini, A.; Kretsinger, R.H.; Engelman, D.M. Small-angle X-ray scattering studies of calmodulin mutants with deletions in the linker region of the central helix indicate that the linker region retains a predominantly alpha-helical conformation. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stathopulos, P.B.; Schindl, R.; Fahrner, M.; Zheng, L.; Gasmi-Seabrook, G.M.; Muik, M.; Romanin, C.; Ikura, M. STIM1/Orai1 coiled-coil interplay in the regulation of store-operated calcium entry. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Protein Structure Modeling with MODELLER. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1654, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franke, D.; Petoukhov, M.V.; Konarev, P.V.; Panjkovich, A.; Tuukkanen, A.; Mertens, H.D.T.; Kikhney, A.G.; Hajizadeh, N.R.; Franklin, J.M.; Jeffries, C.M.; et al. ATSAS 2.8: A comprehensive data analysis suite for small-angle scattering from macromolecular solutions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2017, 50, 1212–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petoukhov, M.V.; Franke, D.; Shkumatov, A.V.; Tria, G.; Kikhney, A.G.; Gajda, M.; Gorba, C.; Mertens, H.D.; Konarev, P.V.; Svergun, D.I. New developments in the ATSAS program package for small-angle scattering data analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Protein | Ca2+ (a) | Elution Volume (mL) (b) | Molecular Weight (kDa) (c) | Stoichiometric Ratio (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STIM1-OASF | − | 13.59 ± 0.14 | 67.6 ± 1.4 | 2.18 |
| STIM1-2β-OASF | − | 12.69 ± 0.05 | 64.9 ± 1.7 | 2.02 |
| STIM2-OASF | − | 12.69 ± 0.02 | 61.4 ± 1.3 | 1.98 |
| STIM2-2β-OASF | − | 12.85 ± 0.02 | 60.8 ± 0.2 | 1.96 |
| STIM1-OASF | + | 13.55 ± 0.01 | 62.3 ± 3.7 | 2.00 |
| STIM1-2β-OASF | + | 13.03 ± 0.30 | 63.0 ± 1.3 | 1.96 |
| STIM2-OASF | + | 12.76 ± 0.08 | 61.8 ± 2.1 | 1.99 |
| STIM2-2β-OASF | + | 12.87 ± 0.20 | 61.3 ± 1.6 | 1.97 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, S.; Zhang, M.; Stathopulos, P.B. The 2β Splice Variation Alters the Structure and Function of the Stromal Interaction Molecule Coiled-Coil Domains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113316
Chung S, Zhang M, Stathopulos PB. The 2β Splice Variation Alters the Structure and Function of the Stromal Interaction Molecule Coiled-Coil Domains. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113316
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Steve, MengQi Zhang, and Peter B. Stathopulos. 2018. "The 2β Splice Variation Alters the Structure and Function of the Stromal Interaction Molecule Coiled-Coil Domains" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113316
APA StyleChung, S., Zhang, M., & Stathopulos, P. B. (2018). The 2β Splice Variation Alters the Structure and Function of the Stromal Interaction Molecule Coiled-Coil Domains. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113316






