Importance of H-Abstraction in the Final Step of Nitrosoalkane Formation in the Mechanism-Based Inactivation of Cytochrome P450 by Amine-Containing Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
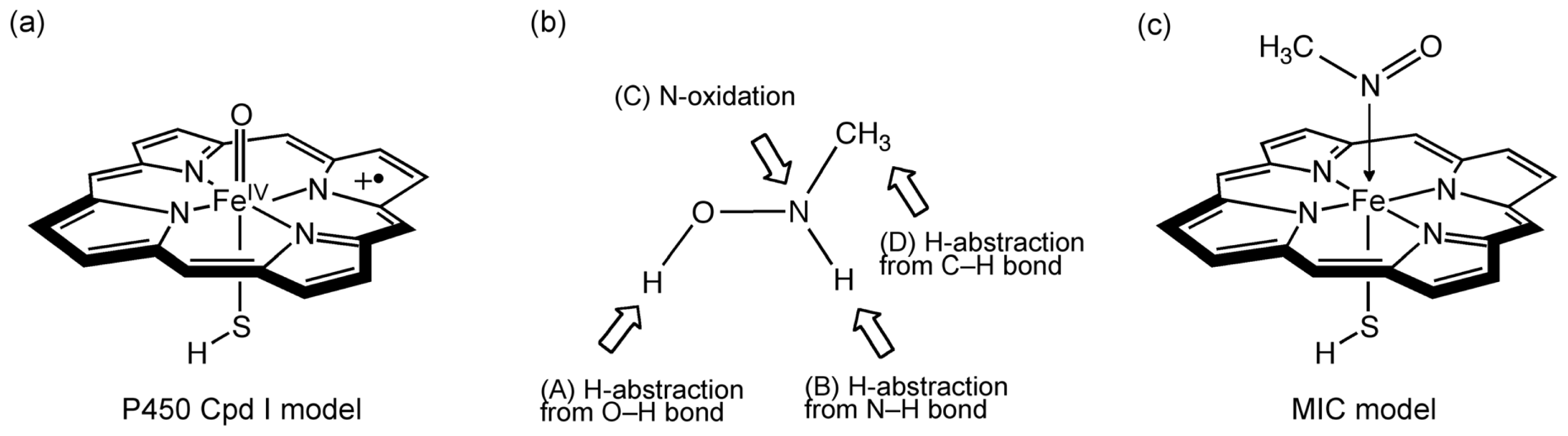
2.1. Models
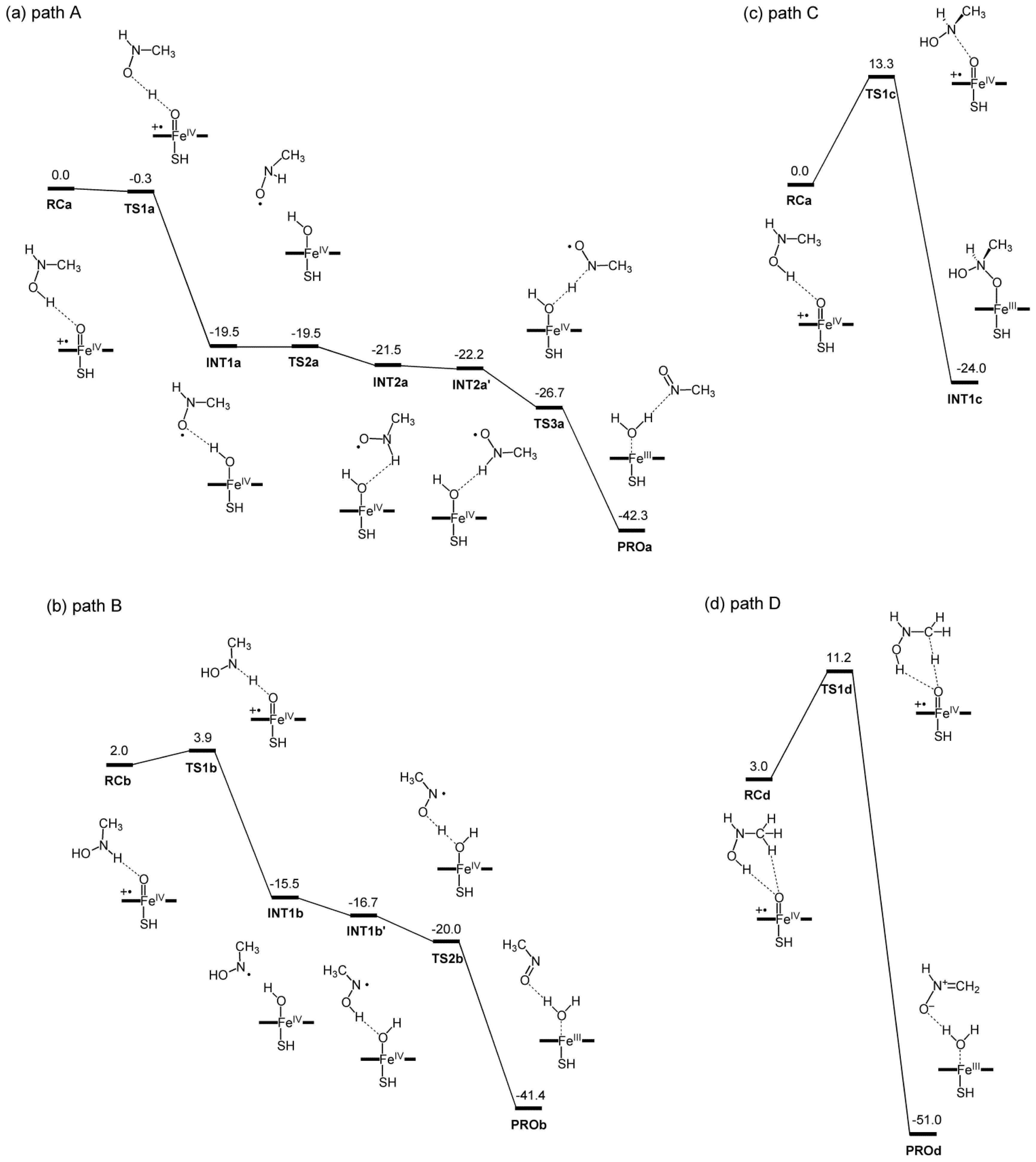
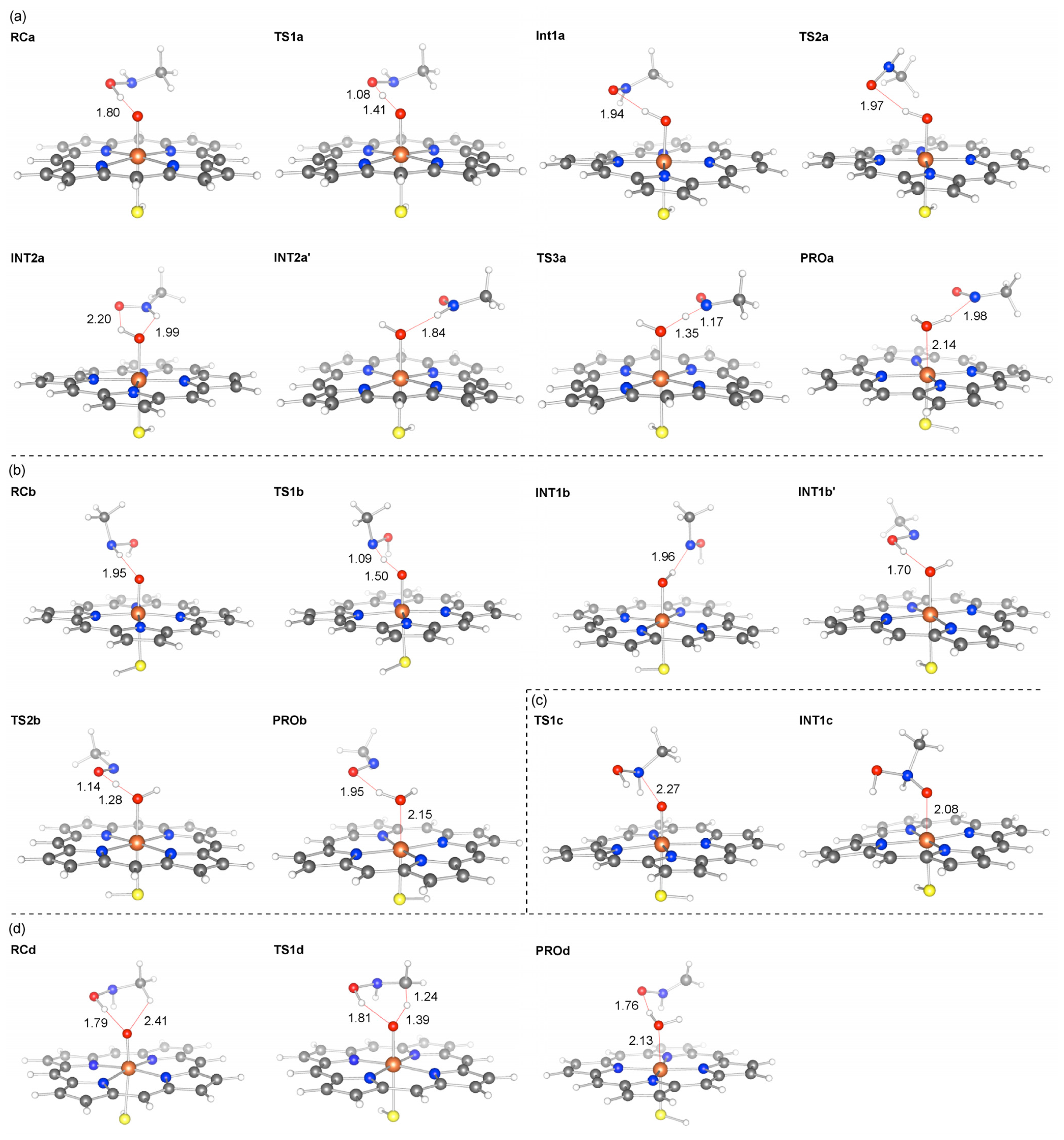
2.2. Reaction Mechanism
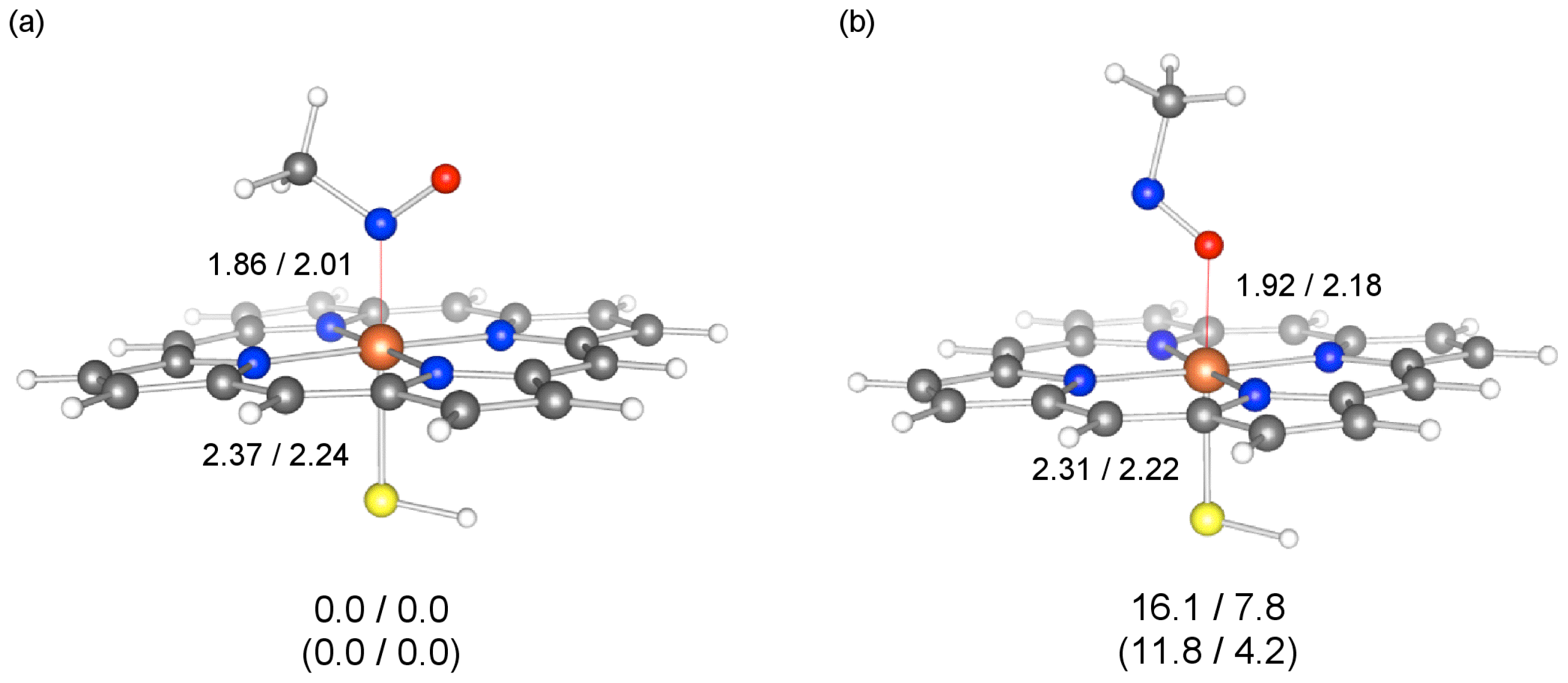
2.3. Coordination Bond in MIC
2.4. Energy Decomposition Analysis of MIC
3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
ijms-14-24692-s001.pdfAcknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism and Biochemistry, 3rd ed; Ortiz de Montellano, P.R. (Ed.) Kluwer/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2005.
- Omura, T. Forty years of cytochrome P450. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1999, 266, 690–698. [Google Scholar]
- Sligar, S.G.; Makris, T.M.; Denisov, I.G. Thirty years of microbial P450 monooxygenase research: Peroxo-heme intermediates—The central bus station in the heme oxygenase catalysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2005, 338, 346–354. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, J.T. Key elements of the chemistry of cytochrome P-450: The oxygen rebound mechanism. J. Chem. Educ 1985, 62, 928–931. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, J.H.; Sono, M. Cytochrome P450 and chloroperoxidase: Thiolate ligated heme enzymes. Spectroscopic determination of their active site structures and mechanistic implications of thiolate ligation. Chem. Rev 1987, 87, 1255–1276. [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich, F.P. Common and uncommon cytochrome P450 reactions related to metabolism and chemical toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol 2001, 14, 611–650. [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb, M.; Toy, P.H. Hypersensitive radical probes and the mechanisms of cytochrome P450 catalyzed hydroxylation reactions. Acc. Chem. Res 2000, 33, 449–455. [Google Scholar]
- Sevrioukova, I.F.; Poulos, T.L. Understanding the mechanism of cytochrome P450 3A4: Recent advances and remaining problems. Dalton Trans 2013, 42, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar]
- Denisov, I.G.; Makris, T.M.; Sligar, S.G.; Schlichting, I. Structure and chemistry of cytochrome P450. Chem. Rev 2005, 105, 2253–2278. [Google Scholar]
- Meunier, B.; de Visser, S.P.; Shaik, S. Mechanism of oxidation reactions catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Chem. Rev 2004, 104, 3947–3980. [Google Scholar]
- Shaik, S.; Kumar, D.; de Visser, S.P.; Altun, A.; Thiel, W. Theoretical perspective on the structure and mechanism of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Chem. Rev 2005, 105, 2279–2328. [Google Scholar]
- Shaik, S.; Hirao, H.; Kumar, D. Reactivity patterns of P450 enzymes: Multifunctionality of the active species, and the two states-two oxidants conundrum. Nat. Prod. Rep 2007, 24, 533–552. [Google Scholar]
- Shaik, S.; Hirao, H.; Kumar, D. Reactivity of high-valent iron-oxo species in enzymes and synthetic reagents: A tale of many states. Acc. Chem. Res 2007, 40, 532–542. [Google Scholar]
- Shaik, S.; Cohen, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Kumar, D.; Thiel, W. P450 enzymes: Their structure, reactivity and selectivity modeled by QM/MM calculations. Chem. Rev 2010, 110, 949–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen, O.; Turpeinen, M.; Hakkola, J.; Honkakoski, P.; Hukkanen, J.; Raunio, H. Inhibition and induction of human cytochrome P450 enzymes: Current status. Arch. Toxicol 2008, 82, 667–715. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.H.; Lu, A.Y.H. Inhibition and induction of cytochrome P450 and the clinical implications. Clin. Pharmacokinet 1998, 35, 361–390. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.F.; Chan, S.Y.; Goh, B.C.; Chan, E.; Duan, W.; Huang, M.; McLeod, H.L. Mechanism-based inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4 by theraputic drugs. Clin. Pharmacokinet 2005, 44, 279–304. [Google Scholar]
- Fontana, E.; Dansette, P.M.; Poli, S.M. Cytochrome P450 enzymes mechanism based inhibitors: Common sub-structures and reativity. Curr. Drug Metab 2005, 6, 413–454. [Google Scholar]
- Kalgutkar, A.S.; Obach, R.S.; Maurer, T.S. Mechanism-based inactivation of cytochrome P450 enzymes: Chemical mechanism, structure activity relationships and relationships to clinical drug drug interactions and idiosyncratic adverse drug reactions. Curr. Drug Metab 2007, 8, 407–447. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.F. Drugs behave as substrates, inhibitors and inducers of human cytochrome P450 3A4. Curr. Drug Metab 2008, 9, 310–322. [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg, P.F.; Kent, U.M.; Bumpus, N.N. Mechanism based inactivation of human cytochrome P450s: Experimental characterization, reactive intermediates, and clinical implications. Chem. Res. Toxicol 2008, 21, 189–205. [Google Scholar]
- Orr, S.T.M.; Ripp, S.L.; Ballard, T.E.; Henderson, J.L.; Scott, D.O.; Obach, R.S.; Sun, H.; Kalgutkar, A.S. Mechanism-based inactivation (MBI) of cytochrome P450 enzymes: Structure activity relationships and discovery strategies to mitigate drug-drug interaction risks. J. Med. Chem 2012, 55, 4896–4933. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, A.; Harriman, S. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes and biomedical aspects of mechanism-based inactivation (MBI). Drug. Discov. Today 2013, 10, e177–e189. [Google Scholar]
- De Visser, S.P.; Kumar, D.; Shaik, S. How do aldehyde side products occur during alkane epoxidation by cytochrome P450? Theory reveals a state specific multistate scenario where the high-spin component leads to all side products. J. Inorg. Biochem 2004, 98, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Rydberg, P.; Olsen, L. Do two different reaction mechanisms contribute to the hydroxylation of primary amines by cytochrome P450? J. Chem. Theory Comput 2011, 7, 3399–3404. [Google Scholar]
- Taxak, N.; Desai, P.V.; Patel, B.; Mohutsky, M.; Klimkowski, V.J.; Gombar, V.; Bharatam, P.V. Metabolic-intermediate complex formation with cytochrome P450: Theoretical studies in elucidating the reaction pathway for the generation of reactive nitroso intermediate. J. Comput. Chem 2012, 33, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Hirao, H.; Cheong, Z.H.; Wang, X.Q. Pivotal role of water in terminating enzymatic function: A density functional theory study of the mechanism-based inactivation of cytochromes P450. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 7787–7794. [Google Scholar]
- Taxak, N.; Patel, B.; Bharatam, P.V. Carbene generation by cytochromes and electronic structure of heme-iron-porphyrin-carbene complex: A quantum chemical study. Inorg. Chem 2013, 52, 5097–5109. [Google Scholar]
- Hirao, H.; Chuanprasit, P.; Cheong, Y.Y.; Wang, X. How is a metabolic intermediate formed in the mechanism-based inactivation of cytochrome P450 by using 1,1-dimethylhydrazine: Hydrogen abstraction or nitrogen oxydation. Chem. Eur. J 2013, 19, 7361–7369. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Prueksaritanont, T.; Lin, J.H. Drug interactions with calcium channel blockers: Possible involvement of metabolite-intermediate complexatoin with CYP3A. Drug Metab. Dispos 2000, 28, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Mansuy, D. Formation of reactive intermediates and metabolites: Effects of macrolide antibiotics on cytochrome P450. Pharmacol. Ther 1987, 33, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Dansette, P.M.; Delaforge, M.; Sartori, E.; Beaune, P.; Jaouen, M.; Mansuy, D. Drug interactions with macrolide antibiotics: Specificity of pseudo suicide inhibition and induction of cytochrome P450. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 1986, 197, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Reidy, G.F.; Mehta, I.; Murray, M. Inhibition of oxidative drug metabolism by orphenadrine: In vitro and in vivo evidence for isozyme-specific complexation of cytochrome P450 and inhibition kinetics. Mol. Pharmacol 1989, 35, 736–743. [Google Scholar]
- Buening, M.K.; Franklin, M.R. SKF 525-A inhbition, induction and 452 nm complex formation. Drug Metab. Dispos 1976, 4, 244–255. [Google Scholar]
- Rydberg, P.; Ryde, U.; Olsen, L. Sulfoxide sulfur and nitrogen oxidation and dealkylation by cytochrome P450. J. Chem. Theory Comput 2008, 4, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wu, W.; Cho, K.B.; Shaik, S. Oxidation of tertiary amnines by cytochrome P450-kinetic isotope effect as a spin state reactivity probe. Chem. Eur. J 2009, 15, 8492–8503. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, K.M.; Jones, J.P. Anillinic N-oxides support cytochrome P450-mediated N-dealkylation through hydrogen-atom transfer. Chem. Eur. J 2010, 16, 8096–8107. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, K.L.; VandenBrink, B.M.; Babu, K.N.; Allen, K.E.; Nelson, W.L.; Kunze, K.L. Sequential metabolism of secondary alkyl amine to metabolic-intermediate complexes: Opposing roles for secondary hydroxylamine primary amine metabolites of desipramine, (S)-fluoxetine and N-desmethyldiltiazem. Drug Metab. Dispos 2010, 38, 963–972. [Google Scholar]
- Correia, M.A.; Ortiz de Montellano, P.R. Inhibition of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. In Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry, 3rd ed; Ortiz de Montellano, P.R., Ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 247–322. [Google Scholar]
- Lindeke, B.; Paulsen, U.; Anderson, E. Cytochrome P455 complex formation in the metabolism of phenylalkylamines-IV: Spectral evidences for metabolic conversion of methamphetamine to N-hydroxymethamphetamine. Biochem. Pharmacol 1979, 28, 3629–3635. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, M.R. The formation of 455 nm complex during cytochrome P-450-dependent N-hydroxyamphetamine metabolism. Mol. Pharmacol 1974, 10, 975–985. [Google Scholar]
- Lindeke, B.; Anderson, E.; Lundkvist, G.; Jonsson, U.; Eriksson, S.O. Autoxidation of N-hydroxyamphetamine and N-hydroxyphentermine. The formation of 2-nitroso-1-phenyl-propanes and 1-phenyl-2-propanone oxime. Acta Pharm. Suec 1975, 12, 183–198. [Google Scholar]
- Mansuy, D.; Battioni, P.; Chottard, J.C.; Riche, C.; Chiaroni, A. Nitrosoalkane complexes of iron-porphyrins: Analogy between the bonding properties of nitrosoalkanes and dioxygen. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1983, 105, 455–463. [Google Scholar]
- Copeland, D.M.; West, A.H.; Richter-Addo, G.B. Crystal structures of ferrous horse heart myoglobin complexed with nitric oxide and nitrosoethane. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Genet 2003, 53, 182–192. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density functional thermochemistry III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correction energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar]
- Vosko, S.H.; Wilk, L.; Nusair, M. Accurate spin-dependant electron liquid correlation energies for local spin density calculations: A critical analysis. Can. J. Phys 1980, 58, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar]
- Dolg, M.; Wedig, U.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H. Energy-adjusted ab initio pseudopotentials for the first row transition elements. J. Chem. Phys 1987, 86, 866–872. [Google Scholar]
- Hehre, W.; Radom, L.; Schleyer, P.R.; Pople, J.A. Ab Initio Molecular Orbital Theory; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi, J.; Mennucci, B.; Cammi, R. Quantum mechanical continuum solvation models. Chem. Rev 2005, 105, 2999–3093. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L.; Schüürmann, G. Model and mechanism: N-hydroxylation of primary aromatic amines by Cytochrome P450. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2013, 52, 744–748. [Google Scholar]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys 2010, 132, 154104–154123. [Google Scholar]
- Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. J. Comput. Chem 2011, 32, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.R.; Becke, A.D. A post Hartree-Fock model for intermolecular interactions. J. Chem. Phys 2005, 123, 024101–024108. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D.; Johnson, E.R. A density functional model of the dispersion interaction. J. Chem. Phys 2005, 123, 154101–154110. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.R.; Becke, A.D. A post Hartree-Fock model for intermolecular interactions. Inclusion of higher order corrections. J. Chem. Phys 2006, 124, 174104–174113. [Google Scholar]
- Kitaura, K.; Morokuma, K. A new energy decomposition scheme for molecular interactions within the Hartree-Fock approximation. Int. J. Quantum Chem 1976, 10, 325–340. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, T.; Rauk, A. A theoretical study of the ethylene-metal bond in complexes between Cu+, Ag+, Au+, Pt0, or Pt2+ and ethylene, based on the Hartree-Fock-Slater transition-state method. Inorg. Chem 1979, 18, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, T.; Rauk, A. Carbon monoxide, carbon monosulfide, molecular nitrogen, phosphorus trifluoride, and methyl isocyanide as σ donors and π acceptors. A theoretical study by the Hartree-Fock-Slater transition-state method. Inorg. Chem 1979, 18, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar]
- Von Hopffgarten, M.; Frenking, G. Energy decomposition analysis. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci 2012, 2, 43–62. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision B.01; Gaussian Inc: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca Guerra, C.; Snijders, J.G.; te Velde, G.; Baerends, E.J. Towards an order-N DFT method. Theor. Chem. Acc 1998, 99, 391–403. [Google Scholar]
- Te Velde, G.; Bickelhaupt, F.M.; Baerends, E.J.; Fonseca Guerra, C.; van Gisbergen, S.J.A.; Snijders, J.G.; Ziegler, T. Chemistry with ADF. J. Comput. Chem 2001, 22, 931–967. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar]


| ΔE(M06) | ΔE(B3LYP) | ΔE(B3LYP-D3) b | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIC(II) | −3.7 | −2.1 | −13.6 |
| MIC(III) | 6.8 | −0.4 | −10.5 |
| Energy term | 1MIC(II) | 1MIC(II) a | 2MIC(III) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrostatic | −104.1 | −67.9 | −75.8 |
| Repulsion | 148.0 | 90.0 | 103.1 |
| Orbital interaction | −67.4 | −45.1 | −45.8 |
| Total interaction | −23.6 | −22.9 | −18.4 |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hirao, H.; Thellamurege, N.M.; Chuanprasit, P.; Xu, K. Importance of H-Abstraction in the Final Step of Nitrosoalkane Formation in the Mechanism-Based Inactivation of Cytochrome P450 by Amine-Containing Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 24692-24705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224692
Hirao H, Thellamurege NM, Chuanprasit P, Xu K. Importance of H-Abstraction in the Final Step of Nitrosoalkane Formation in the Mechanism-Based Inactivation of Cytochrome P450 by Amine-Containing Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(12):24692-24705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224692
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirao, Hajime, Nandun M. Thellamurege, Pratanphorn Chuanprasit, and Kai Xu. 2013. "Importance of H-Abstraction in the Final Step of Nitrosoalkane Formation in the Mechanism-Based Inactivation of Cytochrome P450 by Amine-Containing Drugs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 12: 24692-24705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224692
APA StyleHirao, H., Thellamurege, N. M., Chuanprasit, P., & Xu, K. (2013). Importance of H-Abstraction in the Final Step of Nitrosoalkane Formation in the Mechanism-Based Inactivation of Cytochrome P450 by Amine-Containing Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(12), 24692-24705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224692




