Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Ramalin Derivatives as Multi-Target Agents for Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
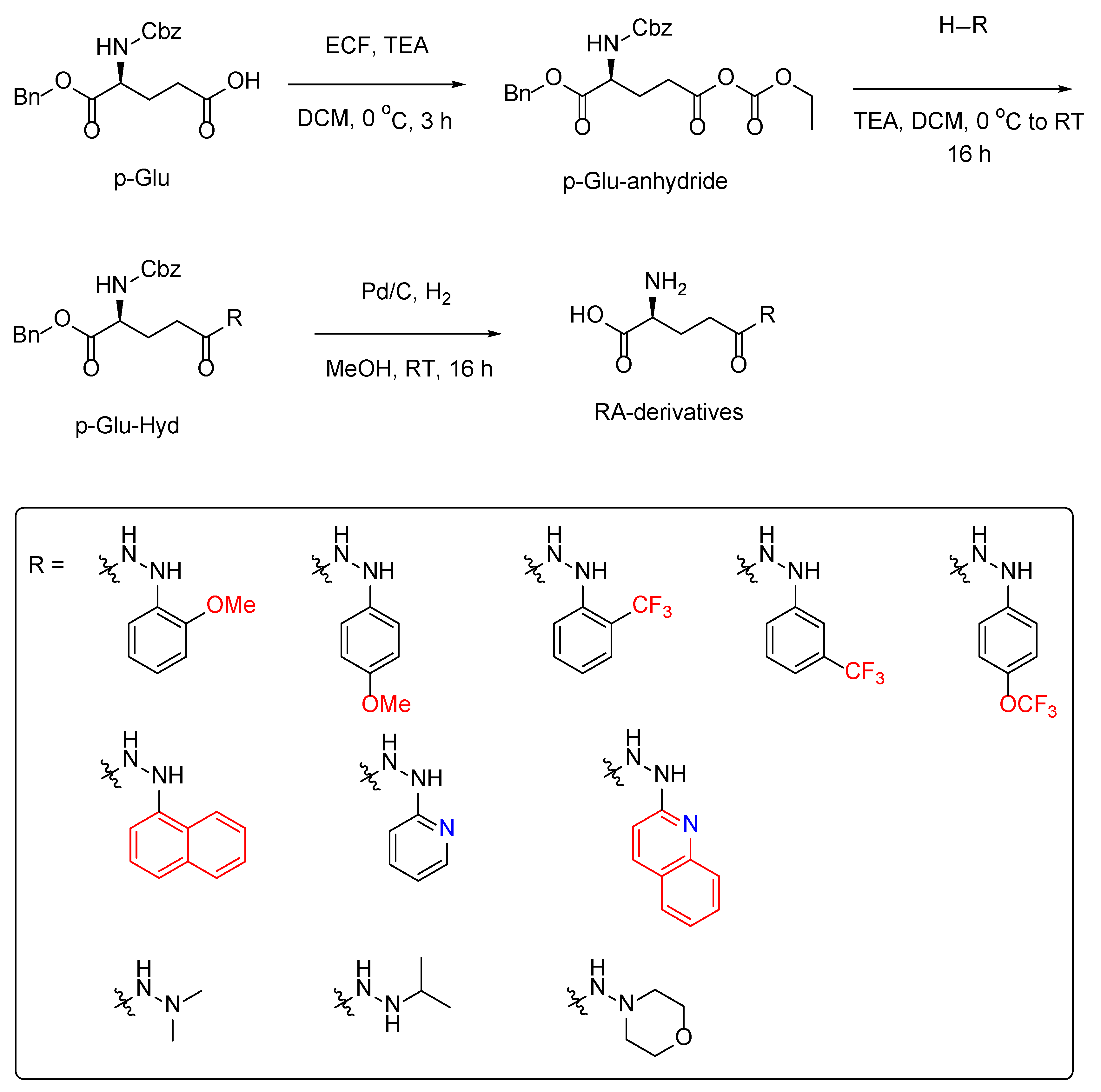
2.1. Synthesis of the Ramalin Derivatives
2.2. Antioxidant Effect of the Ramalin Derivatives
2.3. Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability Evaluation
2.4. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Ramalin Derivatives
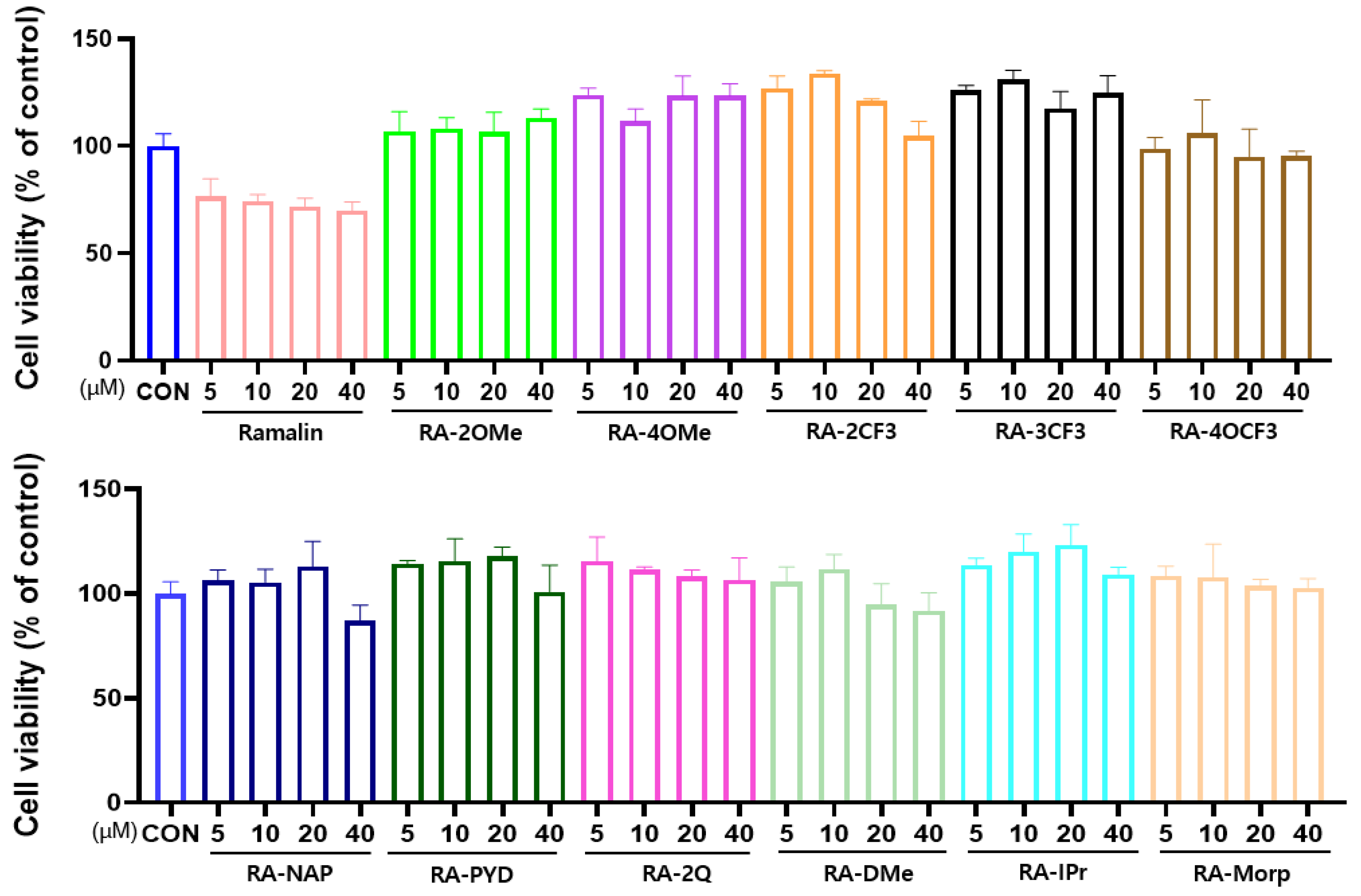
2.4.1. Effect of Ramalin Derivatives on Cell Viability
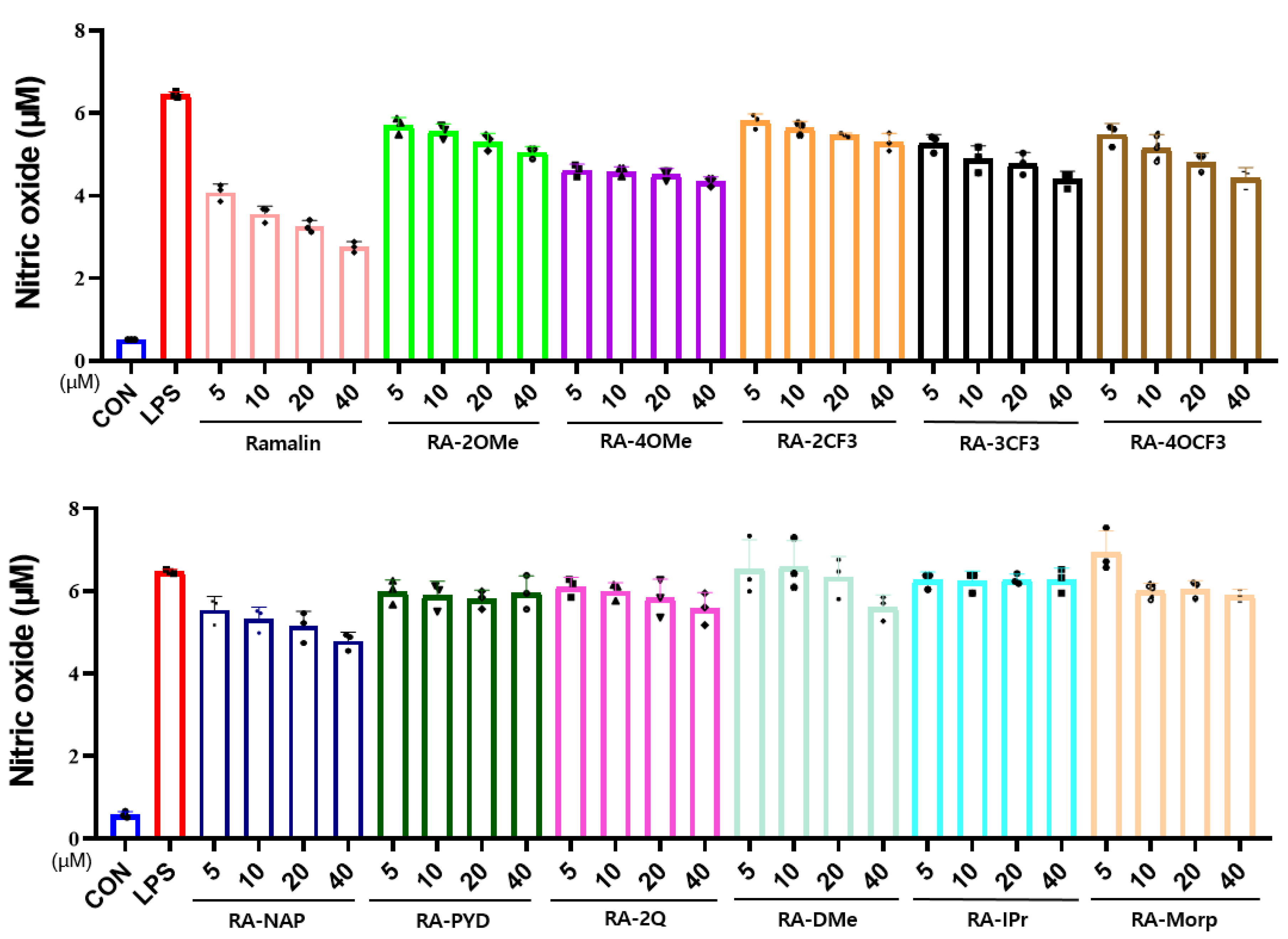
2.4.2. Effects of Ramalin Derivatives on Nitric Oxide Production
2.4.3. Effect of Ramalin Derivatives on NLRP3 Level
2.5. BACE-1 Inhibitory Activities of Ramalin Derivatives
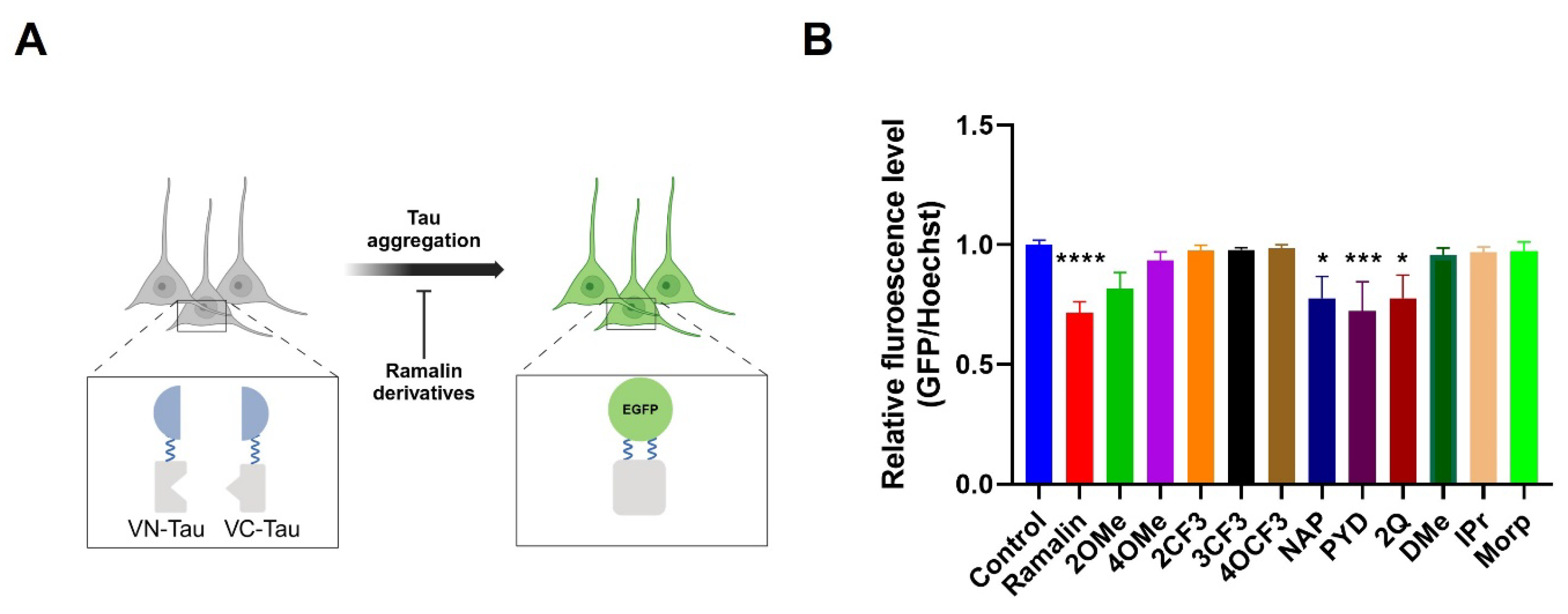
2.6. Anti-Tau Aggregation Effects of Ramalin Derivatives
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Information
4.2. Synthesis and Characterization
4.2.1. General Method for the Synthesis of p-Glu-Hyd Analogues
4.2.2. General Method for the Synthesis of RA Analogues
4.3. Antioxidant Activity Assay
4.4. Cytotoxicity and Anti-Inflammation Activity Assays
4.4.1. Cell Culture
4.4.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4.3. Nitric Oxide Production Assay
4.4.4. NLRP3 ELISA Assay
4.5. BACE-1 Activity Assay
4.6. Anti-Tau Aggregation Inhibition Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tahami Monfared, A.A.; Byrnes, M.J.; White, L.A.; Zhang, Q. Alzheimer’s Disease: Epidemiology and Clinical Progression. Neurol. Ther. 2022, 11, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Wiste, H.J.; Therneau, T.M.; Weigand, S.D.; Knopman, D.S.; Mielke, M.M.; Lowe, V.J.; Vemuri, P.; Machulda, M.M.; Schwarz, C.G.; et al. Associations of Amyloid, Tau, and Neurodegeneration Biomarker Profiles With Rates of Memory Decline Among Individuals Without Dementia. JAMA 2019, 321, 2316–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakir Hussain, M.; Mishra, A.K. Advancements in understanding and addressing Alzheimer’s disease: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2024, 12, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slot, R.E.R.; Sikkes, S.A.M.; Berkhof, J.; Brodaty, H.; Buckley, R.; Cavedo, E.; Dardiotis, E.; Guillo-Benarous, F.; Hampel, H.; Kochan, N.A.; et al. Subjective cognitive decline and rates of incident Alzheimer’s disease and non-Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 15, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Recent advances in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms, clinical trials and new drug development strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.S.; Ahn, E.H.; Ye, K. Delta-secretase cleavage of Tau mediates its pathology and propagation in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, R.; Sterling, K.; Song, W. Amyloid beta-based therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: Challenges, successes and future. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.G.; Song, E.J.; Lee, D.; Park, J.; Nam, Y.; Kim, J.I.; Moon, M. Traditional Oriental Medicines and Alzheimer’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.E.; Nikolic, K.; Ramsay, R.R. One for All? Hitting Multiple Alzheimer’s Disease Targets with One Drug. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Garcia-Ptacek, S.; Jonsson, L.; Wimo, A.; Nordstrom, P.; Eriksdotter, M. Long-term Effects of Cholinesterase Inhibitors on Cognitive Decline and Mortality. Neurology 2021, 96, e2220–e2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Das, B.; Hou, H.; He, W.; Yan, R. BACE1 deletion in the adult mouse reverses preformed amyloid deposition and improves cognitive functions. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppner, F.L.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Becher, B. Immune attack: The role of inflammation in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassar, R. β-secretase (BACE) as a drug target for Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 1589–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citron, M. Strategies for disease modification in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, M.F.; Kost, J.; Tariot, P.N.; Aisen, P.S.; Cummings, J.L.; Vellas, B.; Sur, C.; Mukai, Y.; Voss, T.; Furtek, C.; et al. Randomized Trial of Verubecestat for Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassar, R. BACE1 inhibitor drugs in clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2014, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariot, P.N.; Riviere, M.E.; Salloway, S.; Burns, J.M.; Snaedal, J.G.; Borowsky, B.; Lopez, C.L.; Liu, F.; Rouzade-Dominguez, M.L.; Cazorla, P.; et al. Reversibility of cognitive worsening observed with BACE inhibitor umibecestat in the Alzheimer’s Prevention Initiative (API) Generation Studies. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 7745–7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, J.R.M.; Resende, R.; Custodio, J.B.A.; Salvador, J.A.R.; Santos, A.E. BACE1 Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2024, 101, S53–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, G.S. Amyloid-beta and tau: The trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Tung, Y.C.; Quinlan, M.; Wisniewski, H.M.; Binder, L.I. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4913–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, K.; Liu, F.; Gong, C.X. Tau and neurodegenerative disease: The story so far. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Rapposelli, S.; Sestito, S.; Herrera-Bravo, J.; Arancibia-Diaz, A.; Salazar, L.A.; Yeskaliyeva, B.; Beyatli, A.; Leyva-Gomez, G.; Gonzalez-Contreras, C.; et al. Multi-Target Mechanisms of Phytochemicals in Alzheimer’s Disease: Effects on Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation and Protein Aggregation. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.X.; Dai, C.L.; Liu, F.; Iqbal, K. Multi-Targets: An Unconventional Drug Development Strategy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 837649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampietro, A.; Perez-Areales, F.J.; Martinez, P.; Arce, E.M.; Galdeano, C.; Munoz-Torrero, D. Unveiling the Multitarget Anti-Alzheimer Drug Discovery Landscape: A Bibliometric Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhaeva, G.F.; Shevtsova, E.F.; Boltneva, N.P.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Kovaleva, N.V.; Rudakova, E.V.; Bachurin, S.O.; Richardson, R.J. Overview of novel multifunctional agents based on conjugates of gamma-carbolines, carbazoles, tetrahydrocarbazoles, phenothiazines, and aminoadamantanes for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 308, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Rao, D.P.; Kaur, K.; Hassan, R.; Abdel-Samea, A.S.; Farhan, S.M.; Brase, S.; Hashem, H. Indole Derivatives: A Versatile Scaffold in Modern Drug Discovery-An Updated Review on Their Multifaceted Therapeutic Applications (2020–2024). Molecules 2024, 29, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talevi, A. Multi-target pharmacology: Possibilities and limitations of the “skeleton key approach” from a medicinal chemist perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Fridkin, M.; Youdim, M. From single target to multitarget/network therapeutics in Alzheimer’s therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2014, 7, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queda, F.; Calo, S.; Gwizdala, K.; Magalhaes, J.D.; Cardoso, S.M.; Chaves, S.; Piemontese, L.; Santos, M.A. Novel Donepezil-Arylsulfonamide Hybrids as Multitarget-Directed Ligands for Potential Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2021, 26, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzior, N.; Wieckowska, A.; Panek, D.; Malawska, B. Recent development of multifunctional agents as potential drug candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 373–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laura Bolognesi, M.; Simoni, E.; Rosini, M.; Minarini, A.; Tumiatti, V.; Melchiorre, C. Multitarget-directed ligands: Innovative chemical probes and therapeutic tools against Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 2797–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, B.; Bhattarai, H.D.; Koh, H.Y.; Lee, S.G.; Han, S.J.; Lee, H.K.; Oh, H.; Shin, H.W.; Yim, J.H. Ramalin, a novel nontoxic antioxidant compound from the Antarctic lichen Ramalina terebrata. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yoon, C.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, E.; Yim, J.H.; Kim, T.K.; Oh, H.; Lee, D.S. The neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory effects of ramalin synthetic derivatives in BV2 and HT22 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2025, 231, 116654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Hong, J.M.; Kim, K.H.; Han, S.J.; Kim, I.C.; Oh, H.; Yim, J.H. Potential of Ramalin and Its Derivatives for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2021, 26, 6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Cho, Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Hong, J.M.; Cho, H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, I.C.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Chloride-Substituted Ramalin Derivatives for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment. Molecules 2024, 29, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Hong, J.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.H.; Han, S.J.; Kim, I.C.; Oh, H.; Jo, D.G.; Yim, J.H. Therapeutic Potential of Ramalin Derivatives with Enhanced Stability in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2024, 29, 5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, F.M.G.; Markert, G.; Deutsch, G.; Antonara, M.; Faaij, N.; Bartelink, I.; Noske, D.; Vandertop, W.P.; Bender, A.; Westerman, B.A. Explaining Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability of Small Molecules by Integrated Analysis of Different Transport Mechanisms. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 7253–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Martinez, J.D.; Valdes, A.; Gallego, R.; Suarez-Montenegro, Z.J.; Alarcon, M.; Ibanez, E.; Alvarez-Rivera, G.; Cifuentes, A. Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Study of Potential Neuroprotective Compounds Recovered From Plants and Agri-Food by-Products. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 924596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzini, V.; Landucci, E.; Graverini, G.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.E.; Bilia, A.R.; Bergonzi, M.C. Stealth and Cationic Nanoliposomes as Drug Delivery Systems to Increase Andrographolide BBB Permeability. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maboko, L.M.; Theron, A.; Panayides, J.L.; Cordier, W.; Fisher, D.; Steenkamp, V. Evaluating Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability, Cytotoxicity, and Activity of Potential Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: In Vitro and In Silico Study. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2024, 12, e70043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Luo, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, R.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, S.; Shu, H. Advancements in strategies for overcoming the blood-brain barrier to deliver brain-targeted drugs. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1353003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, R.; Zeng, W.; Siramshetty, V.B.; Williams, J.; Kabir, M.; Hagen, N.; Padilha, E.C.; Wang, A.Q.; Mathe, E.A.; Xu, X.; et al. Development and validation of PAMPA-BBB QSAR model to predict brain penetration potential of novel drug candidates. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1291246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Kang, J.-K.; Ahn, K.J.; Hyun, C.-G. DMSO Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW264.7 Macrophages by Inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK Activation. BioChem 2023, 3, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brion, J.P. Neurofibrillary tangles and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. Neurol. 1998, 40, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.H.; Choi, Y.P. In vitro generation of tau aggregates conformationally distinct from parent tau seeds of Alzheimer’s brain. Prion 2019, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunkova, M.; Alwasel, S.H.; Alhazza, I.M.; Jomova, K.; Kollar, V.; Rusko, M.; Valko, M. Management of oxidative stress and other pathologies in Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 2491–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Hardy, J.; Blennow, K.; Chen, C.; Perry, G.; Kim, S.H.; Villemagne, V.L.; Aisen, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. The Amyloid-beta Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5481–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, E.A.; Noorani, B.; Alqahtani, F.; Bhalerao, A.; Raut, S.; Sivandzade, F.; Cucullo, L. Understanding the brain uptake and permeability of small molecules through the BBB: A technical overview. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2021, 41, 1797–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, F.; Salihoglu, H.; Pratsch, K.; Herzog, E.; Pigoni, M.; Sgobio, C.; Lichtenthaler, S.F.; Neumann, U.; Herms, J. Tau deletion reduces plaque-associated BACE1 accumulation and decelerates plaque formation in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e102345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
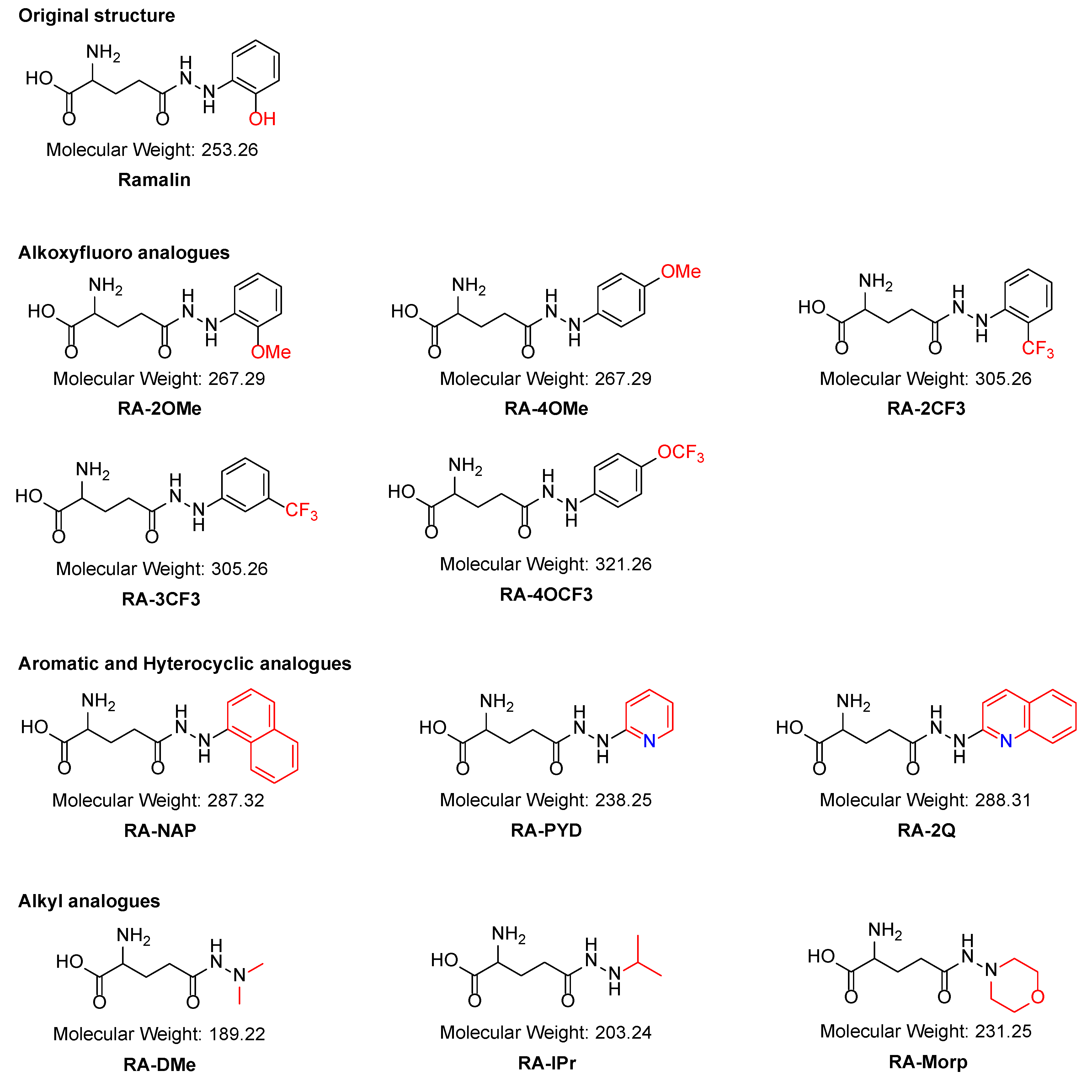

| Test Samples | TPSA (Å2) 1 | iLogP 2 | XlogP 3 | BBB Permeability | MW | DPPH IC50 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ramalin | 128 | 0.65 | −1.69 | × | 253.26 | 1.25 ± 0.01 |
| RA-2OMe | 113.68 | 1.58 | −1.91 | × | 267.28 | 2.81 ± 0.03 |
| RA-4OMe | 113.68 | 1.49 | −1.91 | × | 267.28 | 5.49 ± 0.63 |
| RA-2CF3 | 104.45 | 1.10 | −1.00 | × | 305.25 | 3.00 ± 0.03 |
| RA-3CF3 | 104.45 | 1.19 | −1.00 | × | 305.25 | 31.68 ± 14.61 |
| RA-4OCF3 | 113.68 | 1.78 | −0.70 | × | 321.26 | 3.77 ± 0.09 |
| RA-NAP | 104.45 | 1.80 | −0.64 | × | 287.31 | 1.77 ± 0.12 |
| RA-PYD | 117.34 | 1.25 | −2.62 | × | 238.24 | 7.40 ± 3.54 |
| RA-2Q | 117.34 | 1.51 | −1.28 | × | 288.30 | 9.7 ± 0.32 |
| RA-DMe | 95.66 | 0.06 | −3.71 | × | 189.21 | 598 ± 143.78 |
| RA-IPr | 104.45 | 0.95 | −3.37 | × | 203.24 | 2580.01 ± 359.3 |
| RA-Morp | 104.89 | 0.97 | −3.90 | × | 231.25 | 4800.01 ± 777.8 |
| Test Samples | BACE-1 IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|
| Ramalin | 2.71 ± 0.49 |
| RA-2OMe | 7.97 ± 2.46 |
| RA-4OMe | 24.99 ± 5.72 |
| RA-2CF3 | 11.56 ± 14 |
| RA-3CF3 | 0.33 ± 0.79 |
| RA-4OCF3 | 9.89 ± 13.59 |
| RA-NAP | 0.66 ± 1.05 |
| RA-PYD | 0.32 ± 0.08 |
| RA-2Q | ND |
| RA-DMe | ND |
| RA-IPr | ND |
| RA-Morp | 16.06 ± 11.89 |
| LY2811376 1 | 3.59 ± 3.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.K.; Hong, J.-M.; Cho, Y.; Jeon, Y.; Cho, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, I.-C.; Han, S.J.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Ramalin Derivatives as Multi-Target Agents for Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2025, 30, 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092030
Kim TK, Hong J-M, Cho Y, Jeon Y, Cho H, Lee J, Kim J, Kim KH, Kim I-C, Han SJ, et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Ramalin Derivatives as Multi-Target Agents for Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092030
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tai Kyoung, Ju-Mi Hong, Yongeun Cho, Yeji Jeon, Heewon Cho, Jeongmi Lee, Jaewon Kim, Kyung Hee Kim, Il-Chan Kim, Se Jong Han, and et al. 2025. "Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Ramalin Derivatives as Multi-Target Agents for Alzheimer’s Disease" Molecules 30, no. 9: 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092030
APA StyleKim, T. K., Hong, J.-M., Cho, Y., Jeon, Y., Cho, H., Lee, J., Kim, J., Kim, K. H., Kim, I.-C., Han, S. J., Oh, H., Jo, D.-G., & Yim, J. H. (2025). Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Ramalin Derivatives as Multi-Target Agents for Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules, 30(9), 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092030






