Disease Resistance Gene Analogs (RGAs) in Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Species a | R-Gene | Accession ID | Domain b | Class | Chr | Disease c | Avr Gene | Pathogen c | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. aestivum (wheat) | Lr10 | AAQ01784 | CNL | NBS | 1A | Leaf rust | AvrLr10 | P. triticina | [23] |
| Lr1 | ABS29034 | CNL | NBS | 5D | Leaf rust | Avr1 | P. triticina | [24] | |
| Pm3b | AAQ96158 | CNL | NBS | 1A | Powdery mildew | AvrPm3b | B. graminis | [25] | |
| Sr33 | AGQ17390 | CNL | NBS | 1D | Stem rust | P. graminis | [26] | ||
| Sr35 | AGP75918 | CNL | NBS | 3A | Stem rust | P. graminis | [27] | ||
| Lr21 | AAP74647 | NL | NBS | 1D | Leaf rust | AvrLr21 | P. triticina | [28] | |
| Cre3 | AAC05834 | NL | NBS | 2D | Cereal cyst | H. avenae | [29] | ||
| Cre1 | AAM94164 | NL | NBS | 2B | Cereal cyst | H. avenae | [30] | ||
| Yr10 | AAG42168 | CNL | NBS | 1B | Stripe rust | P. striiformis | [31] | ||
| Stpk-V (Pm21) | AEF30547 | STK | Oth-R | 6V | Powdery mildew | B. graminis | [32] | ||
| Lr34 | ACN41354 | ABC transporter | Oth-R | 7D | Leaf rust, Powdery mildew, Stripe rust | P. triticina; P. striiformis; B. graminis | [33] | ||
| Yr36 | ACF33195 | Kinase-START | Oth-R | 6B | Stripe rust | P. striiformis | [34] | ||
| H. vulgare (barley) | Mla6 | CAC29241 | CNL | NBS | 1 | Powdery mildew | AvrMla6 | B. graminis | [35] |
| Mla1 | AAG37356 | CNL | NBS | 1 | Powdery mildew | AvrMla1 | B. graminis | [36] | |
| Mla13 | AAO16014 | CNL | NBS | 1 | Powdery mildew | AvrMla13 | B. graminis | [37] | |
| Rpg1 | AAM81980 | LRR-PK | RLK | 7 | Stem rust | Avr-Rpg1 | P. graminis | [38] | |
| Mlo | CAB06083 | TM | Oth-R | 4 | Powdery mildew | E. graminis | [39] | ||
| S. lycopersicum (tomato) | Prf | AAC49408 | CNL | NBS | 5 | Bacterial speck | AvrPto | P. syringae | [40] |
| Mi | AAC67238 | CNL | NBS | 6 | Root knot | M. javanica | [41] | ||
| I2 | AAB63274 | NL | NBS | 11 | Fusarium wilt | Avr1 | F. oxysporum | [42] | |
| Ph-3 | AIB02970 | CNL | NBS | 9 | Late blight | P. infestans | [43] | ||
| Sw-5 | AAG31013 | CNL | NBS | 9 | Tomato spotted wilt | TSWV | [44] | ||
| Tm-2 | AAQ10735 | CNL | NBS | 9 | Tobacco mosaic | TMV | [45] | ||
| Bs4 | AAR21295 | TNL | NBS | 5 | Bacterial spot | AvrBs4 | X. campestris | [46] | |
| Hero | CAD29729 | CNL | NBS | 4 | Potato cyst | G. rostochiensis | [47] | ||
| Cf-2 | 2207203A | LRR-TM | RLP | 6 | Leaf mold | Avr2 | C. fulvum | [48] | |
| Cf-4 | CAA05268 | LRR-TM | RLP | 1 | Leaf mold | Avr4 | C. fulvum | [49] | |
| Cf-5 | AAC78591 | LRR-TM | RLP | 6 | Leaf mold | Avr5 | C. fulvum | [50] | |
| Cf-9 | CAA05274 | LRR-TM | RLP | 1 | Leaf mold | Avr9 | C. fulvum | [51] | |
| Ve1,2 | AAK58681.2 | LRR-TM | RLP | 9 | Verticillium wilt | V. dahliae | [52] | ||
| Hcr9-4E | CAA05269 | LRR-TM | RLP | 1 | Leaf mold | Avr4E | C. fulvum | [49] | |
| Fen | 2115395A | STK | Oth-R | 5 | Bacterial speck | AvrPto | P. syringae | [53] | |
| Pto | A49332 | STK | Oth-R | 5 | Bacterial speck | AvrPto | P. syringae | [54] | |
| Pti1 | NP_001233803 | STK | Oth-R | 12 | Bacterial speck | P. syringae | [55] | ||
| S. tuberosum (potato) | Rx | CAB50786 | CNL | NBS | 12 | PVX | PVX | [56] | |
| RB | Q7XBQ9 | CNL | NBS | 8 | Late blight | Avr1, Ipio, Ipib | P.infestans | [57] | |
| Rx2 | CAB56299 | LZ-NL | NBS | 5 | PVX | PVX | [58] | ||
| R1 | AAL39063 | LZ-NL | NBS | 5 | Late blight | Avr1 | P. infestans | [59] | |
| L. sativa (lettuce) | Rgc2 (Dm3) | Q9ZSD1 | NL | NBS | Downy mildew | Avr3 | B. lactucae | [60] | |
| P. nigrum (black pepper) | Bs2 | AAF09256 | CNL | NBS | Bacterial spot | AvrBs2 | X. campestris | [61] | |
| O. sativa (rice) | Xa1 | BAA25068 | NL | NBS | 4 | Bacterial blight | AvrXoo | X. oryzae | [62] |
| Pib | BAA76282 | CNL | NBS | 2 | Blast | M. grisea | [63] | ||
| Pi-ta | AAK00132 | NL | NBS | 12 | Blast | Avr-Pita | M. grisea | [64] | |
| Pi36 | ABI64281 | CNL | NBS | 8 | Blast | Avr-Pi36 | M. grisea | [65] | |
| Pia | BAK39926 | CNL | NBS | 11 | Blast | AvrPia | M. oryzae | [66] | |
| Pi-Kh | AAY33493 | NL | NBS | 11 | Blast | Avr-Pik | M. oryzae | [67] | |
| Pi37 | ABI94578 | NL | NBS | 1 | Blast | M. grisea | [68] | ||
| Xa5 | A2XZI2 | NL | NBS | 5 | Bacterial blight | AvrXa5 | X. oryzae | [69] | |
| Xa13 | ABD78944 | SET | Oth-R | 8 | Bacterial blight | AvrXa13 | X. oryzae | [70] | |
| Pi54 | CCD33085 | CNL | NBS | Blast | AvrPi54 | M. oryzae | [71] | ||
| Pi9 | ABB88855 | CNL | NBS | 6 | Blast | AvrPi9 | M. grisea | [72] | |
| Piz-t/Pi2 | ABC73398 | CNL | NBS | 6 | Blast | AvrPiz-t | M. grisea | [73] | |
| Rpr1 | BAA75812 | CNL | NBS | 11 | Blast | M. grisea | [74] | ||
| Pid3 | ACN62386 | CNL | NBS | 6 | Blast | M. grisea | [75] | ||
| Xa21 | AAC49123 | LRR-STK | RLK | 11 | Bacterial blight | AvrXa21 | X. oryzae | [76] | |
| Xa3/Xa26 | ABD36512 | LRR-STK | RLK | 11 | Bacterial blight | X. oryzae | [77] | ||
| CEBiP | BAE95828 | RLK | 3 | [78] | |||||
| Xa10 | AGE45112 | Oth-R | 11 | Bacterial blight | AvrXa10 | X. oryzae | [79] | ||
| Xa25 | AGS56390 | TM | Oth-R | 12 | Bacterial blight | X. oryzae | [80] | ||
| Xa27 | AEW90324 | LRR-TM | RLP | 6 | Bacterial blight | AvrXa27 | X. oryzae | [81] | |
| Pi-d2 | ACR15163 | B-lectin, STK | RLK | 6 | Blast | M. grisea | [82] | ||
| Z. mays (maize) | Rp1-D | AAD47197 | NL | NBS | 10 | Rust | P. sorghi | [83] | |
| Hm1 | Q41867 | 1 | Corn leaf blight | C. carbonum | [84] | ||||
| A. thaliana (Arabidopsis) | RPM1 | CAA61131 | CNL | NBS | 3 | Downy mildew | AvrB, AvrRpm1 | P. syringae | [85] |
| RPS2 | AAA21874 | NL | NBS | 4 | Downy mildew | AvrRpt2 | P. syringae | [86] | |
| RPP8/HRT | AAC83165 | CNL | NBS | 5 | Downy mildew | AvrRPP8 | P. parasitica | [87] | |
| RPP13 | AAF42832 | CNL | NBS | 3 | Downy mildew | ATR13 | P. parasitica | [88] | |
| RCY1 | BAC67706 | CNL | NBS | 5 | Mosaic type | CMV | [89] | ||
| RPP1 | AAC72977 | TNL | NBS | 3 | Downy mildew | ATR1 | P. parasitica | [90] | |
| RPP4 | AAM18462 | TNL | NBS | 4 | Downy mildew | P. parasitica | [91] | ||
| RPS4 | CAB50708 | TNL | NBS | 5 | Powdery mildew | AvrRps4 | P. syringae | [92] | |
| RPP5 | AAF08790 | TNL | NBS | 4 | Downy mildew | AvrRp5 | P. parasitica | [93] | |
| RPS5 | AAC26126 | NL | NBS | 1 | Downy mildew | AvrRphB | P. syringae | [94] | |
| RRS1 | ADM88042 | WRKY-TNL | NBS | 5 | Bacterial wilt | AvrRRS1 | R. solanacearum | [95] | |
| RPP27 | CAE51864 | LRR-TM | RLP | 1 | Downy mildew | P. parasitica | [96] | ||
| RFO1 | AAY86486 | LRR-STK | RLK | 1 | Fusarium wilt | F. oxysporum | [97] | ||
| PBS1 | AAG38109 | STK | Oth-R | 5 | AvrPphB | P. syringae | [98] | ||
| FLS2 | AED95370 | LRR-STK | RLK | 5 | Powdery mildew | AvrPto, AvrPtoB | P. syringae | [99] | |
| BAK1 | AT4G33430 | LRR-STK | RLK | 4 | AvrPto, AvrPtoB | P. syringae | [100] | ||
| NDR1 | AAB95208 | TM | Oth-R | 3 | AvrB, AvrRpt2 | P. syringae; P. parasitica | [101] | ||
| RPW8 | AAK09267 | RPW8 | Oth-R | 3 | Powdery mildew | E. cruciferarum | [102] | ||
| L. usitatissimum (flax) d | L6 | AAA91022 | TNL | NBS | 5 | Rust | AvrL6 | M. lini | [103] |
| L, L1-L11 | AAD25974 | TNL | NBS | 5 | Rust | AvrBs3 | M. lini | [104] | |
| M | AAB47618 | TNL | NBS | 8 | Rust | AvrM | M. lini | [105] | |
| P , P1-4 | AAK28806 | TNL | NBS | 14 | Rust | M. lini | [106] | ||
| B. vulgaris (sugar beet) | Hs1pro-1 | AAB48305 | LRR-TM | RLP | 1 | Beet cyst | H. schachtii | [107] | |
| N. tabacum (tobacco) | N | AAA50763 | TNL | NBS | Tobacco mosaic | TMV | [108] |
| Species a | Genome Size (Mb) b | Total Annotated Genes b | Total RGAs (%) c | NBS Coding Genes d | PPR e | RLK f | RLP g | Other h | Identification Method Used i | Reference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNL | TNL | CN | NL | TN | N | Total | ||||||||||
| Dicots | ||||||||||||||||
| A. thaliana (Arabidopsis) | 125 | 25,498 | 5.27 | 51 | 79 | 8 | 20 | 17 | 26 | 201 | 441 | 600 | 56 | 46 | H, P, B | [109–113] |
| A. lyrata (lyrata) | 207 | 32,670 | 0.56 | 21 | 103 | 17 | 14 | 20 | 10 | 185 | H, B | [114] | ||||
| P. trichocarpa (black cottonwood) | 485 | 45,555 | 3.18 | 119 | 64 | 19 | 83 | 13 | 46 | 344 | 600 | 379 | 127 | MEME, CO, Paircoil2, MC | [111,115–117] | |
| V. vinifera (grape) | 475 | 30,434 | 3.81 | 203 | 97 | 26 | 12 | 14 | 0 | 352 | 600 | 210 | H, B, MEME | [111,118] | ||
| L. usitatissimum (flax) | 373 | 43,484 | 0.34 | 31 | 57 | 10 | 5 | 22 | 7 | 132 | 16 | MEME/MAST | [119] | |||
| S. lycopersicum (tomato) | 900 | 34,727 | 0.84 | 118 | 18 | 19 | 43 | 5 | 49 | 252 | 16 | 13 | 13 | H, B | [120,121] | |
| C. papaya (papaya) | 372 | 28,629 | 0.18 | 4 | 6 | 44 | 54 | TBN, MEME, CW, MC, H | [122] | |||||||
| C. sativus (cucumber) | 367 | 26,682 | 0.26 | 25 | 19 | 1 | 17 | 5 | 3 | 70 | H, CO, ME, CX, SMART, P, B | [123] | ||||
| S. tuberosum (potato) | 844 | 39,031 | 1.47 | 65 | 37 | 24 | 184 | 12 | 113 | 435 | 142 | H, B | [124] | |||
| M. truncatula (Medicago) | 454 | 62,388 | 1.20 | 152 | 118 | 25 | 0 | 38 | 328 | 661 | 92 | B, H | [111] | |||
| G. raimondii (cotton) | 880 | 40,976 | 1.19 | 35 | 41 | 18 | 96 | 9 | 31 | 230 | 60 | 144 | 56 | B, CO, SMART, MC, CW, IPS, ME5, | [125,126] | |
| B. rapa, (chinese cabbage) | 485 | 41,174 | 0.60 | 19 | 93 | 15 | 27 | 23 | 29 | 206 | 42 | B, H | [111] | |||
| B. oleracea (cabbage) | 630 | 45,758 | 0.52 | 6 | 40 | 5 | 24 | 29 | 53 | 157 | 82 | B, H | [111] | |||
| F. vesca (strawberry) | 240 | 34,809 | 0.27 | 61 | 16 | 8 | 1 | 86 | 8 | B, MU, ME, MEME | [127] | |||||
| M. x domestica (apple) | 742 | 57,386 | 1.86 | 218 | 161 | 54 | 276 | 69 | 182 | 960 | 110 | H, B, CW, MEME | [17] | |||
| L. japonicus (lotus) | 472 | 19,848 | 0.42 | 9 | 8 | 19 | 3 | 16 | 29 | 84 | BP, CO, P, MEME | [128] | ||||
| T. cacao (cocoa) | 430 | 28,798 | 1.09 | 82 | 8 | 46 | 104 | 4 | 53 | 297 | 17 | B, H | [111] | |||
| P. patens (moss) | 510 | 35,938 | 0.46 | 9 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 20 | 103 | 45 | B, CO, MU, ME | [129,130] | ||
| Average | 500 | 37,433 | 1 | 69 | 56 | 19 | 55 | 18 | 56 | 263 | 436 | 264 | 71 | 72 | ||
| Monocots | ||||||||||||||||
| O. sativa (rice) | 420 | 59,855 | 4.22 | 159 | 0 | 7 | 40 | 3 | 45 | 254 | 477 | 1429 | 90 | 281 | H, B, MEME, P | [110,130–133] |
| T. aestivum (wheat) | 17,000 | 94,000 | 2.37 | 98 | 0 | 555 | 318 | 971 | 1266 | H, B, MEME | [134] | |||||
| Z. mayes (maize) | 2300 | 32,540 | 0.90 | 58 | 0 | 21 | 31 | 0 | 69 | 179 | 113 | 2 | P, H, B, CO | [135,136] | ||
| S. bicolor (sorghum) | 739 | 34,496 | 1.29 | 36 | 0 | 99 | 133 | 0 | 64 | 332 | 114 | P, H, B, CO, ME, CW | [137,138] | |||
| H. vulgare (barley) | 5100 | 30,400 | 1.38 | 101 | 51 | 145 | 34 | 331 | 89 | [139,140] | ||||||
| B. distachyon (Brachypodium) | 272 | 25,532 | 1.23 | 133 | 0 | 28 | 87 | 0 | 34 | 282 | 34 | P, H, B, CO, CW | [140,141] | |||
| T. urartu (Red wild einkorn) | 4940 | 34,879 | 1.63 | 235 | 0 | 44 | 218 | 38 | 535 | 35 | H | [140,142] | ||||
| A. tauschii (Tausch’s goatgrass) | 4360 | 43,150 | 1.94 | 296 | 0 | 63 | 288 | 81 | 728 | 112 | H | [140,143] | ||||
| Average | 4391 | 44,357 | 2 | 140 | 0 | 39 | 187 | 1 | 85 | 452 | 477 | 771 | 90 | 242 | ||
2. Structure and Functional Mechanisms of Resistance Gene Analogs (RGA)
2.1. Nucleotide Binding Site Leucine Rich Repeat (NBS-LRR) Family
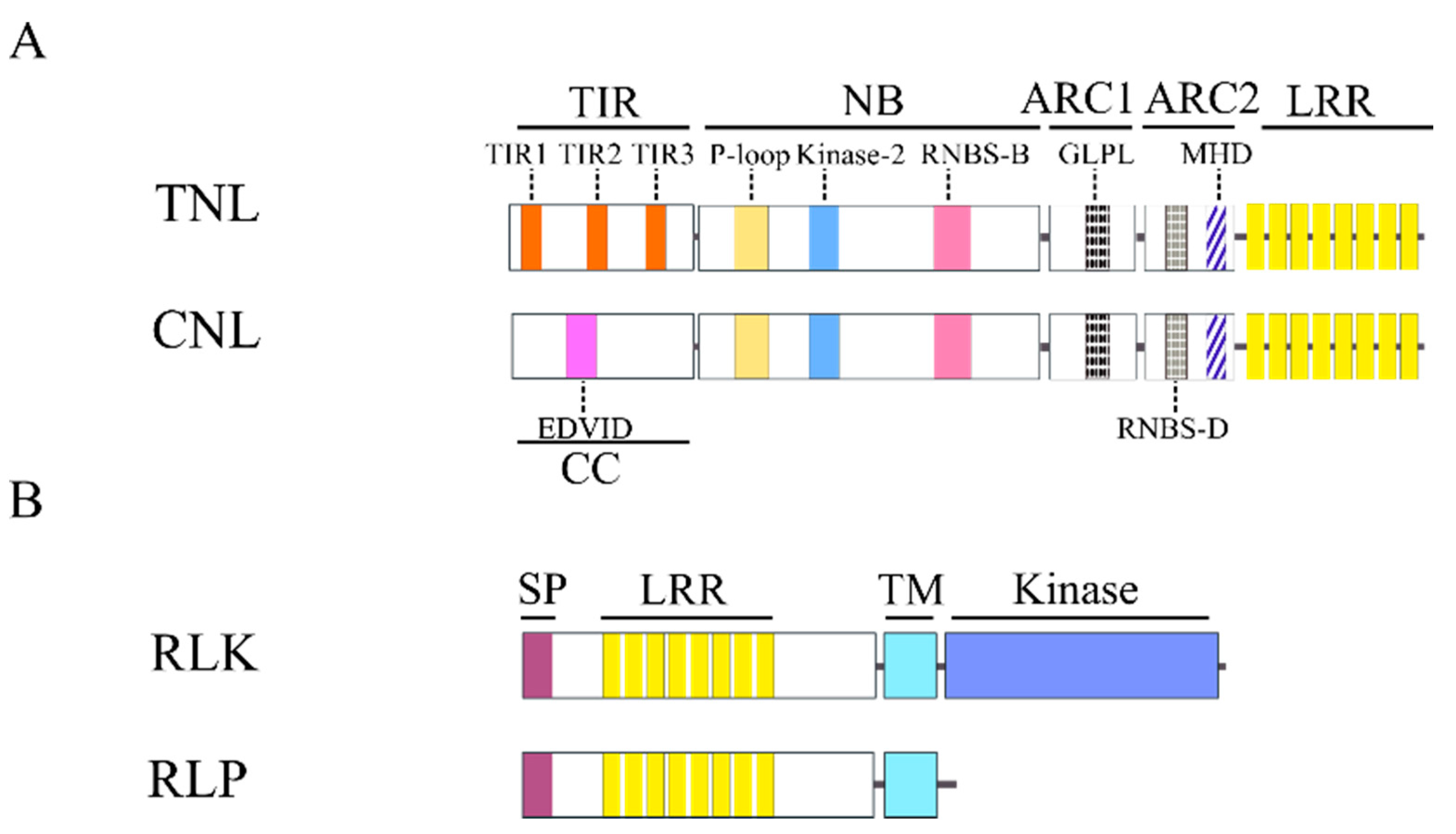
2.2. Receptor Like Kinase (RLK) and Receptor Like Protein (RLP) Families
2.2.1. RLK Family
2.2.2. RLP Family
2.3. Oth-R-Genes
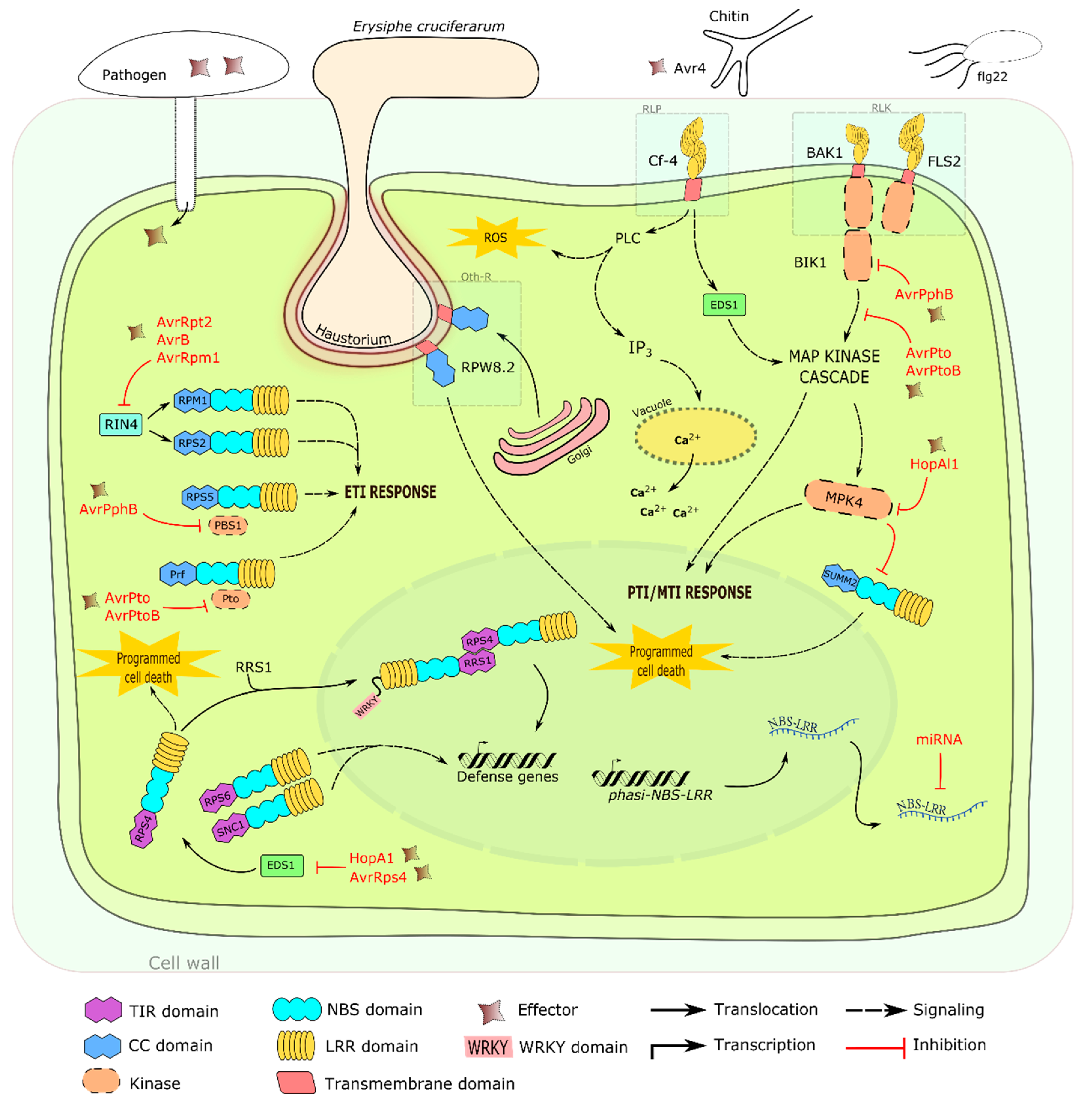
3. Other Defense Related Mechanisms
| Species | R-Gene | Accession ID | Domain a | Chr | Disease | Avr | Pathogen b | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. vulgare (barley) | Rar1 | AAF18432 | CHORD | 2 | Powdery mildew | B. graminis | [217] | |
| S. lycopersicum (tomato) | Asc | AAF67518 | TLC | 3 | Black mold rot; Black shoulder | A. alternate | [218] | |
| O. sativa (rice) | Rf1 | BAC77666 | PPR | 10 | [214] | |||
| LYP4/6 | TM | X. oryzae; M. oryzae | [219] | |||||
| Z. mays (maize) | Rf2 | AAC49371 | PPR | 9 | [213] | |||
| A. thaliana (Arabidopsis) | RPF2 | NP_176454 | PPR | 1 | [211] | |||
| RPF3 | NP_176481 | PPR | 1 | [212] | ||||
| Rtm1 | AT1G05760 | Jacalin like | 1 | Tobacco etch | TEV | [220] | ||
| Rwm1 | AEE33357 | PGK | 1 | Mosaic type | WMV | [221] | ||
| EDS1 | AAD20950 | Lipase-like | 3 | AvrRps4 | P. syringae | [222] | ||
| NPR1 | AAC49611 | Ankyrin | 1 | P. syringae | [223] |
4. Bioinformatics Approaches for RGA Identification and Characterization
| Software | Latest Version | Input Type a | Required Database | Description | Parallel Support b | URL c | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMMER | 3.1b2 | D/P | HMM model | Protein or DNA sequence homolog search toolkits using profile hidden Markov models and featured by remote homolog identification. The latest version is as fast as BLAST thanks to the underlying mathematical models. | HT/MPI | hmmer.janelia.org | [236] |
| MEME | 4.10 | D/P | Discover novel and ungapped motifs from nucleotide or protein sequences without well trained dataset samples. | MPI | meme-suite.org | [237] | |
| mCUDA-MEME | 3.0.15 | D/P | An ultrafast scalable motif discovery program running on graphics processing unit (GPU). The algorithm is based on MEME using a hybrid combination of CUDA, MPI and OpenMPI parallel programming models. | CUDA/MPI | bit.ly/18X8LmA | [238] | |
| BLAST+ | 2.30 | D/P | BLAST databases, like nr or nt database | Classical similarity search toolkits for bioinformatics data mining. The latest version significantly improves the speed on CPU and efficiency on RAM for long queries. | HT | blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | [239] |
| pfam_scan.pl | 1.0 | P | Pfam-A HMM model | A Perl script for PFAM database search, which invokes “hmmscan” in the HMMER toolkit package to search known HMM models. | bit.ly/1M41KRu | ||
| InterproScan | 5.9 | P | PFAM, SMART, PANTHER, PROSITE, Superfamily, etc. | A tool that combines different protein signature recognition methods native to the InterPro member databases into one resource with lookup of corresponding InterPro and GO annotations. | HT | www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro | [240] |
| Phobius | 1.01 | P | HMM model | A HMM based tool for transmembrane (TM) topology and signal peptides (SP) prediction from proteins. A pre-training HMM model has been embedded in the tool. | phobius.sbc.su.se | [241] | |
| TMHMM | 2.0 | P | HMM model | A HMM based tool with similar functions to Phobius. | www.cbs.dtu.dk/services | [242] | |
| nCOILS | 2.2 | P | Scoring matrix | A program to detect CC domains by comparing and scoring protein sequences with a known coiled-coils database with the MTK or MTIDK calculation matrix, which reports a probability that the sequence adopts a coiled-coil conformation. | embnet.vital-it.ch | [243] |
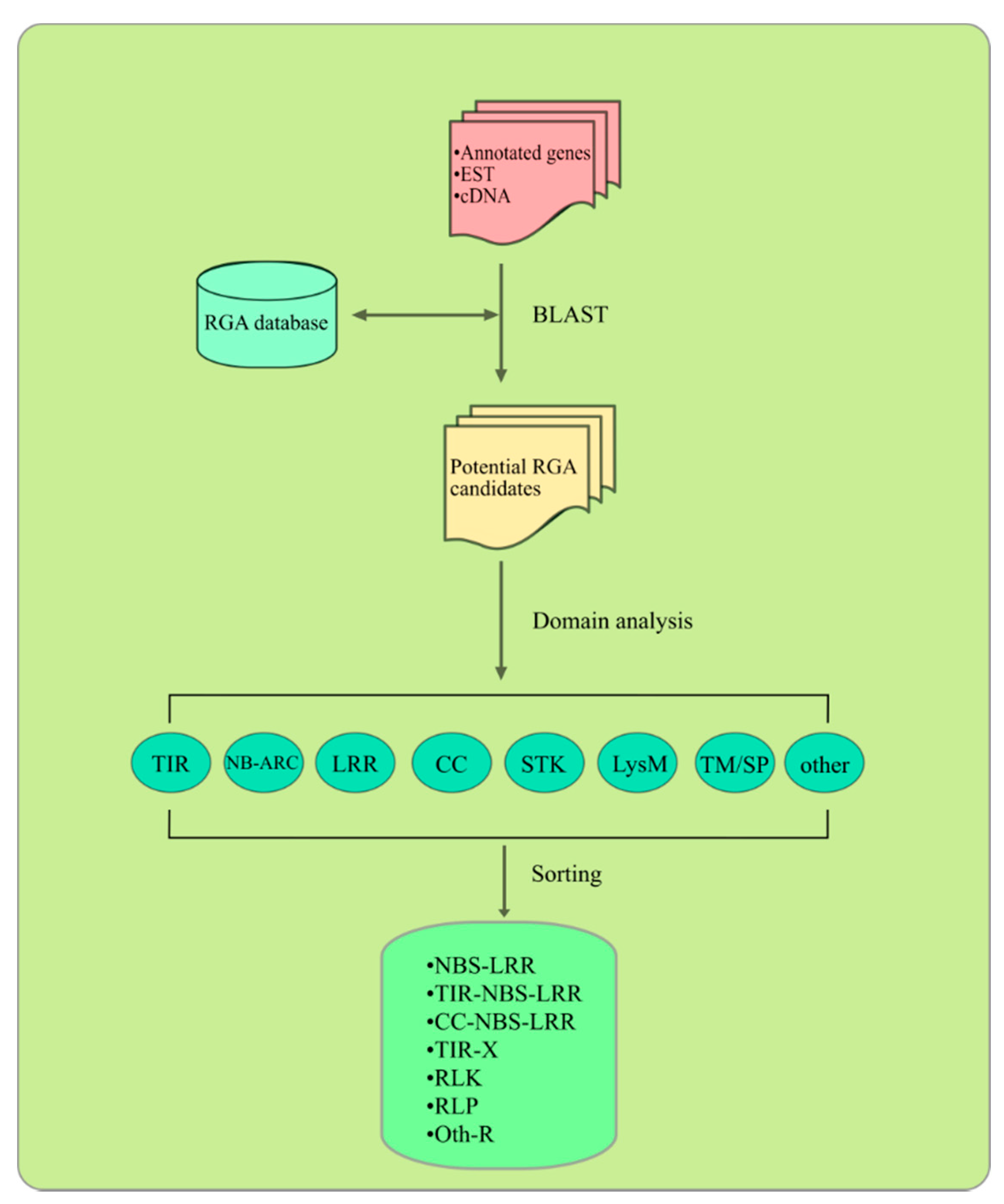
5. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of RGAs

6. Genome Organization of RGAs
7. Applications of RGAs
7.1. RGAs Are R-Gene Candidates for Disease Resistance
7.2. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) with Mapped RGAs Helps Co-Localization of QTL to Resistance Genes
7.3. RGA Mapping in Plants with Limited Genome Information
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grant, M.R.; McDowell, J.M.; Sharpe, A.G.; de Torres Zabala, M.; Lydiate, D.J.; Dangl, J.L. Independent deletions of a pathogen-resistance gene in Brassica and Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15843–15848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buerstmayr, H.; Ban, T.; Anderson, J.A. QTL mapping and marker-assisted selection for fusarium head blight resistance in wheat: A review. Plant Breed. 2009, 128, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, J.F.; Olfert, O.; Mukerji, M.K. Extraction precision of sieving and brine floatation for removal of wheat midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae), cocoons and larvae from soil. J. Econ. Entomol. 1986, 80, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacquard, S.; Kracher, B.; Maekawa, T.; Vernaldi, S.; Schulze-Lefert, P.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E. Mosaic genome structure of the barley powdery mildew pathogen and conservation of transcriptional programs in divergent hosts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2219–E2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooker, A.L. The genetics and expression of resistance in plants to rusts of the genus Puccinia. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1967, 5, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, M.; Foolad, M.R.; Nowakowska, M.; Kozik, E.U. Potato and tomato late blight caused by Phytophthora infestans: An overview of pathology and resistance breeding. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, G.M. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato: The right pathogen, of the right plant, at the right time. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2000, 1, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdon, J.J.; Barrett, L.G.; Rebetzke, G.; Thrall, P.H. Guiding deployment of resistance in cereals using evolutionary principles. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulbert, S.H. Structure and evolution of the rp1 complex conferring rust resistance in maize. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1997, 35, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Biezen, E.A.; Jones, J.D. Plant disease-resistance proteins and the gene-for-gene concept. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobe, B.; Deisenhofer, J. The leucine-rich repeat: A versatile binding motif. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994, 19, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, R.A.; Wellings, C.R.; Park, R.F. Wheat Rusts: An Atlas of Resistance Genes; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 1–204. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; McAdams, S.A.; Bryan, G.T.; Hershey, H.P.; Valent, B. Direct interaction of resistance gene and avirulence gene products confers rice blast resistance. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4004–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, P.N.; Lawrence, G.J.; Catanzariti, A.M.; Teh, T.; Wang, C.I.; Ayliffe, M.A.; Kobe, B.; Ellis, J.G. Direct protein interaction underlies gene-for-gene specificity and coevolution of the flax resistance genes and flax rust avirulence genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8888–8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, J.M.; Woffenden, B.J. Plant disease resistance genes: Recent insights and potential applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameline-Torregrosa, C.; Wang, B.B.; O’Bleness, M.S.; Deshpande, S.; Zhu, H.; Roe, B.; Young, N.D.; Cannon, S.B. Identification and characterization of nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat genes in the model plant Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, P.; Kumar, G.; Acharya, V.; Singh, A.K. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of NBS-encoding genes in Malus x domestica and expansion of NBS genes family in Rosaceae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilbirligi, M.; Gill, K.S. Identification and analysis of expressed resistance gene sequences in wheat. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 53, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordberg, H.; Cantor, M.; Dusheyko, S.; Hua, S.; Poliakov, A.; Shabalov, I.; Smirnova, T.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Dubchak, I. The genome portal of the department of energy joint genome institute: 2014 updates. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D26–D31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodstein, D.M.; Shu, S.; Howson, R.; Neupane, R.; Hayes, R.D.; Fazo, J.; Mitros, T.; Dirks, W.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; et al. Phytozome: A comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1178–D1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, M.K.; Stein, J.; Naithani, S.; Wei, S.; Dharmawardhana, P.; Kumari, S.; Amarasinghe, V.; Youens-Clark, K.; Thomason, J.; Preece, J.; et al. Gramene 2013: Comparative plant genomics resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D1193–D1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Dai, L.; Wang, G. Recent progress in elucidating the structure, function and evolution of disease resistance genes in plants. J. Genet. Genom. 2007, 34, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuillet, C.; Travella, S.; Stein, N.; Albar, L.; Nublat, A.; Keller, B. Map-based isolation of the leaf rust disease resistance gene Lr10 from the hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15253–15258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutier, S.; McCallum, B.D.; Loutre, C.; Banks, T.W.; Wicker, T.; Feuillet, C.; Keller, B.; Jordan, M.C. Leaf rust resistance gene Lr1, isolated from bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is a member of the large psr567 gene family. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahiaoui, N.; Srichumpa, P.; Dudler, R.; Keller, B. Genome analysis at different ploidy levels allows cloning of the powdery mildew resistance gene Pm3b from hexaploid wheat. Plant J. 2004, 37, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periyannan, S.; Moore, J.; Ayliffe, M.; Bansal, U.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Deal, K.; Luo, M.; Kong, X.; Bariana, H.; et al. The gene Sr33, an ortholog of barley Mla genes, encodes resistance to wheat stem rust race Ug99. Science 2013, 341, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saintenac, C.; Zhang, W.; Salcedo, A.; Rouse, M.N.; Trick, H.N.; Akhunov, E.; Dubcovsky, J. Identification of wheat gene Sr35 that confers resistance to Ug99 stem rust race group. Science 2013, 341, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Brooks, S.A.; Li, W.; Fellers, J.P.; Trick, H.N.; Gill, B.S. Map-based cloning of leaf rust resistance gene Lr21 from the large and polyploid genome of bread wheat. Genetics 2003, 164, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lagudah, E.S.; Moullet, O.; Appels, R. Map-based cloning of a gene sequence encoding a nucleotide-binding domain and a leucine-rich region at the Cre3 nematode resistance locus of wheat. Genome 1997, 40, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Majnik, J.; Ogbonnaya, F.C.; Moullet, O.; Lagudah, E.S. The cre1 and cre3 nematode resistance genes are located at homeologous loci in the wheat genome. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Frick, M.; Huel, R.; Nykiforuk, C.L.; Wang, X.; Gaudet, D.A.; Eudes, F.; Conner, R.L.; Kuzyk, A.; Chen, Q.; et al. The stripe rust resistance gene Yr10 encodes an evolutionary-conserved and unique CC-NBS-LRR sequence in wheat. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1740–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, A.; Xing, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Qian, C.; Ni, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D.; et al. Serine/threonine kinase gene Stpk-V, a key member of powdery mildew resistance gene Pm21, confers powdery mildew resistance in wheat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7727–7732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krattinger, S.G.; Lagudah, E.S.; Spielmeyer, W.; Singh, R.P.; Huerta-Espino, J.; McFadden, H.; Bossolini, E.; Selter, L.L.; Keller, B. A putative ABC transporter confers durable resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in wheat. Science 2009, 323, 1360–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Uauy, C.; Distelfeld, A.; Blechl, A.; Epstein, L.; Chen, X.; Sela, H.; Fahima, T.; Dubcovsky, J. A kinase-START gene confers temperature-dependent resistance to wheat stripe rust. Science 2009, 323, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halterman, D.; Zhou, F.; Wei, F.; Wise, R.P.; Schulze-Lefert, P. The MLA6 coiled-coil, NBS-LRR protein confers AvrMla6-dependent resistance specificity to Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei in barley and wheat. Plant J. 2001, 25, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Kurth, J.; Wei, F.; Elliott, C.; Vale, G.; Yahiaoui, N.; Keller, B.; Somerville, S.; Wise, R.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Cell-autonomous expression of barley Mla1 confers race-specific resistance to the powdery mildew fungus via a Rar1-independent signaling pathway. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halterman, D.A.; Wei, F.; Wise, R.P. Powdery mildew-induced Mla mRNAs are alternatively spliced and contain multiple upstream open reading frames. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brueggeman, R.; Rostoks, N.; Kudrna, D.; Kilian, A.; Han, F.; Chen, J.; Druka, A.; Steffenson, B.; Kleinhofs, A. The barley stem rust-resistance gene Rpg1 is a novel disease-resistance gene with homology to receptor kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9328–9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschges, R.; Hollricher, K.; Panstruga, R.; Simons, G.; Wolter, M.; Frijters, A.; van Daelen, R.; van der Lee, T.; Diergaarde, P.; Groenendijk, J.; et al. The barley Mlo gene: A novel control element of plant pathogen resistance. Cell 1997, 88, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmeron, J.M.; Oldroyd, G.E.; Rommens, C.M.; Scofield, S.R.; Kim, H.S.; Lavelle, D.T.; Dahlbeck, D.; Staskawicz, B.J. Tomato Prf is a member of the leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes and lies embedded within the Pto kinase gene cluster. Cell 1996, 86, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, S.B.; Bodeau, J.; Yaghoobi, J.; Kaloshian, I.; Zabel, P.; Williamson, V.M. The root knot nematode resistance gene Mi from tomato is a member of the leucine zipper, nucleotide binding, leucine-rich repeat family of plant genes. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ori, N.; Eshed, Y.; Paran, I.; Presting, G.; Aviv, D.; Tanksley, S.; Zamir, D.; Fluhr, R. The I2C family from the wilt disease resistance locus I2 belongs to the nucleotide binding, leucine-rich repeat superfamily of plant resistance genes. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Vossen, J.; Li, G.; Li, T.; Zheng, Z.; Gao, J.; Guo, Y.; Visser, R.G.; et al. The Ph-3 gene from Solanum pimpinellifolium encodes CC-NBS-LRR protein conferring resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brommonschenkel, S.H.; Tanksley, S.D. Map-based cloning of the tomato genomic region that spans the Sw-5 tospovirus resistance gene in tomato. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1997, 256, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanfermeijer, F.C.; Dijkhuis, J.; Sturre, M.J.; de Haan, P.; Hille, J. Cloning and characterization of the durable tomato mosaic virus resistance gene Tm-2(2) from Lycopersicon esculentum. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 52, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schornack, S.; Ballvora, A.; Gurlebeck, D.; Peart, J.; Baulcombe, D.; Ganal, M.; Baker, B.; Bonas, U.; Lahaye, T. The tomato resistance protein Bs4 is a predicted non-nuclear TIR-NB-LRR protein that mediates defense responses to severely truncated derivatives of AvrBs4 and overexpressed AvrBs3. Plant J. 2004, 37, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, K.; Kumar, A.; Kriseleit, D.; Kloos, D.U.; Phillips, M.S.; Ganal, M.W. The broad-spectrum potato cyst nematode resistance gene Hero from tomato is the only member of a large gene family of NBS-LRR genes with an unusual amino acid repeat in the LRR region. Plant J. 2002, 31, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, M.S.; Jones, D.A.; Keddie, J.S.; Thomas, C.M.; Harrison, K.; Jones, J.D. The tomato Cf-2 disease resistance locus comprises two functional genes encoding leucine-rich repeat proteins. Cell 1996, 84, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parniske, M.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Golstein, C.; Thomas, C.M.; Jones, D.A.; Harrison, K.; Wulff, B.B.; Jones, J.D. Novel disease resistance specificities result from sequence exchange between tandemly repeated genes at the Cf-4/9 locus of tomato. Cell 1997, 91, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.S.; Hatzixanthis, K.; Jones, D.A.; Harrison, K.; Jones, J.D. The tomato Cf-5 disease resistance gene and six homologs show pronounced allelic variation in leucine-rich repeat copy number. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.A.; Thomas, C.M.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Balint-Kurti, P.J.; Jones, J.D. Isolation of the tomato Cf-9 gene for resistance to Cladosporium fulvum by transposon tagging. Science 1994, 266, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawchuk, L.M.; Hachey, J.; Lynch, D.R.; Kulcsar, F.; van Rooijen, G.; Waterer, D.R.; Robertson, A.; Kokko, E.; Byers, R.; Howard, R.J.; et al. Tomato Ve disease resistance genes encode cell surface-like receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6511–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.B.; Frary, A.; Wu, T.; Brommonschenkel, S.; Chunwongse, J.; Earle, E.D.; Tanksley, S.D. A member of the tomato Pto gene family confers sensitivity to fenthion resulting in rapid cell death. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.B.; Brommonschenkel, S.H.; Chunwongse, J.; Frary, A.; Ganal, M.W.; Spivey, R.; Wu, T.; Earle, E.D.; Tanksley, S.D. Map-based cloning of a protein kinase gene conferring disease resistance in tomato. Science 1993, 262, 1432–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Loh, Y.T.; Bressan, R.A.; Martin, G.B. The tomato gene Pti1 encodes a serine/threonine kinase that is phosphorylated by Pto and is involved in the hypersensitive response. Cell 1995, 83, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendahmane, A.; Kanyuka, K.; Baulcombe, D.C. The Rx gene from potato controls separate virus resistance and cell death responses. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Bradeen, J.M.; Naess, S.K.; Raasch, J.A.; Wielgus, S.M.; Haberlach, G.T.; Kuang, H.; Liu, J.; Austin-Phillips, S.; Buell, C.R.; et al. Gene RB cloned from Solanum bulbocastanum confers broad spectrum resistance to potato late blight. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9128–9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendahmane, A.; Querci, M.; Kanyuka, K.; Baulcombe, D.C. Agrobacterium transient expression system as a tool for the isolation of disease resistance genes: Application to the Rx2 locus in potato. Plant J. 2000, 21, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballvora, A.; Ercolano, M.R.; Weiss, J.; Meksem, K.; Bormann, C.A.; Oberhagemann, P.; Salamini, F.; Gebhardt, C. The R1 gene for potato resistance to late blight (Phytophthora infestans) belongs to the leucine zipper/NBS/LRR class of plant resistance genes. Plant J. 2002, 30, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, B.C.; Shen, K.A.; Rohani, P.; Gaut, B.S.; Michelmore, R.W. Receptor-like genes in the major resistance locus of lettuce are subject to divergent selection. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1833–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, T.H.; Dahlbeck, D.; Clark, E.T.; Gajiwala, P.; Pasion, R.; Whalen, M.C.; Staskawicz, B.J.; Stall, R.E. Expression of the Bs2 pepper gene confers resistance to bacterial spot disease in tomato. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14153–14158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, S.; Yamanouchi, U.; Katayose, Y.; Toki, S.; Wang, Z.X.; Kono, I.; Kurata, N.; Yano, M.; Iwata, N.; Sasaki, T. Expression of Xa1, a bacterial blight-resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.X.; Yano, M.; Yamanouchi, U.; Iwamoto, M.; Monna, L.; Hayasaka, H.; Katayose, Y.; Sasaki, T. The Pib gene for rice blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Plant J. 1999, 19, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, G.T.; Wu, K.S.; Farrall, L.; Jia, Y.; Hershey, H.P.; McAdams, S.A.; Donaldson, G.K.; Faulk, K.N.; Tarchini, R.; Valent, B. tA single amino acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 2033–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lin, F.; Wang, L.; Pan, Q. The in silico map-based cloning of Pi36, a rice coiled-coil nucleotide-binding site leucine-rich repeat gene that confers race-specific resistance to the blast fungus. Genetics 2007, 176, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, Y.; Kanzaki, H.; Abe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Tamiru, M.; Saitoh, H.; Fujibe, T.; Matsumura, H.; Shenton, M.; Galam, D.C.; et al. A multifaceted genomics approach allows the isolation of the rice Pia-blast resistance gene consisting of two adjacent NBS-LRR protein genes. Plant J. 2011, 66, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, T.R.; Madhav, M.S.; Singh, B.K.; Shanker, P.; Jana, T.K.; Dalal, V.; Pandit, A.; Singh, A.; Gaikwad, K.; Upreti, H.C.; et al. High-resolution mapping, cloning and molecular characterization of the Pi-kh gene of rice, which confers resistance to Magnaporthe grisea. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2005, 274, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Chen, S.; Que, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Pan, Q. The blast resistance gene Pi37 encodes a nucleotide binding site leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a resistance gene cluster on rice chromosome 1. Genetics 2007, 177, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, A.S.; McCouch, S.R. The rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5 encodes a novel form of disease resistance. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Yuan, M.; Yao, J.; Ge, X.; Yuan, B.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Fu, B.; Li, Z.; Bennetzen, J.L.; et al. Promoter mutations of an essential gene for pollen development result in disease resistance in rice. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Soubam, D.; Singh, P.K.; Thakur, S.; Singh, N.K.; Sharma, T.R. A novel blast resistance gene, Pi54rh cloned from wild species of rice, Oryza rhizomatis confers broad spectrum resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2012, 12, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Lu, G.; Zeng, L.; Wang, G.L. Two broad-spectrum blast resistance genes, Pi9(t) and Pi2(t), are physically linked on rice chromosome 6. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2002, 267, 472–480. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Qu, S.; Liu, G.; Dolan, M.; Sakai, H.; Lu, G.; Bellizzi, M.; Wang, G.L. The eight amino-acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Tada, Y.; Yokozeki, Y.; Akagi, H.; Hayashi, N.; Fujimura, T.; Ichikawa, N. Chemical induction of disease resistance in rice is correlated with the expression of a gene encoding a nucleotide binding site and leucine-rich repeats. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 40, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Tao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zou, Y.; Lei, C.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, Z.; et al. Identification of a new rice blast resistance gene, Pid3, by genomewide comparison of paired nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat genes and their pseudogene alleles between the two sequenced rice genomes. Genetics 2009, 182, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Chen, L.L.; Kim, H.S.; Pi, L.Y.; Holsten, T.; Gardner, J.; Wang, B.; Zhai, W.X.; Zhu, L.H.; et al. A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science 1995, 270, 1804–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S. Point mutations with positive selection were a major force during the evolution of a receptor-kinase resistance gene family of rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaku, H.; Nishizawa, Y.; Ishii-Minami, N.; Akimoto-Tomiyama, C.; Dohmae, N.; Takio, K.; Minami, E.; Shibuya, N. Plant cells recognize chitin fragments for defense signaling through a plasma membrane receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11086–11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.; Gu, K.; Qiu, C.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Goh, M.; Murata-Hori, M.; Luo, Y.; et al. The rice TAL effector-dependent resistance protein XA10 triggers cell death and calcium depletion in the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. A paralog of the MtN3/saliva family recessively confers race-specific resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 1958–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bimolata, W.; Kumar, A.; Sundaram, R.M.; Laha, G.S.; Qureshi, I.A.; Reddy, G.A.; Ghazi, I.A. Analysis of nucleotide diversity among alleles of the major bacterial blight resistance gene Xa27 in cultivars of rice (Oryza sativa) and its wild relatives. Planta 2013, 238, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shang, J.; Chen, D.; Lei, C.; Zou, Y.; Zhai, W.; Liu, G.; Xu, J.; Ling, Z.; Cao, G.; et al. A B-lectin receptor kinase gene conferring rice blast resistance. Plant J. 2006, 46, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, N.; Drake, J.; Ayliffe, M.; Sun, Q.; Ellis, J.; Hulbert, S.; Pryor, T. Molecular characterization of the maize Rp1-D rust resistance haplotype and its mutants. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johal, G.S.; Briggs, S.P. Reductase activity encoded by the Hm1 disease resistance gene in maize. Science 1992, 258, 985–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, M.R.; Godiard, L.; Straube, E.; Ashfield, T.; Lewald, J.; Sattler, A.; Innes, R.W.; Dangl, J.L. Structure of the Arabidopsis RPM1 gene enabling dual specificity disease resistance. Science 1995, 269, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bent, A.F.; Kunkel, B.N.; Dahlbeck, D.; Brown, K.L.; Schmidt, R.; Giraudat, J.; Staskawicz, B.J.; Leung, J. RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana: A leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 1994, 265, 1856–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, J.M.; Dhandaydham, M.; Long, T.A.; Aarts, M.G.; Goff, S.; Holub, E.B.; Dangl, J.L. Intragenic recombination and diversifying selection contribute to the evolution of downy mildew resistance at the RPP8 locus of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1861–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner-Eddy, P.D.; Crute, I.R.; Holub, E.B.; Beynon, J.L. RPP13 is a simple locus in Arabidopsis thaliana for alleles that specify downy mildew resistance to different avirulence determinants in Peronospora parasitica. Plant J. 2000, 21, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Miller, J.; Nozaki, Y.; Takeda, M.; Shah, J.; Hase, S.; Ikegami, M.; Ehara, Y.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P.; Sukamto. RCY1, an Arabidopsis thaliana RPP8/HRT family resistance gene, conferring resistance to cucumber mosaic virus requires salicylic acid, ethylene and a novel signal transduction mechanism. Plant J. 2002, 32, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botella, M.A.; Parker, J.E.; Frost, L.N.; Bittner-Eddy, P.D.; Beynon, J.L.; Daniels, M.J.; Holub, E.B.; Jones, J.D. Three genes of the Arabidopsis RPP1 complex resistance locus recognize distinct Peronospora parasitica avirulence determinants. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1847–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Biezen, E.A.; Freddie, C.T.; Kahn, K.; Parker, J.E.; Jones, J.D. Arabidopsis RPP4 is a member of the RPP5 multigene family of TIR-NB-LRR genes and confers downy mildew resistance through multiple signalling components. Plant J. 2002, 29, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassmann, W.; Hinsch, M.E.; Staskawicz, B.J. The Arabidopsis RPS4 bacterial-resistance gene is a member of the TIR-NBS-LRR family of disease-resistance genes. Plant J. 1999, 20, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noel, L.; Moores, T.L.; van Der Biezen, E.A.; Parniske, M.; Daniels, M.J.; Parker, J.E.; Jones, J.D. Pronounced intraspecific haplotype divergence at the RPP5 complex disease resistance locus of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, R.F.; Henk, A.; Mowery, P.; Holub, E.; Innes, R.W. A mutation within the leucine-rich repeat domain of the Arabidopsis disease resistance gene RPS5 partially suppresses multiple bacterial and downy mildew resistance genes. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deslandes, L.; Olivier, J.; Theulieres, F.; Hirsch, J.; Feng, D.X.; Bittner-Eddy, P.; Beynon, J.; Marco, Y. Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum in Arabidopsis thaliana is conferred by the recessive RRS1 R gene, a member of a novel family of resistance genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2404–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tor, M.; Brown, D.; Cooper, A.; Woods-Tor, A.; Sjolander, K.; Jones, J.D.; Holub, E.B. Arabidopsis downy mildew resistance gene RPP27 encodes a receptor-like protein similar to CLAVATA2 and tomato Cf-9. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, A.C.; Ausubel, F.M. Resistance to fusarium oxysporum1, a dominant Arabidopsis disease-resistance gene, is not race specific. Genetics 2005, 171, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiderski, M.R.; Innes, R.W. The Arabidopsis PBS1 resistance gene encodes a member of a novel protein kinase subfamily. Plant J. 2001, 26, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, S.; Kaneko, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Kotani, H.; Kato, T.; Asamizu, E.; Miyajima, N.; Sasamoto, S.; Kimura, T.; Hosouchi, T.; et al. Sequence and analysis of chromosome 5 of the plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 2000, 408, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, S.K.; Wang, Z.Y.; Kim, S.H. Identification of Arabidopsis BAK1-associating receptor-like kinase 1 (BARK1) and characterization of its gene expression and brassinosteroid-regulated root phenotypes. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 1620–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Century, K.S.; Shapiro, A.D.; Repetti, P.P.; Dahlbeck, D.; Holub, E.; Staskawicz, B.J. NDR1, a pathogen-induced component required for Arabidopsis disease resistance. Science 1997, 278, 1963–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Ellwood, S.; Calis, O.; Patrick, E.; Li, T.; Coleman, M.; Turner, J.G. Broad-spectrum mildew resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana mediated by RPW8. Science 2001, 291, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, G.J.; Finnegan, E.J.; Ayliffe, M.A.; Ellis, J.G. The L6 gene for flax rust resistance is related to the Arabidopsis bacterial resistance gene RPS2 and the tobacco viral resistance gene N. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.G.; Lawrence, G.J.; Luck, J.E.; Dodds, P.N. Identification of regions in alleles of the flax rust resistance gene L that determine differences in gene-for-gene specificity. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.A.; Lawrence, G.J.; Morrish, B.C.; Ayliffe, M.A.; Finnegan, E.J.; Ellis, J.G. Inactivation of the flax rust resistance gene M associated with loss of a repeated unit within the leucine-rich repeat coding region. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, P.N.; Lawrence, G.J.; Ellis, J.G. Six amino acid changes confined to the leucine-rich repeat beta-strand/beta-turn motif determine the difference between the P and P2 rust resistance specificities in flax. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Kleine, M.; Kifle, S.; Harloff, H.J.; Sandal, N.N.; Marcker, K.A.; Klein-Lankhorst, R.M.; Salentijn, E.M.; Lange, W.; Stiekema, W.J.; et al. Positional cloning of a gene for nematode resistance in sugar beet. Science 1997, 275, 832–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitham, S.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P.; Choi, D.; Hehl, R.; Corr, C.; Baker, B. The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: Similarity to toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell 1994, 78, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, B.C. Genome-wide analysis of NBS-LRR-encoding genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 809–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz-Laylin, L.K.; Krishnamurthy, N.; Tor, M.; Sjolander, K.V.; Jones, J.D. Phylogenomic analysis of the receptor-like proteins of rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Tehrim, S.; Zhang, F.; Tong, C.; Huang, J.; Cheng, X.; Dong, C.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, R.; Hua, W.; et al. Genome-wide comparative analysis of NBS-encoding genes between Brassica species and Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiu, S.H.; Karlowski, W.M.; Pan, R.; Tzeng, Y.H.; Mayer, K.F.; Li, W.H. Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurin, C.; Andres, C.; Aubourg, S.; Bellaoui, M.; Bitton, F.; Bruyere, C.; Caboche, M.; Debast, C.; Gualberto, J.; Hoffmann, B.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of Arabidopsis pentatricopeptide repeat proteins reveals their essential role in organelle biogenesis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2089–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.L.; Fitz, J.; Schneeberger, K.; Ossowski, S.; Cao, J.; Weigel, D. Genome-wide comparison of nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat-encoding genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, A.; Rinaldi, C.; Duplessis, S.; Baucher, M.; Geelen, D.; Duchaussoy, F.; Meyers, B.C.; Boerjan, W.; Martin, F. Genome-wide identification of NBS resistance genes in Populus trichocarpa. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 66, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zan, Y.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Song, Y.; Wang, J. Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of populus leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase genes. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuskan, G.A.; Difazio, S.; Jansson, S.; Bohlmann, J.; Grigoriev, I.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; Ralph, S.; Rombauts, S.; Salamov, A.; et al. The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science 2006, 313, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yue, J.X.; Tian, D.; Chen, J.Q. Recent duplications dominate NBS-encoding gene expansion in two woody species. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2008, 280, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, S.M.; Pardeshi, V.C.; Barvkar, V.T.; Gupta, V.S.; Kadoo, N.Y. Genome-wide identification and characterization of nucleotide binding site leucine-rich repeat genes in linseed reveal distinct patterns of gene structure. Genome 2013, 56, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andolfo, G.; Sanseverino, W.; Aversano, R.; Frusciante, L.; Ercolano, M.R. Genome-wide identification and analysis of candidate genes for disease resistance in tomato. Mol. Breed. 2013, 33, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomato Genome Consortium. The tomato genome sequence provides insights into fleshy fruit evolution. Nature 2012, 485, 635–641. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, R.; Hou, S.; Feng, Y.; Yu, Q.; Dionne-Laporte, A.; Saw, J.H.; Senin, P.; Wang, W.; Ly, B.V.; Lewis, K.L.; et al. The draft genome of the transgenic tropical fruit tree papaya (Carica papaya Linnaeus). Nature 2008, 452, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Huang, S.; Garcia-Mas, J.; Weng, Y. A 1,681-locus consensus genetic map of cultivated cucumber including 67 NB-LRR resistance gene homolog and ten gene loci. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, R.; Ponce, O.; Ramirez, M.; Mostajo, N.; Orjeda, G. Genome-wide identification and mapping of NBS-encoding resistance genes in Solanum tuberosum group phureja. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. Systematic analysis and comparison of nucleotide-binding site disease resistance genes in a diploid cotton Gossypium raimondii. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Huang, J.Q.; Li, N.Y.; Ma, X.F.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.F.; Liang, Y.; Bao, Y.M.; Dai, X.F. Genome-wide analysis of the gene families of resistance gene analogues in cotton and their response to Verticillium wilt. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Gao, Z.H.; Wang, F.; Duan, K.; Ye, Z.W.; Gao, Q.H. Genome-wide identification and comparative expression analysis of NBS-LRR-encoding genes upon Colletotrichum gloeosporioides infection in two ecotypes of Fragaria vesca. Gene 2013, 527, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, M. Identification and characterization of NBS-encoding disease resistance genes in Lotus japonicus. Plant Syst. Evol. 2010, 289, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.T.; Pan, X.H.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.Q. A primary survey on bryophyte species reveals two novel classes of nucleotide-binding site (NBS) genes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, N.; Hattori, M.; Andres, C.; Iida, K.; Lurin, C.; Schmitz-Linneweber, C.; Sugita, M.; Small, I. On the expansion of the pentatricopeptide repeat gene family in plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.Q.; Araki, H.; Jing, Z.; Jiang, K.; Shen, J.; Tian, D. Genome-wide identification of NBS genes in japonica rice reveals significant expansion of divergent non-TIR NBS-LRR genes. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2004, 271, 402–415. [Google Scholar]
- Dardick, C.; Chen, J.; Richter, T.; Ouyang, S.; Ronald, P. The rice kinase database. A phylogenomic database for the rice kinome. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Chand, S.; Singh, N.K.; Sharma, T.R. Genome-wide distribution, organisation and functional characterization of disease resistance and defence response genes across rice species. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouktila, D.; Khalfallah, Y.; Habachi-Houimli, Y.; Mezghani-Khemakhem, M.; Makni, M.; Makni, H. Large-scale analysis of NBS domain-encoding resistance gene analogs in Triticeae. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2014, 37, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.S.; Wang, F.; Tan, S.J.; Wang, M.X.; Sui, N.; Zhang, X.S. Transcript profiles of maize embryo sacs and preliminary identification of genes involved in the embryo sac-pollen tube interaction. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Ma, W.; Miao, W.; Yamada, T.; Zhang, M. Systematic analysis and comparison of nucleotide-binding site disease resistance genes in maize. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 2431–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mace, E.; Tai, S.; Innes, D.; Godwin, I.; Hu, W.; Campbell, B.; Gilding, E.; Cruickshank, A.; Prentis, P.; Wang, J.; et al. The plasticity of NBS resistance genes in sorghum is driven by multiple evolutionary processes. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, B. A genomic analysis of disease-resistance genes encoding nucleotide binding sites in Sorghum bicolor. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2010, 33, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Barley Genome Sequencing Consortium. A physical, genetic and functional sequence assembly of the barley genome. Nature 2012, 491, 711–716. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L.; Si, W.; Zhao, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X. Dynamic evolution of NBS-LRR genes in bread wheat and its progenitors. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2015, 290, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Wu, S. Genome wide analysis of nucleotide-binding site disease resistance genes in Brachypodium distachyon. Comp. Funct. Genom. 2012, 2012, 418208–418220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, H.Q.; Zhao, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, C.; Fan, H.; Li, D.; Dong, L.; Tao, Y.; et al. Draft genome of the wheat A-genome progenitor Triticum urartu. Nature 2013, 496, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Zhao, S.; Kong, X.; Zhao, G.; He, W.; Appels, R.; Pfeifer, M.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Aegilops tauschii draft genome sequence reveals a gene repertoire for wheat adaptation. Nature 2013, 496, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, T.P.; Jackson, S. The first 50 plant genomes. Plant Gen. 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Jones, J.D. Plant disease resistance genes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1997, 48, 575–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, S.T.; Coaker, G.; Day, B.; Staskawicz, B.J. Host-microbe interactions: Shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 2006, 124, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, T.; Cheng, W.; Spiridon, L.N.; Toller, A.; Lukasik, E.; Saijo, Y.; Liu, P.; Shen, Q.H.; Micluta, M.A.; Somssich, I.E.; et al. Coiled-coil domain-dependent homodimerization of intracellular barley immune receptors defines a minimal functional module for triggering cell death. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alber, T. Structure of the leucine zipper. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1992, 2, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bent, A.F. Plant disease resistance genes: Function meets structure. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1757–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, G.B.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Sessa, G. Understanding the functions of plant disease resistance proteins. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 23–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tameling, W.I.; Elzinga, S.D.; Darmin, P.S.; Vossen, J.H.; Takken, F.L.; Haring, M.A.; Cornelissen, B.J. The tomato R gene products I-2 and MI-1 are functional ATP binding proteins with ATPase activity. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2929–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ooijen, G.; van den Burg, H.A.; Cornelissen, B.J.; Takken, F.L. Structure and function of resistance proteins in solanaceous plants. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2007, 45, 43–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rairdan, G.J.; Collier, S.M.; Sacco, M.A.; Baldwin, T.T.; Boettrich, T.; Moffett, P. The coiled-coil and nucleotide binding domains of the Potato Rx disease resistance protein function in pathogen recognition and signaling. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, S.M.; Hamel, L.P.; Moffett, P. Cell death mediated by the N-terminal domains of a unique and highly conserved class of NB-LRR protein. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, B.C.; Dickerman, A.W.; Michelmore, R.W.; Sivaramakrishnan, S.; Sobral, B.W.; Young, N.D. Plant disease resistance genes encode members of an ancient and diverse protein family within the nucleotide-binding superfamily. Plant J. 1999, 20, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, B.C.; Morgante, M.; Michelmore, R.W. TIR-X and TIR-NBS proteins: Two new families related to disease resistance TIR-NBS-LRR proteins encoded in Arabidopsis and other plant genomes. Plant J. 2002, 32, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leipe, D.D.; Koonin, E.V.; Aravind, L. STAND, a class of P-loop NTPases including animal and plant regulators of programmed cell death: Multiple, complex domain architectures, unusual phyletic patterns, and evolution by horizontal gene transfer. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Wendel, J.; Fluhr, R. Divergent evolution of plant NBS-LRR resistance gene homologues in dicot and cereal genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 2000, 50, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takken, F.L.; Albrecht, M.; Tameling, W.I. Resistance proteins: Molecular switches of plant defence. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukasik, E.; Takken, F.L. STANDing strong, resistance proteins instigators of plant defence. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takken, F.L.; Goverse, A. How to build a pathogen detector: Structural basis of NB-LRR function. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deslandes, L.; Rivas, S. Catch me if you can: Bacterial effectors and plant targets. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidrich, K.; Wirthmueller, L.; Tasset, C.; Pouzet, C.; Deslandes, L.; Parker, J.E. Arabidopsis EDS1 connects pathogen effector recognition to cell compartment-specific immune responses. Science 2011, 334, 1401–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Halane, M.K.; Kim, S.H.; Gassmann, W. Pathogen effectors target Arabidopsis EDS1 and alter its interactions with immune regulators. Science 2011, 334, 1405–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhang, J.; Kong, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ba, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. Disruption of PAMP-induced MAP kinase cascade by a Pseudomonas syringae effector activates plant immunity mediated by the NB-LRR protein SUMM2. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, S. MAPK cascades in plant disease resistance signaling. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscaill, P.; Rivas, S. Transcriptional control of plant defence responses. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 20, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Tsuda, K.; Parker, J.E. Effector-triggered immunity: From pathogen perception to robust defense. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2015, 66, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.J.; Sohn, K.H.; Wan, L.; Bernoux, M.; Sarris, P.F.; Segonzac, C.; Ve, T.; Ma, Y.; Saucet, S.B.; Ericsson, D.J.; et al. Structural basis for assembly and function of a heterodimeric plant immune receptor. Science 2014, 344, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinchilla, D.; Zipfel, C.; Robatzek, S.; Kemmerling, B.; Nurnberger, T.; Jones, J.D.; Felix, G.; Boller, T. A flagellin-induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defence. Nature 2007, 448, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stergiopoulos, I.; de Wit, P.J. Fungal effector proteins. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 233–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panstruga, R.; Dodds, P.N. Terrific protein traffic: The mystery of effector protein delivery by filamentous plant pathogens. Science 2009, 324, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Berkey, R.; Ma, X.; Pan, Z.; Bendigeri, D.; King, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, S. A comprehensive mutational analysis of the Arabidopsis resistance protein RPW8.2 reveals key amino acids for defense activation and protein targeting. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 4242–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, J.; Jeong, D.H.; de Paoli, E.; Park, S.; Rosen, B.D.; Li, Y.; Gonzalez, A.J.; Yan, Z.; Kitto, S.L.; Grusak, M.A.; et al. MicroRNAs as master regulators of the plant NB-LRR defense gene family via the production of phased, trans-acting siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 2540–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Cai, C.; Zhai, J.; Lin, F.; Li, L.; Shreve, J.; Thimmapuram, J.; Hughes, T.J.; Meyers, B.C.; Ma, J. Coordination of microRNAs, phasiRNAs, and NB-LRR genes in response to a plant pathogen: Insights from analyses of a set of soybean Rps gene near isogenic lines. Plant Gen. 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaprasad, P.V.; Chen, H.M.; Patel, K.; Bond, D.M.; Santos, B.A.; Baulcombe, D.C. A microRNA superfamily regulates nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeats and other mRNAs. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Triplett, L.; Leach, J.E.; Wang, G.L. Novel insights into rice innate immunity against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 213–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, A.J.; Wood, A.J.; Lightfoot, D.A. Plant receptor-like serine threonine kinases: Roles in signaling and plant defense. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleecker, A.B.; Kende, H. Ethylene: A gaseous signal molecule in plants. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 16, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Higuchi, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Seki, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Kato, T.; Tabata, S.; Shinozaki, K.; Kakimoto, T. Identification of CRE1 as a cytokinin receptor from Arabidopsis. Nature 2001, 409, 1060–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becraft, P.W. Receptor kinase signaling in plant development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 18, 163–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Han, S.W.; Sririyanum, M.; Park, C.J.; Seo, Y.S.; Ronald, P.C. A type I-secreted, sulfated peptide triggers Xa21-mediated innate immunity. Science 2009, 326, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, C.; Yuan, C.; Peng, C.; Yin, J.; Li, W.; He, M.; Wang, J.; Ma, B. A receptor like kinase gene with expressional responsiveness on Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae is essential for Xa21-mediated disease resistance. Rice 2015, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Bartley, L.E.; Chen, X.; Dardick, C.; Chern, M.; Ruan, R.; Canlas, P.E.; Ronald, P.C. OsWRKY62 is a negative regulator of basal and Xa21-mediated defense against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice. Mol. Plant 2008, 1, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekrasov, V.; Ludwig, A.A.; Jones, J.D. CITRX thioredoxin is a putative adaptor protein connecting Cf-9 and the ACIK1 protein kinase during the Cf-9/Avr9 induced defence response. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 4236–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, S.; Rougon-Cardoso, A.; Smoker, M.; Schauser, L.; Yoshioka, H.; Jones, J.D. CITRX thioredoxin interacts with the tomato Cf-9 resistance protein and negatively regulates defence. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriels, S.H.; Ekengren, S.K.; van Ooijen, G.; Abd-El-Haliem, A.M.; van den Berg, G.C.; Vossen, J.H.; Rainey, D.Y.; Martin, G.B.; Takken, F.L.; de Wit, P.J.; et al. An NB-LRR protein required for HR signalling mediated by both extra and intracellular resistance proteins. Plant J. 2007, 50, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radutoiu, S.; Madsen, L.H.; Madsen, E.B.; Felle, H.H.; Umehara, Y.; Gronlund, M.; Sato, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Tabata, S.; Sandal, N.; et al. Plant recognition of symbiotic bacteria requires two LysM receptor-like kinases. Nature 2003, 425, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, E.B.; Madsen, L.H.; Radutoiu, S.; Olbryt, M.; Rakwalska, M.; Szczyglowski, K.; Sato, S.; Kaneko, T.; Tabata, S.; Sandal, N.; et al. A receptor kinase gene of the LysM type is involved in legume perception of rhizobial signals. Nature 2003, 425, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Trotochaud, A.E.; Clark, S.E. The Arabidopsis CLAVATA2 gene encodes a receptor-like protein required for the stability of the CLAVATA1 receptor-like kinase. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeau, J.A.; Sack, F.D. Control of stomatal distribution on the Arabidopsis leaf surface. Science 2002, 296, 1697–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, M.; Shinohara, H.; Sakagami, Y.; Matsubayashi, Y. Arabidopsis CLV3 peptide directly binds CLV1 ectodomain. Science 2008, 319, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo, E.; Sharma, V.K.; Kovaleva, V.; Raikhel, N.V.; Fletcher, J.C. CLV3 is localized to the extracellular space, where it activates the Arabidopsis CLAVATA stem cell signaling pathway. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotochaud, A.E.; Hao, T.; Wu, G.; Yang, Z.; Clark, S.E. The CLAVATA1 receptor-like kinase requires CLAVATA3 for its assembly into a signaling complex that includes KAPP and a Rho-related protein. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Kuroha, T.; Hnilova, M.; Khatayevich, D.; Kanaoka, M.M.; McAbee, J.M.; Sarikaya, M.; Tamerler, C.; Torii, K.U. Direct interaction of ligand-receptor pairs specifying stomatal patterning. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Pennill, L.A.; Ning, J.; Lee, S.W.; Ramalingam, J.; Webb, C.A.; Zhao, B.; Nelson, J.C.; Sun, Q.; Leach, J.E.; et al. Diversity in nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat genes in cereals. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 1871–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanseverino, W.; Ercolano, M.R. In silico approach to predict candidate R proteins and to define their domain architecture. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gururani, M.A.; Venkatesh, J.; Upadhyaya, C.P.; Nookaraju, A.; Pandey, S.K.; Park, S.W. Plant disease resistance genes: Current status and future directions. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 78, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Emerson, B.; Ratanasut, K.; Patrick, E.; O’Neill, C.; Bancroft, I.; Turner, J.G. Origin and maintenance of a broad-spectrum disease resistance locus in Arabidopsis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.F.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.L.; Wang, T.T.; Fan, J.; Lei, Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.J.; Zhao, J.Q.; Xiao, S.; et al. Ectopic expression of resistance to powdery mildew8.1 confers resistance to fungal and oomycete pathogens in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 1484–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panstruga, R. Discovery of novel conserved peptide domains by ortholog comparison within plant multi-protein families. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 59, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wretblad, S.; Bohman, S.; Dixelius, C. Overexpression of a Brassica nigra cDNA gives enhanced resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in B. napus. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandwagt, B.F.; Kneppers, T.J.; Nijkamp, H.J.; Hille, J. Overexpression of the tomato Asc-1 gene mediates high insensitivity to AAL toxins and fumonisin B1 in tomato hairy roots and confers resistance to Alternaria alternata f. sp. lycopersici in Nicotiana umbratica plants. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spassieva, S.D.; Markham, J.E.; Hille, J. The plant disease resistance gene Asc-1 prevents disruption of sphingolipid metabolism during AAL-toxin-induced programmed cell death. Plant J. 2002, 32, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scofield, S.R.; Tobias, C.M.; Rathjen, J.P.; Chang, J.H.; Lavelle, D.T.; Michelmore, R.W.; Staskawicz, B.J. Molecular basis of gene-for-gene specificity in bacterial speck disease of tomato. Science 1996, 274, 2063–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Frederick, R.D.; Zhou, J.; Halterman, D.A.; Jia, Y.; Martin, G.B. Initiation of plant disease resistance by physical interaction of AvrPto and Pto kinase. Science 1996, 274, 2060–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, H.; Komori, T.; Uemura, S.; Kanda, Y.; Shimotani, K.; Nakai, K.; Furuichi, T.; Takebayashi, K.; Sugimoto, T.; Sano, S.; et al. Chloroplast-mediated activation of plant immune signalling in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 926–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirsadeghi, S.; Robson, C.A.; Vanlerberghe, G.C. The role of the mitochondrion in plant responses to biotic stress. Physiol. Plant. 2007, 129, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, J.; Mireau, H. The Rf and Rf-like PPR in higher plants, a fast-evolving subclass of PPR genes. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz-Linneweber, C.; Small, I. Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins: A socket set for organelle gene expression. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonietz, C.; Forner, J.; Holzle, A.; Thuss, S.; Binder, S. RNA processing factors2 is required for 5′ end processing of nad9 and cox3 mRNAs in mitochondria of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonietz, C.; Forner, J.; Hildebrandt, T.; Binder, S. RNA processing factor3 is crucial for the accumulation of mature ccmC transcripts in mitochondria of Arabidopsis accession columbia. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Wise, R.P.; Schnable, P.S. The rf2 nuclear restorer gene of male-sterile T-cytoplasm maize. Science 1996, 272, 1334–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Wu, H.; Su, D.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Luo, D.; et al. Cytoplasmic male sterility of rice with boro II cytoplasm is caused by a cytotoxic peptide and is restored by two related PPR motif genes via distinct modes of mRNA silencing. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kwak, K.J.; Lee, K.; Hong, S.W.; Kang, H. MicroRNA400-guided cleavage of pentatricopeptide repeat protein mRNAs renders Arabidopsis thaliana more susceptible to pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Andrade, J.; Ramirez, V.; Lopez, A.; Vera, P. Mediated plastid RNA editing in plant immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirasu, K.; Lahaye, T.; Tan, M.W.; Zhou, F.; Azevedo, C.; Schulze-Lefert, P. A novel class of eukaryotic zinc-binding proteins is required for disease resistance signaling in barley and development in C. elegans. Cell 1999, 99, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandwagt, B.F.; Mesbah, L.A.; Takken, F.L.; Laurent, P.L.; Kneppers, T.J.; Hille, J.; Nijkamp, H.J. A longevity assurance gene homolog of tomato mediates resistance to Alternaria alternata f. sp. lycopersici toxins and fumonisin B1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4961–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Li, J.F.; Ao, Y.; Qu, J.; Li, Z.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Feng, D.; Qi, K.; et al. Lysin motif-containing proteins LYP4 and LYP6 play dual roles in peptidoglycan and chitin perception in rice innate immunity. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3406–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, S.T.; Mahajan, S.K.; Whitham, S.A.; Yamamoto, M.L.; Carrington, J.C. Cloning of the Arabidopsis RTM1 gene, which controls restriction of long-distance movement of tobacco etch virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouibrahim, L.; Mazier, M.; Estevan, J.; Pagny, G.; Decroocq, V.; Desbiez, C.; Moretti, A.; Gallois, J.L.; Caranta, C. Cloning of the Arabidopsis rwm1 gene for resistance to watermelon mosaic virus points to a new function for natural virus resistance genes. Plant J. 2014, 79, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, A.; Feys, B.J.; Frost, L.N.; Jones, J.D.; Daniels, M.J.; Parker, J.E. EDS1, an essential component of R gene-mediated disease resistance in Arabidopsis has homology to eukaryotic lipases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3292–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Glazebrook, J.; Clarke, J.D.; Volko, S.; Dong, X. The Arabidopsis NPR1 gene that controls systemic acquired resistance encodes a novel protein containing ankyrin repeats. Cell 1997, 88, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickman, M.B.; Fluhr, R. Centrality of host cell death in plant-microbe interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 543–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.A.; Daudi, A.; Finch, P.; Butt, V.S.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Souda, P.; Ausubel, F.M.; Bolwell, G.P. A peroxidase-dependent apoplastic oxidative burst in cultured Arabidopsis cells functions in MAMP-elicited defense. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 2013–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daudi, A.; Cheng, Z.; O’Brien, J.A.; Mammarella, N.; Khan, S.; Ausubel, F.M.; Bolwell, G.P. The apoplastic oxidative burst peroxidase in Arabidopsis is a major component of pattern-triggered immunity. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindschedler, L.V.; Dewdney, J.; Blee, K.A.; Stone, J.M.; Asai, T.; Plotnikov, J.; Denoux, C.; Hayes, T.; Gerrish, C.; Davies, D.R.; et al. Peroxidase-dependent apoplastic oxidative burst in Arabidopsis required for pathogen resistance. Plant J. 2006, 47, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Arora, P.K.; Mohanta, N.; Parida, P.; Bae, H. Identification of new members of the MAPK gene family in plants shows diverse conserved domains and novel activation loop variants. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolser, D.M.; Kerhornou, A.; Walts, B.; Kersey, P. Triticeae resources in Ensembl Plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Wang, J.; Cai, J.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Wu, F.X. Improving protein function prediction using domain and protein complexes in PPI networks. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Williams, N.; Misleh, C.; Li, W.W. MEME: Discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W369–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.J. Hidden markov models and their applications in biological sequence analysis. Curr. Genom. 2009, 10, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.; Copley, R.R.; Doerks, T.; Ponting, C.P.; Bork, P. SMART: A web-based tool for the study of genetically mobile domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T.; Klimke, W.; Maglott, D.R. NCBI reference sequences: Current status, policy and new initiatives. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanseverino, W.; Roma, G.; de Simone, M.; Faino, L.; Melito, S.; Stupka, E.; Frusciante, L.; Ercolano, M.R. PRGdb: A bioinformatics platform for plant resistance gene analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D814–D821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, S.R. Accelerated Profile HMM Searches. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Elkan, C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1994, 2, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Schmidt, B.; Liu, W.; Maskell, D.L. CUDA-MEME: Accelerating motif discovery in biological sequences using CUDA-enabled graphics processing units. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2010, 31, 2170–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdobnov, E.M.; Apweiler, R. InterProScan-an integration platform for the signature-recognition methods in InterPro. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 847–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kall, L.; Krogh, A.; Sonnhammer, E.L. A combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction method. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupas, A.; van Dyke, M.; Stock, J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science 1991, 252, 1162–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, O.; Gandhi, S.; Heesacker, A.; Whitaker, B.; Taylor, C.; Plocik, A.; Kesseli, R.; Kozik, A.; Michelmore, R.W.; Knapp, S.J. Genetic diversity and genomic distribution of homologs encoding NBS-LRR disease resistance proteins in sunflower. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2008, 280, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, B.W.; Paidi, M.; Ming, R.; Alam, M.; Nishijima, W.T.; Zhu, Y.J. Genome-wide analysis of Carica papaya reveals a small NBS resistance gene family. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2009, 281, 609–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, J.M.; Simon, S.A. Recent insights into R gene evolution. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2006, 7, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, D.E.; Alexander, H.M. TIR-NBS-LRR genes are rare in monocots: Evidence from diverse monocot orders. BMC Res. Notes 2009, 2, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lim, C.J.; Lee, B.W.; Choi, J.P.; Oh, S.K.; Ahmad, R.; Kwon, S.Y.; Ahn, J.; Hur, C.G. A genome-wide comparison of NB-LRR type of resistance gene analogs (RGA) in the plant kingdom. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazebrook, J. Genes controlling expression of defense responses in Arabidopsis—2001 status. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2001, 4, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.X.; Meyers, B.C.; Chen, J.Q.; Tian, D.; Yang, S. Tracing the origin and evolutionary history of plant nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) genes. New Phytol. 2012, 193, 1049–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelkowski, J.; Koczyk, G. Resistance gene analogues of Arabidopsis thaliana: Recognition by structure. J. Appl. Genet. 2003, 44, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, K.; Lu, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Kuang, H. Dynamic nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeat-encoding genes in the grass family. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.S.; Budai-Hadrian, O.; Sela, M.; Carmel-Goren, L.; Zamir, D.; Fluhr, R. Comparative genetics of nucleotide binding site-leucine rich repeat resistance gene homologues in the genomes of two dicotyledons: Tomato and arabidopsis. Genetics 2000, 155, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.J.; Ekramoddoullah, A.K. Isolation, genetic variation and expression of TIR-NBS-LRR resistance gene analogs from western white pine (Pinus monticola Dougl. ex. D. Don.). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2003, 270, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marone, D.; Russo, M.A.; Laido, G.; de Leonardis, A.M.; Mastrangelo, A.M. Plant nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) genes: Active guardians in host defense responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7302–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monosi, B.; Wisser, R.J.; Pennill, L.; Hulbert, S.H. Full-genome analysis of resistance gene homologues in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelmore, R.W.; Meyers, B.C. Clusters of resistance genes in plants evolve by divergent selection and a birth-and-death process. Genome Res. 1998, 8, 1113–1130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hall, B.G. Building phylogenetic trees from molecular data with MEGA. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, N.D. The genetic architecture of resistance. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2000, 3, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Dolan, M.; Sakai, H.; Wang, G.L. The genomic dynamics and evolutionary mechanism of the Pi2/9 locus in rice. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, K.; Jin, X.; Hang, Y.; Chen, J.Q.; Tian, D. Genome-wide investigation on the genetic variations of rice disease resistance genes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 62, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jupe, F.; Pritchard, L.; Etherington, G.J.; Mackenzie, K.; Cock, P.J.; Wright, F.; Sharma, S.K.; Bolser, D.; Bryan, G.J.; Jones, J.D.; et al. Identification and localisation of the NB-LRR gene family within the potato genome. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Wing, R.A.; Wise, R.P. Genome dynamics and evolution of the Mla (powdery mildew) resistance locus in barley. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1903–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, A.J.; Pan, Q.; Pollack, J.; Rose, L.; Kozik, A.; Willits, N.; Luo, Y.; Kochetkova, E.; Guittet, M.; Michelmore, R.W. Functional analysis of the plant disease resistance gene Pto using DNA shuffling. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 23073–23083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.Y.; Pi, L.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Gardner, J.; Holsten, T.; Ronald, P.C. Evolution of the rice Xa21 disease resistance gene family. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geddy, R.; Brown, G.G. Genes encoding pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) proteins are not conserved in location in plant genomes and may be subject to diversifying selection. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhardt, C.; Valkonen, J.P. Organization of genes controlling disease resistance in the potato genome. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2001, 39, 79–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perazzolli, M.; Malacarne, G.; Baldo, A.; Righetti, L.; Bailey, A.; Fontana, P.; Velasco, R.; Malnoy, M. Characterization of resistance gene analogues (RGAs) in apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.) and their evolutionary history of the Rosaceae family. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, T.; Nei, M. Divergent evolution and evolution by the birth-and-death process in the immunoglobulin VH gene family. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1994, 11, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sudupak, M.A.; Bennetzen, J.L.; Hulbert, S.H. Unequal exchange and meiotic instability of disease-resistance genes in the Rp1 region of maize. Genetics 1993, 133, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bar-Hen, A.; Charcosset, A.; Bourgoin, M.; Guiard, J. Relationship between genetic markers and morphological traits in a maize inbred line collection. Euphytica 1995, 84, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Schneeberger, K.; Ossowski, S.; Gunther, T.; Bender, S.; Fitz, J.; Koenig, D.; Lanz, C.; Stegle, O.; Lippert, C.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of multiple Arabidopsis thaliana populations. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Kurata, N.; Wei, X.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, A.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, K.; Lu, H.; Li, W.; et al. A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice. Nature 2012, 490, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, K.W.; Wang, S.; Lun, Y.; Gardiner, L.; MacLachlan, R.; Hucl, P.; Wiebe, K.; Wong, D.; Forrest, K.L.; Sharpe, A.G.; et al. A haplotype map of allohexaploid wheat reveals distinct patterns of selection on homoeologous genomes. Genome Biol. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, M.A.; Chia, J.M.; Elshire, R.J.; Ersoz, E.S.; Hurwitz, B.L.; Peiffer, J.A.; McMullen, M.D.; Sun, Q.; Grills, G.S.; Ross-Ibarra, J.; et al. A first-generation haplotype map of maize. Science 2009, 326, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, J.M.; Song, C.; Bradbury, P.J.; Costich, D.; de Leon, N.; Doebley, J.; Elshire, R.J.; Gaut, B.; Geller, L.; Glaubitz, J.C.; et al. Maize HapMap2 identifies extant variation from a genome in flux. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genomes Project, C.; Abecasis, G.R.; Altshuler, D.; Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Gibbs, R.A.; Hurles, M.E.; McVean, G.A. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 2010, 467, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Linden, C.G.; Wouters, D.C.; Mihalka, V.; Kochieva, E.Z.; Smulders, M.J.; Vosman, B. Efficient targeting of plant disease resistance loci using NBS profiling. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, D.; Song, W. A genetic linkage map based on AFLP and NBS markers in cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis). Bot. Stud. 2008, 49, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, A.M.; Marcel, T.C.; Kohutova, Z.; Stam, P.; van der Linden, C.G.; Niks, R.E. Peroxidase profiling reveals genetic linkage between peroxidase gene clusters and basal host and non-host resistance to rusts and mildew in barley. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossen, J.H.; Dezhsetan, S.; Esselink, D.; Arens, M.; Sanz, M.J.; Verweij, W.; Verzaux, E.; van der Linden, C.G. Novel applications of motif-directed profiling to identify disease resistance genes in plants. Plant Methods 2013, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Keyser, E.; Shu, Q.Y.; van Bockstaele, E.; de Riek, J. Multipoint-likelihood maximization mapping on 4 segregating populations to achieve an integrated framework map for QTL analysis in pot azalea (Rhododendron simsii hybrids). BMC Mol. Biol. 2010, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sekhwal, M.K.; Li, P.; Lam, I.; Wang, X.; Cloutier, S.; You, F.M. Disease Resistance Gene Analogs (RGAs) in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19248-19290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819248
Sekhwal MK, Li P, Lam I, Wang X, Cloutier S, You FM. Disease Resistance Gene Analogs (RGAs) in Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(8):19248-19290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819248
Chicago/Turabian StyleSekhwal, Manoj Kumar, Pingchuan Li, Irene Lam, Xiue Wang, Sylvie Cloutier, and Frank M. You. 2015. "Disease Resistance Gene Analogs (RGAs) in Plants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 8: 19248-19290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819248
APA StyleSekhwal, M. K., Li, P., Lam, I., Wang, X., Cloutier, S., & You, F. M. (2015). Disease Resistance Gene Analogs (RGAs) in Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(8), 19248-19290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160819248







