Hormonal Influence on Coenzyme Q10 Levels in Blood Plasma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
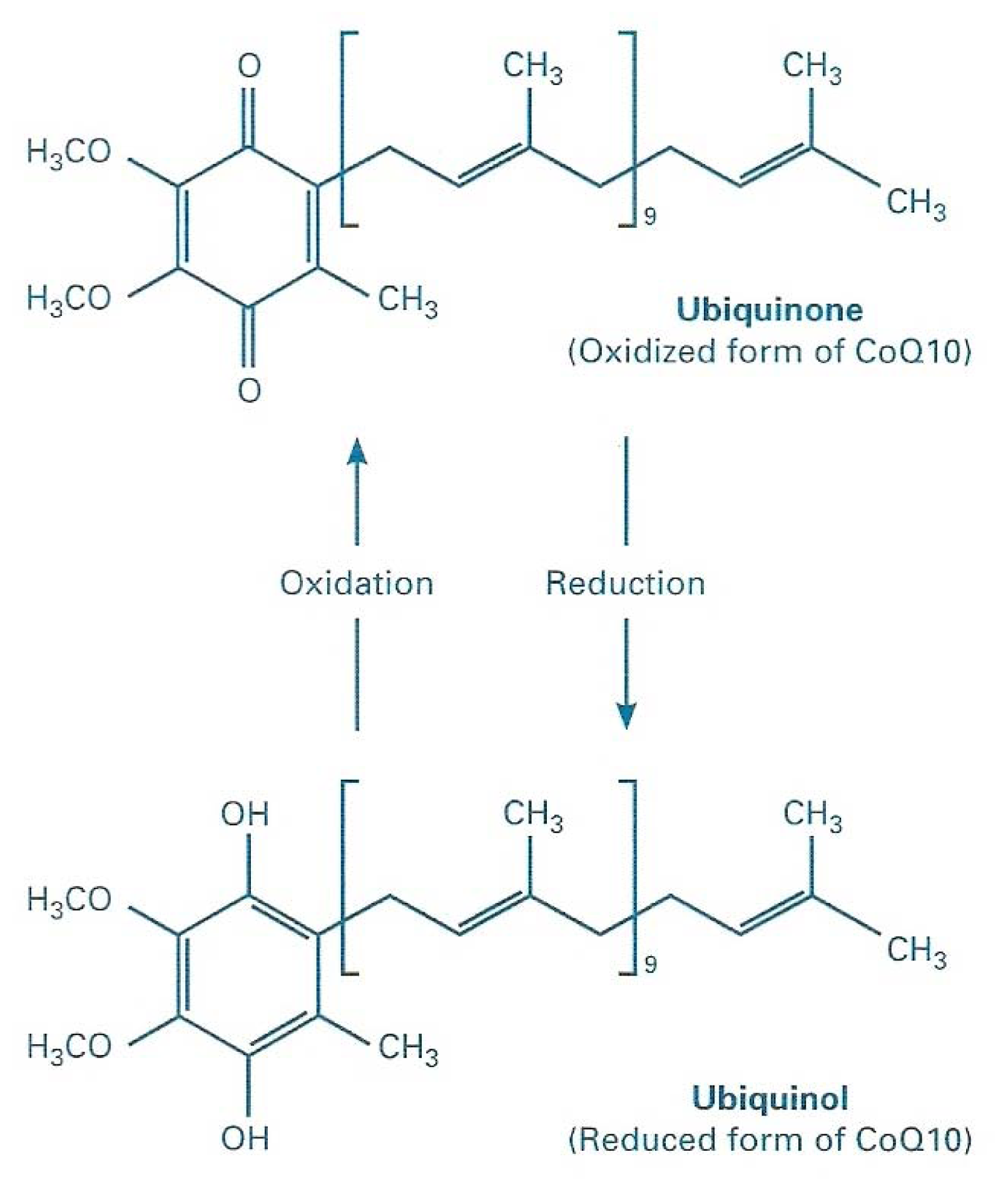
2. CoQ10 Functions
2.1. Bioenergetical Role of CoQ10
2.2. CoQ10 and Oxidative Stress
3. Clinical Significance of CoQ10 Measurement
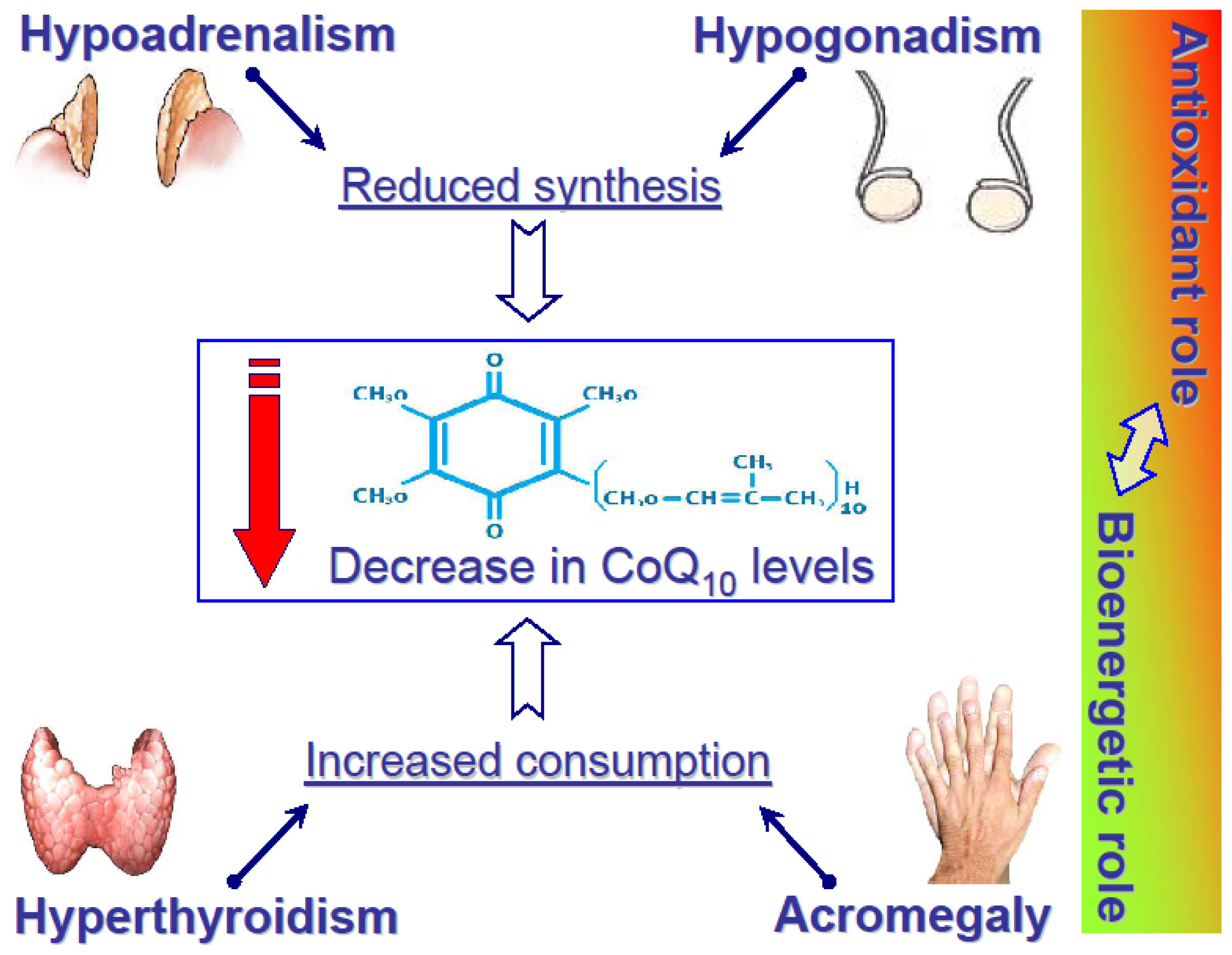
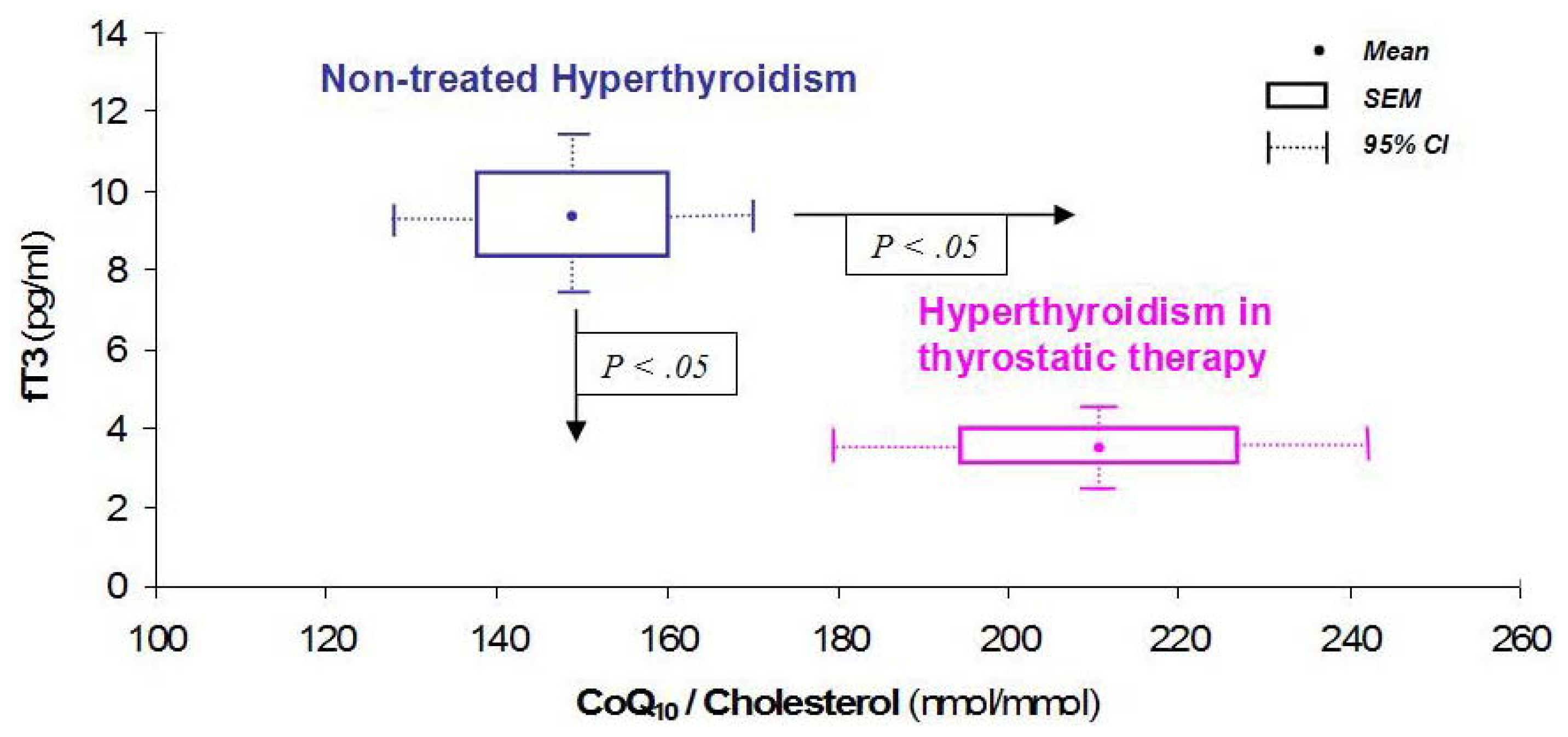
4. CoQ10 and Thyroid
5. CoQ10 in Other Endocrine Diseases
5.1. Adrenal Disease
5.2. Gonadal Disease
5.3. Growth Hormone
6. Conclusions
References
- Crane, F.L. Biochemical functions of coenzyme Q10. J. Am. Coll. Nutr 2001, 20, 591–598. [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Sparna, T.; Kaltschmidt, C. Activation of NFκB by reactive oxygen intermediates in the nervous system. Antioxid. Redox Signal 1999, 1, 129–144. [Google Scholar]
- Littarru, G.P.; Tiano, L. Clinical aspects of coenzyme Q10: An update. Nutrition 2010, 26, 250–254. [Google Scholar]
- Littarru, G.P.; Mosca, F.; Fattorini, D.; Bompadre, S.; Battino, M. Assay of coenzyme Q10 in plasma by a single dilution step. Methods Enzymol 2004, 378, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, A.; Festa, R.; Di Donna, V.; Leone, E.; Littarru, G.P.; Silvestrini, A.; Meucci, E.; Pontecorvi, A. Hormones and antioxidant systems: Role of pituitary and pituitary-dependent axes. J. Endocrinol. Invest 2010, 33, 422–433. [Google Scholar]
- Littarru, G.P. The Mitochondrion: A Main Energy Plant. In Energy and Defence; CESI: Roma, Italy, 1994; pp. 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Littarru, G.P. Radical Formation in vivo. In Energy and Defence; CESI: Roma, Italy, 1994; pp. 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.; Hamasaki, N. Mitochondrial oxidative stress and mitochondrial DNA. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med 2003, 41, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Turrens, J.F.; Boveris, A. Generation of superoxyde anion by the NADH dehydrogenase of bovine mitochondria. Biochem. J 1980, 191, 421–427. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, A.R.; Jones, O.T.G. Enzymic mechanism of superoxyde production. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1057, 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, S.P.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Hunt, J.V. Protein glycation and oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus and ageing. Free Radical. Biol. Med 1991, 10, 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Littarru, G.P. Antioxidant Mechanisms. In Energy and Defence; CESI: Roma, Italy, 1994; pp. 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, S.R.; Witting, P.K.; Stocker, R. A role for reduced coenzyme Q in atherosclerosis? Biofactors 1999, 9, 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker, R.; Bowry, V.W.; Frei, B. Ubiquinol-10 protects human low density lipoprotein more efficiently against lipid peroxidation than does α-tocopherol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 1646–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, D.; Bowry, V.W.; Stocker, R. Dietary supplementation with coenzyme Q10 results in increased levels of ubiquinol-10 within circulating lipoproteins and increased resistance of human low-density lipoprotein to the initiation of lipid peroxidation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1126, 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Lakka, H.M.; Laaksonen, D.E.; Lakka, T.A.; Niskanen, L.K.; Kumpusalo, E.; Tuomilehto, J.; Salonen, J.T. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA 2002, 288, 2709–2716. [Google Scholar]
- Isomaa, B.; Almgren, P.; Tuomi, T.; Forsén, B.; Lahti, K.; Nissén, M.; Taskinen, M.R.; Groop, L. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 683–689. [Google Scholar]
- Griffth, R.L.; Virella, G.T.; Stevenson, H.C.; Lopes-Virella, M.F. Low density lipoprotein metabolism by human macrophages activated with low density lipoprotein immune complexes. A possible mechanism of foam cell formation. J. Exp. Med 1988, 168, 1041–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, E.C.; Hirsch, I.B.; Brunzell, J.D.; Chait, A. Reduced plasma peroxyl radical trapping capacity and increased susceptibility of LDL to oxidation in poorly controlled IDDM. Diabetes 1994, 43, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasetti, M.; Alleva, R.; Solenghi, M.D.; Littarru, G.P. Distribution of antioxidants among blood components and lipoproteins: Significance of lipids/CoQ10 ratio as a possible marker of increased risk for atherosclerosis. Biofactors 1999, 9, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer, M.J.; Hennekens, C.H.; Manson, J.E.; Colditz, G.A.; Rosner, B.; Willett, W.C. Vitamin E consumption and the risk of coronary disease in women. N. Engl. J. Med 1993, 328, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Riemersma, R.A.; Wood, D.A.; Macintyre, C.C.; Elton, R.A.; Gey, K.F.; Oliver, M.F. Anti-oxidants and pro-oxidants in coronary heart disease. Lancet 1991, 337, 677. [Google Scholar]
- Rimm, E.B.; Stampfer, M.J.; Ascherio, A.; Giovannucci, E.; Colditz, G.A.; Willett, W.C. Vitamin E consumption and the risk of coronary heart disease in men. N. Engl. J. Med 1993, 328, 1450–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.B.; Wander, G.S.; Rastogi, A.; Shukla, P.K.; Mittal, A.; Sharma, J.P.; Mehrotra, S.K.; Kapoor, R.; Chopra, R.K. Randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial of coenzyme Q10 in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther 1998, 12, 347–353. [Google Scholar]
- Kuklinski, B.; Weissenbacher, E.; Fähnrich, A. Coenzyme Q10 and antioxidants in acute myocardial infarction. Mol. Aspects Med 1994, 15, S143–S147. [Google Scholar]
- Yalcin, A.; Kilinc, E.; Sagcan, A.; Kultursay, H. Coenzime Q10 concentrations in coronary artery disease. Clin. Biochem 2004, 37, 706–709. [Google Scholar]
- Golbidi, S.; Laher, I. Antioxidant therapy in human endocrine disorders. Med. Sci. Monit 2010, 16, RA9–24. [Google Scholar]
- Resch, U.; Helsel, G.; Tatzber, F.; Sinzinger, H. Antioxidant status in thyroid dysfunction. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med 2002, 40, 1132–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Ademoglu, E.; Gokkusu, C.; Yarman, S.; Azizlerli, H. The effect of methimazole on oxidants and antioxidants system in patients with hyperthyroidism. Pharmacol. Res 1998, 38, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, G.; Solaroli, E.; Zaccheroni, V.; Grossi, G.; Bargossi, A.M.; Melchionda, N.; Marchesini, G. Oxidative stress and anti-oxidant metabolites in patients with hyperthyroidism: effect of treatment. Horm. Metab. Res 1990, 31, 620–624. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, A.; de Marinis, L.; Calabrò, F.; Fiumara, C.; Goglia, A.; Littarru, G.P. Physiopathological Relevance of Coenzyme Q10 in Thyroid Disorders: CoQ10 Concentrations in Normal and Diseased Human Thyroid Tissue. In Biomedical and Clinical Aspects of Coenzyme Q; Folkers, K., Littarru, G.P., Yamagami, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, A.; Conte, G.; de Marinis, L.; Oradei, A.; Littarru, G.P. Thyroid hormone and oxidative metabolism: Coenzyme Q10 in thyroid’s disease. Coenzyme Q Biol. Med 1993, 1, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Asayama, K.; Kato, K. Oxidative muscular injury and its relevance to hyperthyroidism. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2000, 8, 293–303. [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfi, C.; FerrarI, D.; Stanic, I.; Pellegrini, L. Circulating levels of CoQ10 in hypo- and hyperthyroidism. Minerva Endocrinol 1994, 19, 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, A.; de Marinis, L.; Calabrò, F.; Sciuto, R.; Oradei, A.; Lippa, S.; Sandric, S.; Littarru, G.P.; Barbarino, A. Evaluation of metabolic status in amiodarone-induced thyroid disorders: Plasma coenzyme Q10 determination. J. Endocrinol. Invest 1989, 12, 511–516. [Google Scholar]
- Menke, T.; Niklowitz, P.; Reinehr, T.; de Sousa, G.J.; Andler, W. Plasma levels of coenzyme Q10 in children with hyperthyroidism. Horm. Res 2004, 61, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, A.; Corbo, G.M.; Gaballo, A.; Valente, S.; Gigliotti, P.; Cimino, V.; de Marinis, L.; Principi, F.; Littarru, G.P. Relationships between plasma CoQ10 levels and thyroid hormones in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Biofactors 2005, 25, 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, A.; Bianchi, A.; Fusco, A.; Sacco, E.; Leone, E.; Tilaro, L.; Porcelli, T.; Giampietro, A.; Principi, F.; de Marinis, L.; et al. Coenzyme Q10 evaluation in pituitary-adrenal axis disease: preliminary data. Biofactors 2005, 25, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, A.; Leone, E.; Silvestrini, A.; Festa, R.; Di Donna, V.; de Marinis, L.; Pontecorvi, A.; Littarru, G.P.; Meucci, E. Evaluation of antioxidant systems in pituitary-adrenal axis diseases. Pituitary 2010, 13, 138–145. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, A.; Leone, E.; Festa, R.; Grande, G.; Silvestrini, A.; de Marinis, L.; Pontecorvi, A.; Maira, G.; Gianpaolo, L.; Meucci, E. Effects of testosterone on antioxidant systems in male secondary hypogonadism. J. Androl 2008, 29, 622–629. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, A.; Calabrò, F.; Fiumara, C.; Conte, G.; Oradei, A.; Lippa, S.; de Marinis, L.; Littarru, G.P. Plasma Coenzyme Q1O determination in acromegaly. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Life Sci. Adv 1992, 11, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
| Patients (No) | CoQ10 (μg/mL) | CoQ10/Chol. (nmol/mmol) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control subjects | 21 | 0.68 ± 0.04 | 217.2 ± 20.3 | 32 |
| Hyperthyroidism | 25 | 0.45 ± 0.03 | 167.0 ± 20.5 | |
| Hypothyroidism | 27 | 1.04 ± 0.07 | 211.1 ± 11.2 | |
| Hypoadrenalism | 19 | 0.67 ± 0.06 | 188.1 ± 10.2 | 39 |
| Hypoadrenalism & Hypothyroidism | 19 | 0.92 ± 0.07 | 231.6 ± 32.4 | |
| Hypogonadism | 10 | 0.66 ± 0.06 | 190.8 ± 13.0 | 40 |
| Hypogonadism & Hypothyroidism | 6 | 1.11 ± 0.02 | 216.0 ± 25.0 | |
| Acromegaly | 10 | 0.50 ± 0.02 | 122.6 ± 11.6 | 41 |
| Acromegaly & Hypothyroidism | 4 | 0.98 ± 0.05 | 202.2 ± 15.3 | |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mancini, A.; Festa, R.; Raimondo, S.; Pontecorvi, A.; Littarru, G.P. Hormonal Influence on Coenzyme Q10 Levels in Blood Plasma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 9216-9225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12129216
Mancini A, Festa R, Raimondo S, Pontecorvi A, Littarru GP. Hormonal Influence on Coenzyme Q10 Levels in Blood Plasma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2011; 12(12):9216-9225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12129216
Chicago/Turabian StyleMancini, Antonio, Roberto Festa, Sebastiano Raimondo, Alfredo Pontecorvi, and Gian Paolo Littarru. 2011. "Hormonal Influence on Coenzyme Q10 Levels in Blood Plasma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 12, no. 12: 9216-9225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12129216
APA StyleMancini, A., Festa, R., Raimondo, S., Pontecorvi, A., & Littarru, G. P. (2011). Hormonal Influence on Coenzyme Q10 Levels in Blood Plasma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(12), 9216-9225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12129216





