Abstract
Ghrelin was discovered in 1999 as the endogenous ligand of the growth-hormone secretagogue receptor 1a (GHSR1a). Since then, ghrelin has been found to exert a plethora of physiological effects that go far beyond its initial characterization as a growth hormone (GH) secretagogue. Among the numerous well-established effects of ghrelin are the stimulation of appetite and lipid accumulation, the modulation of immunity and inflammation, the stimulation of gastric motility, the improvement of cardiac performance, the modulation of stress, anxiety, taste sensation and reward-seeking behavior, as well as the regulation of glucose metabolism and thermogenesis. Due to a variety of beneficial effects on systems’ metabolism, pharmacological targeting of the endogenous ghrelin system is widely considered a valuable approach to treat metabolic complications, such as chronic inflammation, gastroparesis or cancer-associated anorexia and cachexia. The aim of this review is to discuss and highlight the broad pharmacological potential of ghrelin pathway modulation for the treatment of anorexia, cachexia, sarcopenia, cardiopathy, neurodegenerative disorders, renal and pulmonary disease, gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, inflammatory disorders and metabolic syndrome.
1. Introduction
In the early 1980s, Cyril Bowers and Frank Momamy generated a group of opioid peptide derivatives that potently stimulated the release of growth hormone (GH) from the anterior pituitary [1,2]. Of appreciable note, these GH-releasing peptides affected GH release independently of the growth-hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) pathway [3,4,5,6] and also activated neuronal populations in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus [3]. Together, these data pointed to the presence of an as-yet unknown endocrine system with metabolic action not only on the pituitary, but also on the hypothalamus. In 1996, Roy Smith and Lex van der Ploeg identified the receptor for the GH-releasing peptides as a full-length seven-transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptor, which henceforth became known as the growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a (GHSR1a) [7]. In 1999, Masayasu Kojima and Kenji Kangawa identified the gastrointestinal peptide hormone ghrelin as the endogenous ligand of GHSR1a [8]. Initially identified as an endogenous GH secretagogue, work by Matthias Tschöp and Mark Heiman soon later identified ghrelin as a neuropeptide with strong ability to enhance food intake and appetite via stimulation of CNS neurocircuitry [9]. While ghrelin remains as of today the only known peripheral gut hormone that is capable of stimulating food intake and body weight gain, a myriad of studies have subsequently revealed that ghrelin is a hormone with a vast spectrum of physiological actions that go far beyond its initial classification as a hunger hormone (Figure 1; for a review, see [10]). In this regard, beyond its ability to stimulate food intake via centrally-regulated signal mechanisms [11,12,13], ghrelin acts on the stomach to enhance gastric acid secretion and gastric motility [14], modulates taste sensation [15], stress and anxiety [16], sleep/wake cycle [17], glucose metabolism [18] and brown fat thermogenesis [19]. Due to these and numerous other beneficial effects on systems metabolism, pharmacological modulation of the endogenous ghrelin system is widely considered a promising approach to treat a variety of metabolic complications, most prominently gastroparesis and pathological underweight associated with anorexia nervosa or cancer cachexia. In this review, we will summarize the various biological actions of ghrelin, with a special focus on the druggability of the endogenous ghrelin system for the aforementioned diseases.
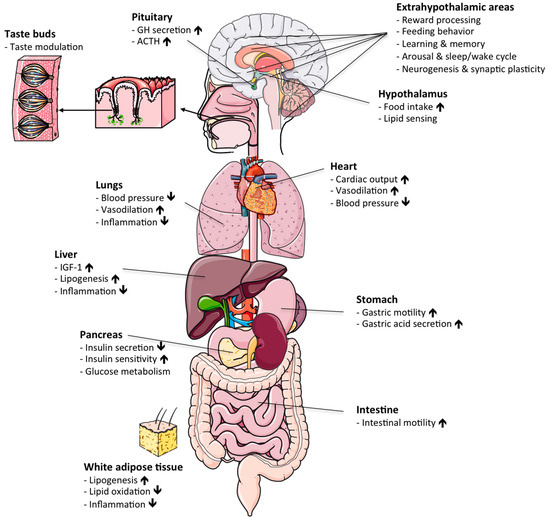
Figure 1.
Physiological actions of ghrelin: schematic illustrating the various hormonal actions of ghrelin in different target organs. ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone. GH, growth hormone. IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1. Up/down arrows denote increase/decrease.
2. Molecular Structure and Synthesis of Ghrelin
Ghrelin is a 28-amino acid peptide that is primarily produced and secreted by X/A-like cells in the oxyntic glands of the gastric mucosa, especially in the gastric fundus [8]. The ghrelin gene encodes the 117-amino acid precursor peptide preproghrelin, which is post-translationally cleaved to produce the mature 28-amino acid ghrelin peptide (Figure 2).
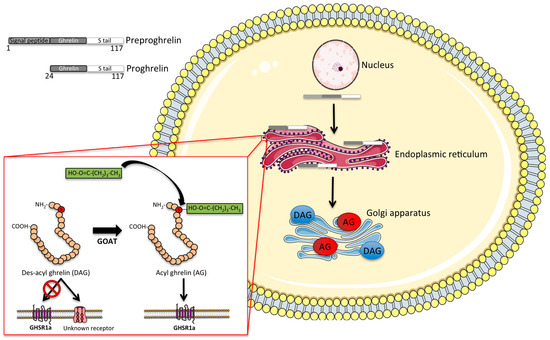
Figure 2.
Intracellular processing of ghrelin: schematic illustrating the intracellular processing of ghrelin. The 117-aminoacid precursor peptide preproghrelin is cleaved to proghrelin, which is in turn cleaved by prohormone convertase 1/3 to the mature 28-amino acid ghrelin peptide. Prior to secretion, des-acyl ghrelin is acylated by the hormone ghrelin-O-acyltransferase (GOAT), which permits its binding to the growth-hormone secretagogue receptor 1a (GHSR1a). AG, acyl ghrelin. DAG, des-acyl ghrelin.
To activate its only known receptor, ghrelin requires attachment (acylation) of a fatty acid (preferably C8 or C10) to its serine 3 residue, a rare post-translational modification achieved by the enzyme ghrelin-o-acyltransferase (GOAT) [20,21]. GOAT is the only enzyme capable of acylating ghrelin in vivo, as indicated by the absence of acyl ghrelin in mice lacking GOAT [22]. The GOAT-mediated ghrelin acylation is necessary for ghrelin to bind and activate the GHSR [21]. However, although ghrelin acylation is required for most of the physiological effects of ghrelin, including the activation of orexigenic hypothalamic neurocircuits [23], some studies suggest a metabolic role also for des-acyl ghrelin. In detail, des-acyl ghrelin has been reported in some studies to affect feeding [24], adiposity [25] and glucose metabolism [26] by mechanisms independent of GHSR signaling. However, some studies report that the des-acyl form of ghrelin rather antagonizes the effect of acyl ghrelin on feeding [27,28]. In addition, des-acyl ghrelin has been shown to affect differentiation of C2C12 muscle cells [29] and further shows some cardioprotective effects on the heart [30], supposedly acting via an as-yet unidentified receptor [31]. In the general circulation, acyl ghrelin is rapidly degraded by various esterases, such as carboxylesterase and butyrylcholinesterase [32]. The half-life of acyl ghrelin accordingly varies between 10 and 30 min in rodents [32,33] and up to 4 h in humans [32].
The ghrelin receptor is primarily expressed in brain, but lower levels can also be found in certain peripheral organs, such as pancreas, spleen, kidney and adrenal gland [34,35]. In rodent brain, GHSR expression is greatest in the pituitary and in the orexigenic neuropeptide Y/agouti-related protein (NPY/AgRP) neurons of the arcuate nucleus (ARC), but is also highly expressed in regions associated with reward processing, such as the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area (VTA) [36].
Ligand-induced activation of GHSR1a leads to an increase in intracellular calcium levels by the activation of G-protein subtype Gaq/11, which stimulates the production of inositol triphosphate (IP3), activation of protein kinase C (PKC) and phospholipase C (PLC) with a concomitant release of calcium from the ER [37]. In addition, GHSR activation entails activation of Gi/o signaling mechanisms [38,39] and induces the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, as well as induction of the PI-3 kinase (PI3K) and phosphorylation of Akt [40,41,42]. In the hypothalamic NPY/AgRP neurons, ghrelin increases levels of the intracellular energy sensor AMPK [43]. AMPK switches off ATP-consuming pathways and turns on ATP-generating pathways, such as glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation. Downstream actions of AMPK include the disinhibition of CPT1, which transports fatty acids into mitochondria for oxidation. In the hypothalamus, ghrelin increases the concentration of fatty acids, the substrate for mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and concurrently increases expression of CPT1 to facilitate fatty acid oxidation [44]. Along this line, ghrelin potently activates the mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2), which functions as a free radical scavenger and whose stimulation is crucial for ghrelin-induced stimulation of NPY neurons and mitochondrial proliferation [45]. Ghrelin activation of UCP2 may thus be part of an endocrine mechanism to buffer the ghrelin-activated cells from excess ROS production by the fatty acid oxidation. This provides a potential mechanism whereby NPY/AgRP neurons can maintain a high ghrelin-induced firing rate during low energy states, whereas the anorexigenic pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons with their lack of GHSR receptor-induced UCP2 activation cannot buffer against ROS, as well, and thus, cannot maintain neuronal firing during starvation [45]. In addition, ghrelin was reported to act via the GHSR to activate the deacetylase Sirt1, which acts through the tumor suppressor gene p53 to increase AMPK levels [46]; blockade of this pathway abolishes the central orexigenic effects of ghrelin [47,48]. Associated with these signaling cascades is upregulation of several transcription factors, including Bsx, forkhead box O1 (FoxO1) and cAMP response element binding protein (pCREB) [49], as well as the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway [50].
While ghrelin was identified as a potent stimulator of GH release from the anterior pituitary [8], it soon became apparent that ghrelin is far more than a GH secretagogue. Accordingly, since its discovery in 1999, a myriad of preclinical and clinical studies have shown that ghrelin exerts a surprising variety of metabolic actions in such distinct areas as the regulation of food intake and satiety [51], modulation of energy expenditure via regulation of brown fat thermogenesis [19], regulation of lipid storage and utility, which is notably independent of ghrelin’s orexigenic effects [9], and modulation of the stress axis [52], sleep/wake rhythm [17], GI motility [14] and glucose metabolism [18].
The most well-established effect of ghrelin is the stimulation of food intake via the activation of orexigenic NPY/AgRP neurons in the ARC [11,12,13]. Although ghrelin may act in other brain regions important for feeding behavior, such as the mesolimbic reward circuits [53] or the brainstem [54], ghrelin does not stimulate feeding in mice lacking NPY/AgRP neurons, demonstrating that this population is essential for ghrelin-induced feeding [55]. Consistent with a role for ghrelin in regulating feeding behavior, circulating levels of acyl ghrelin rise shortly prior to anticipated meal time and return to baseline levels within the first hour after a meal [56,57,58,59,60]. While both total ghrelin levels and acyl ghrelin levels have been reported to progressively increase during fasting in pigs [61] and rodents [62], acyl ghrelin levels seem to be rather suppressed by long-term fasting in humans [60]. Such discrepancies may be due to different measurement methods, as Gahete and colleagues observed a fasting-induced increase in acyl ghrelin in mice using a commercial ELISA kit [62], whereas Kirchner and colleagues did not observe fasting-induced increase in acyl ghrelin as measured with MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry [63]. Suppression of acyl ghrelin during fasting would however be consistent with the observation that acylation of ghrelin relies predominantly on dietary rather than endogenously-derived lipids [63]. Notably, ghrelin enhances adiposity independently of its orexigenic effects by increasing lipid storage and by decreasing lipid utilization [9,64].
3. Ghrelin and Inflammation
Apart from its well-established orexigenic and lipogenic effects, ghrelin possesses anti-inflammatory effects and ameliorates anti-oxidative stress under a variety of pathological conditions. This was first demonstrated in a rat model of surgically-induced septic shock, where concurrent ghrelin treatment was shown to reduce the mortality rate by nearly 50% [65,66]. Soon thereafter, both ghrelin and its receptor were shown to be expressed in human immune cells, and ghrelin acts on both immune cells and endothelial cells to block the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by inflammatory stimuli such as leptin, TNF-α and endotoxins [67,68]. Research since then has clearly established the anti-inflammatory actions of ghrelin and has shown its potential in the treatment of a multitude of inflammatory disorders. In a rat model of arthritis, daily treatment with the ghrelin analog GHRP-2 for eight days ameliorated arthritis scores and abolished the effects of arthritis on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis [69]. Ghrelin abolishes the inflammation, weight loss, diarrhea and abnormal colonic histology in mice and rats with trinitrobenzene-induced colitis [70,71]. Ghrelin similarly prevents inflammation, oxidative stress and organ damage associated with pancreaticobiliary inflammation [72] and several other inflammatory conditions, such as chronic airway respiratory infection [73], experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis [74] and diabetic neuropathy [75]. Beneficial effects of ghrelin have also been demonstrated in several conditions of acute inflammation. Twice-daily ghrelin injections for one week were shown to ameliorate deleterious post-infarct inflammatory myocardial remodeling caused by coronary artery ligation in rats [76]. Furthermore, ghrelin completely reversed the histological and biochemical alterations caused by experimentally-induced subarachnoid-hemorrhage in rats, normalizing plasma cytokine levels and brain oxidative stress markers, which was associated with improved neurological scores 48 h after hemorrhage, [77]. Similar effects of ghrelin, including enhanced seven-day survival, were observed in rats with cerebral ischemia induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion [78]. Finally, both the acylated and desacylated forms of ghrelin have been shown to reverse the pro-inflammatory effect of chronic high-fat diet feeding [79,80,81,82].
Despite a plethora of animal studies supporting the therapeutic anti-inflammatory potential of ghrelin, only a few human trials have been conducted on the use of ghrelin in inflammatory disorders. Kodama and colleagues reported that three-week administration of ghrelin to patients with chronic respiratory infection reduced neutrophil density and air sputum inflammatory cytokine levels, as well as increased exercise tolerance [73]. In a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial, three weeks of ghrelin treatment in patients with COPD similarly improved respiratory symptoms and respiratory strength [83]. More recently, a randomized trial showed ghrelin treatment to reduce inflammation and pulmonary complications during the postoperative period following esophagectomy [84].
4. Ghrelin GI Motility
One of the earliest established functions of ghrelin is its effect on the GI tract. In particular, Masuda and colleagues showed as early as 2000 that ghrelin stimulates both gastric motility and gastric acid secretion in rats, effects that were notably abolished by bilateral vagotomy [14]. In addition, ghrelin stimulates fasting-like gastric motor activity, likely via a pathway involving the stimulation of NPY neurons, preganglionic dorsal vagal complex (DVC) neurons and vagal afferent neurons [85,86,87], but also via direct action on the GI tract through intrinsic cholinergic neurons in the small intestine [88]. The ability of ghrelin to stimulate gastric motility was later confirmed also in human subjects [89]. Induced gastrointestinal dysfunction is associated with impaired ghrelin signaling [90], and ghrelin levels are found to be reduced in multiple GI disorders, such as gastritis [91], H. pylori infection [92], dyspepsia and reflux disease [93,94]. Ghrelin has further been shown to improve gastric emptying in multiple rodent models of dyspepsia and gastroparesis [95,96,97,98,99], suggesting its therapeutic potential for the treatment of GI disorders. In humans, ghrelin treatment of patients with dyspepsia increased food intake and subjective appetite [100], while a randomized clinical trial in gastroparesis patients showed ghrelin to relieve gastroparesis symptoms, including nausea and vomiting [101]. Treatment with the ghrelin signaling potentiator rikkunshito was further shown to improve symptoms of dyspepsia, associated with an increase in plasma ghrelin levels [102]. Finally, relamorelin (also known as RM-131), a selective GHSR agonist [103], was shown to substantially improve symptoms of delayed gastric emptying in a randomized phase 1b trial of diabetic patients [104] and is currently in a clinical phase 2b trial for the treatment of diabetic gastroparesis [10,105].
5. Anorexia/Cachexia
Anorexia is defined as pathological underweight associated with the loss of the desire to eat. Anorexia can be associated with psychological disorders, such as anorexia nervosa, or with chronic organic diseases that cause a loss of appetite, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), end-stage cancer or sepsis. In the most severe cases, anorexia co-exists with cachexia, which is defined as excessive skeletal muscle and adipose tissue wasting as a result of a chronic imbalance between anabolic and catabolic processes. Cachexia is typically characterized by an abnormal release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and activation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), both important factors contributing to the pathologically-negative energy balance that is typically observed in patients with cachexia. Due to its orexigenic and lipogenic action, ghrelin is commonly acknowledged to possess therapeutic potential for the treatment of anorexia and cachexia (for a review, see [106]).
There are several preclinical and clinical studies supporting a role for ghrelin in the treatment of pathological underweight and cachexia. In this regard, treatment with ghrelin or ghrelin analogs has been shown to increase food intake and body weight in several rodent models of anorexia/cachexia, even though partial resistance to the effects of ghrelin has sometimes been observed in rodent models of cachexia [107,108]. In rats, ghrelin treatment suppresses the cachectic weight loss induced by human melanoma cancer cell implantations [109]. Improved food intake and prevention of tissue wasting has further been observed upon ghrelin treatment in a mouse model of lung cancer-induced cachexia [110], as well as in a series of studies evaluating the role of ghrelin and its analogs in rodent tumor-bearing models of cachexia [108,111,112,113,114]. In line with these data, ghrelin stimulates feeding and lean body mass accrual in a rat model of chronic kidney disease-induced cachexia [115], attenuates cachexia in rats with heart failure [116], inhibits skeletal muscle breakdown after burn injury in rats [117] and inhibits angiotensin II-induced cachexia in mice [118].
In humans, a number of studies have demonstrated that ghrelin levels are elevated in patients suffering from anorexia nervosa [119,120,121,122,123] and cachexia [124,125] and that the ability of ghrelin to acutely stimulate subjective hunger is blunted in anorexia nervosa patients [126], which raised the possibility that ghrelin action is limited in these disorders. However, other studies demonstrated that long-term treatment with ghrelin can indeed stimulate hunger and feeding in patients with anorexia nervosa [127]. Other than the duration of treatment, the discrepant results may be explained by the mode of administration, which varied between the different studies from continuous ghrelin infusion [126] to twice daily 5-min i.v. infusion [127]. Most recently, it was shown that intranasal administration of the ghrelin receptor agonist GHRP-2 for one year was effective in improving appetite, body weight and glycemia in a severely emaciated anorexia nervosa patient [128]. There is by now also numerous human trials showing that ghrelin and ghrelin agonists can effectively improve anorexia and cachexia in cancer patients with few adverse effects [129,130,131]. Of special interest is the recently developed ghrelin receptor agonist anamorelin, which holds promise for the treatment of cancer anorexia-cachexia [132,133,134,135]. Similarly, several studies report that chronic ghrelin treatment improves appetite in patients suffering from renal failure [136,137].
6. Cardiovascular Disorders
Ghrelin and its receptor are both expressed in the rodent and human heart [138,139], and ghrelin is known to exert effects on the cardiovascular system in rodents and healthy human subjects [140,141]. Soon after its discovery, ghrelin was shown to improve cardiac function in a rat model of heart failure [116]. Ghrelin has also been shown to prevent cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis after myocardial infarction [142] and protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat heart [143]. Consequently, ghrelin treatment has been found to reduce mortality in rodent models of cardiovascular disease [144]. Ghrelin may exert its protective effect on the heart through multiple pathways, including activating AMPK and autophagy [145,146], as well as modulating ER stress [147].
Although there is scarce data on the use of ghrelin for cardiovascular disorders in human subjects, it was shown that intravenous administration of ghrelin for three weeks reduces arterial blood pressure, improves left ventricular function, work capacity and peak oxygen consumption during exercise in patients with chronic heart failure [116,148], as well as reversing endothelial dysfunction in patients with metabolic syndrome [149], suggesting its therapeutic potential for human patients suffering from cardiovascular and circulatory disorders.
7. Sarcopenia
Sarcopenia refers to the degenerative loss of skeletal muscle mass, commonly associated with aging, but may also accompany cachexia more generally. Ghrelin levels are generally found to be lower in elderly compared to younger subjects [150,151,152,153], and elderly subjects with sarcopenia have lower ghrelin levels than those without sarcopenia [153].
In rodents, ghrelin has been found to prevent muscle-wasting associated with tumors and cisplatin treatment [154], and enhancing ghrelin signaling with the ghrelin-potentiators rikkunshito was found to inhibit age-related sarcopenia and to prolong survival in a rodent model of senescence [155]. Chronic central ghrelin treatment may also enhance bone mass in rodents [156].
In humans, a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled cross-over trial found that oral administration of the ghrelin mimetic ibutamoren (MK-677) for 12 months in healthy elderly subjects increased GH and IGF-1 levels to that of younger adults and prevented lean mass loss without severe side effects [157].
8. Renal Failure
In mice, ghrelin levels are sharply increased by removal of the kidneys, and numerous studies in humans have shown ghrelin levels to be elevated in end-stage renal disease and chronic kidney failure, which likely reflects an impaired renal clearance of ghrelin [158,159,160,161,162]. Nonetheless, treatment with ghrelin has been shown to improve renal function and attenuate renal fibrosis and inflammation in rodent models of kidney disease or injury [163,164,165]. To date, no human data on the use of ghrelin to treat kidney disease are available.
9. Neurodegenerative Disorders
Aside from its central effects on hunger and appetite, ghrelin signaling plays a role in numerous higher brain functions, such as arousal and sleep-wake cycle [17,166], as well enhancing memory, learning, synaptic plasticity [16,167,168,169] and neurogenesis [170]. Ghrelin may in addition have a neuroprotective function in both hypothalamic and cortical neurons by inhibiting apoptosis [171,172,173] and inflammation [174]. Since ghrelin levels generally decline with age and exert a positive effect on memory, learning and neuroplasticity, the role of ghrelin in etiology and possible treatment of neurodegenerative disorders has garnered some interest (for extensive reviews, see [175,176]).
9.1. Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease
Although it was initially reported that plasma levels of ghrelin were not changed in patients with Alzheimer’s disease [177], Gahete and colleagues later reported that several components of the ghrelin system, including ghrelin, GOAT and GHSR, were reduced in the temporal gyrus in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease [178]. Although there are no reports on genetic association between ghrelin gene polymorphisms and AD [179], it was later reported that ghrelin gene variants are associated with cognitive dysfunction [180]. However, the exact nature of the relationship between ghrelin and cognitive function in healthy subjects is still unclear, since plasma ghrelin levels have been reported to rather be inversely associated with cognitive function in elderly non-demented patients [181]. Additionally, a more recent study in healthy young subjects concluded that, in contrast to the animal data, acute ghrelin administration did not enhance any parameters of cognitive function, including memory, mental speed or attention [182].
More specifically pertaining to Alzheimer’s disease, ghrelin has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce abnormal tau phosphorylation of hippocampal neurons [183], as well as modulate the production of inflammatory cytokines induced by β-amyloid fibrils in microglia [184]. Central intracerebroventricular (ICV) administration of ghrelin ameliorated the cognitive dysfunction and neurodegeneration induced by intrahippocampal injections of amyloid-β oligomers in mice and rats, with associated improvements in cerebral glucose metabolism [185,186]. Oral administration of the ghrelin agonist LY444711 similarly improved cognition and reduced cerebral inflammation and beta-amyloid levels in the APP-SwDI genetic mouse model of AD (APP-Swedish K760N/M671L, Dutch E693Q and Iowa D694N mouse) [187,188]. Finally, peripheral administration of ghrelin rescued the impaired neurogenesis occurring in the 5XFAD (five familial AD mutations) genetic mouse model of AD [189]. However, in contrast to the abundant rodent studies, there are to date no trials on the effects of ghrelin in human Alzheimer’s or dementia patients.
9.2. Parkinson’s Disease
Interest in the relation between ghrelin and Parkinson’s began with the observation that ghrelin could protect striatal dopaminergic neurons, which express the GHSR, from degeneration caused by the neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) [190], possibly by preventing the activation of microglia [191]. Andrews and colleagues elaborated these results by showing that knocking out the ghrelin receptor in striatal neurons aggravated the neurotoxic effects of MPTP treatment and that the neuroprotective effects further involve enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis and UCP2-mediated reduction of reactive oxygen species [192]. The ability of ghrelin to protect against mitochondrial dysfunction and degeneration of dopaminergic neurons was demonstrated also in cells [146]. Most recently, ghrelin was shown to be essential to the neuroprotective effects of caloric restriction in the MPTP model of PD [193], an effect that requires the acylated (active) form of ghrelin [193]. PD often presents with gastrointestinal symptoms, such as delayed gastric emptying [194]. Ghrelin was shown to effectively treat symptoms of delayed gastric emptying in a rat model of PD utilizing the neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine [195]. In humans, it was shown that PD patients had an impaired postprandial ghrelin response [196], but no trials on the therapeutic potential of ghrelin for neurological or gastrointestinal aspects of PD have been performed to date.
9.3. Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease characterized by progressive demyelination of neuronal axons. Neuroinflammation is central to the pathophysiology of MS [197], and given the anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions of ghrelin, which include protection against demyelination and axonal loss [198], it may have therapeutic potential for MS. Patients with MS have been found to have higher levels of ghrelin in the cerebrospinal fluid [199] and sometimes, but not always, in plasma [200,201], which may be interpreted as a protective response to the presence of neuroinflammation. MS may also be associated with genetic variation in the gene encoding the ghrelin receptor [202].
In several rodent models of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), which is often used as a model for human MS, ghrelin has been shown to reduce the disease severity and associated neuroinflammation [74,203]. However, no clinical data with ghrelin in MS patients are currently available.
9.4. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease affecting mainly motor neurons in the brain, brainstem and spinal cord. The pathophysiology of ALS includes several metabolic alterations, which may interact with ghrelin signaling, such as loss of appetite [204], as well as neuroinflammation and reactive astrogliosis [205]. Despite ALS patients generally exhibiting lower BMI than healthy controls, several investigators have reported substantially lower ghrelin levels in ALS patients [206,207], suggesting that impaired ghrelin signaling may contribute to the disease progression. In line with this notion, ghrelin has shown neuroprotective effects on spinal cord motor neurons against glutamate-induced cell death in vitro, likely acting at least in part via the ERK/PI3K/GSK pathway, and inhibition of microglia [208,209]. Finally there is some preliminary evidence suggesting that ghrelin can slow down the disease progression of ALS in a mouse model [210], highlighting the need for further investigation of this relation in subsequent clinical trials.
10. Pulmonary Disease
Studies on the ghrelin system in pulmonary disease started with observations that ghrelin levels were increased in cachexic lung cancer patients, as well as underweight patients with COPD. These elevations were however likely unrelated to the lung pathology and rather secondary to the low BMI in these patients, since normal-weight subjects with either lung cancer or COPD had normal ghrelin levels [125,211,212,213,214]. Several studies even found decreased ghrelin levels despite underweight in COPD patients [215,216], although one recent study found that ghrelin levels were increased in patients with severe vs. moderate COPD, despite similar BMI [217]. A similar paradoxical phenomena with decreased ghrelin levels despite underweight was shown in cystic fibrosis patients [218], as well as tuberculosis patients [219,220], although other studies show normal or elevated ghrelin levels in cystic fibrosis, depending on disease severity [221].
A therapeutic potential of ghrelin for the treatment of lung cancer was suggested by the observation that GHSR expression is elevated in cancerous vs. normal lung tissue [222,223] and that ghrelin exerts anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects on these cells in vitro [222], although a later study in a mouse lung cancer model was unable to show that ghrelin receptor agonism reduced the tumor growth progression [113].
In pulmonary hypertension, ghrelin levels have been found to be inversely associated with pulmonary arterial pressure [224]. In rodents, ghrelin has been shown to ameliorate the progression of pulmonary hypertension induced by monocrotaline or hypoxia and improve blood circulation [225,226,227,228], at least in part by preventing endothelial cell damage and maintaining NO release [229]. Ghrelin may also protect against hypoxia-induced lung injury by preventing hypoxia-induced increases in angiogenesis and HIF1-alpha and VEGF expression [230].
In rodents, ghrelin and ghrelin agonists have been shown to exert therapeutic effects, mainly by anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative actions, and improve survival in several different models of lung injury. In three rat studies on sepsis-induced lung injury, sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture was shown to decrease ghrelin levels, and administration of ghrelin to restore plasma levels reduced the lung injury and inflammation, increased pulmonary blood flow and improved survival [231,232,233]. Similar effects were observed in rat models of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced lung injury [234,235,236], pancreatitis-induced lung injury [237], paraquat-induced injury [238], bleomycin-induced injury [239] and lung contusion [240]. Ghrelin was also found to ameliorate the catabolic conditions and respiratory dysfunction induced by chronic cigarette smoking in rats [241], likely in part by inhibiting the pro-inflammatory effects of cigarette smoking in bronchial epithelial cells [242].
In humans, therapeutic effects of ghrelin and ghrelin agonists have been demonstrated for COPD. Kodama and colleagues showed ghrelin to suppress airway inflammation and increase functional exertion capacity in patients with chronic respiratory failure [73]. Miki and colleagues later showed that ghrelin enhanced exercise capacity, expiratory pressure and improved respiratory symptoms in COPD patients [83,243] and showed benefits on exertional dyspnea [244], These effects may be dose-dependent [245,246]. For lung cancer, treatment with the potent ghrelin analog anamorelin has shown benefits on appetite, lean mass retention, performance and quality of life [133,134,135].
11. Metabolic Disease
11.1. Obesity
Possibly the greatest interest in the therapeutic potential of ghrelin concerns its use for the treatment of obesity and metabolic syndrome, given its well-established role in stimulating appetite and inducing adiposity [9,247]. Conversely, it was established early on that antagonism of ghrelin signaling with the ghrelin antagonist d-Lys-3-GHRP-6 could reduce food intake and promote short-term weight loss or prevent weight gain in obese mice [248]. Results using knock-out models have however been inconsistent. Most studies indicate that deletion of ghrelin has no effect on growth, feeding behavior or susceptibility to diet-induced obesity, but at most might influence food preference [249,250,251]. However, one study shows that ghrelin-deficient mice may be protected from diet-induced obesity if HFD-feeding is initiated before adulthood [252]. In another study, mice lacking the ghrelin-acylating enzyme GOAT showed no phenotypic difference from wildtype mice when fed a standard high-fat diet, but did exhibit reduced fat gain and glucose intolerance when fed a high-fat/high-sugar diet [253]. Deletion of the GHSR seems to have a more convincing effect of lowering body weight and susceptibility to obesity [254,255,256], although some investigators found that GHSR deletion had no effect on these parameters [251,257].
In 2006, Zorilla and colleagues reported that vaccination of rats to produce anti-ghrelin antibodies results in decreased food efficiency and fat gain [258]. Thus, antagonism of ghrelin signaling was regarded as one of the most promising potential treatments for obesity. The first results along this line were published by Shearman and colleagues, using an RNA Spiegelmer to block ghrelin signaling in diet-induced obese mice for seven days, with which they achieved a two-gram weight loss in five days. Although ghrelin blockade transiently suppressed feeding, food intake rebounded to baseline within three days of treatment, and weight rebound was observed starting at four days of treatment, suggesting that ghrelin blockade induced a counter-regulatory response to prevent weight loss [259].
In 2007, the results of several different quinazolinone derivative-based GHSR antagonists were reported, which induced 10–15% weight loss in diet-induced obese (DIO) mice [260,261]. It was later reported that GHSR antagonism may also retard the development of ovariectomy-induced obesity in female mice [262]. More modest results have been demonstrated with GHSR inverse agonists [84] and GHSR fusion proteins [263]. Pharmacological inhibition of the GOAT enzyme was also shown to reduce food intake and weight gain in mice on a medium chain triglyceride (MCT)-rich high-fat diet [264]. However, in some studies, antagonism of ghrelin signaling did not affect feeding or long-term body weight [265,266], suggesting that there are compensatory mechanisms acting to restore homeostasis. Several such counter-regulatory responses to ghrelin antagonism that may act to promote a positive energy balance have been observed. For instance, Shearman and colleagues observed that inactivating plasma ghrelin with their ghrelin-binding RNA Spiegelmer caused a 15-fold increase in circulating levels of acyl ghrelin [259]. Gagnon and colleagues further observed that the prevention of HFD-induced weight gain obtained with a GHSR fusion protein reduced leptin gene transcription in visceral adipose tissue by as much as 90% [263]. An additional phenomena that may limit the potency of ghrelin signaling blockade is the ghrelin resistance that DIO mice are known to exhibit at both the peripheral and central level [267,268,269]. The limited efficacy of targeting ghrelin signaling in obesity has also been confirmed in humans: a randomized clinical trial with an anti-ghrelin vaccine demonstrated no additional weight loss compared to placebo, despite a clear induction of anti-ghrelin antibodies [270].
11.2. Prader Willi Syndrome
Prader Willi syndrome (PWS) is a genetic disorder characterized by numerous behavioral, neurological and physiological symptoms, chief among which are infertility, severe obesity and hyperphagia. Unlike subjects with simple and hypothalamic obesity [271], subjects with PWS also exhibit greatly elevated circulating ghrelin levels [272,273], which due to the hyperphagic pro-obesity effects of ghrelin was logically proposed as a potential cause of the hyperphagia and obesity observed in PWS. Current data do however not clearly support a causal relationship between ghrelin and obesity in PWS. A recent study reported that total ghrelin levels are substantially elevated in children with PWS long before any hyperphagia is evident, suggesting that elevated ghrelin levels may not be a major driving factor of obesity in PWS [274]. Consistent with this notion, acute treatment with the somatostatin analog octreotide was shown to greatly reduce circulating ghrelin levels in PWS subjects, but had no effects on body weight, body composition or resting energy expenditure [275]. A later randomized cross-over trial with octreotide for 16 weeks was shown to similarly reduce circulating ghrelin levels without affecting appetite or body mass [276]. However, since octreotide affects numerous metabolic hormones aside from ghrelin, trials with more selective ghrelin signaling antagonists in PWS are warranted. In addition, several studies have reported that abnormal feeding regulation and weight gain in PWS is more related to changes in the ratio of des-acyl ghrelin to acyl ghrelin than total levels per se [277,278], suggesting that GOAT inhibitors may be of particular interest for the treatment of PWS.
11.3. Diabetes and Hyperglycemia
Aside from hyperphagia and obesity, ghrelin is also extensively involved in the regulation of glucose metabolism [279]. Acyl ghrelin chiefly has hyperglycemic effects [280] and promotes insulin resistance [281,282], acting on both pancreatic islets to suppress insulin secretion [283] and on hepatocytes to stimulate glucose output [284], whereas des-acyl ghrelin may counteract the hyperglycemic effects of acyl ghrelin and enhance insulin sensitivity [282,284,285,286]. Consequently, there has been some interest in the potential of ghrelin antagonism to ameliorate diabetes and hyperglycemia. Several studies have shown that GHSR antagonists improve glucose tolerance associated with obesity by enhancing insulin secretion [261,287], and it was more recently demonstrated that ghrelin inhibition with the GHSR antagonist GHRP-6 could reverse diabetic symptoms also in a genetic mouse model of maturity-onset diabetes of the young, type 3 (MODY3) caused by mutations of the HNF1-alpha homeobox gene [288]. In humans, no clinical trials on the use of ghrelin signaling antagonists to treat hyperglycemia or diabetes have been performed to date.
11.4. Novel Approaches to Target the Ghrelin System in Metabolic Disease
A different approach to attempt to modulate the ghrelin system for therapeutic effect is to target either the cells producing ghrelin or the cells on which ghrelin acts. Using transgenic mice expressing the receptor for diphtheria toxin in ghrelin-secreting cells, it was shown that targeted ablation of ghrelin-secreting cells in adult mice with diphtheria toxin injections had no effect, not even transiently, on food intake, body weight or susceptibility to diet-induced obesity, despite reducing circulating ghrelin levels by 85–90% [289]. Altogether, to date, the evidence that blockade or antagonism of ghrelin signaling at either the peptide or receptor level could be an effective treatment against obesity must be considered weak, with effect sizes that even in the best cases are modest compared to treatments that target other gut hormones [290,291,292].
One intriguing alternative, to date untested, is to interfere with the overall activity of cells in the CNS that respond to ghrelin. In the CNS, the by far highest concentration of ghrelin receptors is found on the orexigenic NPY/AgRP neurons of the arcuate nucleus [293], which powerfully drive feeding when stimulated. These neurons are essential for normal feeding behavior, as evidenced by the rapid arrest of feeding and dramatic weight loss seen when these neurons are ablated in adult mice [294]. In obese leptin-deficient mice, AgRP neuron ablation was similarly observed to cause dramatic and sustained weight loss, along with normalization of glucose tolerance and fertility, demonstrating the potential of interference with this neuronal population to powerfully influence metabolic homeostasis [295]. Aside from the NPY/AgRP neurons, ghrelin is also known to act to a lesser extent in several other brain regions to influence feeding and hedonic behavior. Ghrelin can stimulate feeding, food reward and dopamine release in several regions associated with reward processing, such as the VTA and nucleus accumbens [53,167,296,297,298], as well as the amygdala [299], hippocampus [300] and dorsal vagal complex of the brainstem [54]. Drugs that target the activity of ghrelin receptor-expressing neurons might thus be expected to have a powerful and concerted effect on both homeostatic and hedonic feeding. Since recent studies have demonstrated the possibility to specifically target cells responding to a particular hormone by chemically hybridizing drugs to various gut hormones [292,301], a similar potential avenue for anti-obesity drugs might be to hybridize ghrelin to cytotoxic or neurotoxic drugs aiming to either permanently or reversibly block neuronal activity of ghrelin-targeted cells.
12. Concluding Remarks
Although ghrelin was initially recognized for its role in feeding and metabolism, and consequently most expectations were pinned on its potential to treat obesity, the evidence to date, from rodent models of obesity, as well as human trials, suggests that antagonism of ghrelin signaling has only modest anti-obesity effects. Ghrelin is however an extremely pleiotropic hormone and may have therapeutic uses for a wide range of other diseases (Figure 3). In rodents, there is extensive evidence for the efficacy of ghrelin in a variety of inflammatory disorders, GI disorders, cardiovascular, renal and pulmonary disorders, as well as neurodegenerative diseases and wasting diseases. In humans, however, only a few of these potential treatments have so far been tested, leaving still wide room for investigations in the efficacy of ghrelin for the treatment of human disease.
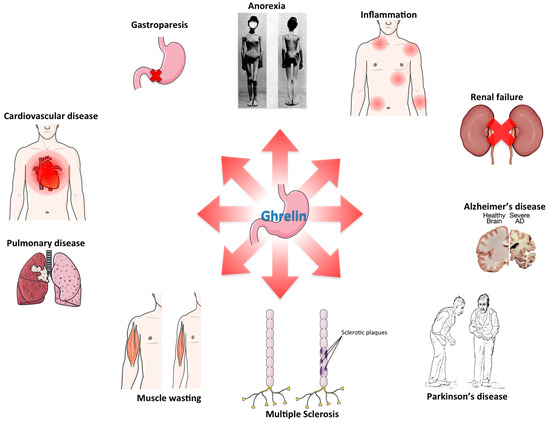
Figure 3.
Avenues for ghrelin therapy: schematic of the various pathological conditions for which there is at least preclinical evidence suggesting potential therapeutic benefit of ghrelin treatment.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by funding from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, the Helmholtz Alliance Imaging and Curing Environmental Metabolic Diseases (ICEMED) and the Helmholtz Initiative on Personalized Medicine iMed by the Helmholtz Association and the Helmholtz cross-program topic “Metabolic Dysfunction”. This work was further supported by grants from the German Research Foundation DFG-TS226/1-1, DFG-TS226/3-1, SFB1123, and the European Research Council ERC AdG HypoFlam No. 695054. The figures were made by using material from Servier Medical Art (Servier) under consideration of a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License, as well as material from Wikimedia Commons. Timo D. Müller and Gustav Colldén have no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise. Matthias H. Tschöp is a scientific advisor for Novo Nordisk, Bionorica SE and Erx Biotech.
Author Contributions
Gustav Colldén conceptualized the review, generated substantial text and provided edits for all sections. Matthias H. Tschöp co-conceptualized the review, generated substantial text and provided edits for all sections. Timo D. Müller co-conceptualized the review, generated substantial text and provided edits for all sections.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bowers, C.Y.; Momany, F.; Reynolds, G.A.; Chang, D.; Hong, A.; Chang, K. Structure-activity relationships of a synthetic pentapeptide that specifically releases growth hormone in vitro. Endocrinology 1980, 106, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momany, F.A.; Bowers, C.Y.; Reynolds, G.A.; Chang, D.; Hong, A.; Newlander, K. Design, synthesis, and biological activity of peptides which release growth hormone in vitro. Endocrinology 1981, 108, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, S.L.; Leng, G.; Robinson, I.C. Systemic administration of growth hormone-releasing peptide activates hypothalamic arcuate neurons. Neuroscience 1993, 53, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, A.D.; Smith, R.G. Desensitization studies using perifused rat pituitary cells show that growth hormone-releasing hormone and His-d-Trp-Ala-Trp-d-Phe-Lys-NH2 stimulate growth hormone release through distinct receptor sites. J. Endocrinol. 1991, 129, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, C.Y.; Reynolds, G.A.; Durham, D.; Barrera, C.M.; Pezzoli, S.S.; Thorner, M.O. Growth hormone (GH)-releasing peptide stimulates GH release in normal men and acts synergistically with GH-releasing hormone. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990, 70, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Chan, W.W.; Butler, B.; Barreto, A.; Smith, R.G. Evidence for a role of protein kinase-C in His-d-Trp-Ala-Trp-d-Phe-Lys-NH2-induced growth hormone release from rat primary pituitary cells. Endocrinology 1991, 129, 3337–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, A.D.; Feighner, S.D.; Cully, D.F.; Arena, J.P.; Liberator, P.A.; Rosenblum, C.I.; Hamelin, M.; Hreniuk, D.L.; Palyha, O.C.; Anderson, J.; et al. A receptor in pituitary and hypothalamus that functions in growth hormone release. Science 1996, 273, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschöp, M.; Smiley, D.L.; Heiman, M.L. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 2000, 407, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.D.; Nogueiras, R.; Andermann, M.L.; Andrews, Z.B.; Anker, S.D.; Argente, J.; Batterham, R.L.; Benoit, S.C.; Bowers, C.Y.; Broglio, F.; et al. Ghrelin. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 437–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, M.A.; Smith, R.G.; Diano, S.; Tschöp, M.; Pronchuk, N.; Grove, K.L.; Strasburger, C.J.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Esterman, M.; Heiman, M.L.; et al. The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron 2003, 37, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, D.; Gao, H.-Z.; Muroya, S.; Kikuyama, S.; Yada, T. Ghrelin directly interacts with neuropeptide-Y-containing neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus: Ca2+ signaling via protein kinase A and N-type channel-dependent mechanisms and cross-talk with leptin and orexin. Diabetes 2003, 52, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Trumbauer, M.E.; Chen, A.S.; Weingarth, D.T.; Adams, J.R.; Frazier, E.G.; Shen, Z.; Marsh, D.J.; Feighner, S.D.; Guan, X.-M.; et al. Orexigenic action of peripheral ghrelin is mediated by neuropeptide Y and agouti-related protein. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Inomata, N.; Ohnuma, N.; Tanaka, S.; Itoh, Z.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin stimulates gastric acid secretion and motility in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.-K.; Martin, B.; Kim, W.; White, C.M.; Ji, S.; Sun, Y.; Smith, R.G.; Sévigny, J.; Tschöp, M.H.; Maudsley, S.; et al. Ghrelin Is Produced in Taste Cells and Ghrelin Receptor Null Mice Show Reduced Taste Responsivity to Salty (NaCl) and Sour (Citric Acid) Tastants. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, V.P.; Monzón, M.E.; Varas, M.M.; Cragnolini, A.B.; Schiöth, H.B.; Scimonelli, T.N.; de Barioglio, S.R. Ghrelin increases anxiety-like behavior and memory retention in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 299, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, A. Ghrelin and sleep-wake regulation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R573–R574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Asnicar, M.; Saha, P.K.; Chan, L.; Smith, R.G. Ablation of ghrelin improves the diabetic but not obese phenotype of ob/ob mice. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, T.; Masaki, T.; Kakuma, T.; Yoshimatsu, H. Centrally administered ghrelin suppresses sympathetic nerve activity in brown adipose tissue of rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 349, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.A.; Solenberg, P.J.; Perkins, D.R.; Willency, J.A.; Knierman, M.D.; Jin, Z.; Witcher, D.R.; Luo, S.; Onyia, J.E.; Hale, J.E. Ghrelin octanoylation mediated by an orphan lipid transferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6320–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Brown, M.S.; Liang, G.; Grishin, N.V.; Goldstein, J.L. Identification of the acyltransferase that octanoylates ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating peptide hormone. Cell 2008, 132, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.-J.; Liang, G.; Li, R.L.; Xie, X.; Sleeman, M.W.; Murphy, A.J.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) is essential for growth hormone-mediated survival of calorie-restricted mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7467–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neary, N.M.; Druce, M.R.; Small, C.J.; Bloom, S.R. Acylated ghrelin stimulates food intake in the fed and fasted states but desacylated ghrelin has no effect. Gut 2006, 55, 135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toshinai, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; Sun, Y.; Smith, R.G.; Yamanaka, A.; Sakurai, T.; Date, Y.; Mondal, M.S.; Shimbara, T.; Kawagoe, T.; et al. Des-acyl ghrelin induces food intake by a mechanism independent of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 2306–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, N.M.; Gill, D.A.S.; Davies, R.; Loveridge, N.; Houston, P.A.; Robinson, I.C.A.F.; Wells, T. Ghrelin and des-octanoyl ghrelin promote adipogenesis directly in vivo by a mechanism independent of the type 1a growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chai, B.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Mulholland, M.W. Effect of des-acyl ghrelin on adiposity and glucose metabolism. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 4710–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inhoff, T.; Mönnikes, H.; Noetzel, S.; Stengel, A.; Goebel, M.; Dinh, Q.T.; Riedl, A.; Bannert, N.; Wisser, A.-S.; Wiedenmann, B.; et al. Desacyl ghrelin inhibits the orexigenic effect of peripherally injected ghrelin in rats. Peptides 2008, 29, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakawa, A.; Inui, A.; Fujimiya, M.; Sakamaki, R.; Shinfuku, N.; Ueta, Y.; Meguid, M.M.; Kasuga, M. Stomach regulates energy balance via acylated ghrelin and desacyl ghrelin. Gut 2005, 54, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filigheddu, N.; Gnocchi, V.F.; Coscia, M.; Cappelli, M.; Porporato, P.E.; Taulli, R.; Traini, S.; Baldanzi, G.; Chianale, F.; Cutrupi, S.; et al. Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin promote differentiation and fusion of C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldanzi, G.; Filigheddu, N.; Cutrupi, S.; Catapano, F.; Bonissoni, S.; Fubini, A.; Malan, D.; Baj, G.; Granata, R.; Broglio, F.; et al. Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin inhibit cell death in cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells through ERK1/2 and PI 3-kinase/AKT. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delhanty, P.J.; Neggers, S.J.; van der Lely, A.J. Des-acyl ghrelin: A metabolically active peptide. Endocr. Dev. 2013, 25, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Vriese, C.; Gregoire, F.; Lema-Kisoka, R.; Waelbroeck, M.; Robberecht, P.; Delporte, C. Ghrelin degradation by serum and tissue homogenates: Identification of the cleavage sites. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 4997–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamizu, T.; Takaya, K.; Irako, T.; Hosoda, H.; Teramukai, S.; Matsuyama, A.; Tada, H.; Miura, K.; Shimizu, A.; Fukushima, M.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and endocrine and appetite effects of ghrelin administration in young healthy subjects. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 150, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.M.; Yu, H.; Palyha, O.C.; McKee, K.K.; Feighner, S.D.; Sirinathsinghji, D.J.; Smith, R.G.; Van der Ploeg, L.H.; Howard, A.D. Distribution of mRNA encoding the growth hormone secretagogue receptor in brain and peripheral tissues. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1997, 48, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanapavan, S.; Kola, B.; Bustin, S.A.; Morris, D.G.; McGee, P.; Fairclough, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Carpenter, R.; Grossman, A.B.; Korbonits, M. The tissue distribution of the mRNA of ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor, GHS-R, in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigman, J.M.; Jones, J.E.; Lee, C.E.; Saper, C.B.; Elmquist, J.K. Expression of ghrelin receptor mRNA in the rat and the mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 494, 528–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.-B.; Leung, P.-K.; Wise, H.; Cheng, C.H.K. Signal transduction mechanism of the seabream growth hormone secretagogue receptor. FEBS Lett. 2004, 577, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, K.A.; Langmead, C.J.; Wise, A.; Milligan, G. Growth hormone secretagogues and growth hormone releasing peptides act as orthosteric super-agonists but not allosteric regulators for activation of the G protein Gα(o1) by the Ghrelin receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mary, S.; Damian, M.; Louet, M.; Floquet, N.; Fehrentz, J.-A.; Marie, J.; Martinez, J.; Banères, J.-L. Ligands and signaling proteins govern the conformational landscape explored by a G protein-coupled receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8304–8309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rak-Mardyla, A.; Gregoraszczuk, E.L. ERK 1/2 and PI-3 kinase pathways as a potential mechanism of ghrelin action on cell proliferation and apoptosis in the porcine ovarian follicular cells. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 2010, 61, 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, G. Ghrelin induces cell migration through GHSR1a-mediated PI3K/Akt/eNOS/NO signaling pathway in endothelial progenitor cells. Metabolism 2013, 62, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grey, C.L.; Chang, J.P. Ghrelin-induced growth hormone release from goldfish pituitary cells involves voltage-sensitive calcium channels. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, D.; Sone, H.; Minokoshi, Y.; Yada, T. Ghrelin raises [Ca2+]i via AMPK in hypothalamic arcuate nucleus NPY neurons. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 366, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, M.; Lage, R.; Saha, A.K.; Pérez-Tilve, D.; Vázquez, M.J.; Varela, L.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Tovar, S.; Raghay, K.; Rodríguez-Cuenca, S.; et al. Hypothalamic fatty acid metabolism mediates the orexigenic action of ghrelin. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, Z.B.; Liu, Z.-W.; Walllingford, N.; Erion, D.M.; Borok, E.; Friedman, J.M.; Tschöp, M.H.; Shanabrough, M.; Cline, G.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. UCP2 mediates ghrelin’s action on NPY/AgRP neurons by lowering free radicals. Nature 2008, 454, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-Y.; Lin, S.-L.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wu, V.-C.; Yang, W.-S.; Wu, K.-D. A low-salt diet increases the expression of renal sirtuin 1 through activation of the ghrelin receptor in rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velásquez, D.A.; Martínez, G.; Romero, A.; Vázquez, M.J.; Boit, K.D.; Dopeso-Reyes, I.G.; López, M.; Vidal, A.; Nogueiras, R.; Diéguez, C. The central Sirtuin 1/p53 pathway is essential for the orexigenic action of ghrelin. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, M.O.; Antunes, C.; Geliang, G.; Liu, Z.-W.; Borok, E.; Nie, Y.; Xu, A.W.; Souza, D.O.; Gao, Q.; Diano, S.; et al. Agrp neurons mediate Sirt1’s action on the melanocortin system and energy balance: Roles for Sirt1 in neuronal firing and synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 11815–11825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lage, R.; Vázquez, M.J.; Varela, L.; Saha, A.K.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Nogueiras, R.; Diéguez, C.; López, M. Ghrelin effects on neuropeptides in the rat hypothalamus depend on fatty acid metabolism actions on BSX but not on gender. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2010, 24, 2670–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.; Fernández-Mallo, D.; Novelle, M.G.; Vázquez, M.J.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Nogueiras, R.; López, M.; Diéguez, C. Hypothalamic mTOR signaling mediates the orexigenic action of ghrelin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, A.M.; Small, C.J.; Ward, H.L.; Murphy, K.G.; Dakin, C.L.; Taheri, S.; Kennedy, A.R.; Roberts, G.H.; Morgan, D.G.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. The novel hypothalamic peptide ghrelin stimulates food intake and growth hormone secretion. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4325–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, S.J.; Xu, L.; Clarke, M.A.; Lemus, M.; Reichenbach, A.; Geenen, B.; Kozicz, T.; Andrews, Z.B. Ghrelin regulates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and restricts anxiety after acute stress. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naleid, A.M.; Grace, M.K.; Cummings, D.E.; Levine, A.S. Ghrelin induces feeding in the mesolimbic reward pathway between the ventral tegmental area and the nucleus accumbens. Peptides 2005, 26, 2274–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulconbridge, L.F.; Cummings, D.E.; Kaplan, J.M.; Grill, H.J. Hyperphagic effects of brainstem ghrelin administration. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2260–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luquet, S.; Phillips, C.T.; Palmiter, R.D. NPY/AgRP neurons are not essential for feeding responses to glucoprivation. Peptides 2007, 28, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, D.E.; Purnell, J.Q.; Frayo, R.S.; Schmidova, K.; Wisse, B.E.; Weigle, D.S. A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natalucci, G.; Riedl, S.; Gleiss, A.; Zidek, T.; Frisch, H. Spontaneous 24-h ghrelin secretion pattern in fasting subjects: Maintenance of a meal-related pattern. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 152, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshinai, K.; Mondal, M.S.; Nakazato, M.; Date, Y.; Murakami, N.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Matsukura, S. Upregulation of Ghrelin expression in the stomach upon fasting, insulin-induced hypoglycemia, and leptin administration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 281, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschöp, M.; Wawarta, R.; Riepl, R.L.; Friedrich, S.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Landgraf, R.; Folwaczny, C. Post-prandial decrease of circulating human ghrelin levels. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2001, 24, RC19–RC21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Prudom, C.E.; Nass, R.; Pezzoli, S.S.; Oliveri, M.C.; Johnson, M.L.; Veldhuis, P.; Gordon, D.A.; Howard, A.D.; Witcher, D.R.; et al. Novel Ghrelin Assays Provide Evidence for Independent Regulation of Ghrelin Acylation and Secretion in Healthy Young Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 1980–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govoni, N.; Iasio, R.D.; Cocco, C.; Parmeggiani, A.; Galeati, G.; Pagotto, U.; Brancia, C.; Spinaci, M.; Tamanini, C.; Pasquali, R.; Ferri, G.-L.; Seren, E. Gastric immunolocalization and plasma profiles of acyl-ghrelin in fasted and fasted-refed prepuberal gilts. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 186, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahete, M.D.; Córdoba-Chacón, J.; Salvatori, R.; Castaño, J.P.; Kineman, R.D.; Luque, R.M. Metabolic regulation of ghrelin O-acyl transferase (GOAT) expression in the mouse hypothalamus, pituitary, and stomach. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 317, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchner, H.; Gutierrez, J.A.; Solenberg, P.J.; Pfluger, P.T.; Czyzyk, T.A.; Willency, J.A.; Schurmann, A.; Joost, H.G.; Jandacek, R.; Hale, J.E.; et al. GOAT links dietary lipids with the endocrine control of energy balance. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theander-Carrillo, C.; Wiedmer, P.; Cettour-Rose, P.; Nogueiras, R.; Perez-Tilve, D.; Pfluger, P.; Castaneda, T.R.; Muzzin, P.; Schürmann, A.; Szanto, I.; et al. Ghrelin action in the brain controls adipocyte metabolism. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Du, J.; Tang, C. Therapeutic effects of ghrelin on endotoxic shock in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 473, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Du, J.-B.; Gao, L.-R.; Pang, Y.-Z.; Tang, C.-S. Effect of ghrelin on septic shock in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2003, 24, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dixit, V.D.; Schaffer, E.M.; Pyle, R.S.; Collins, G.D.; Sakthivel, S.K.; Palaniappan, R.; Lillard, J.W.; Taub, D.D. Ghrelin inhibits leptin- and activation-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression by human monocytes and T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.G.; Gavrila, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Gunnlaugsson, S.; Stoll, L.L.; McCormick, M.L.; Sigmund, C.D.; Tang, C.; Weintraub, N.L. Ghrelin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappaB activation in human endothelial cells. Circulation 2004, 109, 2221–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granado, M.; Priego, T.; Martín, A.I.; Villanúa, M.A.; López-Calderón, A. Anti-inflammatory effect of the ghrelin agonist growth hormone-releasing peptide-2 (GHRP-2) in arthritic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E486–E492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Rey, E.; Chorny, A.; Delgado, M. Therapeutic action of ghrelin in a mouse model of colitis. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1707–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, P.C.; Brzozowski, T.; Engel, M.; Burnat, G.; Gaca, P.; Kwiecien, S.; Pajdo, R.; Konturek, S.J. Ghrelin ameliorates colonic inflammation. Role of nitric oxide and sensory nerves. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 2009, 60, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kasımay, O.; Işeri, S.O.; Barlas, A.; Bangir, D.; Yeğen, C.; Arbak, S.; Yeğen, B.C. Ghrelin ameliorates pancreaticobiliary inflammation and associated remote organ injury in rats. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2006, 36, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, T.; Ashitani, J.-I.; Matsumoto, N.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. Ghrelin treatment suppresses neutrophil-dominant inflammation in airways of patients with chronic respiratory infection. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 21, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theil, M.-M.; Miyake, S.; Mizuno, M.; Tomi, C.; Croxford, J.L.; Hosoda, H.; Theil, J.; von Hörsten, S.; Yokote, H.; Chiba, A.; et al. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by ghrelin. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2859–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyoraku, I.; Shiomi, K.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. Ghrelin reverses experimental diabetic neuropathy in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 389, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-X.; Yuan, M.-J.; Huang, H.; Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S.-B.; Li, H.-T.; Wang, T. Ghrelin inhibits post-infarct myocardial remodeling and improves cardiac function through anti-inflammation effect. Peptides 2009, 30, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erşahin, M.; Toklu, H.Z.; Erzik, C.; Cetinel, S.; Akakin, D.; Velioğlu-Oğünç, A.; Tetik, S.; Ozdemir, Z.N.; Sener, G.; Yeğen, B.C. The anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of ghrelin in subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced oxidative brain damage in rats. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheyuo, C.; Wu, R.; Zhou, M.; Jacob, A.; Coppa, G.; Wang, P. Ghrelin suppresses inflammation and neuronal nitric oxide synthase in focal cerebral ischemia via the vagus nerve. Shock 2011, 35, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barazzoni, R.; Zanetti, M.; Semolic, A.; Cattin, M.R.; Pirulli, A.; Cattin, L.; Guarnieri, G. High-fat diet with acyl-ghrelin treatment leads to weight gain with low inflammation, high oxidative capacity and normal triglycerides in rat muscle. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hai, J.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Peng, H.; Cao, M.; Zhang, Q. Administration of ghrelin improves inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis during and after non-alcoholic fatty liver disease development. Endocrine 2013, 43, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barazzoni, R.; Semolic, A.; Cattin, M.R.; Zanetti, M.; Guarnieri, G. Acylated ghrelin limits fat accumulation and improves redox state and inflammation markers in the liver of high-fat-fed rats. Obesity 2014, 22, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gortan Cappellari, G.; Zanetti, M.; Semolic, A.; Vinci, P.; Ruozi, G.; Falcione, A.; Filigheddu, N.; Guarnieri, G.; Graziani, A.; Giacca, M.; et al. Unacylated Ghrelin Reduces Skeletal Muscle Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Inflammation and Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperglycemia and Whole-Body Insulin Resistance in Rodents. Diabetes 2016, 65, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Maekura, R.; Nagaya, N.; Nakazato, M.; Kimura, H.; Murakami, S.; Ohnishi, S.; Hiraga, T.; Miki, M.; Kitada, S.; et al. Ghrelin treatment of cachectic patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, A.; Takiguchi, S.; Miyazaki, Y.; Miyata, H.; Takahashi, T.; Kurokawa, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Nakajima, K.; Mori, M.; Kangawa, K.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study of the Anti-inflammatory Effect of Ghrelin During the Postoperative Period of Esophagectomy. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujino, K.; Inui, A.; Asakawa, A.; Kihara, N.; Fujimura, M.; Fujimiya, M. Ghrelin induces fasted motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract in conscious fed rats. J. Physiol. 2003, 550, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyano, Y.; Sakata, I.; Kuroda, K.; Aizawa, S.; Tanaka, T.; Jogahara, T.; Kurotani, R.; Sakai, T. The role of the vagus nerve in the migrating motor complex and ghrelin- and motilin-induced gastric contraction in suncus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swartz, E.M.; Browning, K.N.; Travagli, R.A.; Holmes, G.M. Ghrelin increases vagally mediated gastric activity by central sites of action. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. Off. J. Eur. Gastrointest. Motil. Soc. 2014, 26, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edholm, T.; Levin, F.; Hellström, P.M.; Schmidt, P.T. Ghrelin stimulates motility in the small intestine of rats through intrinsic cholinergic neurons. Regul. Pept. 2004, 121, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tack, J.; Depoortere, I.; Bisschops, R.; Delporte, C.; Coulie, B.; Meulemans, A.; Janssens, J.; Peeters, T. Influence of ghrelin on interdigestive gastrointestinal motility in humans. Gut 2006, 55, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahata, M.; Muto, S.; Oridate, N.; Ohnishi, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Sadakane, C.; Saegusa, Y.; Hattori, T.; Asaka, M.; Takeda, H. Impaired ghrelin signaling is associated with gastrointestinal dysmotility in rats with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G42–G53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checchi, S.; Montanaro, A.; Pasqui, L.; Ciuoli, C.; Cevenini, G.; Sestini, F.; Fioravanti, C.; Pacini, F. Serum ghrelin as a marker of atrophic body gastritis in patients with parietal cell antibodies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 4346–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isomoto, H.; Nakazato, M.; Ueno, H.; Date, Y.; Nishi, Y.; Mukae, H.; Mizuta, Y.; Ohtsuru, A.; Yamashita, S.; Kohno, S. Low plasma ghrelin levels in patients with Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis. Am. J. Med. 2004, 117, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Cha, D.Y.; Cheon, S.J.; Yeo, M.; Cho, S.W. Plasma ghrelin levels and their relationship with gastric emptying in patients with dysmotility-like functional dyspepsia. Digestion 2009, 80, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindo, T.; Futagami, S.; Hiratsuka, T.; Horie, A.; Hamamoto, T.; Ueki, N.; Kusunoki, M.; Miyake, K.; Gudis, K.; Tsukui, T.; et al. Comparison of gastric emptying and plasma ghrelin levels in patients with functional dyspepsia and non-erosive reflux disease. Digestion 2009, 79, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trudel, L.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C.; Bouin, M.; Plourde, V.; Eberling, P.; Poitras, P. Ghrelin/motilin-related peptide is a potent prokinetic to reverse gastric postoperative ileus in rat. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 282, G948–G952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Malik, N.M.; Sanger, G.J.; Andrews, P.L.R. Ghrelin alleviates cancer chemotherapy-associated dyspepsia in rodents. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.-C.; Wang, Z.-G.; Wang, W.-G.; Yan, J.; Zheng, Q. Gastric motor effects of ghrelin and growth hormone releasing peptide 6 in diabetic mice with gastroparesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.-C.; Wang, Z.-G.; Lv, R.; Wang, W.-G.; Han, X.-D.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Ai, K.-X. Ghrelin improves delayed gastrointestinal transit in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 2572–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Yan, J.; Zheng, Q. Therapeutic effects of ghrelin and growth hormone releasing peptide 6 on gastroparesis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic guinea pigs in vivo and in vitro. Chin. Med. J. 2008, 121, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akamizu, T.; Iwakura, H.; Ariyasu, H.; Hosoda, H.; Murayama, T.; Yokode, M.; Teramukai, S.; Seno, H.; Chiba, T.; Noma, S.; et al. Repeated administration of ghrelin to patients with functional dyspepsia: Its effects on food intake and appetite. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 158, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wo, J.M.; Ejskjaer, N.; Hellström, P.M.; Malik, R.A.; Pezzullo, J.C.; Shaughnessy, L.; Charlton, P.; Kosutic, G.; McCallum, R.W. Randomised clinical trial: Ghrelin agonist TZP-101 relieves gastroparesis associated with severe nausea and vomiting—Randomised clinical study subset data. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, M.; Matsumura, T.; Tsuchiya, N.; Sadakane, C.; Inami, R.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Imazeki, F.; Yokosuka, O. Rikkunshito improves the symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia, accompanied by an increase in the level of plasma ghrelin. Hepatogastroenterology 2012, 59, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.; Finan, B.; Clemmensen, C.; van der Ploeg, L.H.T.; Tschöp, M.H.; Müller, T.D. The Pentapeptide RM-131 Promotes Food Intake and Adiposity in Wildtype Mice but Not in Mice Lacking the Ghrelin Receptor. Front. Nutr. 2014, 1, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, A.; Camilleri, M.; Busciglio, I.; Burton, D.; Stoner, E.; Noonan, P.; Gottesdiener, K.; Smith, S.A.; Vella, A.; Zinsmeister, A.R. Randomized controlled phase Ib study of ghrelin agonist, RM-131, in type 2 diabetic women with delayed gastric emptying: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lembo, A.; Camilleri, M.; McCallum, R.; Sastre, R.; Breton, C.; Spence, S.; White, J.; Currie, M.; Gottesdiener, K.; Stoner, E.; et al. Relamorelin Reduces Vomiting Frequency and Severity and Accelerates Gastric Emptying in Adults with Diabetic Gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.D.; Perez-Tilve, D.; Tong, J.; Pfluger, P.T.; Tschöp, M.H. Ghrelin and its potential in the treatment of eating/wasting disorders and cachexia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2010, 1, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chance, W.T.; Dayal, R.; Friend, L.A.; Thomas, I.; Sheriff, S. Continuous intravenous infusion of ghrelin does not stimulate feeding in tumor-bearing rats. Nutr. Cancer 2008, 60, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Andersson, M.; Iresjö, B.-M.; Lönnroth, C.; Lundholm, K. Effects of ghrelin on anorexia in tumor-bearing mice with eicosanoid-related cachexia. Int. J. Oncol. 2006, 28, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanada, T.; Toshinai, K.; Kajimura, N.; Nara-Ashizawa, N.; Tsukada, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Osuye, K.; Kangawa, K.; Matsukura, S.; Nakazato, M. Anti-cachectic effect of ghrelin in nude mice bearing human melanoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 301, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubouchi, H.; Yanagi, S.; Miura, A.; Matsumoto, N.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. Ghrelin relieves cancer cachexia associated with the development of lung adenocarcinoma in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 743, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBoer, M.D.; Zhu, X.X.; Levasseur, P.; Meguid, M.M.; Suzuki, S.; Inui, A.; Taylor, J.E.; Halem, H.A.; Dong, J.Z.; Datta, R.; et al. Ghrelin treatment causes increased food intake and retention of lean body mass in a rat model of cancer cachexia. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 3004–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perboni, S.; Bowers, C.; Kojima, S.; Asakawa, A.; Inui, A. Growth hormone releasing peptide 2 reverses anorexia associated with chemotherapy with 5-fluoruracil in colon cancer cell-bearing mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 6303–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northrup, R.; Kuroda, K.; Duus, E.M.; Barnes, S.R.; Cheatham, L.; Wiley, T.; Pietra, C. Effect of ghrelin and anamorelin (ONO-7643), a selective ghrelin receptor agonist, on tumor growth in a lung cancer mouse xenograft model. Support. Care Cancer Off. J. Multinatl. Assoc. Support. Care Cancer 2013, 21, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borner, T.; Loi, L.; Pietra, C.; Giuliano, C.; Lutz, T.A.; Riediger, T. The ghrelin receptor agonist HM01 mimics the neuronal effects of ghrelin in the arcuate nucleus and attenuates anorexia-cachexia syndrome in tumor-bearing rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 311, R89–R96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deboer, M.D.; Zhu, X.; Levasseur, P.R.; Inui, A.; Hu, Z.; Han, G.; Mitch, W.E.; Taylor, J.E.; Halem, H.A.; Dong, J.Z.; et al. Ghrelin treatment of chronic kidney disease: Improvements in lean body mass and cytokine profile. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaya, N.; Uematsu, M.; Kojima, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Yoshihara, F.; Shimizu, W.; Hosoda, H.; Hirota, Y.; Ishida, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Chronic administration of ghrelin improves left ventricular dysfunction and attenuates development of cardiac cachexia in rats with heart failure. Circulation 2001, 104, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramaniam, A.; Joshi, R.; Su, C.; Friend, L.A.; Sheriff, S.; Kagan, R.J.; James, J.H. Ghrelin inhibits skeletal muscle protein breakdown in rats with thermal injury through normalizing elevated expression of E3 ubiquitin ligases MuRF1 and MAFbx. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 296, R893–R901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, M.; Yamaki, A.; Furuya, M.; Inomata, N.; Minamitake, Y.; Ohsuye, K.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin improves body weight loss and skeletal muscle catabolism associated with angiotensin II-induced cachexia in mice. Regul. Pept. 2012, 178, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, B.; Cuntz, U.; Fruehauf, E.; Wawarta, R.; Folwaczny, C.; Riepl, R.L.; Heiman, M.L.; Lehnert, P.; Fichter, M.; Tschöp, M. Weight gain decreases elevated plasma ghrelin concentrations of patients with anorexia nervosa. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 145, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tolle, V.; Kadem, M.; Bluet-Pajot, M.-T.; Frere, D.; Foulon, C.; Bossu, C.; Dardennes, R.; Mounier, C.; Zizzari, P.; Lang, F.; et al. Balance in ghrelin and leptin plasma levels in anorexia nervosa patients and constitutionally thin women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, Y.; Hosoda, H.; Nin, K.; Ooya, C.; Hayashi, H.; Akamizu, T.; Kangawa, K. Plasma levels of active form of ghrelin during oral glucose tolerance test in patients with anorexia nervosa. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 149, R1–R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Naruo, T.; Yasuhara, D.; Tatebe, Y.; Nagai, N.; Shiiya, T.; Nakazato, M.; Matsukura, S.; Nozoe, S. Fasting plasma ghrelin levels in subtypes of anorexia nervosa. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2003, 28, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Guillén, L.; Barrios, V.; Campos-Barros, A.; Argente, J. Ghrelin levels in obesity and anorexia nervosa: Effect of weight reduction or recuperation. J. Pediatr. 2004, 144, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaya, N.; Uematsu, M.; Kojima, M.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Okumura, H.; Hosoda, H.; Shimizu, W.; Yamagishi, M.; Oya, H.; et al. Elevated circulating level of ghrelin in cachexia associated with chronic heart failure: Relationships between ghrelin and anabolic/catabolic factors. Circulation 2001, 104, 2034–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.; Nagaya, N.; Isobe, T.; Imazu, M.; Okumura, H.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Kohno, N. Increased Plasma Ghrelin Level in Lung Cancer Cachexia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miljic, D.; Pekic, S.; Djurovic, M.; Doknic, M.; Milic, N.; Casanueva, F.F.; Ghatei, M.; Popovic, V. Ghrelin has partial or no effect on appetite, growth hormone, prolactin, and cortisol release in patients with anorexia nervosa. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 1491–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, M.; Ohwada, R.; Akamizu, T.; Shibasaki, T.; Takano, K.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin increases hunger and food intake in patients with restricting-type anorexia nervosa: A pilot study. Endocr. J. 2009, 56, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruta, I.; Fuku, Y.; Kinoshita, K.; Yoneda, K.; Morinaga, A.; Amitani, M.; Amitani, H.; Asakawa, A.; Sugawara, H.; Takeda, Y.; et al. One-year intranasal application of growth hormone releasing peptide-2 improves body weight and hypoglycemia in a severely emaciated anorexia nervosa patient. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2015, 6, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neary, N.M.; Small, C.J.; Wren, A.M.; Lee, J.L.; Druce, M.R.; Palmieri, C.; Frost, G.S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Coombes, R.C.; Bloom, S.R. Ghrelin increases energy intake in cancer patients with impaired appetite: Acute, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2832–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaya, N.; Itoh, T.; Murakami, S.; Oya, H.; Uematsu, M.; Miyatake, K.; Kangawa, K. Treatment of cachexia with ghrelin in patients with COPD. Chest 2005, 128, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, F.; Lutz, T.A.; Maeder, M.T.; Thuerlimann, B.; Bueche, D.; Tschöp, M.; Kaufmann, K.; Holst, B.; Brändle, M.; von Moos, R.; et al. Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of intravenous ghrelin for cancer-related anorexia/cachexia: A randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, double-crossover study. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietra, C.; Takeda, Y.; Tazawa-Ogata, N.; Minami, M.; Yuanfeng, X.; Duus, E.M.; Northrup, R. Anamorelin HCl (ONO-7643), a novel ghrelin receptor agonist, for the treatment of cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome: Preclinical profile. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2014, 5, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.M.; Boccia, R.V.; Graham, C.D.; Yan, Y.; Duus, E.M.; Allen, S.; Friend, J. Anamorelin for patients with cancer cachexia: An integrated analysis of two phase 2, randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, J.S.; Abernethy, A.P.; Currow, D.C.; Friend, J.; Duus, E.M.; Yan, Y.; Fearon, K.C. Anamorelin in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and cachexia (ROMANA 1 and ROMANA 2): Results from two randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, K.; Katakami, N.; Yokoyama, T.; Atagi, S.; Yoshimori, K.; Kagamu, H.; Saito, H.; Takiguchi, Y.; Aoe, K.; Koyama, A.; et al. Anamorelin (ONO-7643) in Japanese patients with non-small cell lung cancer and cachexia: Results of a randomized phase 2 trial. Support. Care Cancer Off. J. Multinatl. Assoc. Support. Care Cancer 2016, 24, 3495–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, K.; Giannitsopoulou, K.; Small, C.J.; Patterson, M.; Frost, G.; Ghatei, M.A.; Brown, E.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Choi, P. Subcutaneous ghrelin enhances acute food intake in malnourished patients who receive maintenance peritoneal dialysis: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashby, D.R.; Ford, H.E.; Wynne, K.J.; Wren, A.M.; Murphy, K.G.; Busbridge, M.; Brown, E.A.; Taube, D.H.; Ghatei, M.A.; Tam, F.W.K.; et al. Sustained appetite improvement in malnourished dialysis patients by daily ghrelin treatment. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacerda-Miranda, G.; Soares, V.M.; Vieira, A.K.G.; Lessa, J.G.; Rodrigues-Cunha, A.C.S.; Cortez, E.; Garcia-Souza, E.P.; Moura, A.S. Ghrelin signaling in heart remodeling of adult obese mice. Peptides 2012, 35, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiras-Fernandez, A.; Kreth, S.; Weis, F.; Ledderose, C.; Pöttinger, T.; Dieguez, C.; Beiras, A.; Reichart, B. Altered myocardial expression of ghrelin and its receptor (GHSR-1a) in patients with severe heart failure. Peptides 2010, 31, 2222–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestergaard, E.T.; Andersen, N.H.; Hansen, T.K.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Moller, N.; Sorensen, K.E.; Sloth, E.; Jorgensen, J.O.L. Cardiovascular effects of intravenous ghrelin infusion in healthy young men. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H3020–H3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, J.N.; do Carmo, J.M.; Adi, A.H.; da Silva, A.A. Chronic central ghrelin infusion reduces blood pressure and heart rate despite increasing appetite and promoting weight gain in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Peptides 2013, 42, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeki, T.; Kishimoto, I.; Schwenke, D.O.; Tokudome, T.; Horio, T.; Yoshida, M.; Hosoda, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin suppresses cardiac sympathetic activity and prevents early left ventricular remodeling in rats with myocardial infarction. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 294, H426–H432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.G.; Yang, J.; Geng, B.; Weintraub, N.L.; Tang, C. Protective effects of ghrelin on ischemia/reperfusion injury in the isolated rat heart. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2004, 43, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatib, M.N.; Shankar, A.; Kirubakaran, R.; Agho, K.; Simkhada, P.; Gaidhane, S.; Saxena, D.; Gode, D.; Gaidhane, A.; Zahiruddin, S.Q.; et al. Effect of ghrelin on mortality and cardiovascular outcomes in experimental rat and mice models of heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-G.; Cai, H.-Q.; Li, Y.-H.; Sui, Y.-B.; Zhang, J.-S.; Chang, J.-R.; Ning, M.; Wu, Y.; Tang, C.-S.; Qi, Y.-F.; et al. Ghrelin protects heart against ERS-induced injury and apoptosis by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Peptides 2013, 48, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Xu, H.; Shen, X.; Jiang, H. Ghrelin protects MES23.5 cells against rotenone via inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Neuropeptides 2016, 56, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, N.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, P. Ghrelin protects H9c2 cardiomyocytes from angiotensin II-induced apoptosis through the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 59, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaya, N.; Moriya, J.; Yasumura, Y.; Uematsu, M.; Ono, F.; Shimizu, W.; Ueno, K.; Kitakaze, M.; Miyatake, K.; Kangawa, K. Effects of ghrelin administration on left ventricular function, exercise capacity, and muscle wasting in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 2004, 110, 3674–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesauro, M.; Schinzari, F.; Iantorno, M.; Rizza, S.; Melina, D.; Lauro, D.; Cardillo, C. Ghrelin improves endothelial function in patients with metabolic syndrome. Circulation 2005, 112, 2986–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigamonti, A.E.; Pincelli, A.I.; Corrà, B.; Viarengo, R.; Bonomo, S.M.; Galimberti, D.; Scacchi, M.; Scarpini, E.; Cavagnini, F.; Müller, E.E. Plasma ghrelin concentrations in elderly subjects: Comparison with anorexic and obese patients. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 175, R1–R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamizu, T.; Murayama, T.; Teramukai, S.; Miura, K.; Bando, I.; Irako, T.; Iwakura, H.; Ariyasu, H.; Hosoda, H.; Tada, H.; et al. Plasma ghrelin levels in healthy elderly volunteers: The levels of acylated ghrelin in elderly females correlate positively with serum IGF-I levels and bowel movement frequency and negatively with systolic blood pressure. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 188, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nass, R.; Farhy, L.S.; Liu, J.; Pezzoli, S.S.; Johnson, M.L.; Gaylinn, B.D.; Thorner, M.O. Age-dependent decline in acyl-ghrelin concentrations and reduced association of acyl-ghrelin and growth hormone in healthy older adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Prat, M.; Papiol, M.; Monteis, R.; Palomera, E.; Cabré, M. Relationship between Plasma Ghrelin Levels and Sarcopenia in Elderly Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 19, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-A.; Splenser, A.; Guillory, B.; Luo, J.; Mendiratta, M.; Belinova, B.; Halder, T.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.-P.; Garcia, J.M. Ghrelin prevents tumour- and cisplatin-induced muscle wasting: Characterization of multiple mechanisms involved. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2015, 6, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujitsuka, N.; Asakawa, A.; Morinaga, A.; Amitani, M.S.; Amitani, H.; Katsuura, G.; Sawada, Y.; Sudo, Y.; Uezono, Y.; Mochiki, E.; et al. Increased ghrelin signaling prolongs survival in mouse models of human aging through activation of sirtuin1. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Ki, K.H.; Yang, J.-Y.; Jang, B.Y.; Song, J.A.; Baek, W.-Y.; Kim, J.H.; An, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.Y.; et al. Chronic central administration of Ghrelin increases bone mass through a mechanism independent of appetite regulation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nass, R.; Pezzoli, S.S.; Oliveri, M.C.; Patrie, J.T.; Harrell, F.E.; Clasey, J.L.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Bach, M.A.; Vance, M.L.; Thorner, M.O. Effects of an oral ghrelin mimetic on body composition and clinical outcomes in healthy older adults: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 149, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, A.; Mori, K.; Sugawara, A.; Mukoyama, M.; Yahata, K.; Suganami, T.; Takaya, K.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; et al. Plasma ghrelin and desacyl ghrelin concentrations in renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2748–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nüsken, K.-D.; Gröschl, M.; Rauh, M.; Stöhr, W.; Rascher, W.; Dötsch, J. Effect of renal failure and dialysis on circulating ghrelin concentration in children. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 2156–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarkovská, Z.; Rosická, M.; Krsek, M.; Sulková, S.; Haluzík, M.; Justová, V.; Lacinová, Z.; Marek, J. Plasma ghrelin levels in patients with end-stage renal disease. Physiol. Res. 2005, 54, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, N.M.; Hamed, S.T.; El-Khatib, M.M.; El-Shehaby, A.M. The relation between dual energy X-ray absorptiometry measurement of body fat composition and plasma ghrelin in patients with end-stage renal disease. Saudi Med. J. 2009, 30, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez Ayala, E.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Heimbürger, O.; Lindholm, B.; Nordfors, L.; Stenvinkel, P. Associations between plasma ghrelin levels and body composition in end-stage renal disease: A longitudinal study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2004, 19, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, R.; Nishimatsu, H.; Suzuki, E.; Satonaka, H.; Nagata, D.; Oba, S.; Sata, M.; Takahashi, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Terauchi, Y.; et al. Ghrelin improves renal function in mice with ischemic acute renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khowailed, A.; Younan, S.M.; Ashour, H.; Kamel, A.E.; Sharawy, N. Effects of ghrelin on sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: One step forward. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2015, 19, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.-X.; Ding, R.; Li, M.; Guo, Y.; Fan, L.-P.; Yue, L.-S.; Li, L.-Y.; Zhao, M. Ghrelin attenuates renal fibrosis and inflammation of obstructive nephropathy. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szentirmai, E.; Kapás, L.; Krueger, J.M. Ghrelin microinjection into forebrain sites induces wakefulness and feeding in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R575–R585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abizaid, A.; Liu, Z.-W.; Andrews, Z.B.; Shanabrough, M.; Borok, E.; Elsworth, J.D.; Roth, R.H.; Sleeman, M.W.; Picciotto, M.R.; Tschöp, M.H.; et al. Ghrelin modulates the activity and synaptic input organization of midbrain dopamine neurons while promoting appetite. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3229–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, V.P.; Perez, M.F.; Salde, E.; Schiöth, H.B.; Ramirez, O.A.; de Barioglio, S.R. Ghrelin induced memory facilitation implicates nitric oxide synthase activation and decrease in the threshold to promote LTP in hippocampal dentate gyrus. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 101, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xing, T.; Wang, M.; Miao, Y.; Tang, M.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Ruan, D.-Y. Local infusion of ghrelin enhanced hippocampal synaptic plasticity and spatial memory through activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in the dentate gyrus of adult rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, B.A.; Beynon, A.L.; Hornsby, A.K.E.; Bekinschtein, P.; Bussey, T.J.; Davies, J.S.; Saksida, L.M. The orexigenic hormone acyl-ghrelin increases adult hippocampal neurogenesis and enhances pattern separation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 51, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, P.S.; Xie, D.; Liu, K.; Chen, L. Ghrelin reduces injury of hippocampal neurons in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Chin. J. Physiol. 2006, 49, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Xia, Q.; Hou, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, H.; Zhu, S. Ghrelin protects cortical neuron against focal ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 359, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.; Kim, E.; Lee, D.H.; Seo, S.; Ju, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, H.; Park, S. Ghrelin inhibits apoptosis in hypothalamic neuronal cells during oxygen-glucose deprivation. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beynon, A.L.; Brown, M.R.; Wright, R.; Rees, M.I.; Sheldon, I.M.; Davies, J.S. Ghrelin inhibits LPS-induced release of IL-6 from mouse dopaminergic neurones. J. Neuroinflammation 2013, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, V.V.; Rodrigues, A.L.S.; De Lima, T.C.; de Barioglio, S.R.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Prediger, R.D. Ghrelin as a neuroprotective and palliative agent in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 6773–6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Du, X.; Jiang, H.; Xie, J. Ghrelin and Neurodegenerative Disorders-a Review. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proto, C.; Romualdi, D.; Cento, R.M.; Spada, R.S.; Di Mento, G.; Ferri, R.; Lanzone, A. Plasma levels of neuropeptides in Alzheimer’s disease. Gynecol. Endocrinol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2006, 22, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahete, M.D.; Córdoba-Chacón, J.; Kineman, R.D.; Luque, R.M.; Castaño, J.P. Role of ghrelin system in neuroprotection and cognitive functions: Implications in Alzheimer’s disease. Peptides 2011, 32, 2225–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, N.; Ohnuma, T.; Kuerban, B.; Komatsu, M.; Arai, H. Genetic association between ghrelin polymorphisms and Alzheimer’s disease in a Japanese population. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2011, 32, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, M.; Mansego, M.L.; Serra-Prat, M.; Palomera, E.; Boquet, X.; Chaves, J.F.; Puig-Domingo, M.; Mataró Ageing Study Group. Glucose impairment and ghrelin gene variants are associated to cognitive dysfunction. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 26, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitznagel, M.B.; Benitez, A.; Updegraff, J.; Potter, V.; Alexander, T.; Glickman, E.; Gunstad, J. Serum ghrelin is inversely associated with cognitive function in a sample of non-demented elderly. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 64, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunath, N.; Müller, N.C.J.; Tonon, M.; Konrad, B.N.; Pawlowski, M.; Kopczak, A.; Elbau, I.; Uhr, M.; Kühn, S.; Repantis, D.; et al. Ghrelin modulates encoding-related brain function without enhancing memory formation in humans. NeuroImage 2016, 142, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, C.-P.; Li, C.-R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Han, L.-L.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Kim, A.; Kim, S.; Liu, G.-L. Ghrelin modulates insulin sensitivity and tau phosphorylation in high glucose-induced hippocampal neurons. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1165–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgarelli, I.; Tamiazzo, L.; Bresciani, E.; Rapetti, D.; Caporali, S.; Lattuada, D.; Locatelli, V.; Torsello, A. Desacyl-ghrelin and synthetic GH-secretagogues modulate the production of inflammatory cytokines in mouse microglia cells stimulated by beta-amyloid fibrils. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, M.; Choi, J.G.; Nam, D.W.; Hong, H.-S.; Choi, Y.-J.; Oh, M.S.; Mook-Jung, I. Ghrelin ameliorates cognitive dysfunction and neurodegeneration in intrahippocampal amyloid-β1-42 oligomer-injected mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 23, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Moon, N.R.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, S.H.; Park, S. Central acylated ghrelin improves memory function and hippocampal AMPK activation and partly reverses the impairment of energy and glucose metabolism in rats infused with β-amyloid. Peptides 2015, 71, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhurandhar, E.J.; Allison, D.B.; van Groen, T.; Kadish, I. Hunger in the absence of caloric restriction improves cognition and attenuates Alzheimer’s disease pathology in a mouse model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunath, N.; van Groen, T.; Allison, D.B.; Kumar, A.; Dozier-Sharpe, M.; Kadish, I. Ghrelin agonist does not foster insulin resistance but improves cognition in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, M.; Cha, M.-Y.; Mook-Jung, I. Impaired hippocampal neurogenesis and its enhancement with ghrelin in 5XFAD mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 41, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Li, L.-J.; Wang, J.; Xie, J.-X. Ghrelin antagonizes MPTP-induced neurotoxicity to the dopaminergic neurons in mouse substantia nigra. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 212, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, M.; Kim, H.G.; Hwang, L.; Seo, J.-H.; Kim, S.; Hwang, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.; Chung, H.; Oh, M.S.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of ghrelin in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of Parkinson’s disease by blocking microglial activation. Neurotox. Res. 2009, 15, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, Z.B.; Erion, D.; Beiler, R.; Liu, Z.-W.; Abizaid, A.; Zigman, J.; Elsworth, J.D.; Savitt, J.M.; DiMarchi, R.; Tschoep, M.; et al. Ghrelin promotes and protects nigrostriatal dopamine function via an UCP2-dependent mitochondrial mechanism. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14057–14065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayliss, J.A.; Lemus, M.B.; Stark, R.; Santos, V.V.; Thompson, A.; Rees, D.J.; Galic, S.; Elsworth, J.D.; Kemp, B.E.; Davies, J.S.; et al. Ghrelin-AMPK Signaling Mediates the Neuroprotective Effects of Calorie Restriction in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 3049–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrinan, S.; Emmanuel, A.V.; Burn, D.J. Delayed gastric emptying in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2014, 29, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasawa, H.; Pietra, C.; Giuliano, C.; Garcia-Rubio, S.; Xu, X.; Yakabi, S.; Taché, Y.; Wang, L. New ghrelin agonist, HM01 alleviates constipation and L-dopa-delayed gastric emptying in 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. Off. J. Eur. Gastrointest. Motil. Soc. 2014, 26, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, M.M.; Möller, J.C.; Mankel, K.; Eggert, K.M.; Bohne, K.; Bodden, M.; Stiasny-Kolster, K.; Kann, P.H.; Mayer, G.; Tebbe, J.J.; et al. Postprandial ghrelin response is reduced in patients with Parkinson’s disease and idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder: A peripheral biomarker for early Parkinson’s disease? J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, P.M. Multiple sclerosis, an autoimmune inflammatory disease: Prospects for its integrative management. Altern. Med. Rev. J. Clin. Ther. 2001, 6, 540–566. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.Y.; Chung, H.; Yoo, Y.S.; Oh, Y.J.; Oh, T.H.; Park, S.; Yune, T.Y. Inhibition of apoptotic cell death by ghrelin improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3815–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, M.M.; Oertel, W.H.; Tackenberg, B. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of ghrelin in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2013, 34, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berilgen, M.S.; Bulut, S.; Ustundag, B.; Tekatas, A.; Ayar, A. Patients with multiple sclerosis have higher levels of serum ghrelin. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2005, 26, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eftekhari, E.; Etemadifar, M.; Ebrahimi, A.; Baradaran, S. The relation between peptide hormones and sex hormone in patients with multiple sclerosis. Iran. J. Neurol. 2013, 12, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rey, L.K.; Wieczorek, S.; Akkad, D.A.; Linker, R.A.; Chan, A.; Hoffjan, S. Polymorphisms in genes encoding leptin, ghrelin and their receptors in German multiple sclerosis patients. Mol. Cell. Probes 2011, 25, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza-Moreira, L.; Delgado-Maroto, V.; Morell, M.; O’Valle, F.; Del Moral, R.G.; Gonzalez-Rey, E. Therapeutic effect of ghrelin in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting antigen-specific Th1/Th17 responses and inducing regulatory T cells. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 30, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, T.; Maier, A.; Wicks, P.; Lang, D.; Linke, P.; Münch, C.; Steinfurth, L.; Meyer, R.; Meyer, T. Severe Loss of Appetite in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients: Online Self-Assessment Study. Interact. J. Med. Res. 2013, 2, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philips, T.; Robberecht, W. Neuroinflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Role of glial activation in motor neuron disease. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, S.T.; Steyn, F.J.; Huang, L.; Mantovani, S.; Pfluger, C.M.M.; Woodruff, T.M.; O’Sullivan, J.D.; Henderson, R.D.; McCombe, P.A. Altered expression of metabolic proteins and adipokines in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 357, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czell, D.; Baldinger, R.; Schneider, U.; Neuwirth, C.; Weber, M. The role of the SenseWear device and ghrelin for metabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2016, 17, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.; Lee, S.; Li, E.; Kim, Y.; Park, S. Ghrelin protects spinal cord motoneurons against chronic glutamate-induced excitotoxicity via ERK1/2 and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3β pathways. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 230, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Li, E.; Park, S. Ghrelin Protects Spinal Cord Motoneurons against Chronic Glutamate Excitotoxicity by Inhibiting Microglial Activation. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Korean Physiol. Soc. Korean Soc. Pharmacol. 2012, 16, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, T.; Murayama, N.; Ogino, R.; Inomata, N.; Inoue, T.; Furuya, M.; Matsuo, T.; Murayama, N.; Ogino, R.; Inomata, N.; et al. Ghrelin attenuates disease progression in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. F1000Research 2014, 5, 223. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, T.; Nagaya, N.; Yoshikawa, M.; Fukuoka, A.; Takenaka, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Haruta, Y.; Oya, H.; Yamagishi, M.; Hosoda, H.; et al. Elevated plasma ghrelin level in underweight patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Cai, B.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, H.; Sun, Q.; Song, A. Circulating leptin and ghrelin in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 2007, 30, 182–185. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ying, B.W.; Song, X.B.; Fan, H.; Wang, L.L.; Li, Y.S.; Cheng, Z.; Cheng, H.; Wen, F.Q. Plasma ghrelin levels and weight loss in Chinese Uygur patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2008, 36, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Bao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, G.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.; Tan, R. The changes of ghrelin, growth hormone, growth hormone releasing hormone and their clinical significances in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2012, 51, 536–539. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.-M.; Liu, X.-J.; Li, S.-Q.; Wang, Z.-L.; Liu, C.-T.; Yuan, Y.-M. Circulating ghrelin in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nutrition 2005, 21, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deveci, Y.; Deveci, F.; Ilhan, N.; Karaca, I.; Turgut, T.; Muz, M.H. Serum ghrelin, IL-6 and TNF-α levels in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Tuberk. Ve Toraks 2010, 58, 162–172. [Google Scholar]
- Uzum, A.K.; Aydin, M.M.; Tutuncu, Y.; Omer, B.; Kiyan, E.; Alagol, F. Serum ghrelin and adiponectin levels are increased but serum leptin level is unchanged in low weight Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease patients. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 25, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stylianou, C.; Galli-Tsinopoulou, A.; Koliakos, G.; Fotoulaki, M.; Nousia-Arvanitakis, S. Ghrelin and leptin levels in young adults with cystic fibrosis: Relationship with body fat. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2007, 6, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.-T.; Yoon, H.I.; Song, J.; Shin, W.G.; Lee, J.H. Relation of ghrelin, leptin and inflammatory markers to nutritional status in active pulmonary tuberculosis. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2010, 29, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ma, A.; Wang, Q.; Han, X.; Cai, J.; Schouten, E.G.; Kok, F.J.; Li, Y. Relation of leptin, ghrelin and inflammatory cytokines with body mass index in pulmonary tuberculosis patients with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.I.; Tsang, D.; Koenig, S.; Wilson, D.; McCloskey, T.; Chandra, S. Plasma ghrelin and leptin in adult cystic fibrosis patients. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2008, 7, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassoni, P.; Allia, E.; Marrocco, T.; Ghè, C.; Ghigo, E.; Muccioli, G.; Papotti, M. Ghrelin and cortistatin in lung cancer: Expression of peptides and related receptors in human primary tumors and in vitro effect on the H345 small cell carcinoma cell line. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2006, 29, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.C.; Sá, S.V.; Goldbaum, T.S.; Catania, M.; Campos, V.C.; Corrêa-Giannella, M.L.; Giannella-Neto, D.; Salgado, L.R. In vivo response to growth hormone-releasing peptide-6 in adrenocorticotropin-dependent Cushing’s syndrome by lung carcinoid tumor is associated with growth hormone secretagogue receptor type 1a mRNA expression. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2007, 30, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, D.; Pan, W.; Zhang, L.; Ge, J. Circulating ghrelin was negatively correlated with pulmonary arterial pressure in atrial septal defect patients. Chin. Med. J. 2013, 126, 3936–3939. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henriques-Coelho, T.; Correia-Pinto, J.; Roncon-Albuquerque, R.; Baptista, M.J.; Lourenço, A.P.; Oliveira, S.M.; Brandão-Nogueira, A.; Teles, A.; Fortunato, J.M.; Leite-Moreira, A.F. Endogenous production of ghrelin and beneficial effects of its exogenous administration in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 287, H2885–H2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenke, D.O.; Tokudome, T.; Shirai, M.; Hosoda, H.; Horio, T.; Kishimoto, I.; Kangawa, K. Exogenous ghrelin attenuates the progression of chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in conscious rats. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenke, D.O.; Gray, E.A.; Pearson, J.T.; Sonobe, T.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Campillo, I.; Kangawa, K.; Umetani, K.; Shirai, M. Exogenous ghrelin improves blood flow distribution in pulmonary hypertension-assessed using synchrotron radiation microangiography. Pflugers Arch. 2011, 462, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-P.; Zhu, J.-J.; Cheng, F.; Jiang, K.-W.; Gu, W.-Z.; Shen, Z.; Wu, Y.-D.; Liang, L.; Du, L.-Z. Ghrelin ameliorates hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via phospho-GSK3 β/β-catenin signaling in neonatal rats. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 47, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Q. Ghrelin protects human pulmonary artery endothelial cells against hypoxia-induced injury via PI3-kinase/Akt. Peptides 2013, 42, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei Bavil, F.; Alipour, M.R.; Keyhanmanesh, R.; Alihemmati, A.; Ghiyasi, R.; Mohaddes, G. Ghrelin Decreases Angiogenesis, HIF-1α and VEGF Protein Levels in Chronic Hypoxia in Lung Tissue of Male Rats. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Dong, W.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, F.; Marini, C.P.; Ravikumar, T.S.; Wang, P. Ghrelin attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung injury and mortality in rats. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wilhelmsen, K.; Jia, C.; Jin, J.; Xue, Q.; Feng, X.; Zhang, F.; Yu, B. Effects of ghrelin on pulmonary NOD2 mRNA expression and NF-κB activation when protects against acute lung injury in rats challenged with cecal ligation and puncture. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 13, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; He, W.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Luo, L.; Huang, X.; Guan, K.; Chen, W. Ghrelin attenuates sepsis-associated acute lung injury oxidative stress in rats. Inflammation 2015, 38, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Shu, Q.; Li, S.; Luo, F. Ghrelin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through NO pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2008, 14, BR141–BR146. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Song, X.; Liang, H.; Huang, L. Growth hormone releasing peptide-2, a ghrelin agonist, attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2010, 222, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zeng, M.; He, W.; Huang, X.; Luo, L.; Zhang, H.; Deng, D.Y.B. Ghrelin protects alveolar macrophages against lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis through growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a-dependent c-Jun N-terminal kinase and Wnt/β-catenin signaling and suppresses lung inflammation. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Xue, C. Ghrelin attenuates acute pancreatitis-induced lung injury and inhibits substance P expression. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 339, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Wang, F.; Zhao, G.; Lu, Z.; Qiu, Q. Protective effect of ghrelin against paraquat-induced acute lung injury in mice. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2014, 32, 190–194. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imazu, Y.; Yanagi, S.; Miyoshi, K.; Tsubouchi, H.; Yamashita, S.-I.; Matsumoto, N.; Ashitani, J.-I.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. Ghrelin ameliorates bleomycin-induced acute lung injury by protecting alveolar epithelial cells and suppressing lung inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 672, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven, B.; Gokce, M.; Saydam, O.; Can, M.; Bektas, S.; Yurtlu, S. Effect of ghrelin on inflammatory response in lung contusion. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2013, 29, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiide, Y.; Inomata, N.; Furuya, M.; Yada, T. Ghrelin ameliorates catabolic conditions and respiratory dysfunction in a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease model of chronic cigarette smoke-exposed rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 755, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, T.; Shen, Y.; Wan, C.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Xu, D.; Wen, F.; et al. Ghrelin Inhibits Interleukin-6 Production Induced by Cigarette Smoke Extract in the Bronchial Epithelial Cell Via NF-κB Pathway. Inflammation 2016, 39, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Maekura, R.; Nagaya, N.; Kitada, S.; Miki, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Tateishi, Y.; Motone, M.; Hiraga, T.; Mori, M.; et al. Effects of ghrelin treatment on exercise capacity in underweight COPD patients: A substudy of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ghrelin treatment. BMC Pulm. Med. 2013, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Maekura, R.; Nagaya, N.; Miki, M.; Kitada, S.; Yoshimura, K.; Mori, M.; Kangawa, K. Effects of ghrelin treatment on exertional dyspnea in COPD: An exploratory analysis. J. Physiol. Sci. JPS 2015, 65, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, N.; Miki, K.; Tsubouchi, H.; Sakamoto, A.; Arimura, Y.; Yanagi, S.; Iiboshi, H.; Yoshida, M.; Souma, R.; Ishimoto, H.; et al. Ghrelin administration for chronic respiratory failure: A randomized dose-comparison trial. Lung 2015, 193, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Maekura, R.; Nakazato, M.; Matsumoto, N.; Kitada, S.; Miki, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Mori, M.; Kangawa, K. Randomized, dose-finding trial of ghrelin treatment for chronic respiratory failure. Clin. Respir. J. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, A.M.; Seal, L.J.; Cohen, M.A.; Brynes, A.E.; Frost, G.S.; Murphy, K.G.; Dhillo, W.S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Ghrelin enhances appetite and increases food intake in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakawa, A.; Inui, A.; Kaga, T.; Katsuura, G.; Fujimiya, M.; Fujino, M.A.; Kasuga, M. Antagonism of ghrelin receptor reduces food intake and body weight gain in mice. Gut 2003, 52, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ahmed, S.; Smith, R.G. Deletion of ghrelin impairs neither growth nor appetite. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 7973–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wortley, K.E.; Anderson, K.D.; Garcia, K.; Murray, J.D.; Malinova, L.; Liu, R.; Moncrieffe, M.; Thabet, K.; Cox, H.J.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; et al. Genetic deletion of ghrelin does not decrease food intake but influences metabolic fuel preference. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8227–8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Butte, N.F.; Garcia, J.M.; Smith, R.G. Characterization of adult ghrelin and ghrelin receptor knockout mice under positive and negative energy balance. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wortley, K.E.; del Rincon, J.-P.; Murray, J.D.; Garcia, K.; Iida, K.; Thorner, M.O.; Sleeman, M.W. Absence of ghrelin protects against early-onset obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3573–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouno, T.; Akiyama, N.; Ito, T.; Okuda, T.; Nanchi, I.; Notoya, M.; Oka, S.; Yukioka, H. Ghrelin O-acyltransferase knockout mice show resistance to obesity when fed high-sucrose diet. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 228, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigman, J.M.; Nakano, Y.; Coppari, R.; Balthasar, N.; Marcus, J.N.; Lee, C.E.; Jones, J.E.; Deysher, A.E.; Waxman, A.R.; White, R.D.; et al. Mice lacking ghrelin receptors resist the development of diet-induced obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3564–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Saha, P.K.; Ma, X.; Henshaw, I.O.; Shao, L.; Chang, B.H.J.; Buras, E.D.; Tong, Q.; Chan, L.; McGuinness, O.P.; et al. Ablation of ghrelin receptor reduces adiposity and improves insulin sensitivity during aging by regulating fat metabolism in white and brown adipose tissues. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lin, L.; Xu, P.; Saito, K.; Wei, Q.; Meadows, A.G.; Bongmba, O.Y.N.; Pradhan, G.; Zheng, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. Neuronal Deletion of Ghrelin Receptor Almost Completely Prevents Diet-Induced Obesity. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfluger, P.T.; Kirchner, H.; Günnel, S.; Schrott, B.; Perez-Tilve, D.; Fu, S.; Benoit, S.C.; Horvath, T.; Joost, H.-G.; Wortley, K.E.; et al. Simultaneous deletion of ghrelin and its receptor increases motor activity and energy expenditure. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G610–G618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorrilla, E.P.; Iwasaki, S.; Moss, J.A.; Chang, J.; Otsuji, J.; Inoue, K.; Meijler, M.M.; Janda, K.D. Vaccination against weight gain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13226–13231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearman, L.P.; Wang, S.-P.; Helmling, S.; Stribling, D.S.; Mazur, P.; Ge, L.; Wang, L.; Klussmann, S.; Macintyre, D.E.; Howard, A.D.; et al. Ghrelin neutralization by a ribonucleic acid-SPM ameliorates obesity in diet-induced obese mice. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, J.; Esler, W.P.; O’Connor, S.; Coish, P.D.G.; Wickens, P.L.; Brands, M.; Bierer, D.E.; Bloomquist, B.T.; Bondar, G.; Chen, L.; et al. Quinazolinone Derivatives as Orally Available Ghrelin Receptor Antagonists for the Treatment of Diabetes and Obesity. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5202–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esler, W.P.; Rudolph, J.; Claus, T.H.; Tang, W.; Barucci, N.; Brown, S.-E.; Bullock, W.; Daly, M.; DeCarr, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Small-Molecule Ghrelin Receptor Antagonists Improve Glucose Tolerance, Suppress Appetite, and Promote Weight Loss. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5175–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maletínská, L.; Matyšková, R.; Maixnerová, J.; Sýkora, D.; Pýchová, M.; Spolcová, A.; Blechová, M.; Drápalová, J.; Lacinová, Z.; Haluzík, M.; et al. The Peptidic GHS-R antagonist [d-Lys(3)]GHRP-6 markedly improves adiposity and related metabolic abnormalities in a mouse model of postmenopausal obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 343, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, J.; Zhu, L.; Anini, Y.; Wang, Q. Neutralizing circulating ghrelin by expressing a growth hormone secretagogue receptor-based protein protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice. Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, B.P.; Hwang, Y.; Taylor, M.S.; Kirchner, H.; Pfluger, P.T.; Bernard, V.; Lin, Y.; Bowers, E.M.; Mukherjee, C.; Song, W.-J.; et al. Glucose and weight control in mice with a designed ghrelin O-acyltransferase inhibitor. Science 2010, 330, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.-C.; Xu, J.; Chinookoswong, N.; Liu, S.; Steavenson, S.; Gegg, C.; Brankow, D.; Lindberg, R.; Véniant, M.; Gu, W. An acyl-ghrelin-specific neutralizing antibody inhibits the acute ghrelin-mediated orexigenic effects in mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, S.; Pinho, F.; Ribeiro, A.M.; Carreira, M.; Casanueva, F.F.; Roy, P.; Monteiro, M.P. Immunization against active ghrelin using virus-like particles for obesity treatment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 6551–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perreault, M.; Istrate, N.; Wang, L.; Nichols, A.J.; Tozzo, E.; Stricker-Krongrad, A. Resistance to the orexigenic effect of ghrelin in dietary-induced obesity in mice: Reversal upon weight loss. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2004, 28, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, D.I.; Enriori, P.J.; Lemus, M.B.; Cowley, M.A.; Andrews, Z.B. Diet-induced obesity causes ghrelin resistance in arcuate NPY/AgRP neurons. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4745–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naznin, F.; Toshinai, K.; Waise, T.M.Z.; NamKoong, C.; Md Moin, A.S.; Sakoda, H.; Nakazato, M. Diet-induced obesity causes peripheral and central ghrelin resistance by promoting inflammation. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 226, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phase I/IIa Clinical Trial with Obese Individuals Shows no Effect of CYT009-GhrQb on Weight Loss. Available online: http://www.evaluategroup.com/Universal/View.aspx?type=Story&id=103189 (accessed on 3 January 2015).
- Kanumakala, S.; Greaves, R.; Pedreira, C.C.; Donath, S.; Warne, G.L.; Zacharin, M.R.; Harris, M. Fasting ghrelin levels are not elevated in children with hypothalamic obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 2691–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DelParigi, A.; Tschöp, M.; Heiman, M.L.; Salbe, A.D.; Vozarova, B.; Sell, S.M.; Bunt, J.C.; Tataranni, P.A. High circulating ghrelin: A potential cause for hyperphagia and obesity in prader-willi syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 5461–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, D.E.; Clement, K.; Purnell, J.Q.; Vaisse, C.; Foster, K.E.; Frayo, R.S.; Schwartz, M.W.; Basdevant, A.; Weigle, D.S. Elevated plasma ghrelin levels in Prader Willi syndrome. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 643–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweh, F.A.; Miller, J.L.; Sulsona, C.R.; Wasserfall, C.; Atkinson, M.; Shuster, J.J.; Goldstone, A.P.; Driscoll, D.J. Hyperghrelinemia in Prader-Willi syndrome begins in early infancy long before the onset of hyperphagia. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2015, 167A, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haqq, A.M.; Stadler, D.D.; Rosenfeld, R.G.; Pratt, K.L.; Weigle, D.S.; Frayo, R.S.; LaFranchi, S.H.; Cummings, D.E.; Purnell, J.Q. Circulating ghrelin levels are suppressed by meals and octreotide therapy in children with Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 3573–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Waele, K.; Ishkanian, S.L.; Bogarin, R.; Miranda, C.A.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Pacaud, D.; Chanoine, J.-P. Long-acting octreotide treatment causes a sustained decrease in ghrelin concentrations but does not affect weight, behaviour and appetite in subjects with Prader-Willi syndrome. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 159, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppens, R.J.; Diène, G.; Bakker, N.E.; Molinas, C.; Faye, S.; Nicolino, M.; Bernoux, D.; Delhanty, P.J.D.; van der Lely, A.J.; Allas, S.; et al. Elevated ratio of acylated to unacylated ghrelin in children and young adults with Prader-Willi syndrome. Endocrine 2015, 50, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauloye, V.; Diene, G.; Kuppens, R.; Zech, F.; Winandy, C.; Molinas, C.; Faye, S.; Kieffer, I.; Beckers, D.; Nergårdh, R.; et al. High unacylated ghrelin levels support the concept of anorexia in infants with prader-willi syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2016, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamri, B.N.; Shin, K.; Chappe, V.; Anini, Y. The role of ghrelin in the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2016, 26, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broglio, F.; Arvat, E.; Benso, A.; Gottero, C.; Muccioli, G.; Papotti, M.; van der Lely, A.J.; Deghenghi, R.; Ghigo, E. Ghrelin, a natural GH secretagogue produced by the stomach, induces hyperglycemia and reduces insulin secretion in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5083–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestergaard, E.T.; Jessen, N.; Møller, N.; Jørgensen, J.O.L. Acyl Ghrelin Induces Insulin Resistance Independently of GH, Cortisol, and Free Fatty Acids. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauna, C.; Meyler, F.M.; Janssen, J.A.M.J.L.; Delhanty, P.J.D.; Abribat, T.; van Koetsveld, P.; Hofland, L.J.; Broglio, F.; Ghigo, E.; van der Lely, A.J. Administration of acylated ghrelin reduces insulin sensitivity, whereas the combination of acylated plus unacylated ghrelin strongly improves insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 5035–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, A.; Dornonville de la Cour, C.; Håkanson, R.; Lundquist, I. Effects of ghrelin on insulin and glucagon secretion: A study of isolated pancreatic islets and intact mice. Regul. Pept. 2004, 118, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauna, C.; Delhanty, P.J.D.; Hofland, L.J.; Janssen, J.A.M.J.L.; Broglio, F.; Ross, R.J.M.; Ghigo, E.; van der Lely, A.J. Ghrelin stimulates, whereas des-octanoyl ghrelin inhibits, glucose output by primary hepatocytes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özcan, B.; Neggers, S.J.; Miller, A.R.; Yang, H.-C.; Lucaites, V.; Abribat, T.; Allas, S.; Huisman, M.; Visser, J.A.; Themmen, A.P.N.; et al. Does des-acyl ghrelin improve glycemic control in obese diabetic subjects by decreasing acylated ghrelin levels? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 170, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broglio, F.; Gottero, C.; Prodam, F.; Gauna, C.; Muccioli, G.; Papotti, M.; Abribat, T.; van der Lely, A.J.; Ghigo, E. Non-acylated ghrelin counteracts the metabolic but not the neuroendocrine response to acylated ghrelin in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 3062–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezaki, K.; Sone, H.; Koizumi, M.; Nakata, M.; Kakei, M.; Nagai, H.; Hosoda, H.; Kangawa, K.; Yada, T. Blockade of pancreatic islet-derived ghrelin enhances insulin secretion to prevent high-fat diet-induced glucose intolerance. Diabetes 2006, 55, 3486–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brial, F.; Lussier, C.R.; Belleville, K.; Sarret, P.; Boudreau, F. Ghrelin Inhibition Restores Glucose Homeostasis in Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor-1α (MODY3)-Deficient Mice. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3314–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarlane, M.R.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L.; Zhao, T.-J. Induced Ablation of Ghrelin Cells in Adult Mice Does Not Decrease Food Intake, Body Weight, or Response to High Fat Diet. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmensen, C.; Finan, B.; Fischer, K.; Tom, R.Z.; Legutko, B.; Sehrer, L.; Heine, D.; Grassl, N.; Meyer, C.W.; Henderson, B.; et al. Dual melanocortin-4 receptor and GLP-1 receptor agonism amplifies metabolic benefits in diet-induced obese mice. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finan, B.; Yang, B.; Ottaway, N.; Smiley, D.L.; Ma, T.; Clemmensen, C.; Chabenne, J.; Zhang, L.; Habegger, K.M.; Fischer, K.; et al. A rationally designed monomeric peptide triagonist corrects obesity and diabetes in rodents. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finan, B.; Clemmensen, C.; Zhu, Z.; Stemmer, K.; Gauthier, K.; Müller, L.; De Angelis, M.; Moreth, K.; Neff, F.; Perez-Tilve, D.; et al. Chemical Hybridization of Glucagon and Thyroid Hormone Optimizes Therapeutic Impact for Metabolic Disease. Cell 2016, 167, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willesen, M.G.; Kristensen, P.; Rømer, J. Co-localization of growth hormone secretagogue receptor and NPY mRNA in the arcuate nucleus of the rat. Neuroendocrinology 1999, 70, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luquet, S.; Perez, F.A.; Hnasko, T.S.; Palmiter, R.D. NPY/AgRP neurons are essential for feeding in adult mice but can be ablated in neonates. Science 2005, 310, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Whiddon, B.B.; Palmiter, R.D. Ablation of neurons expressing agouti-related protein, but not melanin concentrating hormone, in leptin-deficient mice restores metabolic functions and fertility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3155–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skibicka, K.P.; Hansson, C.; Alvarez-Crespo, M.; Friberg, P.A.; Dickson, S.L. Ghrelin directly targets the ventral tegmental area to increase food motivation. Neuroscience 2011, 180, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.J.; Sun, B.; Chen, K.; Lv, B.; Luo, X.; Yan, J.Q. Ghrelin signaling in the ventral tegmental area mediates both reward-based feeding and fasting-induced hyperphagia on high-fat diet. Neuroscience 2015, 300, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skibicka, K.P.; Shirazi, R.H.; Rabasa-Papio, C.; Alvarez-Crespo, M.; Neuber, C.; Vogel, H.; Dickson, S.L. Divergent circuitry underlying food reward and intake effects of ghrelin: Dopaminergic VTA-accumbens projection mediates ghrelin’s effect on food reward but not food intake. Neuropharmacology 2013, 73, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Crespo, M.; Skibicka, K.P.; Farkas, I.; Molnár, C.S.; Egecioglu, E.; Hrabovszky, E.; Liposits, Z.; Dickson, S.L. The amygdala as a neurobiological target for ghrelin in rats: Neuroanatomical, electrophysiological and behavioral evidence. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanoski, S.E.; Fortin, S.M.; Ricks, K.M.; Grill, H.J. Ghrelin signaling in the ventral hippocampus stimulates learned and motivational aspects of feeding via PI3K-Akt signaling. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finan, B.; Yang, B.; Ottaway, N.; Stemmer, K.; Müller, T.D.; Yi, C.-X.; Habegger, K.; Schriever, S.C.; García-Cáceres, C.; Kabra, D.G.; et al. Targeted estrogen delivery reverses the metabolic syndrome. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).