Functional Implications of MicroRNAs in Crohn’s Disease Revealed by Integrating MicroRNA and Messenger RNA Expression Profiling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Differentially Expressed Microrna
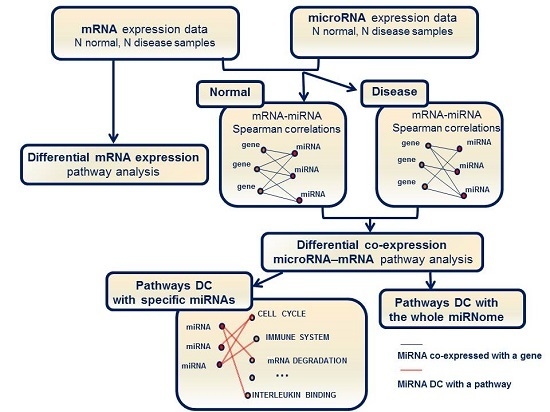
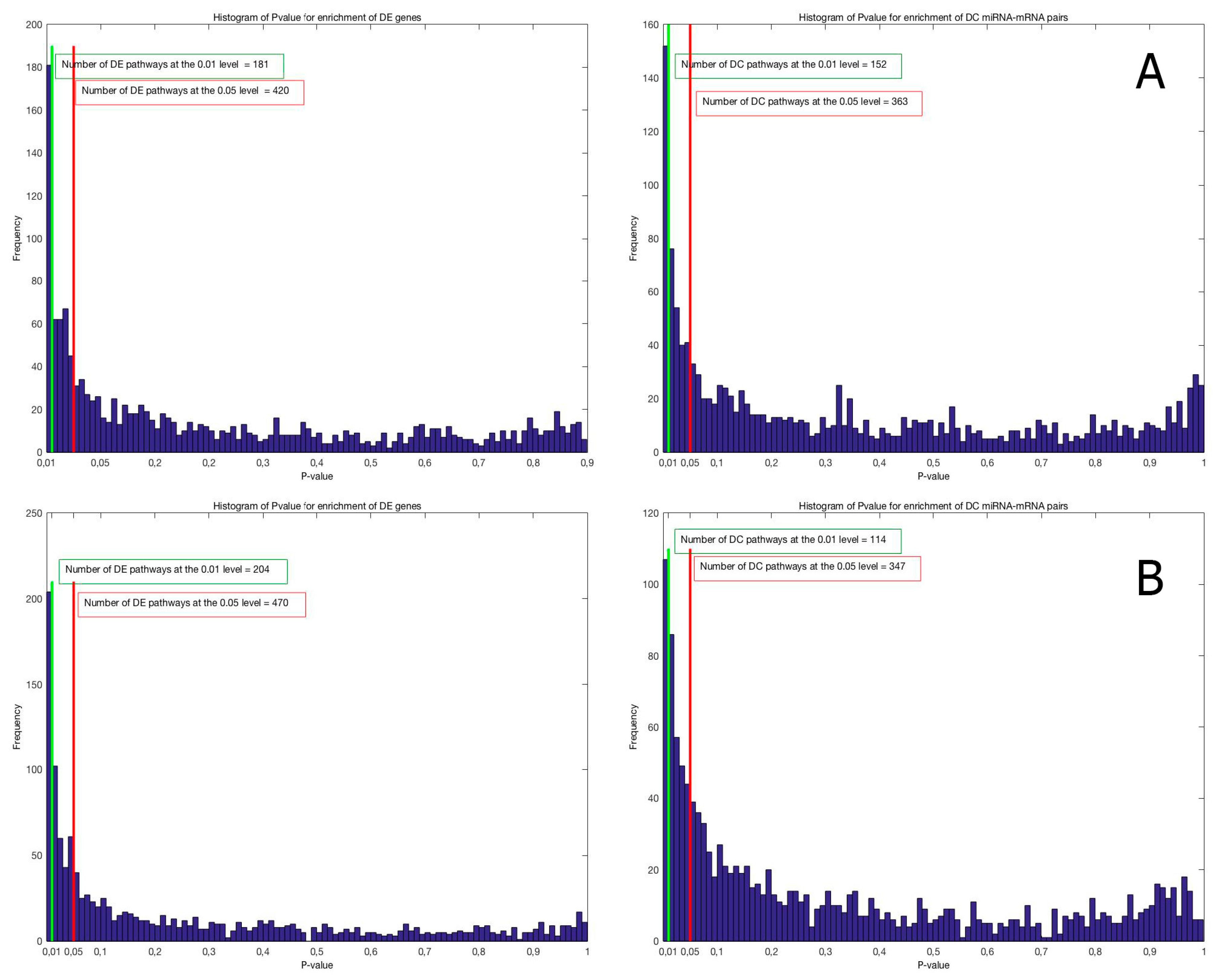
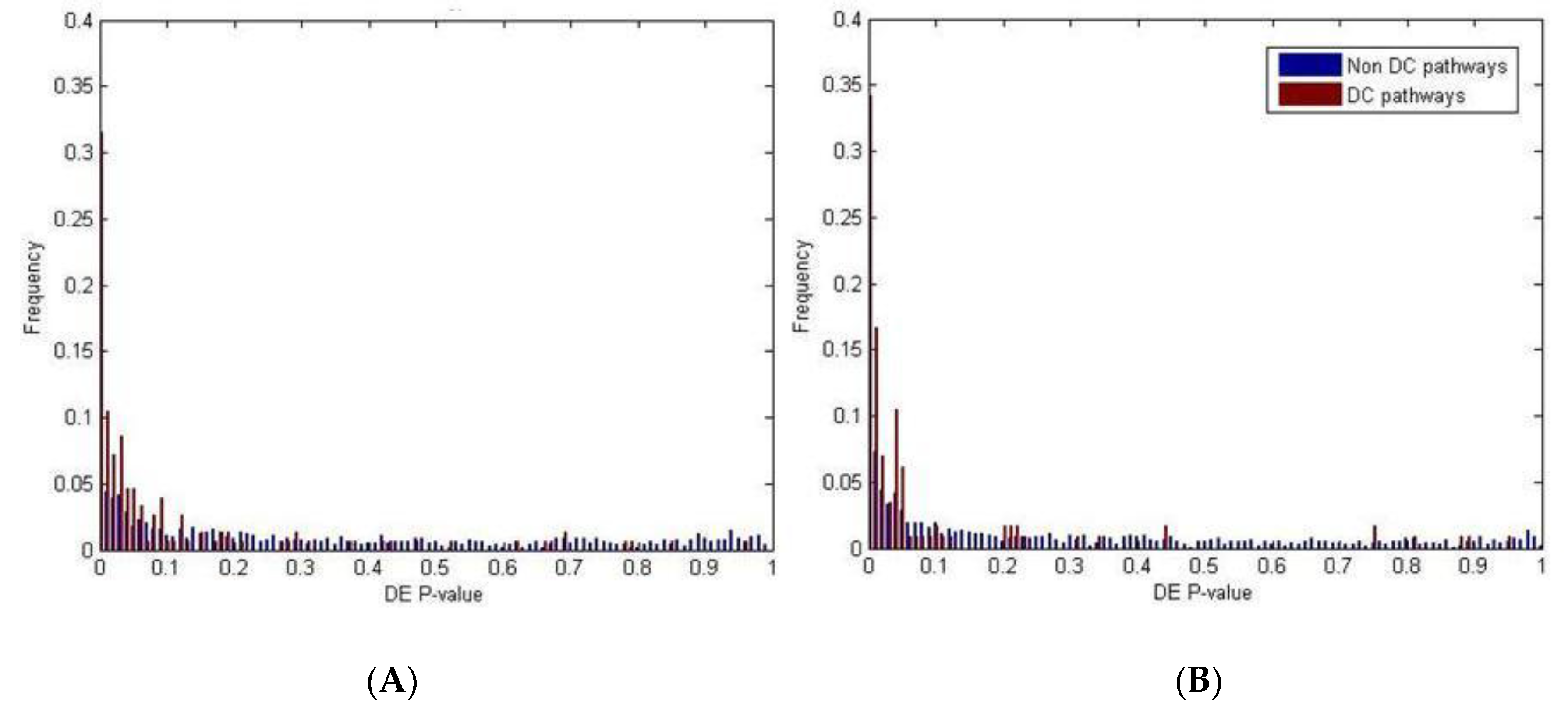
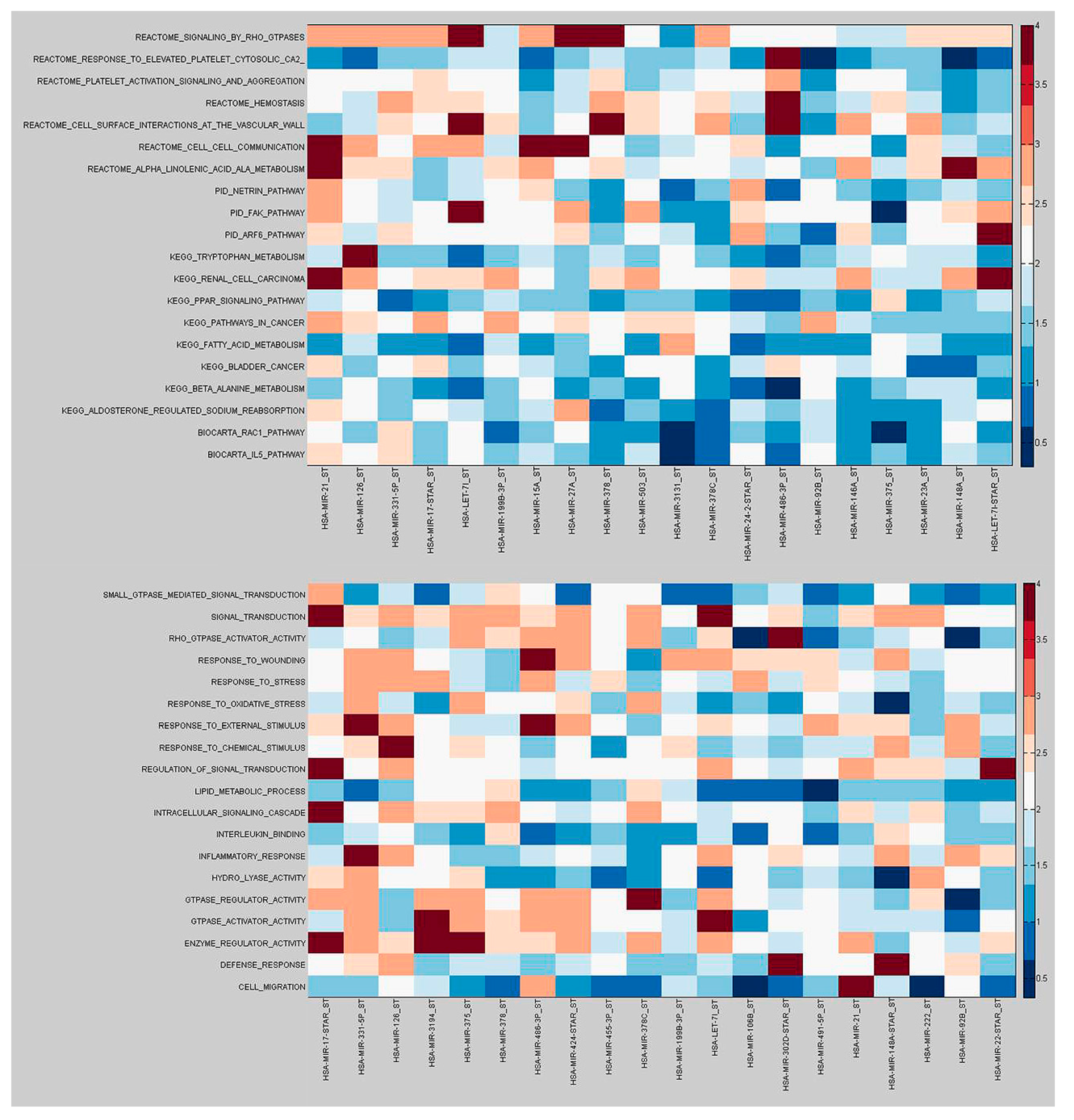
2.2. Identification of Molecular Pathways That Are Differentially Expressed and Differentially Co-Expressed with miRNAs
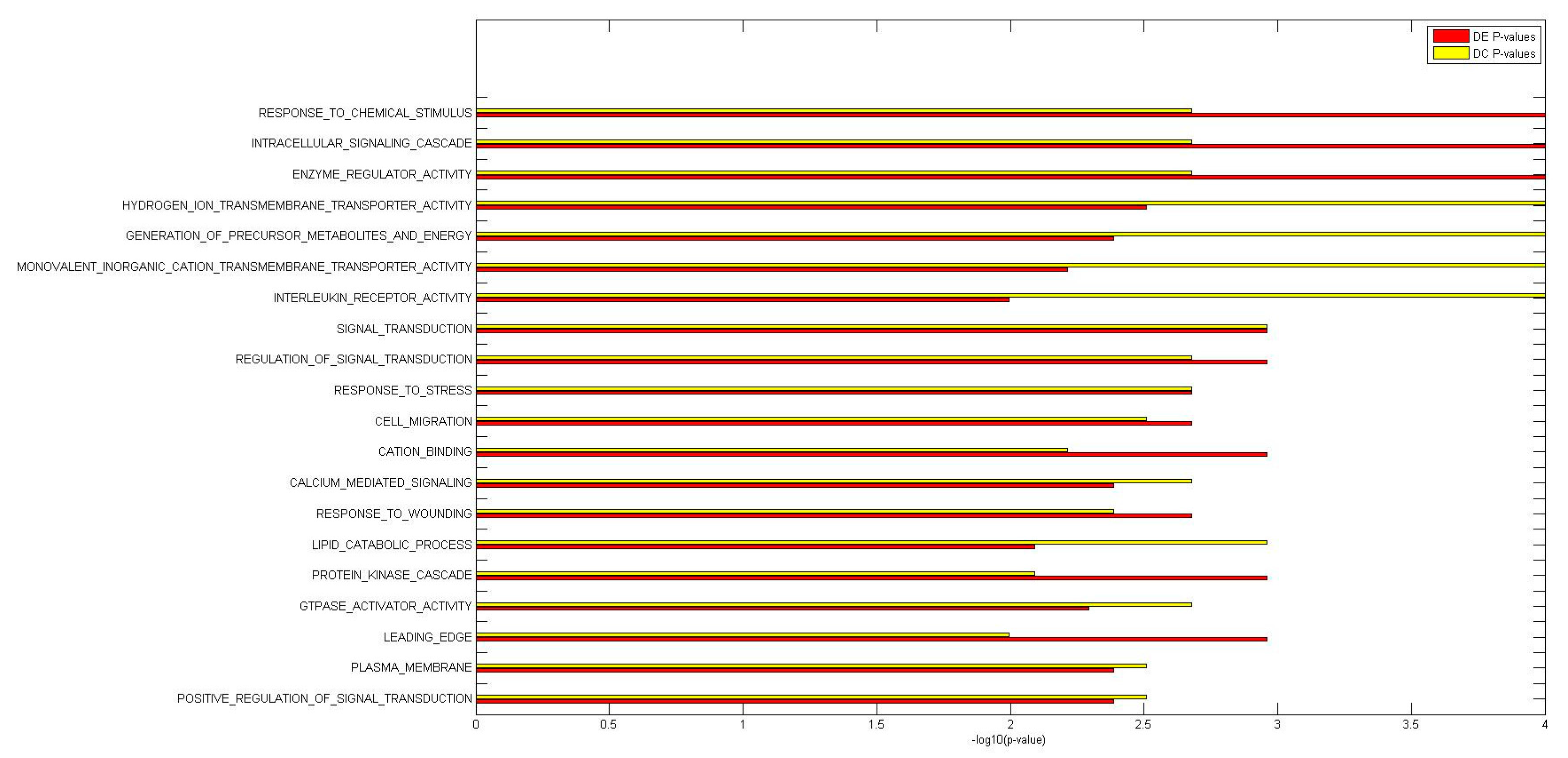
2.3. Functional Implications of Specific miRNAs by Differential Co-Expression Pathway Analysis
2.4. Differential miRNA–mRNA Co-Expression Highlights Known Inflammatory Bowel Disease miRNAs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Recruitment, Biopsy Collection and RNA Extraction
4.2. Microarray Analysis
4.3. Differential Expression Analysis of MicroRNAs and mRNAs
4.4. Pathway Enrichment Analysis for Differential Expression
4.5. Pathway Enrichment Analysis for Differential Co-Expression between miRNAs and mRNAs
4.6. Pathway Enrichment Analysis for Differential Co-Expression Based on the Entire set of microRNAs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.Z.; van Sommeren, S.; Huang, H.; Ng, S.C.; Alberts, R.; Takahashi, A.; Ripke, S.; Lee, J.C.; Jostins, L.; Shah, T.; et al. Association analyses identify 38 susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease and highlight shared genetic risk across populations. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jostins, L.; Ripke, S.; Weersma, R.K.; Duerr, R.H.; McGovern, D.P.; Hui, K.Y.; Lee, J.C.; Schumm, L.P.; Sharma, Y.; Anderson, C.A.; et al. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2012, 491, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, O.; Creanza, T.M.; Bossa, F.; Palumbo, O.; Maglietta, R.; Ancona, N.; Corritore, G.; Latiano, T.; Martino, G.; Biscaglia, G.; et al. Genome-wide pathway analysis using gene expression data of colonic mucosa in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iborra, M.; Bernuzzi, F.; Invernizzi, P.; Danese, S. MicroRNAs in autoimmunity and inflammatory bowel disease: Crucial regulators in immune response. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, T.; Naito, Y.; Mizushima, K.; Nukigi, Y.; Okada, H.; Suzuki, T.; Hirata, I.; Omatsu, T.; Okayama, T.; Handa, O.; et al. Increased intestinal expression of heme oxygenase-1 and its localization in patients with ulcerative colitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, S229–S233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zikusoka, M.; Trindade, A.; Dassopoulos, T.; Harris, M.L.; Bayless, T.M.; Brant, S.R.; Chakravarti, S.; Kwon, J.H. MicroRNAs are differentially expressed in ulcerative colitis and alter expression of macrophage inflammatory peptide-2 alpha. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1624–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasseu, M.; Tréton, X.; Guichard, C.; Pedruzzi, E.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Richard, C.; Aparicio, T.; Daniel, F.; Soulé, J.C.; Moreau, R.; et al. Identification of restricted subsets of mature microRNA abnormally expressed in inactive colonic mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, S.; Dassopoulos, T.; Harris, M.L.; Bayless, T.M.; Meltzer, S.J.; Brant, S.R.; Kwon, J.H. Identification of microRNAs associated with ileal and colonic Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2010, 16, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duttagupta, R.; DiRienzo, S.; Jiang, R.; Bowers, J.; Gollub, J.; Kao, J.; Kearney, K.; Rudolph, D.; Dawany, N.B.; Showe, M.K.; et al. Genome-wide maps of circulating miRNA biomarkers for ulcerative colitis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Welker, N.C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Reuss, S.A.; Zhang, X.; Lee, H.; Liu, Y.; Bronner, M.P. Novel specific microRNA biomarkers in idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease unrelated to disease activity. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, M.; Bjerrum, J.T.; Seidelin, J.B.; Troelsen, J.T.; Olsen, J.; Nielsen, O.H. miR-20b, miR-98, miR-125b-1*, and let-7e* as new potential diagnostic biomarkers in ulcerative colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 4289–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iborra, M.; Bernuzzi, F.; Correale, C.; Vetrano, S.; Fiorino, G.; Beltrán, B.; Marabita, F.; Locati, M.; Spinelli, A.; Nos, P.; et al. Identification of serum and tissue micro-RNA expression profiles in different stages of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 173, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Wu, R.; Wu, R.; Gong, J.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, N.; Li, J. Altered microRNA expression in inflamed and non-inflamed terminal ileal mucosa of adult patients with active Crohn’s disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koukos, G.; Polytarchou, C.; Kaplan, J.L.; Oikonomopoulos, A.; Ziring, D.; Hommes, D.W.; Wahed, R.; Kokkotou, E.; Pothoulakis, C.; Winter, H.S.; et al. A microRNA signature in pediatric ulcerative colitis: Deregulation of the miR-4284/CXCL5 pathway in the intestinal epithelium. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahm, A.M.; Hand, N.J.; Tsoucas, D.M.; Le Guen, C.L.; Baldassano, R.N.; Friedman, J.R. Rectal microRNAs are perturbed in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease of the colon. J. Crohns Colitis 2014, 8, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brest, P.; Lapaquette, P.; Souidi, M.; Lebrigand, K.; Cesaro, A.; Vouret-Craviari, V.; Mari, B.; Barbry, P.; Mosnier, J.F.; Hébuterne, X.; et al. A synonymous variant in IRGM alters a binding site for miR-196 and causes deregulation of IRGM-dependent xenophagy in Crohn’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwiers, A.; Kraal, L.; van de Pouw Kraan, T.C.; Wurdinger, T.; Bouma, G.; Kraal, G. Cutting edge: A variant of the IL-23R gene associated with inflammatory bowel disease induces loss of microRNA regulation and enhanced protein production. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1573–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, A.Y.; Chuang, J.C.; Zhai, Z.; Wu, F.; Kwon, J.H. NOD2 expression is regulated by microRNAs in colonic epithelial HCT116 cells. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairfax, B.P.; Humburg, P.; Makino, S.; Naranbhai, V.; Wong, D.; Lau, E.; Jostins, L.; Plant, K.; Andrews, R.; McGee, C.; et al. Innate immune activity conditions the effect of regulatory variants upon monocyte gene expression. Science 2014, 343, 1246949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskerville, S.; Bartel, D.P. Microarray profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA 2005, 11, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalla, R.; Ventham, N.T.; Kennedy, N.A.; Quintana, J.F.; Nimmo, E.R.; Buck, A.H.; Satsangi, J. MicroRNAs: New players in IBD. Gut 2015, 64, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creanza, T.M.; Liguori, M.; Liuni, S.; Nuzziello, N.; Ancona, N. Meta-analysis of differential connectivity in gene co-expression networks in multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharbati, J.; Lewin, A.; Kutz-Lohroff, B.; Kamal, E.; Einspanier, R.; Sharbati, S. Integrated microRNA-mRNA-analysis of human monocyte derived macrophages upon Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Yang, J.C.; Jeng, J.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Lu, T.H.; Tzeng, S.L.; Wu, Y.C.; Wu, C.J.; Rau, C.S. Circulating microRNA signatures in mice exposed to lipoteichoic acid. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Motte CdCde, L.; Fiocchi, C. Platelets in inflammatory bowel disease: Clinical, pathogenic, and therapeutic implications. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorelli, L.; de Salvo, C.; Mercado, J.R.; Vecchi, M.; Pizarro, T.T. Central role of the gut epithelial barrier in the pathogenesis of chronic intestinal inflammation: Lessons learned from animal models and human genetics. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Limbergen, J.; Radford-Smith, G.; Satsangi, J. Advances in IBD genetics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, T.T.; Monteleone, G. Immunity, inflammation, and allergy in the gut. Science 2005, 307, 1920–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Horin, S.; Chowers, Y. Neuroimmunology of the gut: Physiology, pathology, and pharmacology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Nam, S.; Brown, C.E.; Zhao, R.; Starr, R.; Ma, Y.; Xie, J.; Horne, D.A.; Malkas, L.H.; Jove, R.; Hickey, R.J. A novel berbamine derivative inhibits cell viability and induces apoptosis in cancer stem-like cells of human glioblastoma, via up-regulation of miRNA-4284 and JNK/AP-1 signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennard-Jones, J.E. Classification of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1989, 170, S2–S6, discussion 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, M.A.; Quintana, F.A.; den Boon, J.A.; Sengupta, S.; Ahlquist, P. Random-set methods identify distinct aspects of the enrichment signal in gene-set analysis. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2007, 1, 85–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatangelo, L.; Maglietta, R.; Distaso, A.; D’Addabbo, A.; Creanza, T.M.; Mukherjee, S.; Ancona, N. Comparative study of gene set enrichment methods. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, P. Permutation Tests: A Practical Guide to Resampling Methods for Testing Hypotheses. In Springer Series in Statistics, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]


| Gene Name | p-Value | FC |
|---|---|---|
| miR-3194 | 0.0005 | −4.52 |
| miR-196A | 0.0005 | −4.47 |
| miR-192 | 0.001 | −4.02 |
| miR-193B | 0.002 | 3.89 |
| miR-19A | 0.002 | 3.81 |
| miR-200A | 0.002 | −3.75 |
| miR-192-STAR | 0.003 | −3.65 |
| LET-7I | 0.003 | 3.64 |
| miR-1273D | 0.003 | 3.59 |
| miR-886-5P | 0.004 | 3.46 |
| miR-668 | 0.004 | 3.45 |
| miR-720 | 0.005 | 3.36 |
| miR-455-3P | 0.005 | 3.35 |
| miR-1913 | 0.005 | −3.32 |
| miR-3138 | 0.005 | 3.29 |
| miR-612 | 0.006 | 3.25 |
| miR-378B | 0.006 | −3.22 |
| miR-551B-STAR | 0.006 | 3.22 |
| miR-323B-3P | 0.006 | −3.22 |
| miR-4264 | 0.006 | 3.22 |
| LET-7I-STAR | 0.007 | 3.16 |
| miR-3150 | 0.007 | −3.13 |
| miR-422A | 0.008 | −3.12 |
| miR-611 | 0.009 | −3.04 |
| miR-3184 | 0.009 | −3.02 |
| miR-4284 | 0.001 | −3.00 |
| miR-129-STAR | 0.001 | −3.00 |
| miR-24 | 0.001 | 3.00 |
| miRNA | Number of DE Canonical Pathways | miRNA | Number of DE GO Terms |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 | 45 | miR-378 | 59 |
| miR-27A | 44 | miR-187 | 58 |
| miR-126 | 42 | miR-3194 | 58 |
| miR-3194 | 39 | miR-126 | 55 |
| miR-486-3P | 39 | miR-17-STAR | 52 |
| miR-148A-STAR | 38 | miR-378C | 52 |
| miR-378 | 38 | miR-331-5P | 50 |
| miR-199B-3P | 35 | miR-623 | 49 |
| miR-302D-STAR | 35 | miR-375 | 44 |
| miR-3133 | 35 | miR-3131 | 43 |
| miR-378C | 35 | miR-378-STAR | 43 |
| miR-17-STAR | 33 | miR-486-3P | 42 |
| miR-187 | 33 | LET-7I | 41 |
| miR-3131 | 33 | miR-148A-STAR | 41 |
| miR-375 | 32 | miR-422A | 41 |
| LET-7I | 31 | miR-1286 | 39 |
| miR-623 | 29 | miR-23A | 39 |
| miR-3120 | 28 | miR-27A | 39 |
| miR-331-5P | 26 | miR-146A | 38 |
| miR-335-STAR | 26 | miR-222 | 37 |
| miR-125B | 24 | miR-335-STAR | 37 |
| miR-199A-3P | 24 | miR-25 | 34 |
| miR-223 | 24 | miR-125B | 32 |
| miR-373-STAR | 22 | miR-200C | 31 |
| miR-22-STAR | 21 | miR-199B-3P | 30 |
| miR-323-5P | 21 | miR-363 | 30 |
| miR-363 | 21 | miR-21 | 29 |
| miR-555 | 21 | miR-4253 | 28 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palmieri, O.; Creanza, T.M.; Bossa, F.; Latiano, T.; Corritore, G.; Palumbo, O.; Martino, G.; Biscaglia, G.; Scimeca, D.; Carella, M.; et al. Functional Implications of MicroRNAs in Crohn’s Disease Revealed by Integrating MicroRNA and Messenger RNA Expression Profiling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071580
Palmieri O, Creanza TM, Bossa F, Latiano T, Corritore G, Palumbo O, Martino G, Biscaglia G, Scimeca D, Carella M, et al. Functional Implications of MicroRNAs in Crohn’s Disease Revealed by Integrating MicroRNA and Messenger RNA Expression Profiling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(7):1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071580
Chicago/Turabian StylePalmieri, Orazio, Teresa Maria Creanza, Fabrizio Bossa, Tiziana Latiano, Giuseppe Corritore, Orazio Palumbo, Giuseppina Martino, Giuseppe Biscaglia, Daniela Scimeca, Massimo Carella, and et al. 2017. "Functional Implications of MicroRNAs in Crohn’s Disease Revealed by Integrating MicroRNA and Messenger RNA Expression Profiling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 7: 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071580
APA StylePalmieri, O., Creanza, T. M., Bossa, F., Latiano, T., Corritore, G., Palumbo, O., Martino, G., Biscaglia, G., Scimeca, D., Carella, M., Ancona, N., Andriulli, A., & Latiano, A. (2017). Functional Implications of MicroRNAs in Crohn’s Disease Revealed by Integrating MicroRNA and Messenger RNA Expression Profiling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(7), 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071580