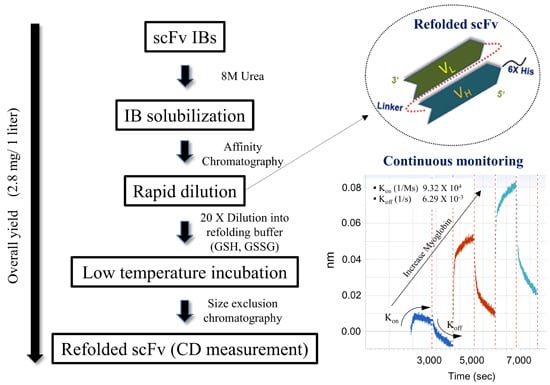
Refolded scFv Antibody Fragment against Myoglobin Shows Rapid Reaction Kinetics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Construction and Expression of 2-7ds scFv for the E. coli System
2.2. Inclusion Body Isolation and Solubilization of the Recombinant Protein scFv

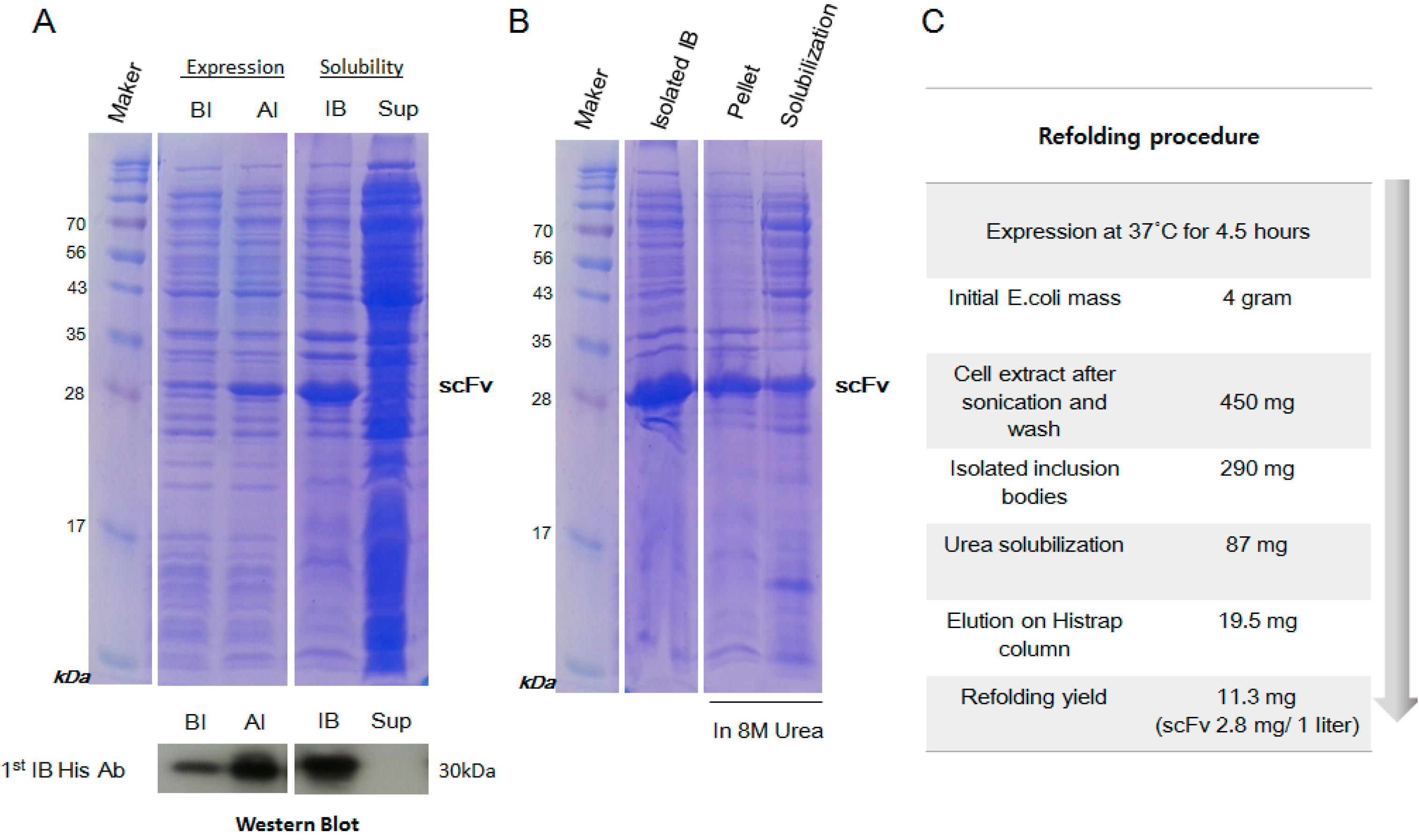
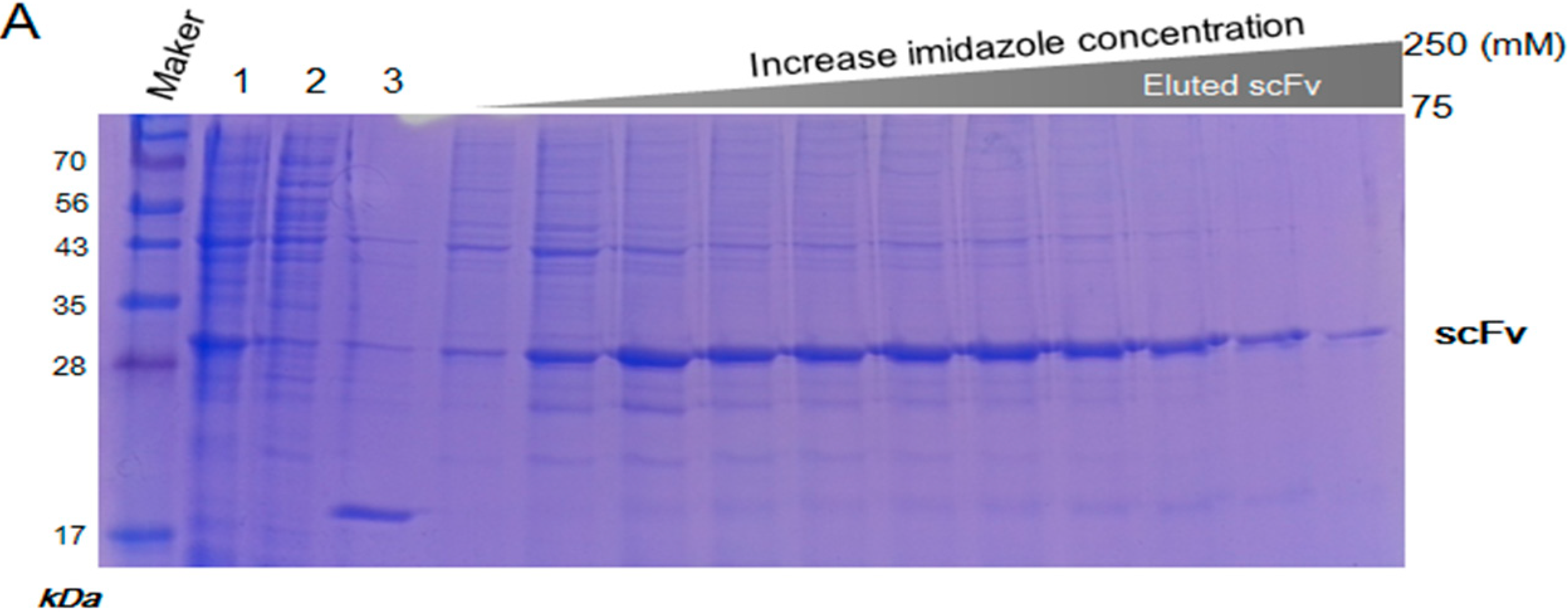
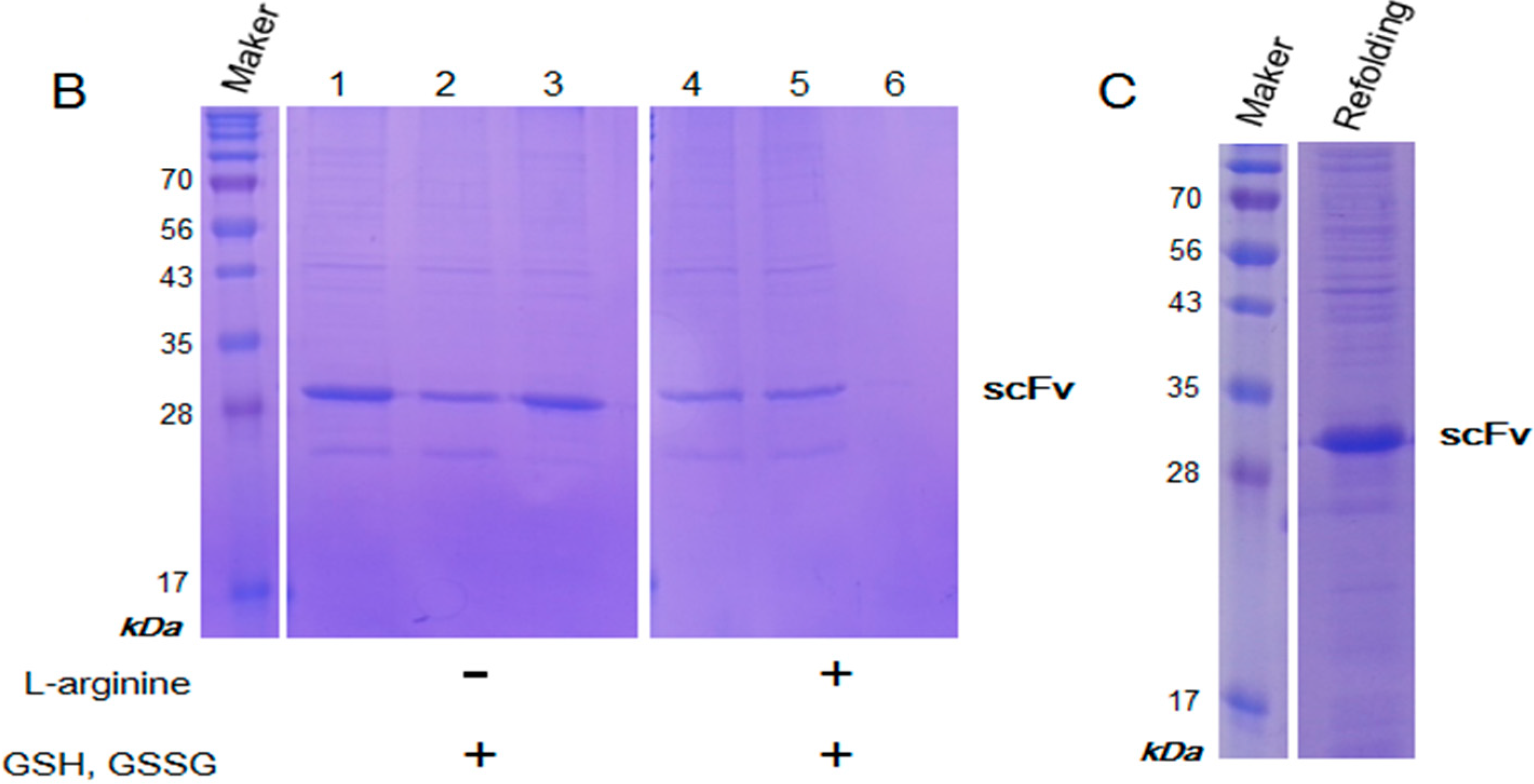
2.3. Purification and Refolding of scFvs by Rapid Dilution
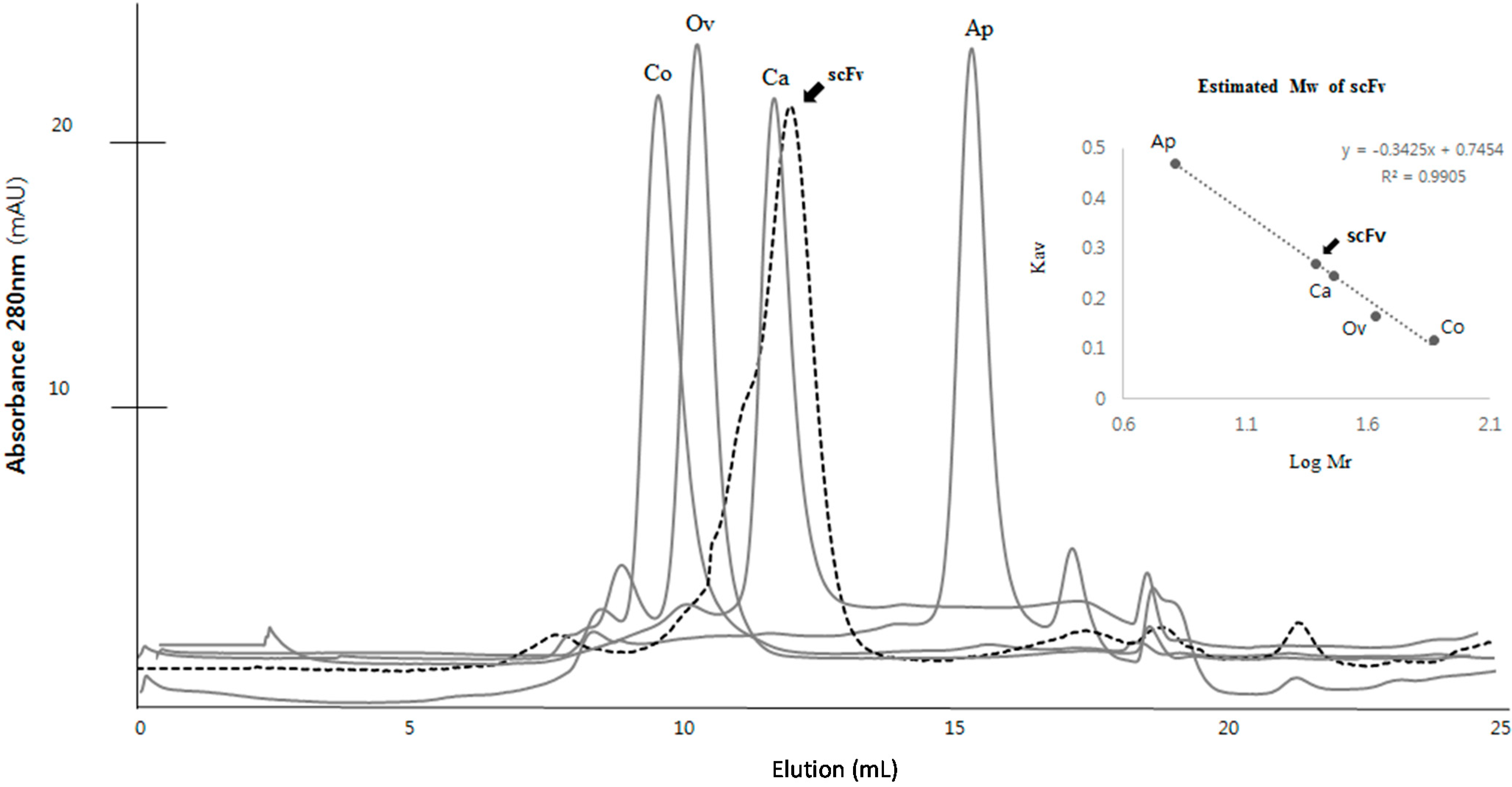

2.4. Kinetics Assay with Myoglobin Antigen

3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Plasmid Construction for the Expression of Recombinant scFv
4.2. Expression and Isolation of scFv from Inclusion Bodies
4.3. Purification and Refolding of scFv
4.4. Circular Dichroism Analysis of scFv
4.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.6. Reaction Kinetics of Myoglobin Binding to scFv
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.H.; Seo, S.M.; Paek, S.H.; Lim, G.S. Premature antibodies with rapid reaction kinetics and their characterization for diagnostic applications. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 420, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.K.; Seo, S.M.; Cho, I.H.; Paek, S.H.; Kim, D.H. Minimum-step immuno-analysis based on continuous recycling of the capture antibody. Analyst 2011, 136, 1374–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paek, S.H.; Cho, I.H.; Seo, S.M.; Kim, D.H. Production of rapidly reversible antibody and its performance characterization as binder for continuous glucose monitoring. Analyst 2011, 136, 4268–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Paek, S.H.; Lim, G.S.; Jeon, J.W. Performance characteristics of monoclonal antibodies as recyclable binders to cardiac troponin I. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 431, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagawa, T.; Oda, M.; Ishimura, M.; Furukawa, K.; Azuma, T. Thermodynamic and kinetic aspects of antibody evolution during the immune response to hapten. Mol. Immunol. 2003, 39, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boes, M. Role of natural and immune igm antibodies in immune responses. Mol. Immunol. 2000, 37, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strandh, M.; Andersson, H.S.; Ohlson, S. Weak affinity chromatography. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 147, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohlson, S.; Jungar, C.; Strandh, M.; Mandenius, C.F. Continuous weak-affinity immunosensing. Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungar, C.; Strandh, M.; Ohlson, S.; Mandenius, C.F. Analysis of carbohydrates using liquid chromatography—Surface plasmon resonance immunosensing systems. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 281, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paek, S.H.; Cho, I.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jeon, J.W.; Lim, G.S. Label-free, needle-type biosensor for continuous glucose monitoring based on competitive binding. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagen, L.; Scheidt, S.; Roberts, L.; Porter, A.; Paul, H. Myoglobinemia following acute myocardial infarction. Am. J. Med. 1975, 58, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, A.; Chan, W.K.; Cheng, S.H.; Leung, C.K.; Choi, C.H. Troponin-I, myoglobin, and mass concentration of creatine kinase-MB in acute myocardial infarction. QJM 1999, 92, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnedenko, O.V.; Mezentsev, Y.V.; Molnar, A.A.; Lisitsa, A.V.; Ivanov, A.S.; Archakov, A.I. Highly sensitive detection of human cardiac myoglobin using a reverse sandwich immunoassay with a gold nanoparticle-enhanced surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 759, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timucin, C.; Gul, O.; Kutuk, O.; Basaga, H. Antibody array-based immunosensor for detecting cardiovascular disease risk markers. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2012, 33, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henares, T.G.; Mizutani, F.; Hisamoto, H. Current development in microfluidic immunosensing chip. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 611, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Iijima, M.; Kado, Y.; Mizohata, E.; Inoue, T.; Sugiyama, A.; Doi, H.; Shibasaki, Y.; Kodama, T. Construction and characterization of functional anti-epiregulin humanized monoclonal antibodies. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobhal, S.; Chaudhary, V.K.; Singh, A.; Pandey, D.; Kumar, A.; Agrawal, S. Expression of recombinant antibody (single chain antibody fragment) in transgenic plant Nicotiana tabacum cv. Xanthi. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 7027–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Odaka, K.; Uehara, T.; Imanaka-Yoshida, K.; Kato, Y.; Oyama, H.; Tadokoro, H.; Akizawa, H.; Tanada, S.; Hiroe, M.; et al. Toward in vivo imaging of heart disease using a radiolabeled single-chain Fv fragment targeting Tenascin-C. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9123–9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmartin, A.A.; Lamp, B.; Rumenapf, T.; Persson, M.A.; Rey, F.A.; Krey, T. High-level secretion of recombinant monomeric murine and human single-chain Fv antibodies from drosophila S2 cells. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2012, 25, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaks, L.; Benhar, I. Production of stabilized scFv antibody fragments in the E. coli bacterial cytoplasm. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1060, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Onishi, H.; Mizukami, M.; Hanagata, H.; Tokunaga, M.; Arakawa, T.; Miyauchi, A. Efficient production of anti-fluorescein and anti-lysozyme as single-chain anti-body fragments (scFv) by Brevibacillus expression system. Protein Expr. Purif. 2013, 91, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huston, J.S.; Levinson, D.; Mudgett-Hunter, M.; Tai, M.S.; Novotny, J.; Margolies, M.N.; Ridge, R.J.; Bruccoleri, R.E.; Haber, E.; Crea, R.; et al. Protein engineering of antibody binding sites: Recovery of specific activity in an anti-digoxin single-chain Fv analogue produced in escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 5879–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worn, A.; Pluckthun, A. Stability engineering of antibody single-chain Fv fragments. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 989–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, V.; Lokman, C.; van den Hondel, C.A.; Punt, P.J. The production of antibody fragments and antibody fusion proteins by yeasts and filamentous fungi. Microb. Cell Fact. 2003, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluckthun, A. Escherichia coli producing recombinant antibodies. Bioprocess Technol. 1994, 19, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Weidenhaupt, M.; Ivanova, N.; Pavlov, M.; Xu, B.; Su, Z.G.; Janson, J.C. Chromatographic methods for the isolation of, and refolding of proteins from, escherichia coli inclusion bodies. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 25, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, L.; Zeng, L.; Wan, L.; Li, S.; Lu, X.; Cheng, J. Evaluation of three in vitro refolding methods for human-derived anti-CTLA4 scFv expressed in E. coli. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 2006, 23, 388–391. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, H.N.; Kim, D.H.; Paek, S.H.; Park, S.G.; Lee, M.K.; Woo, E.J. Purification and characterization of Fab fragments with rapid reaction kinetics against myoglobin. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Umetsu, M.; Tsumoto, K.; Hara, M.; Ashish, K.; Goda, S.; Adschiri, T.; Kumagai, I. How additives influence the refolding of immunoglobulin-folded proteins in a stepwise dialysis system. Spectroscopic evidence for highly efficient refolding of a single-chain Fv fragment. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8979–8987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.P.; Park, Y.C.; Lee, J.; Sim, S.J.; Chang, H.N. Effects of l-arginine on refolding of lysine-tagged human insulin-like growth factor 1 expressed in Escherichia coli. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 35, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tischer, A.; Lilie, H.; Rudolph, R.; Lange, C. l-arginine hydrochloride increases the solubility of folded and unfolded recombinant plasminogen activator rPA. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 1783–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Liu, Z. Dynamic redox environment-intensified disulfide bond shuffling for protein refolding in vitro: Molecular simulation and experimental validation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 15127–15133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St John, R.J.; Carpenter, J.F.; Randolph, T.W. High-pressure refolding of disulfide-cross-linked lysozyme aggregates: Thermodynamics and optimization. Biotechnol. Prog. 2002, 18, 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.L.; Zabetakis, D.; Acevedo-Velez, G.; Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P. Comparison of an antibody and its recombinant derivative for the detection of the small molecule explosive 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 759, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramatsu, H.; Yoshikawa, K.; Hayashi, T.; Takasu, S.; Kawada, Y.; Uchida, K.; Sato, S.; Takahashi, T.; Saga, S.; Ueda, R. Production and characterization of an active single-chain variable fragment antibody recognizing CD25. Cancer Lett. 2005, 225, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rio, D.C.; Ares, M., Jr.; Hannon, G.J.; Nilsen, T.W. Purification of rna using trizol (tri reagent). Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2010, 2010, pdb-prot5439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lilie, H.; Schwarz, E.; Rudolph, R. Advances in refolding of proteins produced in E. coli. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1998, 9, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetlaufer, D.B.; Branca, P.A.; Chen, G.X. The oxidative folding of proteins by disulfide plus thiol does not correlate with redox potential. Protein Eng. 1987, 1, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, H.-N.; Jang, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-W.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, S.-G.; Lee, M.K.; Paek, S.-H.; Woo, E.-J. Refolded scFv Antibody Fragment against Myoglobin Shows Rapid Reaction Kinetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 23658-23671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151223658
Song H-N, Jang J-H, Kim Y-W, Kim D-H, Park S-G, Lee MK, Paek S-H, Woo E-J. Refolded scFv Antibody Fragment against Myoglobin Shows Rapid Reaction Kinetics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(12):23658-23671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151223658
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Hyung-Nam, Jun-Hyuck Jang, Young-Wan Kim, Dong-Hyung Kim, Sung-Goo Park, Myung Kyu Lee, Se-Hwan Paek, and Eui-Jeon Woo. 2014. "Refolded scFv Antibody Fragment against Myoglobin Shows Rapid Reaction Kinetics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 12: 23658-23671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151223658
APA StyleSong, H.-N., Jang, J.-H., Kim, Y.-W., Kim, D.-H., Park, S.-G., Lee, M. K., Paek, S.-H., & Woo, E.-J. (2014). Refolded scFv Antibody Fragment against Myoglobin Shows Rapid Reaction Kinetics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(12), 23658-23671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151223658