Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Adipose Tissue Biology: A Brief Overviews
3. Adiponectin: Biosynthesis, Structure and Downstream Signaling
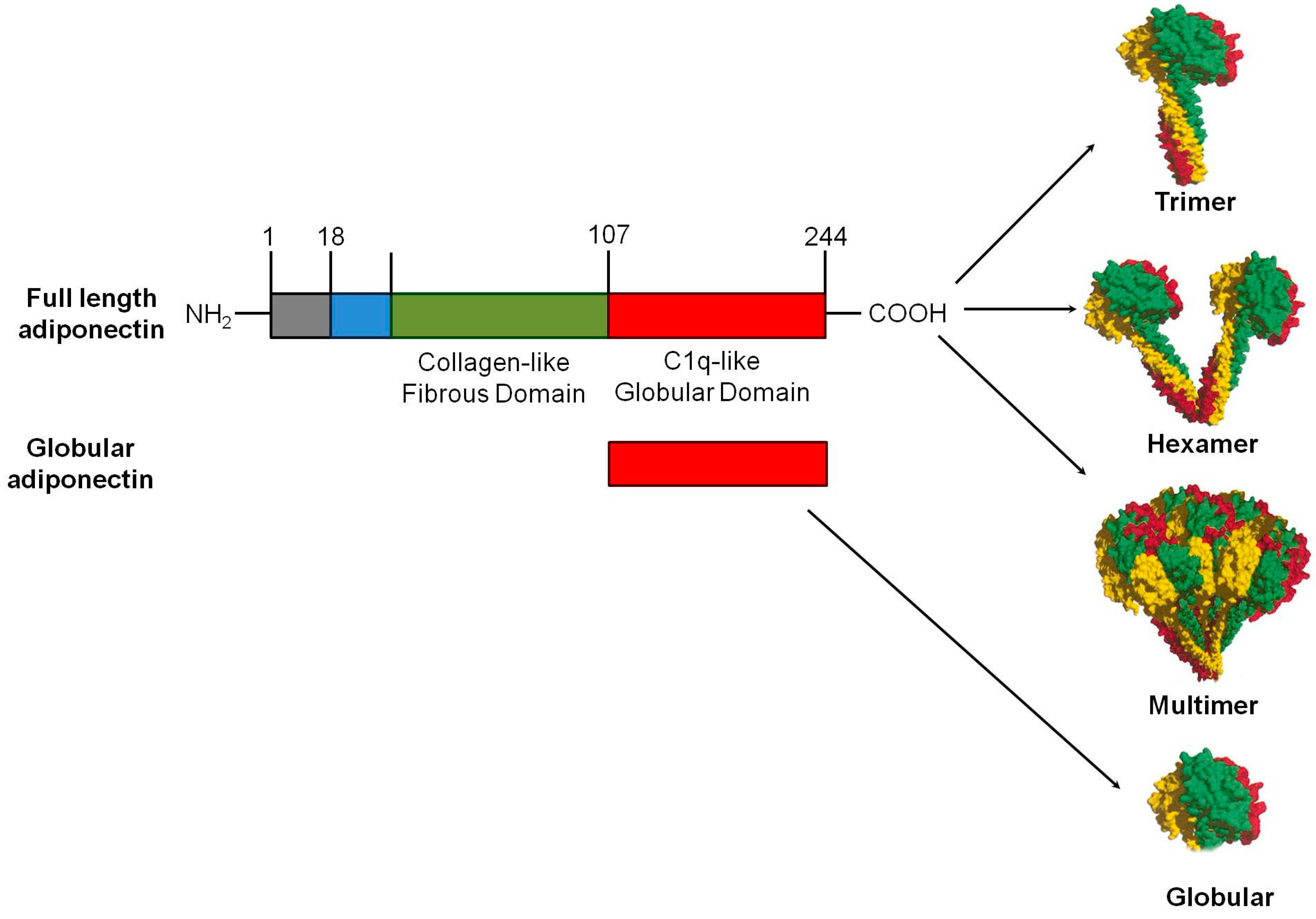
3.1. Structural Features, Synthesis and Post Translational Modification of Adiponectin
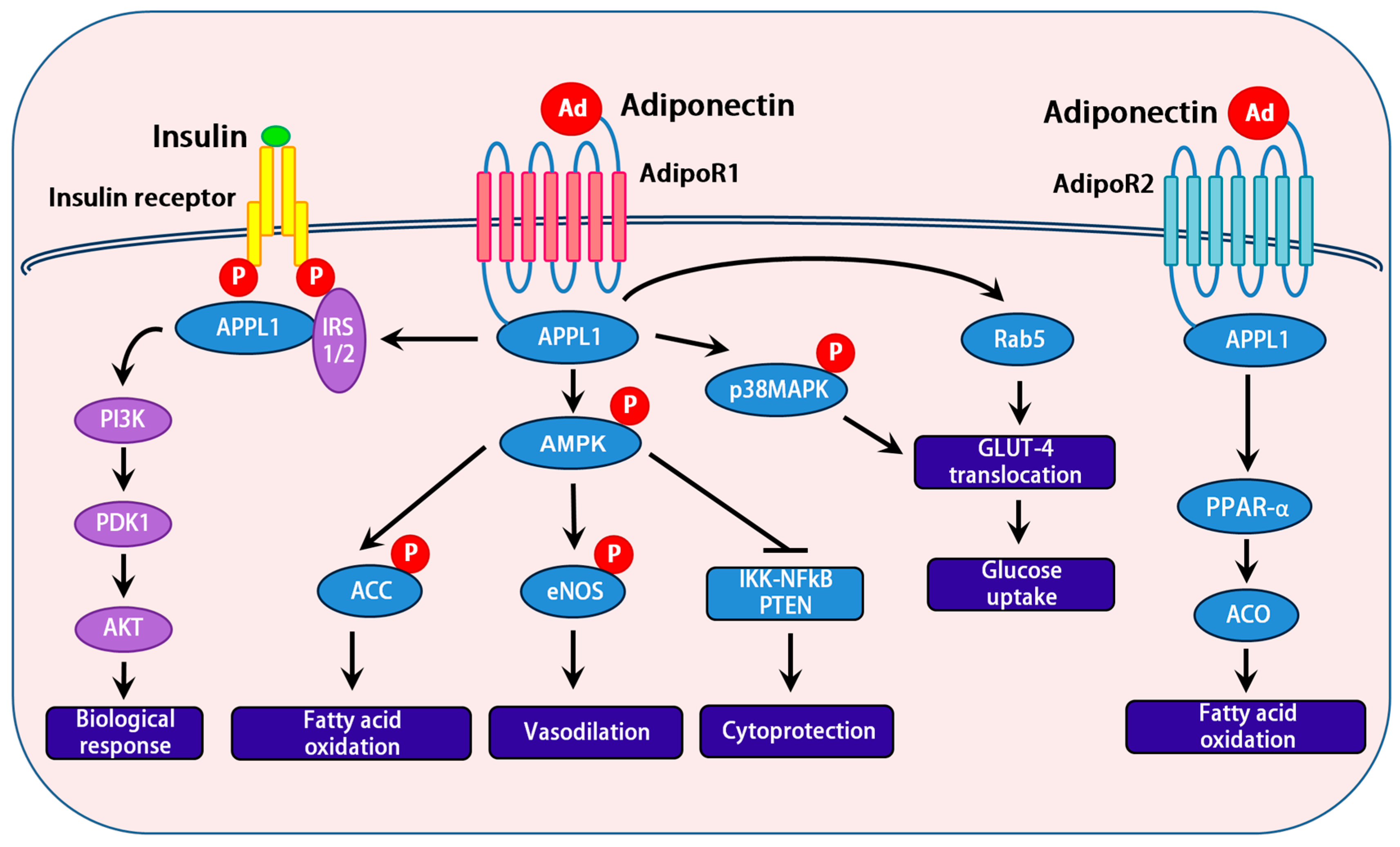
3.2. Adiponectin Receptors
3.3. Role of APPL1 and APPL2 in Adiponectin Signaling
3.4. Downstream Signaling Events of Adiponectin
3.5. Interactions between the AMPK and Insulin Signaling Pathways
4. Adiponectin Signaling in Key Metabolic Tissues
4.1. Skeletal Muscle
4.2. Vascular Endothelium
4.3. Adipocyte/Adipose Tissue
4.4. Liver
5. Can We Increase Circulatory Adiponectin Status?
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghoshal, K.; Bhattacharyya, M. Adiponectin: Probe of the molecular paradigm associating diabetes and obesity. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, P.E.; Williams, S.; Fogliano, M.; Baldini, G.; Lodish, H.F. A novel serum protein similar to c1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26746–26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Okubo, K.; Shimomura, I.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Matsubara, K. cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apm1 (adiposemost abundant gene transcript 1). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 221, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Tobe, T.; Choi-Miura, N.-H.; Mazda, T.; Tomita, M. Isolation and characterization of gbp28, a novel gelatin-binding protein purified from human plasma. J. Biochem. 1996, 120, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Terauchi, Y.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Mori, Y.; Ide, T.; Murakami, K.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Nishida, M.; Arita, Y.; Kumada, M.; Ohashi, K.; Sakai, N.; Shimomura, I.; Kobayashi, H. Adiponectin reduces atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein e-deficient mice. Circulation 2002, 106, 2767–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I.; Sata, M.; Arita, Y.; Nishida, M.; Maeda, N.; Kumada, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Nagaretani, H.; Nishizawa, H. Role of adiponectin in preventing vascular stenosis the missing link of adipo-vascular axis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 37487–37491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahima, R.S.; Flier, J.S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 11, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuzzi, G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausman, G.J. The comparative anatomy of adipose tissue. In New Perspectives in Adipose Tissue: Structure, Function and Development; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.; Liang, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipoq is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10697–10703. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Díez, J.J.; Iglesias, P. The role of the novel adipocyte-derived hormone adiponectin in human disease. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 148, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berner, H.S.; Lyngstadaas, S.P.; Spahr, A.; Monjo, M.; Thommesen, L.; Drevon, C.A.; Syversen, U.; Reseland, J.E. Adiponectin and its receptors are expressed in bone-forming cells. Bone 2004, 35, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoda-Murakami, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Takahashi, K.; Kawamata, S.; Saito, K.; Choi-Miura, N.-H.; Tomita, M. Change in expression of gbp28/adiponectin in carbon tetrachloride-administrated mouse liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaigle, A.L.M.; Jonas, J.-C.; Bauche, I.B.; Cornu, O.; Brichard, S.M. Induction of adiponectin in skeletal muscle by inflammatory cytokines: In vivo and in vitro studies. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 5589–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.V.; Abraheem, A.; Dotsenko, O.; Creamer, J.; Gunning, M.; Hughes, E.A.; Lip, G.Y.H. Circulating serum adiponectin levels in patients with coronary artery disease: Relationship to atherosclerotic burden and cardiac function. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 264, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminos, J.E.; Nogueiras, R.N.; Gallego, R.A.; Bravo, S.; Tovar, S.; Garcã-Caballero, T.S.; Casanueva, F.F.; Diéguez, C. Expression and regulation of adiponectin and receptor in human and rat placenta. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 4276–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Tobe, T.; Minoshima, S.; Asakawa, S.; Sumiya, J.; Yoda, M.; Nakano, Y.; Shimizu, N.; Tomita, M. Organization of the gene for gelatin-binding protein (gbp28). Gene 1999, 229, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Arita, Y.; Yamagata, K.; Matsukawa, Y.; Okutomi, K.; Horie, M.; Shimomura, I.; Hotta, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Kihara, S. Genomic structure and mutations in adipose-specific gene, adiponectin. Int. J. Obes. 2000, 24, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissebah, A.H.; Sonnenberg, G.E.; Myklebust, J.; Goldstein, M.; Broman, K.; James, R.G.; Marks, J.A.; Krakower, G.R.; Jacob, H.J.; Weber, J. Quantitative trait loci on chromosomes 3 and 17 influence phenotypes of the metabolic syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.USA 2000, 97, 14478–14483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Otabe, S.; Dina, C.; Yasuda, K.; Populaire, C.L.; Lecoeur, C.C.; Vatin, V.; Durand, E.; Hara, K.; Okada, T. Genome-wide search for type 2 diabetes in japanese affected sib-pairs confirms susceptibility genes on 3q, 15q, and 20q and identifies two new candidate loci on 7p and 11p. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Takahashi, M.; Maeda, K.; Miyagawa, J.; Hotta, K.; Shimomura, I.; Nakamura, T.; Miyaoka, K.; et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 425, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, K.; Funahashi, T.; Arita, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Matsuda, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Iwahashi, H.; Kuriyama, H.; Ouchi, N.; Maeda, K. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magkos, F.; Sidossis, L.S. Recent advances in the measurement of adiponectin isoform distribution. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2007, 10, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajvani, U.B.; Hawkins, M.; Combs, T.P.; Rajala, M.W.; Doebber, T.; Berger, J.P.; Wagner, J.A.; Wu, M.; Knopps, A.; Xiang, A.H. Complex distribution, not absolute amount of adiponectin, correlates with thiazolidinedione-mediated improvement in insulin sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12152–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruebis, J.; Tsao, T.-S.; Javorschi, S.; Ebbets-Reed, D.; Erickson, M.R.S.; Yen, F.T.; Bihain, B.E.; Lodish, H.F. Proteolytic cleavage product of 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein increases fatty acid oxidation in muscle and causes weight loss in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.V.; Schraw, T.D.; Kim, J.-Y.; Khan, T.; Rajala, M.W.; Follenzi, A.; Scherer, P.E. Secretion of the adipocyte-specific secretory protein adiponectin critically depends on thiol-mediated protein retention. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 3716–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, L.; Wang, H.; Farmer, S.R. Adiponectin secretion is regulated by sirt1 and the endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductase ero1-lα. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 4698–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, L.; Xu, A.; Lam, K.S.L.; Wetzel, M.D.; Xiang, R.; Zhang, J.; Xin, X.; Dong, L.Q.; Liu, F. A disulfide-bond a oxidoreductase-like protein (dsba-l) regulates adiponectin multimerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18302–18307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizzell, N.; Rajesh, M.; Jepson, M.J.; Nagai, R.; Carson, J.A.; Thorpe, S.R.; Baynes, J.W. Succination of thiol groups in adipose tissue proteins in diabetes succination inhibits polymerization and secretion of adiponectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25772–25781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, C.; Wang, J.; Ahmad, N.S.; Bogan, J.S.; Tsao, T.-S.; Lodish, H.F. T-cadherin is a receptor for hexameric and high-molecular-weight forms of acrp30/adiponectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10308–10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbard, L.W.; Garlatti, M.L.; Young, L.J.T.; Cardiff, R.D.; Oshima, R.G.; Ranscht, B. T-cadherin supports angiogenesis and adiponectin association with the vasculature in a mouse mammary tumor model. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denzel, M.S.; Scimia, M.-C.; Zumstein, P.M.; Walsh, K.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Ranscht, B. T-cadherin is critical for adiponectin-mediated cardioprotection in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4342–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker-Duffen, J.L.; Nakamura, K.; Silver, M.; Kikuchi, R.; Tigges, U.; Yoshida, S.; Denzel, M.S.; Ranscht, B.; Walsh, K. T-cadherin is essential for adiponectin-mediated revascularization. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 24886–24897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miaczynska, M.; Christoforidis, S.; Giner, A.; Shevchenko, A.; Uttenweiler-Joseph, S.; Habermann, B.; Wilm, M.; Parton, R.G.; Zerial, M. Appl proteins link rab5 to nuclear signal transduction via an endosomal compartment. Cell 2004, 116, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallop, J.L.; McMahon, H.T. Biochemical Society Symposia. In Bar Domains and Membrane Curvature: Bringing Your Curves to the Bar; Portland Press Limited: London, UK, 2005; pp. 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Habermann, B. The BAR-domain family of proteins: A case of bending and binding? EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.C.S.; Schekman, R. Bar domains go on a bender. Science 2004, 303, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.; Vajjhala, P.; Lee, J.S.; Winsor, B.; Munn, A.L. The bar domain proteins: Molding membranes in fission, fusion, and phagy. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 37–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, J.C.; Legg, J.A.; Machesky, L.M. Bar domain proteins: A role in tubulation, scission and actin assembly in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, B.J.; Kent, H.M.; Mills, I.G.; Vallis, Y.; Butler, P.J.G.; Evans, P.R.; McMahon, H.T. Bar domains as sensors of membrane curvature: The amphiphysin bar structure. Science 2004, 303, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Kikani, C.K.; Riojas, R.A.; Langlais, P.; Wang, L.; Ramos, F.J.; Fang, Q.; Christ-Roberts, C.Y.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, R.-Y. Appl1 binds to adiponectin receptors and mediates adiponectin signalling and function. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nechamen, C.A.; Thomas, R.M.; Dias, J.A. Appl1, appl2, akt2 and foxo1a interact with fshr in a potential signaling complex. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 260, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, A.H.; Combs, T.P.; Du, X.; Brownlee, M.; Scherer, P.E. The adipocyte-secreted protein acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepa, S.S.; Zhou, L.; Ryu, J.; Wang, C.; Mao, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, N.; Musi, N.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Liu, F. Appl1 mediates adiponectin-induced lkb1 cytosolic localization through the PP2A-PKCzeta signaling pathway. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Fu, Z.; Wu, J.; Aylor, K.W.; Barrett, E.J.; Cao, W.; Liu, Z. Globular adiponectin ameliorates metabolic insulin resistance via AMPK-mediated restoration of microvascular insulin responses. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 4067–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Zhou, L.; Reyes, C.M.; Liu, F.; Dong, L.Q. Appl1 mediates adiponectin-stimulated p38 mapk activation by scaffolding the tak1-mkk3-p38 mapk pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E103–E110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.K.Y.; Lam, K.S.L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Carling, D.; Wu, D.; Wong, C.; Xu, A. Adiponectin-induced endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation and nitric oxide production are mediated by appl1 in endothelial cells. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Palanivel, R.; Cresser, J.; Schram, K.; Ganguly, R.; Thong, F.S.L.; Tuinei, J.; Xu, A.; Abel, E.D.; Sweeney, G. An appl1-ampk signaling axis mediates beneficial metabolic effects of adiponectin in the heart. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E721–E729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoki, K.; Zhu, T.; Guan, K.-L. Tsc2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell 2003, 115, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoki, K.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wu, J.; Guan, K.-L. Tsc2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by akt and suppresses mtor signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, H.F.; Witczak, C.A.; Fujii, N.; Jessen, N.; Taylor, E.B.; Arnolds, D.E.; Sakamoto, K.; Hirshman, M.F.; Goodyear, L.J. Distinct signals regulate as160 phosphorylation in response to insulin, aicar, and contraction in mouse skeletal muscle. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treebak, J.T.; Glund, S.; Deshmukh, A.; Klein, D.K.; Long, Y.C.; Jensen, T.E.; Jãrgensen, S.B.; Viollet, B.; Andersson, L.; Neumann, D. Ampk-mediated as160 phosphorylation in skeletal muscle is dependent on ampk catalytic and regulatory subunits. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochhead, P.A.; Salt, I.P.; Walker, K.S.; Hardie, D.G.; Sutherland, C. 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside mimics the effects of insulin on the expression of the 2 key gluconeogenic genes pepck and glucose-6-phosphatase. Diabetes 2000, 49, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Takashima, S.; Maeda, N.; Ouchi, N.; Komamura, K.; Shimomura, I.; Hori, M.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Funahashi, T.; Kitakaze, M. Exacerbation of heart failure in adiponectin-deficient mice due to impaired regulation of AMPK and glucose metabolism. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 67, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.-M.; Doyle, P.J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Watson, D.G.; Cooney, G.J.; Kraegen, E.W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-α activation lowers muscle lipids and improves insulin sensitivity in high fat-fed rats. Diabetes 2001, 50, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Minokoshi, Y.A.; Ito, Y.; Waki, H.; Uchida, S.; Yamashita, S.; Noda, M.; Kita, S.; Ueki, K. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating amp-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ceddia, R.B.; Somwar, R.; Maida, A.; Fang, X.; Bikopoulos, G.; Sweeney, G. Globular adiponectin increases glut4 translocation and glucose uptake but reduces glycogen synthesis in rat skeletal muscle cells. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, W.L.; Brozinick, J.T.; Wang, L.-P.; Hawkins, E.D.; Sargent, K.M.; Liu, Y.; Narra, K.; Hoehn, K.L.; Knotts, T.A.; Siesky, A. Inhibition of ceramide synthesis ameliorates glucocorticoid-, saturated-fat-, and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, S.A. Ceramides in insulin resistance and lipotoxicity. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 42–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, K.; Han, J. The p38 signal transduction pathway activation and function. Cell. Signal. 2000, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.J.; Lee, G.Y.; Chung, J.-J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, J.B. Adiponectin increases fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle cells by sequential activation of amp-activated protein kinase, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, A.L.; Joly, E.R.; Prentki, M.; Coderre, L. Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase participate in the stimulation of glucose uptake by dinitrophenol in adult cardiomyocytes. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis-an inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; Wannamethee, G.; Sarwar, N.; Tchernova, J.; Cherry, L.; Wallace, A.M.; Danesh, J.; Whincup, P.H. Adiponectin and coronary heart disease. Circulation 2006, 114, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwashima, Y.; Katsuya, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Ouchi, N.; Ohishi, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Fu, Y.; Motone, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Matsuo, A. Hypoadiponectinemia is an independent risk factor for hypertension. Hypertension 2004, 43, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.S.L.; Xu, A. Adiponectin: Protection of the endothelium. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2005, 5, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, R.; Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Sato, K.; Funahashi, T.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin stimulates angiogenesis in response to tissue ischemia through stimulation of amp-activated protein kinase signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 28670–28674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, M.; Izumiya, Y.; Higuchi, A.; Shibata, R.; Qiu, J.; Kudo, C.; Shin, H.K.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Ouchi, N. Adiponectin prevents cerebral ischemic injury through endothelial nitric oxide synthase-dependent mechanisms. Circulation 2008, 117, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Kumada, M.; Fujita, K.; Hiuge, A.; Hibuse, T.; Ryo, M.; Nishizawa, H.; Maeda, N. Adiponectin replenishment ameliorates obesity-related hypertension. Hypertension 2006, 47, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, Y.; Folco, E.J.; Minami, M.; Wara, A.K.; Feinberg, M.W.; Sukhova, G.K.; Colvin, R.A.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Luster, A.D. Adiponectin inhibits the production of cxc receptor 3 chemokine ligands in macrophages and reduces t-lymphocyte recruitment in atherogenesis. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrocki, A.R.; Hofmann, S.M.; Teupser, D.; Basford, J.E.; Durand, J.L.; Jelicks, L.A.; Woo, C.W.; Kuriakose, G.; Factor, S.M.; Tanowitz, H.B. Lack of association between adiponectin levels and atherosclerosis in mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Kihara, S.; Kumada, M.; Sato, K.; Inoue, T.; Funahashi, T.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin stimulates angiogenesis by promoting cross-talk between amp-activated protein kinase and akt signaling in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Walsh, K.; Kumada, M.; Abe, Y.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y. Selective suppression of endothelial cell apoptosis by the high molecular weight form of adiponectin. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, e27–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobashi, C.; Urakaze, M.; Kishida, M.; Kibayashi, E.; Kobayashi, H.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Takata, M.; Temaru, R.; Sato, A. Adiponectin inhibits endothelial synthesis of interleukin-8. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Muraguchi, M. Adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived plasma protein, inhibits endothelial NF-κB signaling through a camp-dependent pathway. Circulation 2000, 102, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Ouchi, N.; Sato, K.; Higuchi, A.; Ishikawa, T.-O.; Herschman, H.R.; Kihara, S.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin promotes revascularization of ischemic muscle through a cyclooxygenase 2-dependent mechanism. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 3487–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Shibata, R.; Pimentel, D.R.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Walsh, K. Cyclooxygenase-2 induction by adiponectin is regulated by a sphingosine kinase-1 dependent mechanism in cardiac myocytes. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sam, F.; Duhaney, T.-A.S.; Sato, K.; Wilson, R.M.; Ohashi, K.; Sono-Romanelli, S.; Higuchi, A.; De Silva, D.S.; Qin, F.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin deficiency, diastolic dysfunction, and diastolic heart failure. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, R.; Izumiya, Y.; Sato, K.; Papanicolaou, K.; Kihara, S.; Colucci, W.S.; Sam, F.; Ouchi, N.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin protects against the development of systolic dysfunction following myocardial infarction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2007, 42, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Nio, Y.; Maki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Takazawa, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Kawamoto, S.; Kubota, N.; Kubota, T. Targeted disruption of adipor1 and adipor2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyder, L.; Vitaliti, A.; Schneider, H.; Hebbard, L.W.; Moritz, D.R.; Wittmer, M.; Ajmo, M.; Klemenz, R. Increased expression of h/t-cadherin in tumor-penetrating blood vessels. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4682–4688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tkachuk, V.A.; Bochkov, V.N.; Philippova, M.P.; Stambolsky, D.V.; Kuzmenko, E.S.; Sidorova, M.V.; Molokoedov, A.S.; Spirov, V.G.; Resink, T.J. Identification of an atypical lipoprotein-binding protein from human aortic smooth muscle as t-cadherin. FEBS Lett. 1998, 421, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.; Philippova, M.; Antropova, J.; Gubaeva, F.; Iljinskaya, O.; Tararak, E.; Bochkov, V.; Erne, P.; Resink, T.; Tkachuk, V. Expression of cell adhesion molecule t-cadherin in the human vasculature. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 115, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moschen, A.R.; Wieser, V.; Tilg, H. Adiponectin: Key player in the adipose tissue-liver crosstalk. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 5467–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, J.P.; Richards, A.A.; Hickman, I.J.; Macdonald, G.A.; Prins, J.B. Adiponectin-a key adipokine in the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2006, 8, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowers, J.R. Endocrine functions of adipose tissue: Focus on adiponectin. Clin. Cornerstone 2008, 9, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Luo, N.; Klein, R.L.; Garvey, W.T. Adiponectin promotes adipocyte differentiation, insulin sensitivity, and lipid accumulation. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Van De Wall, E.; Laplante, M.; Azzara, A.; Trujillo, M.E.; Hofmann, S.M.; Schraw, T.; Durand, J.L.; Li, H.; Li, G. Obesity-associated improvements in metabolic profile through expansion of adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2621–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, T.P.; Pajvani, U.B.; Berg, A.H.; Lin, Y.; Jelicks, L.A.; Laplante, M.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Rajala, M.W.; Parlow, A.F.; Cheeseboro, L. A transgenic mouse with a deletion in the collagenous domain of adiponectin displays elevated circulating adiponectin and improved insulin sensitivity. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Weigert, J.; Neumeier, M.; Wanninger, J.; Schãffler, A.; Luchner, A.; Schnitzbauer, A.A.; Aslanidis, C.; Buechler, C. Low-abundant adiponectin receptors in visceral adipose tissue of humans and rats are further reduced in diabetic animals. Arch. Med. Res. 2010, 41, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordlie, R.C.; Foster, J.D.; Lange, A.J. Regulation of glucose production by the liver. Ann. Rev. Nutr. 1999, 19, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, T.P.; Berg, A.H.; Obici, S.; Scherer, P.E.; Rossetti, L. Endogenous glucose production is inhibited by the adipose-derived protein ACRP30. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajvani, U.B.; Du, X.; Combs, T.P.; Berg, A.H.; Rajala, M.W.; Schulthess, T.; Engel, J.R.; Brownlee, M.; Scherer, P.E. Structure-function studies of the adipocyte-secreted hormone acrp30/adiponectin implications for metabolic regulation and bioactivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9073–9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrocki, A.R.; Rajala, M.W.; Tomas, E.; Pajvani, U.B.; Saha, A.K.; Trumbauer, M.E.; Pang, Z.; Chen, A.S.; Ruderman, N.B.; Chen, H. Mice lacking adiponectin show decreased hepatic insulin sensitivity and reduced responsiveness to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ agonists. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 2654–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Wang, Y.; Keshaw, H.; Xu, L.Y.; Lam, K.S.L.; Cooper, G.J.S. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin alleviates alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, N.L.; Trent, C.M.; Raetzsch, C.F.; Flurkey, K.; Boysen, G.; Perfetti, M.T.; Jeong, Y.-C.; Klebanov, S.; Patel, K.B.; Khodush, V.R. Low utilization of circulating glucose after food withdrawal in snell dwarf mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35069–35077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towler, M.C.; Hardie, D.G. AMP-activated protein kinase in metabolic control and insulin signaling. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Ishihara, K.; Miyake, K.; Kaji, Y.; Kawamitsu, H.; Fujii, M.; Sugimura, K.; Ohara, T. Inverse correlation between serum adiponectin concentration and hepatic lipid content in japanese with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2005, 54, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuppalanchi, R.; Marri, S.; Kolwankar, D.; Considine, R.V.; Chalasani, N. Is adiponectin involved in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis? A preliminary human study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2005, 39, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaser, S.; Moschen, A.; Cayon, A.; Kaser, A.; Crespo, J.; Pons-Romero, F.; Ebenbichler, C.F.; Patsch, J.R.; Tilg, H. Adiponectin and its receptors in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut 2005, 54, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Campbell-Sargent, C.; Mirshahi, F.; Rizzo, W.B.; Contos, M.J.; Sterling, R.K.; Luketic, V.A.; Shiffman, M.L.; Clore, J.N. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Association of insulin resistance and mitochondrial abnormalities. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, A.; Tam, P.K.H.; Lam, K.S.L.; Chan, L.; Hoo, R.L.C.; Liu, J.; Chow, K.H.M.; Wang, Y. Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to the increased vulnerabilities of adiponectin knockout mice to liver injury. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Murakami, K.; Motojima, K.; Komeda, K.; Ide, T.; Kubota, N.; Terauchi, Y.; Tobe, K. The mechanisms by which both heterozygous peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor î³ (pparî³) deficiency and pparî³ agonist improve insulin resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 41245–41254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, T.P.; Wagner, J.A.; Berger, J.; Doebber, T.; Wang, W.-J.; Zhang, B.B.; Tanen, M.; Berg, A.H.; O′rahilly, S.; Savage, D.B. Induction of adipocyte complement-related protein of 30 kilodaltons by pparî³ agonists: A potential mechanism of insulin sensitization. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.A.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Kong, A.P.S.; Bandukwala, R.; Aroda, V.; Carter, L.; Baxi, S.; Mudaliar, S.R.; Henry, R.R. Modulation of circulating and adipose tissue adiponectin levels by antidiabetic therapy. Diabetes 2003, 52, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, N.; Terauchi, Y.; Kubota, T.; Kumagai, H.; Itoh, S.; Satoh, H.; Yano, W.; Ogata, H.; Tokuyama, K.; Takamoto, I. Pioglitazone ameliorates insulin resistance and diabetes by both adiponectin-dependent and-independent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8748–8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Wang, H.; Hoo, R.L.C.; Sweeney, G.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Chu, W.; Qin, G.; Lam, K.S.L. Selective elevation of adiponectin production by the natural compounds derived from a medicinal herb alleviates insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in obese mice. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.; Gholamhoseinian, A.; Fallah, H. Zataria multiflora increases insulin sensitivity and pparî³ gene expression in high fructose fed insulin resistant rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2014, 17, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Arbeláez, D.; Lahera, V.; Oubiña, P.; Valero-Muñoz, M.; de las Heras, N.; Rodríguez, Y.; García, R.G.; Camacho, P.A.; López-Jaramillo, P. Aged garlic extract improves adiponectin levels in subjects with metabolic syndrome: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, crossover study. Med. Inflamm. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Kim, D.H.; Tsenovoy, P.L.; Peterson, S.J.; Rezzani, R.; Rodella, L.F.; Aronow, W.S.; Ikehara, S.; Abraham, N.G. Treatment of obese diabetic mice with a heme oxygenase inducer reduces visceral and subcutaneous adiposity, increases adiponectin levels, and improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. l-cysteine supplementation increases adiponectin synthesis and secretion, and glut4 and glucose utilization by upregulating disulfide bond a-like protein expression mediated by mcp-1 inhibition in 3t3-l1 adipocytes exposed to high glucose. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 414, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlet, E.; Jain, S.K. Manganese supplementation increases adiponectin and lowers icam-1 and creatinine blood levels in zucker type 2 diabetic rats, and downregulates icam-1 by upregulating adiponectin multimerization protein (DSBA-l) in endothelial cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 429, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decochez, K.; Rippley, R.K.; Miller, J.L.; De Smet, M.; Yan, K.X.; Matthijs, Z.; Riffel, K.A.; Song, H.; Zhu, H.; Maynor, H.O. A dual ppar α/γ agonist increases adiponectin and improves plasma lipid profiles in healthy subjects. Drugs R&D 2006, 7, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Furuhashi, M.; Ura, N.; Higashiura, K.; Murakami, H.; Tanaka, M.; Moniwa, N.; Yoshida, D.; Shimamoto, K. Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system increases adiponectin concentrations in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 2003, 42, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, T.J.; Davidson, L.E.; Janiszewski, P.M.; Després, J.-P.; Hudson, R.; Ross, R. Associations of the limb fat to trunk fat ratio with markers of cardiometabolic risk in elderly men and women. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2009, 64, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrila, A.; Chan, J.L.; Yiannakouris, N.; Kontogianni, M.; Miller, L.C.; Orlova, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. Serum adiponectin levels are inversely associated with overall and central fat distribution but are not directly regulated by acute fasting or leptin administration in humans: Cross-sectional and interventional studies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4823–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurimae, J.; Hofmann, P.; Jurimae, T.; Mãestu, J.; Purge, P.; Wonisch, M.; Pokan, R.; Von Duvillard, S.P. Plasma adiponectin response to sculling exercise at individual anaerobic threshold in college level male rowers. Int. J. Sports Med. 2006, 27, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jürimäe, J.; Purge, P.; Jürimäe, T. Adiponectin is altered after maximal exercise in highly trained male rowers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 93, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriketos, A.D.; Gan, S.K.; Poynten, A.M.; Furler, S.M.; Chisholm, D.J.; Campbell, L.V. Exercise increases adiponectin levels and insulin sensitivity in humans. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 629–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numao, S.; Katayama, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Matsuo, T.; Tanaka, K. Influence of acute aerobic exercise on adiponectin oligomer concentrations in middle-aged abdominally obese men. Metabolism 2011, 60, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, A.V.; Usmani, A.; Rajamanickam, A.; Moheet, A. Thiazolidinediones and risk of heart failure in patients with or at high risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2011, 11, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronoff, S.; Rosenblatt, S.; Braithwaite, S.; Egan, J.W.; Mathisen, A.L.; Schneider, R.L. Pioglitazone hydrochloride monotherapy improves glycemic control in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes: A 6-month randomized placebo-controlled dose-response study. The pioglitazone 001 study group. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billington, E.O.; Grey, A.; Bolland, M.J. The Effect of Thiazolidinediones on Bone Mineral Density and Bone Turnover: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard, P. Discrepancies in bone mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes—A meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2007, 18, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.D.; Ferrara, A.; Peng, T.; Hedderson, M.; Bilker, W.B.; Quesenberry, C.P.; Vaughn, D.J.; Nessel, L.; Selby, J.; Strom, B.L. Risk of bladder cancer among diabetic patients treated with pioglitazone. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, V. Effect of thiazolidinediones on body weight in patients with diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Med. 2003, 115, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, F.L.; Patz, A. Macular EDEMA. A complication of diabetic retinopathy. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1984, 28, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061321
Achari AE, Jain SK. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061321
Chicago/Turabian StyleAchari, Arunkumar E., and Sushil K. Jain. 2017. "Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061321
APA StyleAchari, A. E., & Jain, S. K. (2017). Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061321



