Synthesis and Evaluation of a Novel Zuranolone Analog with High GABAA Receptor PAM Activity and Excellent Pharmacokinetic Profiles
Abstract
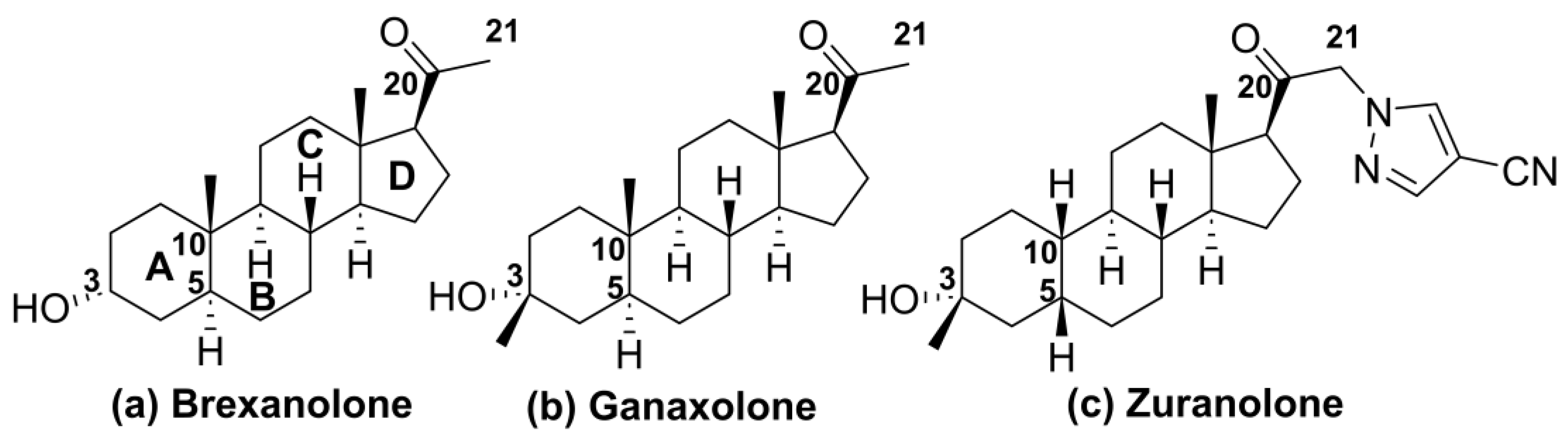
1. Introduction
2. Results
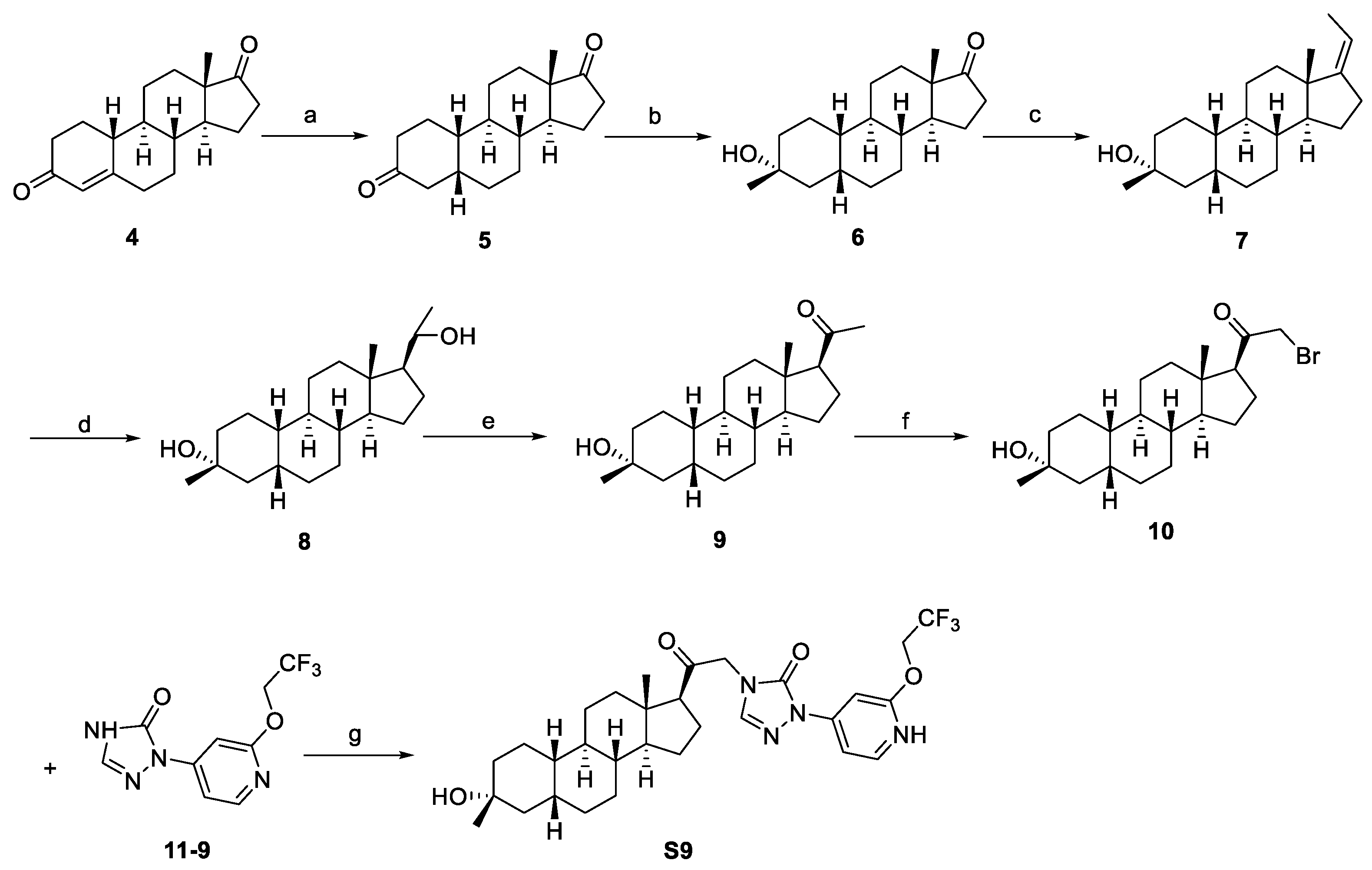
2.1. Synthesis Overview
2.2. Physicochemical Parameters of Zuranolone and Synthetic Compounds
2.3. Preliminary Structure–Activity Relationship Study
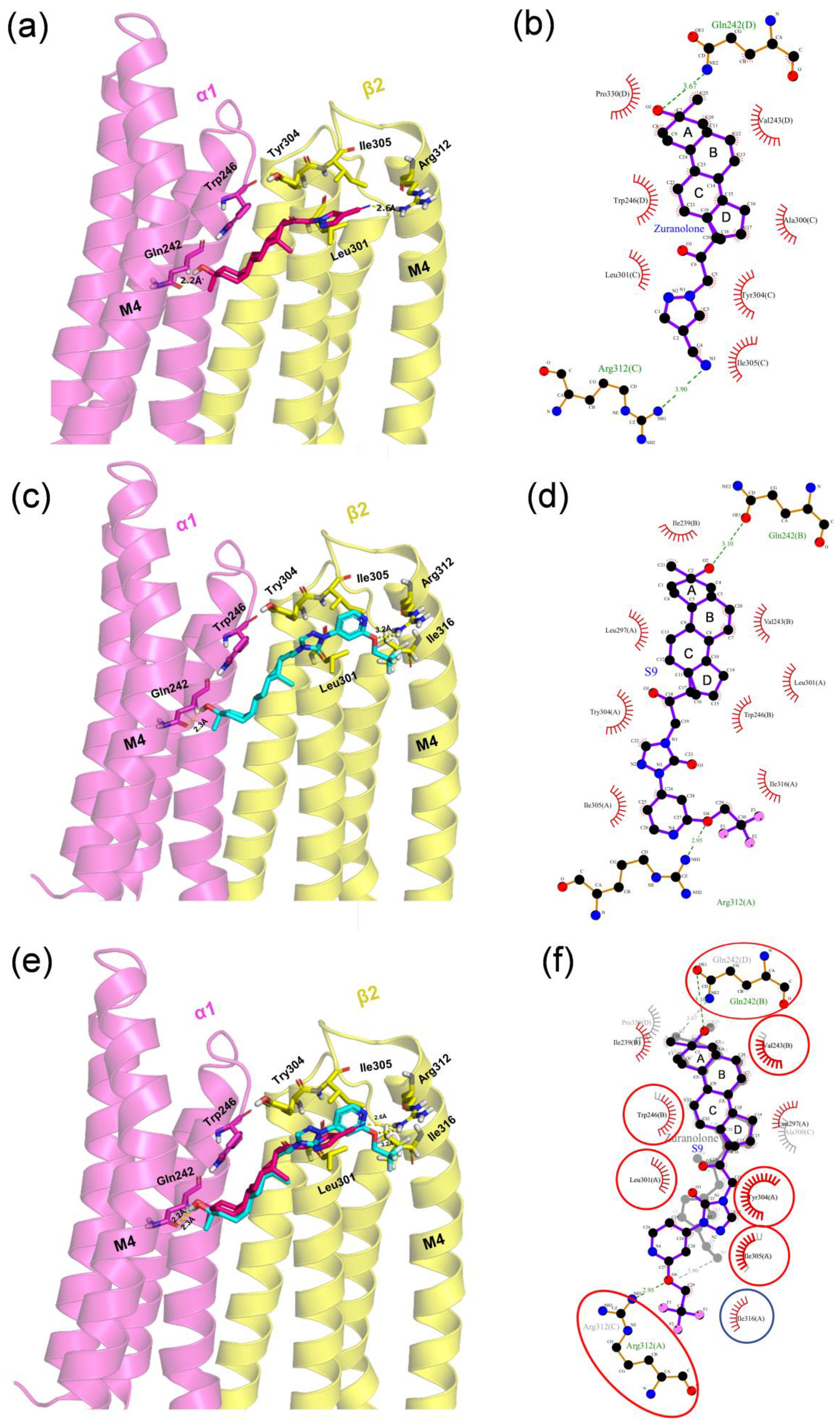
2.4. Molecular Docking Analysis
2.5. In Vitro Studies of Bioactivity
2.5.1. Study on GABAA Receptor Pharmacology
2.5.2. Study on Metabolic Stability in Liver Microsomes
2.6. In Vivo Evaluation of Bioactivities of Zuranolone and S9 in Rats
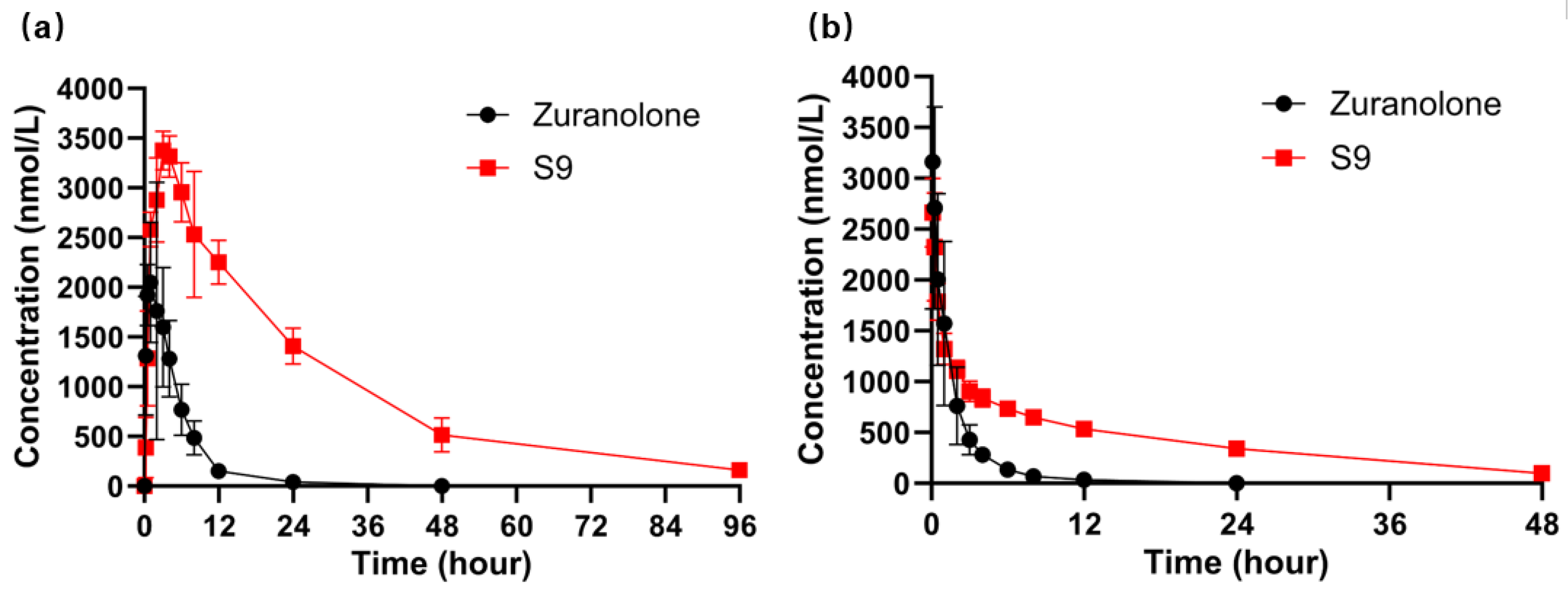
2.6.1. Pharmacokinetic Study of S9 and Zuranolone
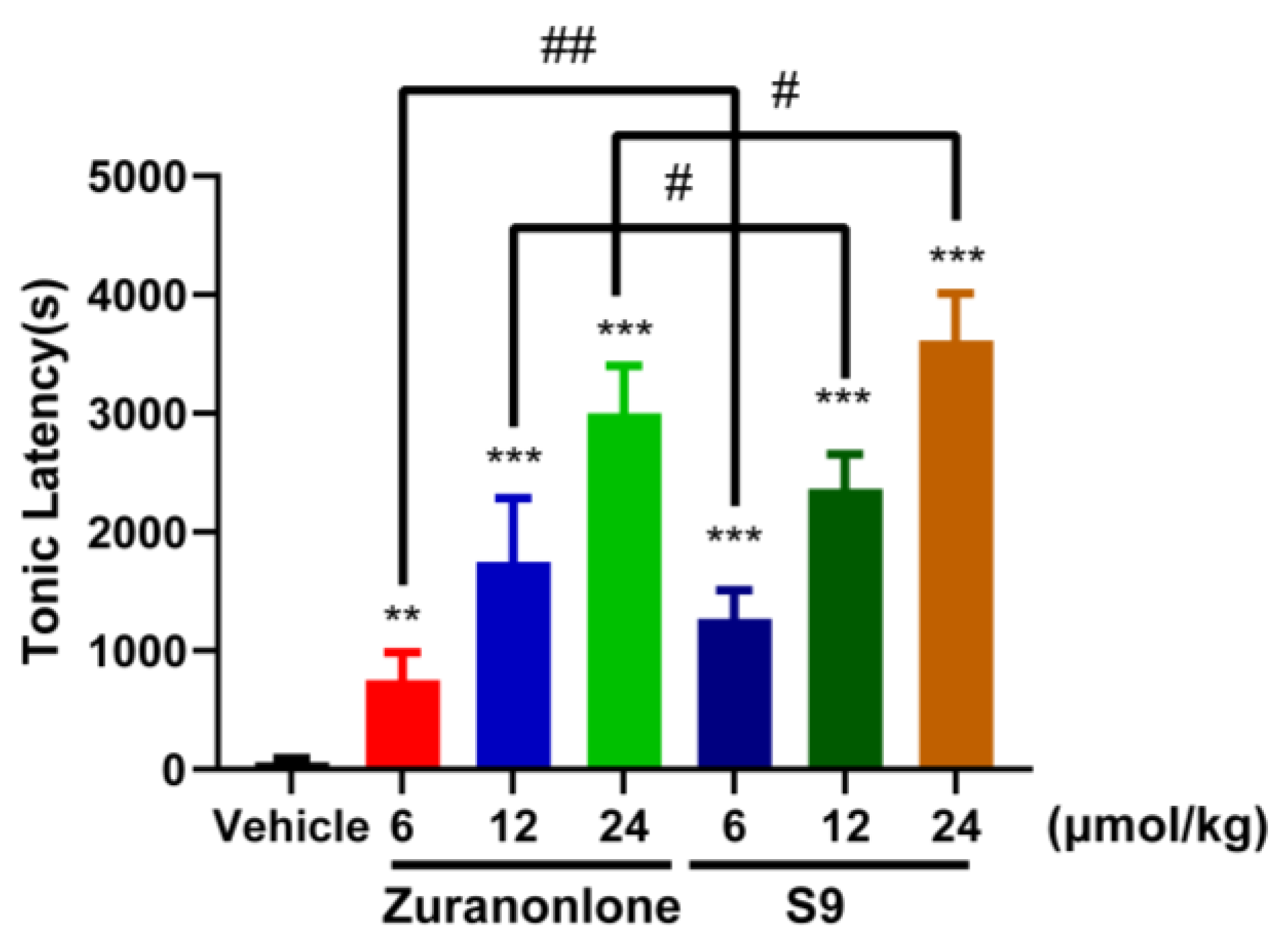
2.6.2. Effects of S9 and Zuranolone on Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-Induced Acute Seizures
2.6.3. Effect of S9 and Zuranolone on Loss of Righting Reflex (LORR)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals
4.3. Chemistry
4.3.1. Structural Characterization
4.3.2. Synthesis
Synthesis of S9
Synthesis of S1–S15
4.4. Molecular Docking
4.5. In Vitro and Vivo Studies of Bioactivity
4.5.1. Quantification Analysis
4.5.2. In Vitro Assay
Electrophysiology Assay
Liver Microsome Assay
4.5.3. In Vivo Evaluation in Rats
Pharmacokinetic Study
Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-Induced Seizure Test
Loss of Righting Reflex (LORR) Test
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olsen, R.W.; Sieghart, W. GABA A receptors: Subtypes provide diversity of function and pharmacology. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carver, C.M.; Reddy, D.S. Neurosteroid interactions with synaptic and extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors: Regulation of subunit plasticity, phasic and tonic inhibition, and neuronal network excitability. Psychopharmacology 2013, 230, 151–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.S.; Estes, W.A. Clinical Potential of Neurosteroids for CNS Disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorumski, C.F.; Paul, S.M.; Covey, D.F.; Mennerick, S. Neurosteroids as novel antidepressants and anxiolytics: GABA-A receptors and beyond. Neurobiol. Stress 2019, 27, 100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belelli, D.; Hogenkamp, D.; Gee, K.W.; Lambert, J.J. Realising the therapeutic potential of neuroactive steroid modulators of the GABAA receptor. Neurobiol. Stress 2019, 23, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerne, R.; Lippa, A.; Poe, M.M.; Smith, J.L.; Jin, X.; Ping, X.; Golani, L.K.; Cook, J.M.; Witkin, J.M. GABAkines—Advances in the discovery, development, and commercialization of positive allosteric modulators of GABAA receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 234, 108035. [Google Scholar]
- Abramian, A.M.; Comenencia-Ortiz, E.; Modgil, A.; Vien, T.N.; Nakamura, Y.; Moore, Y.E.; Maguire, J.L.; Terunuma, M.; Davies, P.A.; Moss, S.J. Neurosteroids promote phosphorylation and membrane insertion of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 13, 7132–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modgil, A.; Parakala, M.L.; Ackley, M.A.; Doherty, J.J.; Moss, S.J.; Davies, P.A. Endogenous and synthetic neuroactive steroids evoke sustained increases in the efficacy of GABAergic inhibition via a protein kinase C-dependent mechanism. Neuropharmacology 2017, 113, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, N.L.; Majewska, M.D.; Harrington, J.W.; Barker, J.L. Structure-activity relationships for steroid interaction with the gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor complex. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1987, 241, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokate, T.G.; Svensson, B.E.; Rogawski, M.A. Anticonvulsant activity of neurosteroids: Correlation with gamma-aminobutyric acid-evoked chloride current potentiation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 270, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorumski, C.F.; Paul, S.M.; Izumi, Y.; Covey, D.F.; Mennerick, S. Neurosteroids, stress and depression: Potential therapeutic opportunities. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carver, C.M.; Reddy, D.S. Neurosteroid Structure-Activity Relationships for Functional Activation of Extrasynaptic δGABA(A) Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 357, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogenkamp, D.J.; Tahir, S.H.; Hawkinson, J.E.; Upasani, R.B.; Alauddin, M.; Kimbrough, C.L.; Acosta-Burruel, M.; Whittemore, E.R.; Woodward, R.M.; Lan, N.C.; et al. Synthesis and in vitro activity of 3 beta-substituentd-3 alpha-hydroxypregnan-20-ones: Allosteric modulators of the GABAA receptor. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, R.B.; Wood, P.L.; Wieland, S.; Hawkinson, J.E.; Belelli, D.; Lambert, J.J.; White, H.S.; Wolf, H.H.; Mirsadeghi, S.; Tahir, S.H.; et al. Characterization of the anticonvulsant properties of ganaxolone (CCD 1042; 3alpha-hydroxy-3beta-methyl-5alpha-pregnan-20-one), a selective, high-affinity, steroid modulator of the gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 280, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Botella, G.; Salituro, F.G.; Harrison, B.L.; Beresis, R.T.; Bai, Z.; Shen, K.; Belfort, G.M.; Loya, C.M.; Ackley, M.A.; Grossman, S.J.; et al. Neuroactive Steroids. 1. Positive Allosteric Modulators of the (γ-Aminobutyric Acid)A Receptor: Structure-Activity Relationships of Heterocyclic Substitution at C-21. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3500–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Botella, G.; Salituro, F.G.; Harrison, B.L.; Beresis, R.T.; Bai, Z.; Blanco, M.J.; Belfort, G.M.; Dai, J.; Loya, C.M.; Ackley, M.A.; et al. Neuroactive Steroids. 2. 3α-Hydroxy-3β-methyl-21-(4-cyano-1H-pyrazol-1′-yl)-19-nor-5β-pregnan-20-one (SAGE-217): A Clinical Next Generation Neuroactive Steroid Positive Allosteric Modulator of the (γ-Aminobutyric Acid)A Receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7810–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althaus, A.L.; Ackley, M.A.; Belfort, G.M.; Gee, S.M.; Dai, J.; Nguyen, D.P.; Kazdoba, T.M.; Modgil, A.; Davies, P.A.; Moss, S.J.; et al. Preclinical characterization of zuranolone (SAGE-217), a selective neuroactive steroid GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator. Neuropharmacology 2020, 181, 108333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligiannidis, K.M.; Meltzer-Brody, S.; Gunduz-Bruce, H.; Doherty, J.; Jonas, J.; Li, S.; Sankoh, A.J.; Silber, C.; Campbell, A.D.; Werneburg, B.; et al. Effect of Zuranolone vs Placebo in Postpartum Depression: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. ZURZUVAETM (Zuranolone) Prescribing Information. In Revised August 2023. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/217369s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Knight, E.M.P.; Amin, S.; Bahi-Buisson, N.; Benke, T.A.; Cross, J.H.; Demarest, S.T.; Olson, H.E.; Specchio, N.; Fleming, T.R.; Aimetti, A.A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of ganaxolone in patients with CDKL5 deficiency disorder: Results from the double-blind phase of a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. ZTALMY® (Ganaxolone) Prescribing Information. In Revised March 2022. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/215904s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Reddy, D.S. Neurosteroids as Novel Anticonvulsants for Refractory Status Epilepticus and Medical Countermeasures for Nerve Agents: A 15-Year Journey to Bring Ganaxolone from Bench to Clinic. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2024, 388, 273–300. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, S.H.; Reddy, D.S. 3β-Methyl-Neurosteroid Analogs Are Preferential Positive Allosteric Modulators and Direct Activators of Extrasynaptic δ-Subunit γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptors in the Hippocampus Dentate Gyrus Subfield. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 365, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.S. Neurosteroid Compounds and Methods for Their Preparation and Use in Treating Central Nervous System Disorders. U.S. Patent 11,542,296, 3 January 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Xu, H.; Ye, L.; Li, C.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, W.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of neuroactive steroids with novel pharmacophore at C-21 let identify a compound with advantageous PK profile and higher EC50 and Emax as PAM on GABAA receptor. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 276, 116602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ji, S.; Yang, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Deng, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Tian, J. LPM682000012, a Synthetic Neuroactive Steroid That Ameliorates Epileptic Seizures by Downregulating the Serpina3n/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2024, 29, 5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisari, M.; Eisenman, L.N.; Krishnan, K.; Bandyopadhyaya, A.K.; Wang, C.; Taylor, A.; Benz, A.; Covey, D.F.; Zorumski, C.F.; Mennerick, S. The influence of neuroactive steroid lipophilicity on GABAA receptor modulation: Evidence for a low-affinity interaction. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 102, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, M.; Eisenman, L.N.; Covey, D.F.; Mennerick, S.; Zorumski, C.F. The sticky issue of neurosteroids and GABA(A) receptors. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, M.; Krishnan, K.; Kudova, E.; Li, P.; Manion, B.D.; Taylor, A.; Elias, G.; Akk, G.; Evers, A.S.; Zorumski, C.F.; et al. Neurosteroid analogues. 18. Structure-activity studies of ent-steroid potentiators of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors and comparison of their activities with those of alphaxalone and allopregnanolone. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Shi, S.; Yi, J.; Wang, N.; He, Y.; Wu, Z.; Peng, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, C.; et al. ADMETlab 3.0: An updated comprehensive online ADMET prediction platform enhanced with broader coverage, improved performance, API functionality and decision support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W422–W431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legesse, D.H.; Fan, C.; Teng, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Howard, R.J.; Noviello, C.M.; Lindahl, E.; Hibbs, R.E. Structural insights into opposing actions of neurosteroids on GABAA receptors. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akk, G.; Li, P.; Bracamontes, J.; Reichert, D.E.; Covey, D.F.; Steinbach, J.H. Mutations of the GABA-A receptor alpha1 subunit M1 domain reveal unexpected complexity for modulation by neuroactive steroids. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracamontes, J.R.; Steinbach, J.H. Steroid interaction with a single potentiating site is sufficient to modulate GABA-A receptor function. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.; Manion, B.D.; Taylor, A.; Bracamontes, J.; Steinbach, J.H.; Reichert, D.E.; Evers, A.S.; Zorumski, C.F.; Mennerick, S.; Covey, D.F. Neurosteroid analogues. 17. Inverted binding orientations of androsterone enantiomers at the steroid potentiation site on γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.; Kerby, J.; Bonnert, T.P.; Whiting, P.J.; Wafford, K.A. Pharmacological characterization of a novel cell line expressing human α4β3δ GABA(A) receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 136, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlfarth, K.M.; Bianchi, M.T.; Macdonald, R.L. Enhanced neurosteroid potentiation of ternary GABA(A) receptors containing the delta subunit. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, M.T.; Macdonald, R.L. Neurosteroids shift partial agonist activation of GABA(A) receptor channels from low- to high-efficacy gating patterns. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10934–10943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, U.; Knoflach, F. Beyond classical benzodiazepines: Novel therapeutic potential of GABAA receptor subtypes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kwon, S.S.; Kong, T.Y.; Cheong, J.C.; Kim, H.S.; In, M.K.; Lee, H.S. AM-2201 Inhibits Multiple Cytochrome P450 and Uridine 5′-Diphospho-Glucuronosyltransferase Enzyme Activities in Human Liver Microsomes. Molecules 2017, 22, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, Á.B.; Alves, A.F.; Ribeiro Portela, A.C.; Oliveira Pires, H.F.; Pessoa de Melo, M.; Medeiros Vilar Barbosa, N.M.; Bezerra Felipe, C.F. Pentylenetetrazole: A review. Neurochem. Int. 2024, 180, 105841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | Zuranolone | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S13 | S14 | S15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pKa (acid) a | 10.8 | 9.52 | 9.07 | 10.4 | 9.68 | 10.3 | 10.0 | 10.5 | 12.0 |
| LogP (pH 7.4) a | 4.78 | 3.79 | 3.70 | 4.53 | 3.88 | 4.61 | 4.20 | 4.52 | 5.75 |
| LogD a | 4.39 | 3.75 | 3.57 | 4.24 | 3.78 | 4.13 | 3.95 | 4.16 | 4.91 |
| TPSA (Å2) a | 78.9 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 99.2 | 100.9 | 86.4 | 64.2 |
| CYP (IC50, μmol/L) b: 1A2/2C8/2D6/3A4 | >30 | - | - | - | - | >30 | - | - | - |
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | R1 | α1β2γ2 | α4β3δ | ||
| EC50 (nmol/L) | Emax (%) | EC50 (nmol/L) | Emax (%) | ||
| Zuranolone | 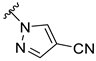 | 123 ± 20 | 894 ± 40 | 93 ± 10 | 1368 ± 125 |
| S1 | 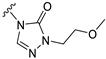 | 227 ± 52 | 735 ± 75 | 86 ± 25 | 609 ± 83 |
| S2 | 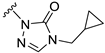 | 58 ± 10 | 320 ± 25 | 140 ± 10 | 450 ± 35 |
| S3 | 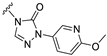 | 167 ± 37 | 389 ± 50 | 134 ± 32 | 474 ± 53 |
| S4 | 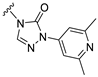 | 171 ± 40 | 691 ± 72 | 41 ± 19 | 563 ± 85 |
| S5 | 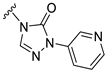 | 373 ± 45 | 773 ± 87 | 61 ± 15 | 391 ± 64 |
| S6 | 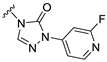 | 280 ± 52 | 736 ± 98 | 143 ± 30 | 507 ± 97 |
| S7 | 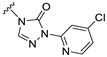 | 109 ± 27 | 624 ± 29 | 72 ± 21 | 589 ± 63 |
| S8 |  | 83 ± 24 | 600 ± 69 | 49 ± 15 | 432 ± 55 |
| S9 | 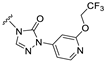 | 50 ± 10 | 675 ± 163 | 34 ± 10 | 967 ± 118 |
| S10 | 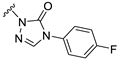 | 12.4 ± 5 | 294 ± 52 | 148 ± 25 | 428 ± 45 |
| S11 | 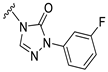 | 594 ± 51 | 495 ± 65 | 96 ± 23 | 936 ± 75 |
| S12 | 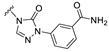 | 153 ± 33 | 764 ± 65 | 159 ± 20 | 386 ± 50 |
| S13 | 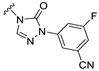 | 72 ± 16 | 518 ± 87 | 37 ± 12 | 549 ± 101 |
| S14 |  | 770 ± 104 | 576 ± 78 | 460 ± 59 | 889 ± 126 |
| S15 | 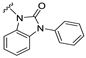 | 31 ± 12 | 305 ± 62 | 55 ± 15 | 470 ± 94 |
| Compounds | RLM | HLM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLint (mg/min/mg) | T1/2 (min) | CLint (mg/min/mg) | T1/2 (min) | |
| Zuranolone | 52 | 48 | 11 | 124 |
| S1 | 243 | 11 | 37 | 34 |
| S3 | 161 | 16 | 17 | 73 |
| S5 | 187 | 11 | 52 | 24 |
| S6 | 83 | 34 | 60 | 40 |
| S7 | 120 | 21 | 18 | 69 |
| S8 | 108 | 29 | 53 | 23 |
| S9 | 8 | 186 | 9 | 154 |
| S10 | 219 | 10 | 38 | 33 |
| S12 | 141 | 18 | 26 | 29 |
| S13 | 27 | 90 | 25 | 40 |
| S14 | 108 | 23 | 41 | 31 |
| S15 | 7 | 210 | 5 | 248 |
| Parameters | Zuranolone | S9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i.v. | i.g. | i.v. | i.g. | |
| Dose (μmol/kg) | 6.1 | 24.4 | 6.1 | 24.4 |
| T1/2 (h) | 2.5 ± 1.3 | 3.8 ± 1.7 | 16.4 ± 0.56 | 19.8 ± 1.5 |
| Tmax (h) | / | 1.2 ± 0.8 | / | 3.7 ± 0.6 |
| C0/Cmax (nmol/L) | 3432 ± 1737 | 2279 ± 554 | 2858 ± 223 | 3604 ± 541 |
| AUC0–t (nmol/L·h) | 5178 ± 1732 | 11,958 ± 3057 | 24,249 ± 2325 | 80,379 ± 7942 |
| F (%) | / | 57.7% | / | 82.9% |
| Compounds a | Brain (nmol/kg) | AUCBrain 0–t (nmol/kg·h) | FAUCBrain 0–t S9/Zuranolone (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 h | 2 h | 6 h | 24 h | |||
| Zuranolone | 3103 ± 795 | 2220 ± 574 | 193 ± 56 | BQL b | 9549 ± 2529 | / |
| S9 | 189 ± 30 | 1895 ± 593 | 2132 ± 683 | 175 ± 35 | 30,969 ± 8450 | 324 |
| Compounds | Dose a (μmol/kg) | Animals with LORR/Total (n) | Latency to LORR (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zuranolone | 19.5 | 9/10 | 30 |
| 15.6 | 2/10 | 35 | |
| 9.8 | 0/10 | / | |
| S9 | 58.3 | 9/10 | 59 |
| 48.6 | 6/10 | 68 | |
| 38.9 | 0/10 | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Deng, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, D.; Zhao, F.; Yang, H.; Wang, W.; Sha, C.; Ma, M.; Zhang, G.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of a Novel Zuranolone Analog with High GABAA Receptor PAM Activity and Excellent Pharmacokinetic Profiles. Molecules 2025, 30, 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091918
Yang Y, Deng X, Xu H, Chen D, Zhao F, Yang H, Wang W, Sha C, Ma M, Zhang G, et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of a Novel Zuranolone Analog with High GABAA Receptor PAM Activity and Excellent Pharmacokinetic Profiles. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091918
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yingjie, Xu Deng, Hengwei Xu, Daoyuan Chen, Fengjuan Zhao, Huijie Yang, Wenyan Wang, Chunjie Sha, Mingxu Ma, Guanqing Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Synthesis and Evaluation of a Novel Zuranolone Analog with High GABAA Receptor PAM Activity and Excellent Pharmacokinetic Profiles" Molecules 30, no. 9: 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091918
APA StyleYang, Y., Deng, X., Xu, H., Chen, D., Zhao, F., Yang, H., Wang, W., Sha, C., Ma, M., Zhang, G., Ye, L., & Tian, J. (2025). Synthesis and Evaluation of a Novel Zuranolone Analog with High GABAA Receptor PAM Activity and Excellent Pharmacokinetic Profiles. Molecules, 30(9), 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091918





