Structural Basis for Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Mechanisms of Carbapenemases Conferring Antibiotic Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
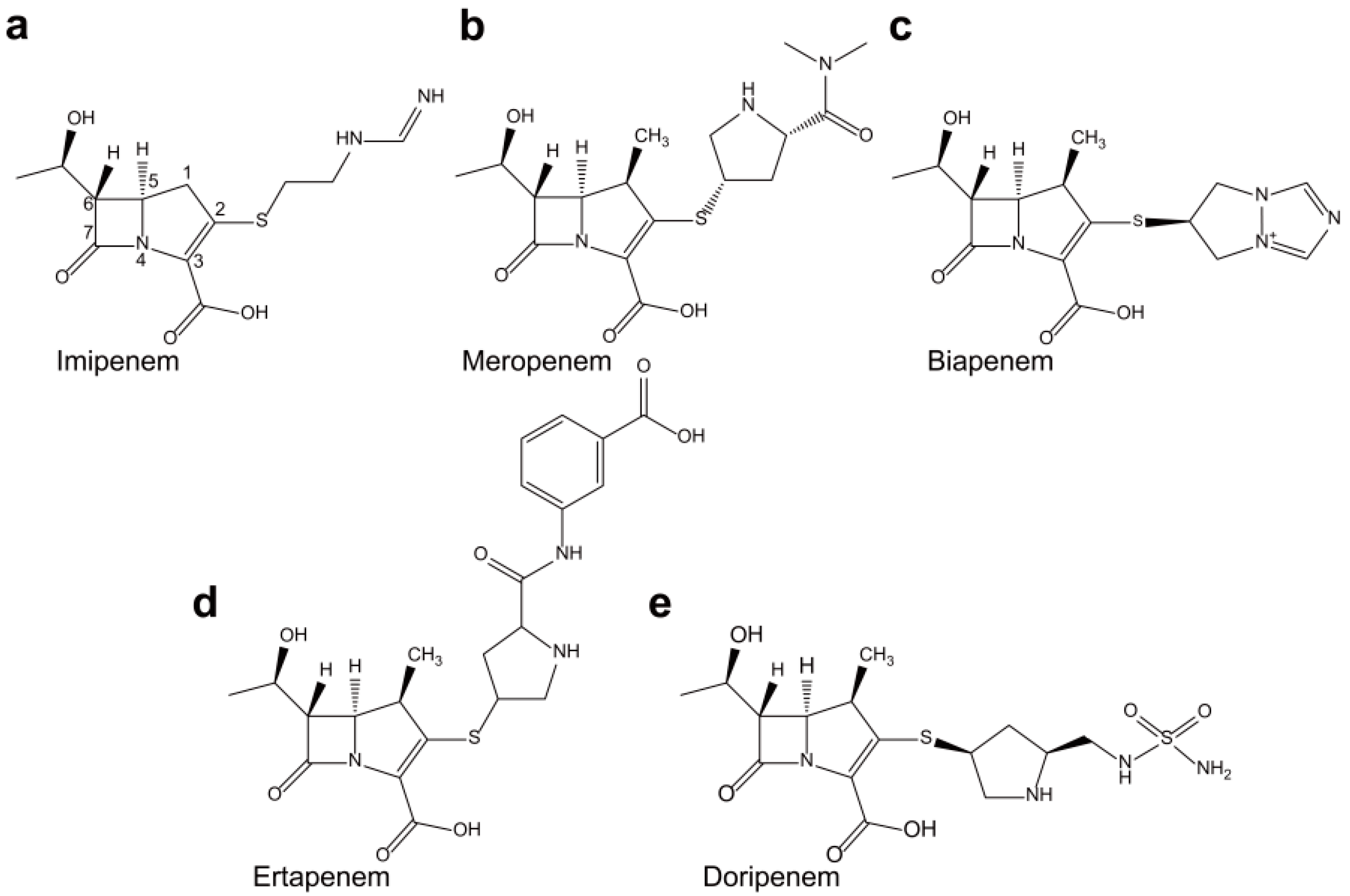
2. Non-Metallo-Carbapenemases: Zinc-Independent Classes A, C, and D
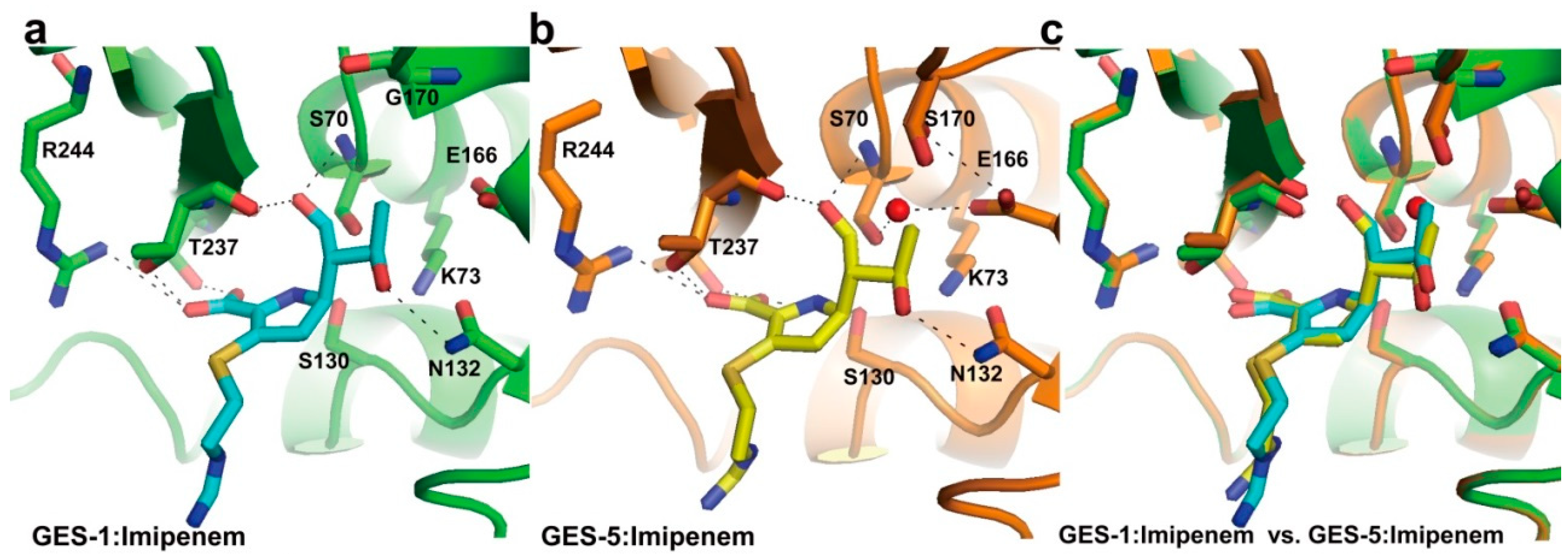
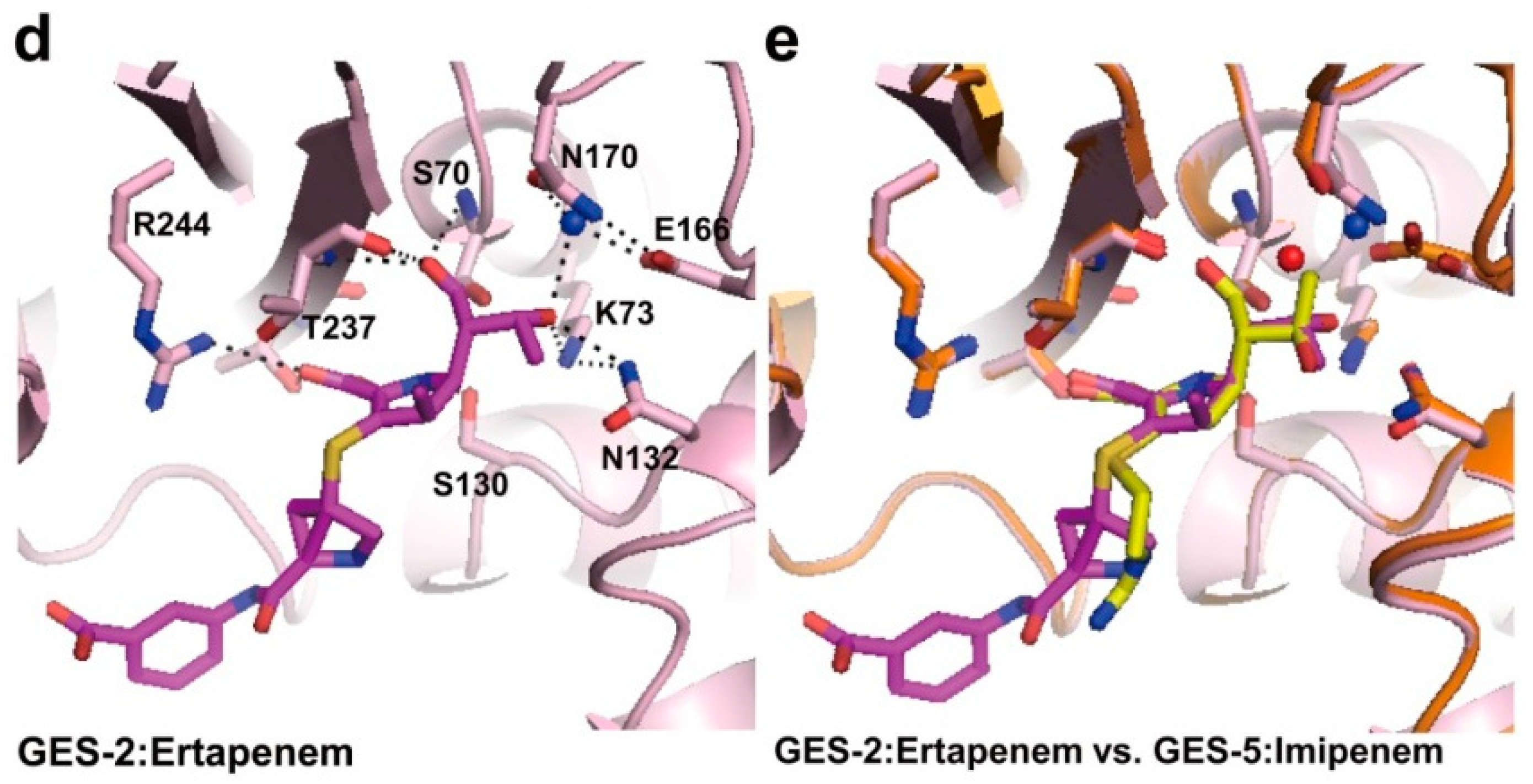
2.1. Class A Carbapenemases
2.2. Structural Components and Catalytic Mechanism of Class A Carbapenemases



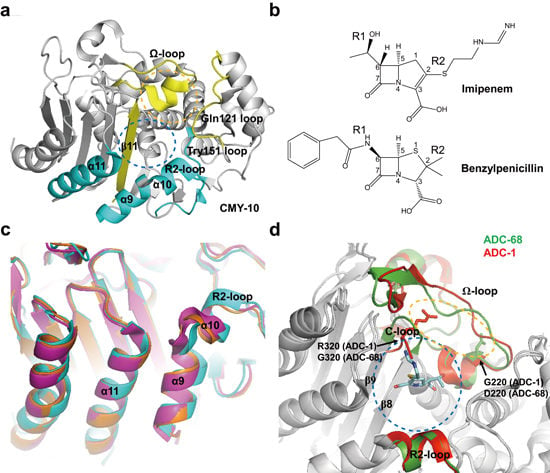
2.3. Class C Carbapenemases
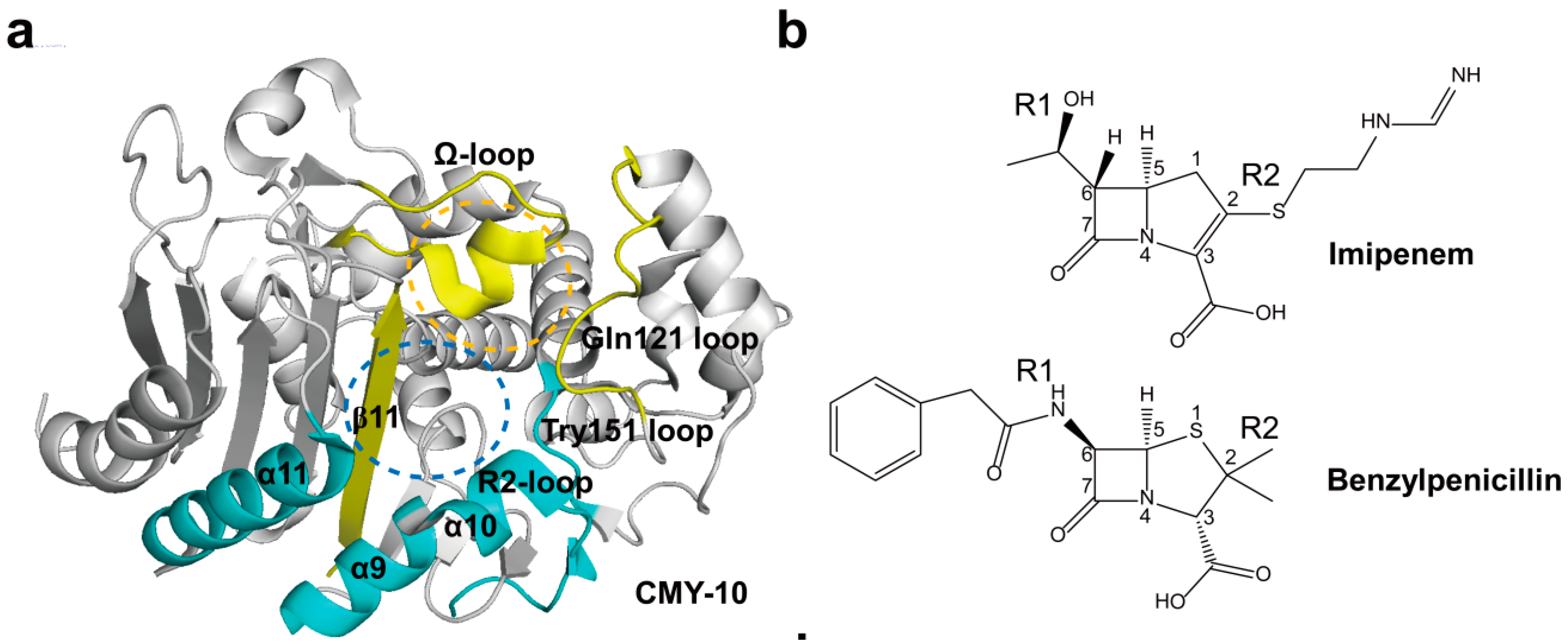
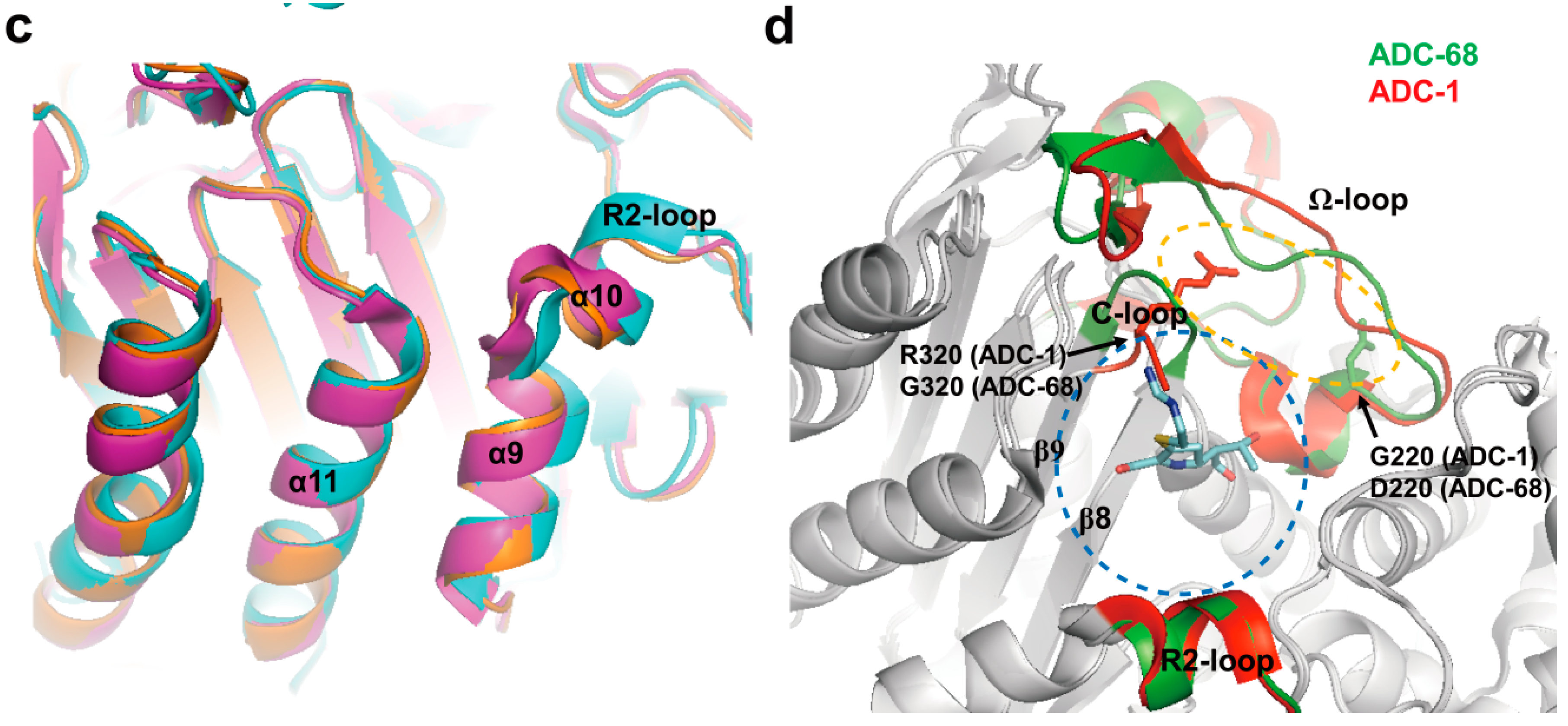
2.4. Structural Components and Catalytic Mechanism of Class C Carbapenemases
2.5. Class D Carbapenemases
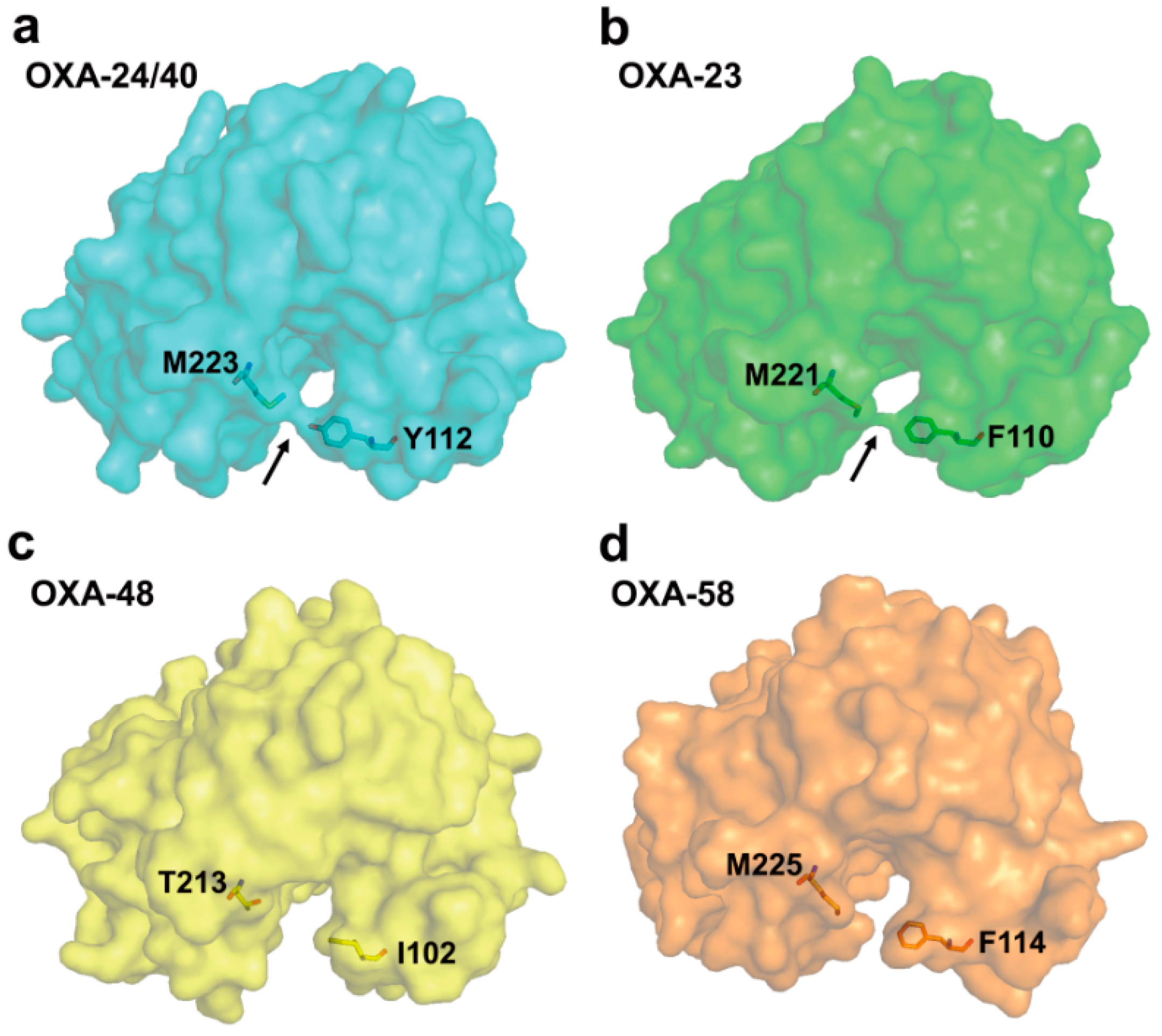
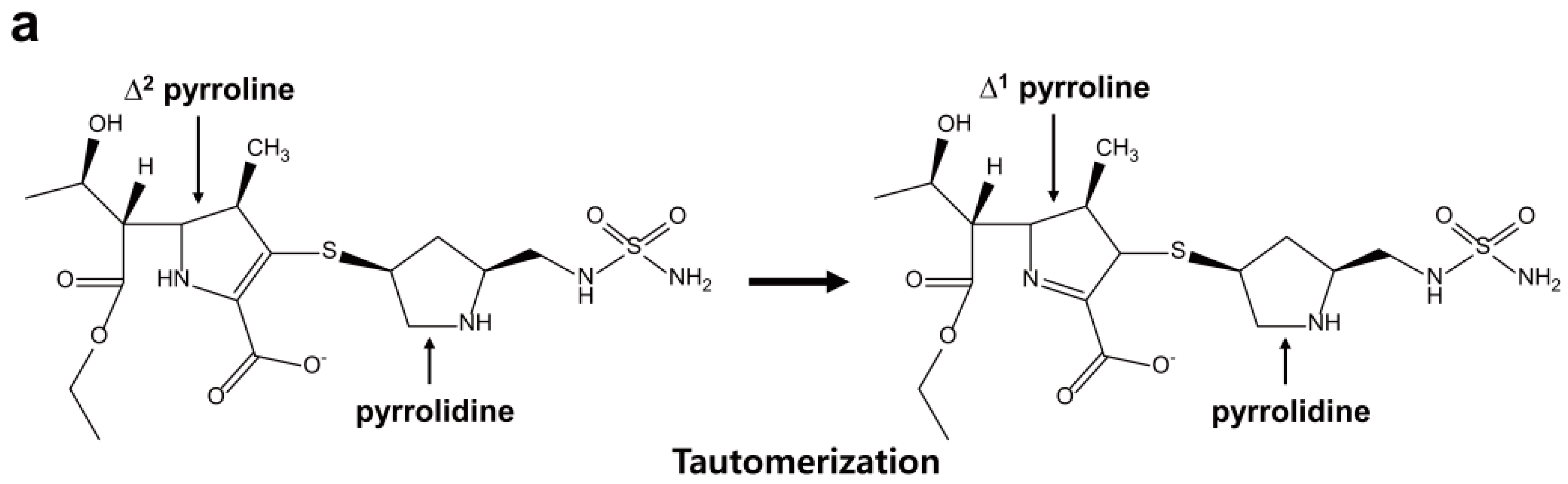
2.6. Structural Components and Catalytic Mechanism of Class D Carbapenemases
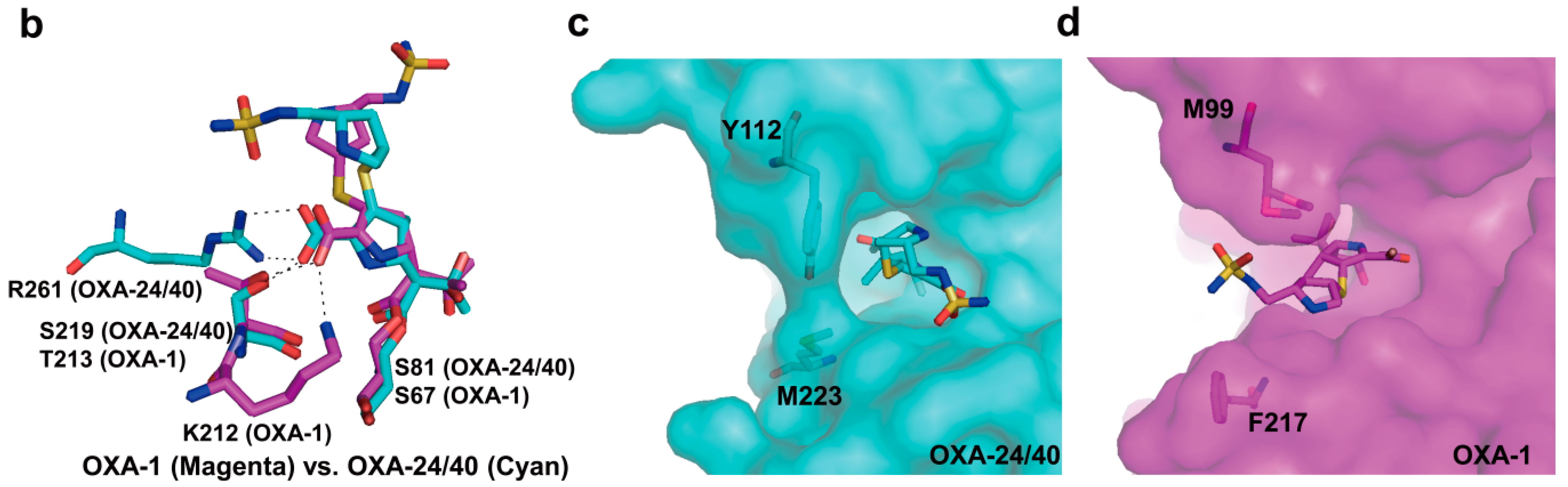
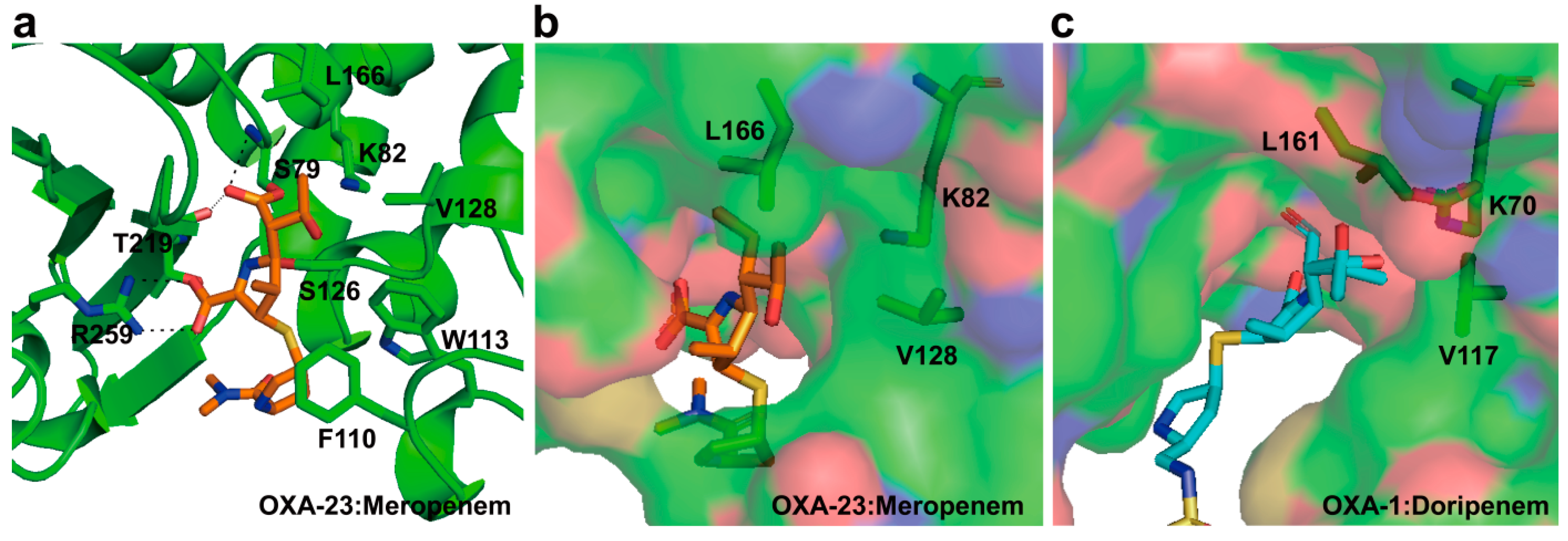
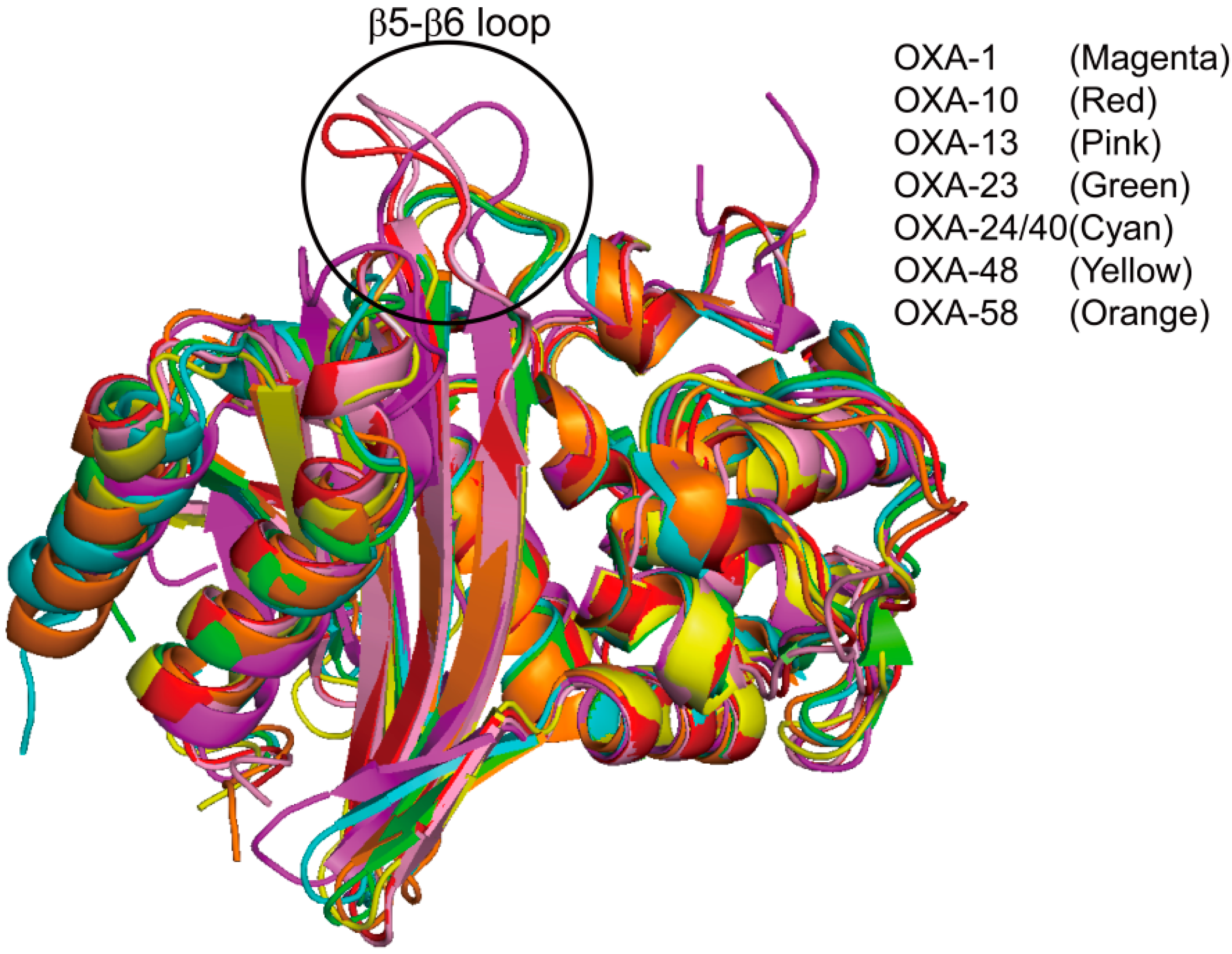
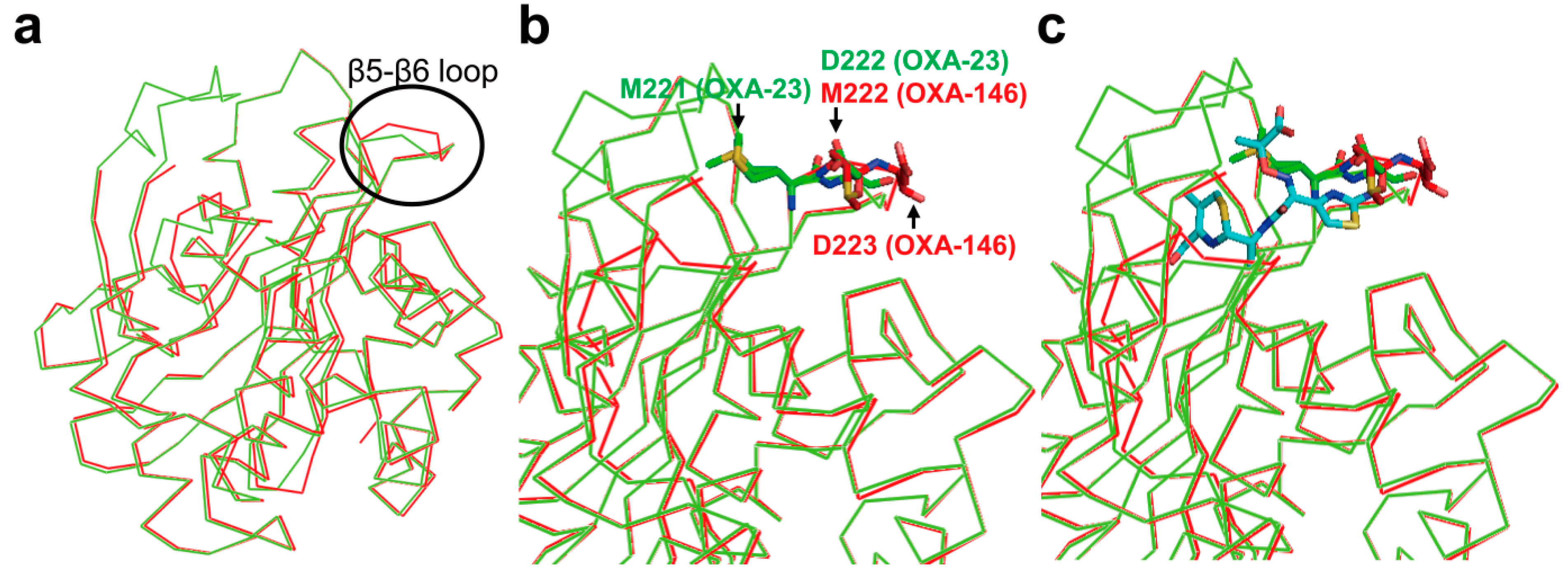
3. Metallo-Carbapenemases: Zinc-Dependent Class B
3.1. Class B Carbapenemases
3.2. Structural Components and Catalytic Mechanism of Class B Carbapenemases
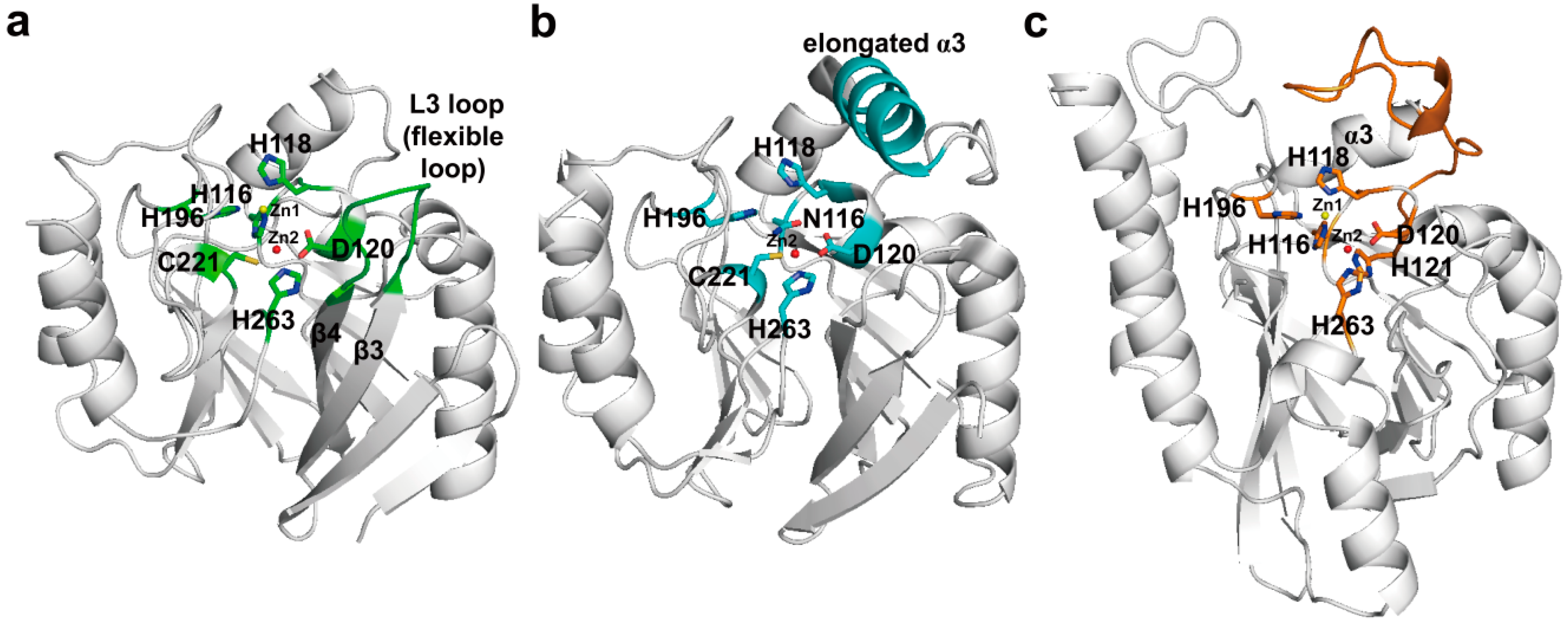
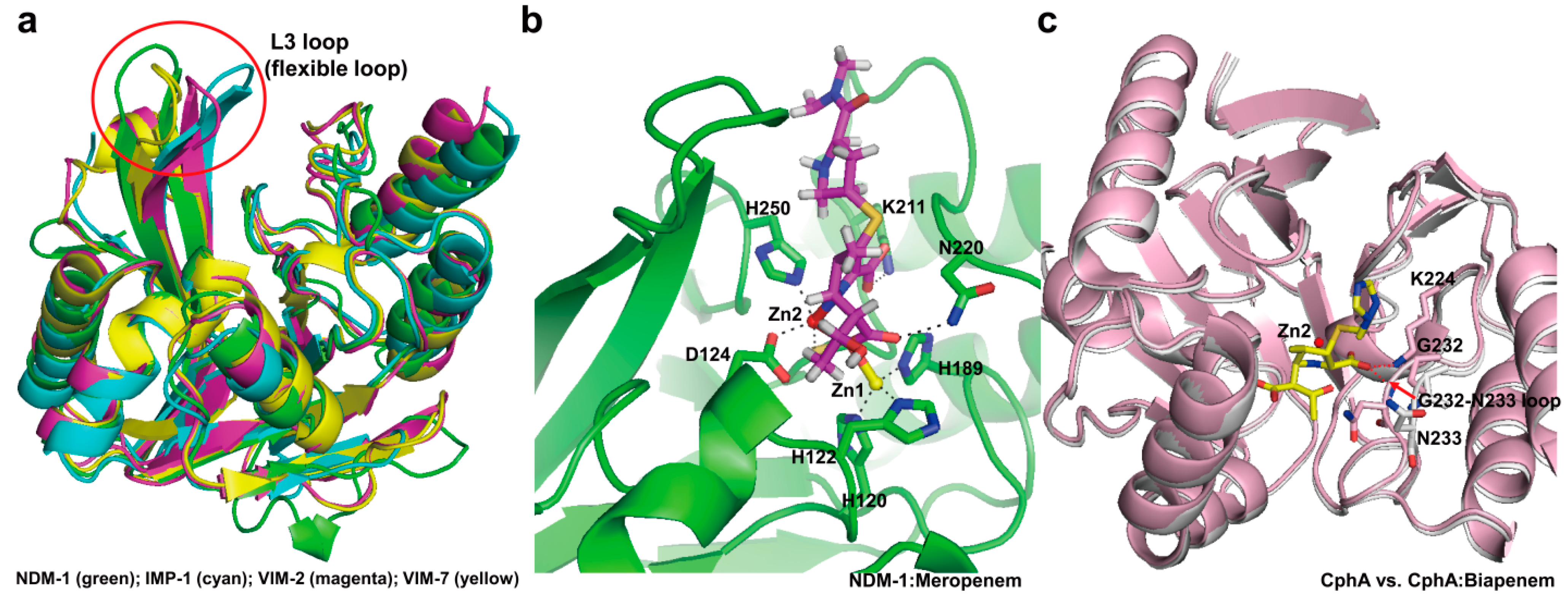
4. Experimental Section

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambler, R.P. The structure of β-lactamases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1980, 289, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queenan, A.M.; Bush, K. Carbapenemases: The versatile β-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 440–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moellering, R.C., Jr.; Eliopoulos, G.M.; Sentochnik, D.E. The carbapenems: New broad spectrum β-lactam antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1989, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richet, H.M.; Mohammed, J.; McDonald, L.C.; Jarvis, W.R. Building communication networks: International network for the study and prevention of emerging antimicrobial resistance. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Carbapenem resistance in gram-negative pathogens: Emerging non-metallo-carbapenemases. Res. J. Microbiol. 2006, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, K.S. Extended-spectrum-β-lactamase, AmpC, and carbapenemase issues. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, I.; Moura, A.; Alves, A.; Saavedra, M.J.; Correia, A. Molecular characterization of a carbapenem-hydrolyzing class A β-lactamase, SFC-1, from Serratia fonticola UTAD54. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2321–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammeri, H.; Guillon, H.; Eb, F.; Nordmann, P. Phenotypic and biochemical comparison of the carbapenem-hydrolyzing activities of five plasmid-borne AmpC β-lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4556–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Yong, D.; Choi, Y.S.; Yum, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Woodford, N.; Livermore, D.M.; Chong, Y. Reduced imipenem susceptibility in Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates with plasmid-mediated CMY-2 and DHA-1 β-lactamases co-mediated by porin loss. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2007, 29, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, Y.M. Characterization of blaCMY-10 a novel, plasmid-encoded AmpC-type β-lactamase gene in a clinical isolate of Enterobacter aerogenes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, P.A.; Urban, C.; Mariano, N.; Projan, S.J.; Rahal, J.J.; Bush, K. Imipenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae is associated with the combination of ACT-1, a plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamase, and the foss of an outer membrane protein. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.H.; Hong, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.J.; Park, K.S.; Karim, A.M.; Jo, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Ko, K.S.; Kang, L.W.; et al. Structure of ADC-68, a novel carbapenem-hydrolyzing class C extended-spectrum β-lactamase isolated from Acinetobacter baumannii. Acta Crystallogr. D 2014, 70, 2924–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal-Shah, M.; Livermore, D.M. Worldwide emergence of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter spp. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1998, 41, 576–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther-Rasmussen, J.; Hoiby, N. Class A carbapenemases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordmann, P.; Mariotte, S.; Naas, T.; Labia, R.; Nicolas, M.H. Biochemical properties of a carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamase from Enterobacter cloacae and cloning of the gene into Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, B.A.; Bush, K.; Keeney, D.; Yang, Y.; Hare, R.; O’Gara, C.; Medeiros, A.A. Characterization of IMI-1 β-lactamase, a class A carbapenem-hydrolyzing enzyme from Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 2080–2086. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naas, T.; Cattoen, C.; Bernusset, S.; Cuzon, G.; Nordmann, P. First identification of blaIMI-1 in an Enterobacter cloacae clinical isolate from France. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1664–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejuk, D.; Novkoski, M.; Juranko, V.; Prajdic-Predrijevac, D.; Todoric, N.; Mikacic, I.; Guzvinec, M.; Andrasevic, A.T. A report of rarely observed resistance pattern to carbapenems in a clinical isolate of Enterobacter cloacae. Lijec. Vjesn. 2013, 135, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Osterblad, M.; Kirveskari, J.; Hakanen, A.J.; Tissari, P.; Vaara, M.; Jalava, J. Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Finland: The first years (2008-11). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2860–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radice, M.; Power, P.; Gutkind, G.; Fernandez, K.; Vay, C.; Famiglietti, A.; Ricover, N.; Ayala, J.A. First class a carbapenemase isolated from Enterobacteriaceae in Argentina. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1068–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boo, T.W.; O’Connell, N.; Power, L.; O’Connor, M.; King, J.; McGrath, E.; Hill, R.; Hopkins, K.L.; Woodford, N. First report of IMI-1-producing colistin-resistant Enterobacter clinical isolate in Ireland, March 2013. Eur. Surveill. 2013, 18, 20548. [Google Scholar]
- Aubron, C.; Poirel, L.; Ash, R.J.; Nordmann, P. Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae, US Rivers. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.S.; Du, X.X.; Zhou, Z.H.; Chen, Y.G.; Li, L.J. First isolation of blaIMI-2 in an Enterobacter cloacae clinical isolate from China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1610–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naas, T.; Vandel, L.; Sougakoff, W.; Livermore, D.M.; Nordmann, P. Cloning and sequence analysis of the gene for a carbapenem-hydrolyzing class A β-lactamase, SME-1, from Serratia marcescens S6. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queenan, A.M.; Shang, W.; Schreckenberger, P.; Lolans, K.; Bush, K.; Quinn, J. SME-3, a novel member of the Serratia marcescens SME family of carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 3485–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naas, T.; Nordmann, P. Analysis of a carbapenem-hydrolyzing class A β-lactamase from Enterobacter cloacae and of its LysR-type regulatory protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 7693–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lahey Clinic Database. β-Lactamase Classification and Amino Acid Sequences for TEM, SHV, and OXA Extended-Spectrum and Inhibitor Resistant Enzymes. Available online: http://www.lahey.org/Studies/ (accessed on 25 April 2015).
- Naas, T.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Minor extended-spectrum β-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; le Thomas, I.; Naas, T.; Karim, A.; Nordmann, P. Biochemical sequence analyses of GES-1, a novel class A extended-spectrum β-lactamase, and the class 1 integron In52 from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Weldhagen, G.F.; Naas, T.; de Champs, C.; Dove, M.G.; Nordmann, P. GES-2, a class A β-lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa with increased hydrolysis of imipenem. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2598–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Weldhagen, G.F.; de Champs, C.; Nordmann, P. A nosocomial outbreak of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates expressing the extended-spectrum β-lactamase GES-2 in South Africa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 49, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, V.B.; Zavascki, A.P.; Rozales, F.P.; Pagano, M.; Magagnin, C.M.; Nodari, C.S.; da Silva, R.C.; Dalarosa, M.G.; Falci, D.R.; Barth, A.L. Detection of blaGES-5 in carbapenem-resistant Kluyvera intermedia isolates recovered from the hospital environment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 622–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, V.B.; Falci, D.R.; Rozales, F.P.; Barth, A.L.; Zavascki, A.P. Carbapenem-resistant GES-5-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Southern Brazil. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 18, 231–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. The difficult-to-control spread of carbapenemase producers among Enterobacteriaceae worldwide. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Heritier, C.; Podglajen, I.; Sougakoff, W.; Gutmann, L.; Nordmann, P. Emergence in Klebsiella pneumoniae of a chromosome-encoded SHV β-lactamase that compromises the efficacy of imipenem. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Frase, H.; Toth, M.; Kumarasiri, M.; Wiafe, K.; Munoz, J.; Mobashery, S.; Vakulenko, S.B. Structural basis for progression toward the carbapenemase activity in the GES family of β-lactamases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19512–19515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, F.; Chudyk, E.I.; van der Kamp, M.W.; Correia, A.; Mulholland, A.J.; Spencer, J. The basis for carbapenem hydrolysis by class A β-lactamases: A combined investigation using crystallography and simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18275–18285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, W.; Bethel, C.R.; Thomson, J.M.; Bonomo, R.A.; van den Akker, F. Crystal structure of KPC-2: Insights into carbapenemase activity in class A β-lactamases. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 5732–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sougakoff, W.; L’Hermite, G.; Pernot, L.; Naas, T.; Guillet, V.; Nordmann, P.; Jarlier, V.; Delettre, J. Structure of the imipenem-hydrolyzing class A β-lactamase SME-1 from Serratia marcescens. Acta Crystallogr. D 2002, 58, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaren, P.; Maveyraud, L.; Raquet, X.; Cabantous, S.; Duez, C.; Pedelacq, J.D.; Mariotte-Boyer, S.; Mourey, L.; Labia, R.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; et al. X-ray analysis of the NMC-A β-lactamase at 1.64-Å resolution, a class A carbapenemase with broad substrate specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26714–26721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotte-Boyer, S.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; Labia, R. A kinetic study of NMC-A β-lactamase, an Ambler class A carbapenemase also hydrolyzing cephamycins. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 143, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Queenan, A.M.; Torres-Viera, C.; Gold, H.S.; Carmeli, Y.; Eliopoulos, G.M.; Moellering, R.C., Jr.; Quinn, J.P.; Hindler, J.; Medeiros, A.A.; Bush, K. SME-type carbapenem-hydrolyzing class A β-lactamases from geographically diverse Serratia marcescens strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 3035–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, I.K.; Lee, Y.N.; Jeong, S.H.; Hong, S.G.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Youn, H. Genetic and biochemical characterization of GES-5, an extended-spectrum class A β-lactamase from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 58, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, F.; Sarmento, A.C.; Henriques, I.; Samyn, B.; van Beeumen, J.; Domingues, P.; Domingues, M.R.; Saavedra, M.J.; Correia, A. Biochemical Characterization of SFC-1, a class A carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 4512–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigit, H.; Queenan, A.M.; Rasheed, J.K.; Biddle, J.W.; Domenech-Sanchez, A.; Alberti, S.; Bush, K.; Tenover, F.C. Carbapenem-resistant strain of Klebsiella oxytoca harboring carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamase KPC-2. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3881–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambler, R.P.; Coulson, A.F.; Frere, J.M.; Ghuysen, J.M.; Joris, B.; Forsman, M.; Levesque, R.C.; Tiraby, G.; Waley, S.G. A standard numbering scheme for the class A β-lactamases. Biochem. J. 1991, 276, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papp-Wallace, K.M.; Endimiani, A.; Taracila, M.A.; Bonomo, R.A. Carbapenems: Past, present, and future. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4943–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drawz, S.M.; Bonomo, R.A. Three decades of β-lactamase inhibitors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 160–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, J.F.; Mobashery, S. Three decades of the class A β-lactamase acyl-enzyme. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2009, 10, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolau, D.P. Carbapenems: A potent class of antibiotics. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2008, 9, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, M.S.; Lovering, A.L.; Strynadka, N.C. β-lactam antibiotic resistance: A current structural perspective. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfand, M.S.; Bonomo, R.A. β-Lactamases: A survey of protein diversity. Curr. Drug. Targets Infect. Disord. 2003, 3, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krissinel, E.; Henrick, K. Secondary-structure matching (SSM), a new tool for fast protein structure alignment in three dimensions. Acta Crystallogr. D 2004, 60, 2256–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLano, W.L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.5.0.4. Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA. Available online: http://www.pymol.org (accessed on 25 April 2015).
- Sougakoff, W.; Naas, T.; Nordmann, P.; Collatz, E.; Jarlier, V. Role of Ser-237 in the substrate specificity of the carbapenem-hydrolyzing class A β-lactamase SME-1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1433, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frase, H.; Shi, Q.; Testero, S.A.; Mobashery, S.; Vakulenko, S.B. Mechanistic basis for the emergence of catalytic competence against carbapenem antibiotics by the GES family of β-lactamases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 29509–29513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, N.K.; Smith, C.A.; Frase, H.; Black, D.J.; Vakulenko, S.B. Kinetic and structural requirements for carbapenemase activity in GES-type β-lactamases. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nukaga, M.; Bethel, C.R.; Thomson, J.M.; Hujer, A.M.; Distler, A.; Anderson, V.E.; Knox, J.R.; Bonomo, R.A. Inhibition of class A β-lactamases by carbapenems: Crystallographic observation of two conformations of meropenem in SHV-1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12656–12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maveyraud, L.; Mourey, L.; Kotra, L.P.; Pedelacq, J.-D.; Guillet, V.; Mobashery, S.; Samama, J.P. Structural basis for clinical longevity of carbapenem antibiotics in the face of challenge by the common class A β-lactamases from antibiotic-resistant bacteria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9748–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzin, A.P.; Nukaga, M.; Nukaga, Y.; Hujer, A.M.; Bonomo, R.A.; Knox, J.R. Structure of the SHV-1 β-lactamase. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 5720–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stec, B.; Holtz, K.M.; Wojciechowski, C.L.; Kantrowitz, E.R. Structure of the wild-type TEM-1 β-lactamase at 1.55 Å and the mutant enzyme Ser70Ala at 2.1 Å suggest the mode of noncovalent catalysis for the mutant enzyme. Acta Crystallogr. D 2005, 61, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Delmas, J.; Sirot, J.; Shoichet, B.; Bonnet, R. Atomic resolution structures of CTX-M β-lactamases: Extended spectrum activities from increased mobility and decreased stability. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Cassidy, C.; Sacchettini, J.C. Crystal structure and activity studies of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis β-lactamase reveal its critical role in resistance to β-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2762–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippon, A.; Arlet, G.; Jacoby, G.A. Plasmid-determined AmpC-type β-lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, G.S.; Cheon, S.H.; An, Y.J.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, K.J. Characterization of blaCMY-11, an AmpC-type plasmid-mediated β-lactamase gene in a Korean clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 49, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Jung, H.I.; Jung, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Ahn, J.B.; Jeong, S.H.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Dissemination of transferable AmpC-type β-lactamase (CMY-10) in a Korean hospital. Microb. Drug Resist. 2004, 10, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauernfeind, A.; Chong, Y.; Schweighart, S. Extended broad spectrum β-lactamase in Klebsiella pneumoniae including resistance to cephamycins. Infection 1989, 17, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decre, D.; Verdet, C.; Raskine, L.; Blanchard, H.; Burghoffer, B.; Philippon, A.; Sanson-Le-Pors, M.J.; Petit, J.C.; Arlet, G. Characterization of CMY-type β-lactamases in clinical strains of Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated in four hospitals in the Paris area. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Song, J.S.; Bak, S.H.; Cho, Y.E.; Kim, D.W.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, K.J.; Lee, S.H. Dissemination of Escherichia coli producing AmpC-type β-lactamase (CMY-11) in Korea. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 24, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Literacka, E.; Empel, J.; Baraniak, A.; Sadowy, E.; Hryniewicz, W.; Gniadkowski, M. Four variants of the Citrobacter freundii AmpC-Type cephalosporinases, including novel enzymes CMY-14 and CMY-15, in a Proteus mirabilis clone widespread in Poland. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4136–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miriagou, V.; Tzouvelekis, L.S.; Villa, L.; Lebessi, E.; Vatopoulos, A.C.; Carattoli, A.; Tzelepi, E. CMY-13, a novel inducible cephalosporinase encoded by an Escherichia coli plasmid. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3172–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Llarena, F.J.; Zamorano, L.; Kerff, F.; Beceiro, A.; Garcia, P.; Miro, E.; Larrosa, N.; Gomez-Bertomeu, F.; Mendez, J.A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.J.; et al. Genetic and kinetic characterization of the novel AmpC β-lactamases DHA-6 and DHA-7. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6544–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.J.; Yang, H.F.; Liu, Y.Y.; Mei, Q.; Ye, Y.; Li, H.R.; Cheng, J.; Li, J.B. ACT-10, a novel plasmid-encoded class C β-lactamase in a Serratia marcescens isolate from China. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 80, 343–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.T.; Chen, T.L.; Siu, L.K.; Chen, C.P.; Fung, C.P. Impact of derepressed AmpC β-lactamase ACT-9 on the clinical efficacy of ertapenem. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4440–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Q.; Ye, Y.; Li, J.B.; Zhang, X.J. ACT-3, a novel plasmid-encoded class C β-lactamase in a Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate from China. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Tzouvelekis, L.S.; Tzelepi, E.; Miriagou, V. Plasmid-encoded ACC-4, an extended-spectrum cephalosporinase variant from Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3763–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.T.; Hung, S.W.; Chuang, Y.C.; Chen, H.E.; Jones, R.N.; Yu, W.L. Identification of a novel cephalosporinase (DHA-3) in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated in Taiwan. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortineau, N.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Plasmid-mediated and inducible cephalosporinase DHA-2 from Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 47, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, A.; Arlet, G.; Schito, G.C.; Lagrange, P.H.; Philippon, A. Characterization of FOX-3, an AmpC-type plasmid-mediated β-lactamase from an Italian isolate of Klebsiella oxytoca. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Jung, H.I.; An, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, K.J.; Suh, P.G.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Structural basis for the extended substrate spectrum of CMY-10, a plasmid-encoded class C β-lactamase. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Bae, I.K.; Lee, S.H. New definitions of extended-spectrum β-lactamase conferring worldwide emerging antibiotic resistance. Med. Res. Rev. 2012, 32, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Cha, S.S.; Lee, S.H. New disturbing trend in antimicrobial resistance of gram-negative pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, F.; Hujer, A.M.; Hujer, K.M.; Decker, B.K.; Rather, P.N.; Bonomo, R.A. Global challenge of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3471–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hujer, K.M.; Hamza, N.S.; Hujer, A.M.; Perez, F.; Helfand, M.S.; Bethel, C.R.; Thomson, J.M.; Anderson, V.E.; Barlow, M.; Rice, L.B.; et al. Identification of a new allelic variant of the Acinetobacter baumannii cephalosporinase, ADC-7 β-lactamase: Defining a unique family of class C enzymes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2941–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacoby, G.A. AmpC β-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galleni, M.; Lamotte-Brasseur, J.; Raquet, X.; Dubus, A.; Monnaie, D.; Knox, J.R.; Frere, J.M. The enigmatic catalytic mechanism of active-site serine β-lactamases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 49, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Minasov, G.; Roth, T.A.; Prati, F.; Shoichet, B.K. The deacylation mechanism of AmpC β-lactamase at ultrahigh resolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2970–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Toth, M.; Antunes, N.T.; Smith, C.A.; Vakulenko, S.B. Structure of the extended-spectrum class C β-lactamase ADC-1 from Acinetobacter baumannii. Acta Crystallogr. D 2014, 70, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crichlow, G.V.; Kuzin, A.P.; Nukaga, M.; Mayama, K.; Sawai, T.; Knox, J.R. Structure of the extended-spectrum class C β-lactamase of Enterobacter cloacae GC1, a natural mutant with a tandem tripeptide insertion. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 10256–10261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, K.; Jacoby, G.A.; Medeiros, A.A. A functional classification scheme for β-lactamases and its correlation with molecular structure. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 1211–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, B.A.; Amyes, S.G. OXA β-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther-Rasmussen, J.; Hoiby, N. OXA-type carbapenemases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, J.A. Imipenem/cilastatin: The first carbapenem antibiotic. Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm. 1985, 19, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bou, G.; Oliver, A.; Martinez-Beltran, J. OXA-24, a novel class D β-lactamase with carbapenemase activity in an Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Heritier, C.; Tolun, V.; Nordmann, P. Emergence of oxacillinase-mediated resistance to imipenem in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.; Young, H.K.; Amyes, S.G. Characterisation of OXA-51, a novel class D carbapenemase found in genetically unrelated clinical strains of Acinetobacter baumannii from Argentina. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Marque, S.; Heritier, C.; Segonds, C.; Chabanon, G.; Nordmann, P. OXA-58, a novel class D β-lactamase involved in resistance to carbapenems in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, S.; Poirel, L.; Seifert, H.; Mugnier, P.; Benhamou, D.; Nordmann, P. OXA-134, a naturally occurring carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D β-lactamase from Acinetobacter lwoffii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 5372–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, P.G.; Poirel, L.; Lehmann, M.; Nordmann, P.; Seifert, H. OXA-143, a novel carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D β-lactamase in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5035–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, S.; Bonnin, R.A.; Poirel, L.; Duranteau, J.; Nordmann, P. Identification of the naturally occurring genes encoding carbapenem-hydrolysing oxacillinases from Acinetobacter haemolyticus, Acinetobacter johnsonii, and Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnin, R.A.; Ocampo-Sosa, A.A.; Poirel, L.; Guet-Revillet, H.; Nordmann, P. Biochemical and genetic characterization of carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamase OXA-229 from Acinetobacter bereziniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3923–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, P.G.; Perez-Llarena, F.J.; Zander, E.; Fernandez, A.; Bou, G.; Seifert, H. OXA-235, a novel class D β-lactamase involved in resistance to carbapenems in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Antunes, N.T.; Toth, M.; Vakulenko, S.B. Crystal structure of carbapenemase OXA-58 from Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Antunes, N.T.; Stewart, N.K.; Toth, M.; Kumarasiri, M.; Chang, M.; Mobashery, S.; Vakulenko, S.B. Structural basis for carbapenemase activity of the OXA-23 β-lactamase from Acinetobacter baumannii. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaitany, K.C.; Klinger, N.V.; June, C.M.; Ramey, M.E.; Bonomo, R.A.; Powers, R.A.; Leonard, D.A. Structures of the class D Carbapenemases OXA-23 and OXA-146: Mechanistic basis of activity against carbapenems, extended-spectrum cephalosporins, and aztreonam. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4848–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.D.; Ortega, C.J.; Renck, N.A.; Bonomo, R.A.; Powers, R.A.; Leonard, D.A. Structures of the class D carbapenemase OXA-24 from Acinetobacter baumannii in complex with doripenem. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 406, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docquier, J.D.; Calderone, V.; de Luca, F.; Benvenuti, M.; Giuliani, F.; Bellucci, L.; Tafi, A.; Nordmann, P.; Botta, M.; Rossolini, G.M.; et al. Crystal structure of the OXA-48 β-lactamase reveals mechanistic diversity among class D carbapenemases. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillana, E.; Beceiro, A.; Bou, G.; Romero, A. Crystal structure of the carbapenemase OXA-24 reveals insights into the mechanism of carbapenem hydrolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5354–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Nukaga, M.; Mayama, K.; Braswell, E.H.; Knox, J.R. Comparison of β-lactamases of classes A and D: 1.5-Å crystallographic structure of the class D OXA-1 oxacillinase. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernot, L.; Frenois, F.; Rybkine, T.; L’Hermite, G.; Petrella, S.; Delettre, J.; Jarlier, V.; Collatz, E.; Sougakoff, W. Crystal structures of the class D β-lactamase OXA-13 in the native form and in complex with meropenem. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 310, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paetzel, M.; Danel, F.; de Castro, L.; Mosimann, S.C.; Page, M.G.; Strynadka, N.C. Crystal structure of the class D β-lactamase OXA-10. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heritier, C.; Poirel, L.; Aubert, D.; Nordmann, P. Genetic and functional analysis of the chromosome-encoded carbapenem-hydrolyzing oxacillinase OXA-40 of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Castanheira, M.; Carrer, A.; Rodriguez, C.P.; Jones, R.N.; Smayevsky, J.; Nordmann, P. OXA-163, an OXA-48-related class D β-lactamase with extended activity toward expanded-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2546–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Testero, S.A.; Amini, K.; Wei, W.; Liu, J.; Balachandran, N.; Monoharan, T.; Stynes, S.; Kotra, L.P.; Golemi-Kotra, D. Hydrolytic mechanism of OXA-58 enzyme, a carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D β-lactamase from Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 37292–37303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couture, F.; Lachapelle, J.; Levesque, R.C. Phylogeny of LCR-1 and OXA-5 with class A and class D β-lactamases. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.D.; Bethel, C.R.; Distler, A.M.; Hujer, A.M.; Bonomo, R.A.; Leonard, D.A. Mutation of the active site carboxy-lysine (K70) of OXA-1 β-lactamase results in a deacylation-deficient enzyme. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 6136–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golemi, D.; Maveyraud, L.; Vakulenko, S.; Tranier, S.; Ishiwata, A.; Kotra, L.P.; Samama, J.P.; Mobashery, S. The first structural and mechanistic insights for class D β-lactamases: Evidence for a novel catalytic process for turnover of β-lactam antibiotics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 6132–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, C.J.; Knowles, J.R. Inhibition of the RTEM β-lactamase from Escherichia coli. Interaction of the enzyme with derivatives of olivanic acid. Biochemistry 1982, 21, 2857–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, F.; Benvenuti, M.; Carboni, F.; Pozzi, C.; Rossolini, G.M.; Mangani, S.; Docquier, J.D. Evolution to carbapenem-hydrolyzing activity in noncarbapenemase class D β-lactamase OXA-10 by rational protein design. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18424–18429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palzkill, T. Metallo-β-lactamase structure and function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1277, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachyra, T.; Pechereau, M.C.; Bruneau, J.M.; Claudon, M.; Frere, J.M.; Miossec, C.; Coleman, K.; Black, M.T. Mechanistic studies of the inactivation of TEM-1 and P99 by NXL104, a novel non-β-lactam β-lactamase inhibitor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 5132–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Llarena, F.J.; Bou, G. β-Lactamase inhibitors: The story so far. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 3740–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, T.R.; Toleman, M.A.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Metallo-β-lactamases: The quiet before the storm? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L.; Walsh, T.R.; Livermore, D.M. The emerging NDM carbapenemases. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, D.; Toleman, M.A.; Giske, C.G.; Cho, H.S.; Sundman, K.; Lee, K.; Walsh, T.R. Characterization of a new metallo-β-lactamase gene, blaNDM-1, and a novel erythromycin esterase gene carried on a unique genetic structure in Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 14 from India. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5046–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Arakawa, Y.; Ohsuka, S.; Wacharotayankun, R.; Kato, N.; Ohta, M. Plasmid-mediated dissemination of the metallo-β-lactamase gene blaIMP among clinically isolated strains of Serratia marcescens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornaglia, G.; Mazzariol, A.; Lauretti, L.; Rossolini, G.M.; Fontana, R. Hospital outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing VIM-1, a novel transferable metallo-β-lactamase. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauretti, L.; Riccio, M.L.; Mazzariol, A.; Cornaglia, G.; Amicosante, G.; Fontana, R.; Rossolini, G.M. Cloning and characterization of blaVIM, a new integron-borne metallo-β-lactamase gene from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Naas, T.; Nicolas, D.; Collet, L.; Bellais, S.; Cavallo, J.D.; Nordmann, P. Characterization of VIM-2, a carbapenem-hydrolyzing metallo-β-lactamase and its plasmid- and integron-borne gene from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate in France. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Shukla, S.K.; Prasad, K.N.; Ovejero, C.M.; Pati, B.K.; Tripathi, A.; Singh, A.; Srivastava, A.K.; Gonzalez-Zorn, B. Prevalence and molecular characterisation of new Delhi metallo-β-lactamases NDM-1, NDM-5, NDM-6 and NDM-7 in multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae from India. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottig, S.; Hamprecht, A.G.; Christ, S.; Kempf, V.A.; Wichelhaus, T.A. Detection of NDM-7 in Germany, a new variant of the new Delhi metallo-β-lactamase with increased carbapenemase activity. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzon, G.; Bonnin, R.A.; Nordmann, P. First identification of novel NDM carbapenemase, NDM-7, in Escherichia coli in France. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordmann, P.; Boulanger, A.E.; Poirel, L. NDM-4 metallo-β-lactamase with increased carbapenemase activity from Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2184–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanheira, M.; Toleman, M.A.; Jones, R.N.; Schmidt, F.J.; Walsh, T.R. Molecular characterization of a β-lactamase gene, blaGIM-1, encoding a new subclass of metallo-β-lactamase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4654–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiguchi, J.; Morita, K.; Kitao, T.; Watanabe, N.; Okazaki, M.; Miyoshi-Akiyama, T.; Kanamori, M.; Kirikae, T. KHM-1, a novel plasmid-mediated metallo-β-lactamase from a Citrobacter freundii clinical isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 4194–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toleman, M.A.; Simm, A.M.; Murphy, T.A.; Gales, A.C.; Biedenbach, D.J.; Jones, R.N.; Walsh, T.R. Molecular characterization of SPM-1, a novel metallo-β-lactamase isolated in Latin America: Report from the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance programme. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Yum, J.H.; Yong, D.; Lee, H.M.; Kim, H.D.; Docquier, J.D.; Rossolini, G.M.; Chong, Y. Novel acquired metallo-β-lactamase gene, blaSIM-1, in a class 1 integron from Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from Korea. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4485–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Rodriguez-Martinez, J.M.; Al Naiemi, N.; Debets-Ossenkopp, Y.J.; Nordmann, P. Characterization of DIM-1, an integron-encoded metallo-β-lactamase from a Pseudomonas stutzeri clinical isolate in the Netherlands. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2420–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Salabi, A.; Borra, P.S.; Toleman, M.A.; Samuelsen, O.; Walsh, T.R. Genetic and biochemical characterization of a novel metallo-β-lactamase, TMB-1, from an Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain isolated in Tripoli, Libya. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2241–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, D.; Toleman, M.A.; Bell, J.; Ritchie, B.; Pratt, R.; Ryley, H.; Walsh, T.R. Genetic and biochemical characterization of an acquired subgroup B3 metallo-β-lactamase gene, blaAIM-1, and its unique genetic context in Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Australia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 6154–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carfi, A.; Pares, S.; Duee, E.; Galleni, M.; Duez, C.; Frere, J.M.; Dideberg, O. The 3-D structure of a zinc metallo-β-lactamase from Bacillus cereus reveals a new type of protein fold. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4914–4921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carfi, A.; Duee, E.; Galleni, M.; Frere, J.M.; Dideberg, O. 1. 85 Å resolution structure of the zincII β-lactamase from Bacillus cereus. Acta Crystallogr. D 1998, 54, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Saez, I.; Hopkins, J.; Papamicael, C.; Franceschini, N.; Amicosante, G.; Rossolini, G.M.; Galleni, M.; Frere, J.M.; Dideberg, O. The 1.5-Å structure of Chryseobacterium meningosepticum zinc β-lactamase in complex with the inhibitor, d-captopril. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 23868–23873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concha, N.O.; Rasmussen, B.A.; Bush, K.; Herzberg, O. Crystal structure of the wide-spectrum binuclear zinc β-lactamase from Bacteroides fragilis. Structure 1996, 4, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concha, N.O.; Janson, C.A.; Rowling, P.; Pearson, S.; Cheever, C.A.; Clarke, B.P.; Lewis, C.; Galleni, M.; Frere, J.M.; Payne, D.J.; et al. Crystal structure of the IMP-1 metallo β-lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its complex with a mercaptocarboxylate inhibitor: Binding determinants of a potent, broad-spectrum inhibitor. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 4288–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Saez, I.; Docquier, J.D.; Rossolini, G.M.; Dideberg, O. The three-dimensional structure of VIM-2, a Zn-β-lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its reduced and oxidised form. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 375, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassaux, P.; Traore, D.A.; Loisel, E.; Favier, A.; Docquier, J.D.; Sohier, J.S.; Laurent, C.; Bebrone, C.; Frere, J.M.; Ferrer, J.L.; et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of the subclass B1 metallo-β-lactamase VIM-4. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borra, P.S.; Leiros, H.K.; Ahmad, R.; Spencer, J.; Leiros, I.; Walsh, T.R.; Sundsfjord, A.; Samuelsen, O. Structural and computational investigations of VIM-7: Insights into the substrate specificity of VIM metallo-β-lactamases. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 411, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.T.; Worrall, L.J.; Gruninger, R.; Strynadka, N.C. New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase: Structural insights into β-lactam recognition and inhibition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11362–11365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hao, Q. Crystal structure of NDM-1 reveals a common β-lactam hydrolysis mechanism. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 2574–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, T.A.; Catto, L.E.; Halford, S.E.; Hadfield, A.T.; Minor, W.; Walsh, T.R.; Spencer, J. Crystal structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa SPM-1 provides insights into variable zinc affinity of metallo-β-lactamases. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 357, 890–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borra, P.S.; Samuelsen, O.; Spencer, J.; Walsh, T.R.; Lorentzen, M.S.; Leiros, H.K. Crystal structures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa GIM-1: Active-site plasticity in metallo-β-lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kwon, D.B.; Kim, J.K.; Tran, T.H.; Nguyen, D.D.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, L.W. Crystallization and preliminary diffraction studies of GIM-1, a class B carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamase. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F 2012, 68, 1226–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, G.; Bebrone, C.; Anne, C.; Galleni, M.; Frere, J.M.; Dideberg, O. A metallo-β-lactamase enzyme in action: Crystal structures of the monozinc carbapenemase CphA and its complex with biapenem. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 345, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, F.; Bromley, E.H.; Saavedra, M.J.; Correia, A.; Spencer, J. Crystal structure of Serratia fonticola Sfh-I: Activation of the nucleophile in mono-zinc metallo-β-lactamases. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 411, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, J.H.; Walsh, T.R.; Taylor, I.A.; Emery, D.C.; Verma, C.S.; Gamblin, S.J.; Spencer, J. The crystal structure of the L1 metallo-β-lactamase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia at 1.7 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 284, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Saez, I.; Mercuri, P.S.; Papamicael, C.; Kahn, R.; Frere, J.M.; Galleni, M.; Rossolini, G.M.; Dideberg, O. Three-dimensional structure of FEZ-1, a monomeric subclass B3 metallo-β-lactamase from Fluoribacter gormanii, in native form and in complex with d-captopril. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 325, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docquier, J.D.; Benvenuti, M.; Calderone, V.; Stoczko, M.; Menciassi, N.; Rossolini, G.M.; Mangani, S. High-resolution crystal structure of the subclass B3 metallo-β-lactamase BJP-1: Rational basis for substrate specificity and interaction with sulfonamides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4343–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiros, H.K.; Borra, P.S.; Brandsdal, B.O.; Edvardsen, K.S.; Spencer, J.; Walsh, T.R.; Samuelsen, O. Crystal structure of the mobile metallo-β-lactamase AIM-1 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Insights into antibiotic binding and the role of Gln157. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4341–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felici, A.; Amicosante, G.; Oratore, A.; Strom, R.; Ledent, P.; Joris, B.; Fanuel, L.; Frere, J.M. An overview of the kinetic parameters of class B β-lactamases. Biochem. J. 1993, 291, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rossolini, G.M.; Franceschini, N.; Riccio, M.L.; Mercuri, P.S.; Perilli, M.; Galleni, M.; Frere, J.M.; Amicosante, G. Characterization and sequence of the Chryseobacterium (Flavobacterium) meningosepticum carbapenemase: A new molecular class B β-lactamase showing a broad substrate profile. Biochem. J. 1998, 332, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laraki, N.; Franceschini, N.; Rossolini, G.M.; Santucci, P.; Meunier, C.; de Pauw, E.; Amicosante, G.; Frere, J.M.; Galleni, M. Biochemical characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa 101/1477 metallo-β-lactamase IMP-1 produced by Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samuelsen, O.; Castanheira, M.; Walsh, T.R.; Spencer, J. Kinetic characterization of VIM-7, a divergent member of the VIM metallo-β-lactamase family. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 2905–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, F.; Arthur, C.J.; Bromley, E.H.; Samyn, B.; Moerman, P.; Saavedra, M.J.; Correia, A.; Spencer, J. Biochemical characterization of Sfh-I, a subclass B2 metallo-β-lactamase from Serratia fonticola UTAD54. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5392–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, P.S.; Bouillenne, F.; Boschi, L.; Lamotte-Brasseur, J.; Amicosante, G.; Devreese, B.; van Beeumen, J.; Frere, J.M.; Rossolini, G.M.; Galleni, M. Biochemical characterization of the FEZ-1 metallo-β-lactamase of Legionella gormanii ATCC 33297T produced in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoczko, M.; Frere, J.M.; Rossolini, G.M.; Docquier, J.D. Postgenomic scan of metallo-β-lactamase homologues in rhizobacteria: Identification and characterization of BJP-1, a subclass B3 ortholog from Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garau, G.; Garcia-Saez, I.; Bebrone, C.; Anne, C.; Mercuri, P.; Galleni, M.; Frere, J.M.; Dideberg, O. Update of the standard numbering scheme for class B β-lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2347–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ark, H.; Brothers, E.N.; Merz, K.M., Jr. Hybrid QM/MM and DFT investigations of the catalytic mechanism and inhibition of the dinuclear zinc metallo-β-lactamase CcrA from Bacteroides fragilis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4232–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Fast, W.; Valentine, A.M.; Benkovic, S.J. Metallo-β-lactamase: Structure and mechanism. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1999, 3, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Fast, W.; Benkovic, S.J. On the mechanism of the metallo-β-lactamase from Bacteroides fragilis. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 10013–10023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.P.; Hajdin, C.; Chandrasekar, S.; Bennett, B.; Yang, K.W.; Crowder, M.W. Mechanistic studies on the mononuclear ZnII-containing metallo-β-lactamase ImiS from Aeromonas sobria. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 10729–10738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malabanan, M.M.; Amyes, T.L.; Richard, J.P. A role for flexible loops in enzyme catalysis. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010, 20, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scrofani, S.D.; Chung, J.; Huntley, J.J.; Benkovic, S.J.; Wright, P.E.; Dyson, H.J. NMR characterization of the metallo-β-lactamase from Bacteroides fragilis and its interaction with a tight-binding inhibitor: Role of an active-site loop. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 14507–14514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.G.; Horton, L.B.; Huang, W.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Palzkill, T. Analysis of the functional contributions of Asn233 in metallo-β-lactamase IMP-1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5696–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.J.; Park, K.S.; Karim, A.M.; Lee, C.-R.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Structural Basis for Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Mechanisms of Carbapenemases Conferring Antibiotic Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9654-9692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16059654
Jeon JH, Lee JH, Lee JJ, Park KS, Karim AM, Lee C-R, Jeong BC, Lee SH. Structural Basis for Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Mechanisms of Carbapenemases Conferring Antibiotic Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(5):9654-9692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16059654
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Jeong Ho, Jung Hun Lee, Jae Jin Lee, Kwang Seung Park, Asad Mustafa Karim, Chang-Ro Lee, Byeong Chul Jeong, and Sang Hee Lee. 2015. "Structural Basis for Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Mechanisms of Carbapenemases Conferring Antibiotic Resistance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 5: 9654-9692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16059654
APA StyleJeon, J. H., Lee, J. H., Lee, J. J., Park, K. S., Karim, A. M., Lee, C.-R., Jeong, B. C., & Lee, S. H. (2015). Structural Basis for Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Mechanisms of Carbapenemases Conferring Antibiotic Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(5), 9654-9692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16059654