Post-Transcriptional Up-Regulation of PDGF-C by HuR in Advanced and Stressed Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. Correlation of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-C (PDGF-C) Expression with Poor Prognosis of Breast Cancers
| Parameter | Characteristics | No. of Patients (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ≤45 | 35 (43.2) |
| >45 | 46 (56.8) | |
| Tumor Size | ≤3 cm | 54 (66.7) |
| >3 cm | 27 (33.3) | |
| Histological Grade | G1 | 26 (32.1) |
| G2 | 45 (55.6) | |
| G3 | 10 (12.3) | |
| Pathological Tumor-Node-Metastasis (PTNM) Staging | I | 21 (25.9) |
| II | 39 (48.2) | |
| III | 15 (18.5) | |
| IV | 6 (7.4) | |
| Histological Type | Ductal | 66 (81.5) |
| Lobular | 11 (13.6) | |
| Others | 4 (4.9) | |
| Lymph Node Metastasis | 0 | 41 (50.6) |
| <4 | 16 (19.8) | |
| ≥4 | 24 (29.6) | |
| HER | Positive | 56 (69.1) |
| Negative | 25 (30.9) | |
| Estrogen receptor (ER) | Positive | 35 (43.2) |
| Negative | 46 (56.8) | |
| Progesterone receptor (PR) | Positive | 37 (45.7) |
| Negative | 44 (54.3) |
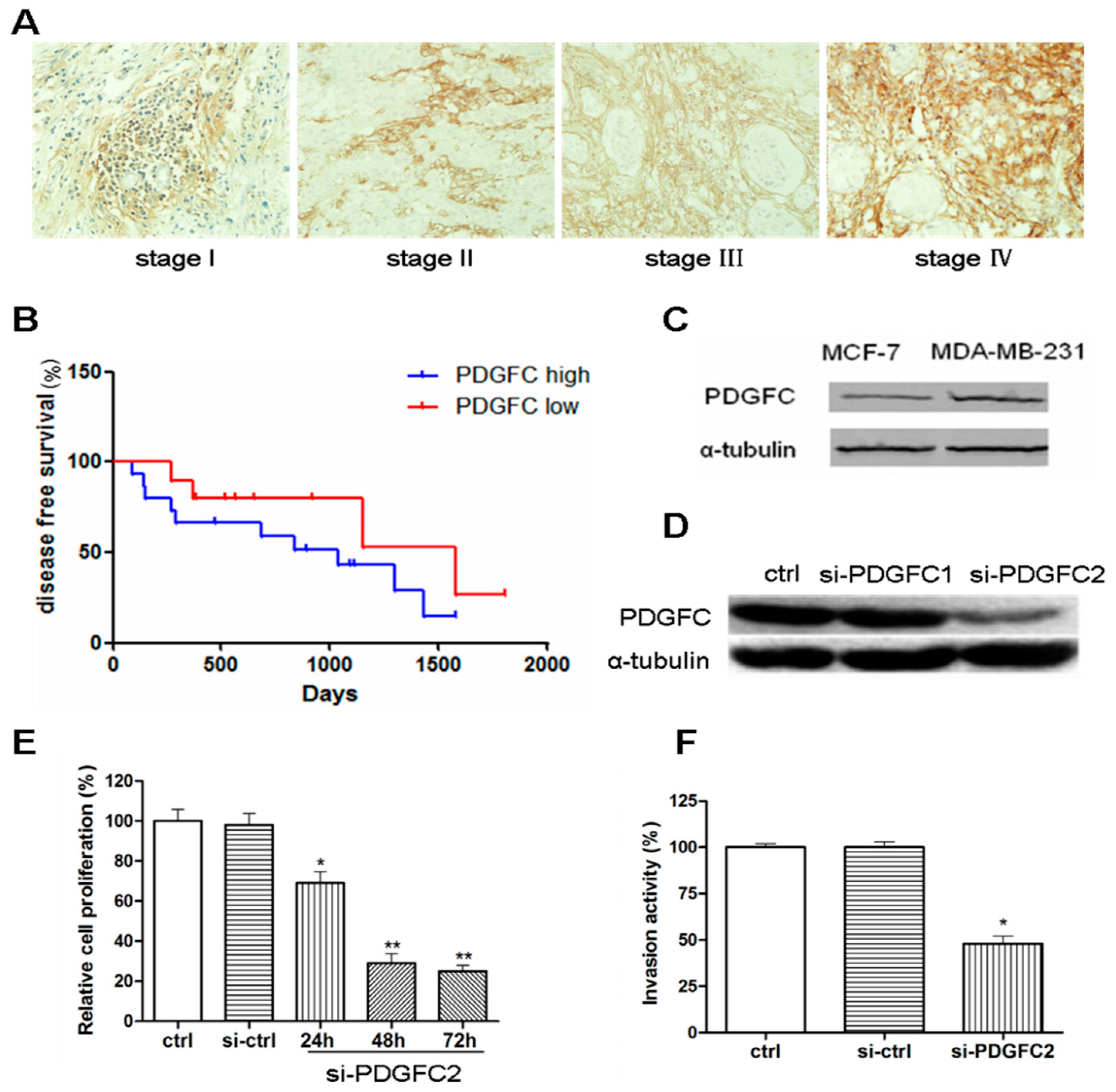
2.1.2. Coordinated Expression of HuR and PDGF-C in Breast Cancers
| Parameter | PDGF-C Expression | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | |||
| Age | ≤45 | 15 | 20 | 0.251 |
| >45 | 26 | 20 | ||
| Tumor Size | ≤3 cm | 29 | 25 | 0.496 |
| >3 cm | 12 | 15 | ||
| Histological Grade | G1 | 7 | 19 | 0.021 |
| G2 | 28 | 17 | ||
| G3 | 6 | 4 | ||
| pTNM Staging | I | 7 | 14 | 0.023 |
| II | 20 | 19 | ||
| III | 9 | 6 | ||
| IV | 5 | 1 | ||
| Histological Type | Ductal | 36 | 30 | 0.306 |
| Lobular | 2 | 9 | ||
| Others | 3 | 1 | ||
| Lymph Node Metastasis | 0 | 26 | 15 | 0.528 |
| <4 | 7 | 9 | ||
| ≥4 | 8 | 16 | ||
| HER | Positive | 29 | 27 | 0.851 |
| Negative | 12 | 13 | ||
| ER | Positive | 24 | 11 | 0.417 |
| Negative | 17 | 29 | ||
| PR | Positive | 11 | 26 | 0.0853 |
| Negative | 30 | 14 | ||
| HuR | Positive | 36 | 21 | 0.029 |
| Negative | 5 | 19 | ||
2.1.3. Direct Targeting and Stabilization of PDGF-C Transcripts by HuR in Breast Cancers
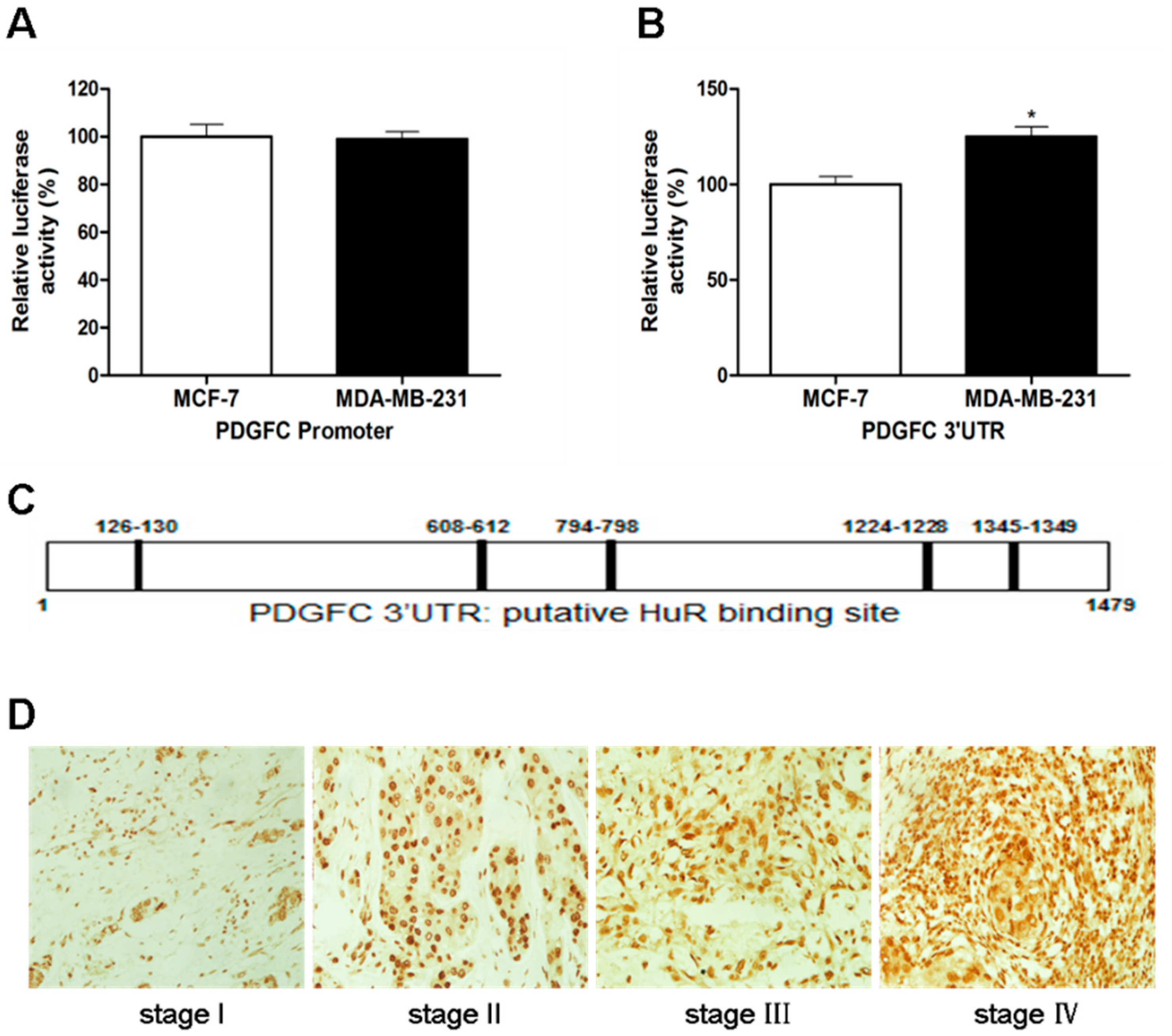
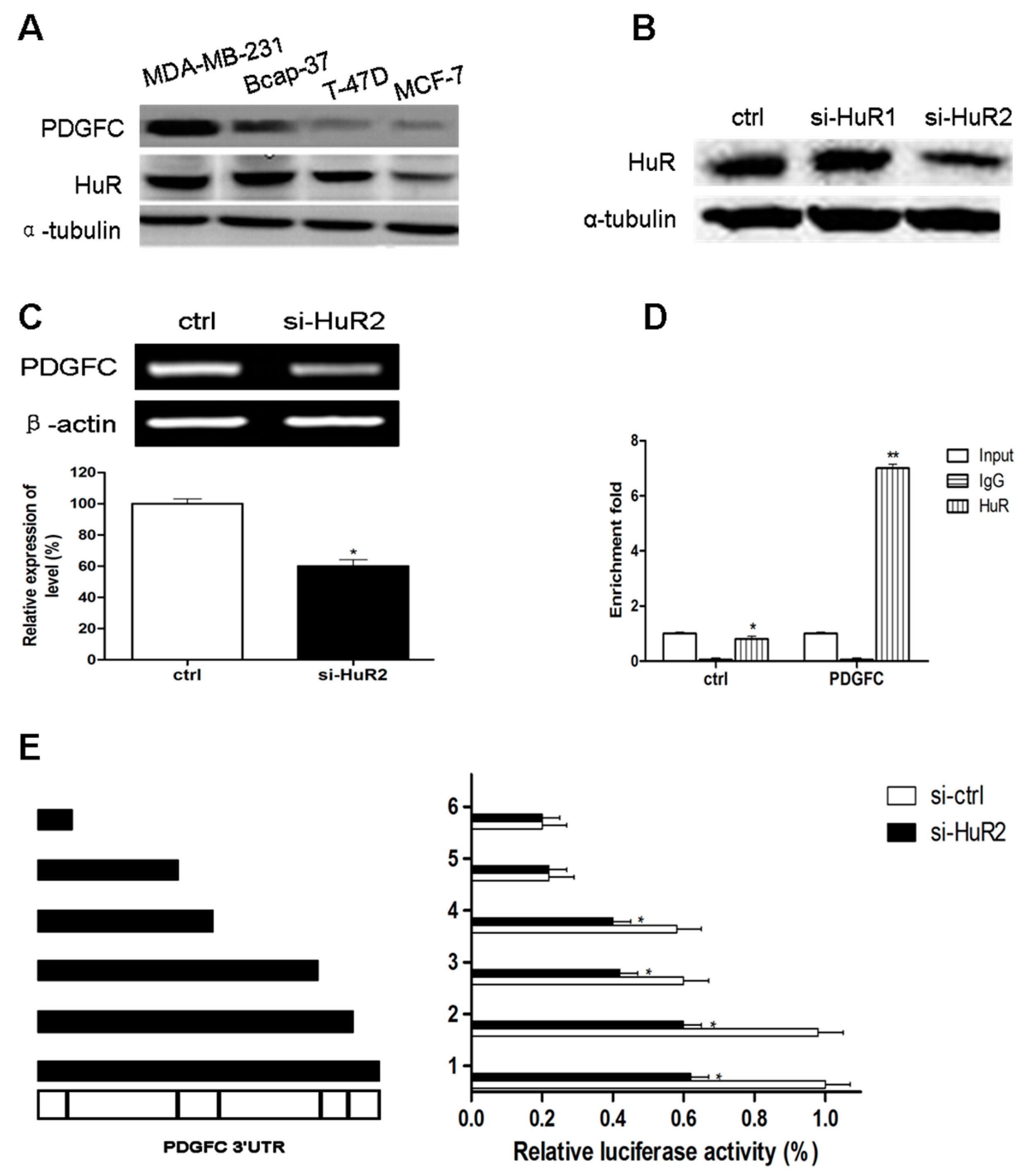
2.1.4. Stress-Induced HuR Regulation of PDGF-C in Breast Cancers

2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
3.2. Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
3.3. Western Blot Analysis
3.4. MTT [3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide] Assay
3.5. Cell Invasion Assay
3.6. Luciferase Reporter Assays
3.7. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for PDGF-C
3.8. Clinical Sample Collection
3.9. Immunohistochemistry
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolch, W.; Pitt, A. Functional proteomics to dissect tyrosine kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montemurro, F.; di Cosimo, S.; Arpino, G. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive and hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: New insights into molecular interactions and clinical implications. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2715–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, N.J.; Najy, A.J.; Ustach, C.V.; Movilla, L.; Kim, H.R. Platelet-derived growth factor-C (PDGF-C) activation by serine proteases: Implications for breast cancer progression. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reigstad, L.J.; Varhaug, J.E.; Lillehaug, J.R. Structural and functional specificities of PDGF-C and PDGF-D, the novel members of the platelet-derived growth factors family. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 5723–5741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lewis, N.L. The platelet-derived growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 9, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Ustach, C.; Kim, H.R. Platelet-derived growth factor signaling and human cancer. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 36, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frings, O.; Augsten, M.; Tobin, N.P.; Carlson, J.; Paulsson, J.; Pena, C.; Olsson, E.; Veerla, S.; Bergh, J.; Ostman, A.; et al. Prognostic significance in breast cancer of a gene signature capturing stromal PDGF signaling. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Son, D.; Na, Y.R.; Hwang, E.S.; Seok, S.H. Platelet-derived growth factor-C (PDGF-C) induces anti-apoptotic effects on macrophages through Akt and Bad phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 6225–6235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, T.J.; Halfon, M.S. Regulation of gene expression in the genomic context. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 9, e201401001. [Google Scholar]
- Fabian, M.R.; Sonenberg, N.; Filipowicz, W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 351–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, L.A.; Abella, V.; Valladares, M.; Figueroa, A. Posttranscriptional regulation by RNA-binding proteins during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4463–4477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. Posttranscriptional regulation of cancer traits by HuR. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2010, 1, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.J.; Cheng, S.; Campbell, C.; Wright, A.; Furneaux, H. Cloning and characterization of HuR, a ubiquitously expressed Elav-like protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8144–8151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.C.; Steitz, J.A. Overexpression of HuR, a nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling protein, increases the in vivo stability of ARE-containing mRNAs. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3448–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallouzi, I.E.; Steitz, J.A. Delineation of mRNA export pathways by the use of cell-permeable peptides. Science 2001, 294, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nathanson, K.L.; Wooster, R.; Weber, B.L. Breast cancer genetics: What we know and what we need. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaraju, S.; Lee, B.S. Adaptive and maladaptive expression of the mRNA regulatory protein HuR. World J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 4, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amadio, M.; Scapagnini, G.; Laforenza, U.; Intrieri, M.; Romeo, L.; Govoni, S.; Pascale, A. Post-transcriptional regulation of HSP70 expression following oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells: The potential involvement of the RNA-binding protein HuR. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2651–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, Y.; Masuda, K.; Kuwano, Y.; Nishida, K.; Kajita, K.; Kurokawa, K.; Satake, Y.; Shoda, K.; Imoto, I.; Rokutan, K. HuR regulates alternative splicing of the TRA2β gene in human colon cancer cells under oxidative stress. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 34, 2857–2873. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruland, O.; Fluge, O.; Akslen, L.A.; Eiken, H.G.; Lillehaug, J.R.; Varhaug, J.E.; Knappskog, P.M. Inverse correlation between PDGFC expression and lymphocyte infiltration in human papillary thyroid carcinomas. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denkert, C.; Weichert, W.; Winzer, K.J.; Muller, B.M.; Noske, A.; Niesporek, S.; Kristiansen, G.; Guski, H.; Dietel, M.; Hauptmann, S. Expression of the ELAV-like protein HuR is associated with higher tumor grade and increased cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human breast carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5580–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Kumar, A.; Zhang, F.; Lee, C.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Arjuna, P. VEGF-independent angiogenic pathways induced by PDGF-C. Oncotarget 2010, 1, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Ishmael, F.T.; Fang, X.; Myers, A.; Cheadle, C.; Huang, S.K.; Atasoy, U.; Gorospe, M.; Stellato, C. Chemokine transcripts as targets of the RNA-binding protein HuR in human airway epithelium. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Caldwell, M.C.; Lin, S.; Furneaux, H.; Gorospe, M. HuR regulates cyclin A and cyclin B1 mRNA stability during cell proliferation. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 2340–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xie, Q.; Xiang, D.; Gao, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z. The expression of RNA-binding protein HuR in non-small cell lung cancer correlates with vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression and lymph node metastasis. Oncol. Basel 2009, 76, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmadi, W.; Al-Ghamdi, M.; Al-Souhibani, N.; Khabar, K.S. miR-29a inhibition normalizes HuR over-expression and aberrant AU-rich mRNA stability in invasive cancer. J. Pathol. 2013, 230, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Bi, J.; Zhang, C. Cytoplasmic HuR expression correlates with angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and poor outcome in lung cancer. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28, S577–S585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, B.; Bi, J.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Chu, H.; Liang, X.; Zhong, C.; Wang, J. Cytoplasmic HuR expression correlates with P-gp, HER-2 positivity, and poor outcome in breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2013, 34, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar]
- Atasoy, U.; Watson, J.; Patel, D.; Keene, J.D. ELAV protein HuA (HuR) can redistribute between nucleus and cytoplasm and is up-regulated during serum stimulation and T cell activation. J. Cell Sci. 1998, 111, 3145–3156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Furneaux, H.; Cheng, H.; Caldwell, M.C.; Hutter, D.; Liu, Y.; Holbrook, N.; Gorospe, M. HuR regulates p21 mRNA stabilization by UV light. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.; Furer-Galban, S.; Lopez, D.S.I.; von Kobbe, C.; Guo, J.; Georas, S.N.; Foufelle, F.; Hardie, D.G.; et al. AMP-activated kinase regulates cytoplasmic HuR. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 22, 3425–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafarga, V.; Cuadrado, A.; Lopez, D.S.I.; Bengoechea, R.; Fernandez-Capetillo, O.; Nebreda, A.R. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase- and HuR-dependent stabilization of p21Cip1 mRNA mediates the G1/S checkpoint. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 4341–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwman, P.; Jonkers, J. The effects of deregulated DNA damage signalling on cancer chemotherapy response and resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazevet, M.; Moulin, M.; Llach-Martinez, A.; Chargari, C.; Deutsch, E.; Gomez, A.M.; Morel, E. Complications of chemotherapy, a basic science update. Presse Med. 2013, 42, e352–e361. [Google Scholar]
- Hubenak, J.R.; Zhang, Q.; Branch, C.D.; Kronowitz, S.J. Mechanisms of injury to normal tissue after radiotherapy: A review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 133, 49e–56e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, V.C.; Khachigian, L.M. Fibroblast growth factor-2 induction of platelet-derived growth factor-C chain transcription in vascular smooth muscle cells is ERK-dependent but not JNK-dependent and mediated by Egr-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40289–40295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, N.-A.; Qu, Y.-Q.; Yang, G.-D.; Wang, T.; Li, R.-L.; Jia, L.-T.; Dong, R. Post-Transcriptional Up-Regulation of PDGF-C by HuR in Advanced and Stressed Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20306-20320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120306
Luo N-A, Qu Y-Q, Yang G-D, Wang T, Li R-L, Jia L-T, Dong R. Post-Transcriptional Up-Regulation of PDGF-C by HuR in Advanced and Stressed Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(11):20306-20320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120306
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Nian-An, Ya-Qi Qu, Guo-Dong Yang, Tao Wang, Ren-Li Li, Lin-Tao Jia, and Rui Dong. 2014. "Post-Transcriptional Up-Regulation of PDGF-C by HuR in Advanced and Stressed Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 11: 20306-20320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120306
APA StyleLuo, N.-A., Qu, Y.-Q., Yang, G.-D., Wang, T., Li, R.-L., Jia, L.-T., & Dong, R. (2014). Post-Transcriptional Up-Regulation of PDGF-C by HuR in Advanced and Stressed Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(11), 20306-20320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120306




