Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity and ACE Inhibitory Peptides of Salmon (Salmo salar) Protein Hydrolysates Obtained by Human and Porcine Gastrointestinal Enzymes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
| Sequences of ACE Inhibitors | Type of Salmon Proteins | IC50 (μM) | Hydrophobicity (Kyte-Doolittle Scale) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IVY | M, S | 0.48 | 7.4 |
| VW | M, S | 1.4 | 3.3 |
| IY | M, S | 2.1 | 3.2 |
| IW | M, S | 4.7 | 3.6 |
| VY | M, S | 7.1 | 2.9 |
| TVY | M | 15 | 2.2 |
| VFPS | M | 0.46 | 4.6 |
| VTVNPYKWLP | M | 5.5 | −1.3 |
| IWHHT | M | 5.8 | −3.5 |
| YALPHA | M | 9.8 | 1.3 |
| ALPHA | M | 10 | 2.6 |
2.1. Protein Content and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Analysis of ex Vivo and in Vitro Salmon Protein Hydrolysates
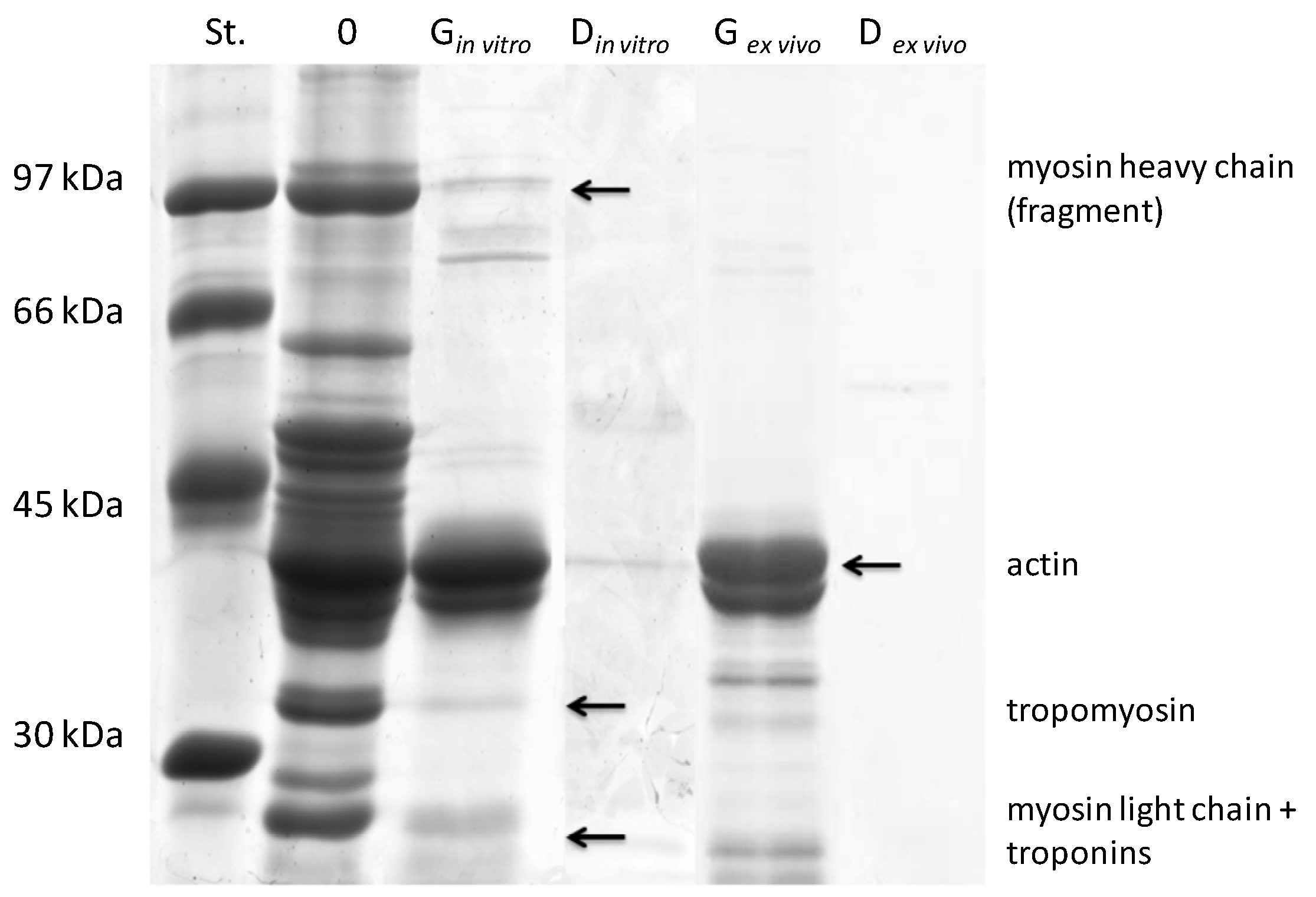
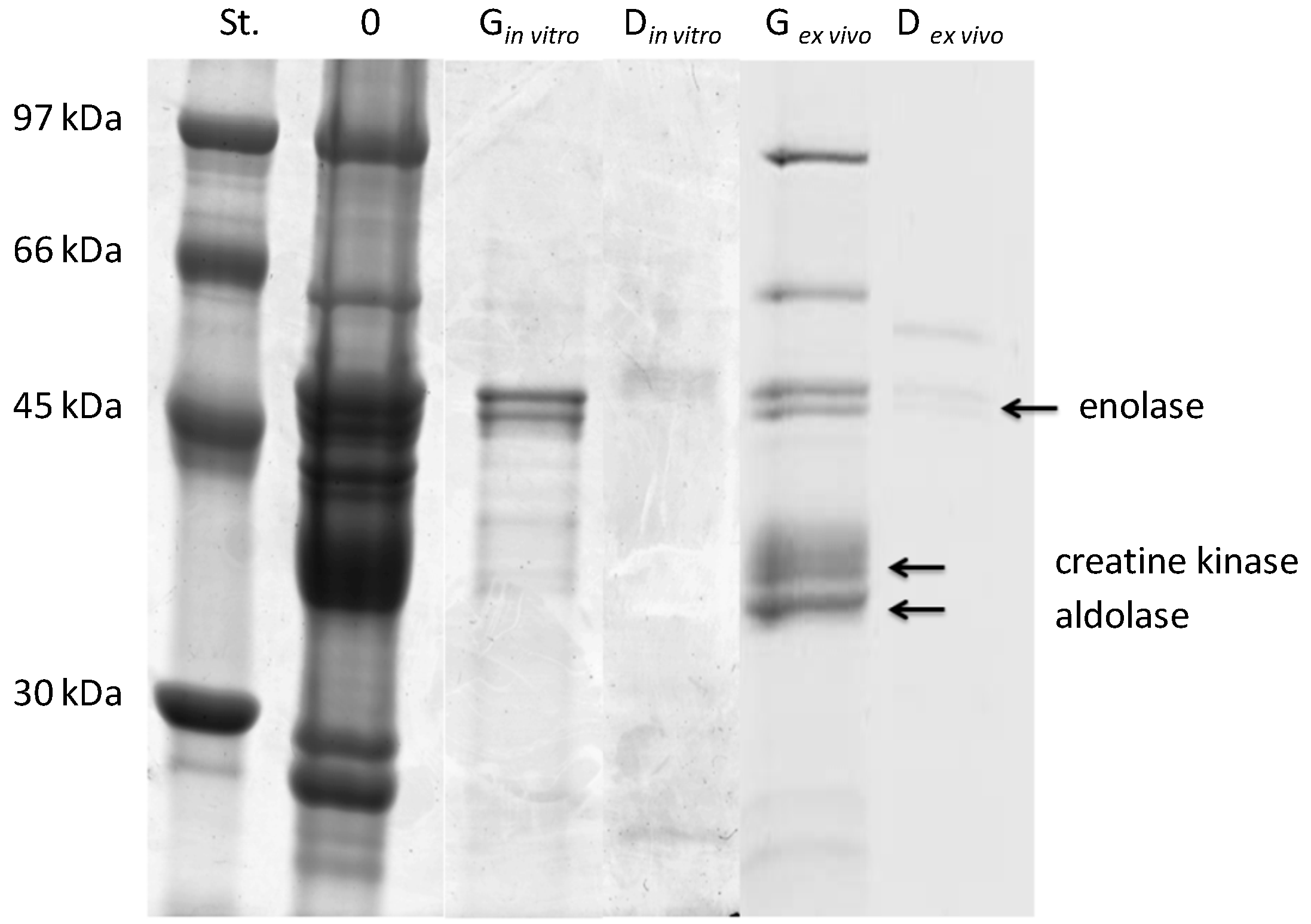
| Hydrolysates | Myofibrillar Proteins | Sarcoplasmic Proteins | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G/Pepsin A | D/Pepsin A and CPP | G/Pepsin A | D/Pepsin A and CPP | |
| Ex vivo digestion | 41.03 ± 1.77 | 9.82 ± 1.54 | 20.06 ± 0.28 | 1.09 ± 0.00 |
| In vitro hydrolysis | 27.73 ± 2.70 | 2.49 ± 0.85 | 5.23 ± 1.17 | 0.44 ± 0.14 |
2.2. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Activity of Hydrolysates
2.3. Identification of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides

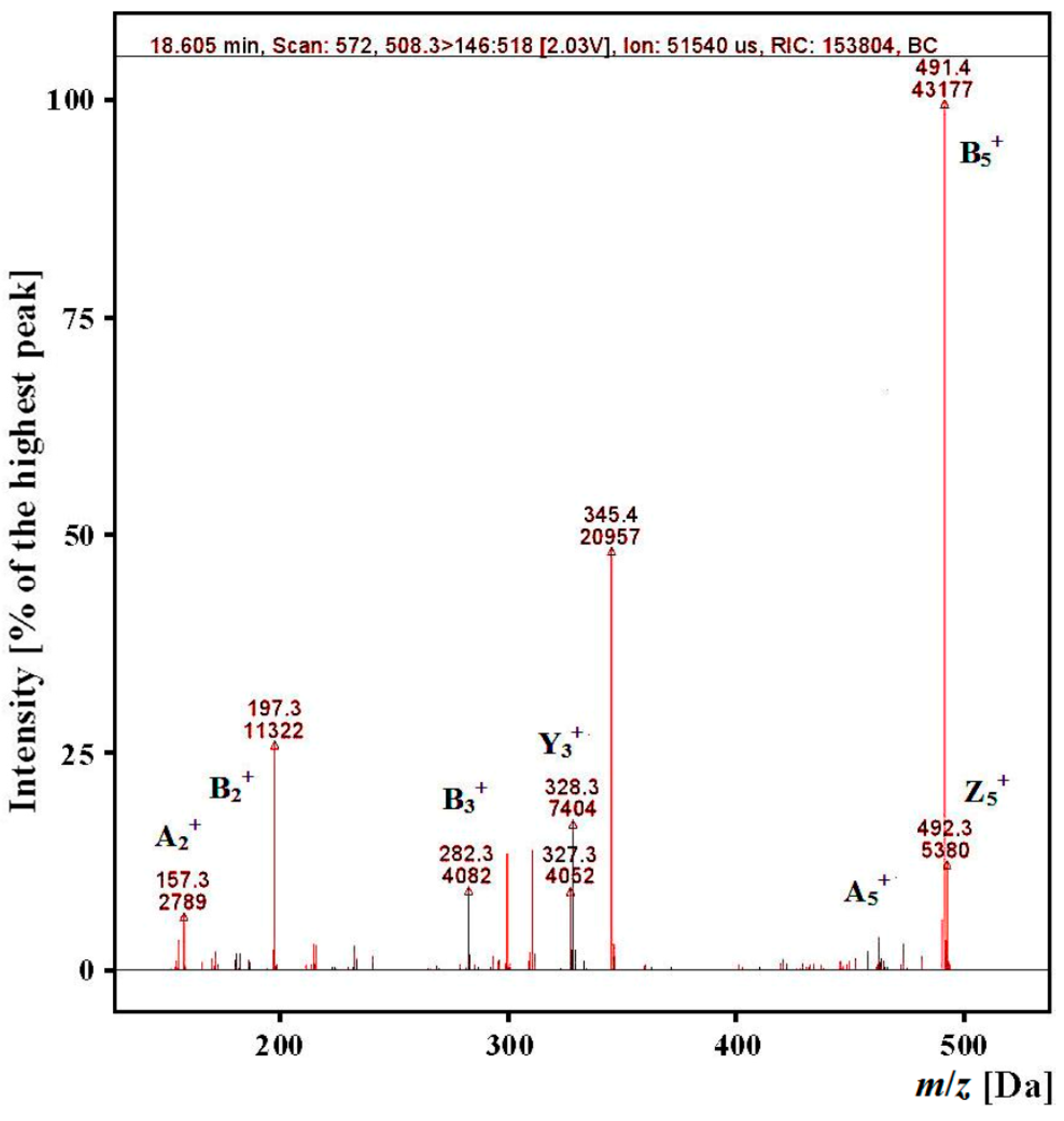
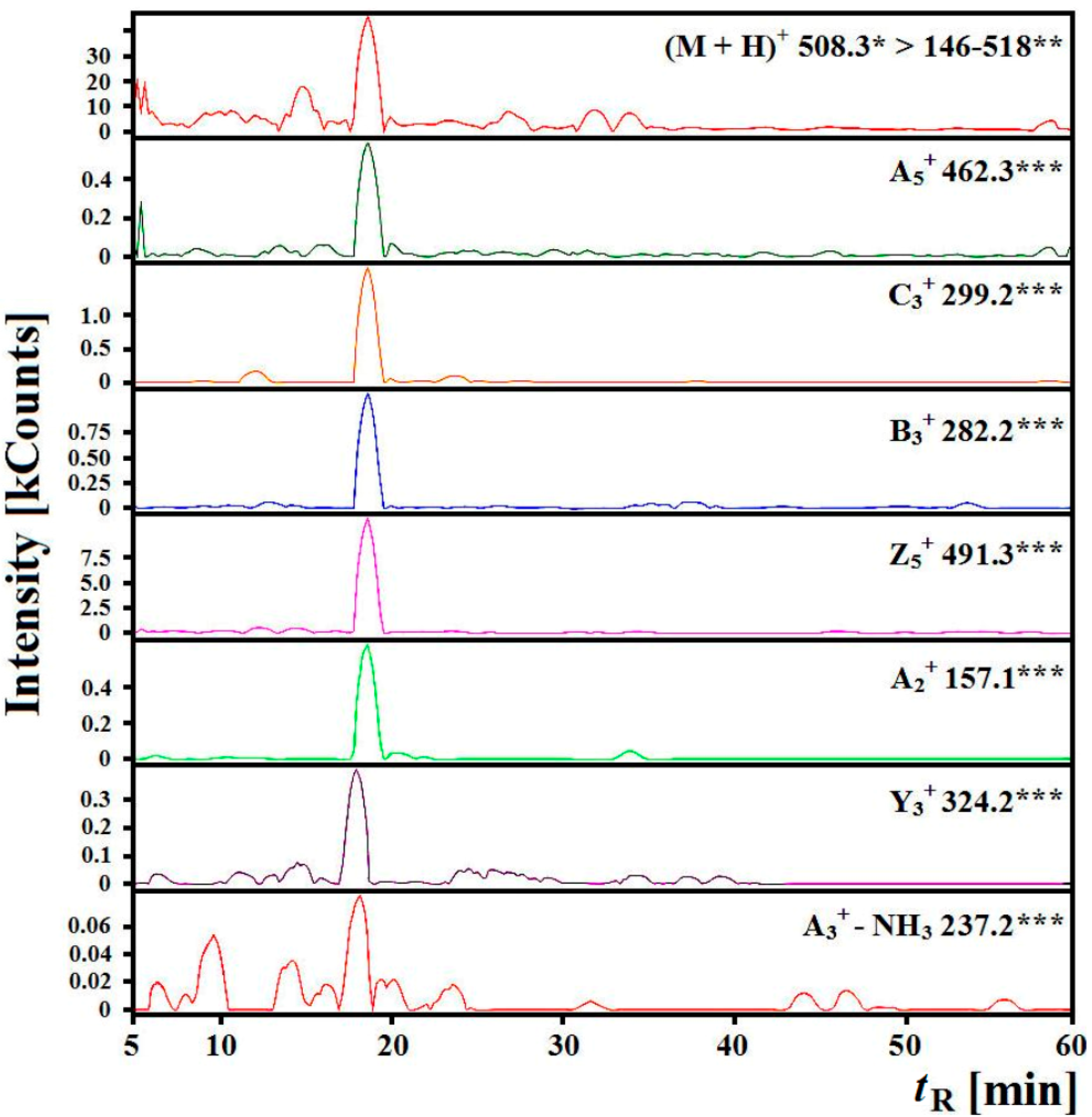
| Sequences | m/z | tR Predicted (min) ** | tR Experimental (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | S | |||
| ALPHA | 508.3 | 17.57 ± 1.76 | 18.59 * | – |
| IVY | 394.2 | – | – | 33.11 * |
| IW | 318.2 | – | 30.82 * | 30.83 * |
| IWHHT | 693.3 | 23.58 ± 2.36 | 25.10 * | – |
| IY | 295.2 | – | 9.51 * | 9.12 * |
| TVY | 382.2 | – | 27.08 * | – |
| VFPS | 449.2 | 24.50 ± 2.45 | nd | – |
| VTVNPYKWLP | 608.8 (2+) | 36.69 ± 3.68 | nd | – |
| VW | 304.2 | – | 21.61 * | nd |
| VY | 281.2 | – | nd | 34.00 |
| YALPHA | 671.4 | 24.04 ± 2.40 | 26.98 | – |


| Sequences | m/z | tR Predicted (min) ** | tR Experimental (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | S | |||
| ALPHA | 508.3 | 17.57 ± 1.76 | nd | – |
| IVY | 394.2 | – | – | nd |
| IW | 318.2 | – | 29.58 * | 31.05 * |
| IWHHT | 693.3 | 23.58 ± 2.36 | 15.79 | – |
| IY | 295.2 | – | 6.61 | 8.29 * |
| TVY | 382.2 | – | 27.26 * | – |
| VFPS | 449.2 | 24.50 ± 2.45 | nd | – |
| VPW | 401.2 | – | 6.15 * | – |
| VTVNPYKWLP | 608.8 (2+) | 36.69 ± 3.68 | 43.15 | – |
| VW | 304.2 | – | 20.79 * | 23.46 |
| VY | 281.2 | – | nd | 15.13 * |
| YALPHA | 671.4 | 24.04 ± 2.40 | 27.88 | – |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. In Silico Assay
3.2.2. Extraction of Myofibryllar Proteins from Salmon Muscle Tissue
3.2.3. Extraction of Sarcoplasmic Proteins from Salmon Muscle Tissue
3.2.4. Ex Vivo Digestion
3.2.5. In Vitro Hydrolysis
3.2.6. Protein Content
3.2.7. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
3.2.8. Angiotensin I-Converting-Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity
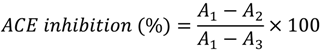
3.2.9. Identification of Bioactive Peptides Using RP–HPLC–MS
3.2.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Darewicz, M.; Dziuba, B.; Minkiewicz, P.; Dziuba, J. The preventive potential of milk and colostrum proteins and protein fragments. Food Rev. Int. 2011, 27, 357–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniak, A.; Minkiewicz, P.; Darewicz, M. Food-originating ACE inhibitors, including antihypertensive peptides, as preventive food components in blood pressure reduction. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 114–134. [Google Scholar]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Dziuba, J.; Darewicz, M.; Iwaniak, A.; Dziuba, M.; Nałęcz, D. Food Peptidomics. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive peptides from marine processing waste and shellfish: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Kumar, B.D.; Hemalatha, R.; Jyothirmayi, T. Fish protein hydrolysates: Proximate composition, amino acid composition, antioxidant activities and applications: A review. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 3020–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.T.; Ross, R.P.; Bolton, D.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Bioactive peptides from muscle sources: Meat and fish. Nutrients 2011, 3, 765–791. [Google Scholar]
- Suetsuna, K.; Osajima, K. The inhibitory activities against angiotensin I-converting enzyme of basic peptides originating from sardine and hair tail meat. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1986, 52, 1981–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, C.; Davenport, M.; Jaczynski, J. Functional and nutritional quality of protein and lipid recovered from fish processing by-products and underutilized aquatic species using isoelectric solubilization/precipitation. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2009, 5, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, L.; van Camp, J.; Smagghe, G. ACE inhibitory peptides derived from enzymatic hydrolysates of animal muscle protein: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8106–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.J.; Je, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Antihypertensive effect of angiotensin I converting enzyme-inhibitory peptide from hydrolysates of Bigeye tuna dark muscle, Thunnus obesus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8398–8403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Qian, Z.J.; Kim, S.K. A novel angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from tuna frame protein hydrolysate and its antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K.; Takahashi, K. Isolation of peptides with angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory effect derived from hydrolysate of upstream chum salmon muscle. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 1611–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K.; Takahashi, K. Inhibition properties of dipeptides from salmon muscle hydrolysate on angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enari, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Kawarasaki, M.; Tada, M.; Tatsuta, K. Identification of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from salmon muscle and their antihypertensive effect. Fish. Sci. 2008, 74, 911–920. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, R.Z.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, W.Y.; Yi, W.X.; Cai, M.Y. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of low-molecular-weight peptides from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) skin. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewart, H.S.; Dennis, D.; Potvin, M.; Tiller, C.; Fang, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, X.; Curtis, J.M.; Cloutier, S.; Du, G.; et al. Development of a salmon protein hydrolysate that lowers blood pressure. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alissa, E.M.; Ferns, G.A. Functional foods and nutraceuticals in the primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases. J. Nutr. Metabol. 2012, 2012, 569486. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau-Ralliard, D.; Goirand, F.; Tardivel, S.; Lucas, A.; Algaron, F.; Mollé, D.; Robert, V.; Auchere, D.; Boudier, J.F.; Gailard, J.L.; et al. Inhibitory effect of αS1- and αS2-casein hydrolysates on angiotensin I-converting enzyme in human endothelial cells in vitro, rat aortic tissue ex vivo, and renovascular hypertensive rats in vivo. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 2906–2921. [Google Scholar]
- Tauzin, J.; Miclo, L.; Gaillard, J.L. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from tryptic hydrolysate of bovine αS2-casein. FEBS Lett. 2002, 531, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loponen, J. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in Finnish cereals: A database survey. Agric. Food Sci. 2004, 13, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, M.; Oe, M.; Ogura, K.; Matsumura, S. Inhibition strength of short peptides derived from an ACE inhibitory peptide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11234–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauchart, C.; Morzel, M.; Chambon, C.; Mirand, P.P.; Reynès, C.; Buffière, C.; Rèmond, D. Peptides reproducibly released by in vivo digestion of beef meat and trout flesh in pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama, K.; Chiba, H.; Yoshikawa, M. Peptide inhibitors for angiotensin I-converting enzyme from thermolysin digest of dried bonito. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1992, 56, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Yokoyama, K.; Yoshikawa, M. Classification and antihypertensive activity of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakano, T.; Muramoto, K.; Kahara, T.; Funayama, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Nakano, T. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) and their antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6245–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczak, E.D.; Usui, H.; Fujita, H.; Yang, Y.; Yokoo, M.; Lipkowski, A.W.; Yoshikawa, M. New antihypertensive peptides isolated from rapeseed. Peptides 2003, 24, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, K.; Yoshida, C.; Suzuki, K.; Maruyama, H.; Futamura, Y.; Araki, Y.; Mishima, S. Antihypertensive effect of peptides from royal jelly in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Dziuba, J.; Minkiewicz, P.; Mogut, D. Determination of theoretical retention times for peptides analyzed by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2011, 10, 209–221. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A.; Claassen, M.; Aebersold, R. Directed mass spectrometry: Towards hypothesis-driven proteomics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2009, 13, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Dziuba, J.; Darewicz, M.; Iwaniak, A. Online programs and databases of peptides and proteolytic enzymes—A brief update for 2007–2008. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 47, 345–355. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, C.; Haslam, N.J.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C. Towards the improved discovery and design of functional peptides: Common features of diverse classes permit generalized prediction of bioactivity. PLoS One 2012, 7, e45012. [Google Scholar]
- Jimsheena, V.K.; Gowda, L.R. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from arachin by simulated gastric digestion. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.L.; Sanders, T.H.; Davis, J.P. Potential ACE-inhibitory activity and nanoLC–MS/MS sequencing of peptides derived from aflatoxin contaminated peanut meal. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 56, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroga, A.V; Aphalo, P.; Ventureira, J.L.; Martínez, E.N.; Añón, M.C. Physicochemical, functional and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory properties of amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) 7S globulin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 397–403. [Google Scholar]
- Welderufael, F.T.; Gibson, T.; Methven, L.; Jauregi, P. Chemical characterisation and determination of sensory attributes of hydrolysates produced by enzymatic hydrolysis of whey proteins following a novel integrative process. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.C.; Abdullah, N.; Shuib, A.S.; Aminudin, N. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from edible mushroom Agaricus bisporus (J.E. Lange) Imbach identified by LC–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 396–401. [Google Scholar]
- Thewissen, B.G.; Pauly, A.; Celus, I.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Inhibition of angiotensin I-converting enzyme by wheat gliadin hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Vercruysse, L.; Smagghe, G.; van der Bent, A.; van Amerongen, A.; Ongenaert, M.; van Camp, J. Critical evaluation of the use of bioinformatics as a theoretical tool to find high-potential sources of ACE inhibitory peptides. Peptides 2009, 30, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojagh, S.M.; Núñez-Flores, R.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Montero, M.P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Lessening of high-pressure-induced changes in Atlantic salmon muscle by the combined use of a fish gelatin–lignin film. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 595–606. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, I.; Slizyte, R.; Dauksas, E. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis as a tool to differentiate wild from farmed cod (Gadus morhua) and to assess the protein composition of klipfis. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 504–510. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.F.; Lyu, Y.C.; Wu, Y.J.; Lu, C.H.; Hwang, D.-F. Species identification of snapper: A food poisoning incident in Taiwan. Food Control 2012, 25, 511–515. [Google Scholar]
- Almaas, H.; Eriksen, E.; Sekse, C.; Comi, I.; Flengsrud, R.; Holm, H.; Jensena, E.; Jacobsena, M.; Langsruda, T.; Vegarud, G.E. Antibacterial peptides derived from caprine whey proteins, by digestion with human gastrointestinal juice. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglingstad, R.A.; Devold, T.G.; Eriksen, E.K.; Holm, H.; Jacobsen, M.; Liland, K.H.; Rukke, E.O.; Vegarud, G.E. Comparison of the digestion of caseins and whey proteins in equine, bovine, caprine and human milks by human gastrointestinal enzymes. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2010, 90, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, E.K.; Holm, H.; Jensen, E.; Aaboe, R.; Devold, T.G.; Jacobsen, M.; Jacobsen, M.; Vegarud, G.E. Different digestion of caprine whey proteins by human and porcine gastrointestinal enzymes. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 374–381. [Google Scholar]
- Khantaphant, S.; Benjakul, S.; Ghomi, M.R. The effects of pretreatments on antioxidative activities of protein hydrolysate from the muscle of brownstripe red snapper (Lutjanus vitta). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Yoshie-Stark, Y.; Ogushi, M. Comparison of ACE inhibitory and DPPH radical scavenging activities of fish muscle hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roepstorff, P.; Fohlman, J. Proposal for a common nomenclature for sequence ions in mass spectra of peptides. Biomed. Mass Spectrom. 1984, 11, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Liang, C.H.; Tanaka, T.; Maki, T.; Osajima, Y.; Matsumoto, K. Depressor effect of wheat germ hydrolysate and its novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide, Ile-Val-Tyr, and the metabolism in rat and human plasma. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, G.; Ogurtsov, A.Y.; Kwok, S.; Wu, W.W.; Wang, G.; Shen, R.F.; Yu, Y.-K. Detection of co-eluted peptides using database search methods. Biol. Direct 2008, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, J.; Zinn, N.; Boehm, M.E.; Lehmann, W.D. De novo sequencing of peptides by MS/MS. Proteomics 2010, 10, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebarle, P.; Verkerk, U.H. Electrospray: From ions in solution to ions in the gas phase, what we know now. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2009, 28, 898–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.E.; Baumgartner, S.; Aldick, T.; Bessant, C.; Giosafatto, V.; Heick, J.; Mamone, G.; O’Connor, G.; Poms, R.; Popping, B.; et al. Current perspectives and recommendations for the development of mass spectrometry methods for the determination of allergens in foods. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Miciński, J.; Darewicz, M.; Bucholska, J. Biological and chemical databases for research into the composition of animal source foods. Food Rev. Int. 2013, 29, 321–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulesteix, A.-L. Over-optimism in bioinformatics research. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulipano, G.; Sibilia, V.; Caroli, A.M.; Cocchi, D. Whey proteins as source of dipeptidyl dipeptidase IV (dipeptidyl peptidase-4) inhibitors. Peptides 2011, 32, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, J.M.; Ortea, I.; Carrera, M. Proteomics and its applications for food authentication and food-technology research. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 52, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, P.; Schirle, M.; Chen, S.S.; Flory, M.R.; Lee, H.; Martin, D.; Ranish, J.; Raught, B.; Schmitt, R.; Werner, T.; et al. Computational prediction of proteotypic peptides for quantitative proteomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darewicz, M.; Minkiewicz, P.; Dziuba, M.; Panfil, T. Application of second and fourth derivatives of UV spectra to identify low molecular weight products of β-casein hydrolysis by plasmin. Zywnosc. Nauk. Technol. Jakosc. 2012, 4, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Udenigwe, C.C.; Howard, A. Meat proteome as source of functional biopeptides. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Szabó, A.; Sahin-Tóth, M. Determinants of chymotrypsin C cleavage specificity in the calcium-binding loop of human cationic trypsinogen. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 4283–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S.J.; Lim, B.O.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. In vitro human digestion models for food applications. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt database. Available online: http://www.uniprot.org (accessed between March and June 2012).
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClustalW2-Multiple Sequence Alignment software. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/ (accessed between March and June 2012).
- Minkiewicz, P.; Dziuba, J.; Iwaniak, A.; Dziuba, M.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP database and other programs for processing bioactive peptide sequences. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 965–981. [Google Scholar]
- BIOPEP database. Available online: http://uwm.edu.pl/biochemia (accessed between July and October 2012).
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; Piñeiro, C.; Vázquez, J.; Gallardo, J.M. Identification of commercial hake and grenadier species by proteomic analysis of the parvalbumin fraction. Proteomics 2006, 6, 5278–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaas, H.; Cases, A.-L.; Devold, T.G.; Holm, H.; Langsrud, T.; Aabakken, L.; Aadnoeyd, T.; Vegaruda, G.E. In vitro digestion of bovine and caprine milk by human gastric and duodenal enzymes. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaas, H.; Holm, H.; Langsrud, T.; Flengsrud, R.; Vegarud, G.E. In vitro studies of the digestion of caprine whey proteins by human gastric and duodenal juice and the effects on selected microorganisms. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 96, 562–569. [Google Scholar]
- Ulleberg, E.K.; Comi, I.; Holm, H.; Herud, E.B.; Jacobsen, M.; Vegarud, G.E. Human gastrointestinal juices intended for use in in vitro digestion models. Food Dig. 2011, 2, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Chiang, L.; Cisternas, E.; Ponce, O. Partial purification of pepsins from adult and juvenile salmon fish Oncorhynchus keta. Effect of NaCl on proteolytic activities. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1987, 87, 793–797. [Google Scholar]
- Krogdahl, A.; Holm, H. Inhibition of human and rat pancreatic proteinases by crude and purified soybean proteinase inhibitors. J. Nutr. 1979, 109, 551–558. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschenbaum, D.M. Molar absorptivity and A1% 1 cm values for proteins at selected wavelengths of the ultraviolet and visible regions. XI. Anal. Biochem. 1975, 68, 465–484. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimsheena, V.K.; Gowda, L.R. Colorimetric, high-throughput assay for screening angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9388–9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Sakai, K.; Okubo, A.; Yamazaki, S.; Takano, T. Purification and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors from sour milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniak, A. Analysis of relationship between the structure and ACE inhibitory activity food derived peptides. The evaluation of suitability of in silico methods in the research on protein precursors of bioactive peptides. Olsztyn UW-M Olsztyn 2011, 162, 1–152. [Google Scholar]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krokhin, O. V Sequence-specific retention calculator. Algorithm for peptide retention prediction in ion-pair RP-HPLC: Application to 300- and 100-A pore size C18 sorbents. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 7785–7795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, V.; Yamchuk, A.; Cortens, J.; Sousa, S.; Ens, W.; Standing, K.G.; Wilkins, J.A.; Krokhin, O.V. Sequence-specific retention calculator. A family of peptide retention time prediction algorithms in reversed-phase HPLC: Applicability to various chromatographic conditions and columns. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8762–8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequence Specific Retention Calculator. SSRCalc Software. Available online: http://hs2.proteome.ca/SSRCalc/SSRCalcX.html (accessed between March and May 2013).
- Fragment Ion Calculator application. Available online: http://db.systemsbiology.net:8080/proteomicsToolkit/FragIonServlet.html (accessed between March and May 2013).
- Monaci, L.; Losito, I.; Palmisano, F.; Visconti, A. Reliable detection of milk allergens in food using a high-resolution, stand-alone mass spectrometer. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Darewicz, M.; Borawska, J.; Vegarud, G.E.; Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity and ACE Inhibitory Peptides of Salmon (Salmo salar) Protein Hydrolysates Obtained by Human and Porcine Gastrointestinal Enzymes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 14077-14101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150814077
Darewicz M, Borawska J, Vegarud GE, Minkiewicz P, Iwaniak A. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity and ACE Inhibitory Peptides of Salmon (Salmo salar) Protein Hydrolysates Obtained by Human and Porcine Gastrointestinal Enzymes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(8):14077-14101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150814077
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarewicz, Małgorzata, Justyna Borawska, Gerd E. Vegarud, Piotr Minkiewicz, and Anna Iwaniak. 2014. "Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity and ACE Inhibitory Peptides of Salmon (Salmo salar) Protein Hydrolysates Obtained by Human and Porcine Gastrointestinal Enzymes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 8: 14077-14101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150814077
APA StyleDarewicz, M., Borawska, J., Vegarud, G. E., Minkiewicz, P., & Iwaniak, A. (2014). Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity and ACE Inhibitory Peptides of Salmon (Salmo salar) Protein Hydrolysates Obtained by Human and Porcine Gastrointestinal Enzymes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(8), 14077-14101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150814077








