Production of Defatted Palm Kernel Cake Protein Hydrolysate as a Valuable Source of Natural Antioxidants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Proximate Analysis
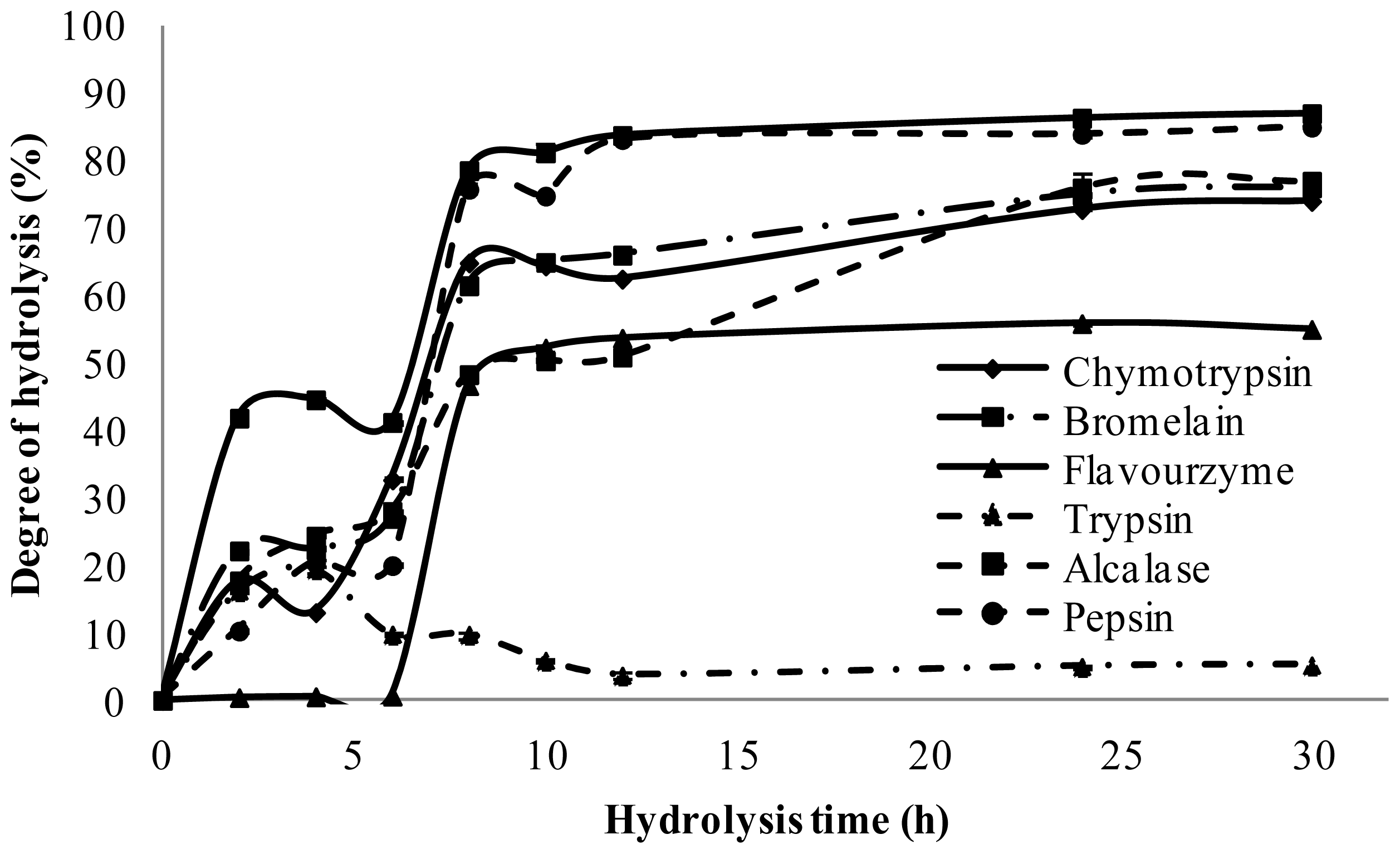
2.2. Degree of Hydrolysis
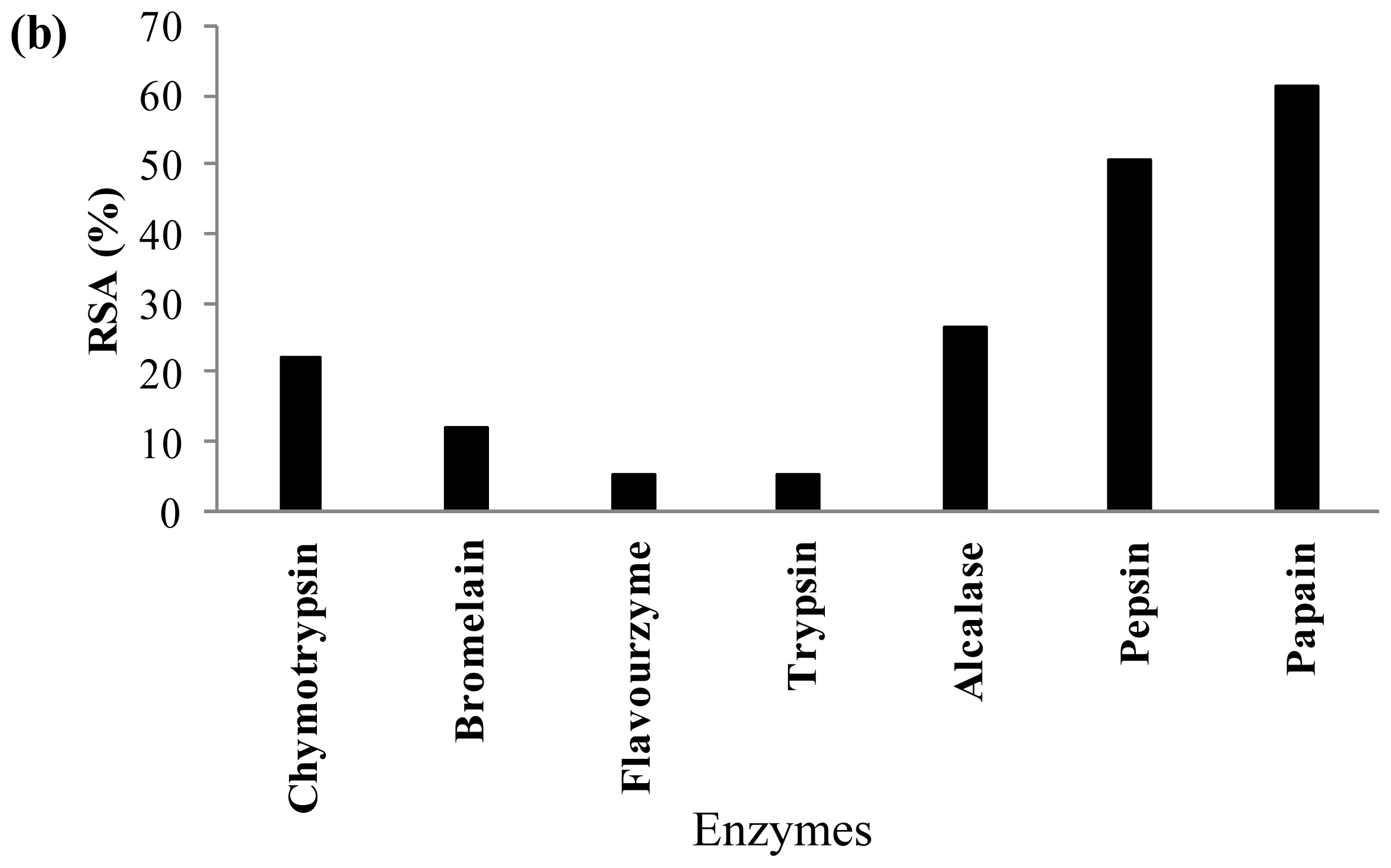
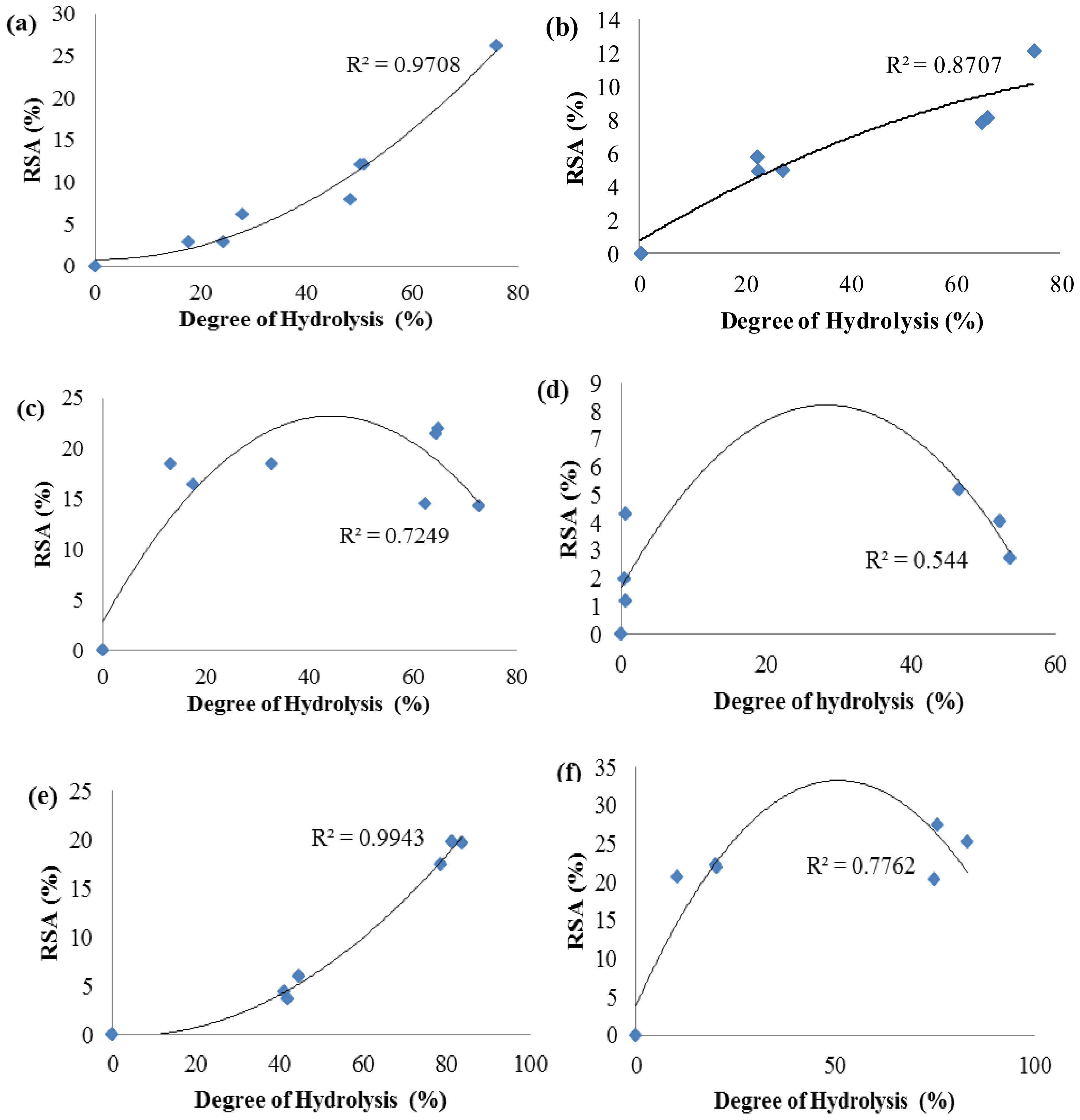
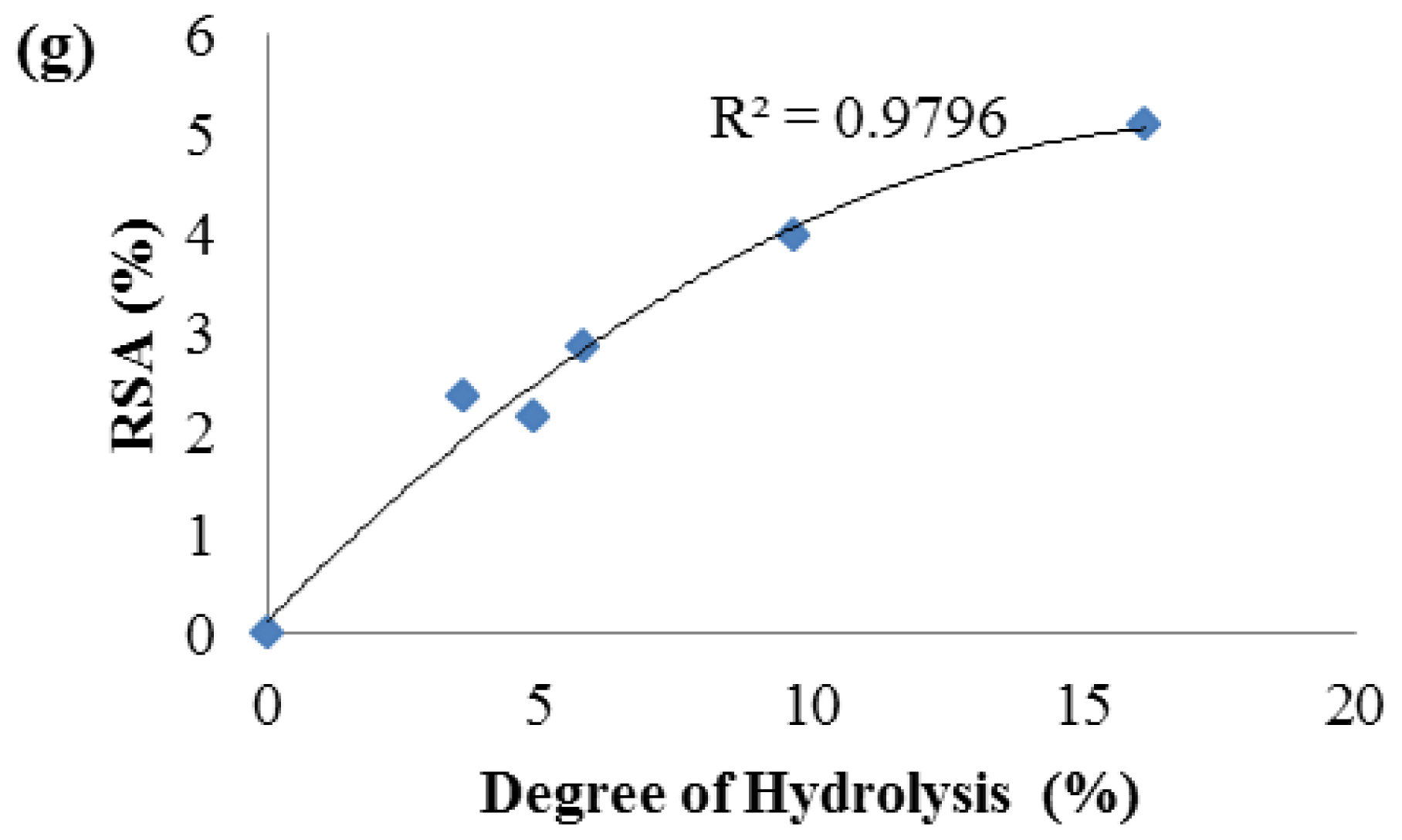
2.3. Antioxidant Activity of Palm Kernel Cake Protein Hydrolysates
2.4. Characterization of Papain Hydrolysate
2.4.1. Hydrophobicity
2.4.2. Isoelectric Properties of Hydrolysates Peptides Produced
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Palm Kernel Cake Protein Isolate
3.3. Preparation of PKC Protein Hydrolysates
3.4. 1,1-Diphenyl-2-Picrylhydrazyl Free Radical Scavenging Assay
3.5. O-Phthaldialdehyde Spectrophotometric Assay
3.6. Characterization of PKC Protein Hydrolysates
3.6.1. Reverse Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography
3.6.2. Isoelectric Point Focusing Fractionation
4. Statistics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Loh, T.; Foo, H.; Tan, B.; Jelan, Z. Effects of Palm Kernel cake on performance and Blood lipids in Rats. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci 2002, 15, 1165–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Castegna, A.; Pocernich, C.B.; Drake, J.; Scapagnini, G.; Calabrese, V. Nutritional approaches to combat oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Biochem 2002, 13, 444–461. [Google Scholar]
- Rizvi, S.I.; Jha, R.; Maurya, P.K. Erythrocyte plasma membrane redox system in human aging. Rejuvenation Res 2006, 9, 470–474. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti, B.; Chakravarti, D.N. Oxidative modification of proteins: Age-related changes. Gerontology 2007, 53, 128–139. [Google Scholar]
- Samaranayaka, A.G.P.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Food-derived peptidic antioxidants: A review of their production, assessment, and potential applications. J. Funct. Foods 2011, 3, 229–254. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.M.; Muramoto, K.; Yamauchi, F. Structural analysis of antioxidative peptides from soybean β-conglycinin. J. Agric. Food Chem 1995, 43, 574–578. [Google Scholar]
- Babizhayev, M.A.; Seguin, M.; Gueyne, J.; Evstigneeva, R.; Ageyeva, E.; Zheltukhina, G. l-carnosine (beta-alanyl-l-histidine) and carcinine (beta-alanylhistamine) act as natural antioxidants with hydroxyl-radical-scavenging and lipid-peroxidase activities. Biochem. J 1994, 304, 509–516. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Huang, J.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Antioxidant activity of peptides isolated from alfalfa leaf protein hydrolysate. Food Chem 2008, 111, 370–376. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, M.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. Riboflavin-sensitized photooxidation of ascorbic acid: Kinetics and amino acid effects. Food Chem 1995, 53, 397–403. [Google Scholar]
- Mine, Y. Bioactive Proteins and Peptides as Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Udenigwe, C.C.; Lu, Y.L.; Han, C.H.; Hou, W.C.; Aluko, R.E. Flaxseed protein-derived peptide fractions: Antioxidant properties and inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in murine macrophages. Food Chem 2009, 116, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Zhou, H.; Qian, H. Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of wheat germ protein hydrolysates (WGPH) prepared with alcalase. Process Biochem 2006, 41, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.J.; Juillerat, M.A.; Lee, C.H. Cholesterol lowering mechanism of soybean protein hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem 2007, 55, 10599–10604. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, F.; Ming, L.; Yi, S.; Zhanxia, L.; Yongquan, W.; Chi, L. The antihypertensive effect of peptides: A novel alternative to drugs? Peptides 2008, 29, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Akpanabiatu, M.; Ekpa, O.; Mauro, A.; Rizzo, R. Nutrient composition of Nigerian palm kernel from the dura and tenera varieties of the oil palm (Elaeis guineensis). Food Chem 2001, 72, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Adler-Nissen, J. Limited enzymic degradation of proteins: A new approach in the industrial application of hydrolases. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol 1982, 32, 138–156. [Google Scholar]
- Rutherfurd, S.M. Methodology for determining degree of hydrolysis of proteins in hydrolysates: A review. J. AOAC Int 2010, 93, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, P.; Petersen, D.; Dambmann, C. Improved method for determining food protein degree of hydrolysis. J. Food Sci 2001, 66, 642–646. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Zhu, B.W.; Zhou, D.Y.; Wu, H.T.; Tan, H.; Yang, J.F.; Li, D.M.; Dong, X.P.; Murata, Y. Preparation and antioxidant activity of enzymatic hydrolysates from purple sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus nudus) gonad. LWT Food Sci. Technol 2010, 44, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.H.; Wang, X.S.; Yang, X.Q. Enzymatic hydrolysis of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate by various proteases and antioxidant properties of the resulting hydrolysates. Food Chem 2009, 114, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Takamura, H.; Matoba, T.; Terao, J. HPLC method for evaluation of the free radical-scavenging activity of foods by using 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem 1998, 62, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S. Antioxidant properties of wheat germ protein hydrolysates evaluated in vitro. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol 2006, 13, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, L.; Cong, T.; Bao, S. In vitro study on antioxidant activities of peanut protein hydrolysate. J. Sci. Food Agric 2007, 87, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Bougatef, A.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Manni, L.; Ravallec, R.; Barkia, A.; Guillochon, D.; Nasri, M. Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-products proteins. Food Chem 2010, 118, 559–565. [Google Scholar]
- Klompong, V.; Benjakul, S.; Kantachote, D.; Shahidi, F. Antioxidative activity and functional properties of protein hydrolysate of yellow stripe trevally (Selaroides leptolepis) as influenced by the degree of hydrolysis and enzyme type. Food Chem 2007, 102, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Jamdar, S.; Rajalakshmi, V.; Pednekar, M.; Juan, F.; Yardi, V.; Sharma, A. Influence of degree of hydrolysis on functional properties, antioxidant activity and ACE inhibitory activity of peanut protein hydrolysate. Food Chem 2010, 121, 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Ji, B.; Wu, Y. Isolation and identification of antioxidative peptides from porcine collagen hydrolysate by consecutive chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Chem 2007, 102, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.Y.; Wu, K.C.; Chiang, S.H. Antioxidant properties and protein compositions of porcine haemoglobin hydrolysates. Food Chem 2007, 100, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; He, Z.; Dai, Y.; Xiong, Y.L.; Xie, M.; Chen, J. Peptide fractionation and free radical scavenging activity of zein hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem 2009, 58, 587–593. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.Y.; Morimae, M.; Matsumura, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Sato, K. Antioxidant activity of some protein hydrolysates and their fractions with different isoelectric points. J. Agric. Food Chem 2008, 56, 9246–9251. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuge, N.E.; Nomura, Y.; Yamamto, M.; Sugisawa, Y. Antioxidative activity of peptides prepared by enzymatic hydrolysis of egg-white albumin. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi 1991, 65, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar]
- Arifin, B.; Bono, A.; Farm, Y.Y.; Ling, A.; Fui, S. Protein extraction from palm kernel meal. J. Appl. Sci 2009, 9, 2996–3004. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Shyu, Y.S.; Wang, Y.T.; Hsu, C.K. Antioxidative properties of protein hydrolysate from defatted peanut kernels treated with esperase. LWT Food Sci. Technol 2010, 43, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Church, F.C.; Swaisgood, H.E.; Porter, D.H.; Catignani, G.L. Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J. Dairy Sci 1983, 66, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Salami, M.; Yousefi, R.; Ehsani, M.R.; Dalgalarrondo, M.; Chobert, J.M.; Haertlé, T.; Razavi, S.H.; Saboury, A.A.; Niasari-Naslaji, A.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A. Kinetic characterization of hydrolysis of camel and bovine milk proteins by pancreatic enzymes. Int. Dairy J 2008, 18, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar]



| Parameters | Amount (%) |
|---|---|
| Protein | 17.6 ± 1.4 |
| Carbohydrates | 50.4 ± 2.3 |
| Crude fat | 5.5 ± 0.3 |
| Crude fiber | 11.5 ± 1.3 |
| Moisture | 8.9 ± 1.1 |
| Ash | 6.1 ± 1.2 |
| Enzyme | Buffer (50 mM) | pH | Temperature (°C) | Enzyme to Substrate Ratio | Agitation Rate (rpm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pepsin | KCl-HCl | 1.5 | 37 | 1:50 | 150 |
| Papain | Phosphate | 6.5 | 65 | 1:50 | 150 |
| Bromelain | Acetate buffer | 5.0 | 55 | 1:50 | 150 |
| Alcalase | Phosphate | 7.5 | 55 | 1:50 | 150 |
| Chymotrypsin | Phosphate | 6.8 | 50 | 1:50 | 150 |
| Trypsin | Tris-HCl | 8.0 | 37 | 1:50 | 150 |
| Flavourzyme | Tris-HCl | 8.0 | 55 | 1:50 | 150 |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarei, M.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Abdul-Hamid, A.; Anwar, F.; Saari, N. Production of Defatted Palm Kernel Cake Protein Hydrolysate as a Valuable Source of Natural Antioxidants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8097-8111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078097
Zarei M, Ebrahimpour A, Abdul-Hamid A, Anwar F, Saari N. Production of Defatted Palm Kernel Cake Protein Hydrolysate as a Valuable Source of Natural Antioxidants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(7):8097-8111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078097
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarei, Mohammad, Afshin Ebrahimpour, Azizah Abdul-Hamid, Farooq Anwar, and Nazamid Saari. 2012. "Production of Defatted Palm Kernel Cake Protein Hydrolysate as a Valuable Source of Natural Antioxidants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 7: 8097-8111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078097
APA StyleZarei, M., Ebrahimpour, A., Abdul-Hamid, A., Anwar, F., & Saari, N. (2012). Production of Defatted Palm Kernel Cake Protein Hydrolysate as a Valuable Source of Natural Antioxidants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(7), 8097-8111. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078097






