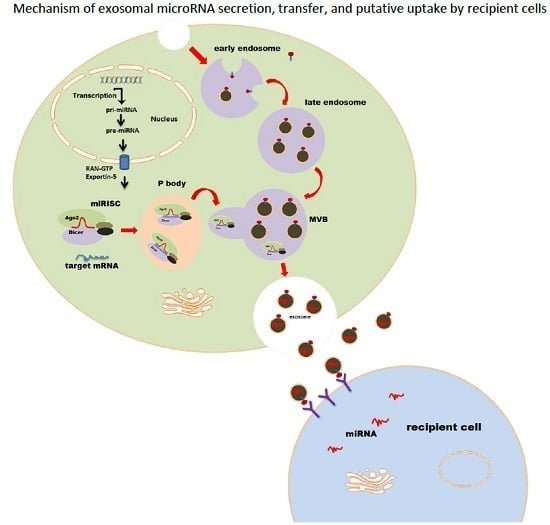
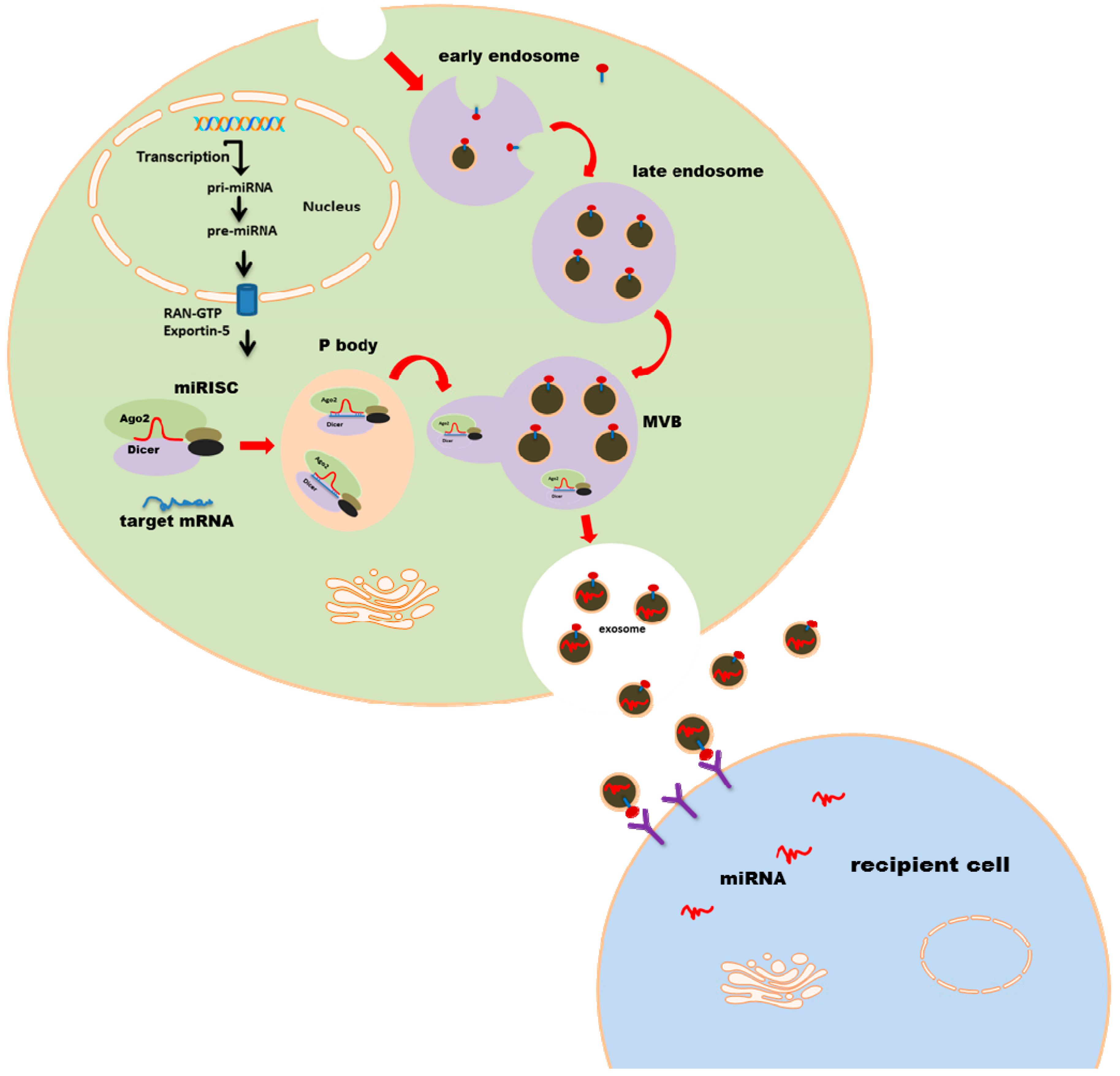
Exosomes as miRNA Carriers: Formation–Function–Future
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. MicroRNA Loading into Exosomes
3. Exosome-Mediated Regulatory Effects in Liver
4. Exosomal miRNA Uptake
5. Regulatory Functions of Secreted miRNAs in Cancer
6. Outlook: miRNAs Secreted in Exosomes as Diagnostic Tools
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalra, H.; Drummen, G.P.; Mathivanan, S. Focus on extracellular vesicles: Introducing the next small big thing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos-Amador, P.; Perez-Cabezas, B.; Izquierdo-Useros, N.; Puertas, M.C.; Martinez-Picado, J.; Pujol-Borrell, R.; Naranjo-Gomez, M.; Borras, F.E. Capture of cell-derived microvesicles (exosomes and apoptotic bodies) by human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Shi, X.; Gao, H. Cellular uptake of elastic nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 098101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Vancells, J.; Rodriguez-Suarez, E.; Embade, N.; Gil, D.; Matthiesen, R.; Valle, M.; Elortza, F.; Lu, S.C.; Mato, J.M.; Falcon-Perez, J.M. Characterization and comprehensive proteome profiling of exosomes secreted by hepatocytes. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 5157–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaj, L.; Atai, N.A.; Chen, W.; Mu, D.; Tannous, B.A.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J.; Maguire, C.A. Heparin affinity purification of extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutters, K.; Reutelingsperger, C. Phosphatidylserine targeting for diagnosis and treatment of human diseases. Apoptosis 2010, 15, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brugger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 2008, 319, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keerthikumar, S.; Gangoda, L.; Liem, M.; Fonseka, P.; Atukorala, I.; Ozcitti, C.; Mechler, A.; Adda, C.G.; Ang, C.S.; Mathivanan, S. Proteogenomic analysis reveals exosomes are more oncogenic than ectosomes. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15375–15396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, S.; Drummen, G.P.; Kuroda, M. Focus on extracellular vesicles: Development of extracellular vesicle-based therapeutic systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathivanan, S.; Lim, J.W.; Tauro, B.J.; Ji, H.; Moritz, R.L.; Simpson, R.J. Proteomics analysis of a33 immunoaffinity-purified exosomes released from the human colon tumor cell line LIM1215 reveals a tissue-specific protein signature. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.T.; Teng, K.; Wu, C.; Adam, M.; Johnstone, R.M. Electron microscopic evidence for externalization of the transferrin receptor in vesicular form in sheep reticulocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 101, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mrnas and micrornas is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, J.; Jung, S.; Keller, S.; Gregory, R.I.; Diederichs, S. Many roads to maturity: MicroRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, R.I.; Chendrimada, T.P.; Cooch, N.; Shiekhattar, R. Human risc couples microRNA biogenesis and posttranscriptional gene silencing. Cell 2005, 123, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L.; et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, M.P.; Ismail, N.; Zhang, X.; Aguda, B.D.; Lee, E.J.; Yu, L.; Xiao, T.; Schafer, J.; Lee, M.L.; Schmittgen, T.D.; et al. Detection of microrna expression in human peripheral blood microvesicles. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Perez-Hernandez, D.; Vazquez, J.; Martin-Cofreces, N.; Martinez-Herrera, D.J.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Sumoylated HNRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, G.L.; Blau, H.M. Argonaute 2/risc resides in sites of mammalian mRNA decay known as cytoplasmic bodies. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eystathioy, T.; Jakymiw, A.; Chan, E.K.; Seraphin, B.; Cougot, N.; Fritzler, M.J. The GW182 protein colocalizes with mRNA degradation associated proteins HDCP1 and HLSM4 in cytoplasmic GW bodies. RNA 2003, 9, 1171–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbings, D.J.; Ciaudo, C.; Erhardt, M.; Voinnet, O. Multivesicular bodies associate with components of mirna effector complexes and modulate miRNA activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Valencia-Sanchez, M.A.; Hannon, G.J.; Parker, R. MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mrnas to mammalian p-bodies. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Habermacher, R.; Martine, U.; Closs, E.I.; Filipowicz, W. Stress-induced reversal of microRNA repression and mRNA p-body localization in human cells. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2006, 71, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Pressman, S.; Andress, A.P.; Kim, K.; White, J.L.; Cassidy, J.J.; Li, X.; Lubell, K.; Lim, D.H.; Cho, I.S.; et al. Silencing by small RNAs is linked to endosomal trafficking. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, S.; Petrasek, J.; Mundkur, S.; Catalano, D.; Levin, I.; Ward, J.; Alao, H.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. Circulating microRNAs in exosomes indicate hepatocyte injury and inflammation in alcoholic, drug-induced, and inflammatory liver diseases. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zheng, R.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Fei, M.; Sun, S. Plasma microRNA-122 as a biomarker for viral-, alcohol-, and chemical-related hepatic diseases. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Ding, J.; Ning, J.; Yi, F.; Chen, J.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, J.; Liang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Du, Q. Circulating microRNA-122 as a potential biomarker for liver injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 1428–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, S.; Marzolf, B.; Troisch, P.; Brightman, A.; Hu, Z.; Hood, L.E.; Galas, D.J. Circulating microRNAs, potential biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4402–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hergenreider, E.; Heydt, S.; Treguer, K.; Boettger, T.; Horrevoets, A.J.; Zeiher, A.M.; Scheffer, M.P.; Frangakis, A.S.; Yin, X.; Mayr, M.; et al. Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, L.; Honsho, M.; Zahn, T.R.; Keller, P.; Geiger, K.D.; Verkade, P.; Simons, K. Alzheimer’s disease β-amyloid peptides are released in association with exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11172–11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampetaki, A.; Kiechl, S.; Drozdov, I.; Willeit, P.; Mayr, U.; Prokopi, M.; Mayr, A.; Weger, S.; Oberhollenzer, F.; Bonora, E.; et al. Plasma microRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial miR-126 and other microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvoza, N.C.; Klinzing, D.C.; Gopez-Cervantes, J.; Baclig, M.O. Association of circulating serum miR-34a and miR-122 with dyslipidemia among patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roderburg, C.; Benz, F.; Vargas Cardenas, D.; Koch, A.; Janssen, J.; Vucur, M.; Gautheron, J.; Schneider, A.T.; Koppe, C.; Kreggenwinkel, K.; et al. Elevated miR-122 serum levels are an independent marker of liver injury in inflammatory diseases. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bihrer, V.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Kronenberger, B.; Forestier, N.; Haupenthal, J.; Shi, Y.; Peveling-Oberhag, J.; Radeke, H.H.; Sarrazin, C.; Herrmann, E.; et al. Serum miR-122 as a biomarker of necroinflammation in patients with chronic hepatitis c virus infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momen-Heravi, F.; Saha, B.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Satishchandran, A.; Szabo, G. Increased number of circulating exosomes and their microRNA cargos are potential novel biomarkers in alcoholic hepatitis. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csak, T.; Bala, S.; Lippai, D.; Satishchandran, A.; Catalano, D.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. MicroRNA-122 regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and vimentin in hepatocytes and correlates with fibrosis in diet-induced steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.K.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Hirsova, P.; Mushref, M.; Liu, Y.; Cao, S.; Contreras, P.C.; Malhi, H.; Kamath, P.S.; et al. Alcohol stimulates macrophage activation through caspase-dependent hepatocyte derived release of CD40L containing extracellular vesicles. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukong, T.N.; Momen-Heravi, F.; Kodys, K.; Bala, S.; Szabo, G. Exosomes from hepatitis c infected patients transmit HCV infection and contain replication competent viral RNA in complex with ago2-miR122-hsp90. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojima, H.; Freeman, C.M.; Schuster, R.M.; Japtok, L.; Kleuser, B.; Edwards, M.J.; Gulbins, E.; Lentsch, A.B. Hepatocyte exosomes mediate liver repair and regeneration via sphingosine-1-phosphate. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.H.; Yang, S.R.; Cho, J.Y.; Cho, H.C.; Shim, S.G.; Paik, Y.H. Serum exosomal microRNAs as novel biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.N. Insulin-like growth factor-1 prevents miR-122 production in neighbouring cells to curtail its intercellular transfer to ensure proliferation of human hepatoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 7170–7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Poll, D.; Parekkadan, B.; Cho, C.H.; Berthiaume, F.; Nahmias, Y.; Tilles, A.W.; Yarmush, M.L. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived molecules directly modulate hepatocellular death and regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, P.; McDaniel, K.; Francis, H.; Kennedy, L.; Alpini, G.; Meng, F. Molecular mechanisms of stem cell therapy in alcoholic liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, J.; Wang, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, G.J.; Jung, Y. MicroRNA125b-mediated hedgehog signaling influences liver regeneration by chorionic plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.Y.; Lai, R.C.; Wong, W.; Dan, Y.Y.; Lim, S.K.; Ho, H.K. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote hepatic regeneration in drug-induced liver injury models. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nong, K.; Wang, W.; Niu, X.; Hu, B.; Ma, C.; Bai, Y.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Ai, K. Hepatoprotective effect of exosomes from human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yan, Y.; Wang, B.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, G.; Song, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Exosomes derived from miR-122-modified adipose tissue-derived mscs increase chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Ren, J.; Jiang, H.F.; Jia, J. Antitumor activities against hepatocellular carcinoma induced by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells pulsed with tumor-derived exosomes. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao 2008, 40, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, P.K.; Bliss, S.A.; Patel, S.A.; Taborga, M.; Dave, M.A.; Gregory, L.A.; Greco, S.J.; Bryan, M.; Patel, P.S.; Rameshwar, P. Gap junction-mediated import of microRNA from bone marrow stromal cells can elicit cell cycle quiescence in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Park, S.R.; Jung, B.K.; Jeon, Y.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, Y.G.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, C.W. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells suppress angiogenesis by down-regulating VEGF expression in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinney, D.G.; di Giuseppe, M.; Njah, J.; Sala, E.; Shiva, S.; St Croix, C.M.; Stolz, D.B.; Watkins, S.C.; Di, Y.P.; Leikauf, G.D.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle micrornas. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Miyaki, S.; Ishitobi, H.; Matsuyama, S.; Nakasa, T.; Kamei, N.; Akimoto, T.; Higashi, Y.; Ochi, M. Mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived exosomes accelerate skeletal muscle regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, B.; Wu, H.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, M.; Mao, F.; Yan, Y.; et al. Exosomes released by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against cisplatin-induced renal oxidative stress and apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Liu, N.; Lin, M.C.; Zheng, J. Positive feedback loop between cancer stem cells and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016, 379, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conigliaro, A.; Costa, V.; Lo Dico, A.; Saieva, L.; Buccheri, S.; Dieli, F.; Manno, M.; Raccosta, S.; Mancone, C.; Tripodi, M.; et al. CD90+ liver cancer cells modulate endothelial cell phenotype through the release of exosomes containing H19 lncRNA. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinado, H.; Aleckovic, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; Garcia-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through meat. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, L.A.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janas, T.; Janas, M.M.; Sapon, K. Mechanisms of RNA loading into exosomes. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianson, H.C.; Svensson, K.J.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Li, J.P.; Belting, M. Cancer cell exosomes depend on cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans for their internalization and functional activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17380–17385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, K.J.; Christianson, H.C.; Wittrup, A.; Bourseau-Guilmain, E.; Lindqvist, E.; Svensson, L.M.; Morgelin, M.; Belting, M. Exosome uptake depends on ERK1/2-heat shock protein 27 signaling and lipid raft-mediated endocytosis negatively regulated by caveolin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17713–17724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlert, C.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes in tumor microenvironment influence cancer progression and metastasis. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksvold, M.P.; Kullmann, A.; Forfang, L.; Kierulf, B.; Li, M.; Brech, A.; Vlassov, A.V.; Smeland, E.B.; Neurauter, A.; Pedersen, K.W. Expression of B-cell surface antigens in subpopulations of exosomes released from B-cell lymphoma cells. Clin. Ther. 2014, 36, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelbrunn, M.; Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gonzalez, S.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Gonzalez, M.A.; Bernad, A.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Unidirectional transfer of microRNA-loaded exosomes from T cells to antigen-presenting cells. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordat, I.; Decraene, C.; Silvestre, T.; Petermann, O.; Auffray, C.; Pietu, G.; Sordat, B. Complementary DNA arrays identify CD63 tetraspanin and α3 integrin chain as differentially expressed in low and high metastatic human colon carcinoma cells. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.K.; Liu, X.W.; Chirco, R.; Fridman, R.; Kim, H.R. Identification of CD63 as a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 interacting cell surface protein. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3934–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.L.; Qu, X.J.; Zhao, M.F.; Teng, Y.E.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.Z.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yang, X.H.; Liu, Y.P. Gastric cancer exosomes promote tumour cell proliferation through PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK activation. Dig. Liver Dis. 2009, 41, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Lasser, C.; Shelke, G.V.; Wang, J.; Radinger, M.; Lunavat, T.R.; Malmhall, C.; Lin, L.H.; Li, J.; Li, L.; et al. Mast cell exosomes promote lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation—Role of kit-stem cell factor signaling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2014, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Seubert, B.; Stahl, E.; Dietz, H.; Reuning, U.; Moreno-Leon, L.; Ilie, M.; Hofman, P.; Nagase, H.; Mari, B.; et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 induces a pro-tumourigenic increase of miR-210 in lung adenocarcinoma cells and their exosomes. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3640–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atay, S.; Banskota, S.; Crow, J.; Sethi, G.; Rink, L.; Godwin, A.K. Oncogenic kit-containing exosomes increase gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell invasion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toricelli, M.; Melo, F.H.; Peres, G.B.; Silva, D.C.; Jasiulionis, M.G. Timp1 interacts with beta-1 integrin and CD63 along melanoma genesis and confers anoikis resistance by activating PI3-K signaling pathway independently of AKT phosphorylation. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzai, N.; Lee, Y.; Youn, B.S.; Fukuda, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Mantel, C.; Akashi, M.; Broxmeyer, H.E. C-kit associated with the transmembrane 4 superfamily proteins constitutes a functionally distinct subunit in human hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 2002, 99, 4413–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumova, S.; Woods, A.; Couchman, J.R. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans on the cell surface: Versatile coordinators of cellular functions. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 32, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeck, E.S.; Iordanskaia, T.; Sevilla, S.; Ferrante, S.C.; Hubal, M.J.; Freishtat, R.J.; Nadler, E.P. Adipocyte exosomes induce transforming growth factor β pathway dysregulation in hepatocytes: A novel paradigm for obesity-related liver disease. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 192, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Jiang, B.; Chen, Q.; Yu, J. miR-146a functions as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer by targeting RAC1. Prostate 2014, 74, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Bachoo, R.; Zhang, C.L. MicroRNA-146a inhibits glioma development by targeting NOTCH1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 3584–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaumik, D.; Scott, G.K.; Schokrpur, S.; Patil, C.K.; Campisi, J.; Benz, C.C. Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses NF-κB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5643–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Vandenboom, T.G.; Wang, Z.; Kong, D.; Ali, S.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. miR-146a suppresses invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katakowski, M.; Buller, B.; Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Rogers, T.; Osobamiro, O.; Shu, W.; Jiang, F.; Chopp, M. Exosomes from marrow stromal cells expressing miR-146b inhibit glioma growth. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, K.; Inoue, K.; Fujiwara, A.; Hatakeyama, K.; Kanto, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Muramatsu, K.; Fukuda, Y.; Ogura, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; et al. Let-7 microRNA family is selectively secreted into the extracellular environment via exosomes in a metastatic gastric cancer cell line. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, G.M.; Common, J.E.; Gopal, F.E.; Srikanta, S.; Lakshman, K.; Lunny, D.P.; Lim, T.C.; Tanavde, V.; Lane, E.B.; Sampath, P. “See-saw” expression of microRNA-198 and FSTL1 from a single transcript in wound healing. Nature 2013, 495, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, G.; Li, P.; Chen, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Jiang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; et al. miR-198 targets shmt1 to inhibit cell proliferation and enhance cell apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 5193–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfimova, N.; Sievers, E.; Eischeid, H.; Kwiecinski, M.; Noetel, A.; Hunt, H.; Becker, D.; Frommolt, P.; Quasdorff, M.; Steffen, H.M.; et al. Control of mitogenic and motogenic pathways by miR-198, diminishing hepatoma cell growth and migration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Kong, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Qin, M.; Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Hong, J.; Chen, Y.X.; et al. miR-198 represses tumor growth and metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting fucosyl transferase 8. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnholt, H.; Drebber, U.; Schulze, F.; Wedemeyer, I.; Schirmacher, P.; Dienes, H.P.; Odenthal, M. MicroRNA gene expression profile of hepatitis c virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Q. The expression and clinical significance of circulating microRNA-21 in serum of five solid tumors. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; et al. A microrna expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappellesso, R.; Tinazzi, A.; Giurici, T.; Simonato, F.; Guzzardo, V.; Ventura, L.; Crescenzi, M.; Chiarelli, S.; Fassina, A. Programmed cell death 4 and microRNA 21 inverse expression is maintained in cells and exosomes from ovarian serous carcinoma effusions. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014, 122, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata-Kawata, H.; Izumiya, M.; Kurioka, D.; Honma, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Furuta, K.; Gunji, T.; Ohta, H.; Okamoto, H.; Sonoda, H.; et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, M.; Paone, A.; Calore, F.; Galli, R.; Croce, C.M. A new role for microRNAs, as ligands of toll-like receptors. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anadol, E.; Schierwagen, R.; Elfimova, N.; Tack, K.; Schwarze-Zander, C.; Eischeid, H.; Noetel, A.; Boesecke, C.; Jansen, C.; Dold, L.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as a marker for liver injury in human immunodeficiency virus patients. Hepatology 2015, 61, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfimova, N.; Schlattjan, M.; Sowa, J.P.; Dienes, H.P.; Canbay, A.; Odenthal, M. Circulating microRNAs: Promising candidates serving as novel biomarkers of acute hepatitis. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Tanahashi, T. Analysis of circulating microRNA by microarray in liver disease. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1024, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roderburg, C.; Luedde, T. Circulating microRNAs as markers of liver inflammation, fibrosis and cancer. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1434–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roderburg, C.; Urban, G.W.; Bettermann, K.; Vucur, M.; Zimmermann, H.; Schmidt, S.; Janssen, J.; Koppe, C.; Knolle, P.; Castoldi, M.; et al. Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebicka, J.; Anadol, E.; Elfimova, N.; Strack, I.; Roggendorf, M.; Viazov, S.; Wedemeyer, I.; Drebber, U.; Rockstroh, J.; Sauerbruch, T.; et al. Hepatic and serum levels of miR-122 after chronic HCV-induced fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietje, A.; Maron, K.N.; Wei, Y.; Feliciano, D.M. Cerebrospinal fluid extracellular vesicles undergo age dependent declines and contain known and novel non-coding RNAs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, G.Y.; Bang, J.Y.; Choi, A.J.; Yoon, J.; Lee, W.C.; Choi, S.; Yoon, S.; Kim, H.C.; Baek, J.H.; Park, H.S.; et al. Exosomal proteins in the aqueous humor as novel biomarkers in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, T.; Tomofuji, T.; Ekuni, D.; Maruyama, T.; Yoneda, T.; Kawabata, Y.; Mizuno, H.; Miyai, H.; Kunitomo, M.; Morita, M. MicroRNAs in salivary exosome as potential biomarkers of aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21294–21309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, S.; Suazo, C.; Boltansky, A.; Ursu, M.; Carvajal, D.; Innocenti, G.; Vukusich, A.; Hurtado, M.; Villanueva, S.; Carreno, J.E.; et al. Urinary exosomes as a source of kidney dysfunction biomarker in renal transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2013, 45, 3719–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Paine, M.S.; Brooks, A.M.; McCubrey, J.A.; Renegar, R.H.; Wang, R.; Terrian, D.M. Senescence-associated exosome release from human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7864–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Odenthal, M.; Fries, J.W.U. Exosomes as miRNA Carriers: Formation–Function–Future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122028
Yu X, Odenthal M, Fries JWU. Exosomes as miRNA Carriers: Formation–Function–Future. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(12):2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122028
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xiaojie, Margarete Odenthal, and Jochen W. U. Fries. 2016. "Exosomes as miRNA Carriers: Formation–Function–Future" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 12: 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122028
APA StyleYu, X., Odenthal, M., & Fries, J. W. U. (2016). Exosomes as miRNA Carriers: Formation–Function–Future. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(12), 2028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122028