Regulatory Efficacy of the Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids from Microalgae Spirulina platensis on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Potent Major Compounds
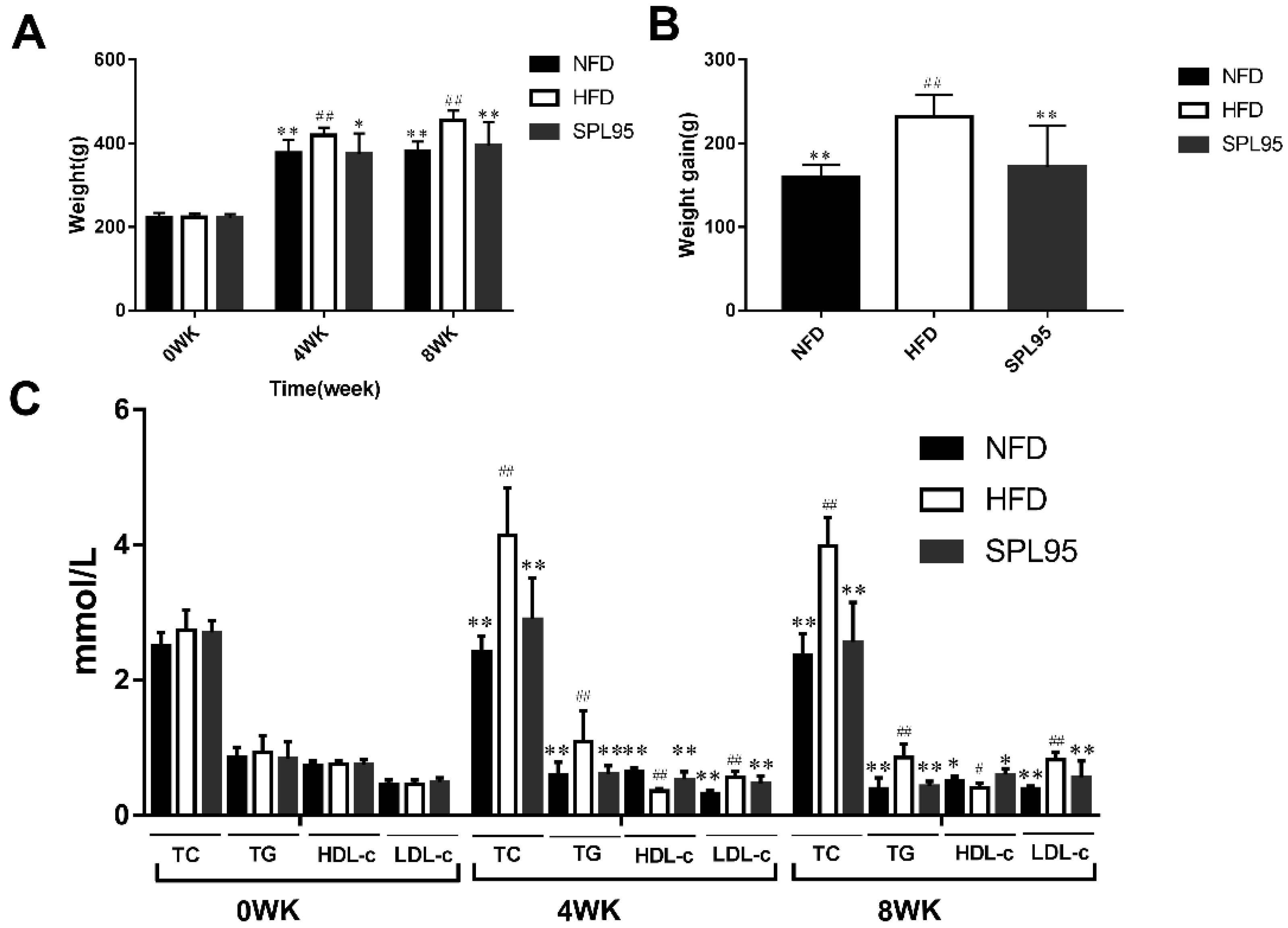
2.2. Effect of SPL95 on Body Weight and Serum Lipids of High-Fat-Diet Rats
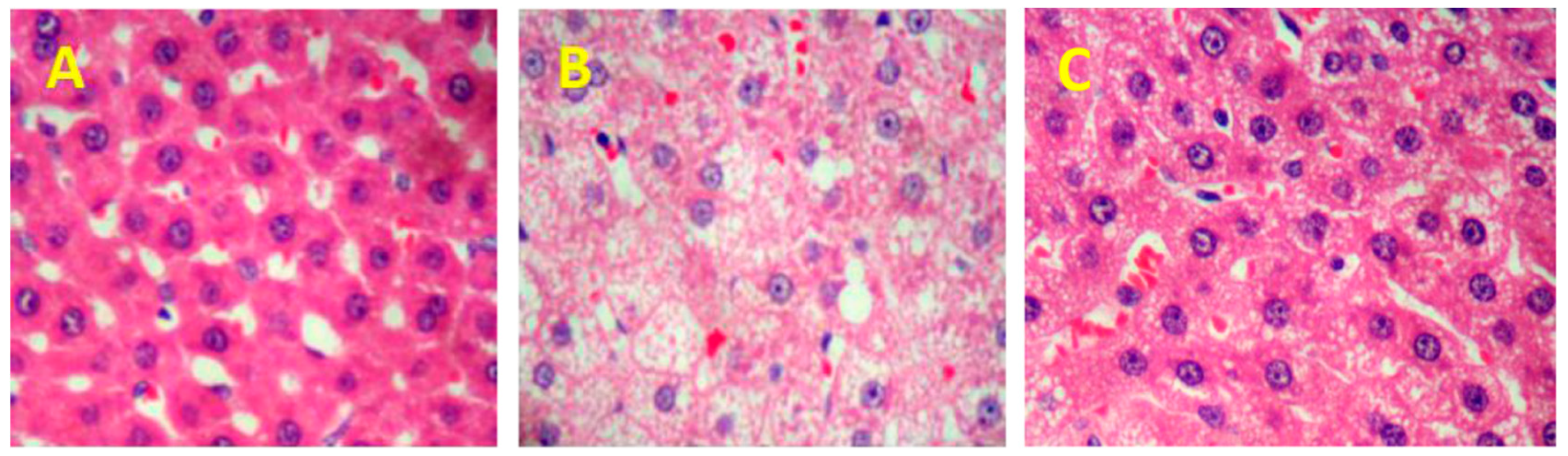
2.3. SPL95 Attenuates HFD-Induced Hepatic Steatosis
2.4. Effect of SPL95 on Liver Function
2.5. Effect of SPL95 on mRNA and Protein Levels Involved in Lipid and Glucose Metabolism
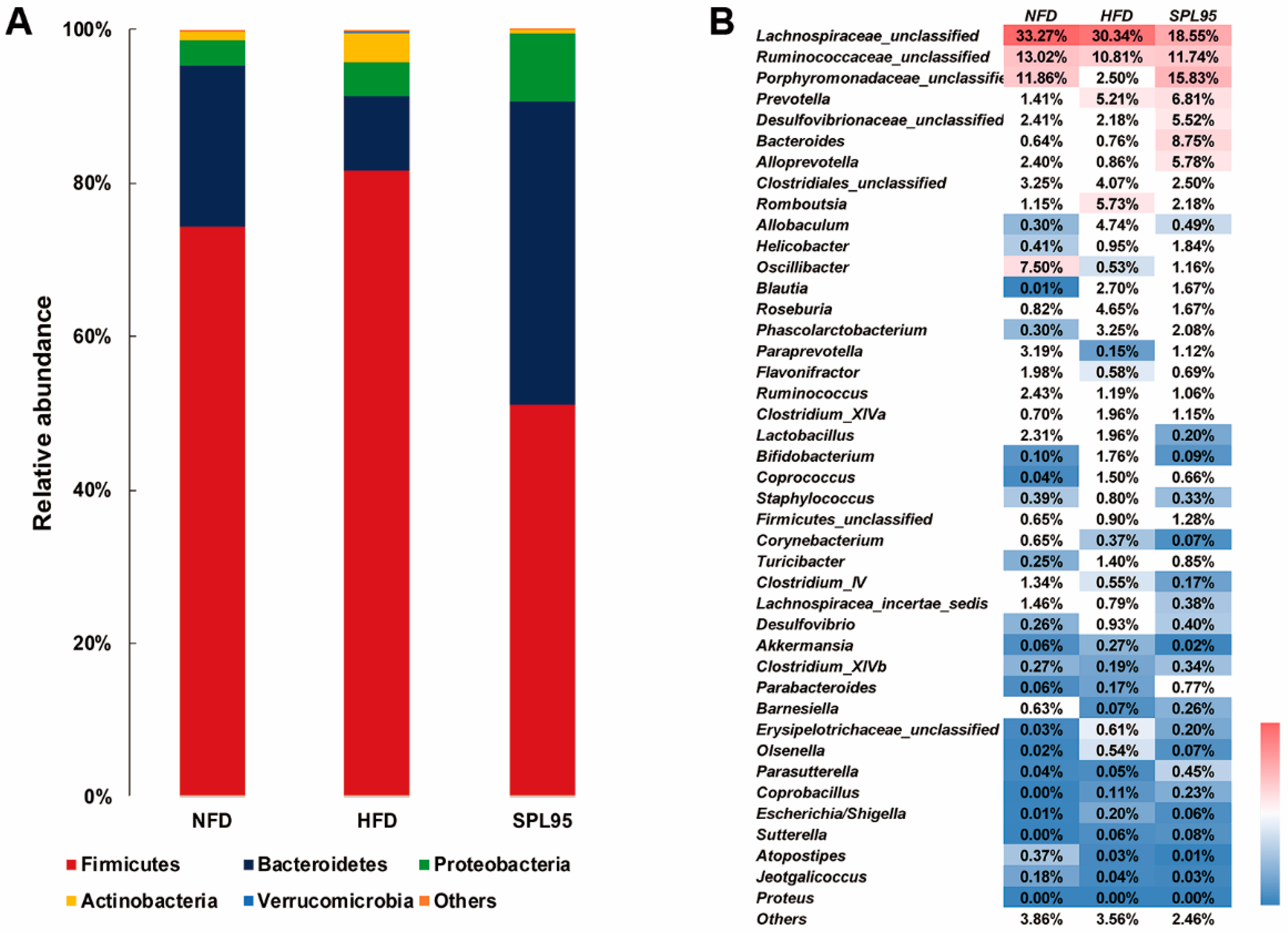
2.6. SPL95 Modulated Gut Microbiota of High-Fat-Diet Rats
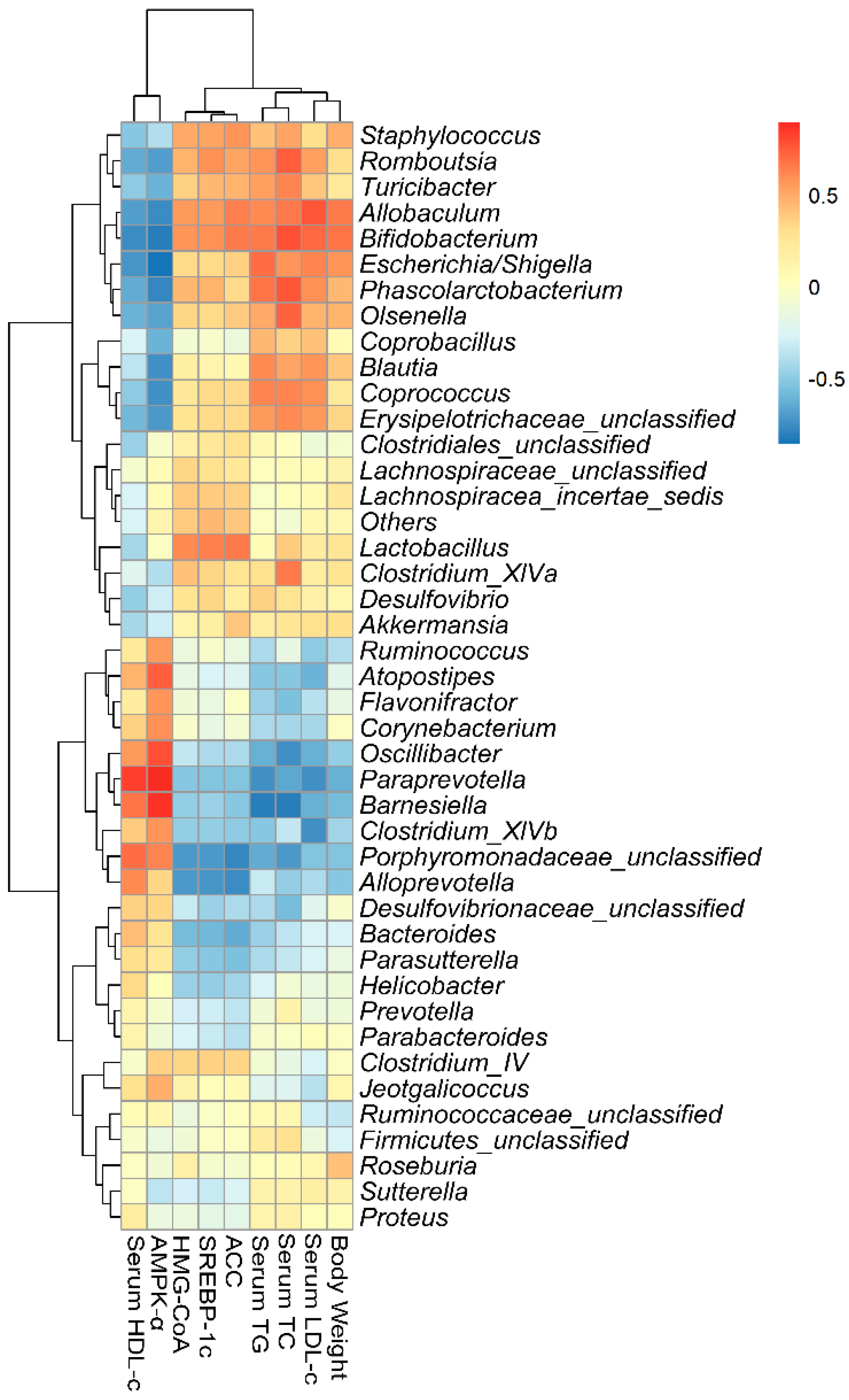
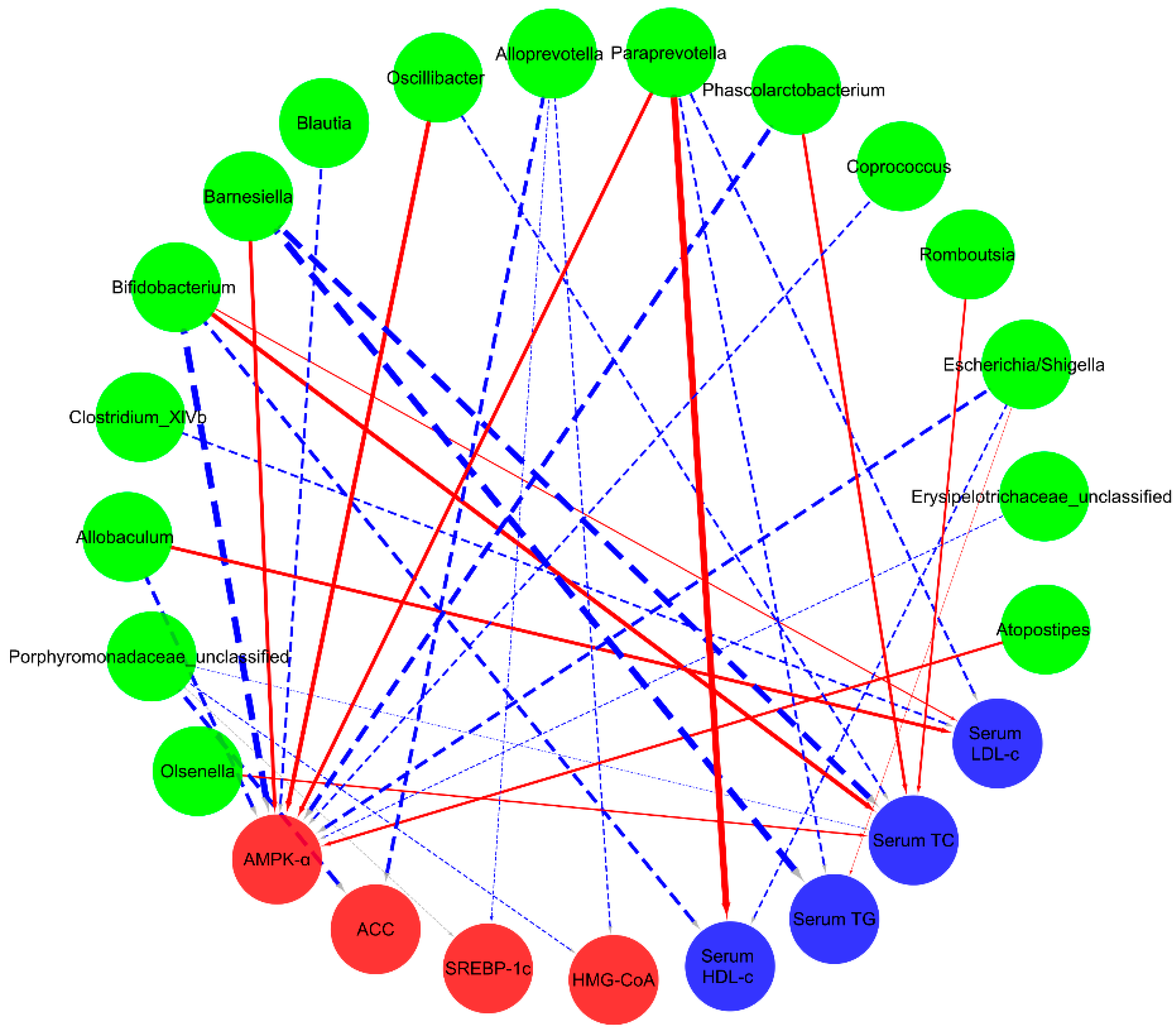
2.7. Correlations of Biochemical Data and Key Phylotypes of Caecal Microbiota
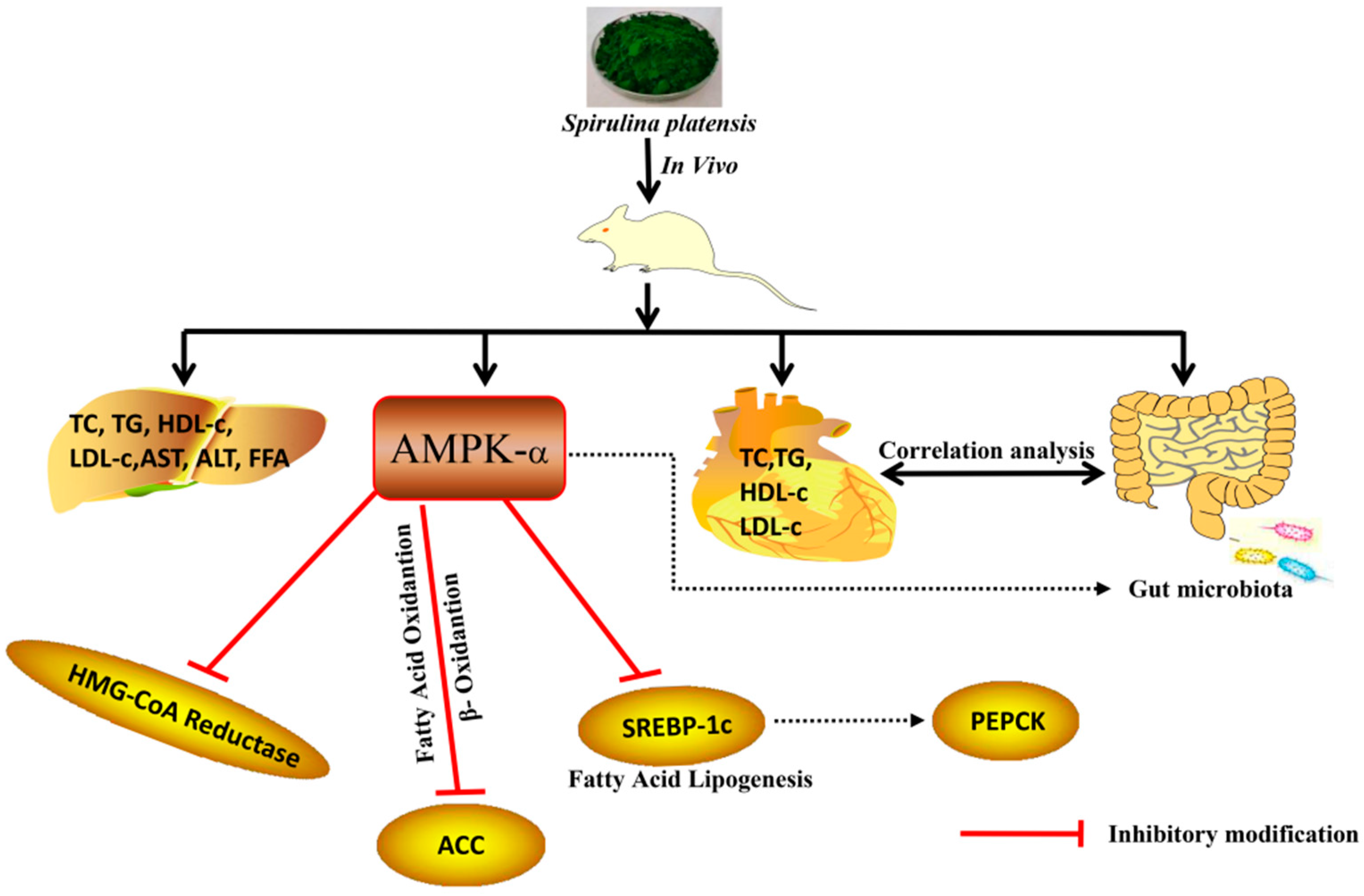
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Spirulina platensis Extracts
4.2. UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS Analysis of SPL95
4.3. Experimental Animals
4.4. Serum Samples Preparation
4.5. Liver Homogenate Preparation
4.6. Biochemical Assays
4.7. Liver Histopathological Analysis
4.8. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR (RT-qPCR) Analysis
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Dynamic Profile of Intestinal Microflora in Response to SPL95
4.11. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, F.; Dong, H.; Fang, K.; Gong, J.; Lu, F.E. Effects of green tea on lipid metabolism in overweight or obese people: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 62, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, T.; Sato, M.; Dehle, F.C.; Brnabic, A.J.M.; Weston, A.; Burge, R. Lifestyle-related metabolic disorders, osteoporosis, and fracture risk in Asia: A systematic review. Value Health Reg. Issues 2016, 9, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waness, A.; Bahlas, S.; Al, S.S. Simvastatin-induced rhabdomyolysis and acute renal injury. Blood Purif. 2008, 26, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, S.; Kaman, L.; Dahiya, D.; Behera, A.; Medhi, B.; Chawla, Y. Effects of preoperative statin on liver reperfusion injury in major hepatic resection: A pilot study. Updates Surg. 2016, 68, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, Y.J.; Yang, C.F.; Liu, B.; Huang, Y.F. Hypotensive, hypoglycaemic and hypolipidaemic effects of bioactive compounds from microalgae and marine micro-organisms. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, C.F.; Liu, B.; Lin, L.; Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L.; Yu, H.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J.B. Bioactive compounds from marine macroalgae and their hypoglycemic benefits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.T.; Chow, T.J. Hypolipidemic, antioxidant, and antiinflammatory activities of microalgae Spirulina. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2010, 28, e33–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serban, M.C.; Sahebkar, A.; Dragan, S.; Stoichescu-Hogea, G.; Ursoniu, S.; Andrica, F.; Banach, M. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of Spirulina supplementation on plasma lipid concentrations. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Taminiau, B.; Walgrave, H.; Daube, G.; Cani, P.D.; Bindels, L.B.; Delzenneet, N.M. Spirulina protects against hepatic inflammation in aging: An effect related to the modulation of the gut microbiota? Nutrients. 2017, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grahame Hardie, D. AMP-activated protein kinase: A key regulator of energy balance with many roles in human disease. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Xu, N.; Zhao, W.X.; Su, J.J.; Liang, M.R.; Xie, Z.W.; Wu, X.L.; Li, Q.L. (-)-Epicatechin regulates blood lipids and attenuates hepatic steatosis in rats fed high-fat diet. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deboseboyd, R.A. Feedback regulation of cholesterol synthesis: Sterol-accelerated ubiquitination and degradation of HMG-CoA reductase. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, M.R. Regulation of mammalian acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2002, 30, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, C.F.; Wai, S.T.C.; Zhang, Y.B.; Portillo, M.Y.; Paoli, P.; Wu, Y.J.; Cheang, W.S.; Liu, B.; Carpéné, C.; et al. Regulation of glucose metabolism by bioactive phytochemicals for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, B.; He, Z.; Wang, S.; Salih, O.; Wang, Q. Study on Co-Liquefaction of Spirulina and Spartina alterniflora in ethanol-water co-solvent for bio-oil. Energy 2018, 155, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignitter, M.; Stolze, K.; Jirsa, F.; Gille, L.; Goodman, B.A.; Somoza, V. Effect of copper on fatty acid profiles in non-and semifermented teas analyzed by LC-MS-based nontargeted screening. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8519–8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, M.; Vicente, M.J.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibanez, E. Characterization by high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry of the lipid fraction of Spirulina platensis pressurized ethanol extract. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 21, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.A.; Azlan, A.; Ismail, A.; Hashim, P.; Gani, S.S.A.; Zainudin, B.H.; Abdullah, N.A. Phenolic composition, antioxidant, anti-wrinkles and tyrosinase inhibitory activities of cocoa pod extract. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buettner, R.; Parhofer, K.G.; Woenckhaus, M.; Wrede, C.E.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Schölmerich, J.; Bollheimer, L.C. Defining high-fat-diet rat models: Metabolic and molecular effects of different fat types. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 36, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, Y.; Maebara, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Nagae, R.; Tokuyama, S.; Michinaga, S. Endothelins reciprocally regulate VEGF-A and angiopoietin-1 production in cultured rat astrocytes: Implications on astrocytic proliferation. Glia 2012, 60, 1954–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Ha, T.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.J.; Ahn, J. Red paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) and its main carotenoid capsanthin ameliorate impaired lipid metabolism in the liver and adipose tissue of high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 31, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobert, J.A. Lovastatin and beyond: The history of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.R.; Ma, H.; Feng, M.; Li, X.G.; Ye, X. Epiberberine reduces serum cholesterol in diet-induced dyslipidemia Syrian golden hamsters via network pathways involving cholesterol metabolism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 774, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahma Naidu, P.; Uddandrao, V.V.S.; Ravindar Naik, R.; Suresh, P.; Meriga, B.; Begum, M.S.; Pandiyan, R.; Saravanan, G. Ameliorative potential of gingerol: Promising modulation of inflammatory factors and lipid marker enzymes expressions in HFD induced obesity in rats. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 419, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Srebps: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, K.T.; Chang, E.B. Diet, gut microbes, and the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 61, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, J.; Watanabe, K.; Jiang, J.; Matsuda, K.; Chao, S.H.; Haryono, P.; La-Ongkham, O.; Sarwoko, M.A.; Sujaya, I.N.; Zhao, L.; et al. Diversity in gut bacterial community of school-age children in Asia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8397–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubeda, C.; Bucci, V.; Caballero, S.; Djukovic, A.; Toussaint, N.C.; Equinda, M.; Lipuma, L.; Ling, L.; Gobourne, A.; No, D.; et al. Intestinal microbiota containing Barnesiella species cures vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium colonization. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Q.S.; Song, G.R.; Zhang, M.F.; Shi, J.J.; Xu, C.Y.; Hao, J.J.; Li, G.Y.; Yu, G.L. Dietary fucoidan improves metabolic syndrome in association with increased Akkermansia population in the gut microbiota of high-fat diet-fed mice. J. Funct. Foods. 2017, 28, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Jin, C.; Hao, L.; Mehal, W.Z.; Strowig, T.; Thaiss, C.A.; Kau, A.L.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature 2012, 482, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.Q.; Xing, X.B.; Du, Z.X.; Guo, Q.Z.; Yu, W.L. The detection and identification of leachables in vaccine from plastic packaging materials using UPLC-QTOF MS with self-built polymer additives library. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6749–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.R.; Zhou, W.B.; Yang, X.L.; Tong, A.J.; Hong, J.L.; Jia, R.B.; Lin, J.; Li, T.T.; Pan, Y.Y.; Lv, X.C.; et al. The regulation mechanisms of soluble starch and glycerol for production of azaphilone pigments in Monascus purpureus FAFU618 as revealed by comparative proteomic and transcriptional analyses. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.C.; Chen, G.; Li, B.; Ji, B.P.; Guo, Y.; Tian, F. Evaluation of antioxidative and hypolipidemic properties of a novel functional diet formulation of Auricularia auricula and Hawthorn. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, C.F.; Chen, M.J.; Lv, X.C.; Liu, B.; Yi, L.Z.; Cornara, L.; Wei, M.C.; Yang, Y.C.; Tundis, R.; et al. Regulatory efficacy of brown seaweed Lessonia nigrescens extract on the gene expression profile and intestinal microflora in type 2 diabetic mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.K.; Zhuo, C.; Teng, C.Y.; Yu, S.M.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Ren, G.M.; Yu, M.; Qu, J.J. Effects of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on chronic pancreatitis and intestinal microbiota in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henschel, A.; Anwar, M.Z.; Manohar, V. Comprehensive meta-analysis of ontology annotated 16S rRNA profiles identifies beta diversity clusters of environmental bacterial communities. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No. | Rt (min) | Compound Name | Probable Formula | Measured [M + H]+ (m/z) | Representative Fragmentation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.65 | Octadecatetraenoic acid | C18H28O2 | 277 | 205.9875, 277.090, 278.0923 | [15,16,17,18] |
| 2 | 1.88 | Heptadecane | C17H36 | 239 | 220.0831, 238.0942, 239.0961, 739.2668 | |
| 3 | 2.82 | Methyl stearate | C19H38O2 | 298 | 136.0620, 137.0634, 298.0974 | |
| 4 | 3.37 | Unknown | C14H2O2 | 220 | 105.0445, 202.0720, 220.0829, 221.0849 | |
| 5 | 4.66 | Gluconic acid | C6H12O7 | 197 | 133.1008, 179.1064, 197.1175, 251.0361 | |
| 6 | 7.51 | Hexose + glycerol + palmitoleic acid | C25H47O9 | 491 | 467.2029, 468.2115, 490.1934, 491.1964 | |
| 7 | 9.92 | Unknown | 509 | 438.1961, 509.2724, 510.2752, 511.2782 | ||
| 8 | 11.28 | Hexose + Sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol + γ-linolenic acid | C31H50O14S | 678 | 537.3036, 677.3709, 678.3750 | |
| 9 | 11.42 | Hydroperoxy octadecatrienoic acid | C18H30O4 | 311 | 311.2577, 312.2608, 513.3030 | |
| 10 | 12.21 | Sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol + linoleic acid | C28H52O12S | 612 | 515.3187, 516.3215, 517.3237, 611.2857 |
| Group | TC (mmol/L) | TG (mmol/L) | HDL-c (mmol/L) | LDL-c (mmol/L) | ALT (mmol/L) | AST (mmol/L) | FFA (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NFD | 1.61 ± 0.30 ** | 0.70 ± 0.05 ** | 0.91 ± 0.09 * | 0.49 ± 0.04 * | 26.89 ± 6.43 ** | 26.12 ± 4.06 ** | 264.51 ± 63.17 ** |
| HFD | 3.59 ± 0.72 ## | 1.61 ± 0.08 ## | 0.39 ± 0.23 # | 0.77 ± 0.16 # | 80.02 ± 10.32 ## | 62.18 ± 10.28 ## | 891.92 ± 222.59 ## |
| SPL95 | 1.63 ± 0.13 ** | 1.26 ± 0.33 **## | 0.91 ± 0.25 ** | 0.42 ± 0.07 ** | 27.34 ± 3.14 ** | 29.57 ± 7.77 ** | 247.40 ± 68.94 ** |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.-T.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wan, X.-Z.; Huang, Z.-R.; Liu, B.; Zhao, C. Regulatory Efficacy of the Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids from Microalgae Spirulina platensis on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103075
Li T-T, Liu Y-Y, Wan X-Z, Huang Z-R, Liu B, Zhao C. Regulatory Efficacy of the Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids from Microalgae Spirulina platensis on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103075
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tian-Tian, Yuan-Yuan Liu, Xu-Zhi Wan, Zi-Rui Huang, Bin Liu, and Chao Zhao. 2018. "Regulatory Efficacy of the Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids from Microalgae Spirulina platensis on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103075
APA StyleLi, T.-T., Liu, Y.-Y., Wan, X.-Z., Huang, Z.-R., Liu, B., & Zhao, C. (2018). Regulatory Efficacy of the Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids from Microalgae Spirulina platensis on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103075






