Abstract
Phospholipase A1 (PLA1) is an enzyme that hydrolyzes phospholipids and produces 2-acyl-lysophospholipids and fatty acids. This lipolytic activity is conserved in a wide range of organisms but is carried out by a diverse set of PLA1 enzymes. Where their function is known, PLA1s have been shown to act as digestive enzymes, possess central roles in membrane maintenance and remodeling, or regulate important cellular mechanisms by the production of various lysophospholipid mediators, such as lysophosphatidylserine and lysophosphatidic acid, which in turn have multiple biological functions.
1. Introduction
Phospholipases form a diverse class of enzymes optimized to hydrolyze phospholipid (PL) substrates at specific ester bonds. Phospholipases vary considerably in structure and function, and as such they are assembled as a group solely on the basis that they are lipolytic enzymes involved in PL metabolism. Two general sets of phospholipases exist, the acyl hydrolases and the phosphodiesterases; and the enzymes within each set are classified according to the cleavage of the ester bond for which they are specific (Figure 1). Phospholipase A1 (PLA1), phospholipase A2 (PLA2), phospholipase B (PLB), and lysophospholipase A1/2 (LysoPLA1/2) constitute the acyl hydrolases, whereas the phosphodiesterases are represented by phospholipase C (PLC) and phospholipase D (PLD).
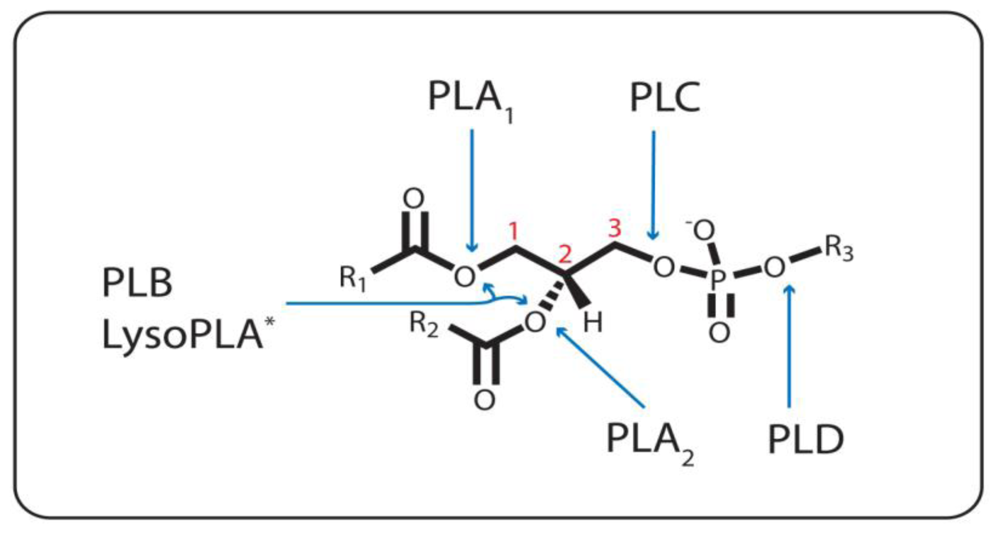
Figure 1.
Ester Bond Specificity of the Phospholipases. PLA1, PLA2, and PLC catalyze the hydrolysis of the ester bond emanating from the sn-1(1), sn-2 (2), and sn-3 (3) carbon, respectively. PLD hydrolyzes the other phosphodiester bond. PLB cleaves both the sn-1 and sn-2 ester bonds. * = LysoPLA can either be specific for the sn-1 or sn-2 bond, or both, when one or the other acyl chain is missing. R1 and R2, (CH2)nCH3; R3, various headgroups.
Phospholipases exist in almost every type of cell analyzed for their presence and most cells contain a multitude of them. For a given PL ester bond, there can be a variety of subtypes of a phospholipase that are specific for it that can either exist as secreted, membrane associated, or in cytoplasmic form. They may also require cofactors for activity, depending on the isoforms. The functions of phospholipases, where known, are as varied as their cellular and tissue localization and properties. Nonetheless, three general functions can be ascribed to the physiologic relevance of phospholipases: (1) they can serve as digestive enzymes, e.g., PLA are ubiquitous in snake and vespid venoms; (2) they can play an important role in membrane maintenance and remodeling, i.e., fatty acid (FA) chains of PLs can be cleaved and exchanged by an acyl hydrolase and an acyltransferase, respectively; and (3) they can regulate important cellular mechanisms, e.g., creation of bioactive lipid molecules used in signal transduction. These three areas of function can be a rather simplistic view accepting that, for example, maintaining acyl composition of membranous PLs can be considered quite an important regulatory function for the cell, even though the reason that cellular membranes require a heterogeneous mixture of PL fatty acids is still not fully understood [1]. These three themes will be explored in more detail in subsequent sections.
Among the different sorts of phospholipases, the most studied and well understood are PLA2, PLC, and PLD, all of which play proven important roles in the creation of bioactive lipid molecules. Although this review will focus on PLA1, a brief overview of the other phospholipases and their biological significance will also be given to gain perspective.
1.1. Phospholipase A1
PLA1 (EC 3.1.1.32) catalyzes the hydrolysis of FAs exclusively at the sn-1 position of PLs. A free fatty acid (FFA) and a lysophospholipid (lysoPL) are the products of a PLA1 reaction (Figure 2). This class of phospholipase is not well understood, and no crystal structures exist for any true PLA1 [2,3]. The assignment of a function for any PLA1 from any organism has yet to be firmly established. Historically, the biological role of this acyl hydrolase was often defined by its anticipated participation in the Lands Cycle, which is a deacylation-reacylation cycle that PLs are suspected to undergo in order to remodel their acyl chains to preserve a homeostatic molecular species composition of PLs in membrane bi-layers [4]. However, only one PLA1 has ever been directly implicated in a Lands Cycle [5], though this cycle has repeatedly been shown to occur at the sn-2 position via the action of PLA2, and studies continue to observe the phenomenon [6–10]. The assignment of a similar function for PLA1, though potentially valid, cannot be decuded based on experimental data. Understanding of these enzymes is limited, though some progress has been made over the past 20 years [11].
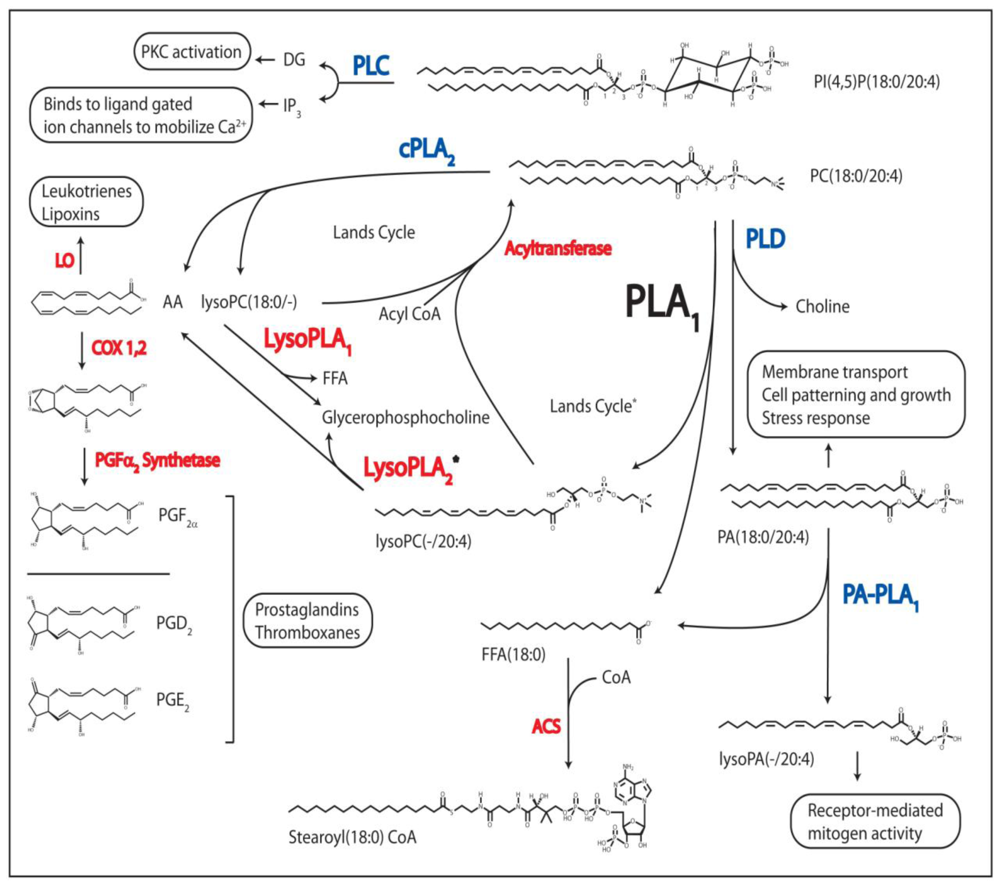
Figure 2.
Regulatory Processes Linked to PL Metabolism. The phospholipases known to produce bioactive lipid molecules are shown in blue, and their second messenger metabolites, or their signal-transduced responses, are boxed. Other enzymes utilized in PL and FA metabolism are in red. DAG, diacylglycerol; IP3, inositol(1,4,5)phosphate; PKC, protein kinase C; AA, arachidonic acid; LO, lipoxygenase; COX 1,2, cyclooxygenase 1 and 2; PG, prostaglandin; FFA, free fatty acid; CoA, coenzyme A; PLC, phospholipase C; cPLA2, cytoplasmic phospholipase A2, PLD, phospholipase D; PA-PLA1, phosphatidic acid phospholipase A1; PLA1, phospholipase A1, LysoPLA1, lysophospholipase A; ACS, acyl-CoA synthetase; PA, glycerophosphatidic acid; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PI, phosphatidylinositol. * = theoretical pathway based on indirect in vitro evidence.
What is intriguing is the observation that despite a theoretical role in the Lands Cycle, none of the PLA1 cloned and characterized have been linked to membrane turnover and remodeling roles. On the contrary, there is some evidence to suggest that some PLA1 enzymes are virulence factors [12] or act to generate bioactive lysoPL molecules. For example, lysoPL mediators such as lysophosphatidic acid (lysoPA) [13] are second messenger signaling components in pathways that vary in complexity and evolutionary conservation, and they have been implicated in numerous processes such as proliferation, protein transport, differentiation, invasion, and morphogenesis [14]. By activating specific G-protein coupled lysoPL receptors, they are now viewed as key factors in cell-to-cell communication [15]. The synthesis and regulation of the formation of lysoPLs are not fully understood, a reason why PLA1 is an important enzyme to study as it could be involved in their formation.
The FA product from a PLA1 reaction also has bioactive potential. This has been shown in plants, where a PLA1 regulates jasmonic acid biosynthesis. Also, it has been postulated for decades that sn-2 arachidonic acid (AA) cleavage from PLs may sometimes be mediated by concerted sequential PLA1/LysoPLA2 activities [16–24]. No cloned PLA1 has been implicated in this alternative route, and therefore it remains circumstantial with regards to the in vitro studies, which provide the most indirect evidence [16,22,23].
1.2. The Other Acyl Hydrolases: Phospholipase A2, B, and Lysophospholipase
PLA2 (EC 3.1.1.4) mediates acyl ester hydrolysis at the sn-2 position of PLs. PLA2 are quite well conserved across taxa, and they consist of a broad range of enzymes that segregate into one of eleven groups within the superfamily [25]. Numerous PLA2 can contribute to lysoPL signaling events [26] and can even down-regulate the bioactive lysoPL platelet activating factor (PAF) with the sn-2 acetate-specific cleavage of PAF by PAF acetyl hydrolase (PAF-AH) [27]. However, PLA2 is most noted for its role in initiating the AA cascade (Figure 2) [28]. The sn-2 reacylation step of the Lands Cycle appears to be quite specific for AA in a number of cells [29]. Once liberated by a cytoplasmic PLA2, AA is converted into over 150 known eicosanoids, including prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxanes, all powerful local hormones that act as mediators in many important processes such as inflammation in the higher eukaryotes [30]. Numerous crystal structures exist in this class of enzymes whose active mechanism either utilizes a catalytic histidine in a so-called dyad or a catalytic serine in either a dyad or a triad [25,27,31].
PLB is able to hydrolyze both the sn-1 and sn-2 FAs of PLs (Figure 1). Glycosylation is a common feature of PLBs, such as the one from Penicillium notatum, which contains numerous asparagines-linked carbohydrates and possess phospholipase and subsequent lysophospholipase activity [32]. The distinction between PLB and LysoPLA can, rightly so, often be muddled since most PLBs possess lysophospholipase activity [33]. On the other hand, some PLB enzymes have been erroneously annotated. For example, a case in which a purified hamster heart cytosol enzyme clearly displayed both sn-1 and sn-2 hydrolysis has been referred to as a PLA [34]. Also, the first so-called PLA1 to be purified, cloned, and crystallized was the outer-membrane phospholipase A (OMPLA) from E. coli and other bacteria [35–37], but it has been known for a long time that it can cleave at both positions sn-1 and sn-2 of diacyl- or lysoPLs and thus should be considered a phospholipase B [2,24].
LysoPLA (EC 3.1.1.5) detoxifies detergent-like lysoPL intermediates in PL metabolism by removing the remaining acyl chain from the lysoPL (Figure 1). This class of enzymes is also not well characterized. LysoPLA could also be important in the regulation of the amount of bioactive lysoPLs used in receptor-mediated or other signaling mechanisms [38]. Some LysoPLA can function equally well as either a LysoPLA1 or a LysoPLA2 [17]. Other LysoPLA can deacylate specific species of lysoPL, like those with AA esterfied to the sn-2 position, for example [18,39]. Such in vitro specificity has helped to fuel the theory that the AA cascade could be initiated by the combined actions of a PLA1 and a LysoPLA2.
1.3. The Phosphodiesterases: Phospholipase C and D
PLC or PI-PLC (EC 3.1.4.11) is mostly known for catalyzing the cleavage of the phosphorylated membrane lipid PI to produce, for example, the intracellular second messengers sn-1,2-diacylglycerol [23] and inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate (Figure 2). The phosphoinositides are a critically important class of PLs which have been extensively researched, along with the mechanisms by which they are metabolized by PLC [40]. PLC-mediated phosphoinositide production is a key regulating component of ion channels and transporters, and controllers of vesicular trafficking and the transport of lipids between intracellular membranes [41]. Other types of PLC include a secreted form in bacteria that prefers PC (E.C. 3.1.4.3), and a GPI-PLC form found in various organisms that specifically recognises non-inositol-acylated glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors.
PLD (EC 3.1.4.4) hydrolyzes the sn-3 phosphodiester bond of mostly PC to generate a choline molecule and PA. PLD has also been studied in detail due to its link with the production of PA, an intracellular lipid messenger implicated in almost every conceivable aspect of intracellular membrane transport [42]. PLD is also a potential regulator of lyso-PA formation, whose biosynthetic formation is unclear, but could involve both PLD and PLA1 [43]. The mode of action and structural characteristics of the various isoforms of PLD are well characterized [42,44].
2. Classification of Phospholipase A1
Over one hundred years ago accumulation of FFAs was observed upon incubation of pancreatic juice with phosphatidylcholine (PC), and the existence of enzymes responsible for the release of these acids was accordingly proposed. Snake venoms were also found to possess PL-hydrolyzing enzymes when in 1903 cobra venom was found to alter PC into products, which could cause red blood cell hemolysis. These products were later determined to be a PC molecule that was missing a FA, and they were thus termed lysophosphatidylcholine (lyso-PC). Only in the early 1960’s however was the positional specificity of FA cleavage of snake venom determined to be the sn-2 position of the glycerol backbone of PLs [44]. Early on, therefore, the study of PLA activity focused on PLA2 activity, as it has remained to this day. Nevertheless, phospholipases of type A were linked to those enzymes cleaving FAs from PLs, and the designation A1 and A2 was employed to signify the acyl hydrolysis from either the sn-1 or sn-2 position of the glycerol moiety, respectively [45]. It wasn’t long before intracellular PLA activities were beginning to be discovered in numerous organisms and tissues, thus opening the way for the possibility that these enzymes were more than just digestive catalysts.
PLA1 specifically hydrolyzes sn-1 acyl esters from PLs producing FFAs and lysoPLs (Figure 2). However, many PLA1 enzymes exhibit some, usually much lower, LysoPLA activity and neutral lipase activity (i.e., hydrolyzing diacylglycerol or triacylglycerol), yet still preferring the sn-1 cleavage site. Enzymes having high PLA1 relative to LysoPLA and neutral lipase activity are thus considered true PLA1 enzymes, and they can only be designated as such by empirical determination after some level of purification or, more preferably, by cloning and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. The vast amount of results from early studies involving the detection of PLA activity from crude tissue or subcellular fractions were flawed due to the inability to precisely determine what enzyme activities are present and how to differentiate particular enzyme activities. Competing and/or downstream enzyme activities on lipid substrates can mask the activity of the enzyme being tested.
PLA1 enzymes have not been formally classified into groups, as have the other major phospholipases. The major obstacle is the lack of available sequence due to only a relatively small proportion of PLA1 enzymes having been cloned thus far (Table 1). The only invariable feature of PLA1 seems to be a lipase consensus motif in the peptide sequence, which follows the amino acid residue pattern [LIV]-{KG}-[LIVFY]-[LIVMST]-G-[HYWV]-S-{YAG}-G-[GSTAC], inside of which resides a common GXSXG motif, containing the catalytic serine of the active site, as part of a catalytic triad.

Table 1.
The Phospholipase A1 Family 1.
PLA1 has been considered as a descendent of neutral lipases, and several PLA1 sequences show substantial sequence similarity to the well characterized pancreatic, hepatic, and endothelial lipases [43,46,47]. Other PLA1 sequences show no similarity to lipase sequences beyond their lipase consensus pattern, nor do they show similarity to other PLA1 sequences. Furthermore, eukaryotic lipases possess two domains whereas prokaryotic lipases only contain one, in which there is little if any conservation in sequence (compare alignments in [48–51].
3. Mammalian Phospholipase A1
A large number of crude protein preparations from mammalian cell and tissue homogenates were enriched for PLA1 activity in the 1970’s and 1980’s, but many of these reports describe PLA1 activity of uncertain origin. A good example of this is the characterization of a “phospholipase A1” from the plasma of rat liver that was found to hydrolyze triacylglycerols, diacylglycerols, and monoacylglycerols, in addition to PLs [71]. This “phospholipase A1” was located on the surface of endothelial cells and was shown to play a role in high density lipoprotein metabolism, and two papers were published characterizing its “phospholipase A1” activity. Interestingly, relatively recently a new member of the lipase family was cloned from endothelial cells and a recombinant form was shown to possess PLA1 activity [72]. Endothelial lipase most likely accounts for the majority of the PLA1 and lipase activities previously reported from enriched rat liver endothelial cell fractions.
It us now generally accepted that mammals have six extracellular and three intracellular PLA1 enzymes [50]. The extracellular PLA1s consist of phosphatidylserine (PS)-specific PLA1 (PS-PLA1), membrane-associated phosphatidic acid (PA)-selective PLA1s (mPA-PLA1α and mPA-PLA1β), these PLA1s may have physiological roles as they produce the lysophospholipids, lyso-PS and lyso-PA known to be lipid mediators with multiple biological functions. The other three extracellular enzymes are either involved in high-density-lipoprotein catabolism of triacylglycerol, hepatic lipase (HL) and endothelial lipase (EL), or digestion of dietary lipids, pancreatic lipase-related protein (PLRP)-2. These three enzymes belong to the lipase gene family showing triacylglycerol-hydrolyzing activity as well as PLA1 activity. The intracellular PLA1s, KIAA0725p and p125, are conserved in a wide range of organisms and have been implicated in vesicular transport.
3.1. Bovine Brain PLA1
One of the first phospholipases of the type A1 to be purified by column chromatography was from bovine brain [21]. The enzyme was isolated from the soluble fraction and eluted at a molecular mass of 365 kDa from a Sephacryl S-300HR column. Lipases are known for their interfacial activation properties, and the 365 kDa molecular weight obtained could reflect the enzyme’s molecular weight upon association with buffer detergent micelles, or it could represent the enzyme in tetramer form. Bovine brain PLA1 migrated as two bands of 112 kDa and 95 kDa by SDS-PAGE. The purified enzyme was shown to be resistant to metal chelators, PMSF, and DFP, but it was inactivated by ZnCl2 and enhanced by Ca2+, Mg2+ and Sr2+. The enzyme exhibited broad substrate specificity in mixed micelles made with CHAPS, but the highest specific activity, 23.8 μmol/min/mg, was exhibited against PE(16:0/20:4), and LysoPLA1 activity was also observed. A subsequent study showed that PC and PI could also be catalyzed at a high rate by bovine brain PLA1 but only in the presence of other PLs like PS, PE, and PA [73]. This same group reported the first chromatographic purification of a LysoPLA2 that showed selectivity towards deacylating arachidonate from lyso-PC(−/20:4) [39]. In addition to its LysoPLA2 activity, this enzyme also showed PLA2 activity, but at a slower rate. Bovine brain LysoPLA2 was isolated from the soluble fraction and is an approximately 95 kDa polypeptide. Moreover, it became clear that prior sn-1 deacylation of PC(16:0/24:0) by bovine brain PLA1 greatly increased the rate of arachidonate deacylation by brain LysoPLA2. These results suggested that in bovine brain AA might possibly be generated by sequential PLA1/LysoPLA2 action, yet this has never been shown in vivo. Even more, the physiological substrates for these two enzymes have never been determined so it is impossible to know whether arachidonoyl-substituted PC or PE are in fact hydrolyzed by these enzymes. Unfortunately, not knowing the in vivo physiological substrates is a recurring theme in PLA1 studies. It is also important to note that the genes encoding these two PLA activities have not been determined.
3.2. Bovine Testis PA-PLA
The phosphatidic acid-preferring phospholipase A1 (PA-PLA1) from bovine testis is well studied. The initial identification of PA-PLA1 was from Mono Q fractions of high-speed supernatants from bovine testis, and to a lesser extent in bovine brain [53]. The enzyme displayed preference for PA in TX-100 detergent mixed micelles, and it also displayed a relatively small amount of LysoPLA1 activity. At the time of its identification, PA was just beginning to be recognized as a second messenger that could affect a number of cellular processes. The production and, particularly, the attenuation of signaling PA can be mediated by multiple phospholipases that regulate the timing, location, amount, and various molecular species of PA [74]. A 14,000-fold purification of native PA-PLA1 was achieved and evidence was provided that the enzyme was a homotetramer of 110 kDa subunits [75]. When the enzyme was examined under the same conditions as the bovine brain PLA1 previously reported (i.e., 3–5 mM MgCl2) [21], the results showed that PE(16:0/24:0) became the preferred substrate. When MgCl2 was removed, PA-PLA1 preference for GPA was restored. It is thus possible that the bovine testis PA-PLA1 and the bovine brain PLA1 are one and the same enzyme.
Further studies eventually led to the cloning of bovine testis PA-PLA1, which was encoded by an 875 amino acid protein with a predicted molecular mass of 97.6 kDa [52]. A ~2000 fold increase in PA-PLA1 activity was observed when the protein was expressed in COS1 cells. A lipase-like consensus sequence was identified and the active site serine residue within a SXSXG motif was experimentally established as being essential for PA-PLA1 activity in the COS1 expression system. Apart from containing a lipase-like consensus motif, the PA-PLA1 sequence differed from other lipases and phospholipases. Homologues were identified in the genomes of Caenorhabditis elegans, yeast, Drosophila, and in human and mouse. A homologue involved in shoot gravitropism has also been identified in A. thaliana [63]. Splice variants were proposed to possibly exist after three cDNAs were found that contained a 123-base deletion, and it was put forth that if splice variants had different substrate specificities, then the seeming discrepancy between the bovine brain and testis substrate specificities may be explained in this manner. A complex array of conditions were created to examine properties of purified PA-PLA1 [75] using an interface composed of unilamellar lipid mixed micelles [76]. In the end, catalytic preference for PA(16:0/18:1) was reported to be observed when the unilamellar micelles contained (i) a low relative amount of PC; (ii) high relative amounts of PE, PS, and cholesterol; (iii) DAG; (iv) PE(18:0/20:4) instead of PE(16:0/18:1); and (v) 10 mol % PA per 100 mol % total phosphoglycerides. The study also showed that PA-PLA1 could bind to membranes composed of anionic phosphoglycerides and could be stabilized by these membranes in the presence of albumin.
Other experiments with PA-PLA1 provided information about the effects of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation on the behavior of the enzyme [77]. The first splice variant, PA-PLA1α, was recombinantly expressed in Sf9 cells and purified, though a homogeneous fraction of enzyme was not shown. The recombinant protein was shown by mass spectrometry to be phosphorylated by protein kinase CK2, with which it also formed complexes, and by extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2. They also showed that protein phosphatase 2A could dephosphorylate some of the phosphoryl modifications, which led them to raise the possibility that the native counterparts of these enzymes could coordinately regulate the phosphorylation state of PA-PLA1 in vivo. The physiological significance of PA-PLA1 still remains to debatably [50], because it is most highly expressed in testis it has been suggested that PA-PLA1 could be involved in PA signaling during spermiogenesis [74,76].
3.3. p125 and KIAA0725p
Budding vesicles mediate transport of proteins between intracellular compartments. One of the components of ER to Golgi COPII-coated vesicles of the secretory pathway is the Sec23p-Sec24p complex. In a study, that attempted to affinity isolate and identify new Sec23p-interacting proteins a novel protein, p125 (111 kDa), was identified. The predicted peptide sequence of p125 was homologous to bovine PA-PLA1 [54]. In addition, the N-terminal region of p125 contains a proline-rich region that was shown to be the functional region of the enzyme in its association with Sec23p. Detection of low levels of recombinant p125 expression showed co-localization with β-COP and ERGIC53, an ER-Golgi intermediate compartment marker. In contrast, detection of high levels of p125 over-expression revealed p125 dispersed throughout the cells, not only in membranes, but also in the cytosol, causing disorganization of the ER-Golgi intermediate compartments. ERGIC-53 also showed a dispersed staining pattern in these cells, and a second type of staining showed that the Golgi itself was dispersed. p125 was also shown to co-localize with p115 and GM130 proteins [78], both of which play a role in vesicle tethering to Golgi membranes [79]. Depletion of p125 by RNAi suggested that p125 is needed for the proper organization and distribution of ER exit sites; however, p125-depleted cells maintained regular rates of protein transport from the ER [80]. Despite these detailed studies, no examination of stereo-specific enzyme activity was undertaken, so p125 may indeed not even be a PLA1.
However, another protein, KIAA0725p, has also been identified as a homologue of both bovine PA-PLA1 and p125 [55]. KIAA0725p is ubiquitously expressed in mammalian cells and is predominantly localized in the cytoplasm. Consistent with its bovine PA-PLA1 homologue, KIAA0725p preferentially cleaves the sn-1 ester linkage of PA; however, in the absence of detergent it also hydrolyzed PE. PA specificity was determined using homogenates of KIAA0725p-expressing cells, and homogenates with the GXSXG seryl residue mutated to alanine showed no PLA1 activity. Like p125, results showed that over-expression of KIAA0725p in cultured cells provoked dispersion of ERGIC53 and β-COP; but, unlike p125, over-expression also caused dispersion of p115 and GM130. This morphological phenotype was not due to PLA1 activity because over-expression of the lipase-inactive mutant caused the same phenotype. However, over-expression of KIAA0725p, but not its lipase-inactive mutant, also caused aggregation of the ER, which was thus determined to be dependent on PLA1 activity. The authors proposed that KIAA0725p may promote fusion of ER membranes by changing cone-shaped PA to inverted-cone shaped lyso-PA, which has been suggested to promote fusion pore formation, the last step of membrane fusion [81]. Recently it has been shown that the isoform iPLA(1) g is a novel membrane transport factor that mediates a membrane transport pathway between the ER and the Golgi that is distinct from the previously characterized COPI- and Rab6-dependent pathways [82].
3.4. PS-PLA1
A novel PLA1 secreted from rat platelets was the first PLA1 discovered which preferentially cleaves FAs from PS [46]. The predicted peptide sequence from the cloned cDNA of PS-PLA1 was found to show significant sequence homology to hepatic lipase, lipoprotein lipase, pancreatic lipase, and endothelial lipase, but the enzyme does not possess appreciable neutral lipase activity. The enzyme was partially purified by sequential column chromatography from the culture medium of thrombin-activated platelets, and from medium of insect Sf9 cells expressing recombinant PS-PLA1 in a baculovirus system. The resulting enzyme was shown to be a 50–55 kDa protein that was equally active towards PS and lyso-PS. PS-PLA1 is also believed to be a glycoprotein. Due to its sequence similarity with lipases, the primary PS-PLA1 peptide sequence reveals that is has a β-9 loop and a lid domain; but PS-PLA1 has shorter versions of each [46], which could explain why diisopropylphosphofluoridate (DFP) inhibits this enzyme, if the truncated lid domain ineffectively covers the active site serine. A subsequent study revealed that PS-PLA1 might be the synthetic route in the production of bioactive lyso-PS since it was shown that it has the ability to efficiently stimulate histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells, especially when in the presence of apoptotic Jurkat cells [83]. In this system, 2-acyl-1-lysoPS was released from apoptotic cells exposed to PS-PLA1 and it was proposed that PS-PLA1 may play an in vivo role in hydrolyzing PS exposed on plasma membranes of apoptotic, dead, and cytokine-stimulated cells, as a means to transduce mast cell activation mediated by 2-acyl-1-lysoPS. PS-PLA1ΔC, a splice variant of the human version of PS-PLA1, shows poor catalytic activity towards PS and the other diacylPLs but is able to deacylate lyso-PS effectively and is therefore a LysoPLA [84]. PS-PLA1ΔC possesses a truncated C-terminal region; therefore peptides on the complete C-terminal domain of PS-PLA1 are thought to play a role in substrate recognition. In a very recent study PS-PLA1 expression in human THP-1-derived macrophages, responsible for the immune responses to allograft rejection, are activated via TLR4. This activation can be inhibited by corticosteroids, which are used at high dosages to suppress chronic allograft rejection [57].
3.5. mPA-PLA1
A sequence similarity search of the PS-PLA1 detected another PLA1 enzyme which was homologous to neutral lipases, that of membrane-associated phosphatidic acid-selective phospholipase A1 alpha and beta (mPA-PLA1α/β) [43,56]. Both recombinant forms show PA-specific substrate specificity. Attempts to purify the recombinant membrane proteins from Sf9 cells failed but medium from mPA-PLA1α-expressing cells was shown to activate a lyso-PA receptor family member, LPA3/EDG7. Medium from cells expressing an active site serine mutant failed to induce a receptor response. These results indicated that cells expressing recombinant mPA-PLA1α were able to produce and release bioactive lyso-PA. When expressed in HeLa cells mPA-PLA1α was recovered from the cell supernatant whereas mPA-PLA1β was still membrane associated [56]. A set of elegant experiments also showed that mPA-PLA1α/β acted after and in concert with both endogenous and exogenous PLD to form lyso-PA. This report thus suggests a possible in vivo metabolic pathway for lyso-PA production involving the sequential action of a PLD and mPA-PLA1α/β. Thus, both PS-PLA1 and mPA-PLA1α/β thus have evolved from lipases to specialize in producing bioactive lyso-PL mediators [5].
3.6. Guinea-Pig Heart Microsomal PLA1
It has been reported that microsomes from guinea-pig heart possess PLA1 activity on PE and PC, and that sn-1 cleavage could be influenced by the sn-2 FA since more efficient hydrolysis was observed when the sn-2 FA was polyunsaturated [85]. The enzyme(s) responsible for PLA1 activity from guinea-pig heart microsomes have not been identified and purified to any extent other than into subcellular fractions, but a few studies are worth mentioning since they are devoted to possible regulatory mechanisms of PLA1 activity in this tissue, and very few other studies exist that begin to explain how some PLA1 activity could be controlled. No PLA1-activating agonists are known, so a possibility that PLA1 could be receptor activated by G-proteins was investigated by measuring the response of PLA1 activity towards guanine nucleotides, which can activate G-proteins. PLA1 activity towards PC(16:0/18:2) was partially inhibited by guanosine 5′-[γ-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]), but not by GTP, guanosine 5′-[γ-thio]diphosphate (GDP[S]), GDP, ATP or adenine 5′-[γ-thio]diphosphate (ATP[S]) [86]. On the other hand, PLA1 activity on PE(16:0/18:2) was stimulated by GTP[S] but not GDP[S] or ATP[S] [86]. PE(16:0/18:2) hydrolysis by guinea-pig heart microsomes was also shown to be stimulated 40–60% by isoprenaline. It has still yet to be shown in vivo if PLA1 activity in guinea-pig heart microsomes is activated by the binding of isoprenaline to adrenergic receptors and mediated via activation of G-proteins. Without either the purification or cloning of the enzymes responsible for this activity in guinea-pig heart microsomes, it is unlikely that any resolution of the issue will be made. It is worth recalling, however, that a ubiquitously expressed mammalian PA-PLA1 homologue, p125, is localized to the ER and interacts with Sec23p, which acts as a GTPase-activating protein that plays a role in uncoating budding vesicles [87]. Whether these PLA1 activities are due to the same or different enzymes is unknown, but it does stress the importance of how substrate specificity is analyzed in vitro, and the caution with which to interpret such data. To confuse the situation even further, guinea-pig heart microsomes were also shown to possess a LysoPLA2 that could hydrolyze lyso-PC(−/18:2 or 20:4) more efficiently than lyso-PC(−/18:1 or 16:0) [18].This result lent some support to the standing possibility that arachidonic and linoleic acids could be released by LysoPLA2 acting in concert with a PLA1.
4. Other PLA1
PLA1 is a ubiquitous enzyme found in nearly every cell where it has been sought, and this includes metazoan and protozoan parasites, and snake venoms.
4.1. Caenorhabditis elegans PLA1
The Caenorhabditis elegans, IPLA-1 and ACL-10 have phospholipase A1 and acyltransferase activity respectively, both of which recognize the sn-1 position of their PI substrate [88]. The PI sn-1 fatty acid remodeling by sequential deacylation and reacylation, which resulted in stearic acid as the major fatty acid at the sn-1 position, has been proposed to be crucial for asymmetric division [5].
4.2. Venom PLA1
The cDNA of one allergen component of Dolichovespula maculate (white-faced hornet) venom has been cloned and shown to encode a PLA1 (Dol m I) with weak lipase activity [47]. In fact, at the time of the study, the derived peptide sequence of Dol m I had no homology to other PLA1 genes because it was similar to mammalian lipases. Now, not only is Dol m I 40% identical to pancreatic, hepatic, lipoprotein, and endothelial lipase, but it also shows homology with PS-PLA1 [46] and mPA-PLA1 [43]. Characterization of the 34–37 kDa enzyme has not been undertaken presumably due to a priority interest in understanding its immunochemical properties as it relates to its contribution to allergenicity. Along these same lines, two homologues of Dol m I have been cloned from Vespula spp. (yellow jacket) (Ves v I and Ves m I) which show 67% sequence identity with the white-faced hornet PLA1 [58,59], and recent success in recombinant expression of PLA1 (Ves v I) from the yellow jacket will allow a more detailed understanding of the molecular and allergological mechanisms of insect venoms, providing a valuable tool for diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in hymenoptera venom allergy [60].
4.3. Trypanosoma brucei PLA1
The PLA1/LysoPLA theorized coordinated route towards the release of unsaturated FAs, (e.g., arachidonic acid (AA)), has been supported by in vitro studies using homogenates from the kinetoplastid protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei, the infective agent of African sleeping sickness [23]. These studies observed robust and optimal activity at pH 6.0–8.5 and a requirement of sn-1 acyl cleavage prior to the release of AA from sn-1-palmitoyl-sn-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine [PC (16:0/20:4)] [89–91]. The liberated unsaturated FAs such as AA from lipids in T. brucei have been implicated in regulating calcium mobilization [92,93], and as a precursor for prostaglandin biosynthesis [94].
Two recent detailed studies describe the cloning and characterization of the cytosolic T. brucei PLA1. TbPLA1 is unique from other eukaryotic PLA1 because it is phylogenetically related to bacterial secreted PLA1 [49,66]. TbPLA1 was most likely acquired by a prokaryotic-to-eukaryotic horizontal gene transfer event of a PLA1 from Sodalis glossinidius, a bacterial endosymbiont of the insect vector of the protozoan parasite, the tsetse fly. These studies employed both in vitro and in vivo analytical techniques to establish that PC is the preferred substrate. The TbPLA1 homozygous null mutants constitute the only PLA1 double knockouts from any organism and helped to established that the enzyme functions in vivo to synthesize lyso-PC metabolites containing long-chain mostly polyunsaturated and highly unsaturated fatty acids.
4.4. Trypanosoma cruzi PLA1
One report described the existence of PLA1 activity in Trypanosoma cruzi, the etiologic agent of Chagas disease [95]. When trypomastigote and amastigote suspensions were radiolabeled with oleic acid and lysed, the radiolabeled PC content decreased over time. In addition, when PC(16:0/18:1) was incubated with epimastigote homogenates at pH 4.7, lyso-PC(−/18:1) was produced, suggesting sn-1 hydrolytic specificity. T. cruzi PLA1 was partially purified (1900-fold by specific activity) from epimastigote homogenate supernatants and a protein band of 38 kDa could be seen by SDS-PAGE, and size exclusion chromatography suggested PLA1 activity eluted with an apparent molecular mass of 40 kDa. T. cruzi PLA1 seems to be a glycoprotein due to its binding to ConA-Sepharose, possesses no divalent cation requirements, and is released from the cell by digitonin together with lysosomal markers. The physiological role played by lysosomal T. cruzi PLA1 has not been determined, though the authors suggest that the FA and lyso-PL products could have a possible role in pathogenesis of the disease.
5. Plant Phospholipase A1
Evidence for the existence of PLA1 in plant cells wasn’t forthcoming until relatively recently when the tonoplasts of Acer pseudoplatanus were shown to be able to hydrolyze sn-2-radiolabeled PC into radiolabeled PA and radiolabeled lyso-PC, revealing PLD and PLA1 activities, respectively [96]. Since then, only a few genes encoding PLA1 have been discovered.
5.1. DAD1
Among the plant hormones jasmonic acid is considered a multifunctional growth and stress regulator [97], and it is structurally similar to “animal” eicosanoids. Jasmonic acid is an oxylipin signaling molecule and a derivative of linolenic acid (C18:3). Jasmonate has been shown to regulate or co-regulate a variety of processes in plants, such as responses to biotic and abiotic stresses, tendril coiling, fruit ripening, and the developmental maturation of stamens and pollen in Arabidopsis. The enzymes involved in the jasmonic acid biosynthetic pathway have been elucidated, but the last one discovered, a phospholipase A1 called Defective in Anther Dehiscence 1 (DAD1), was one of the most important because it is the enzyme responsible for the initial release of C18:3 from cellular lipids [61]. Starting from an Arabidopsis thaliana DAD1 mutant, the WT DAD1 gene was isolated and found to encode a chloroplastic 45 kDa PLA1 lipolytic enzyme. A rescued phenotype was attained by either complementing the mutant with WT DAD1 or after supplying exogenous jasmonic acid. The DAD1 protein sequence showed some apparent similarities with fungal lipases, it possessed a consensus GHSLG motif, and eleven homologous proteins were identified in Arabidopsis alone. A maltose binding-DAD1 fusion protein lacking 72 amino acid residues (an N-terminal transit peptide) was recombinantly expressed and used to examine lipase activity. PC was the only PL tested, and the activity on it was more than 80% greater than on TAG, which suggested that the C18:3 precursor for jasmonic acid biosynthesis is stored in cellular PLs. DAD1 is thought to be of prime importance for the regulation of jasmonic acid levels. A PLA1 from Capsicum annuum (hot pepper) showed a considerable degree of overall sequence identity to Arabidopsis [98].
5.2. AtLCAT3
In a search for A. thaliana sterol acyltransferases, one of the four enzymes found to be homologous to lecithin (PC): Cholesterol acyltransferases was determined to possess PLA1 activity [62,63]. AtLCAT3 (Arabidopsis thaliana lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase 3) heterologous expression in yeast resulted in the PC, PS, and PE content to be half as much as those species in control yeast, while lyso-PC, lyso-PE and FFA were strongly increased. There was also a higher TAG content in the cells expressing AtLCAT3. AtLCAT3 fractionated with yeast microsomes, which subsequently shown to be able to hydrolyze various PL species, including lyso-PC and PA. However, neither acyltransferase activity nor TAG activity was observed with yeast microsomes expressing the enzyme. The analogous serine, histidine and aspartic acid residues that are part of the conserved catalytic triad of Homo sapiens LCAT were shown to be essential for activity of AtLCAT3. The physiological role of AtLCAT3 is as yet unknown.
6. Bacterial PLA1
The discovery of prokaryotic versions of PLA1 enzymes have up to now been confined to only one subclass of bacteria, the proteobacteria [68]. PLA1 from Serratia liquefaciens (PhlA) was identified as one of a number of proteins that are excreted to the outside environment. The impetus for studying PhlA was to use S. liquefaciens as a model organism to study the genetic basis for secreting proteins across both the periplasmic and outer membranes in gram-negative bacteria. As a result, very little biochemical information regarding PhlA is known. In fact, phospholipase activities of this enzyme were only examined against egg yolk PC imbedded in agar plates in which transparent halos were observed after the addition of cells expressing the enzymes. The presence of a halo around the colony indicated secreted phospholipase A activity, but did not discern between sn-1 and sn-2 specificity. PhlA encodes a 34 kDa polypeptide that has an N-terminal signal peptide. Immediately downstream from the PhlA gene is PhlB, which encodes a protein of 24 kDa.
The bacterial exoenzyme PhlA was shown to have growth-phase-dependent expression and secretion, where a very low rate of PhlA production was measured during exponential growth, and a burst of expression and secretion was observed during stationary phase. In another report it was shown that PhlA expression is regulated at the level of transcription initiation, and they present sequence data of two dual promoters upstream of PhlA that regulate expression differentially during anaerobic conditions or growth-phase [99]. A subsequent study revealed that PhlA secreted from in E. coli was dependent on an intact flhD gene, the regulator of the flagellar/chomotaxis opero [67,100]. Mutant flhD strains of E. coli do not secrete recombinant PhlA, which accumulates inside the cell. Interestingly, the PLA1 activity of accumulated PhlA is attenuated by PhlB, which forms an enzymatically inactive complex with PhlA, thus neutralizing possibly lethal intracellular phospholipase activity.
A homologue (74% identity) of PhlA was identified in Yersinia enterocolitica (YplA) [70]. The YplA sequence revealed two ORFs in tandem like that of the PhlA and PhlB, but the YplB accessory protein was less similar to PhlB. Again, the phospholipase A activity was confirmed by testing on lecithin plates only. An insertion mutant of YplA was created and used in a mouse model to show that secreted YplA could play a role as a virulence factor in the pathogenesis of infection with Y. enterocolitica. Neither PhlA nor YplA are homologous to bacterial lipases.
7. PLA1 in Biotechnology
LysoPLs are commonly used as surfactants in food technology and cosmetics [101], and as components of liposomes used in drug delivery [102]. Lyso-PLs are currently produced commercially via their chemical synthesis [103] or via the action of extracts from porcine pancreas, which contains a PLA2. Viable alternative processes produce lyso-PLs enzymatically and with greater efficiency are being investigated, recently reviewed in [104].
Phospholipases are useful tools in analytical PL analysis. Though there are a number of sources of PLA2 commercially available at various levels of purification, no PLA1 in any form is commercially available, mainly due to the difficulty in producing and purifying the enzyme, especially on an industrial scale. The ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila has been studied as a potential natural source for PLA1 [105], which is secreted from this organism. However, high levels of PLA1 are undoubtedly best obtained through recombinant expression techniques. Since purified PLA1 is expected to have broad industrial applications, a number of PLA1 genes from a variety of microorganisms have been cloned and attempted to be expressed and purified to fulfill this need, but they have not been characterized.
Serratia spp. MK1 PLA1 (PlaA), a homologue of PhlA and YplA, has been isolated from Serratia spp. MK1 in Korean soil and cloned and expressed in E. coli [69]. Though the enzyme is secreted naturally, over-expression resulted in accumulation of recombinant enzyme inside the cell, and co-expression of its accessory protein, PlaS, was essential for cell viability and high expression levels. The histidine affinity tag on the recombinant protein was used in a one-step purification of the enzyme, which yielded under the best conditions 2.2 mg/L, the purity level was neither reported nor shown. Also, PLA1 in organisms adapted to lower temperatures have recently been found [106].
The genomic DNA and cDNA encoding a 269 amino acid PLA1 protein from Aspergillus oryzae have also been cloned [64]. The peptide sequence of the PLA1 showed 47% identity with that of mono- and diacylglycerol lipase from another fungus, Penicillium camembertii. A. oryzae PLA1 is a secretary enzyme and it was recombinantly expressed in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and purified from the extracellular broth at a level of 3.9 mg/L. Under a complex array of conditions, this expression was optimized to produce approximately 2 g/L on an industrial scale fermentor [107]. However, the enzyme was only partially purified from the culture broth by ion exchange chromatography and the yield was calculated based on its specific activity. Recently a PLA1 from Thermomyces lanuginosus expressed in Aspergillus has been commercialized as a lectinase [65].
8. Perspective
Phospholipases A1 are enzymes that hydrolyze phospholipids at the sn-1 fatty acids from phospholipids and produces 2-acyl-lysophospholipids. This PLA1 activity is conserved in a wide range of organisms, but is carried out by a diverse range of enzymes.
Despite PLA1 activities being detected in many tissues and cell lines, only a limited number of PLAs have been cloned and their activity and substrates identified and characterized, and even fewer have been studied that their function is known.
PLA1s have been shown to have a diverse range of cellular functions including, digestive enzymes, central roles in membrane maintenance and remodeling via the Lands cycle of important phospholipids or glycolipids such as glycosylphosphatidylinositols. It is now emerging that they also regulate and facilitate the production of various lysophospholipid mediators, such as lysophosphatidylserine and lysophosphatidic acid, which in turn have multiple important biological functions.
Thus, phospholipases A1 are an emerging class of enzyme that play important roles in the cellular functions including those of various diseases and pathogens that affect human health.
Acknowledgements
Research in the author’s laboratory is supported in part by a Wellcome Trust Senior Research Fellowship (067441), and Wellcome Trust project grants (086658 and 093228) and a Wellcome Trust Prize Studentship (G.S.R).
References
- Lands, WE. Stories about acyl chains. Biochim. Biophys Acta 2000, 1483, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima, M; Nakaike, S; Tamori, Y; Nojima, S. Detergent-resistant phospholipase A of Escherichia coli K-12, purification and properties. Eur. J. Biochem 1977, 73, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Withers-Martinez, C; Carriere, F; Verger, R; Bourgeois, D; Cambillau, C. A pancreatic lipase with a phospholipase A1 activity: crystal structure of a chimeric pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 from guinea pig. Structure 1996, 4, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Lands, WE. Metabolism of glycerolipids. 2. The enzymatic acylation of lysolecithin. J. Biol. Chem 1960, 235, 2233–2237. [Google Scholar]
- Imae, R; Inoue, T; Kimura, M; Kanamori, T; Tomioka, NH; Kage-Nakadai, E; Mitani, S; Arai, H. Intracellular phospholipase A1 and acyltransferase, which are involved in Caenorhabditis elegans stem cell divisions, determine the sn-1 fatty acyl chain of phosphatidylinositol. Mol Biol Cell 2010, 21, 3114–3124, and reference therein. [Google Scholar]
- Zarini, S; Gijon, MA; Folco, G; Murphy, RC. Effect of arachidonic acid reacylation on leukotriene biosynthesis in human neutrophils stimulated with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. J. Biol Chem 2006, 281, 10134–10142. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold, SL; Zimmerman, GA; Prescott, SM; McIntyre, TM. Phospholipid remodeling in human neutrophils. Parallel activation of a deacylation/reacylation cycle and platelet-activating factor synthesis. J. Biol. Chem 1989, 264, 21652–21659. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, A; Sugiura, T; Waku, K. Acyltransferases and transacylases involved in fatty acid remodeling of phospholipids and metabolism of bioactive lipids in mammalian cells. J. Biochem (Tokyo) 1997, 122, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Blank, ML; Smith, ZL; Snyder, F. Contributing factors in the trafficking of [3H]arachidonate between phospholipids. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1992, 1124, 262–272. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, R; Matabosch, X; Llebaria, A; Balboa, MA; Balsinde, J. Blockade of arachidonic acid incorporation into phospholipids induces apoptosis in U937 promonocytic cells. J. Lipid. Res 2006, 47, 484–491. [Google Scholar]
- Waite, M. The Phospholipases (Handbook of Lipid Research); Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Shimuta, K; Ohnishi, M; Iyoda, S; Gotoh, N; Koizumi, N; Watanabe, H. The hemolytic and cytolytic activities of Serratia marcescens phospholipase A (PhlA) depend on lysophospholipid production by PhlA. BMC Microbiol 2009, 9, 261. [Google Scholar]
- Fahy, E; Subramaniam, S; Brown, HA; Glass, CK; Merrill, AH, Jr; Murphy, RC; Raetz, CR; Russell, DW; Seyama, Y; Shaw, W; et al. A comprehensive classification system for lipids. J. Lipid. Res 2005, 46, 839–862. [Google Scholar]
- Hla, T; Lee, MJ; Ancellin, N; Paik, JH; Kluk, MJ. Lysophospholipids—receptor revelations. Science 2001, 294, 1875–1878. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, I; Fukushima, N; Ye, X; Chun, J. Lysophospholipid receptors: signaling and biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2004, 73, 321–354. [Google Scholar]
- Gauster, M; Rechberger, G; Sovic, A; Horl, G; Steyrer, E; Sattler, W; Frank, S. Endothelial lipase releases saturated and unsaturated fatty acids of high density lipoprotein phosphatidylcholine. J. Lipid. Res 2005, 46, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A; Loo, R; Chen, Z; Dennis, EA. Regiospecificity and catalytic triad of lysophospholipase I. J. Biol. Chem 1997, 272, 22030–22036. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur, G. Lysophospholipase A2 activity in guinea-pig heart microsomal fractions displaying high activities with 2-acylglycerophosphocholines with linoleic and arachidonic acids. Biochem. J 1989, 261, 581–586. [Google Scholar]
- Badiani, K; Arthur, G. 2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine lysophospholipase A2 activity in guinea-pig heart microsomes. Biochem. J 1991, 275, 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne, RD; Morgan, A. The control of free arachidonic acid levels. Trends Biochem. Sci 1990, 15, 365–366. [Google Scholar]
- Pete, MJ; Ross, AH; Exton, JH. Purification and properties of phospholipase A1 from bovine brain. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 19494–19500. [Google Scholar]
- Pete, MJ; Wu, DW; Exton, JH. Subcellular fractions of bovine brain degrade phosphatidylcholine by sequential deacylation of the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1996, 1299, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgley, EL; Ruben, L. Phospholipase from Trypanosoma brucei releases arachidonic acid by sequential sn-1, sn-2 deacylation of phospholipids. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol 2001, 114, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch, H. Intracellular phospholipases A. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1980, 604, 191–246. [Google Scholar]
- Six, DA; Dennis, EA. The expanding superfamily of phospholipase A2 enzymes: classification and characterization. Biochim. Biophys Acta 2000, 1488, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Balsinde, J; Balboa, MA; Dennis, EA. Antisense inhibition of group VI Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 blocks phospholipid fatty acid remodeling in murine P388D1 macrophages. J. Biol. Chem 1997, 272, 29317–29321. [Google Scholar]
- Tjoelker, LW; Eberhardt, C; Unger, J; Trong, HL; Zimmerman, GA; McIntyre, TM; Stafforini, DM; Prescott, SM; Gray, PW. Plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase is a secreted phospholipase A2 with a catalytic triad. J. Biol. Chem 1995, 270, 25481–25487. [Google Scholar]
- Gilroy, DW; Newson, J; Sawmynaden, P; Willoughby, DA; Croxtall, JD. A novel role for phospholipase A2 isoforms in the checkpoint control of acute inflammation. FASEB J 2004, 18, 489–498. [Google Scholar]
- Chilton, FH; O'Flaherty, JT; Ellis, JM; Swendsen, CL; Wykle, RL. Selective acylation of lyso platelet activating factor by arachidonate in human neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem 1983, 258, 7268–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Bogatcheva, NV; Sergeeva, MG; Dudek, SM; Verin, AD. Arachidonic acid cascade in endothelial pathobiology. Microvasc. Res 2005, 69, 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, DL; White, SP; Otwinowski, Z; Yuan, W; Gelb, MH; Sigler, PB. Interfacial catalysis: The mechanism of phospholipase A2. Science 1990, 250, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, N; Kitamura, N; Saito, K. Primary structure of protein moiety of Penicillium notatum phospholipase B deduced from the cDNA. Eur. J. Biochem 1991, 202, 783–787. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, KS; Patton, JL; Fido, M; Hines, LK; Kohlwein, SD; Paltauf, F; Henry, SA; Levin, DE. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae PLB1 gene encodes a protein required for lysophospholipase and phospholipase B activity. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 19725–19730. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, YZ; Tam, SW; Arthur, G; Chen, H; Choy, PC. The purification and characterization of a phospholipase A in hamster heart cytosol for the hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem 1987, 262, 16927–16936. [Google Scholar]
- Dekker, N. Outer-membrane phospholipase A: known structure, unknown biological function. Mol. Microbiol 2000, 35, 711–717. [Google Scholar]
- Homma, H; Kobayashi, T; Chiba, N; Karasawa, K; Mizushima, H; Kudo, I; Inoue, K; Ikeda, H; Sekiguchi, M; Nojima, S. The DNA sequence encoding pldA gene, the structural gene for detergent-resistant phospholipase A of E. coli. J. Biochem (Tokyo) 1984, 96, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Scandella, CJ; Kornberg, A. A membrane-bound phospholipase A1 purified from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 1971, 10, 4447–4456. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A; Dennis, EA. Mammalian lysophospholipases. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1999, 1439, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pete, MJ; Exton, JH. Purification of a lysophospholipase from bovine brain that selectively deacylates arachidonoyl-substituted lysophosphatidylcholine. J. Biol. Chem 1996, 271, 18114–18121. [Google Scholar]
- James, SR; Downes, CP. Structural and mechanistic features of phospholipases C: Effectors of inositol phospholipid-mediated signal transduction. Cell. Signal 1997, 9, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Katan, M. Families of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C: structure and function. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1998, 1436, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- McDermott, M; Wakelam, MJ; Morris, AJ. Phospholipase D. Biochem. Cell Biol 2004, 82, 225–253. [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda, H; Aoki, J; Hiramatsu, T; Ishida, M; Bandoh, K; Nagai, Y; Taguchi, R; Inoue, K; Arai, H. A novel phosphatidic acid-selective phospholipase A1 that produces lysophosphatidic acid. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 34254–34263. [Google Scholar]
- de Hass, GH; Daemen, FJM; van Deenen, DL. Positional specificity of phosphatide acyl hydrolase (phospholipase A). Nature 1962, 196, 68. [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch, H; van Deenen, LL. Chemical structure and biochemical significance of lysolecithins from rat liver. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1965, 106, 326–337. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T; Aoki, J; Nagai, Y; Dohmae, N; Takio, K; Doi, T; Arai, H; Inoue, K. Serine phospholipid-specific phospholipase A that is secreted from activated platelets. A new member of the lipase family. J. Biol. Chem 1997, 272, 2192–2198. [Google Scholar]
- Soldatova, L; Kochoumian, L; King, TP. Sequence similarity of a hornet (D. maculata) venom allergen phospholipase A1 with mammalian lipases. FEBS Lett 1993, 320, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, J; Nagai, Y; Hosono, H; Inoue, K; Arai, H. Structure and function of phosphatidylserine-specific phospholipase A1. Biochim. Biophys Acta 2002, 1582, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Richmond, GS; Smith, TK. A novel phospholipase from Trypanosoma brucei. Mol. Microbiol 2007, 63, 1078–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, J; Inoue, A; Makide, K; Saiki, N; Arai, H. Structure and function of extracellular phospholipase A1 belonging to the pancreatic lipase gene family. Biochimie 2007, 89, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, KE; Ransac, S; Dijkstra, BW; Colson, C; van Heuvel, M; Misset, O. Bacterial lipases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev 1994, 15, 29–63. [Google Scholar]
- Higgs, HN; Han, MH; Johnson, GE; Glomset, JA. Cloning of a phosphatidic acid-preferring phospholipase A1 from bovine testis. J. Biol. Chem 1998, 273, 5468–5477. [Google Scholar]
- Higgs, HN; Glomset, JA. Identification of a phosphatidic acid-preferring phospholipase A1 from bovine brain and testis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 1994, 91, 9574–9578. [Google Scholar]
- Tani, K; Mizoguchi, T; Iwamatsu, A; Hatsuzawa, K; Tagaya, M. p125 is a novel mammalian Sec23p-interacting protein with structural similarity to phospholipid-modifying proteins. J. Biol. Chem 1999, 274, 20505–20512. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, K; Sonoda, H; Mizoguchi, T; Aoki, J; Arai, H; Nagahama, M; Tagaya, M; Tani, K. A novel phospholipase A1 with sequence homology to a mammalian Sec23p-interacting protein, p125. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 11329–11335. [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu, T; Sonoda, H; Takanezawa, Y; Morikawa, R; Ishida, M; Kasahara, K; Sanai, Y; Taguchi, R; Aoki, J; Arai, H. Biochemical and molecular characterization of two phosphatidic acid-selective phospholipase A1s, mPA-PLA1 alpha and mPA-PLA1 beta. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 49438–49447. [Google Scholar]
- Hosono, H; Homma, M; Ogasawara, Y; Makide, K; Aoki, J; Niwata, H; Watanabe, M; Inoue, K; Ohkohchi, N; Kohda, Y. Expression of Phosphatidylserine-Specific Phospholipase A1 mRNA in Human THP-1-Derived Macrophages. Cell Transplant 2010, 19, 759–764. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, DR. Allergens in hymenoptera venom. XXVI: The complete amino acid sequences of two vespid venom phospholipases. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol 1994, 104, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- King, TP; Lu, G; Gonzalez, M; Qian, N; Soldatova, L. Yellow jacket venom allergens, hyaluronidase and phospholipase: sequence similarity and antigenic cross-reactivity with their hornet and wasp homologs and possible implications for clinical allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol 1996, 98, 588–600. [Google Scholar]
- Seismann, H; Blank, S; Cifuentes, L; Braren, I; Bredehorst, R; Grunwald, T; Ollert, M; Spillner, E. Recombinant phospholipase A1 (Ves v 1) from yellow jacket venom for improved diagnosis of hymenoptera venom hypersensitivity. Clin. Mol Allergy 2010, 8, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro, S; Kawai-Oda, A; Ueda, J; Nishida, I; Okada, K. The DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCIENCE1 gene encodes a novel phospholipase A1 catalyzing the initial step of jasmonic acid biosynthesis, which synchronizes pollen maturation, anther dehiscence, and flower opening in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 2191–2209. [Google Scholar]
- Noiriel, A; Benveniste, P; Banas, A; Stymne, S; Bouvier-Nave, P. Expression in yeast of a novel phospholipase A1 cDNA from Arabidopsis thaliana. Eur. J. Biochem 2004, 271, 3752–3764. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T; Morita, MT; Fukaki, H; Yamauchi, Y; Uehara, M; Niihama, M; Tasaka, M. SGR2, a phospholipase-like protein, and ZIG/SGR4, a SNARE, are involved in the shoot gravitropism of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, I; Koishi, R; Yao, Y; Tsuji, T; Serizawa, N. Molecular cloning and expression of the gene encoding a phospholipase A1 from Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem 1999, 63, 820–826. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I-H; Garcia, HS; Hill, CG, Jr. Phospholipase A1-catalyzed synthesis of phospholipids enriched in n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid residues. Enzyme Microb. Technol 2007, 40, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Richmond, G; Smith, TK. The role and characterization of phospholipase A1 in mediating lysophosphatidylcholine synthesis in Trypanosoma brucei. Biochem. J 2007, 405, 319–329. [Google Scholar]
- Givskov, M; Molin, S. Secretion of Serratia liquefaciens phospholipase from Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol 1993, 8, 229–242. [Google Scholar]
- Givskov, M; Olsen, L; Molin, S. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene for extracellular phospholipase A1 from Serratia liquefaciens. J. Bacteriol 1988, 170, 5855–5862. [Google Scholar]
- Song, JK; Kim, MK; Rhee, JS. Cloning and expression of the gene encoding phospholipase A1 from Serratia sp. MK1 in Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol 1999, 72, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Schmiel, DH; Wagar, E; Karamanou, L; Weeks, D; Miller, VL. Phospholipase A of Yersinia enterocolitica contributes to pathogenesis in a mouse model. Infect. Immun 1998, 66, 3941–3951. [Google Scholar]
- Kucera, GL; Sisson, PJ; Thomas, MJ; Waite, M. On the substrate specificity of rat liver phospholipase A1. J. Biol. Chem 1988, 263, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, K; Dichek, HL; Cioffi, JA; Choi, SY; Leeper, NJ; Quintana, L; Kronmal, GS; Cooper, AD; Quertermous, T. Cloning of a unique lipase from endothelial cells extends the lipase gene family. J. Biol. Chem 1999, 274, 14170–14175. [Google Scholar]
- Pete, MJ; Exton, JH. Phospholipid interactions affect substrate hydrolysis by bovine brain phospholipase A1. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1995, 1256, 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X; Devaiah, SP; Zhang, W; Welti, R. Signaling functions of phosphatidic acid. Prog Lipid Res 2006, 45, 250. [Google Scholar]
- Higgs, HN; Glomset, JA. Purification and properties of a phosphatidic acid-preferring phospholipase A1 from bovine testis. Examination of the molecular basis of its activation. J. Biol. Chem 1996, 271, 10874–10882. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q; Higgs, HN; Glomset, JA. Membrane lipids have multiple effects on interfacial catalysis by a phosphatidic acid-preferring phospholipase A1 from bovine testis. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 9335–9344. [Google Scholar]
- Han, MH; Han, DK; Aebersold, RH; Glomset, JA. Effects of protein kinase CK2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2, and protein phosphatase 2A on a phosphatidic acid preferring phospholipase A1. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 27698–27708. [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi, T; Nakajima, K; Hatsuzawa, K; Nagahama, M; Hauri, HP; Tagaya, M; Tani, K. Determination of functional regions of p125, a novel mammalian Sec23p-interacting protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2000, 279, 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, N; Lowe, M; Levine, TP; Rabouille, C; Warren, G. The vesicle docking protein p115 binds GM130, a cis-Golgi matrix protein, in a mitotically regulated manner. Cell 1997, 89, 445–455. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoi, W; Ezawa, I; Nakamoto, K; Uesaki, S; Gabreski, G; Aridor, M; Yamamoto, A; Nagahama, M; Tagaya, M; Tani, K. p125 is localized in endoplasmic reticulum exit sites and involved in their organization. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 10141–10148. [Google Scholar]
- Chernomordik, L. Non-bilayer lipids and biological fusion intermediates. Chem. Phys Lipids 1996, 81, 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa, RK; Aoki, J; Kano, F; Murata, M; Yamamoto, A; Tsujimoto, M; Arai, H. Intracellular phospholipase A1 gamma (iPLA1 gamma) is a novel factor involved in coat protein complex I- and Rab6-independent retrograde transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex. J. Biol. Chem 2009, 284, 26620–26630. [Google Scholar]
- Hosono, H; Aoki, J; Nagai, Y; Bandoh, K; Ishida, M; Taguchi, R; Arai, H; Inoue, K. Phosphatidylserine-specific phospholipase A1 stimulates histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells through production of 2-acyl-1-lysophosphatidylserine. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 29664–29670. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, Y; Aoki, J; Sato, T; Amano, K; Matsuda, Y; Arai, H; Inoue, K. An alternative splicing form of phosphatidylserine-specific phospholipase A1 that exhibits lysophosphatidylserine-specific lysophospholipase activity in humans. J. Biol. Chem 1999, 274, 11053–11059. [Google Scholar]
- Badiani, K; Arthur, G. Evidence for receptor and G-protein regulation of a phosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolysing phospholipase A1 in guinea-pig heart microsomes: stimulation of phospholipase A1 activity by DL-isoprenaline and guanine nucleotides. Biochem. J 1995, 312, 805–809. [Google Scholar]
- Badiani, K; Lu, X; Arthur, G. Evidence for the regulation of guinea-pig heart microsomal phosphatidylcholine-hydrolysing phospholipase A1 by guanosine 5′-[gamma-thio]triphosphate. Biochem. J 1992, 288, 965–968. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihisa, T; Barlowe, C; Schekman, R. Requirement for a GTPase-activating protein in vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Science 1993, 259, 1466–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, A; Aoki, J. Phospholipase A1, struture, distrubition and function. Future Lipidol 2006, 1, 623–636. [Google Scholar]
- Tizard, IR; Mellors, A; Holmes, WL; Nielsen, K. The generation of phospholipase A and hemolytic fatty acids by autolysing suspensions of Trypanosoma congolense. Tropenmed. Parasitol 1978, 29, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Hambrey, PN; Mellors, A; Tizard, IR. The phospholipases of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Trypanosoma species. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol 1981, 2, 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Opperdoes, FR; van Roy, J. The phospholipases of Trypanosoma brucei bloodstream forms and cultured procyclics. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol 1982, 5, 309–319. [Google Scholar]
- Eintracht, J; Maathai, R; Mellors, A; Ruben, L. Calcium entry in Trypanosoma brucei is regulated by phospholipase A2 and arachidonic acid. Biochem. J 1998, 336, 659–666. [Google Scholar]
- Catisti, R; Uyemura, SA; Docampo, R; Vercesi, AE. Calcium mobilization by arachidonic acid in trypanosomatids. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol 2000, 105, 261–271. [Google Scholar]
- Kubata, BK; Duszenko, M; Kabututu, Z; Rawer, M; Szallies, A; Fujimori, K; Inui, T; Nozaki, T; Yamashita, K; Horii, T; Urade, Y; Hayaishi, O. Identification of a novel prostaglandin f(2alpha) synthase in Trypanosoma brucei. J. Exp. Med 2000, 192, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Wainszelbaum, M; Isola, E; Wilkowsky, S; Cannata, JJ; Florin-Christensen, J; Florin-Christensen, M. Lysosomal phospholipase A1 in Trypanosoma cruzi: An enzyme with a possible role in the pathogenesis of Chagas’ disease. Biochem. J 2001, 355, 765–770. [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier, E; Pugin, A. Phospholipase activities associated with the tonoplast from Acer pseudoplatanus cells: Identification of a phospholipase A1 activity. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1995, 1233, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Browse, J. Jasmonate: An oxylipin signal with many roles in plants. Vitam. Horm 2005, 72, 431–456. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, YS; Kim, EY; Mang, HG; Kim, WT. Heterologous expression, and biochemical and cellular characterization of CaPLA1 encoding a hot pepper phospholipase A1 homolog. Plant J 2008, 53, 895–908. [Google Scholar]
- Givskov, M; Molin, S. Expression of extracellular phospholipase from Serratia liquefaciens is growth-phase-dependent, catabolite-repressed and regulated by anaerobiosis. Mol. Microbiol 1992, 6, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Givskov, M; Eberl, L; Christiansen, G; Benedik, MJ; Molin, S. Induction of phospholipase-and flagellar synthesis in Serratia liquefaciens is controlled by expression of the flagellar master operon flhD. Mol. Microbiol 1995, 15, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara, R; Uehara, K. Recent trends in cosmetics and toiletries. Inform 1995, 6, 672. [Google Scholar]
- Barbara, FH. Lipsomes offer hope as medical tools. Inform 1995, 6, 793. [Google Scholar]
- D’Arrigo, P; Stefano Servi, S. Synthesis of Lysophospholipids. Molecules 2010, 15, 1354–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Guberman, A; Hartmann, M; Tiedtke, A; Florin-Christensen, J; Florin-Christensen, M. A method for the preparation of Tetrahymena thermophila phospholipase A1 suitable for large-scale production. J. Appl. Microbiol 1999, 86, 226–230. [Google Scholar]
- de Maria, L; Vind, J; Oxenball, KM; Svendsen, A; Patkar, S. Phospholipases and their industrial applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2007, 74, 290–300. [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara, M; Kamata, M; Koyama, T; Yazawa, K. New phospholipase A1-producing bacteria from a marine fish. Mar. Biotechnol. (N. Y ) 2008, 10, 382–387. [Google Scholar]
- Shiba, Y; Ono, C; Fukui, F; Watanabe, I; Serizawa, N; Gomi, K; Yoshikawa, H. High-level secretory production of phospholipase A1 by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem 2001, 65, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).