Modulation of Astrocyte Activity by Cannabidiol, a Nonpsychoactive Cannabinoid
Abstract
:1. Astrocytes
2. Astrocytes as Potential Therapeutic Target. Role of Cannabinoid System
3. Neurodegeneration
3.1. Stroke, Hypoxia-Ischemia
3.2. Sciatic Nerve Transection
4. Chronic Neurodegenerative Diseases
4.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
4.2. Autoimmune Diseases
4.3. Huntington’s Disease
5. Epilepsy
6. Neuropsychiatric Disorders
7. Neurogenesis
8. Receptors Involved
9. Remarks
9.1. Serum-Free Sensitization to CBD Toxicity
9.2. Astrocyte Activity Markers
9.3. Astrocyte Heterogeneity
9.4. The Interaction of CBD with Other CNS Cells
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, A.; Furlan, F.A. Astrocytes and human cognition: Modeling information integration and modulation of neuronal activity. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 92, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C.J.; Massie, A.; De Keyser, J. Immune players in the CNS: The astrocyte. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 824–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Molecular dissection of reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofroniew, M.V.; Vinters, H.V. Astrocytes: Biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridet, J.L.; Malhotra, S.K.; Privat, A.; Gage, F.H. Reactive astrocytes: Cellular and molecular cues to biological function. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransohoff, R.M. How neuroinflammation contributes to neurodegeneration. Science 2016, 353, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, L.; Stella, N. Cannabinoids and neuroinflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, N. Cannabinoid and cannabinoid-like receptors in microglia, astrocytes, and astrocytomas. Glia 2010, 58, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete, M.; Díez, A.; Araque, A. Astrocytes in endocannabinoid signalling. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, C.; Tolón, R.M.; Pazos, M.R.; Moreno, M.; Koester, E.C.; Cravatt, B.F.; Hillard, C.J.; Romero, J. Endocannabinoids regulate the activity of astrocytic hemichannels and the microglial response against an injury: In vivo studies. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 79, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, C.; Kim, W.K.; Chavarría, I.; Hillard, C.J.; Mackie, K.; Tolón, R.M.; Williams, K.; Romero, J. A glial endogenous cannabinoid system is upregulated in the brains of macaques with simian immunodeficiency virus-induced encephalitis. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2530–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassano, T.; Calcagnini, S.; Pace, L.; De Marco, F.; Romano, A.; Gaetani, S. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Signaling in Neurodegenerative Disorders: From Pathogenesis to a Promising Therapeutic Target. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panikashvili, D.; Simeonidou, C.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Hanus, L.; Breuer, A.; Mechoulam, R.; Shohami, E. An endogenous cannabinoid (2-AG) is neuroprotective after brain injury. Nature 2001, 413, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shohami, E.; Cohen-Yeshurun, A.; Magid, L.; Algali, M.; Mechoulam, R. Endocannabinoids and traumatic brain injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez Del Pulgar, T.; De Ceballos, M.L.; Guzmán, M.; Velasco, G. Cannabinoids protect astrocytes from ceramide-induced apoptosis through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 36527–36533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Holgado, E.; Vela, J.M.; Arévalo-Martín, A.; Almazán, G.; Molina-Holgado, F.; Borrell, J.; Guaza, C. Cannabinoids promote oligodendrocyte progenitor survival: Involvement of cannabinoid receptors and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt signaling. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9742–9753. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lubman, D.I.; Cheetham, A.; Yücel, M. Cannabis and adolescent brain development. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 148, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callén, L.; Moreno, E.; Barroso-Chinea, P.; Moreno-Delgado, D.; Cortés, A.; Mallol, J.; Casadó, V.; Lanciego, J.L.; Franco, R.; Lluis, C.; et al. Cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 form functional heteromers in brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 20851–20865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuardi, A.W. Cannabidiol: From an inactive cannabinoid to a drug with wide spectrum of action. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2008, 30, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, A.A.; Borrelli, F.; Capasso, R.; Di Marzo, V.; Mechoulam, R. Non-psychotropic plant cannabinoids: New therapeutic opportunities from an ancient herb. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, K.; Mishima, K.; Fujiwara, M. Therapeutic Potential of Non-Psychotropic Cannabidiol in Ischemic Stroke. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 2197–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Sagredo, O.; Pazos, M.R.; García, C.; Pertwee, R.; Mechoulam, R.; Martínez-Orgado, J. Cannabidiol for neurodegenerative disorders: Important new clinical applications for this phytocannabinoid? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, S. Cannabidiol (CBD) and its analogs: A review of their effects on inflammation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.C.; Fogaça, M.V.; Sonego, A.B.; Guimarães, F.S. Cannabidiol, neuroprotection and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 112, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, A.J.; Grimaldi, M.; Axelrod, J.; Wink, D. Cannabidiol and (−)Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol are neuroprotective antioxidants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8268–8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, A.; Tolón, M.R.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Romero, J.; Martinez-Orgado, J. The neuroprotective effect of cannabidiol in an in vitro model of newborn hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in mice is mediated by CB(2) and adenosine receptors. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazos, M.R.; Cinquina, V.; Gómez, A.; Layunta, R.; Santos, M.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Martínez-Orgado, J. Cannabidiol administration after hypoxia-ischemia to newborn rats reduces long-term brain injury and restores neurobehavioral function. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, F.J.; Lafuente, H.; Rey-Santano, M.C.; Mielgo, V.E.; Gastiasoro, E.; Rueda, M.; Pertwee, R.G.; Castillo, A.I.; Romero, J.; Martínez-Orgado, J. Neuroprotective effects of the nonpsychoactive cannabinoid cannabidiol in hypoxic-ischemic newborn piglets. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozela, E.; Pietr, M.; Juknat, A.; Rimmerman, N.; Levy, R.; Vogel, Z. Cannabinoids Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol differentially inhibit the lipopolysaccharide-activated NF-kappaB and interferon-beta/STAT proinflammatory pathways in BV-2 microglial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juknat, A.; Pietr, M.; Kozela, E.; Rimmerman, N.; Levy, R.; Gao, F.; Coppola, G.; Geschwind, D.; Vogel, Z. Microarray and pathway analysis reveal distinct mechanisms underlying cannabinoid-mediated modulation of LPS-induced activation of BV-2 microglial cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSabato, D.J.; Quan, N.; Godbout, J.P. Neuroinflammation: The devil is in the details. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuvone, T.; Esposito, G.; Esposito, R.; Santamaria, R.; Di Rosa, M.; Izzo, A.A. Neuroprotective effect of cannabidiol, a non-psychoactive component from Cannabis sativa, on beta-amyloid-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juknat, A.; Pietr, M.; Kozela, E.; Rimmerman, N.; Levy, R.; Coppola, G.; Geschwind, D.; Vogel, Z. Differential transcriptional profiles mediated by exposure to the cannabinoids cannabidiol and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in BV-2 microglial cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 2512–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, E.H.; Dalkara, T.; Moskowitz, M.A. Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robel, S.; Berninger, B.; Götz, M. The stem cell potential of glia: Lessons from reactive gliosis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindy, M.S.; Bhat, A.N.; Bhat, N.R. Transient ischemia stimulates glial fibrillary acid protein and vimentin gene expression in the gerbil neocortex, striatum and hippocampus. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1992, 13, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.M.; Wang, C.K.; Kuo, J.S.; Lin, T.N. Changes in the level of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) after mild and severe focal cerebral ischemia. Chin. J. Physiol. 1999, 42, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petito, C.K.; Halaby, I.A. Relationship between ischemia and ischemic neuronal necrosis to astrocyte expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 1993, 11, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, G.; Jander, S.; Schroeter, M. Inflammation and glial responses in ischemic brain lesions. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, T.J.; Hind, W.H.; Rasid, N.A.; O’Sullivan, S.E. Cannabinoids in experimental stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, K.; Mishima, K.; Irie, K.; Hazekawa, M.; Mishima, S.; Fujioka, M.; Orito, K.; Egashira, N.; Katsurabayashi, S.; Takasaki, K.; et al. Cannabidiol prevents a post-ischemic injury progressively induced by cerebral ischemia via a high-mobility group box1-inhibiting mechanism. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavon, A.P.; Soares, L.M.; Bonato, J.M.; Milani, H.; Guimarães, F.S.; Weffort de Oliveira, R.M. Protective effects of cannabidiol against hippocampal cell death and cognitive impairment induced by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in mice. Neurotox. Res. 2014, 26, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, N.; Ceprian, M.; Jimenez, L.; Pazos, M.R.; Martínez-Orgado, J. Neuroprotective Effects of Cannabidiol in Hypoxic Ischemic Insult. The Therapeutic Window in Newborn Mice. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceprián, M.; Jiménez-Sánchez, L.; Vargas, C.; Barata, L.; Hind, W.; Martínez-Orgado, J. Cannabidiol reduces brain damage and improves functional recovery in a neonatal rat model of arterial ischemic stroke. Neuropharmacology 2017, 116, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafuente, H.; Alvarez, F.J.; Pazos, M.R.; Alvarez, A.; Rey-Santano, M.C.; Mielgo, V.; Murgia-Esteve, X.; Hilario, E.; Martinez-Orgado, J. Cannabidiol reduces brain damage and improves functional recovery after acute hypoxia-ischemia in newborn pigs. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 70, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhao, R.; Gao, K.; Wei, Z.; Yin, M.Y.; Lau, L.T.; Chui, D.; Yu, A.C. Astrocytes: Implications for neuroinflammatory pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2011, 8, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hind, W.H.; England, T.J.; O’Sullivan, S.E. Cannabidiol protects an in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier from oxygen-glucose deprivation via PPARγ and 5-HT1A receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekny, M.; Nilsson, M. Astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis. Glia 2005, 50, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekny, M.; Pekna, M. Astrocyte intermediate filaments in CNS pathologies and regeneration. J. Pathol. 2004, 204, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, M.; Benitez, S.U.; Cartarozzi, L.P.; Del Bel, E.; Guimarães, F.S.; Oliveira, A.L. Neuroprotection and reduction of glial reaction by cannabidiol treatment after sciatic nerve transection in neonatal rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 38, 3424–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, V.L.R.; Rao, A.M.; Dogan, A.; Bowen, K.K.; Hatcher, J.; Rothstein, J.D.; Dempsey, R.J. Glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 down-regulation precedes delayed neuronal death in gerbil hippocampus following transient global cerebral ischemia. Neurochem. Int. 2000, 36, 531–537. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, E.H.; Lansbury, P.T.; Kelly, J.W. Amyloid diseases: Abnormal protein aggregation in neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9989–9990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Abraham, W.C. Astrocytes and synaptic plasticity in health and disease. Exp. Brain Res. 2017, 235, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, A.; Wilhelmsson, U.; Pekna, M.; Pekny, M. Increased cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of old GFAP(−/−)Vim(−/−) mice. Neurochem. Res. 2004, 29, 2069–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; De Filippis, D.; Carnuccio, R.; Izzo, A.A.; Iuvone, T. The marijuana component cannabidiol inhibits beta-amyloid-induced tau protein hyperphosphorylation through Wnt/beta-catenin pathway rescue in PC12 cells. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 84, 253–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karl, T.; Garner, B.; Cheng, D. The therapeutic potential of the phytocannabinoid cannabidiol for Alzheimer’s disease. Behav. Pharmacol. 2017, 28, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Scuderi, C.; Savani, C.; Steardo, L., Jr.; De Filippis, D.; Cottone, P.; Iuvone, T.; Cuomo, V.; Steardo, L. Cannabidiol in vivo blunts beta-amyloid induced neuroinflammation by suppressing IL-1beta and iNOS expression. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 151, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Scuderi, C.; Valenza, M.; Togna, G.I.; Latina, V.; De Filippis, D.; Cipriano, M.; Carratù, M.R.; Iuvone, T.; Steardo, L. Cannabidiol reduces Aβ-induced neuroinflammation and promotes hippocampal neurogenesis through PPARγ involvement. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapp, B.D.; Nave, K.A. Multiple sclerosis: An immune or neurodegenerative disorder? Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 31, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izikson, L.; Klein, R.S.; Charo, I.F.; Weiner, H.L.; Luster, A.D. Resistance to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice lacking the CC chemokine receptor (CCR)2. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, L.; Trauger, S.A.; Blain, M.; Nadeau, M.; Patel, B.; Alvarez, J.I.; Mascanfroni, I.D.; Yeste, A.; Kivisäkk, P.; Kallas, K.; et al. Regulation of astrocyte activation by glycolipids drives chronic CNS inflammation. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwin, S.K.; Rao, V.T.; Moore, C.S.; Antel, J.P. Astrocytes in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2016, 22, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, L.F.; Vanderhaeghen, J.J.; Bignami, A.; Gerstl, B. An acidic protein isolated from fibrous astrocytes. Brain Res. 1971, 28, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, L.; Quintana, F.J.; Weiner, H.L. The innate immune system in demyelinating disease. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 248, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farez, M.F.; Correale, J. Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling in astrocytes: Implications for progressive multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 361, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, W.D.; Sonett, J.R.; Brosnan, C.F.; Elkin, R.; Bornstein, M.B. Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol: A novel treatment for experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 1989, 23, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryce, G.; Ahmed, Z.; Hankey, D.J.; Jackson, S.J.; Croxford, J.L.; Pocock, J.M.; Ledent, C.; Petzold, A.; Thompson, A.J.; Giovannoni, G.; et al. Cannabinoids inhibit neurodegeneration in models of multiple sclerosis. Brain 2003, 126, 2191–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresz, K.; Pryce, G.; Ponomarev, E.D.; Marsicano, G.; Croxford, J.L.; Shriver, L.P.; Ledent, C.; Cheng, X.; Carrier, E.J.; Mann, M.K.; et al. Direct suppression of CNS autoimmune inflammation via the cannabinoid receptor CB1 on neurons and CB2 on autoreactive T cells. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lago, E.; Moreno-Martet, M.; Cabranes, A.; Ramos, J.A.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Cannabinoids ameliorate disease progression in a model of multiple sclerosis in mice, acting preferentially through CB1 receptor-mediated anti-inflammatory effects. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozela, E.; Lev, N.; Kaushansky, N.; Eilam, R.; Rimmerman, N.; Levy, R.; Ben-Nun, A.; Juknat, A.; Vogel, Z. Cannabidiol inhibits pathogenic T cells, decreases spinal microglial activation and ameliorates multiple sclerosis-like disease in C57BL/6 mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozela, E.; Juknat, A.; Kaushansky, N.; Rimmerman, N.; Ben-Nun, A.; Vogel, Z. Cannabinoids decrease the th17 inflammatory autoimmune phenotype. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozela, E.; Juknat, A.; Kaushansky, N.; Ben-Nun, A.; Coppola, G.; Vogel, Z. Cannabidiol, a non-psychoactive cannabinoid, leads to EGR2-dependent anergy in activated encephalitogenic T cells. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozela, E.; Juknat, A.; Gao, F.; Kaushansky, N.; Coppola, G.; Vogel, Z. Pathways and gene networks mediating the regulatory effects of cannabidiol, a nonpsychoactive cannabinoid, in autoimmune T cells. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecha, M.; Feliú, A.; Iñigo, P.M.; Mestre, L.; Carrillo-Salinas, F.J.; Guaza, C. Cannabidiol provides long-lasting protection against the deleterious effects of inflammation in a viral model of multiple sclerosis: A role for A2A receptors. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 59, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feliú, A.; Moreno-Martet, M.; Mecha, M.; Carrillo-Salinas, F.J.; de Lago, E.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Guaza, C. A Sativex(®)-like combination of phytocannabinoids as a disease-modifying therapy in a viral model of multiple sclerosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3579–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobel, R.A.; Ahmed, A.S. White matter extracellular matrix chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate proteoglycans in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haylock-Jacobs, S.; Keough, M.B.; Lau, L.; Yong, V.W. Chondroitin sulphate proteoglycans: Extracellular matrix proteins that regulate immunity of the central nervous system. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacoppo, S.; Galuppo, M.; Pollastro, F.; Grassi, G.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. A new formulation of cannabidiol in cream shows therapeutic effects in a mouse model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Daru 2015, 23, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roze, E.; Bonnet, C.; Betuing, S.; Caboche, J. Huntington’s disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 685, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Consroe, P.; Laguna, J.; Allender, J.; Snider, S.; Stern, L.; Sandyk, R.; Kennedy, K.; Schram, K. Controlled clinical trial of cannabidiol in Huntington’s disease. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 40, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdeolivas, S.; Satta, V.; Pertwee, R.G.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Sagredo, O. Sativex-like combination of phytocannabinoids is neuroprotective in malonate-lesioned rats, an inflammatory model of Huntington’s disease: Role of CB1 and CB2 receptors. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, L.K.; Schousboe, A.; Waagepetersen, H.S. The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: Aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardos, J.; Héja, L.; Jemnitz, K.; Kovács, R.; Palkovits, M. The nature of early astroglial protection—Fast activation and signaling. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 153, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringer, J.L. Repeated seizures increase GFAP and vimentin in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1996, 717, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.B. Cannabis and epilepsy: An ancient treatment returns to the fore. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 70, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechoulam, R.; Carlini, E.A. Toward drugs derived from cannabis. Naturwissenschaften 1978, 65, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karler, R.; Cely, W.; Turkanis, S.A. The anticonvulsant activity of cannabidiol and cannabinol. Life Sci. 1973, 13, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, P.; Olsen, D.M.; Borys, H.K.; Karler, R.; Turkanis, S.A. The influence of cannabidiol and delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol on cobalt epilepsy in rats. Epilepsia 1979, 20, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karler, R.; Turkanis, SA. The cannabinoids as potential antiepileptics. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1981, 21, 437S–448S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, K.; You, C.; Lei, D.; Zhang, H. High dosage of cannabidiol (CBD) alleviates pentylenetetrazole-induced epilepsy in rats by exerting an anticonvulsive effect. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 8820–8827. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Jie, W.; Liu, J.H.; Yang, J.M.; Gao, T.M. An astroglial basis of major depressive disorder? An overview. Glia 2017, 65, 1227–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, C.L.; Calfa, G.D.; Molina, V.A. Astrocyte plasticity induced by emotional stress: A new partner in psychiatric physiopathology? Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 65, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, F.S.; Chiaretti, T.M.; Graeff, F.G.; Zuardi, A.W. Antianxiety effect of cannabidiol in the elevated plus-maze. Psychopharmacology 1990, 100, 558–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casarotto, P.C.; Gomes, F.V.; Resstel, L.B.; Guimarães, F.S. Cannabidiol inhibitory effect on marble-burying behaviour: Involvement of CB1 receptors. Behav. Pharmacol. 2010, 21, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamaschi, M.M.; Queiroz, R.H.; Chagas, M.H.; de Oliveira, D.C.; De Martinis, B.S.; Kapczinski, F.; Quevedo, J.; Roesler, R.; Schröder, N.; Nardi, A.E.; et al. Cannabidiol reduces the anxiety induced by simulated public speaking in treatment-naïve social phobia patients. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leweke, F.M.; Piomelli, D.; Pahlisch, F.; Muhl, D.; Gerth, C.W.; Hoyer, C.; Klosterkötter, J.; Hellmich, M.; Koethe, D. Cannabidiol enhances anandamide signaling and alleviates psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.M.; Neves, M.C.L.D.; Roque, M.A.V.; Queiroz, D.A.B.; Corrêa de Freitas, A.A.; de Fátima, Â.; Moreira, F.A.; Garcia, F.D. Is there a role for cannabidiol in psychiatry? World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.V.; Llorente, R.; Del Bel, E.A.; Viveros, M.P.; López-Gallardo, M.; Guimarães, F.S. Decreased glial reactivity could be involved in the antipsychotic-like effect of cannabidiol. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 164, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Whittard, J.; Higuera-Matas, A.; Morris, C.V.; Hurd, Y.L. Cannabidiol, a nonpsychotropic component of cannabis, inhibits cue-induced heroin seeking and normalizes discrete mesolimbic neuronal disturbances. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14764–14769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurd, Y.L.; Yoon, M.; Manini, A.F.; Hernandez, S.; Olmedo, R.; Ostman, M.; Jutras-Aswad, D. Early Phase in the Development of Cannabidiol as a Treatment for Addiction: Opioid Relapse Takes Initial Center Stage. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacagnina, M.J.; Rivera, P.D.; Bilbo, S.D. Glial and Neuroimmune Mechanisms as Critical Modulators of Drug Use and Abuse. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 156–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, J.S.; Cameron, H.A. Could adult hippocampal neurogenesis be relevant for human behavior? Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 227, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez-David, I.; Hen, R.; Gardier, A.M.; David, D.J. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis: An actor in the antidepressant-like action. Ann. Pharm. Fr. 2013, 71, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colangelo, A.M.; Cirillo, G.; Lavitrano, M.L.; Alberghina, L.; Papa, M. Targeting reactive astrogliosis by novel biotechnological strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.; Jaber, M.; Gaillard, A. Potentials of endogenous neural stem cells in cortical repair. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revest, J.M.; Dupret, D.; Koehl, M.; Funk-Reiter, C.; Grosjean, N.; Piazza, P.V.; Abrous, D.N. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is involved in anxiety-related behaviors. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.C.; Ortega, Z.; Palazuelos, J.; Fogaça, M.V.; Aguiar, D.C.; Díaz-Alonso, J.; Ortega-Gutiérrez, S.; Vázquez-Villa, H.; Moreira, F.A.; Guzmán, M.; et al. The anxiolytic effect of cannabidiol on chronically stressed mice depends on hippocampal neurogenesis: Involvement of the endocannabinoid system. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinjyo, N.; Di Marzo, V. The effect of cannabichromene on adult neural stem/progenitor cells. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagan, S.; Venance, L.; Torrens, Y.; Cordier, J.; Glowinski, J.; Giaume, C. Anandamide and WIN 55212–2 inhibit cyclic AMP formation through G-protein-coupled receptors distinct from CB1 cannabinoid receptors in cultured astrocytes. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, L.; Stella, N. Endothelin-1 increases 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) production in astrocytes. Glia 2003, 44, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurolo, E.; Iyer, A.M.; Spliet, W.G.; Van Rijen, P.C.; Troost, D.; Gorter, J.A.; Aronica, E. CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor expression during development and in epileptogenic developmental pathologies. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, W.S.; Hu, S.; Min, X.; Cabral, G.A.; Lokensgard, J.R.; Peterson, P.K. Synthetic cannabinoid WIN55,212–2 inhibits generation of inflammatory mediators by IL-1beta-stimulated human astrocytes. Glia 2005, 49, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metna-Laurent, M.; Marsicano, G. Rising stars: Modulation of brain functions by astroglial type-1 cannabinoid receptors. Glia 2015, 63, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira da Cruz, J.F.; Robin, L.M.; Drago, F.; Marsicano, G.; Metna-Laurent, M. Astroglial type-1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1): A new player in the tripartite synapse. Neuroscience 2016, 323, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Buck, J. Cannabinoids protect cells from oxidative cell death: A receptor-independent mechanism. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 293, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rimmerman, N.; Kozela, E.; Levy, R.; Vogel, Z.; Juknat, A. Cannabinoid Signaling Through Non-CB1R/Non-CB2R Targets in Microglia. In endoCANNABINOIDS; Abood, M., Sorensen, R., Stella, N., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 24, pp. 143–171. [Google Scholar]
- Rimmerman, N.; Juknat, A.; Kozela, E.; Levy, R.; Bradshaw, H.B.; Vogel, Z. The non-psychoactive plant cannabinoid, cannabidiol affects cholesterol metabolism-related genes in microglial cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.C.; Moreira, F.A.; Gomes, F.V.; Del Bel, E.A.; Guimarães, F.S. Multiple mechanisms involved in the large-spectrum therapeutic potential of cannabidiol in psychiatric disorders. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 3364–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massi, P.; Vaccani, A.; Ceruti, S.; Colombo, A.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Parolaro, D. Antitumor effects of cannabidiol, a nonpsychoactive cannabinoid, on human glioma cell lines. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcu, J.P.; Christian, R.T.; Lau, D.; Zielinski, A.J.; Horowitz, M.P.; Lee, J.; Pakdel, A.; Allison, J.; Limbad, C.; Moore, D.H.; et al. Cannabidiol enhances the inhibitory effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on human glioblastoma cell proliferation and survival. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabissi, M.; Morelli, M.B.; Santoni, M.; Santoni, G. Triggering of the TRPV2 channel by cannabidiol sensitizes glioblastoma cells to cytotoxic chemotherapeutic agents. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carracedo, A.; Geelen, M.J.; Diez, M.; Hanada, K.; Guzmán, M.; Velasco, G. Ceramide sensitizes astrocytes to oxidative stress: Protective role of cannabinoids. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimmerman, N.; Ben-Hail, D.; Porat, Z.; Juknat, A.; Kozela, E.; Daniels, M.P.; Connelly, P.S.; Leishman, E.; Bradshaw, H.B.; Shoshan-Barmatz, V.; et al. Direct modulation of the outer mitochondrial membrane channel, voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1) by cannabidiol: A novel mechanism for cannabinoid-induced cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meares, G.P.; Ma, X.; Qin, H.; Benveniste, E.N. Regulation of CCL20 expression in astrocytes by IL-6 and IL-17. Glia 2012, 60, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middeldorp, J.; Hol, E.M. GFAP in health and disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyash, V.; Kettenmann, H. Heterogeneity in astrocyte morphology and physiology. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 63, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamanian, J.L.; Xu, L.; Foo, L.C.; Nouri, N.; Zhou, L.; Giffard, R.G.; Barres, B.A. Genomic analysis of reactive astrogliosis. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6391–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, R.M. A polarizing question: Do M1 and M2 microglia exist? Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, L.; Zeira, M.; Reich, S.; Har-Noy, M.; Mechoulam, R.; Slavin, S.; Gallily, R. Cannabidiol lowers incidence of diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice. Autoimmunity 2006, 39, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, V.L.; Singh, U.P.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Critical Role of Mast Cells and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ in the Induction of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells by Marijuana Cannabidiol In Vivo. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5211–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
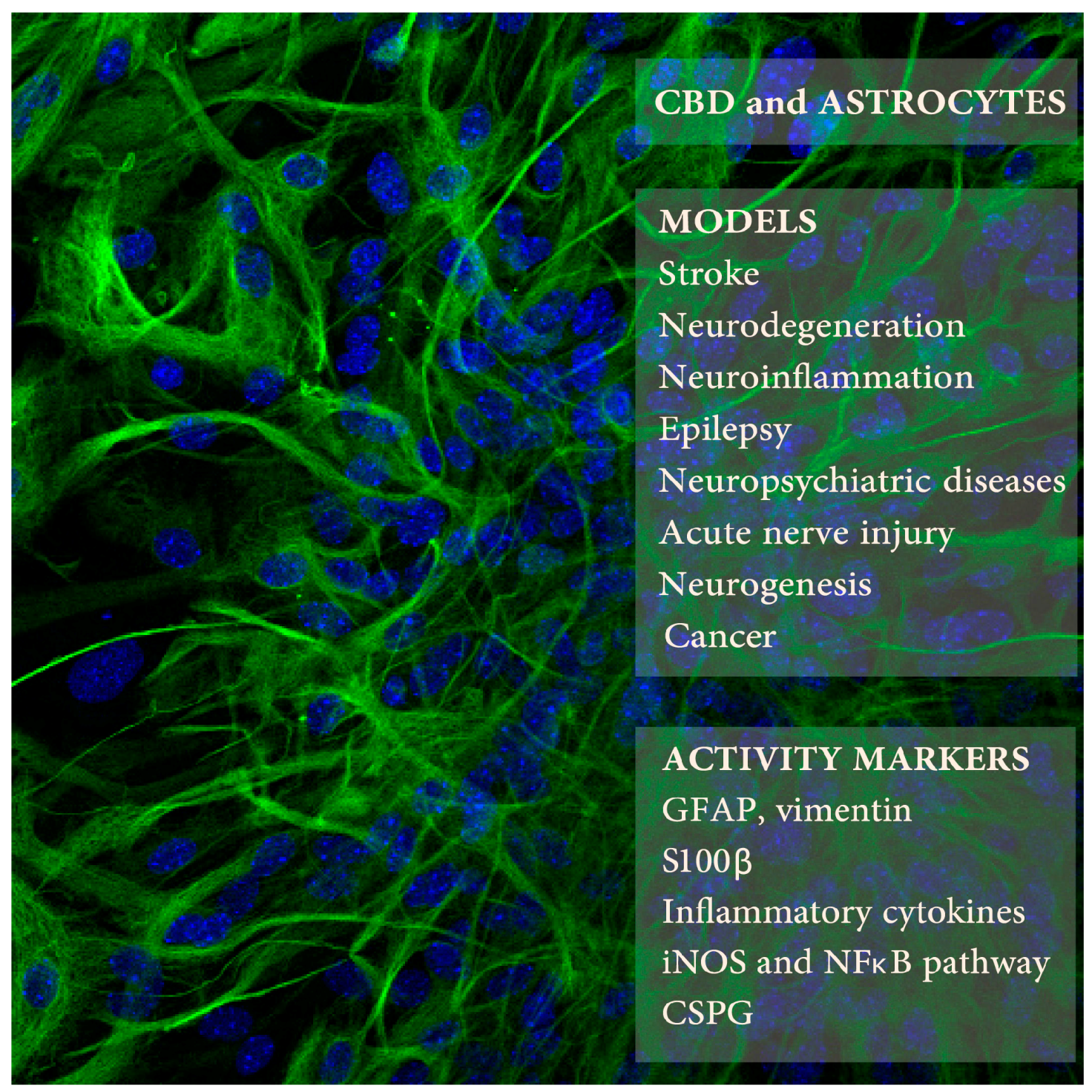
| CBD Doses/Times | Animals or Cells | Procedure | Astrocyte Activity Measures | Other CBD Activities | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypoxia-Ischemia | |||||
| 0.1, 1, 3 mg/kg i.p. just before and 3 h after the MCAO occlusion | ddY mice, 25–35 g | Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), 4 h | Day 3: decreased GFAP IHC (infarct including striatum) | Decreased infarct size, reduced microglia activation and apoptosis, improved neurological score, motor coordination; Infarct size reduction—not CB1 and CB2 mediated | [41] |
| 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg i.p., 30 min before, 3, 24, 48 h after BCCAO | Swiss mice, 35–45 days old (30–40 g) | Bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO) using aneurysm clips, 17 min | Day 7: decreased GFAP IHC in hippocampus (HPC) | Reduced neuronal cell death and improved spatial learning | [42] |
| 1 mg/kg s.c. 10 min, 1, 3, 6, 12, 18, 24 h after HI | C57BL6 mice, 9–10 days old | Left common carotid artery electrocoagulation, 3 h later followed by hypoxia (10% O2) for 90 min | Day 7: decreased GFAP level (astrocyte viability) | Reduced ipsilateral hemisphere volume loss and microglia activation | [43] |
| 5 mg/kg i.p., 15/30 min after MCAO | Wistar rat pups, 7–9 days old | MCA occlusion, 3 h | Day 7: no effect on GFAP; Day 15: reduced GFAP (parieto-occipital cortex) | Improved neurobehavioral scores, reduced neuronal damage and microglia activation, no effect on infarct size | [44] |
| 1 mL of 0.1 mg/kg i.v. per ~1.7 kg weight, 15, 240 min after the HI | Piglets, 1–3 days old | Clamping both carotid arteries with vascular occluders and low oxygen (8–10%) for 20 min | 72 h post HI: CBD reversed astrocyte loss and morphology (GFAP IHC, less swallen), decreased HI-elevated S100β in the CSF | Reduced neuronal and astrocytic cell death, less TNFα(+) cells, improved brain activity and neurobehavioral performance | [45] |
| 100 nM, 1 and 10 μM before or immediately after the OGD, and 2 and 4 h into reperfusion | Human brain microvascular endothelial cell (HBMEC) and human astrocyte (HA) co-cultures (BBB model) | Oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD), 4 h | 4–32 h post OGD: improved BBB permeability; 32 h post OGD: decreased cell damage (LDH release) and VCAM1 (ELISA); minor but significant decreases in IL-6 and VEGF (but not of IFNγ, IL-10, IL-1β, IL-2, CCL3, CCL4, or TNFα) | Protective effect up to 2 h into reperfusion; PPARγ and partially 5-HT1A mediated (not via CB1, CB2, TRPV1, A2A) Monocultures HBMEC: CBD increased IL-6, VEGF but decreased VCAM1; HA: CBD decreased VCAM1 | [47] |
| Neurodegeneration | |||||
| 5, 15, 30 mg/kg i.p., daily for 5 days post lesion | Wistar rat pups, 2 days old | Unilateral sciatic nerve transection at mid-thigh | Day 5: decreased GFAP IHC (only 15 mg/mL CBD analyzed) in ventral horn of the lumbar spinal cords | CBD 15 mg/mL rescued synaptic and sensory neurons losses, reduces microglia activation | [50] |
| 2.5 or 10 mg/kg i.p., daily for 7 days starting day 3 after Aβ | C57BL/6J mice, 3–5 month old | Human Aβ (1–42, 10 ng/mL) inoculation into the right dorsal hippocampus (HPC) | Day 10: decreased GFAP mRNA (in situ) and protein IHC in HPC | Decreased iNOS and IL-1β levels | [57] |
| 10 mg/kg i.p., for 15 days | Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats, 300–350 g | Human Aβ (1–42; 30 ng) into HPC CA1 | Day 15: Decreased GFAP, S100β in HPC homogenates and GFAP IHC in HPC CA1 | Decreased neuronal damage, neuroinflammatory signaling, increased calbindin levels in HPC CA1 and neurogenesis in the HPC DG; PPARγ mediated | [58] |
| 10−9–10−7 M | Cultured newborn SD rat astrocytes | Aβ (1–42) 1 µg/mL | 24 h: inhibition of S100β, NO, TNFα, IL-1β release (ELISA) and GFAP, S100β, iNOS, NF-κB (p-p50/p65) levels (WB) | PPARγ mediated | [58] |
| 1, 5 μM | Cultured newborn Wistar rat astrocytes | IL-1β + TNFα (both 10 ng/mL); serum free | 6 h: decreased CCL-2 (ELISA) | 7 days of CBD 5 mg/kg i.p. ameliorated TMEV EAE, decreased leukocyte infiltration, VCAM1, CCL2, CCL5, CCR2 in the PFC; reduced microglial Iba1, TNFα, IL-1β; A2A mediated | [74] |
| 1% CBD in propylene glycol on hind limbs daily post immunization from days 14 (EAE onset)-28 | C57BL/6 mice, 12 week old (males) | MOG35–55-induced EAE | Day 28: decreased GFAP IHC and WB in the spinal cords | Diminished clinical EAE score, T cell infiltration and demyelination in the spinal cord, decreased TNFα, IL-6, TGFβ, oxidative markers and apoptosis, increased IL-10 | [78] |
| Sativex-like botanical extracts *—10 mg/kg i.p. daily days 70–80 post virus injection | SJL/J mice, 4 week old, (females) | TMEV-induced EAE | Day 80: reduced GFAP and vimentin, CSPG (CS56) IHC, brevican mRNA in spinal cord | Improved motor deficits, decreased myelin and axon damage, T cell infiltration, ICAM1, microglial Iba1, IL-1β, TNFα, IFNγ and increased Arg1 and IL10; Δ9-THC-BDS or Δ9-CBD-BDS alone mimicked Sativex-like mix in EAE via CB1 and PPARγ, respectively | [75] |
| 100 nM, 0.5 and 1 μM | Cultured postnatal Wistar rat astrocytes | TGFβ1 + βFGF (both 10 ng/mL) 24, 48 or 72 h; cultured 1 h in no serum DMEM before stimulation | 24 h: reduced brevican and XT-I mRNA. 48 h and 72 h: reduced neurocan (IHC and WB on supernantants) | [75] | |
| 3 mg/kg of Sativex-like botanical extracts * i.p., 30 min before and 2 h after injection | SD rats, 12 weeks old | Intrastriatal malonate induced Huntington-like neurodegeneration | 48 h: decreased GFAP IHC in striatum | Decreased striatal edema, microglial Iba1, iNOS and IGF1, minor prevention of cell death, reversed malonate-induced CB1 decrease; CB1 and CB2 mediated | [81] |
| Other | |||||
| 10, 20, 50 mg/kg 1 h before each PTZ | SD rats, 170 g | Chronic epilepsy, i.p. PTZ for 28 days | Day 28: reduced astrocyte hyperplasia (GFAP IHC in HPC CA1, CA3) | Antiepileptic, decreased neuronal loss and NMDAR1 in the HPC | [90] |
| 30 and 60 mg/kg i.p., days 6–28 of MK-801 injections | C57BL/6J mice, 6 weeks old | Schizophrenia model based on NMDA receptor hypofunction, 28 days of 1 mg/kg MK-801 | Day 31: Slight decrease of GFAP IHC in mPFC | Improved cognitive scores and reduced anxiety, decreased microglial Iba-1 | [98] |
| 30 mg/kg i.p. 2 h after each stressor | Wild type and GFAP-TK mice, 3 months old | Chronic unpredictable stress (CUS, 14 days), model of depression/anhedonia | Day 15: In WT increased HPC neurogenesis, including non-stressed controls, reversed CUS-decreased neurogenesis (NeuN, BrdU, and Dcx) | Day 14 and 15—decreased anxiety; effect ablated in GFAP-TK/ganciclovir mice; CB1 mediated, AEA increased (not 2-AG or PEA) | [107] |
| 50, 100, 250, 500 nM | HiB5 hippocampal progenitor cell line | BrdU expression, cell number | Increased BrdU and S phase cell cycle | CB1/CB2 mediated | [107] |
| 1 µM | 8-week old mouse whole brain neural/stem progenitor cells (NSPCs) | Whole brain NSPCs in vitro proliferation and differentiation into neurons or astrocytes | Day 2: Increase in nestin mRNA (B27 supplemented medium) and cell viability, no effect on GFAP mRNA | No effect on nestin in complete medium | [108] |
| 10 µM 1–3 days | Human glioblastoma multiforme cells (U87MG, MZC) | Cell death and viability, colony formation following CBD alone and in combination with BCNU, TMZ, and DOXO | Days 1–3: potentiates cytotoxicity of BCNU, TMZ, and DOXO chemotherapeutics | TRPV2-dependent Ca2+ influx | [121] |
| 10 µM 1–3 days | Normal human astrocytes (NHA) | Cell death and viability following CBD alone and in combination with BCNU, TMZ, and DOXO | No effect on cell viability alone or in combination with BCNU, TMZ, and DOXO chemotherapeutics | [121] | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozela, E.; Juknat, A.; Vogel, Z. Modulation of Astrocyte Activity by Cannabidiol, a Nonpsychoactive Cannabinoid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081669
Kozela E, Juknat A, Vogel Z. Modulation of Astrocyte Activity by Cannabidiol, a Nonpsychoactive Cannabinoid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(8):1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081669
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozela, Ewa, Ana Juknat, and Zvi Vogel. 2017. "Modulation of Astrocyte Activity by Cannabidiol, a Nonpsychoactive Cannabinoid" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 8: 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081669
APA StyleKozela, E., Juknat, A., & Vogel, Z. (2017). Modulation of Astrocyte Activity by Cannabidiol, a Nonpsychoactive Cannabinoid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(8), 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081669




