Crossing Paths in Human Renal Cell Carcinoma (hRCC)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
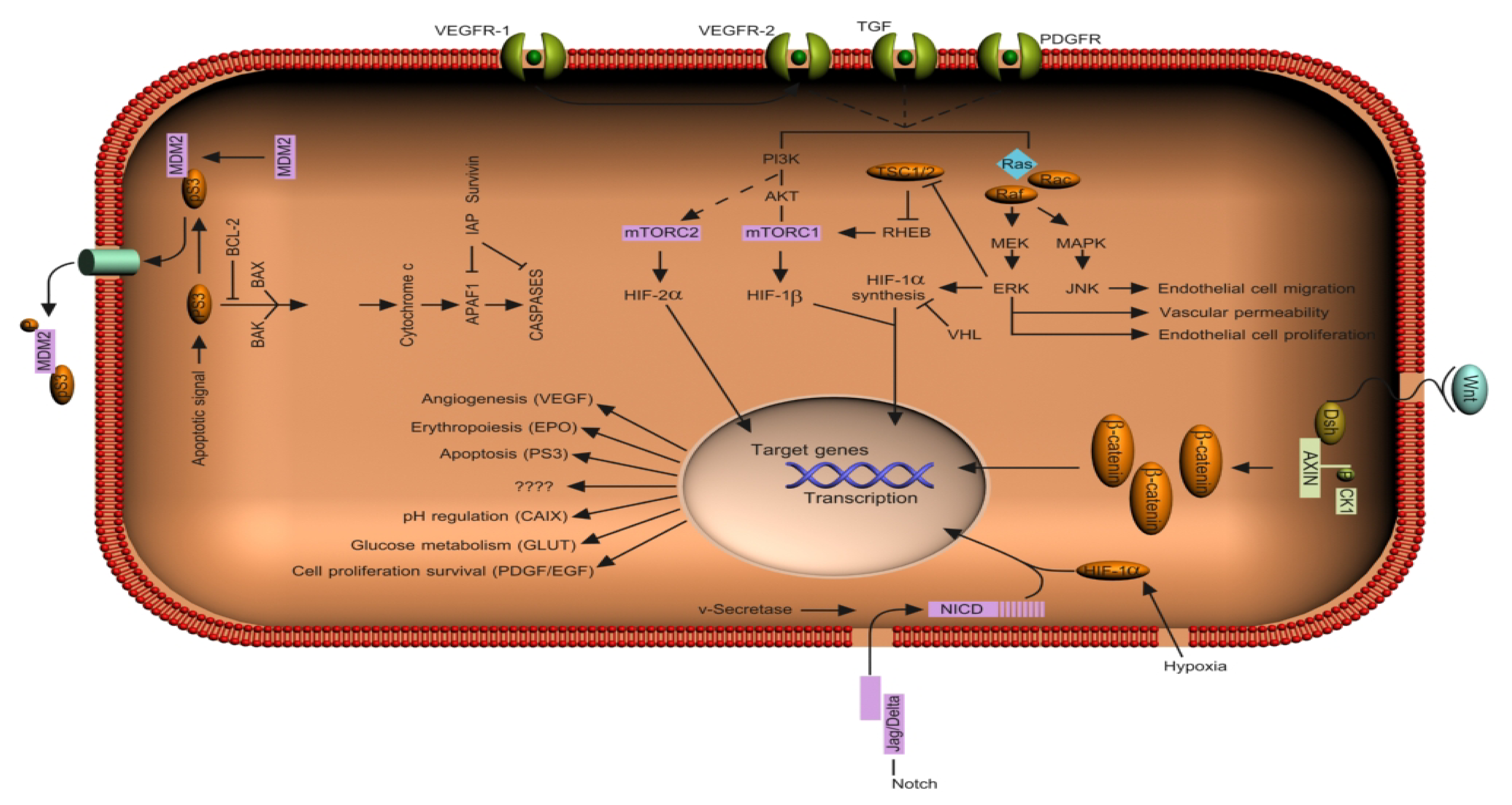
2. Signaling Pathways in hRCC
2.1. The Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) Pathway
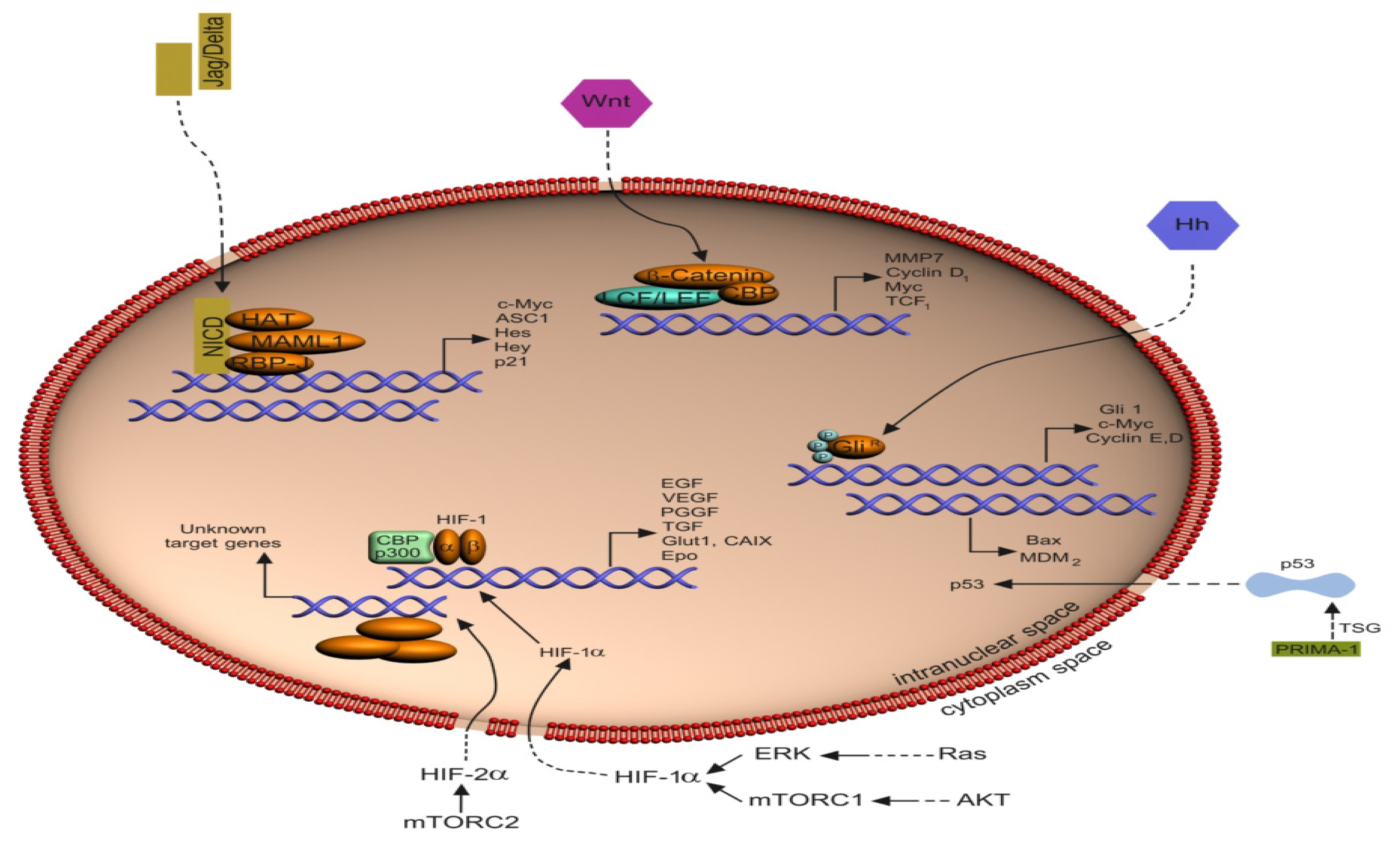
2.2. The Notch Signaling Pathway
2.3. The HIF Pathway
2.4. The VEGF Pathway
2.5. The Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway
2.6. The CAIX Pathway
2.7. The GLUT 1-5 Transporters Pathway
2.8. The p53 Pathway
2.9. The Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β) Pathway
2.10. The Transforming Growth Factor-α (TGF-α) Pathway
3. Pathway Crosstalk
3.1. Crosstalk between the Notch Pathway and HIF Signaling
3.2. Crosstalk between the Notch Pathway and EGFR Signaling
3.3. Crosstalk between the Notch Pathway and VEGF Signaling
3.4. Crosstalk between the Notch Pathway and p53 Signaling
4. Conclusions
4.1. The Backbone of Intracellular Crosstalk
4.2. The Hyper-Network Concept
4.3. Targeted Therapies are the Option of Choice
- Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cohen, H.T.; McGovern, F.J. Renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med 2005, 353, 2477–2490. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, F.; Tory, K.; Gnarra, J.; Yao, M.; Duh, F.M.; Orcutt, M.L.; Stackhouse, T.; Kuzmin, I.; Modi, W.; Geil, L.; et al. Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science 1993, 260, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Van Houwelingen, K.P.; van Dijk, B.A.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.A.; Schouten, L.J.; Gorissen, H.J.; Schalken, J.A.; van de barndt, P.A.; Oosterwijk, E. Prevalence of von Hippel-Lindau gene mutations in sporadic renal cell carcinoma: Results from The Netherlands cohort study. BMC Cancer 2005, 5, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Gallou, C.; Joly, D.; Mejean, A.; Staroz, F.; Martin, N.; Tarlet, G.; Orfanelli, M.T.; Bouvier, R.; Droz, D.; Chretien, Y.; et al. Mutations of the VHL gene in sporadic renal cell carcinoma: Definition of a risk factor for VHL patients to develp an RCC. Hum. Mutat 1999, 13, 464–475. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, K.; Yao, M.; Yoshida, M.; Kishida, T.; Shuin, T.; Miura, T.; Moriyama, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Sakai, N.; Kanoko, S.; et al. Comprehensive mutational analysis of the VHL gene in sporadic renal cell carcinoma: relationship to clinicopathological parameters. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 34, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Yang, K.; Lindblad, P.; Egevad, L.; Hemminki, K. VHL gene alterations in renal cell carcinoma patients: novel hotspot or founder mutations and linkage disequilibrium. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5393–5400. [Google Scholar]
- Brauch, H.; Weirich, G.; Brieger, J.; Glavac, D.; Rodl, H.; Eichinger, M.; Feurer, M.; Weidt, E.; Puranakanitstha, C.; Neuhaus, C.; et al. VHL alterations in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma: association with advanced tumor stage and a novel hot spot mutation. Cancer Res 2000, 60, 1842–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Haase, V.H. The VHL/HIF oxygen-sensing pathway and its relevance to kidney disese. Kidney Int 2006, 69, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Ivan, M.; Kondo, K.; Yang, H.; Kim, W.; Valiando, J.; Ohh, M.; Salic, A.; Asara, J.M.; Lane, W.S.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr. HIF alpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science 2001, 292, 464–468. [Google Scholar]
- Jakkola, P.; Mole, D.R.; Tian, Y.M.; Wilson, M.I.; Gielbert, J.; Gaskell, S.J.; Kriegsheim, A.V.; Hebestreit, H.F.; Mukherji, M.; Schofield, C.J.; et al. Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2- regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 2001, 292, 468–472. [Google Scholar]
- Kucejova, B.; Peña-Llopis, S.; Yamasaki, T.; Sivanand, S.; Tran, T.A.; Alexander, S.; Wolff, N.C.; Lotan, Y.; Xie, X.J.; Kabbani, W.; et al. Interplay Between pVHL and mTORC1 Pathways in Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res 2011, 9, 1255–65. [Google Scholar]
- Maeshima, A.; Yamashita, S.; Nojima, Y. Identification of renal progenitor-like tubular cells that participate in the regeneration processes of the kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2003, 14, 3138–3146. [Google Scholar]
- Challen, G.A.; Martinez, G.; Davis, M.J.; Taylor, D.F.; Crowe, M.; Teasdale, R.D.; Grimmond, S.M.; Little, M.H. Identifying the molecular phenotype of renal progenitor cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2004, 15, 2344–2357. [Google Scholar]
- Hishikawa, K.; Marumo, T.; Miura, S.; Nakanishi, A.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Shibata, K.; Ichiyanagi, T.; Kohike, H.; Komori, T.; Takahashi, I.; et al. Musculin/MyoR is expressed in kidney side population cells and can regulate their function. J. cell Biol 2005, 169, 921–928. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa, L.; Ingles-Esteve, J.; Aguilera, C.; Bigas, A. Phosphorylation by glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta down-regulates Notch activity, a link for Notch and Wnt pathways. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 32227–32237. [Google Scholar]
- Ronchini, C.; Capobianco, A.J. Induction of cyclin D1 transcription and CDK2 activity by Notch(ic): Implication for cell cycle disruption in transformation by Notch(ic). Mol. Cell Biol 2001, 21, 5925–5934. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Du, R.; Gao, J.; Ning, X.; Xie, H.; Lin, X.; Liu, J.; Fan, D. Expression and clinical significance of Notch receptors in human renal cell carcinoma. Pathology 2009, 41, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Semenza, G.L. Hydroxylation of HIF-1: Oxygen sensing at the molecular level. Physiology (Bethesda) 2004, 19, 176–182. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.J.; Wang, L.Y.; Chodosh, L.A.; Keith, B.; Simon, M.C. Differential roles of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2 alpha in hypoxic gene regulation. Mol. Cell Biol 2003, 23, 9361–9374. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, V.; Davis, D.A.; Haque, M.; Huang, L.E.; Yarchoan, R. Differential gene up-regulation by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha in HEK293T cells. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 3299–3306. [Google Scholar]
- Raval, R.R.; Lau, K.W.; Tran, M.G.; Sowter, H.M.; Mandriota, S.J.; Li, J.L.; Pugh, C.W.; Maxwell, P.H.; Harris, A.L.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) and HIF-2 in von Hippel-Lindau associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Cell Biol 2005, 25, 5675–5686. [Google Scholar]
- Grabmaier, K.; de Weijert, M.C.A.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Schalken, J.A.; Oosterwijk, E. Strict regulation of CAIX (G250/MN) by HIF-1 alpha in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2004, 23, 5624–5631. [Google Scholar]
- Warnecke, C.; Zaborowska, Z.; Kurreck, J; Erdman, VA; Frei, U; Wiesener, M; et al. Differentiating the functional role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha and HIF-2 alpha (EPAS-1) by the use of RNA interference: erythropoietin is a HIF-2 alpha target gene in Hep3B and Kelly cells. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1462–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, M.; Hirai, S.; Yamada-Okabe, H.; Hamada, K.; Tabuchi, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamashita, A.; Kishida, T.; Nakaigawa, N.; Nagashima, Y.; et al. Loss of von Hippel-Lindau protein causes cell density dependent deregulation of CyclinD1 expression through hypoxia-inducible factor. Oncogene 2003, 22, 2728–2738. [Google Scholar]
- Gunaratnam, L.; Morley, M.; Franovic, A.; de Paulsen, N.; Mekhail, K.; Parolin, D.A.; Nakamura, E.; Lorimer, I.A.; Lee, S. Hypoxia inducible factor activates the transforming growth factor-alpha/epidermal growth factor receptor growth stimulatory pathway in VHL (−/−) renal cell carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 44966–44974. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, M.; Hu, C.J.; Johnson, R.S.; Brown, E.J.; Keith, B.; Simon, M.C. Acute postnatal ablation of HIF-2 alpha results in anemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2301–2306. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesener, M.S.; Turley, H.; Allen, W.E.; Willam, C.; Eckardt, K.U.; Talks, K.L.; Wood, S.M.; Gatter, K.C.; Harris, A.L.; Pugh, C.W.; et al. Induction of endothelial PAS domain protein-1 by hypoxia: Characterization and comparison with hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha. Blood 1998, 92, 2260–2268. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, C.W.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: Role of the HIF system. Nat. Med 2003, 9, 677–684. [Google Scholar]
- An, J.; Retting, M.B. Mechanism of von Hippel-Linhau protein-mediated suppression of nuclear KB (NF-kB) activity. Mol. Cell Biol 2005, 25, 7546–7556. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesener, M.S.; Jürgensen, J.S.; Rosenberger, C.; Scholze, C.K.; Hörstrup, J.H.; Warnecke, C.; Mandriota, S.; Bechmann, I.; Frei, U.A.; Pugh, C.W.; et al. Widespread hypoxia-inducible expression of HIF-1 alpha in distinct cell populations of different organs. FASEB J 2003, 17, 271–273. [Google Scholar]
- De Paulsen, N.; Brychzy, A.; Fournier, M.C.; Klausner, R.D.; Gnarra, J.R.; Pause, A.; Lee, S. Role of transforming growth factor-alpha in von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) (−/−) clear cell renal carcinoma cell proliferation: a posible mechanism coupling VHL tumor suppressor inactivation and tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.Y.; Poellinger, L.; Walker, C.L. Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha in renal cell carcinoma associated with loss of Tsc-2 tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Res 2003, 63, 2675–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Verheul, H.M.W.; van Erp, K.; Homs, M.Y.V.; Yoon, G.S.; van Der Groep, P.; Rogers, C.; Hansel, D.E.; Netto, G.J.; Pili, R. The relationship of vascular endothelial growth factor and coagulation factor (fibrin and fibrinogen) expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urology 2010, 75, 608–614. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Xu, B.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhou, H.; Chen, W.; Shen, T.; Han, X.; Huang, S. Hydrogen peroxide inhibits mTOR signaling by activation of AMPKα leading to apoptosis of neuronal cells. Lab Invest 2010, 90, 762–773. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, D.W.; Cachianes, G.; Kuang, W.J.; Goeddel, D.V.; Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science 1989, 246, 1306–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, N.; Henzel, W.J. Pituitary folicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endotelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1989, 1161, 851–858. [Google Scholar]
- Hicklin, D.J.; Ellis, L.M. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J. Clin. Oncol 2005, 23, 1011–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr. Rev 2004, 25, 581–611. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, N. VEGF as therapeutic target in cancer. Oncology 2005, 69, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, A.K.; Dimberg, A.; Kreuger, J.; Claesson-Welsh, L. VEGF receptor signalling-in control of vascular function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2006, 7, 359–371. [Google Scholar]
- Vincenti, V.; Cassano, C.; Rocchi, M.; Persico, G. Assignment of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene to human chromosome 6p21.3. Circulation 1996, 93, 1493–1495. [Google Scholar]
- Fuh, G.; Garcia, K.C.; de Vos, A.M. The interaction of neuropilin-1 with vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor flt-1. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 26690–26695. [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman-Poltorak, Z.; Cohen, T.; Herzog, Y.; Neufeld, G. Neuropilin-2 is a receptor for the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) forms VEGF-145 and VEGF-165 [corrected]. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 18040–18045. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Shen, T.; Chen, W.; Xu, B.; Han, X.; Zhang, F.; Scott, R.S.; Alexander, J.S.; et al. The fungicide ciclopirox inhibits lymphatic endothelial cell tube formation by suppressing VEGFR-3-mediated ERK signaling pathway. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2098–2107. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, K.; Hosoya, Y.; Sumi, S.; Honda, M.; Moriguchi, H.; Yano, M.; Ueda, Y. Studies of the expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in human renal cell carcinomas: a comparison of immunohistochemical method versus ligand binding assay. Oncology 1997, 54, 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Meserburger, A.S.; Hennenlotter, J.; Simon, P.; Kruck, S.; Koch, E.; Horstmann, M.; Kuehs, U.; Kufer, R.; Stenzl, A.; Kuczyk, M.A. Membranous expression and prognostic implications of epidermal growth factor receptor protein in human renal cell cancer. Anticancer Res 2005, 25, 11901–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, J.; Maeda, S.; Umezu, K.; Sugiyama, T.; Kamidono, S. Amplifications and overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in human renal-cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1990, 45, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, K.; Tosaka, A.; Tajeuchi, S.; Kobayashi, N. Epidermal growth factor receptor content in human renal cell carcinomas. Cancer 1994, 73, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar]
- Ciardello, F.; Torotra, G. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N. Engl. J. Med 2008, 358, 1160–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, Y.S.; Huang, C.Y.; Kuo, Y.Z.; Kang, W.Y.; Liu, G.Y.; Huang, A.M.; Yu, H.J.; Lai, M.K.; Huang, S.P.; Wu, W.J.; et al. Characterization of membranous and cytoplasmic EGFR expression in human normal renal cortex and renal cell carcinoma. J. Biomed. Sci 2009, 16, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Langner, C.; Ratschek, M.; Rehak, P.; Schips, L.; Ziguener, R. Are heterogenous results of EGFR immunoreactivity in renal cell carcinoma related to non-standarised criteria for staining evaluation? J. Clin. Pathol 2004, 57, 773–775. [Google Scholar]
- Kallio, J.P.; Hirvikoski, P.; Helin, H.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.; Luukkaala, T.; Tammela, T.L.; Martikainen, P.M. Membranous location of EGFR immunostaining is associated with good prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmockel, G.; Riess, S.; Bassukas, I.D.; Dammrich, J. Epidermal growth factor family and renal cell carcinoma: expression and prognostic impact. Eur. Urol 1997, 31, 478–484. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlman, D.L.; Nguyen, P.; Manivel, J.C.; Zhang, G.; Hagen, K.; Fraley, E.; Aeppli, D.; Niehans, G.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor and transforming growth factor alpha expression in papillary and non-papillary renal cell carcinoma: correlation with metastatic behaviour and prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res 1995, 1, 913–920. [Google Scholar]
- Moch, H.; Sauter, G.; Gasser, T.C.; Bubendorf, L.; Richter, J.; Presti, J.C., Jr; Waldman, F.M.; Mihatsch, M.J. EGF-r gene copy number changes in renal cell carcinoma detected by fluorescence in situ hybridation. J. Pathol 1998, 184, 424–429. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.Y.; Makino, K.; Xia, W.; Matin, A.; Wen, Y.; Kwong, K.Y.; Bourguignon, L.; Hung, M.C. Nuclear localization of EGF receptor and its potential new role as a transcription factor. Nat. Cell Biol 2001, 3, 802–808. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, H.W.; Hsu, S.C.; li-Seyed, M.; Gunduz, M.; Xia, W.; Wei, Y.; Bartholomeusz, G.; Shih, J.Y.; Hung, M.C. Nuclear interaction of EGFR and STAT3 in the activation of the iNOS/NO pathway. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 575–589. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Manning, B.D. The TSC1-TSC2 complex: A molecular switchboard controlling cell growth. Biochem. J 2008, 412, 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, R.S. Multiple roles of the tuberous sclerosis complex genes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2003, 38, 368–375. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Lin, Y.; Ortiz-Vega, S.; Yonezawa, K.; Avruch, J. Rheb binds and regulates the mTOR kinase. Curr. Biol 2005, 15, 702–713. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.D.; Kariya, K.; Kotani, G.; Shirouzu, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Kataoka, T. Coassociation of Rap1A and Ha-Ras with Raf-1 N-terminal region interferes with ras-dependent activation of Raf-1. J. Biol. Chem 1997, 272, 11702–11705. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, H.S.; Monks, T.J.; Everitt, J.I.; Walker, C.L.; Lau, S.S. Cell proliferation is insufficient, but loss of tuberin is necessary, for chemically induced nephrocarcinogenicity. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol 2002, 283, F262–F270. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, H.S.; Monks, T.J.; Walker, C.L.; Lau, S.S. Transformation of kidney epithelial cells by a quinol thioether via inactivation of the tuberous sclerosis-2 tumor suppressor gene. Mol. Carcinog 2001, 31, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.D.; Gard, J.M.; Nagle, R.B.; Dietrich, J.D.; Monks, T.J.; Lau, S.S. ERK crosstalks with 4EBP1 to activate cyclin D1 translation during quinol-thioether-induced tuberous sclerosis renal cell carcinoma. Toxixol. Sci 2011, 124, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Opavsky, R.; Pastorekova, S.; Zelnik, V.; Gibadulinová, A.; Stanbridge, E.J.; Závada, J.; Kettmann, R.; Pastorek, J. Human MN/CA9 gene, a novel member of the carbonic anhydrase family: structure and exon to protein domain relationships. Genomics 1996, 33, 480–487. [Google Scholar]
- Pastorek, J.; Pastoreková, S.; Callebaut, I.; Mornon, J.P.; Zelník, V.; Opavský, R.; Zat’ovicová, M.; Liao, S.; Portetelle, D.; Stanbridge, E.J.; et al. Cloning and characterization of MN, a human tumor-associated protein with a domain homologous to carbonic anhydrase and putative helix-loop-helix DNA binding segment. Oncogene 1994, 9, 2877–2888. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, S.; Liao, S.Y.; Ivanova, A.; Danilkovitch-Miagkova, A.; Tarasova, N.; Weirich, G.; Merrill, M.J.; Proescholdt, M.A.; Oldfield, E.H.; Lee, J.; et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible cell-surface transmembrane carbonic anhydrase in human cancer. Am. J. Pathol 2001, 158, 905–919. [Google Scholar]
- Uemura, H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Saga, S.; Yoshikawa, K.; Hirao, Y.; Oosterwijk, E. MN/CA IX/G250 as a potential target for immunotherapy of renal cell carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 741–746. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.Y.; Aurelio, O.N.; Jan, K.; Zavada, J.; Stanbridge, E.J. Identification of the MN/CA9 protein as a reliable diagnostic biomarker of clear cell carcinoma of the kidney. Cancer Res 1997, 57, 2827–2831. [Google Scholar]
- McKiernan, J.M.; Buttyan, R.; Bander, N.H.; de la Taille, A.; Stifelman, M.D.; Emanuel, E.R.; Bagiella, E.; Rubin, M.A.; Katz, A.E.; Olsson, C.A.; et al. The detection of renal carcinoma cells in the peripheral blood with an enhanced reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay for MN/CA9. Cancer 1999, 86, 492–497. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, Y.; Kanda, K.; Tsuji, M.; Kanayama, H.; Kagawa, S. MN/CA9 gene expression as a potential biomarker in renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int 1999, 83, 743–747. [Google Scholar]
- McKiernan, J.M.; Buttyan, R.; Bander, N.H.; Stifelman, M.D.; Katz, A.E.; Chen, M.W.; Olsson, C.A.; Sawczuk, I.S. Expression of the tumor associated gene MN: a potential biomarker for human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 1997, 57, 2362–2365. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, M.H.; Seligson, D.; Han, K.R.; Pantuck, A.J.; Dorey, F.J.; Huang, Y.; Horvath, S.; Leibovich, B.C.; Chopra, S.; Liao, S.Y.; et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX is a independent predictor of survival in advanced renal clear cell carcinoma:implications for prognosis and therapy. Clin. Cancer Res 2003, 9, 802–811. [Google Scholar]
- Rak, J.; Yu, J.L.; Kerbel, R.S.; Coomber, B.L. What do oncogenic mutations have to do with angiogenesis/vascular dependence of tumors? Cancer Res 2002, 62, 1931–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Isselbacher, K.J. Sugar and amino acid transport by cells in culture -differences between normal and malignant cells. N. Engl. J. Med 1972, 286, 929–933. [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka, M. Transport of sugars in tumor cell membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1974, 355, 77–104. [Google Scholar]
- Manolescu, A.R.; Witkowska, K.; Kinnaird, A.; Cessford, T.; Cheeseman, C. Facilitated hexose transporters: new perspectives on form and function. Physiology (Bethesda) 2007, 22, 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- Douard, V.; Ferraris, R.P. Regulation of the fructose transporter GLUT5 in health and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab 2008, 295, 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Nagase, Y.; Takata, K.; Moriyama, N.; Aso, Y.; Murakami, T.; Hirano, H. Immunohistochemical localization of glucose transporters in human renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Urol 1995, 153, 798–801. [Google Scholar]
- Warburg, O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, I.; Rudolph, P.; Weichert-Jacobsen, K. Value of p53 expression, cellular proliferation, and DNA content as prognostic indicators in renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol 1997, 32, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmockel, G.; Wittman, A.; Dammrich, J.; Bassukas, I.D. Expression of p53 and bcl-2 in primary locally confined renal cell carcinomas: no evidence for prognostic significance. Anticancer Res 1996, 16, 3807–3811. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, R.E.; Anglard, P.; Liu, S.; Gnarra, J.R.; Linehan, W.M. Chromosome 17p deletions and p53 mutations in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 1993, 53, 3092–3097. [Google Scholar]
- Moch, H.; Sauter, G.; Gasser, T.C.; Buchholz, N.; Bubendorf, L.; Ritcher, J.; Jiang, F.; Dellas, A.; Mihatsch, M.J. P53 protein expression is associated with rapid tumor cell proliferation and prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Res 1997, 25, S25–S30. [Google Scholar]
- Bot, F.J.; Godschalk, J.C.; Krishnadath, K.K.; van der Kwast, T.H.; Bosman, F.T. Prognostic factors in renal-cell carcinoma: immunohistochemical detection of p53 protein versus clinico-pathological parameters. Int. J. Cancer 1994, 57, 634–637. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, A.; Pandha, H.S. Renal-cell carcinoma: tumour markers, T-cell epitopes, and potential for new therapies. Lancet Oncol 2003, 4, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, F.; Wahl, G.M. Regulating the p53 pathway: in vitro hypotheses, in vivo veritas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 909–923. [Google Scholar]
- Resiman, D.; Loging, W.T. Trancriptional regulation of the p53 tumor suppressor gene. Semin. Cancer Biol 1998, 8, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi, A.; Oya, M.; Shimada, T.; Uchida, A.; Marumo, K.; Murai, M. Activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in renal cell carcinoma: a study of incidence and its association with pathological features and clinical outcome. J. Urol 2002, 168, 762–765. [Google Scholar]
- Takaoka, A.; Hayakawa, S.; Yanai, H.; Stoiber, D.; Negishi, H.; Kikuchi, H.; Sasaki, S.; Imai, K.; Shibue, T.; Honda, K.; Taniguchi, T. Integration of interferon-alpha/beta signaling to p53 responses in tumour suppression and antiviral defence. Nature 2003, 424, 516–523. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, A.; Kamai, T.; Abe, H.; Arai, K.; Yoshida, K. Is Stat3 and/or p53 mRNA expression a prognostic marker for renal cell carcinoma? Biomecidal Res 2009, 30, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Warburton, H.E.; Brady, M.; Vlatković, N.; Linehan, W.M.; Parsons, K.; Boyd, M.T. P53 regulation and function in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 6498–6503. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Xu, B.; Beevers, C.S.; Odaka, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, W.; Shen, T.; et al. Curcumin inhibits protein phosphatases 2A and 5, leading to activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and death in tumor cells. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 868–875. [Google Scholar]
- Wrana, J.L.; Attisano, L.; Wieser, R.; Ventura, F.; Massage, J. Mechanisms of activation of the TGF-β receptor. Nature 1994, 370, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Massague, J. TGF-β signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem 1998, 67, 753–791. [Google Scholar]
- Cardillo, M.R.; Lazzereschi, D.; Gandini, O.; Di Silverio, F.; Colleta, G. Transforming growth factor-β pathway in human renal cell carcinoma and surrounding normal-appearing renal parenchyma. Anal. Ouant. Cytol. Histol 2001, 23, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, L.I. The role for transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) in human cancer. Crit. Rev. Onco 1999, 10, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Heldin, C.H.; Miyazono, K.; te Dijke, P. TGF-β signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature 1997, 390, 465–471. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, G.T.; Kim, S.J.; Ma, K.A.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, D. ACE inhibitors attenuate expression of renal transforming growth factor-β1 in humans. Am. J. Kidney Dis 2000, 36, 894–902. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrow, M.G.; Moses, H.L. Transforming growth factor β and cell cycle regulation. Cancer Res 1995, 55, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Polyak, K. Negative regulation of cell growth by TGF-β. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1242, 185–199. [Google Scholar]
- Gary Lee, Y.C.; Melkerneker, D.; Thompson, P.J.; Light, R.W.; Lane, K.B. Transforming growth factor beta induces vascular endothelial growth factor elaboration from pleural mesothelial cells in vivo and in vitro. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 2002, 165, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Benckert, C.; Jonas, S.; Cramer, T.; Von Marschall, Z.; Schäfer, G.; Peters, M.; Wagner, K.; Radke, C.; Wiedenmann, B.; Neuhaus, P.; et al. Transforming growth factor beta 1 stimulates vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription in human cholangiocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 2003, 63, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Stover, D.G.; Bierie, B.; Moses, H.L. A delicate balance: TGF-beta and the tumor microenvironment. J. Cell Biochem 2007, 101, 851–861. [Google Scholar]
- Jakowlew, S.B. Transforming growth factor-beta in cancer and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2006, 25, 435–457. [Google Scholar]
- Zavadil, J.; Bottinger, E. TGF-beta and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5764–5774. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Lu, S.L.; Li, A.G.; He, W.; Corless, C.L.; Kulesz-Martin, M.; Wang, X.J. Distinct mechanisms of TGF-beta 1-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis during skin carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Invest 2005, 115, 1714–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Humes, H.D.; Cieslinski, D.A.; Coimbra, T.M.; Messana, J.M.; Galvao, C. Epidermal growth factor enhances renal tubule regeneration and repair and accelerates the recovery of renal function in postischemic acute renal failure. J. Clin. Invest 1989, 84, 1757–1761. [Google Scholar]
- Gomella, L.G.; Sargent, E.R.; Wade, T.P.; Anglard, P.; Linehan, W.M.; Kasid, A. Expression of transforming growth factor α in normal human adult kidney and enhanced expression of transforming growth-factor α and β1 in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 1989, 49, 6972–6975. [Google Scholar]
- Atlas, I.; Mendelsohn, J.; Baselga, J.; Fair, W.R.; Masui, H.; Kumar, R. Growth regulation of human renal carcinoma cells: role of transforming growth factor α. Cancer Res 1992, 52, 3335–3339. [Google Scholar]
- Gogusev, J.; Augusti, M.; Chrétein, Y.; Droz, D. Interleukin-6 and TNF α production in human renal cell carcinoma. Kidney Int 1993, 44, 585–592. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, M.V.; Zheng, X.; Pereira, T.; Gradin, K.; Jin, S.; Lundkvist, J.; Ruas, J.L.; Poellinger, L.; Lendahl, U.; Bondesson, M. Hypoxia requires notch signaling to maintain the undifferentiated cell state. Dev. Cell 2005, 9, 617–628. [Google Scholar]
- Mailhos, C.; Modlich, U.; Lewis, J.; Harris, A.; Bicknell, R.; Ish-Horowicz, D. Delta4, an endothelial specific notch ligand expressed at sites of physiological and tumor angiogenesis. Differentiation 2001, 69, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Sahlgren, C.; Gustafsson, M.V.; Jin, S.; Poellinger, L.; Lendahl, U. Notch signaling mediates hypoxia-induced tumor cell migration and invasion. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci 2008, 105, 6392–6397. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Wen, H.; Brayton, C.; Das, P.; Smithson, L.A.; Fauq, A.; Fan, X.; Crain, B.J.; Price, D.L.; Golde, T.E.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor and Notch pathways participate in the tumor suppressor funtion of γ-secretase. J. Biol. Chem 2007, 282, 32264–32273. [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe, D.; Kopan, R. Notch and presenilins: regulated intramembrane proteolysis links development and degeneration. Annu. Rev. Neurosci 2003, 26, 565–597. [Google Scholar]
- De Strooper, B.; Annaert, W.G.; Cupers, P.; Saftig, P.; Craessaerts, K.; Mumm, J.S.; Schrieter, E.H.; Schrijvers, V.; Wolfe, M.S.; Ray, W.J.; et al. A presenilin-1-dependent gamma-secretase-like protease mediates release of Notch intracellular domain. Nature 1999, 398, 518–522. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.J.; Shirakawa, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.J.; Shirakawa, T.; Li, Y.; Soma, A.; Oka, M.; Dotto, G.P.; Fairman, R.M.; et al. Regulation of Notch1 and Dll4 by vascular endothelial growth factor in arterial endothelial cells: implications for modulating arteriogenesis and angiogenesis. Mol. Cell Biol 2003, 23, 14–25. [Google Scholar]
- Shawber, C.J.; Das, I.; Francisco, E.; Kitajewski, J. Notch signaling in primary endothelial cells. Am. N. Y. Acad. Sci 2003, 995, 162–170. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.O.; Wang, C.Y. Notch signaling in the regulation of tumor angiogenesis. Trends Cell Biol 2006, 16, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Shawber, C.J.; Kitajewski, J. Notch function in the vasculature: Insights from zebrafish, mouse and man. Bioessays 2004, 26, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, S.J. Notch signaling: A simple pathway becomes complex. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2006, 7, 678–689. [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbut, G.D.; Kankel, M.W.; Lake, R.J.; Artavanis-Tsakonas, S. Crossing paths with Notch in the hyper-network. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 2007, 19, 166–175. [Google Scholar]
- Kopan, R.; Ilagan, M.X. The canonical Notch signaling pathway: Unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell 2009, 137, 216–233. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, M.; Petitjean, A.; Marcel, V.; Pétré, A.; Mounawar, M.; Plymoth, A.; de Fromentel, C.C.; Hainaut, P. Recent advances in p53 research: an interdisciplinary perspective. Cancer Gene Ther 2009, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, T.; Sontang, E.; Chen, P.; Levine, A. Transcriptional control of human p53-regulated genes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2008, 9, 402–412. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, M.; Pear, W.S.; Aster, J.C. The multifaceted role of Notch in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev 2007, 17, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Mungamuri, S.K.; Yang, X.; Thor, A.D.; Somasundaran, K. Survival signaling by Notch1: Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-dependent inhibition of p53. Cancer Res 2006, 66, 4715–4724. [Google Scholar]
- Stiewe, T. The p53 family in differentiation and tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Balint, K.; Xiao, M.; Pinnix, C.C.; Soma, A.; Veres, I.; Juhasz, I.; Brown, E.J.; Capobianco, A.J.; Herlyn, M.; Liu, Z.J. Activation of Notch1 signaling is required for β-catenin-mediated human primary melanoma progession. J. Clin. Invest 2005, 115, 3166–3176. [Google Scholar]
- Dotto, G.P. Crosstalk of Notch with p53 and p63 in cancer growth control. Nat. Rev 2009, 9, 587. [Google Scholar]
- Pastoric, M.; Das, H.K. Regulation of transcription of the human presenilin-1 gene by ets transcription factors and the p53 protooncogene. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 34938–34945. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Aster, J.C.; Blacklow, S.C.; Lake, R.; Artavanis-Tsakonas, S.; Griffin, J.D. MAML1 a human homologue of Drosophila mastermind, is a transcriptional co-activator for Notch receptors. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 484–489. [Google Scholar]
- Colaluca, I.N.; Tosoni, D.; Nuciforo, P.; Senic-Matuglia, F.; Galimberti, V.; Viale, G.; Pece, S.; Di Fiore, P.P. NUMB controls p53 tumour suppressor activity. Nature 2008, 451, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Vivekanad, P.; Rebay, I. Intersection of signal transduction pathways and development. Ann. Rev. Genet 2006, 40, 139–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, C.A.; Sartorius, C.A.; Abdel-Hafiz, H; Spillman, M.A.; Horwitz, K.B.; Jacobsen, B.M. Progesterone receptor action: Translating studies in breast cancer models to clinical insights. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 630, 94–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ciardiello, F.; Tortora, G. Interactions between the epidermal growth factor receptor and type I protein kinase A. Biological significance and therapeutic implications. Clin. Cancer Res 1998, 4, 821–828. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, N.; Bhandari, R.; Natarajan, V.T.; Visweswariah, S.S. Crosstalk between receptor guanylyl cyclase C and c-src tyrosine kinase regulates colon cancer cell cytostasis. Mol. Cell Biol 2009, 29, 5277–5289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.L.; Partin, J.V.; Brucheimer, E.M.; Strup, S.E.; Kyprianou, N. TGF-beta signaling and androgen receptor status determine apoptotic crosstalk in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2008, 68, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallego, G.A.; Villaamil, V.M.; Grande, E.; Caínzos, I.S.; Aparicio, L.M.A. Crossing Paths in Human Renal Cell Carcinoma (hRCC). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12710-12733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012710
Gallego GA, Villaamil VM, Grande E, Caínzos IS, Aparicio LMA. Crossing Paths in Human Renal Cell Carcinoma (hRCC). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(10):12710-12733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012710
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallego, Guadalupe Aparicio, Vanessa Medina Villaamil, Enrique Grande, Isabel Santamarina Caínzos, and Luís M. Antón Aparicio. 2012. "Crossing Paths in Human Renal Cell Carcinoma (hRCC)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 10: 12710-12733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012710
APA StyleGallego, G. A., Villaamil, V. M., Grande, E., Caínzos, I. S., & Aparicio, L. M. A. (2012). Crossing Paths in Human Renal Cell Carcinoma (hRCC). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(10), 12710-12733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012710



