A Sensitive and Effective Proteomic Approach to Identify She-Donkey’s and Goat’s Milk Adulterations by MALDI-TOF MS Fingerprinting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
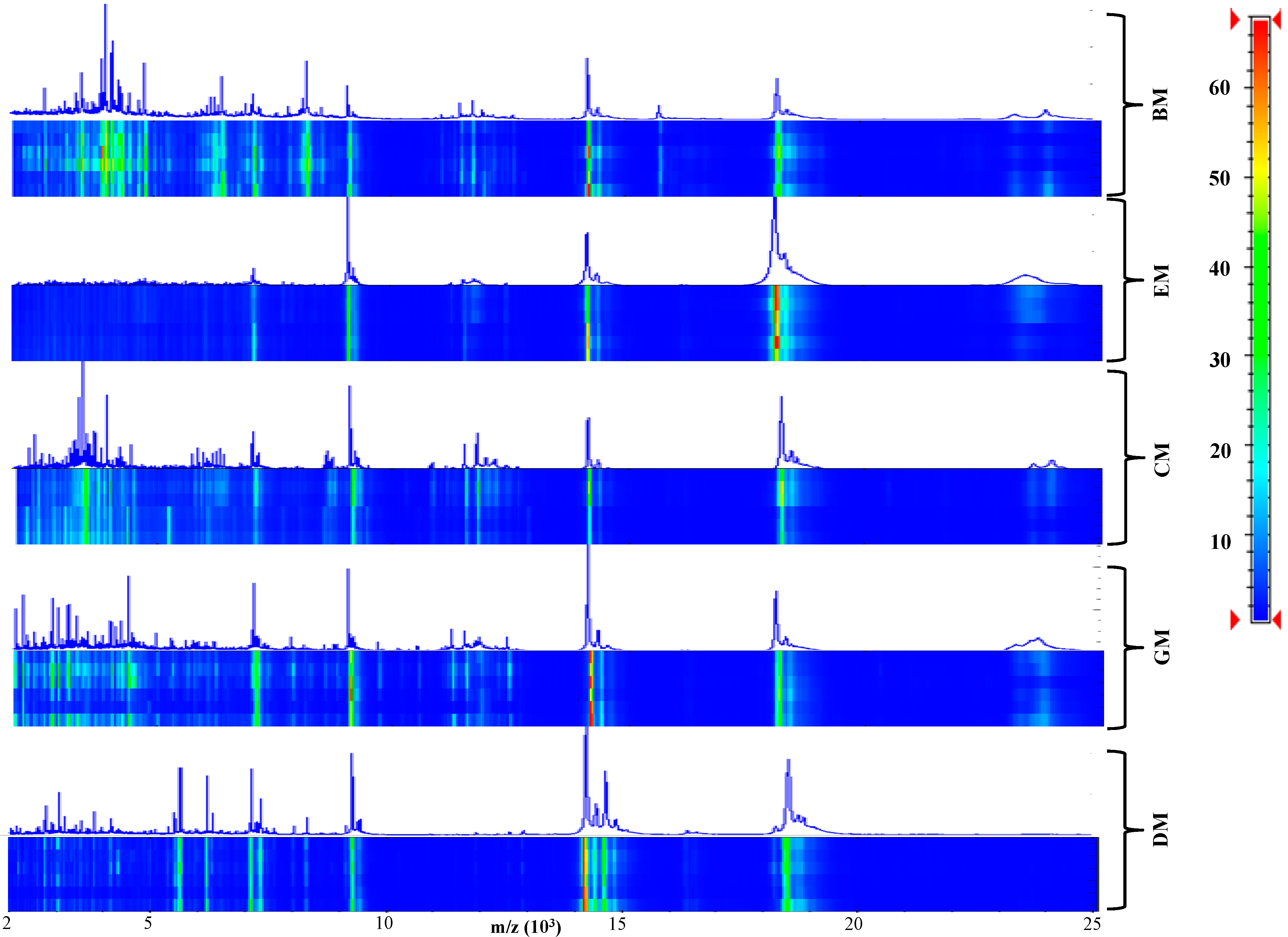
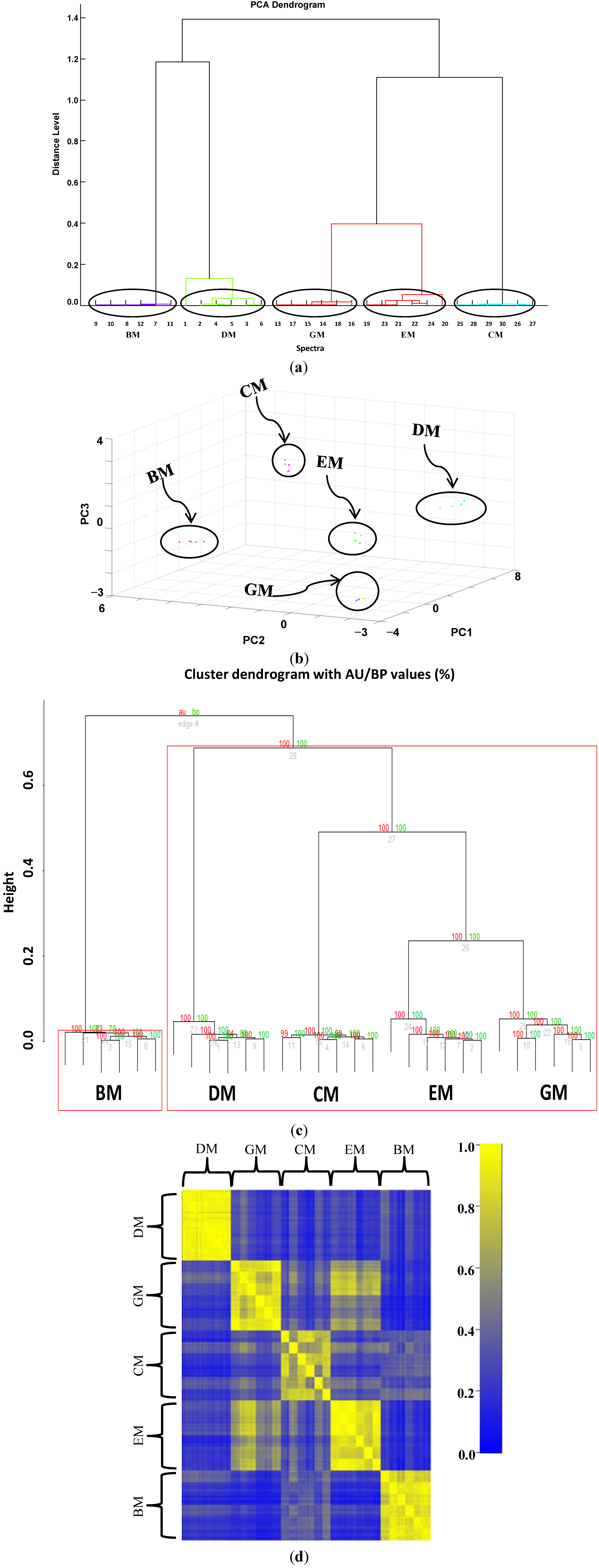
2.1. Assessing the Performance of the MALDI-TOF MS Profiles in Discriminating Milk Species
2.2. Assessing the Performance of the MALDI-TOF MS Profiles in Discriminating She-Donkey’s Milk (DM) and Goat’s Milk (GM) Adulteration with Cow’s Milk (CM)
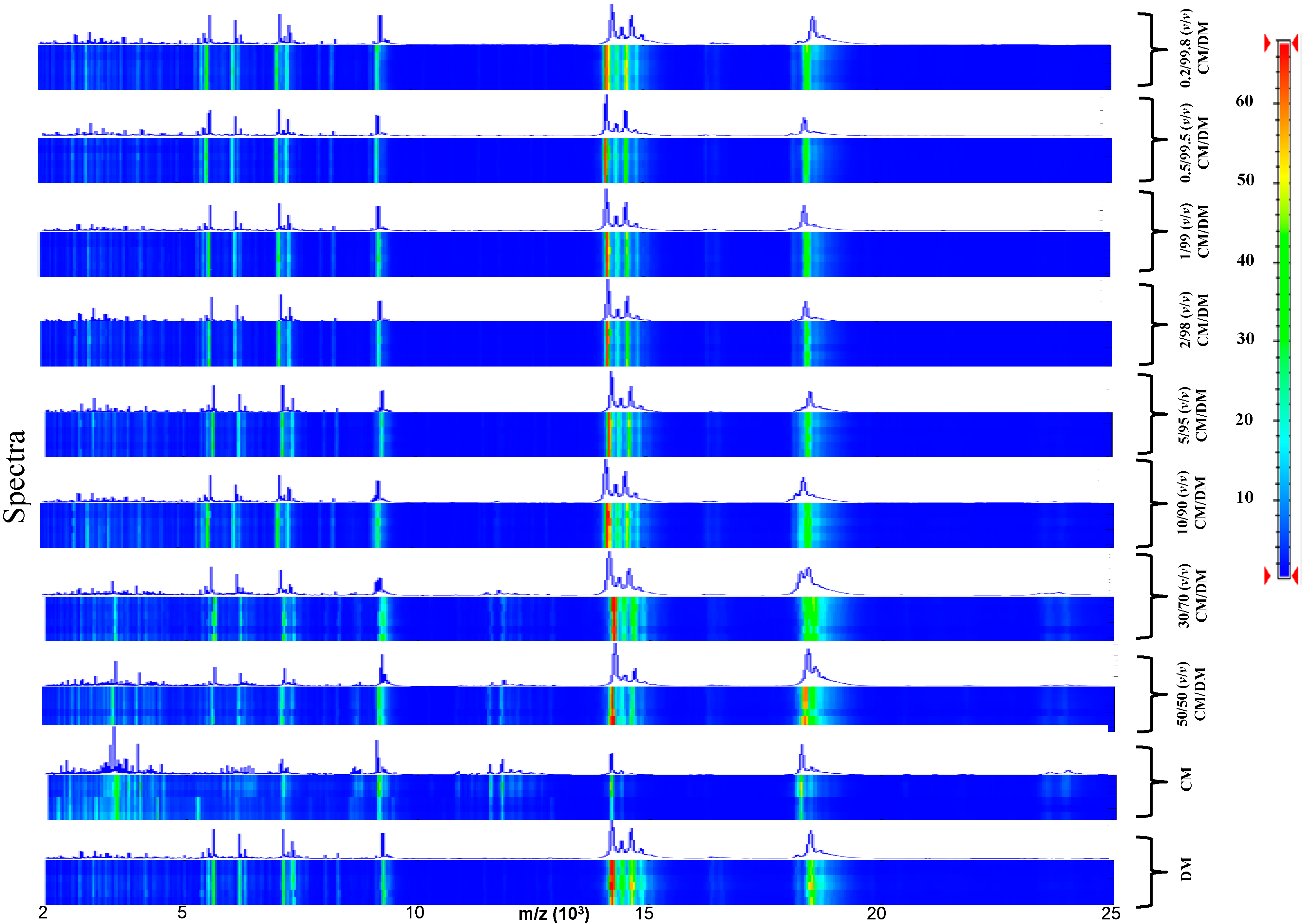
| Adulteration | 50/50 (v/v) | 30/70 (v/v) | 10/90 (v/v) | 5/95 (v/v) | 2/98 (v/v) | 1/99 (v/v) | 0.5/99.5 (v/v) | 0.2/99.8 (v/v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM/DM | √ 0.720 | √ 0.907 | √ 0.961 | √ 0.921 | √ 0.902 | √ 0.954 | √ 0.885 | × 0.946 |
| CM/GM | √ 0.782 | √ 0.854 | √ 0.908 | √ 0.967 | √ 0.961 | √ 0.968 | √ 0.974 | × 0.961 |
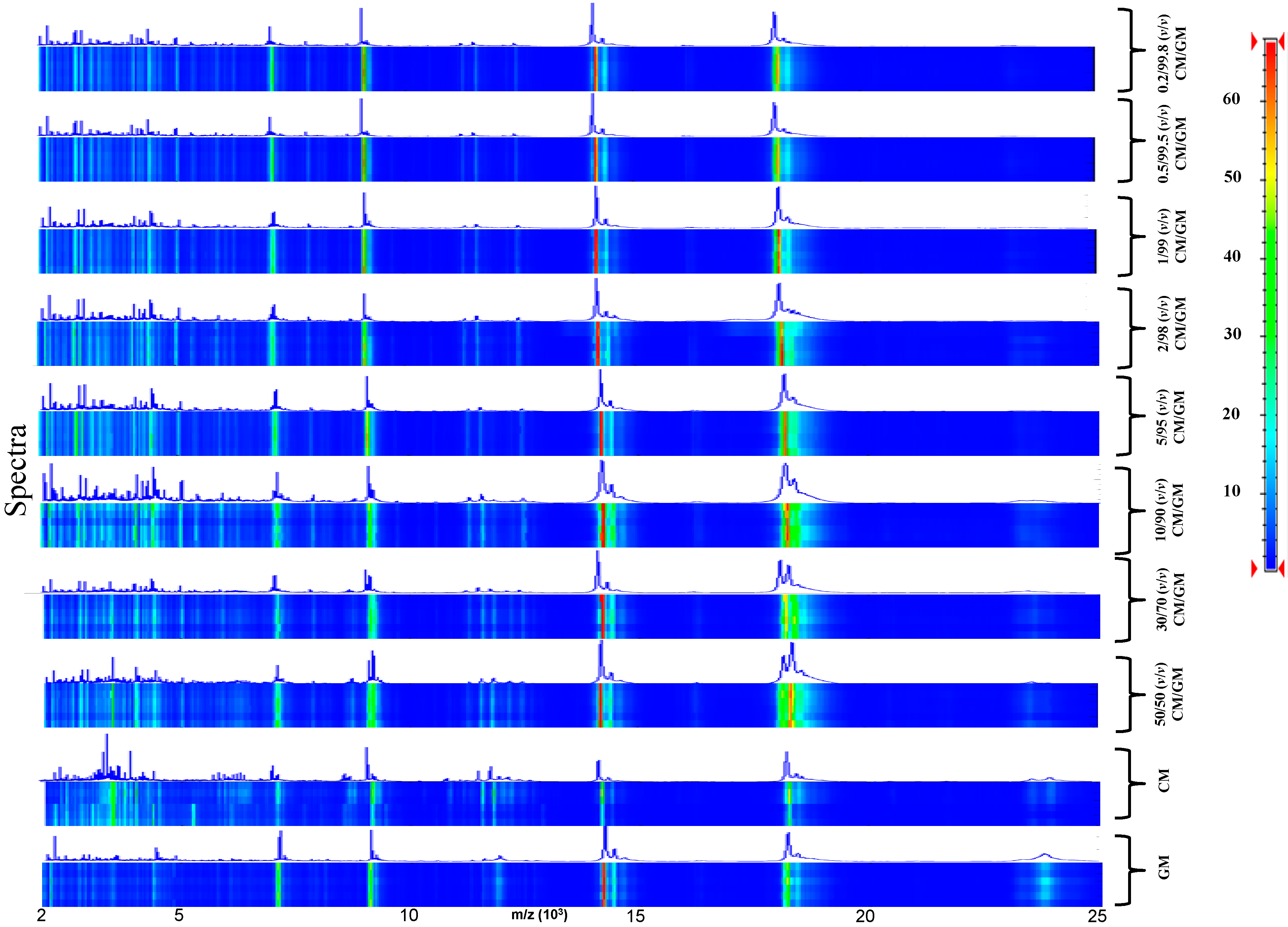
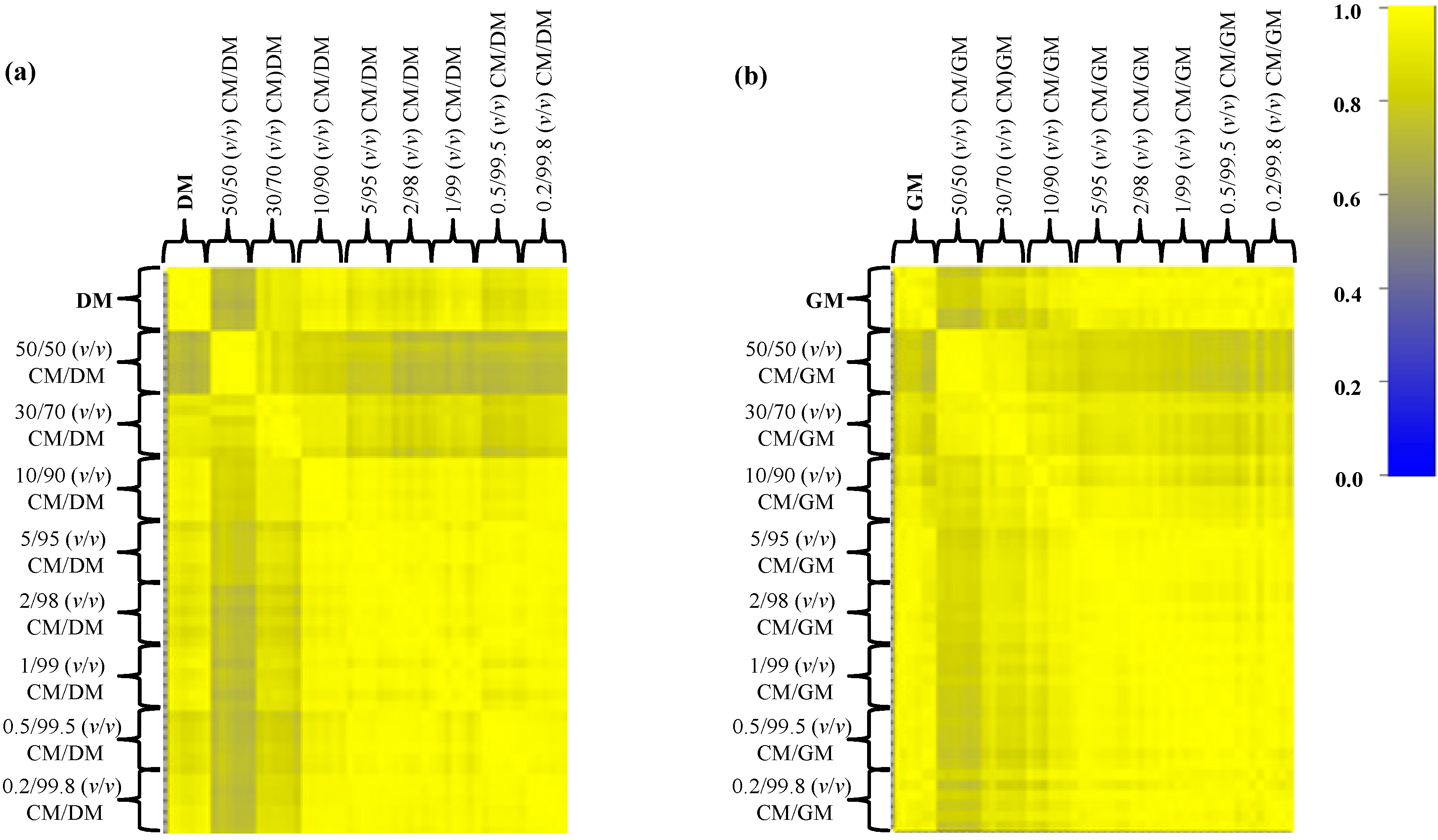
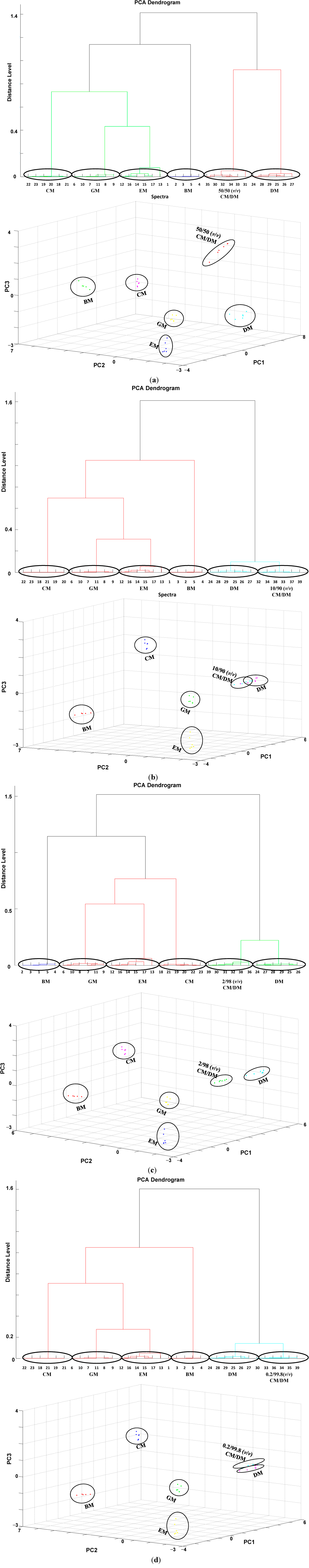
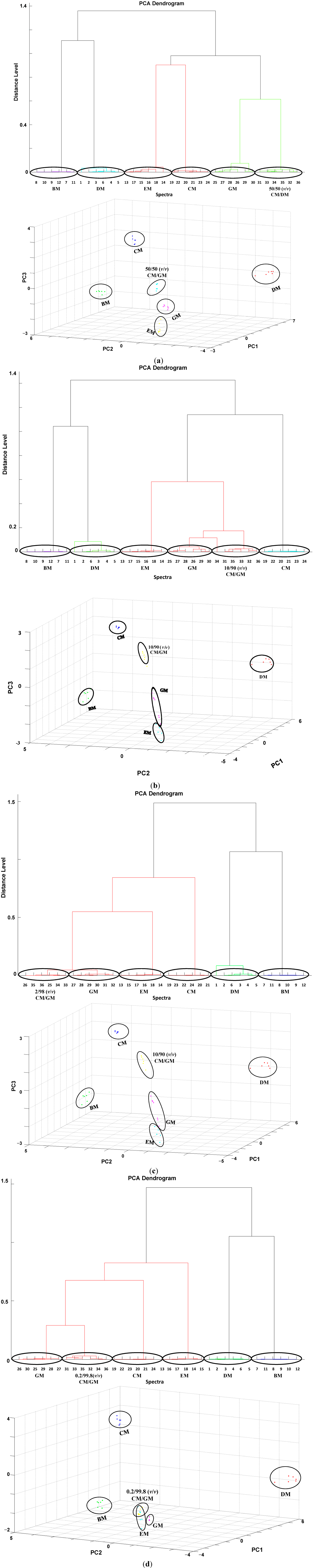
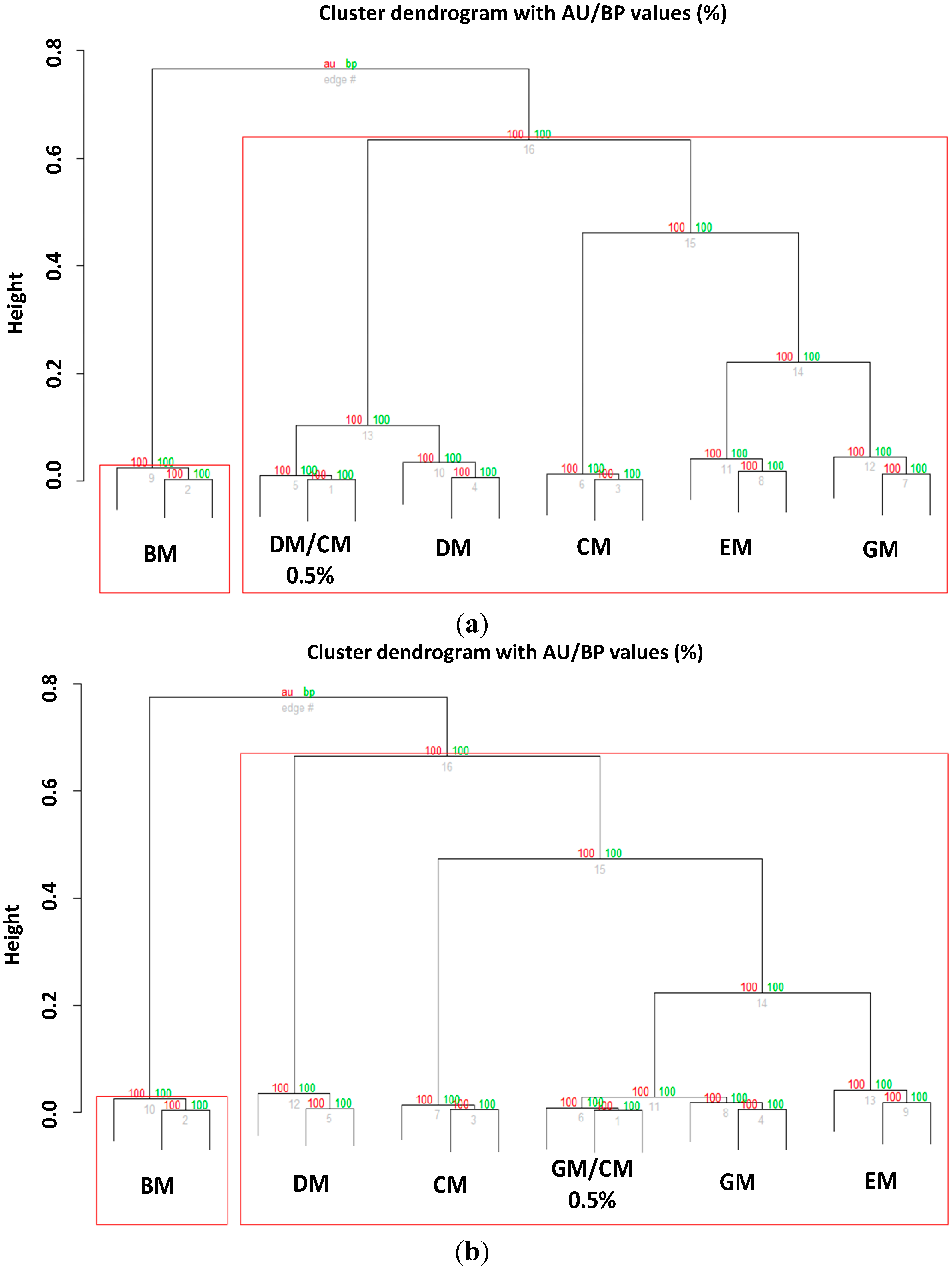
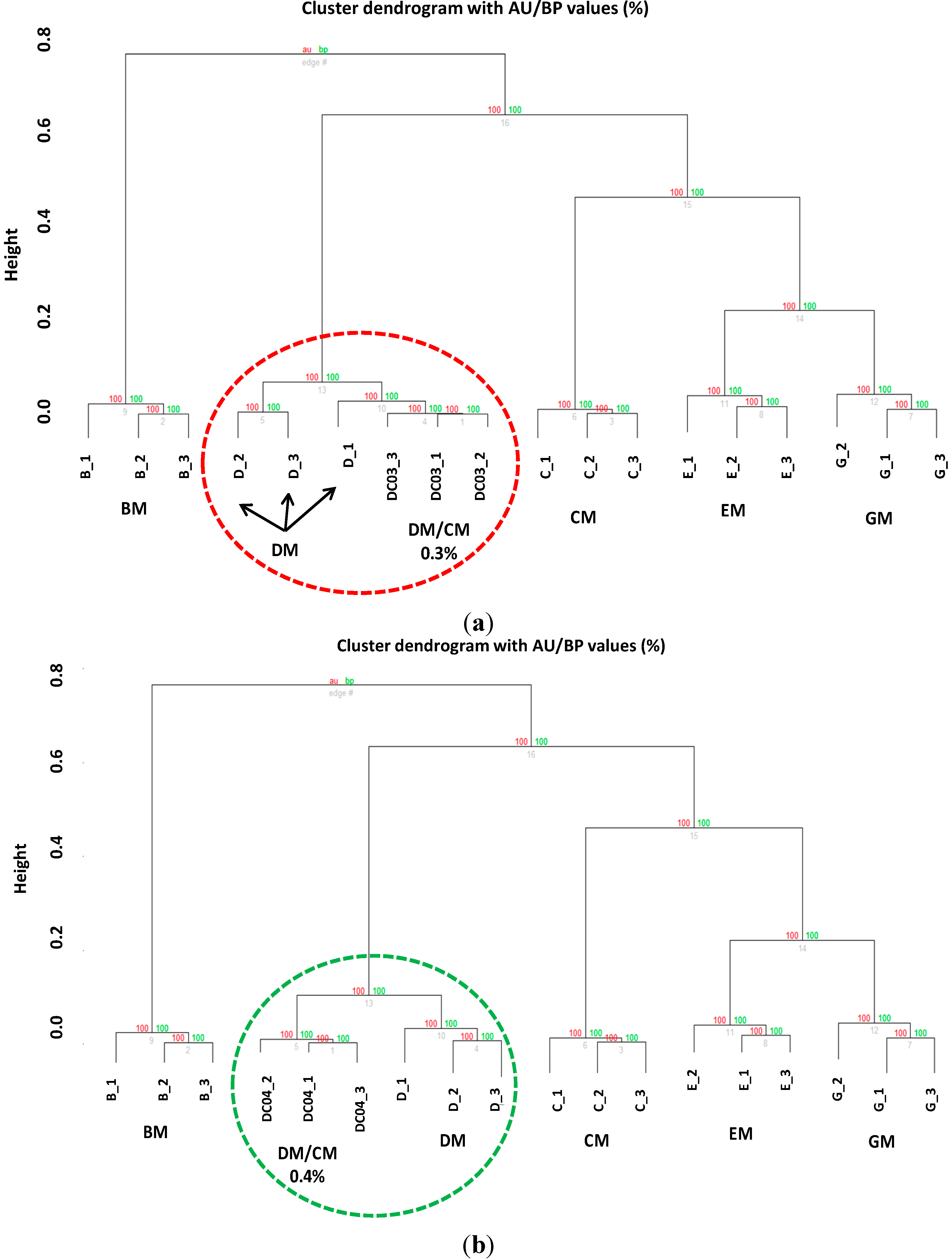
2.3. Assessing the Performance of the MALDI-TOF MS Profiles in Discriminating DM and GM Adulteration with EM and BM
| Adulteration | 50/50 (v/v) | 30/70 (v/v) | 10/90 (v/v) | 5/95 (v/v) | 2/98 (v/v) | 1/99 (v/v) | 0.5/99.5 (v/v) | 0.2/99.8 (v/v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM/DM | √ 0.664 | √ 0.804 | √ 0.959 | √ 0.974 | √ 0.984 | √ 0.967 | √ 0.888 | √ 0.895 |
| EM/GM | √ 0.846 | √ 0.902 | √ 0.891 | √ 0.823 | √ 0.871 | √ 0.790 | √ 0.878 | × 0.964 |
| BM/DM | √ 0.644 | √ 0.813 | √ 0.948 | √ 0.969 | √ 0.954 | √ 0.983 | √ 0.978 | √ 0.957 |
| BM/GM | √ 0.583 | √ 0.754 | √ 0.822 | √ 0.876 | √ 0.873 | √ 0.805 | √ 0.828 | √ 0.778 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Milk Sampling and Preparation
3.2. MALDI-TOF MS Spectra Acquisition
3.3. MALDI-TOF MS Spectra Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salimei, E.; Fantuz, F. Equid milk for human consumption. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 24, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncada, P.; Gaviraghi, A.; Liberatori, S.; Canas, B.; Bini, L.; Greppi, G.F. Identification of caseins in goat milk. Proteomics 2002, 2, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W. Hypo-allergenic & therapeutic significance of goat milk. Small Rumin. Res. 1994, 14, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, G.; Carroccio, A.; Cavataio, F.; Montalto, G.; Soresi, M.; Balsamo, V. Use of ass’s milk in multiple food allergy. JPGN 1992, 14, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Addeo, F.; Pizzano, R.; Nicolai, M.A.; Caira, S.; Chianese, L. Fast isoelectric focusing and antipeptide antibodies for detecting bovine casein in adulterated water buffalo milk and derived mozzarella cheese. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10063–10066. [Google Scholar]
- Enne, G.; Elez, D.; Fondrini, F.; Bonizzi, I.; Feligini, M.; Aleandri, R. High performance liquid chromatography of governing liquid to detect illegal bovine milk’s addition in water buffalo mozzarella: Comparison with results from raw milk and cheese matrix. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1094, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunsolo, V.; Muccilli, V.; Saletti, R.; Foti, S. Applications of mass spectrometry techniques in the investigation of milk proteome. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 17, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, R.; Passalacqua, S.; Salemi, S.; Garozzo, D. Identification of adulteration in water buffalo mozzarella and in ewe cheese by using whey proteins as biomarkers and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 37, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwenka, C.; Muller, L.; Lindner, W. Detection of the adulteration of water buffalo milk and mozzarella with cow’s milk by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of β-lactoglobulin variants. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 901–908. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.K.; Chang, L.W.; Chung, Y.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Ling, Y.C. Quantification of cow milk adulteration in goat milk using high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunsolo, V.; Cairone, E.; Muccilli, V.; Saletti, R.; Foti, S. Sequence and phosphorylation level determination of two donkey β-caseins by mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 13, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar]
- Cunsolo, V.; Cairone, E.; Fontanini, D.; Criscione, A.; Muccilli, V.; Saletti, R.; Foti, S. Sequence determination of αs1-casein isoforms from donkey by mass spectrometry methods. J. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 44, 1742–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Cunsolo, V.; Muccilli, V.; Fasoli, E.; Saletti, R.; Righetti, P.G.; Foti, S. Poppea’s bath liquor: The secret proteome of she-donkey’s milk. J. Proteomics 2011, 74, 2083–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saletti, R.; Muccilli, V.; Cunsolo, V.; Fontanini, D.; Capocchi, A.; Foti, S. MS-based characterization of αs2-casein isoforms in donkey’s milk. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, M.G.; Cantisani, A.; Napolitano, L.; Conti, A.; Godovac-Zimmermann, J. The amino acid sequence of two isoforms of α-lactalbumin from donkey (Equus asinus) milk is identical. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 1992, 373, 931–935. [Google Scholar]
- Godovac-Zimmermann, J.; Conti, A.; Napolitano, L. The primary structure of donkey (Equus asinus) lysozyme contains the Ca(II) binding site of α-lactalbumin. Biol. Chem. 1988, 369, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Herrouin, M.; Mollé, D.; Fauquant, J.; Ballestra, F.; Maubois, J.L.; Leonil, J. New genetic variants identified in donkey’s milk whey proteins. J. Protein Chem. 2000, 19, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godovac-Zimmermann, J.; Conti, A.; James, L.; Napolitano, L. Microanalysis of the amino-acid sequence of monomeric β-lactoglobulin I from Donkey (Equus asinus) milk. Biol. Chem. 1988, 369, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, R.; Passalacqua, S.; Salemi, S.; Malvagna, P.; Spina, E.; Garozzo, D. Identification of adulteration in milk by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 36, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunsolo, V.; Muccilli, V.; Saletti, R.; Foti, S. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the monitoring of she-donkey’s milk contamination or adulteration. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 48, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanton, C.; Delogu, G.; Maccioni, E.; Podda, G.; Seraglia, R.; Traldi, P. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry in the dairy industry 2. The protein fingerprint of ewe cheese and its application to detection of adulteration by bovine milk. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1998, 12, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar]
- Calvano, C.D.; de Ceglie, C.; Monopolia, A.; Zambonina, C.G. Detection of sheep and goat milk adulterations by direct MALDI-TOF MS analysis of milk tryptic digests. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putignani, L.; del Chierico, F.; Onori, M.; Mancinelli, L.; Argentieri, M.; Bernaschi, P.; Coltella, L.; Lucignano, B.; Pansani, L.; Ranno, S.; et al. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry proteomic phenotyping of clinically relevant fungi. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentleman, R.C.; Carey, V.J.; Bates, D.M.; Bolstad, B.; Dettling, M.; Dudoit, S.; Ellis, B.; Gautier, L.; Ge, Y.; Gentry, J.; et al. Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Girolamo, F.; Masotti, A.; Salvatori, G.; Scapaticci, M.; Muraca, M.; Putignani, L. A Sensitive and Effective Proteomic Approach to Identify She-Donkey’s and Goat’s Milk Adulterations by MALDI-TOF MS Fingerprinting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 13697-13719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150813697
Di Girolamo F, Masotti A, Salvatori G, Scapaticci M, Muraca M, Putignani L. A Sensitive and Effective Proteomic Approach to Identify She-Donkey’s and Goat’s Milk Adulterations by MALDI-TOF MS Fingerprinting. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(8):13697-13719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150813697
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Girolamo, Francesco, Andrea Masotti, Guglielmo Salvatori, Margherita Scapaticci, Maurizio Muraca, and Lorenza Putignani. 2014. "A Sensitive and Effective Proteomic Approach to Identify She-Donkey’s and Goat’s Milk Adulterations by MALDI-TOF MS Fingerprinting" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 8: 13697-13719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150813697
APA StyleDi Girolamo, F., Masotti, A., Salvatori, G., Scapaticci, M., Muraca, M., & Putignani, L. (2014). A Sensitive and Effective Proteomic Approach to Identify She-Donkey’s and Goat’s Milk Adulterations by MALDI-TOF MS Fingerprinting. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(8), 13697-13719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150813697







