A Novel Combination RNAi toward Warburg Effect by Replacement with miR-145 and Silencing of PTBP1 Induces Apoptotic Cell Death in Bladder Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
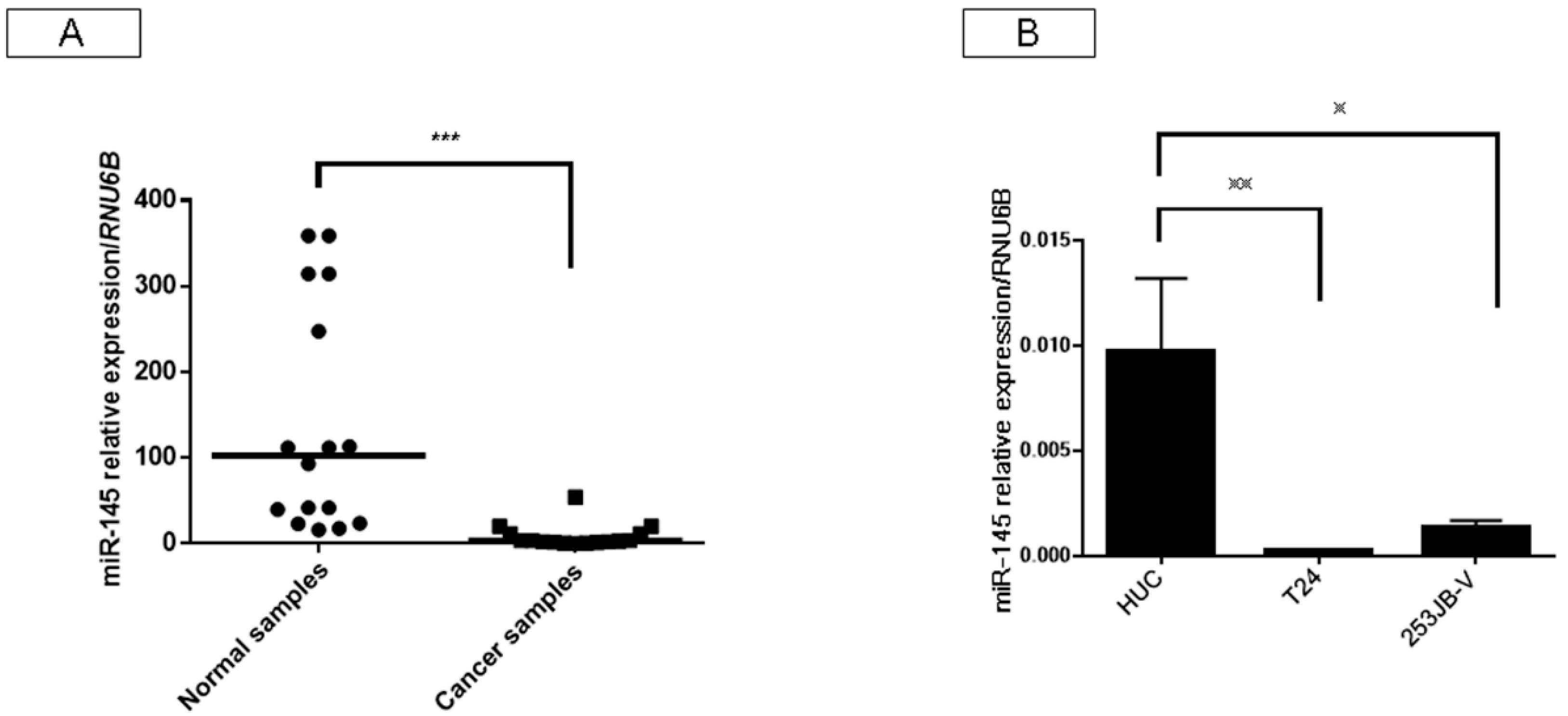
2.1. Expression of miR-145 Was Extremely Downregulated in Clinical Tumor Samples from Bladder Cancer Patients and Bladder Cancer Cell Lines
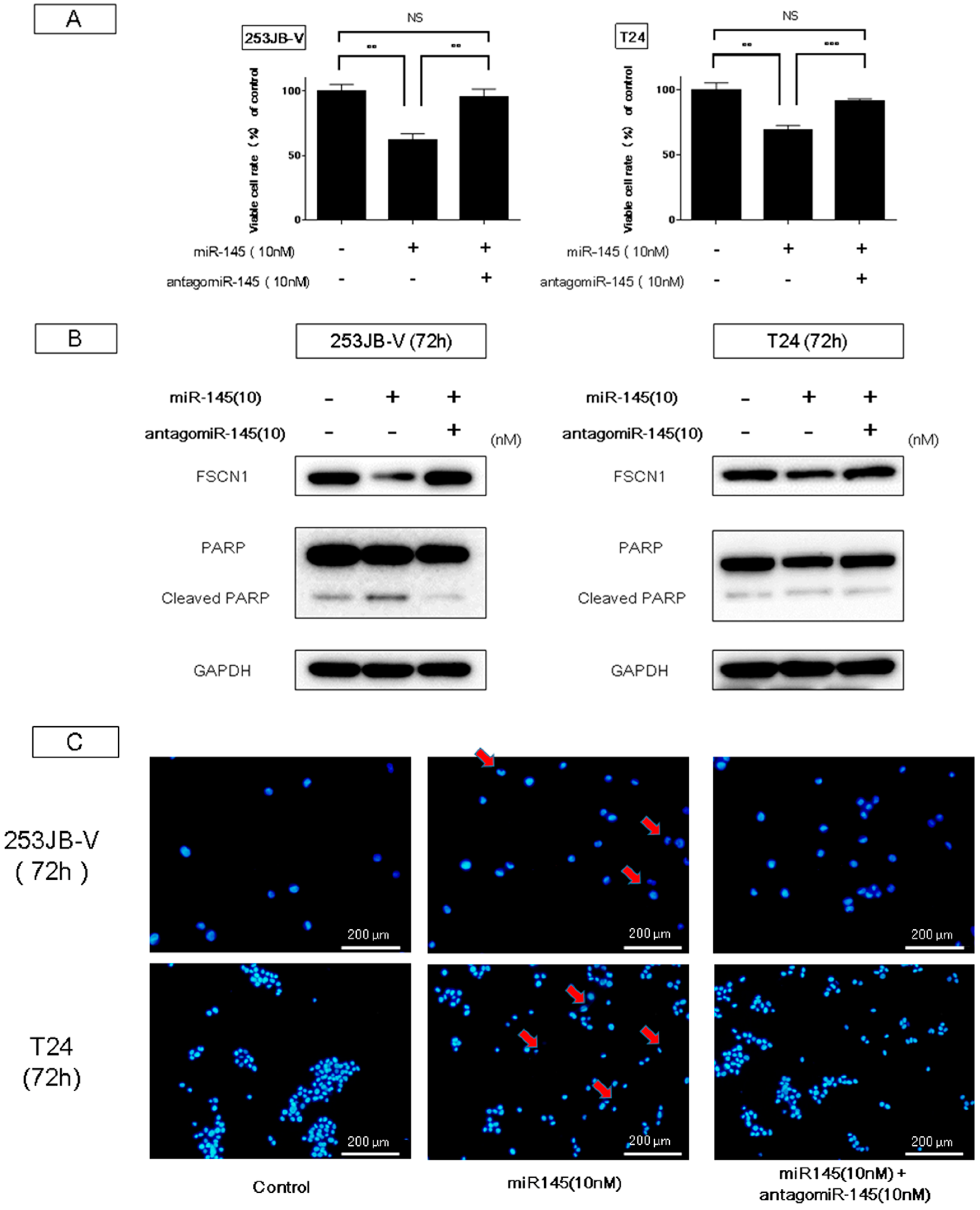
2.2. Ectopic Expression of miR-145 in Bladder Cancer Cells Induced Apoptosis
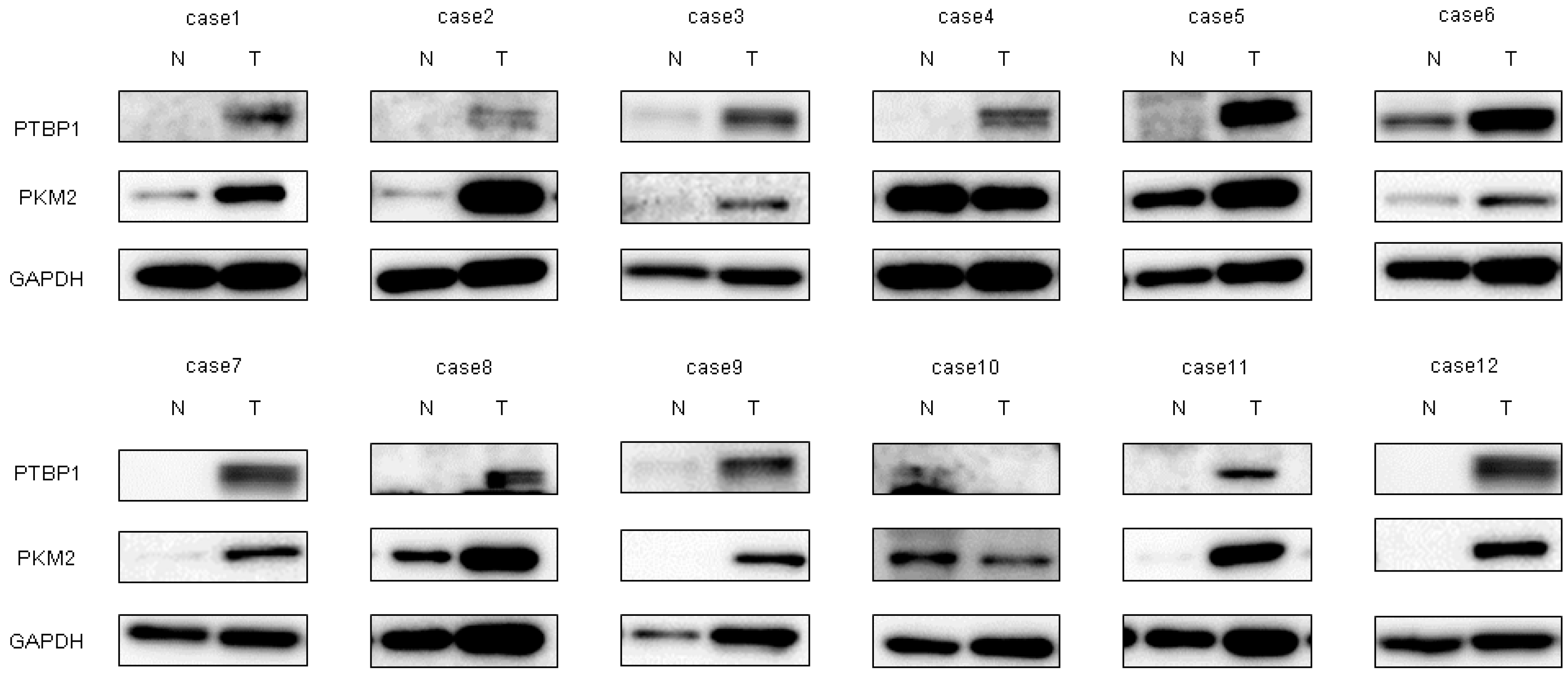
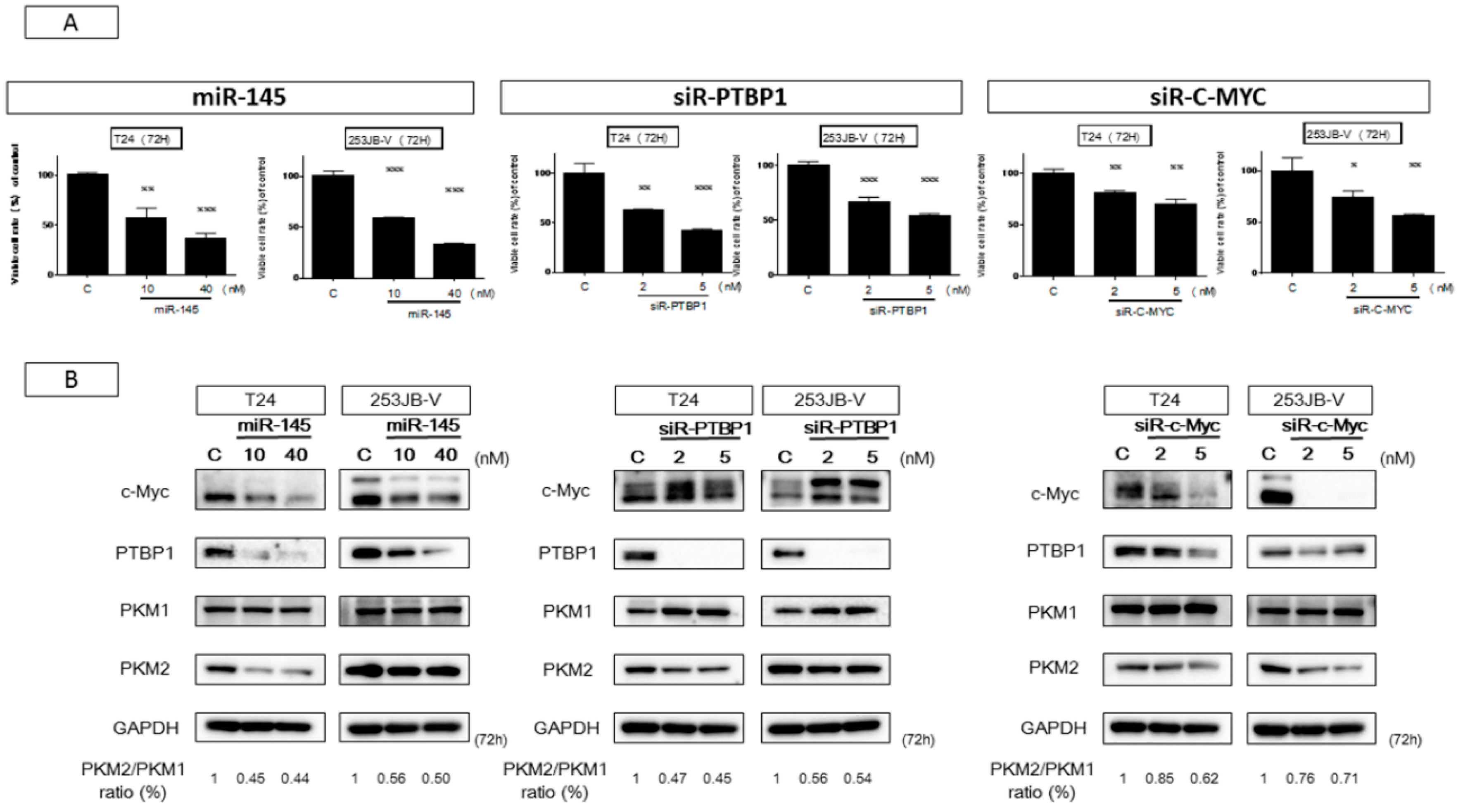
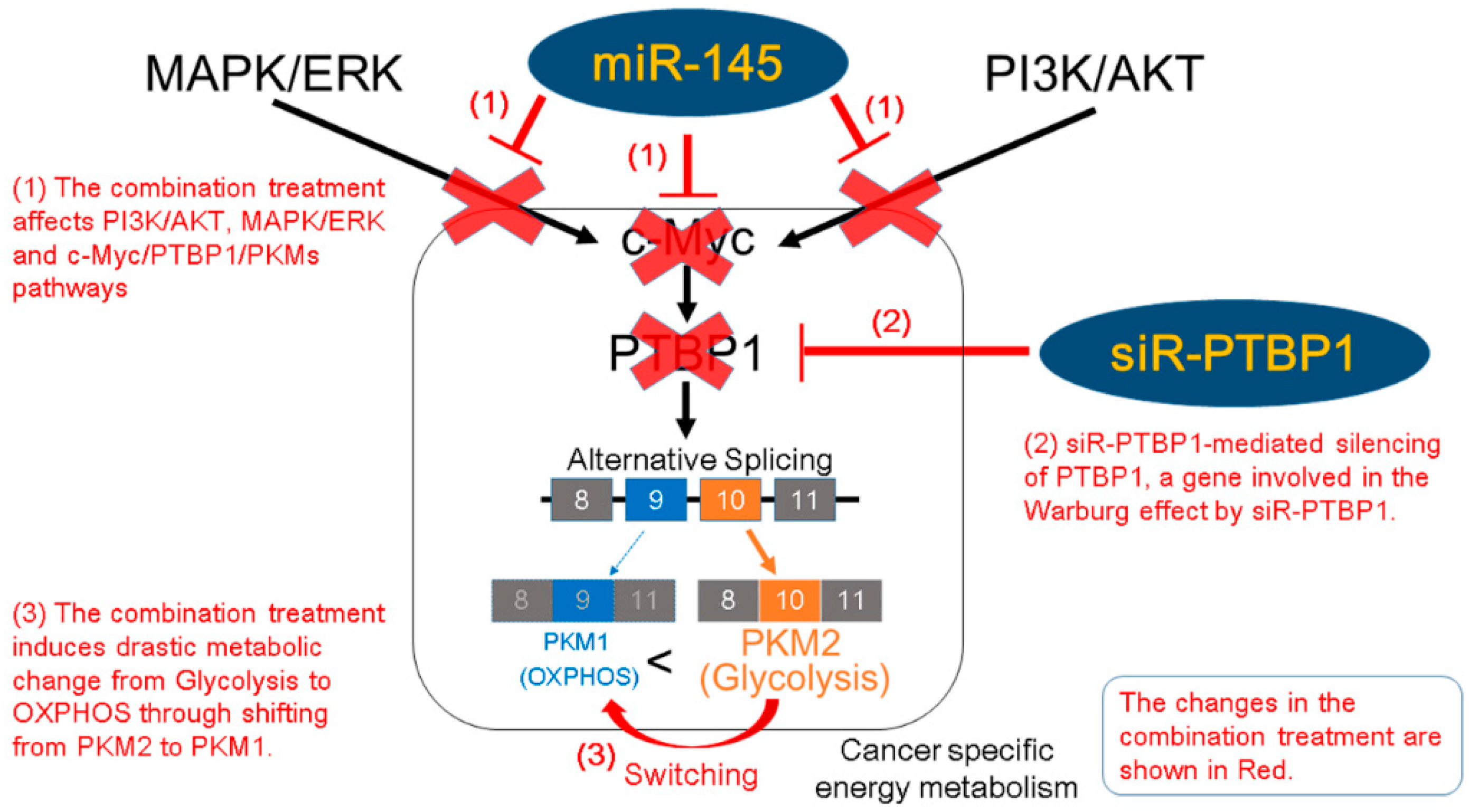
2.3. miR-145 Impaired the PTBP1/PKMs Axis, Reducing the Cancer-Specific Energy Metabolism, through Silencing of c-Myc
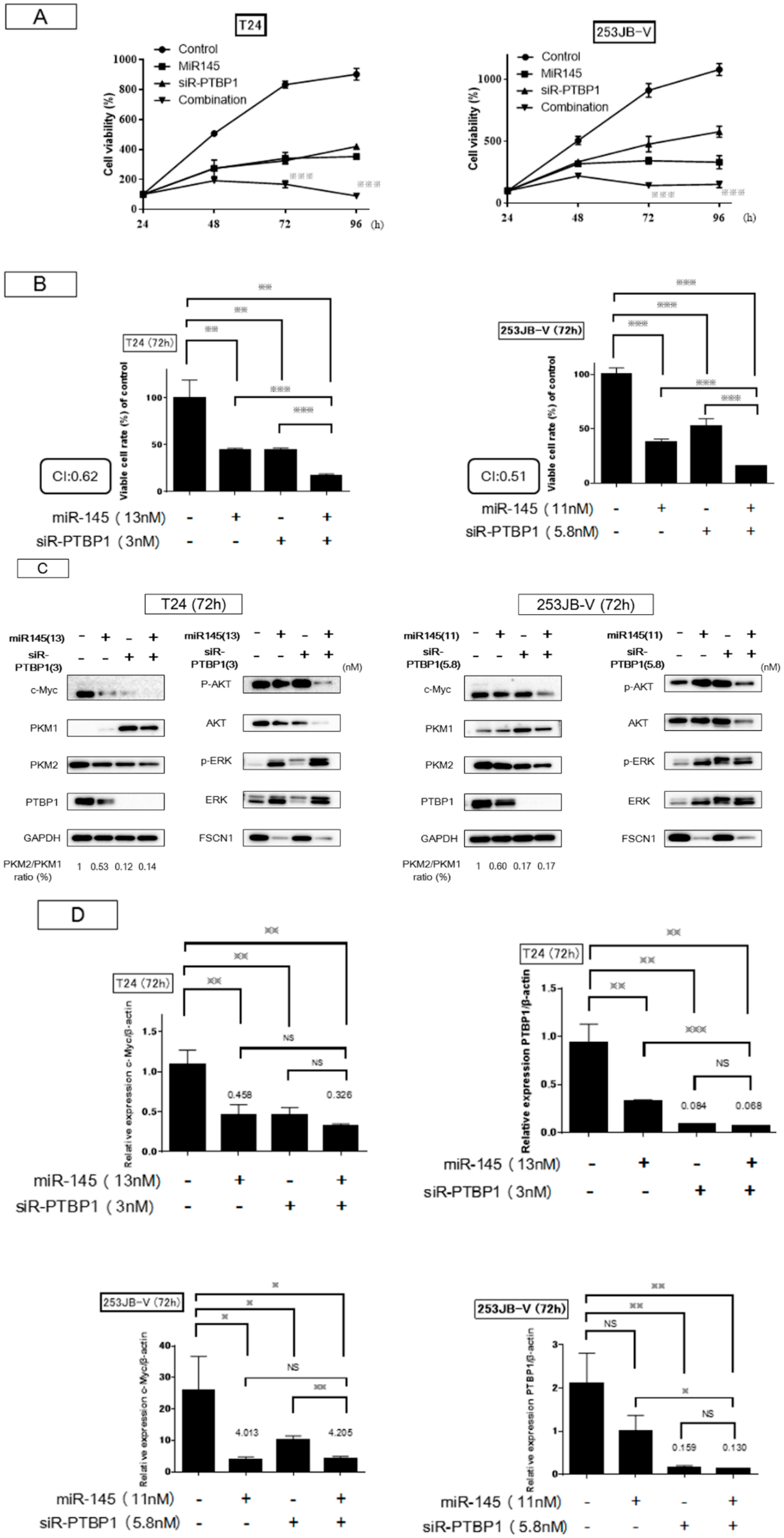
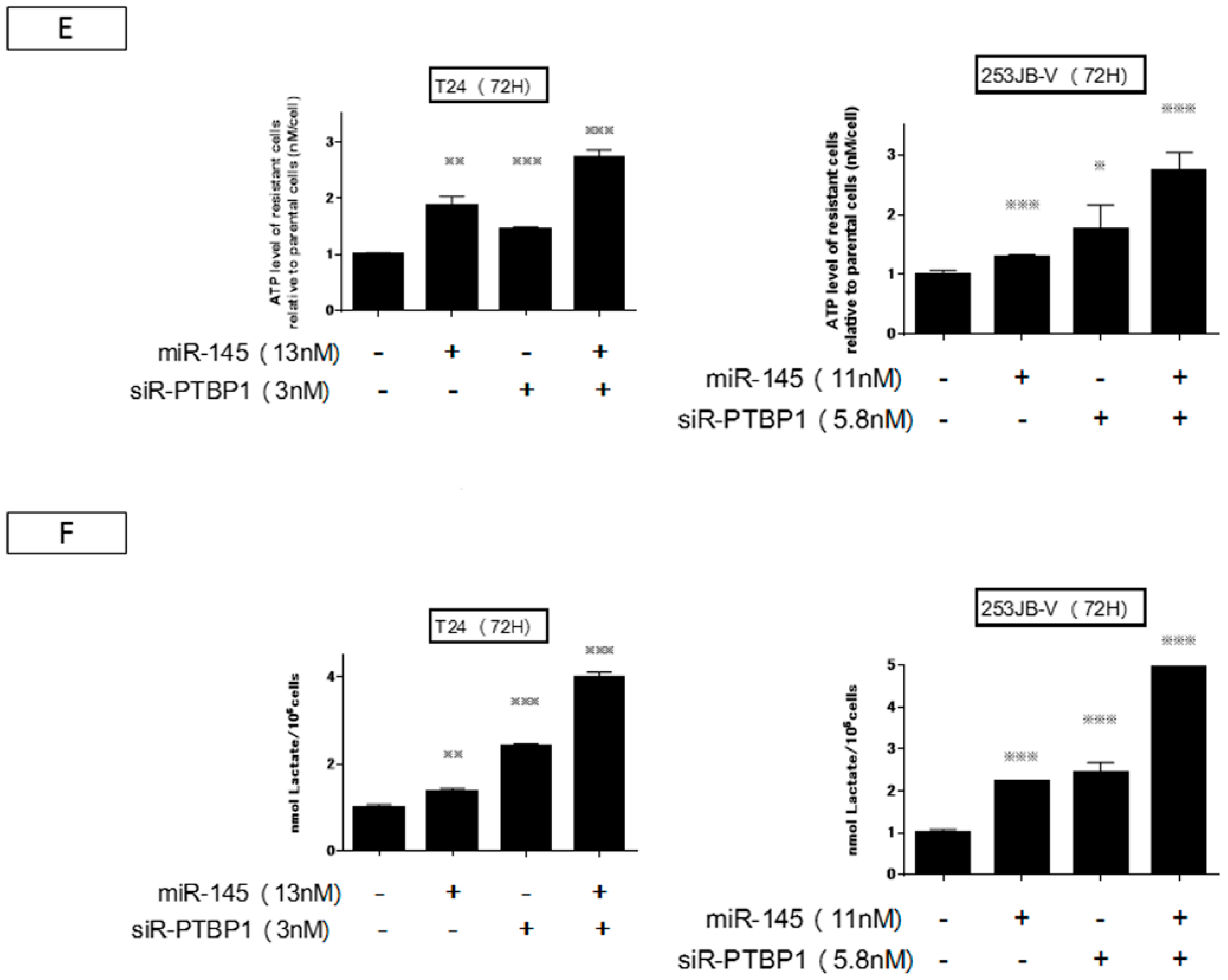
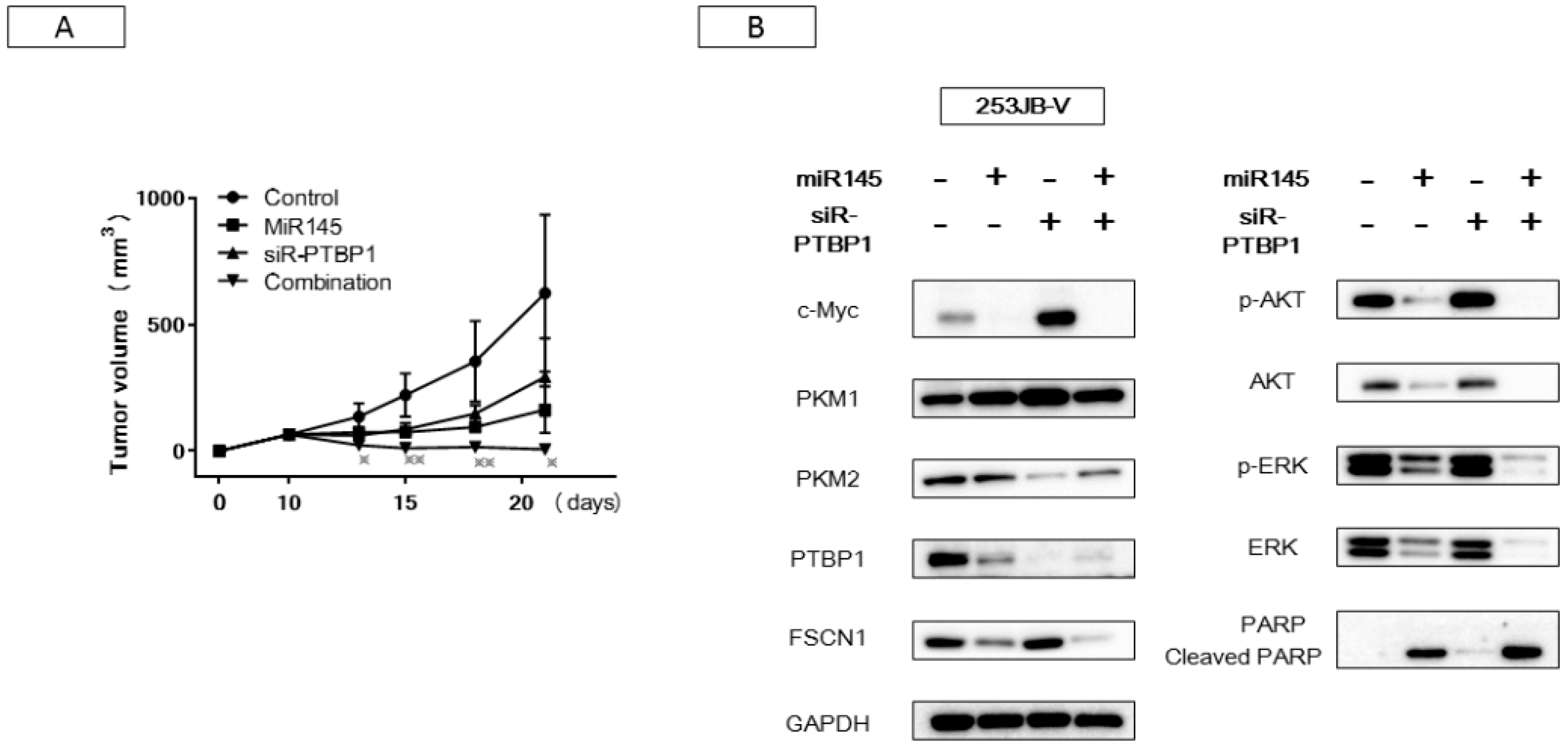
2.4. Increased Expression of miR-145 Combined with Knockdown of PTBP1 Contributed to the Greater and Longer Growth Suppression Compared with Each Single Treatment
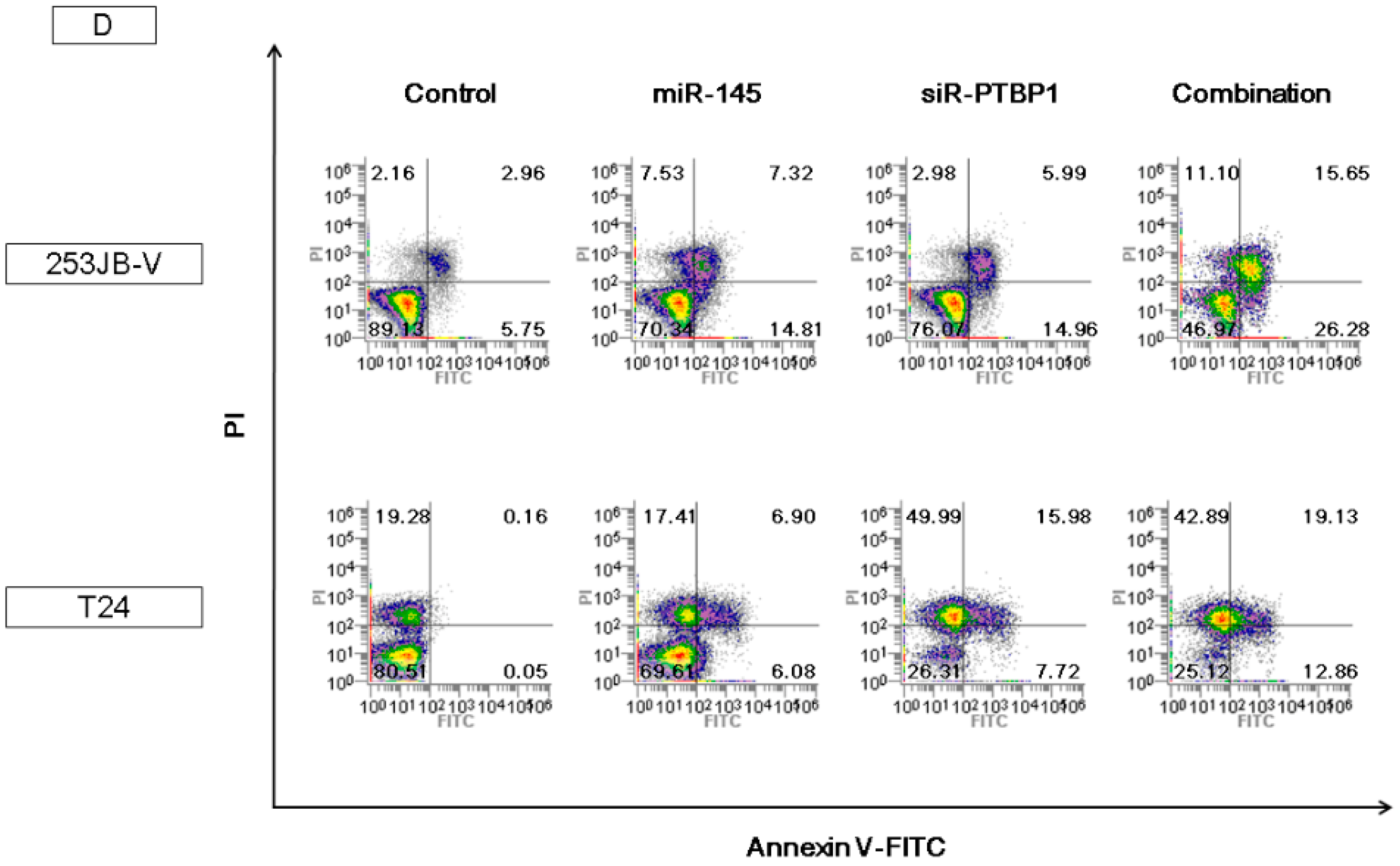
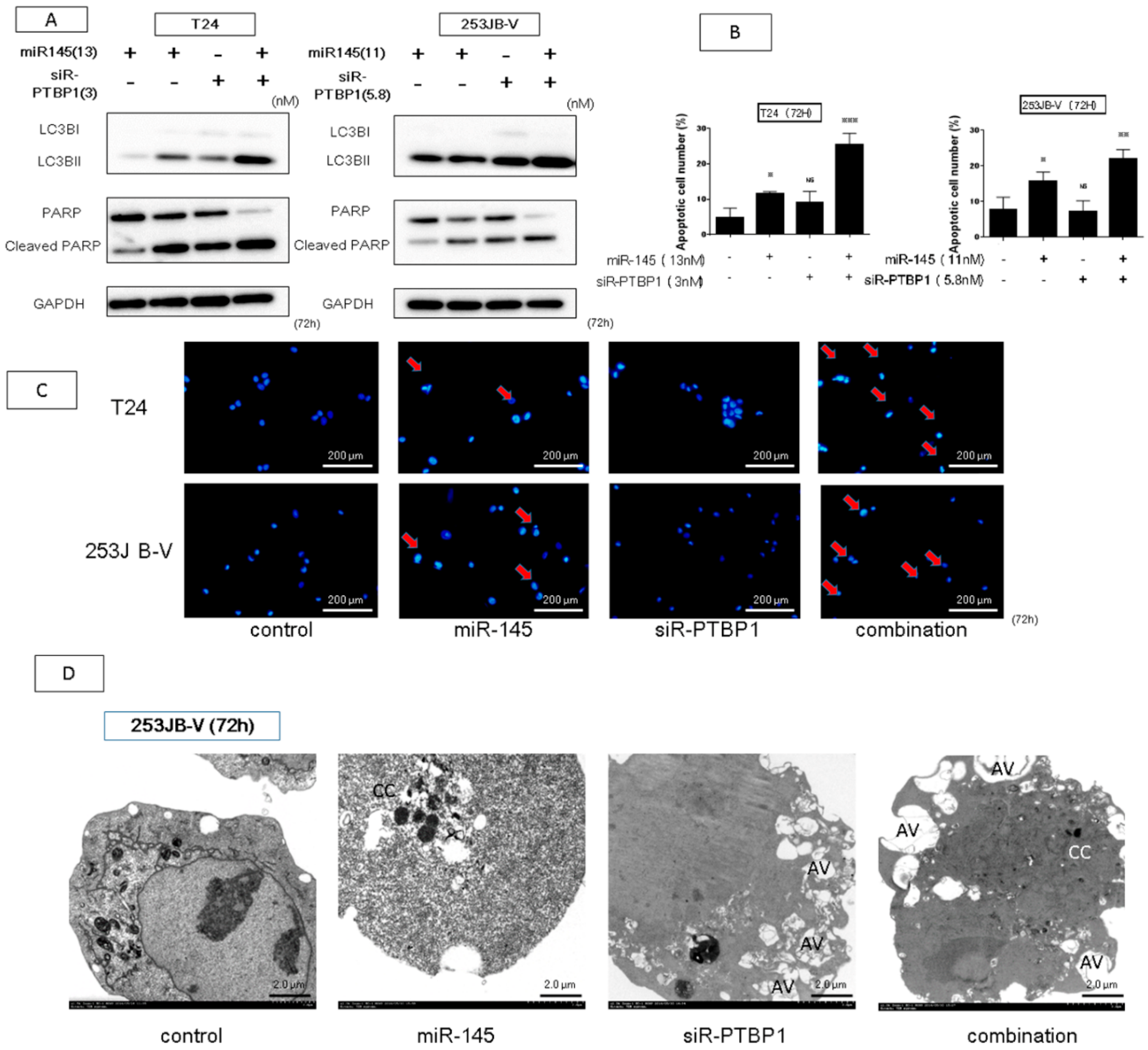
2.5. The Combination Treatment of Ectopic Expression of miR-145 and Knockdown of PTBP1 Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy
2.6. Antitumor Effect of miR-145 and/or siR-PTBP1 on 253JB-V Cell Xenografted Tumors in Nude Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples
4.2. Cell Culture and Cell Viability
4.3. Transfection Experiments
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR
4.6. Hoechst 33342 Staining
4.7. Apoptosis Assay Using Flow Cytometry
4.8. Lactate Assay
4.9. ATP Assay
4.10. In Vivo Xenograft Model
4.11. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chamie, K.; Litwin, M.S.; Bassett, J.C.; Daskivich, T.J.; Lai, J.; Hanley, J.M.; Konety, B.R.; Saigal, C.S. Urologic Diseases in America Project. Recurrence of high-risk bladder cancer: A population-based analysis. Cancer 2013, 119, 3219–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, H.; Bahnson, R.; Cohen, S.; Eisenberger, M.; Herr, H.; Kozlowski, J.; Lange, P.; Montie, J.; Pollack, A.; Raghaven, D.; et al. NCCN urothelial cancer practice guidelines. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Oncology (Williston Park) 1998, 12, 225–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herr, H.W.; Dotan, Z.; Donat, S.M.; Bajorin, D.F. Defining optimal therapy for muscle invasive bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.C.; Chang, S.S.; Dalbagni, G.; Pruthi, R.S.; Seigne, J.D.; Skinner, E.C.; Wolf, J.S., Jr.; Schellhammer, P.F. Guideline for the management of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer (stages Ta, T1, and Tis): 2007 update. J. Urol. 2007, 178, 2314–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubben, H.; Lutzeyer, W.; Fischer, N.; Deutz, F.; Lagrange, W.; Giani, G. Natural history and treatment of low and high risk superficial bladder tumors. J. Urol. 1988, 139, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gakis, G.; Efstathiou, J.; Lerner, S.P.; Cookson, M.S.; Keegan, K.A.; Guru, K.A.; Shipley, W.U.; Heidenreich, A.; Schoenberg, M.P.; Sagaloswky, A.I.; et al. ICUD-EAU International Consultation on Bladder Cancer 2012: Radical cystectomy and bladder preservation for muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.P.; Shah, N.D.; Weight, C.J.; Thompson, R.H.; Wang, J.K.; Karnes, R.J.; Han, L.C.; Ziegenfuss, J.Y.; Frank, I.; Tollefson, M.K.; et al. Population-based trends in urinary diversion among patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2013, 112, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Hirata, I.; Iio, A.; Itoh, T.; Kojima, K.; Nakashima, R.; Kitade, Y.; Naoe, T. Role of anti-oncomirs miR-143 and -145 in human colorectal tumors. Cancer Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudbery, I.; Enright, A.J.; Fraser, A.G.; Dunham, I. Systematic analysis of off-target effects in an RNAi screen reveals microRNAs affecting sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, M.S.; Chen, Y.; Deng, G.; Shahryari, V.; Suh, S.O.; Saini, S.; Majid, S.; Liu, J.; Khatri, G.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. The functional significance of microRNA-145 in prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, S.; Yamada, N.; Kumazaki, M.; Yasui, Y.; Iwasaki, J.; Naito, S.; Akao, Y. socs7, a target gene of microRNA-145, regulates interferon-beta induction through STAT3 nuclear translocation in bladder cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatani, A.; Nakagawa, Y.; Akao, Y.; Maruyama, N.; Nagasaka, M.; Shibata, T.; Tahara, T.; Hirata, I. Downregulation of anti-oncomirs miR-143/145 cluster occurs before APC gene aberration in the development of colorectal tumors. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2013, 46, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Naoe, T. MicroRNA-143 and -145 in colon cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 2007, 26, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, T.; Iio, A.; Nakagawa, Y.; Naoe, T.; Tanigawa, N.; Akao, Y. Decreased expression of microRNA-143 and -145 in human gastric cancers. Oncology 2009, 77, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Kitade, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Naoe, T. Downregulation of microRNAs-143 and -145 in B-cell malignancies. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1914–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Naoe, T. MicroRNAs 143 and 145 are possible common onco-microRNAs in human cancers. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 16, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, S.; Mori, T.; Hoshino, Y.; Yamada, N.; Nakagawa, T.; Sasaki, N.; Akao, Y.; Maruo, K. Comparative study of anti-oncogenic microRNA-145 in canine and human malignant melanoma. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, N.; Noguchi, S.; Mori, T.; Naoe, T.; Maruo, K.; Akao, Y. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-145 targets catenin δ-1 to regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, S.; Yasui, Y.; Iwasaki, J.; Kumazaki, M.; Yamada, N.; Naito, S.; Akao, Y. Replacement treatment with microRNA-143 and -145 induces synergistic inhibition of the growth of human bladder cancer cells by regulating PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Cancer Lett. 2013, 328, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, H.; Seki, N.; Itesako, T.; Chiyomaru, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Enokida, H. Aberrant expression of microRNAs in bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2013, 10, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, R.; Yoshino, H.; Enokida, H.; Goto, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Yonemori, M.; Inoguchi, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Seki, N. Regulation of UHRF1 by dual-strand tumor-suppressor microRNA-145 (miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p): Inhibition of bladder cancer cell aggressiveness. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 28460–28487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamoto, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Takahara, K.; Iwatsuki, A.; Takai, T.; Komura, K.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Uchimoto, T.; Saito, K.; Tanda, N.; et al. Intravesical administration of exogenous microRNA-145 as a therapy for mouse orthotopic human bladder cancer xenograft. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21628–21635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburg, O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Inoue, H.; Tanaka, T. The M1- and M2-type isozymes of rat pyruvate kinase are produced from the same gene by alternative RNA splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 13807–13812. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clower, C.V.; Chatterjee, D.; Wang, Z.; Cantley, L.C.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Krainer, A.R. The alternative splicing repressors hnRNP A1/A2 and PTB influence pyruvate kinase isoform expression and cell metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1894–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, C.J.; Chen, M.; Assanah, M.; Canoll, P.; Manley, J.L. HnRNP proteins controlled by c-Myc deregulate pyruvate kinase mRNA splicing in cancer. Nature 2010, 463, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Sugito, N.; Kumazaki, M.; Shinohara, H.; Yamada, N.; Nakagawa, Y.; Ito, Y.; Otsuki, Y.; Uno, B.; Uchiyama, K.; et al. MicroRNA-124 inhibits cancer cell growth through PTB1/PKM1/PKM2 feedback cascade in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 363, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, S.; Iwasaki, J.; Kumazaki, M.; Mori, T.; Maruo, K.; Sakai, H.; Yamada, N.; Shimada, K.; Naoe, T.; Kitade, Y.; et al. Chemically modified synthetic microRNA-205 inhibits the growth of melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Sakai, M.; Sugito, N.; Kumazaki, M.; Shinohara, H.; Yamada, N.; Nakayama, T.; Ueda, H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Ito, Y.; et al. PTBP1-associated microRNA-1 and -133b suppress the Warburg effect in colorectal tumors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18940–18952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, M.; Zhu, S.; Wu, F.; Wu, H.; Walia, V.; Kumar, S.; Elble, R.; Watabe, K.; Mo, Y.Y. p53 represses c-Myc through induction of the tumor suppressor miR-145. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, N.; Tsujimura, N.; Kumazaki, M.; Shinohara, H.; Taniguchi, K.; Nakagawa, Y.; Naoe, T.; Akao, Y. Colorectal cancer cell-derived microvesicles containing microRNA-1246 promote angiogenesis by activating Smad 1/5/8 signaling elicited by PML down-regulation in endothelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1839, 1256–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case | Age | Sex | Size (cm) | Grade | T Stage | miR-145 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 63 | M | 4 | 2 | pTa | D |
| 2 | 68 | M | 1 | 1 | pTa | D |
| 3 | 79 | F | 2 | 2 | pT1 | D |
| 4 | 49 | M | 3 | 3 | pT1 | D |
| 5 | 74 | F | 4 | 3 | pT2 | D |
| 6 | 71 | M | 3 | 3 | pT1 | D |
| 7 | 67 | M | 5 | 2 | pT1 | D |
| 8 | 84 | F | 3 | 1 | pT1 | D |
| 9 | 75 | M | 3 | 1 | pTa | D |
| 10 | 79 | F | 2 | 2 | pTa | D |
| 11 | 60 | M | 4 | 1 | pTa | D |
| 12 | 86 | M | 20 | 3 | pT1 | D |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takai, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Inamoto, T.; Minami, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Sugito, N.; Kuranaga, Y.; Shinohara, H.; Kumazaki, M.; Tsujino, T.; et al. A Novel Combination RNAi toward Warburg Effect by Replacement with miR-145 and Silencing of PTBP1 Induces Apoptotic Cell Death in Bladder Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010179
Takai T, Yoshikawa Y, Inamoto T, Minami K, Taniguchi K, Sugito N, Kuranaga Y, Shinohara H, Kumazaki M, Tsujino T, et al. A Novel Combination RNAi toward Warburg Effect by Replacement with miR-145 and Silencing of PTBP1 Induces Apoptotic Cell Death in Bladder Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(1):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010179
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakai, Tomoaki, Yuki Yoshikawa, Teruo Inamoto, Koichiro Minami, Kohei Taniguchi, Nobuhiko Sugito, Yuki Kuranaga, Haruka Shinohara, Minami Kumazaki, Takuya Tsujino, and et al. 2017. "A Novel Combination RNAi toward Warburg Effect by Replacement with miR-145 and Silencing of PTBP1 Induces Apoptotic Cell Death in Bladder Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 1: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010179
APA StyleTakai, T., Yoshikawa, Y., Inamoto, T., Minami, K., Taniguchi, K., Sugito, N., Kuranaga, Y., Shinohara, H., Kumazaki, M., Tsujino, T., Takahara, K., Ito, Y., Akao, Y., & Azuma, H. (2017). A Novel Combination RNAi toward Warburg Effect by Replacement with miR-145 and Silencing of PTBP1 Induces Apoptotic Cell Death in Bladder Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(1), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010179








