Short Hairpin RNA (shRNA) Ether à go-go 1 (Eag1) Inhibition of Human Osteosarcoma Angiogenesis via VEGF/PI3K/AKT Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
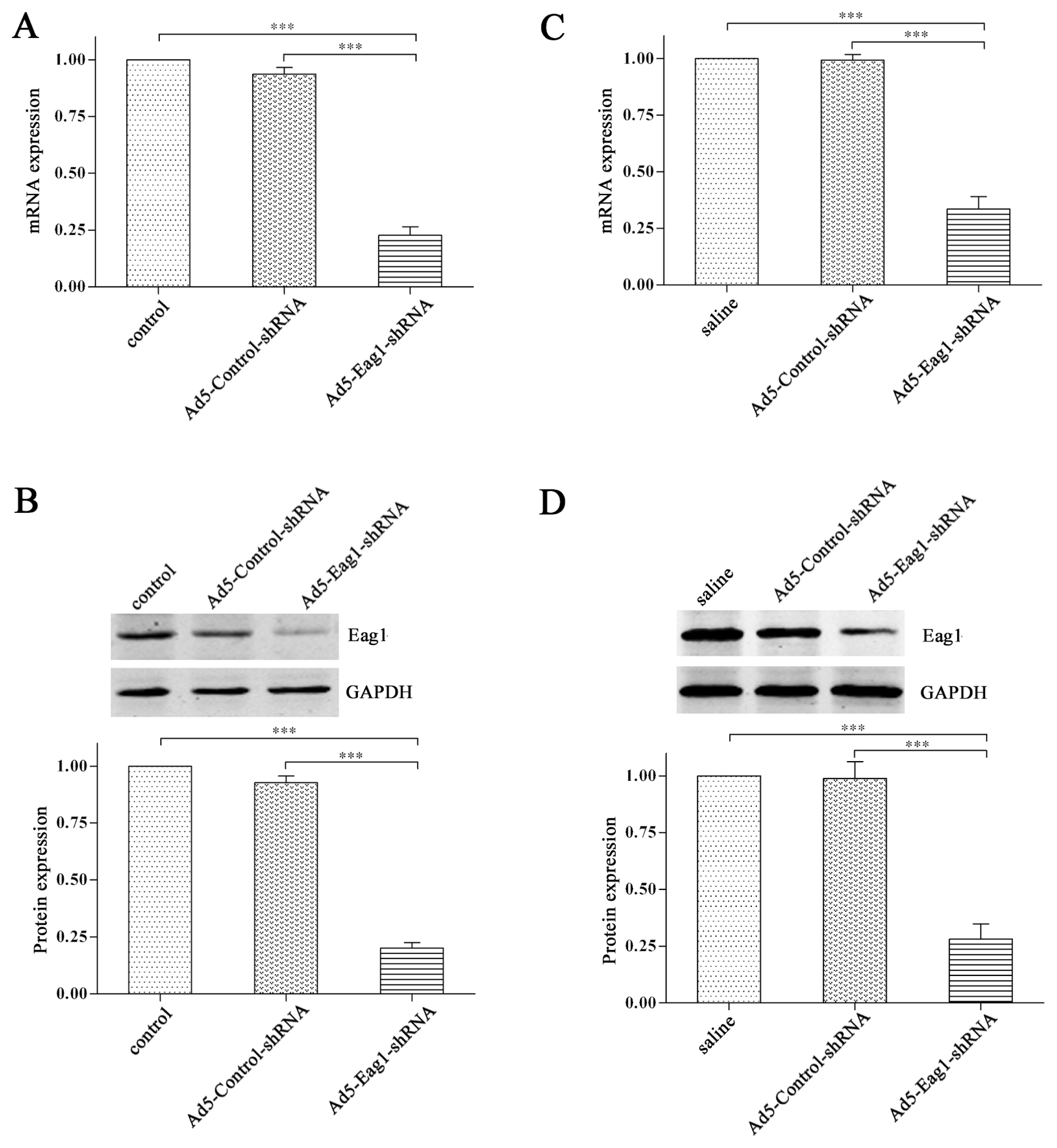
2.1. Knockdown Efficiency of Ad5-Eag1-shRNA
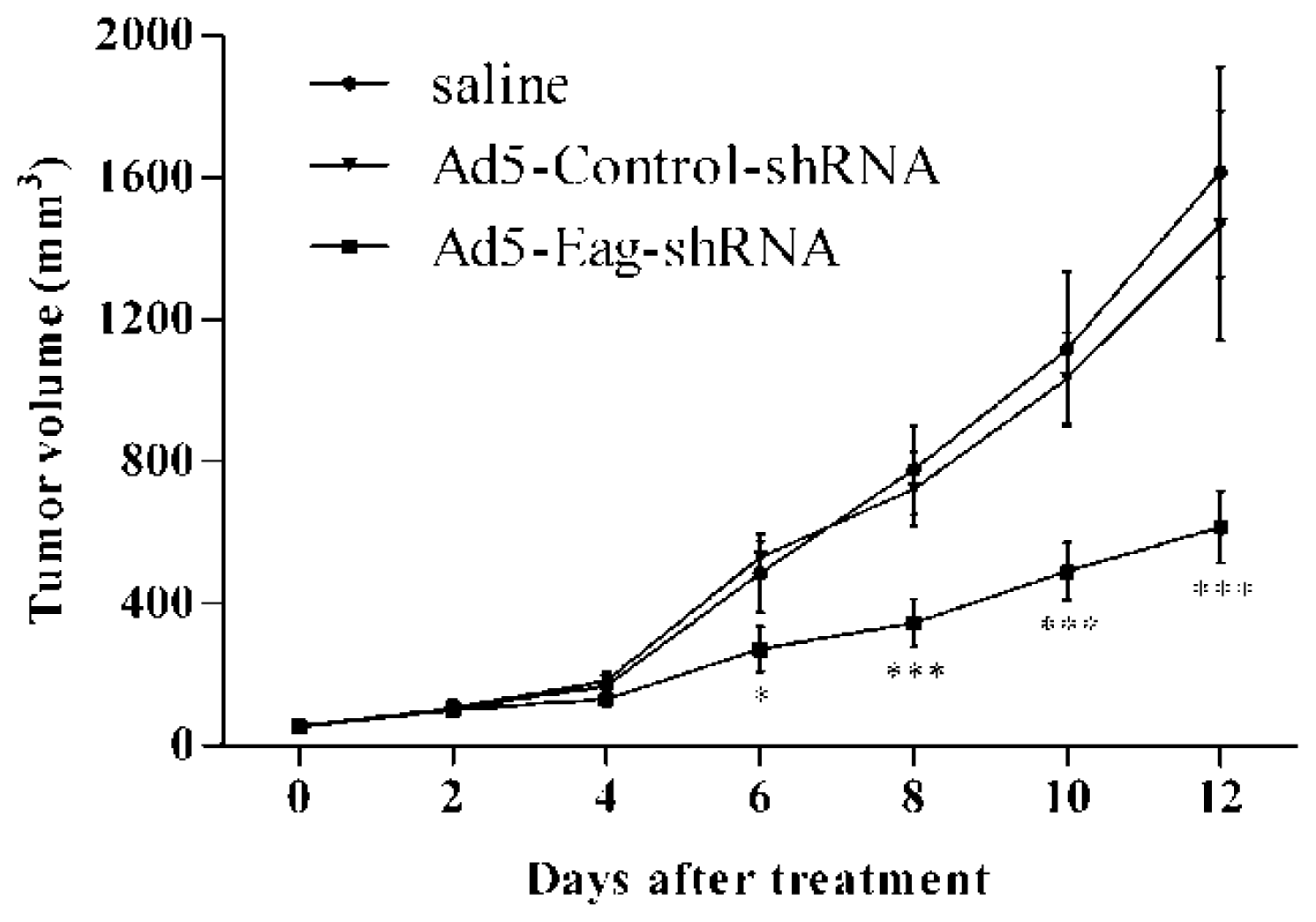
2.2. Eag1 Silencing Inhibits Osteosarcoma Growth in Vivo
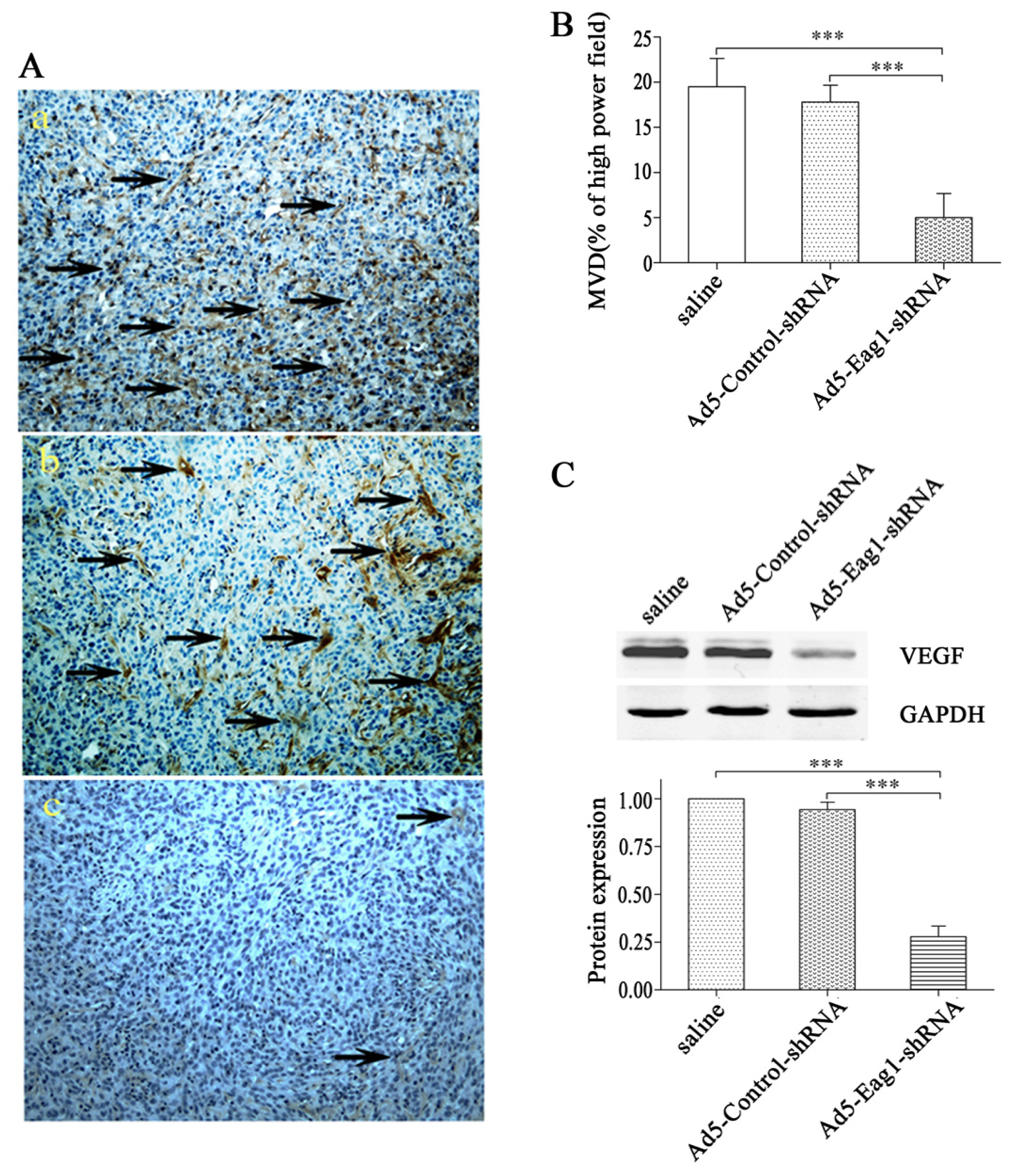
2.3. Eag1 Silencing Inhibits Angiogenesis of Xenografted Osteosarcoma
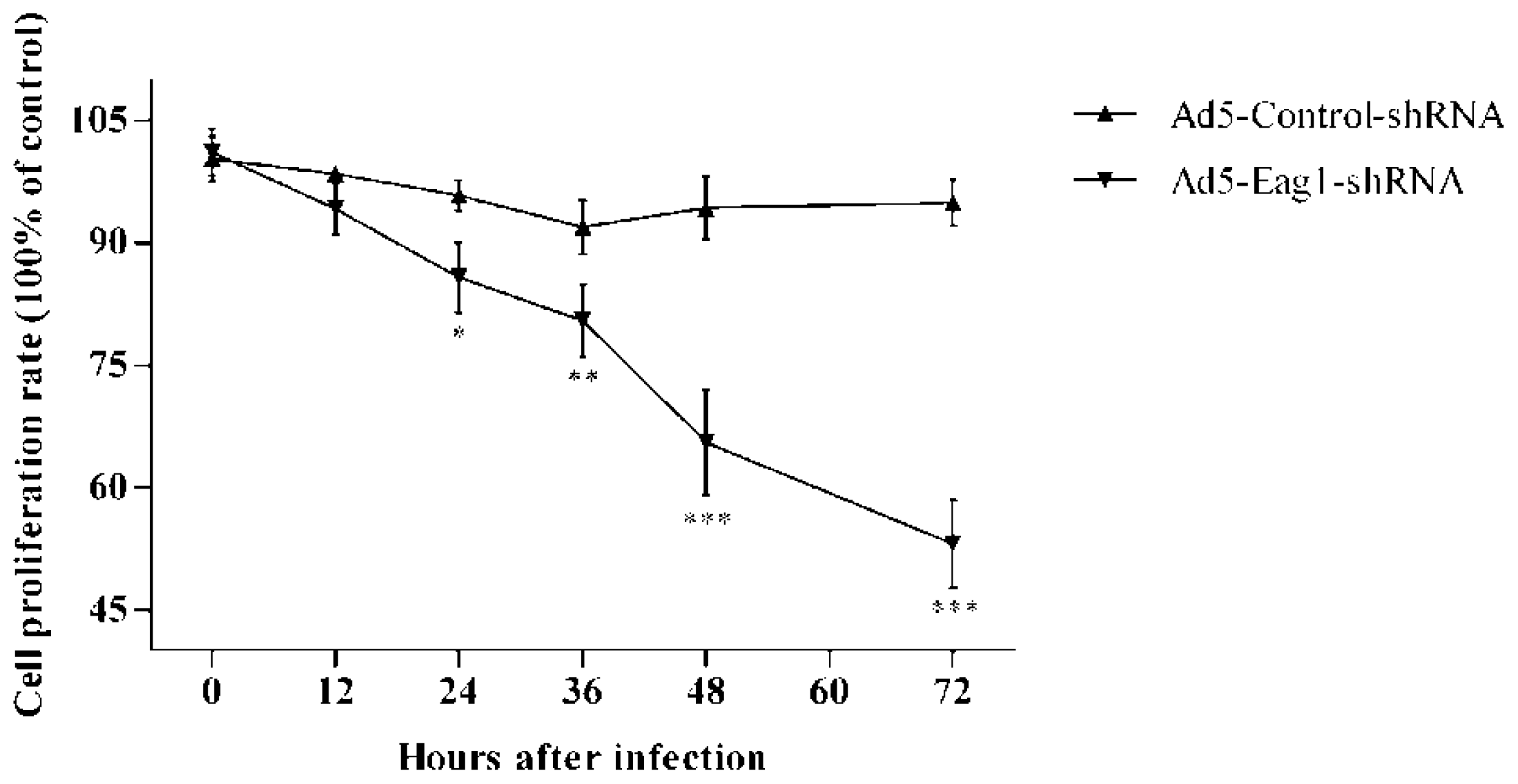
2.4. Eag1 Silencing Reduces the Proliferation of Osteosarcoma Cells
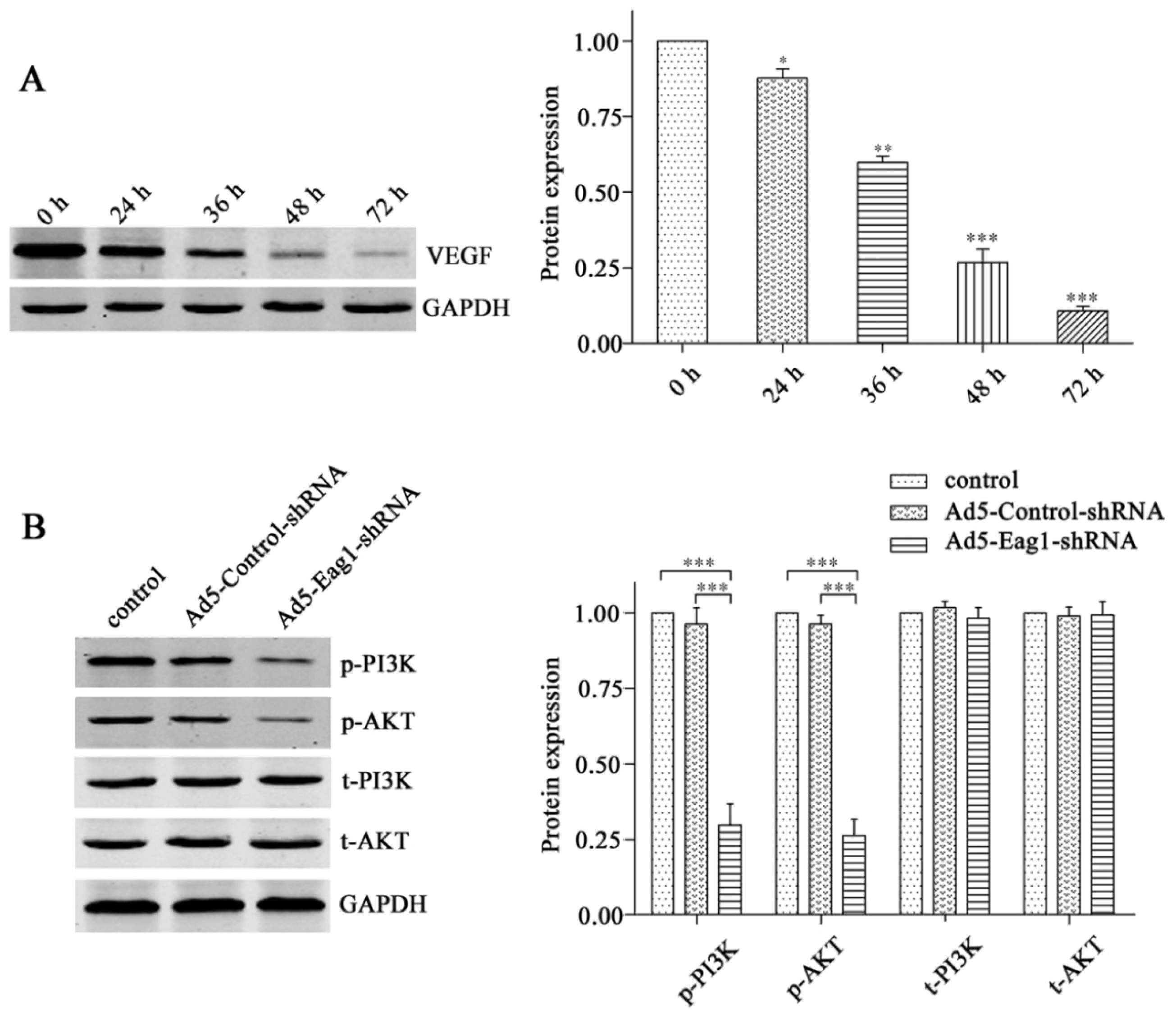
2.5. Eag1 Silencing Inhibits VEGF/PI3K/AKT Signaling in Osteosarcoma Cells
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Cell Culture
4.3. Tumor Model
4.4. Histological Sections and Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Adenovirus Infection
4.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.7. Real-Time PCR
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
- Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Pardo, L.A.; Contreras-Jurado, C.; Zientkowska, M.; Alves, F.; Stuhmer, W. Role of voltage-gated potassium channels in cancer. J. Membr. Biol 2005, 205, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, J. Ether à go-go potassium channels and cancer. Cancer Lett 2006, 233, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmerlein, B.; Weseloh, R.M.; de Queiroz, F.M.; Knötgen, H.; Sánchez, A.; Rubio, M.E.; Martin, S.; Schliephacke, T.; Jenke, M.; Heinz-Joachim-Radzun; et al. Overexpression of Eag1 potassium channels in clinical tumours. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, L.A.; del Camino, D.; Sánchez, A.; Alves, F.; Brüggemann, A.; Beckh, S.; Stühmer, W. Oncogenic potential of EAG K+ channels. EMBO J 1999, 18, 5540–5547. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, V.; Sowter, H.; Shaw, R.; Bali, A.; Khan, R. Eag and HERG potassium channels as novel therapeutic targets in cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol 2010, 8, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Folkman, J. Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin. Oncol 2002, 29, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Downie, B.R.; Sánchez, A.; Knötgen, H.; Contreras-Jurado, C.; Gymnopoulos, M.; Weber, C.; Stühmer, W.; Pardo, L.A. Eag1 expression interferes with hypoxia homeostasis and induces angiogenesis in tumors. J. Biol. Chem 2008, 283, 36234–36240. [Google Scholar]
- Rini, B.I.; Small, E.J. Biology and clinical development of vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol 2005, 23, 1028–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, T.M.; Chen, Y.L.; Wu, Y.Y.; Yuan, A.; Chao, Y.C.; Chung, Y.C.; Wu, M.H.; Yang, S.C.; Pan, S.H.; Shih, J.Y.; et al. Targeting neuropilin 1 as an antitumor strategy in lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res 2007, 13, 4759–4768. [Google Scholar]
- Los, M.; Voest, E.E.; Inne, H.M.; Rinkes, B. VEGF as a target of therapy in gastrointestinal oncology. Dig. Surg. 2005, 22, 282–293. [Google Scholar]
- Damron, T.A.; Ward, W.G.; Stewart, A. Osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing’s sarcoma: National Cancer Data Base report. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res 2007, 459, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sluga, M.; Windhager, R.; Pfeiffer, M.; Ofner, P.; Lang, S.; Dominkus, M.; Nehrer, S.; Zoubek, A.; Kotz, R. Osteosarcoma and Ewing’s sarcoma—The most frequent malignant bone tumors in children-therapy and outcome. Z. Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb 2002, 140, 652–655. [Google Scholar]
- Bielack, S.S.; Kempf-Bielack, B.; Delling, G.; Exner, G.U.; Flege, S.; Helmke, K.; Kotz, R.; Salzer-Kuntschik, M.; Werner, M.; Winkelmann, W.; et al. Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma of the extremities or trunk: an analysis of 1702 patients treated on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J. Clin. Oncol 2002, 20, 776–790. [Google Scholar]
- Eppert, K.; Wunder, J.S.; Aneliunas, V.; Kandel, R.; Andrulis, I.L. von Willebrand factor expression in osteosarcoma metastasis. Mod. Pathol 2005, 18, 388–397. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, P.M. Chemokines and the molecular basis of cancer metastasis. N. Engl. J. Med 2001, 345, 833–835. [Google Scholar]
- Kawauchi, T. Cell Adhesion and Its Endocytic Regulation in Cell Migration during Neural Development and Cancer Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 4564–4590. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, H.M.; Seo, K.H.; Han, S.J.; Ahn, K.Y.; Choi, I.H.; Koh, G.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Ra, M.S.; Im, S.Y. Nuclear factor kappaB dependency of platelet-activating factor-induced angiogenesis. Cancer Res 2002, 62, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, N.; Davis-Smyth, T. The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr. Rev 1997, 18, 4–25. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, L.E.; Golijanin, D.; Itin, A.; Pode, D.; Keshet, E. Selective ablation of immature blood vessels in established human tumors follows vascular endothelial growth factor withdrawal. J. Clin. Invest 1999, 103, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun, M.; D’Amore, P.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 1996, 7, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P.; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med 2003, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar]
- Stuttfeld, E.; Ballmer-Hofer, K. Structure and function of VEGF receptors. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 915–922. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.C.; Zhou, S.; da Costa, L.T.; Yu, J.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2509–2514. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.S.; Mei, J.; Tong, T.L.; Hu, M.; Xue, H.M.; Cai, X.S. Inhibitory effects of VEGF-siRNA mediated by adenovirus on osteosarcoma-bearing nude mice. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm 2009, 24, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- García-Becerra, R.; Díaz, L.; Camacho, J.; Barrera, D.; Ordaz-Rosado, D.; Morales, A.; Ortiz, C.S.; Avila, E.; Bargallo, E.; Arrecillas, M; et al. Calcitriol inhibits Ether-à go-go potassium channel expression and cell proliferation in human breast cancer. Exp. Cell Res 2010, 316, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Wu, X.; Zhong, D.; Zhai, W.; Ding, Z.; Zhou, Y. Short Hairpin RNA (shRNA) Ether à go-go 1 (Eag1) Inhibition of Human Osteosarcoma Angiogenesis via VEGF/PI3K/AKT Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12573-12583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012573
Wu J, Wu X, Zhong D, Zhai W, Ding Z, Zhou Y. Short Hairpin RNA (shRNA) Ether à go-go 1 (Eag1) Inhibition of Human Osteosarcoma Angiogenesis via VEGF/PI3K/AKT Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(10):12573-12583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012573
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jin, Xinyu Wu, Daixing Zhong, Wenliang Zhai, Zhenqi Ding, and Yong Zhou. 2012. "Short Hairpin RNA (shRNA) Ether à go-go 1 (Eag1) Inhibition of Human Osteosarcoma Angiogenesis via VEGF/PI3K/AKT Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 10: 12573-12583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012573
APA StyleWu, J., Wu, X., Zhong, D., Zhai, W., Ding, Z., & Zhou, Y. (2012). Short Hairpin RNA (shRNA) Ether à go-go 1 (Eag1) Inhibition of Human Osteosarcoma Angiogenesis via VEGF/PI3K/AKT Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(10), 12573-12583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012573



