Regulation of Human Breast Cancer by the Long Non-Coding RNA H19
Abstract
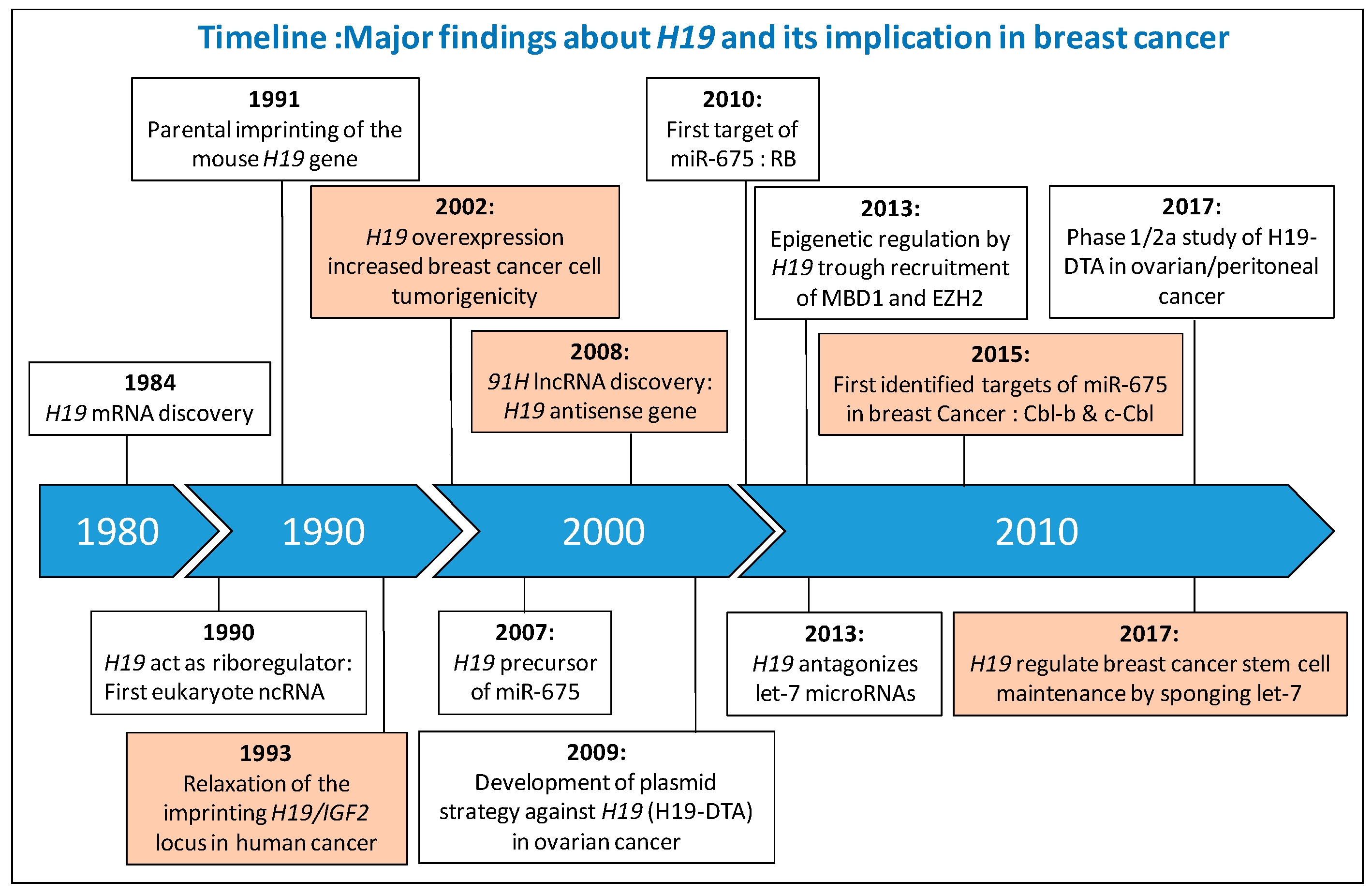
1. Introduction
2. H19 Gene Locus
3. H19 Gene Locus in Human Breast Cancer
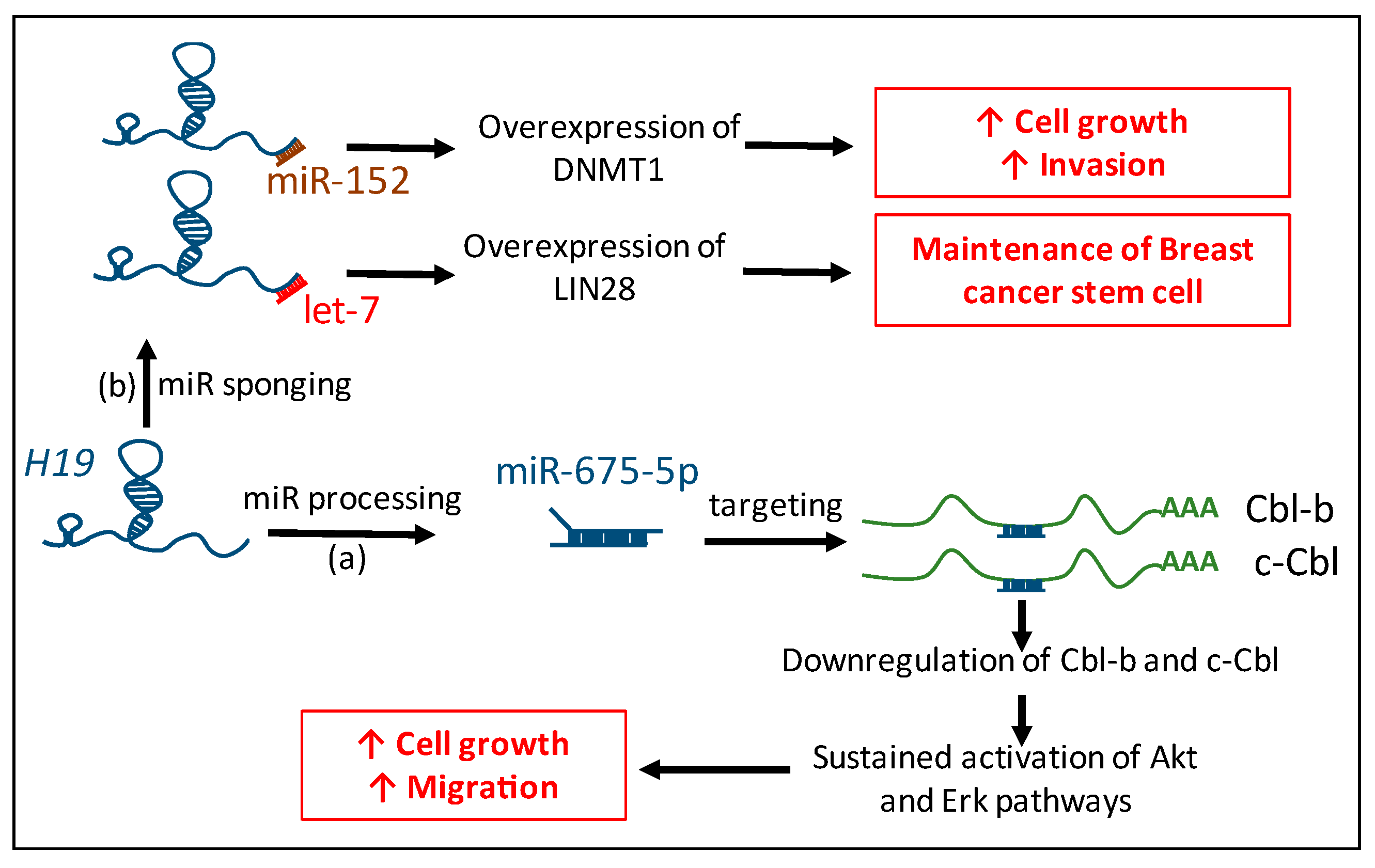
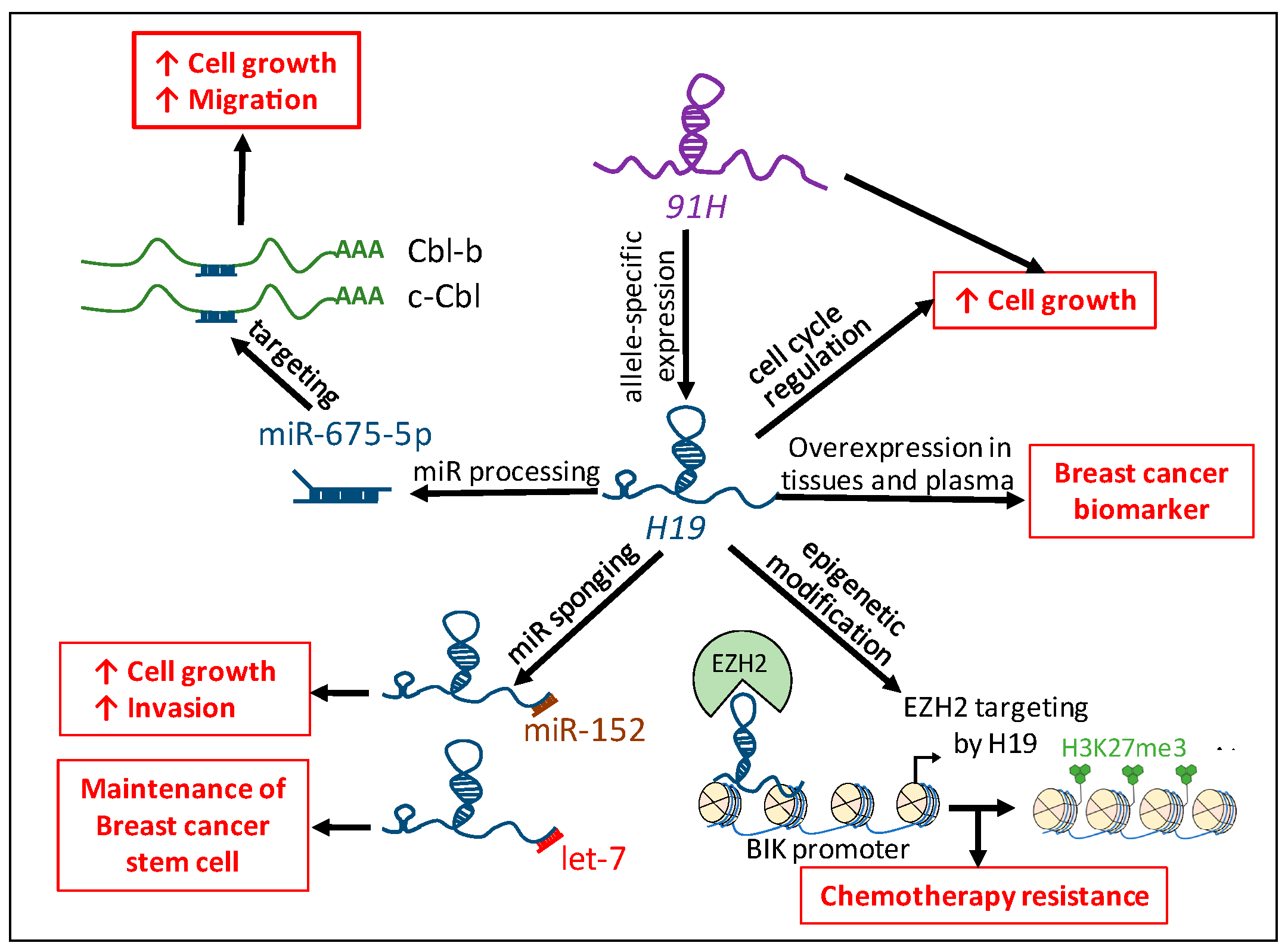
3.1. H19: Precursor of miR-675-5p and miR-675-3p
3.2. Competing Endogenenous RNAs (ceRNAs): Sequestration of miRs by H19
3.3. Epigenetics Modification Induced by H19
3.4. 91H: H19 Antisense Transcript
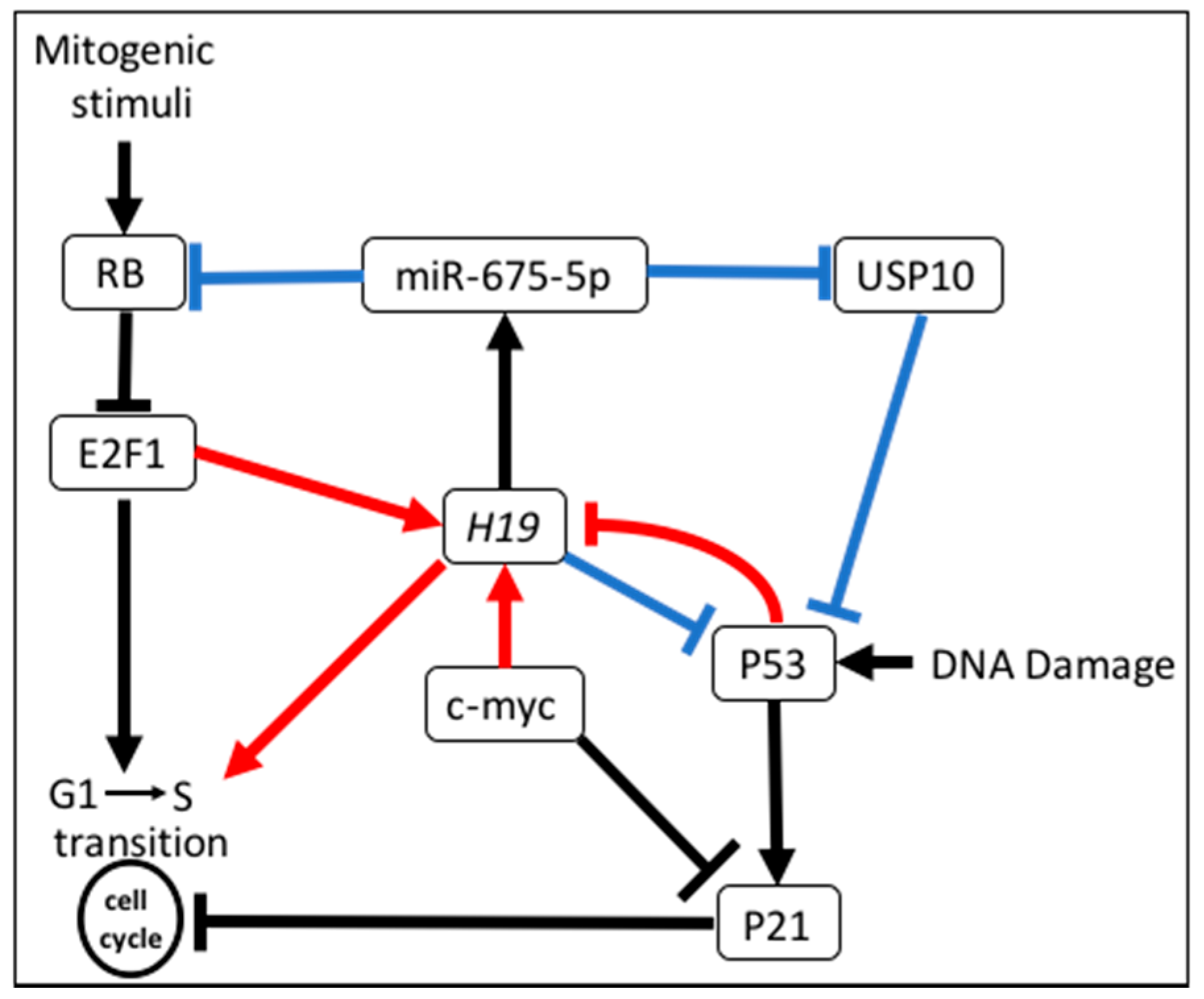
3.5. Regulation of Cell Cycle
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| ENCODE | Encyclopedia of DNA |
| ncRNAs | Non-coding RNAs |
| lncRNas | Long non-coding RNAs |
| miRs | MicroRNAs |
| siRNAs | Small non-coding RNAs |
| piRNAs | PIWI-interacting RNAs |
| snoRNAs | Small nucleolar RNA |
| Her-2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| IGF2 | Insulin growth factor 2 |
| BC | Breast cancer |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| RB | Retinoblastoma |
| DNMT1 | DNA Methyltransferase 1 |
| EMT | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| MET | Mesenchymal-epithelial transition |
| BIK | BCL2 Interacting Killer |
| NOXA | NADPH Oxidase Activator 1 |
| MBD1 | Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 1 |
| PTX | Paclitaxel |
| PEG1 | Paternally-Expressed Gene 1 Protein |
| SAHH | S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase |
| E2F1 | E2F Transcription Factor 1 |
| CPCs | c-kit+ cardiac progenitor cells |
| USP10 | Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 10 |
References
- World Health Organization. Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dean-Colomb, W.; Esteva, F.J. Her2-positive Breast Cancer: Herceptin and Beyond. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 2806–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerk, S.; Schwarzenbacher, D.; Adiprasito, J.B.; Stotz, M.; Hutterer, G.C.; Gerger, A.; Ling, H.; Calin, G.A.; Pichler, M. Current status of long non-coding RNAs in human breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birney, E.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J.A.; Dutta, A.; Guigó, R.; Gingeras, T.R.; Margulies, E.H.; Weng, Z.; Snyder, M.; Dermitzakis, T.; Thurman, R.E.; et al. Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature 2007, 447, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapranov, P.; Cheng, J.; Dike, S.; Nix, D.A.; Duttagupta, R.; Willingham, A.T.; Stadler, P.F.; Hertel, J.; Hackermüller, J.; Hofacker, I.L.; et al. RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science 2007, 316, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, H.; Fang, X. A Brief review on the human encyclopedia of DNA elements (ENCODE) project. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2013, 11, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.S.; Motoharu, O. From snoRNA to miRNA: Dual function regulatory non-coding RNAs. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hon, C.C.; Ramiloski, J.A.; Harshbarger, J.; Bertin, N.; Rackham, O.J.L.; Gough, J.; Denisenko, E.; Schmeier, S.; Poulsen, T.M.; Severin, J.; et al. An Atlas of human long non-coding RNAs with accurate 5′ ends. Nature 2017, 543, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. The diversity of long non-coding RNAs and their generation. Trends Genet. 2017, 33, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H.Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Chen, Y. Long noncoding RNAs and Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Luo, Y.L.; Mao, Y.S.; Ji, J.J. The link between long noncoding RNAs and depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 73, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, A.H.; Kaur, S.; Pociot, F. Long non-coding RNAs as novel players in β cell function and type 1 diabetes. Hum. Genom. 2017, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhan, A.; Soleimani, M.; Mandal, S.S. Long Noncoding RNA and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angrand, P.O.; Vennin, C.; Le Bourhis, X.; Adriaenssens, E. The role of long non-coding RNAs in genome formatting and expression. Front. Genet. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brannan, C.I.; Dees, E.C.; Ingram, R.S.; Tilghman, S.M. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1990, 10, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomei, M.S.; Zemel, S.; Tilghman, S.M. Parental imprinting of the mouse H19 gene. Nature 1991, 351, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennin, C.; Dahmani, F.; Spruyt, N.; Adriaenssens, E. Role of long non-coding RNA in cells: Example of the H19/IGF2 locus. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaval, K.; Wagschal, A.; Feil, R. Epigenetic deregulation of imprinting in congenital diseases of aberrant growth. BioEssays 2006, 28, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainier, S.; Johnson, L.A.; Dobry, C.J.; Ping, A.J.; Grundy, P.E.; Feinberge, A.P. Relaxation of imprinted genes in human cancer. Nature 1993, 362, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveh, E.; Matouk, I.J.; Gilon, M.; Hochberg, A. The H19 long non-coding RNA in cancer initiation, progression and metastasis—A proposed unifying theory. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Cullen, B.R. The Imprinted H19 noncoding RNA is a primary microRNA precursor. RNA 2007, 13, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berteaux, N.; Aptel, N.; Cathala, G.; Genton, C.; Coll, J.; Daccache, A.; Spruyt, N.; Hondermarck, H.; Dugimont, T.; Curgy, J.J.; et al. A novel H19 antisense RNA overexpressed in breast cancer contributes to paternal IGF2 expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 6731–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.K.; Lin, Q.F.; Shen, D.; Liu, Z.L.; Su, J.; Mao, W.D. Clinical implication of long noncoding RNA 91H expression profile in osteosarcoma patients. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 4645–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, X.; Deng, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Xu, M.; Yan, J.; et al. lncRNA H19/miR-675 axis represses prostate cancer metastasis by targeting TGFBI. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 3766–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Fang, J.; Xu, A.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z. H19-derived miR-675 contributes to bladder cancer cell proliferation by regulating P53 activation. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lottin, S.; Adriaenssens, E.; Dupressoir, T.; Bertaux, N.; Montpellier, C.; Coll, J.; Dugimont, T.; Curgy, J.J. Overexpression of an ectopic H19 gene enhances the tumorigenic properties of breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 1885–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaenssens, E.; Dumont, L.; Lottin, S.; Bolle, D.; Leprêtre, A.; Delobelle, A.; Bouali, F.; Dugimont, T.; Coll, J.; Curgy, J.J. H19 overexpression in breast adenocarcinoma stromal cells is associated with tumor values and steroid receptor status but independent of P53 and Ki-67 expression. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berteaux, N.; Lottin, S.; Adriaenssens, E.; Coppenolle, F.W.; Leroy, X.; Coll, J.; Dugimont, T.; Curgy, J.J. Hormonal regulation of H19 gene expression in prostate epithelial cells. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 183, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Weger, S.; Bruce, M.C.; Murphy, L.C.; Raouf, A. Estrogen regulates luminal progenitor cell differentiation through H19 gene expression. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Wang, G.; Peng, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, Q.N.; Li, T.L.; Cai, J.Q.; Zhou, H.H.; Zhu, Y.S. H19 lncRNA mediates 17β-estradiol-induced cell proliferation in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 3045–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, W.P.; Enders, K.O.N.; Simon, S.M.N.; Jin, H.; Yu, J.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Kwok, T.T. Oncofetal H19-derived miR-675 regulates tumor suppressor RB in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennin, C.; Spruyt, N.; Dahmani, F.; Julien, S.; Bertucci, F.; Finetti, P.; Chassat, T.; Bourette, R.P.; Le Bourhis, X.; Adriaenssens, E. H19 non-coding RNA-derived miR-675 enhances tumorigenesis and metastasis of breast cancer cells by downregulating c-Cbl and Cbl-b. Oncotarget 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.L.; Wang, P.; Zhou, L.Y.; Yin, J.Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, T.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Qin, Y.; Lin, J.; Deng, Z.Q. Over-expression of miR-675 in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (ffpe) tissues of breast cancer patients. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 11195–11201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cordero, F.; Ferrero, G.; Polidoro, S.; Fiorito, G.; Campanella, G.; Sacerdote, C.; Mattiello, A.; Masala, G.; Agnoli, C.; Frasca, G.; et al. Differentially methylated microRNAs in prediagnostic samples of subjects who developed breast cancer in the european prospective investigation into nutrition and cancer (epic-italy) cohort. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jin, C.; Li, W. Long non-coding RNA H19 inhibits adipocyte differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through epigenetic modulation of histone deacetylases. Sci. Rep. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; An, X.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, L.; Zuo, S.; Liu, N.; Yang, G.; Wang, H.; Cheng, X.; et al. The H19 long noncoding RNA is a novel negative regulator of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 111, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Ma, W.; Bi, C.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Han, Z.; Huang, Q.; Ding, F.; Li, Y.; Yan, G.; et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 mediates melatonin inhibition of premature senescence of C-kit+ cardiac progenitor cells by promoting miR-675. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, V.; Lo Dico, A.; Rizzo, A.; Rajata, F.; Tripodi, M.; Alessandro, R.; Conigliaro, A. MiR-675-5p supports hypoxia induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colon cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Dingfang, B.; Yuanyuan, M.; Zhu, J.; Chen, G.; Sun, L.; Li, T.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. H19 Overexpression induces resistance to 1,25(OH)2D3 by targeting VDR through miR-675-5p in colon cancer cells. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hao, W.; Yao, B.; Xu, W.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X. lncRNA H19/miR-675 axis regulates cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting VDAC1 in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.W.; Zhang, H.; Duan, C.J.; Duan, C.J.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, Y.D.; He, D.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.F. miR-675-5p enhances tumorigenesis and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting REPS2. Oncotarget 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yu, B.; Li, J.; Su, L.; Yan, M.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, B. Overexpression of lncRNA H19 enhances carcinogenesis and metastasis of gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Xiang, T.; Wu, Q.F.; Wang, W.X. Long noncoding RNA H19-derived miR-675 enhances proliferation and invasion via RUNX1 in gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Res. 2016, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, M.; Gao, W.; Xu, J.; Wang, P.; Shu, Y. The long non-coding RNA H19-derived miR-675 modulates human gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting tumor suppressor RUNX1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 448, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; She, Q.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Shen, X.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Y.; et al. Long noncoding RNA H19/miR-675 axis promotes gastric cancer via FADD/Caspase 8/Caspase 3 signaling pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2364–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wenkang, L.; Wang, P.; Tao, T.; Zhang, J.; Qian, J.; Liu, N.; You, Y. Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes glioma cell invasion by deriving miR-675. PLoS ONE 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, J.M.; Elahi, A.; Clark, C.W.; Wang, J.; Humphries, L.A.; Centeno, B.; Bloom, G.; Fuchs, B.C.; Yeatman, T.; Shibata, D. miR-675 mediates downregulation of Twist1 and Rb in AFP-secreting hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Shan, B.; Deng, X.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Hong, J.; Gao, Y.; et al. Down-regulation of miR-675-5p contributes to tumor progression and development by targeting pro-tumorigenic GPR55 in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jia, L.; Li, W. Long Noncoding RNA H19 Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation via TGF-β1/Smad3/HDAC Signaling Pathway by Deriving miR-675: H19/miR-675 Promotes Osteogenesis. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 3481–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.L.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Deng, Q.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. The Imprinted H19 gene regulates human placental trophoblast cell proliferation via encoding miR-675 that targets nodal modulator 1 (NOMO1). RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Leung, F.; Lu, W. miR-9-5p, miR-675-5p and miR-138-5p damages the strontium and LRP5-mediated skeletal cell proliferation, differentiation, and adhesion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, B.K.; Pfeifer, K.; Dutta, A. The H19 long noncoding RNA gives rise to microRNAs miR-675-3p and miR-675-5p to promote skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.W.; Wang, P.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Sun, L.; Zhu, J.; Zuo, S.; Ma, J.; Li, T.Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Chang, G.W.; et al. Effect of long noncoding RNA H19 overexpression on intestinal barrier function and its potential role in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 2582–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, T.R.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, A.Y. Cadherin 11, a miR-675 target, induces N-cadherin expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in melasma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2967–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, T.R.; Lee, A.Y. Reduced MiR-675 in exosome in H19 RNA-related melanogenesis via MITF as a direct target. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keniry, A.; Oxley, D.; Monnier, P.; Kyba, M.; Dandolo, L.; Smits, G.; Reik, W. The H19 lincRNA is a developmental reservoir of miR-675 that suppresses growth and Igf1r. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaenssens, E.; Lottin, S.; Berteaux, N.; Hornez, L.; Fauquette, W.; Fafeur, V.; Peyrat, J.P.; Le Bourhis, X.; Hondermarck, H.; Coll, J.; et al. Cross-talk between mesenchyme and epithelium increases H19 gene expression during scattering and morphogenesis of epithelial cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 275, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Salmena, L.; Weiss, D.; Tan, S.M.; Ala, U.; Karreth, F.; Poliseno, L.; Provero, P.; Di Cunto, F.; et al. Coding-independent regulation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by competing endogenous mRNAs. Cell 2011, 147, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Li, T.T.; Wang, K.L.; Xiao, G.Q.; Wang, J.H.; Zhao, H.D.; Kang, Z.J.; Fan, W.J.; Zhu, L.L.; Li, M.; et al. H19/let-7/LIN28 reciprocal negative regulatory circuit promotes breast cancer stem cell maintenance. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Ren, K.; Li, X.; Han, X.; Wang, J. Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer through upregulating DNMT1 expression by sponging miR-152. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Ye, X.L.; Xu, J.; Cao, M.G.; Fang, Z.Y.; Li, L.Y.; Guan, G.H.; Liu, G.; Qian, Y.H.; Xie, D. The lncRNA H19 mediates breast cancer cell plasticity during EMT and MET plasticity by differentially sponging miR-200b/c and let-7b. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.F.; Jia, H.Z.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhao, X.S.; Zou, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.F. LncRNA H19 regulates ID2 expression through competitive binding to hsa-miR-19a/b in acute myelocytic leukemia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3687–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, M.; Zhong, Z.; Huang, M.; Tian, Q.; Jiang, R.; Chen, J. lncRNA H19 regulates epithelial–mesenchymal transition and metastasis of bladder cancer by miR-29b-3p as competing endogenous RNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1864, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.W.; Tian, L.H.; Yang, B.; Guo, R.M. Long noncoding RNA H19 acts as a competing endogenous RNA to mediate CTGF expression by sponging miR-455 in cardiac fibrosis. DNA Cell Biol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazal, S.; McKinnon, B.; Zhou, J.; Mueller, M.; Men, Y.; Yuang, L.; Mueller, M.; Flannery, C.; Huang, Y.; Taylor, H.S. H19 lncRNA alters stromal cell growth via IGF signaling in the endometrium of women with endometriosis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Hu, Q.; Nie, E.; Yu, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhi, T.; Jiang, K.; Shen, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Hypoxia induces H19 expression through direct and indirect Hif-1α activity, promoting oncogenic effects in glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallen, A.N.; Zhou, X.B.; Xu, J.; Qiao, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, L.; Lu, L.; Liu, C.; Yi, J.S.; Zhang, H.; et al. The imprinted H19 lncRNA antagonizes Let-7 microRNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imig, J.; Brunschweiger, A.; Brümmer, A.; Guennewig, B.; Mittal, N.; Kishore, S.; Tsikrika, P.; Gerber, A.P.; Zavolan, M.; Hall, J. miR-CLIP Capture of a miRNA targetome uncovers a lincRNA H19–miR-106a interaction. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 11, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhou, J.; Yan, L.; Jurczak, J.; Lee, H.Y.; Yang, L.; Mueller, M.; Zhou, X.B.; Dandolo, L.; et al. The H19/let-7 double-negative feedback loop contributes to glucose metabolism in muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 13799–13811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.C.; Fu, W.M.; Wang, F.B.; Sun, Y.X.; Xu, L.L.; Wong, C.W.; Chan, K.M.; Li, G.; Waye, M.M.Y.; Zhang, J.F. H19 Activates Wnt signaling and promotes osteoblast differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shuming, G.; Cai, C. H19 functions as a ceRNA in promoting metastasis through decreasing miR-200s activity in osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 2016, 35, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, D.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, X. Long noncoding RNA H19 competitively binds miR-17-5p to regulate YES1 expression in thyroid cancer. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 2326–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, J. Long non-coding RNA H19 increases bladder cancer metastasis by associating with EZH2 and inhibiting E-cadherin expression. Cancer Lett. 2013, 333, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, C.; Jiang, R.; Lin, X.; Shao, M. LncRNA H19 inhibits autophagy by epigenetically silencing of DIRAS3 in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Oncotarget 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monnier, P.; Martinet, C.; Pontis, J.; Stancheva, I.; Ait-Si-Ali, S.; Dandolo, L. H19 lncRNA controls gene expression of the imprinted gene network by recruiting MBD1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20693–20698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, L.; Zhong, T.; Mueller, M.; Men, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xie, J.; Giang, K.; Chung, H.; Sun, X.; et al. H19 lncRNA alters DNA methylation genome wide by regulating S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; He, B.; Gao, T.; Pan, Y.; Sun, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Ying, H.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Up-regulation of 91H promotes tumor metastasis and predicts poor prognosis for patients with colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennin, C.; Spruyt, N.; Robin, Y.M.; Chassat, T.; Le Bourhis, X.; Adriaenssens, E. The long non-coding RNA 91H increases aggressive phenotype of breast cancer cells and up-regulates H19/IGF2 expression through epigenetic modifications. Cancer Lett. 2017, 385, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berteaux, N.; Lottin, S.; Monté, D.; Pinte, S.; Quatannens, B.; Coll, J.; Hondermarck, H.; Curgy, J.J.; Dugimont, T.; Adriaenssens, E. H19 mRNA-like noncoding RNA promotes breast cancer cell proliferation through positive control by E2F1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 29625–29636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsyte-Lovejoy, D.; Lau, S.K.; Boutros, P.C.; Khosravi, F.; Jurisica, I.; Andrulis, I.L.; Tsao, M.S.; Penn, L.Z. The c-Myc oncogene directly induces the H19 noncoding RNA by allele-specific binding to potentiate tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5330–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugimont, T.; Montpellier, C.; Adriaenssens, E.; Lottin, S.; Dumont, L.; Iotsova, V.; Lagrou, C.; Stéhelin, D.; Coll, J.; Curgy, J.J. The H19 TATA-less promoter is efficiently repressed by wild-type tumor suppressor gene product P53. Oncogene 1998, 16, 2395–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Bi, J.; Xue, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhi, K.; Hua, J.; Fang, G. Up-regulated long non-coding RNA H19 Contributes to proliferation of gastric cancer cells. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lichun, W.; Lian, L.; Yang, J.; Song, X.; Liu, J. Circulating lncRNA H19 in plasma as a novel biomarker for breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2016, 17, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yin, C.; Dang, Y.; Ye, F.; Zhang, G. Identification of the long non-coding RNA H19 in plasma as a novel biomarker for diagnosis of gastric cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.S.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, X.Q.; Lv, J.M.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.X.; Xu, T.P. H19 serves as a diagnostic biomarker and up-regulation of H19 expression contributes to poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Neoplasma 2016, 63, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gofrit, O.N.; Benjamin, S.; Halachmi, S.; Leibovitch, I.; Dotan, Z.; Lamm, D.L.; Ehrlich, N.; Yutkin, V.; Ben-Am, M.; Hocherg, A. DNA based therapy with diphtheria toxin-A BC-819: A phase 2b marker lesion trial in patients with intermediate risk nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2014, 191, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, O.; Edelman, D.; Levy, T.; Fishman, A.; Hubert, A.; Segev, Y.; Raveh, E.; Gilon, M.; Hichberg, A. A phase 1/2a, dose-escalation, safety, pharmacokinetic, and preliminary efficacy study of intraperitoneal administration of BC-819 (H19-DTA) in subjects with recurrent ovarian/peritoneal cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2017, 295, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Targets of miR-675-5p | Cellular Context | Proteins Function | References |
| c-Cbl & Cbl-b | Breast cancer | Ubiquitin ligase E3 | [33] |
| HDAC 4/5/6 | Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells | Histone deacetylase | [36] |
| CaMKIId | Cardiomyocyte hypertrophy | Serine threonine protein kinase | [37] |
| USP10 | c-kit+ cardiac progenitor cells | Ubiquitin-specific protease | [38] |
| RB | Colorectal cancer | Cell cycle regulator | [32] |
| DDB2 | Colon cancer cells | Transcriptional repressor | [39] |
| VDR | Colon cancer cells | Vitamin D receptor | [40] |
| VDAC1 | Diabetic cardiomyopathy | Required for mitochondria-mediated apoptosis | [41] |
| REPS2 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Repressor of cell proliferation and migration | [42] |
| CALN1 | Gastric cancer | Calcium-binding protein | [43] |
| RUNX1 | Gastric cancer | Transcription factor | [44,45] |
| FADD | Gastric cancer | Apoptotic adaptor that recruits caspase 8 or 10 | [46] |
| Cadherin 13 | Glioma cell | Atypical cadherin lacking the cytoplasmic domain | [47] |
| RB & TWIST1 | Hepatocellular carcinomas | Twist1: Transcription factor | [48] |
| GPR55 | Non-small cell lung cancer | G protein-coupled receptor | [49] |
| TGF-ß1 | Osteoblast differenciation | Growth factor | [50] |
| TGF-ß1 | Prostate cancer | Growth factor | [25] |
| NOMO1 | Placental trophoblast cell | Nodal signaling pathway | [51] |
| ATP8A2 | Skeletal cell | Catalytic component of a P4-ATPase flippase complex | [52] |
| CDC6 | Skeletal muscle | Essential for the initiation of DNA replication | [53] |
| VDR | Ulcerative Colitis | Vitamin D receptor | [54] |
| Targets of miR-675-3p | Cellular Context | Proteins Function | References |
| Cadherin 11 | Melanogenesis | Type II classical cadherin | [55] |
| MITF | Melanogenesis | Transcription factor | [56] |
| IGF1R | Placenta | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | [57] |
| TGF-ß1 | Osteoblast differenciation | Growth factor | [50] |
| SMAD1 & SMAD5 | Skeletal muscle | Intracellular signal transducer and transcriptional modulator | [53] |
| miRNAs Sponged by H19 | Cellular Context | References |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-19a/b | Acute myelocytic leukemia | [63] |
| miR-29b-3p | Bladder cancer | [64] |
| miR-152 | Breast cancer | [61] |
| let-7 | Breast cancer stem cells | [60] |
| miR-455 | Cardiac fibrosis | [65] |
| let7 | Endometriosis | [66] |
| miR-181-d | Gliobastoma | [67] |
| let-7 | HEK293 | [68] |
| miR-106-a & miR-17-5p | Hela Cells, myboblast | [69] |
| let-7 | Muscle cells | [70] |
| let-7b & miR-200b/c | Mouse breast cancer | [62] |
| miR 141 miR 22 | Osteoblast | [71] |
| mir-200s | Osteosarcoma | [72] |
| miR-17-5p | Thyroid cancer | [73] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Collette, J.; Le Bourhis, X.; Adriaenssens, E. Regulation of Human Breast Cancer by the Long Non-Coding RNA H19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112319
Collette J, Le Bourhis X, Adriaenssens E. Regulation of Human Breast Cancer by the Long Non-Coding RNA H19. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112319
Chicago/Turabian StyleCollette, Jordan, Xuefen Le Bourhis, and Eric Adriaenssens. 2017. "Regulation of Human Breast Cancer by the Long Non-Coding RNA H19" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112319
APA StyleCollette, J., Le Bourhis, X., & Adriaenssens, E. (2017). Regulation of Human Breast Cancer by the Long Non-Coding RNA H19. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112319




