Synthesis, Characterization, and Cementitious Activity of the Magnesium Silicate Hydrate and Calcium Silicate Hydrate from Coal Gangue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Raw Coal Gangue Characterization
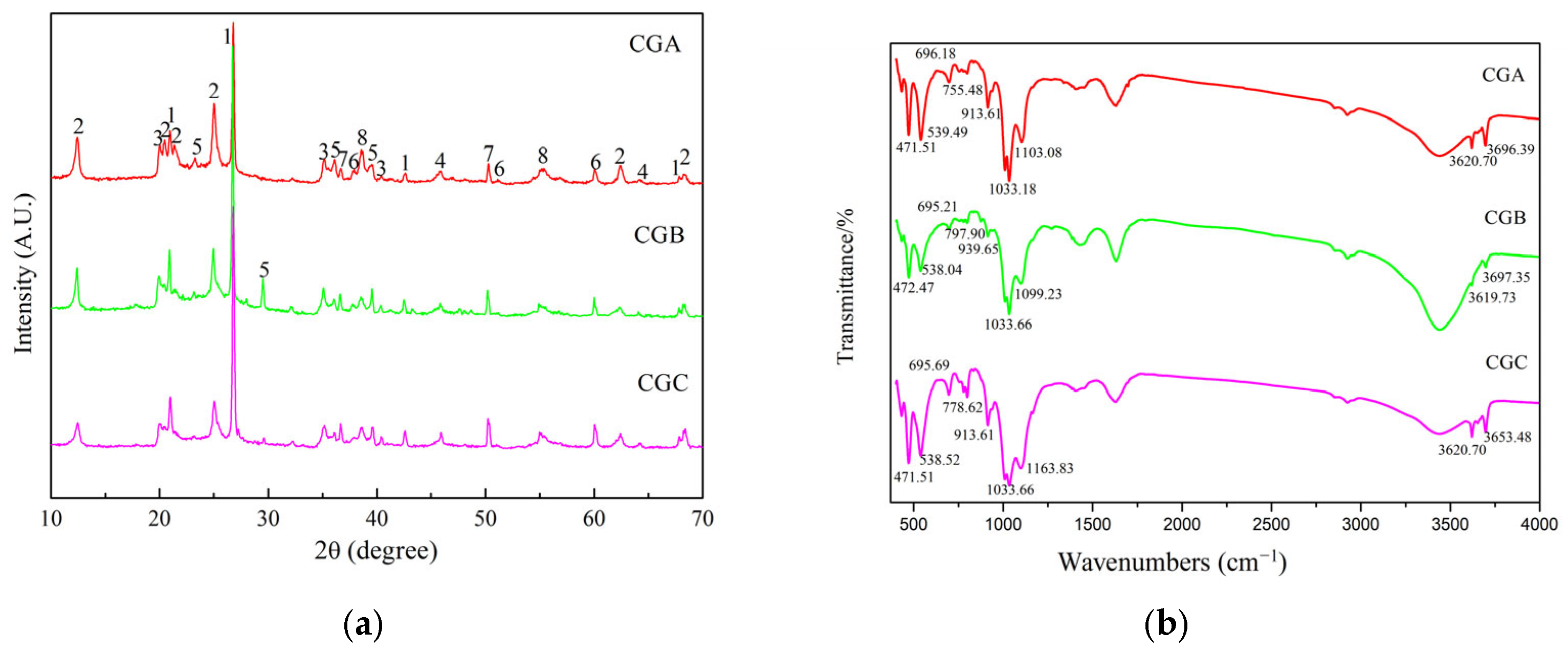
2.1.1. XRD Analysis of Raw Coal Gangue
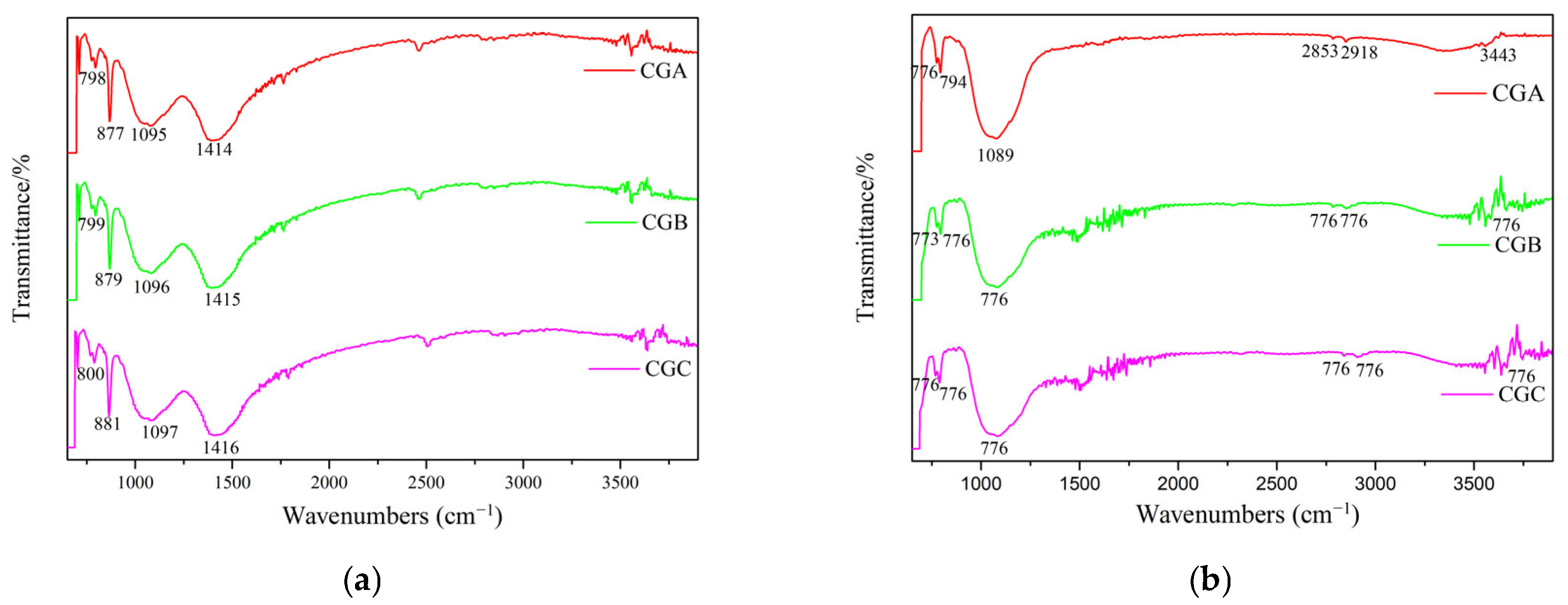
2.1.2. FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis of Raw Coal Gangue
- (i)
- The bonds could be observed in the region between 4000 cm−1 and 3500 cm−1 due to the structural OH− of coal gangue. CGA, CGB, and CGC showed stretching vibrations of outer OH− groups at 3696.39 cm−1, 3697.35 cm−1, and 3653.48 cm−1 and the inner OH− groups at 3620.70 cm−1, 3619.73 cm−1, and 3620.70 cm−1, respectively. The inner OH− groups were stronger than the outer OH− groups and existed between the tetrahedral and the octahedral sheets. The outer OH− groups could be combined with the oxygens of the next tetrahedral layer to form weak hydrogen bonds [7,19].
- (ii)
- The 939.65 cm−1 and 913.61 cm−1 bands were attributed to the stretching vibration of Al-O-H.
- (iii)
- The 539.49 cm−1, 538.52 cm−1, and 538.04 cm−1 bands arose from the Si-O-Alvi vibration.
- (iv)
- Bands at 1163.83 cm−1, 1103.08 cm−1, 1099.23 cm−1, 797.90 cm−1, 778.62 cm−1, and 755.48 cm−1 originated from Si-O-Si vibration.
- (v)
- The stretching vibrations of Si-O at 1033.66 cm−1, 1033.18 cm−1, 696.18 cm−1, 695.21 cm−1, 695.69 cm−1, 472.47 cm−1, and 471.51 cm−1, respectively.
2.1.3. TG-DSC Analysis of Raw Coal Gangue
2.2. Activity Evaluation
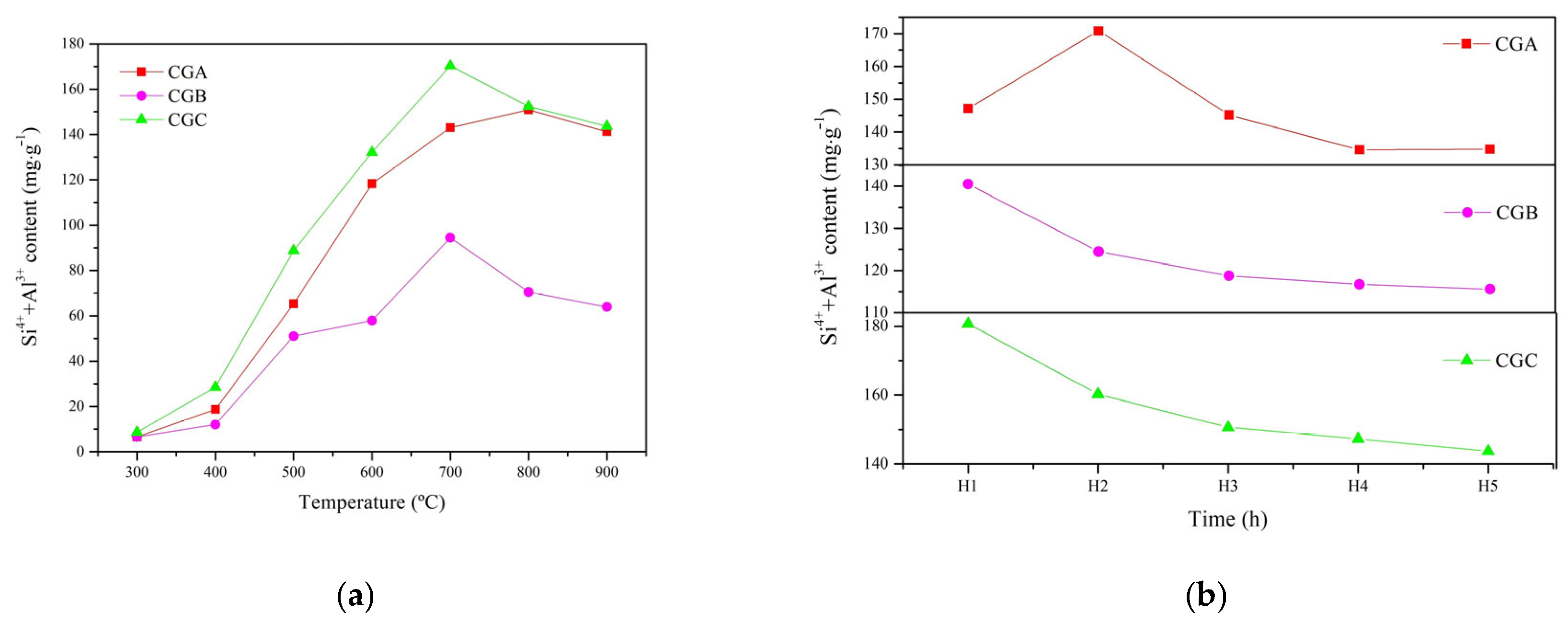
2.2.1. ICP-AES Analysis
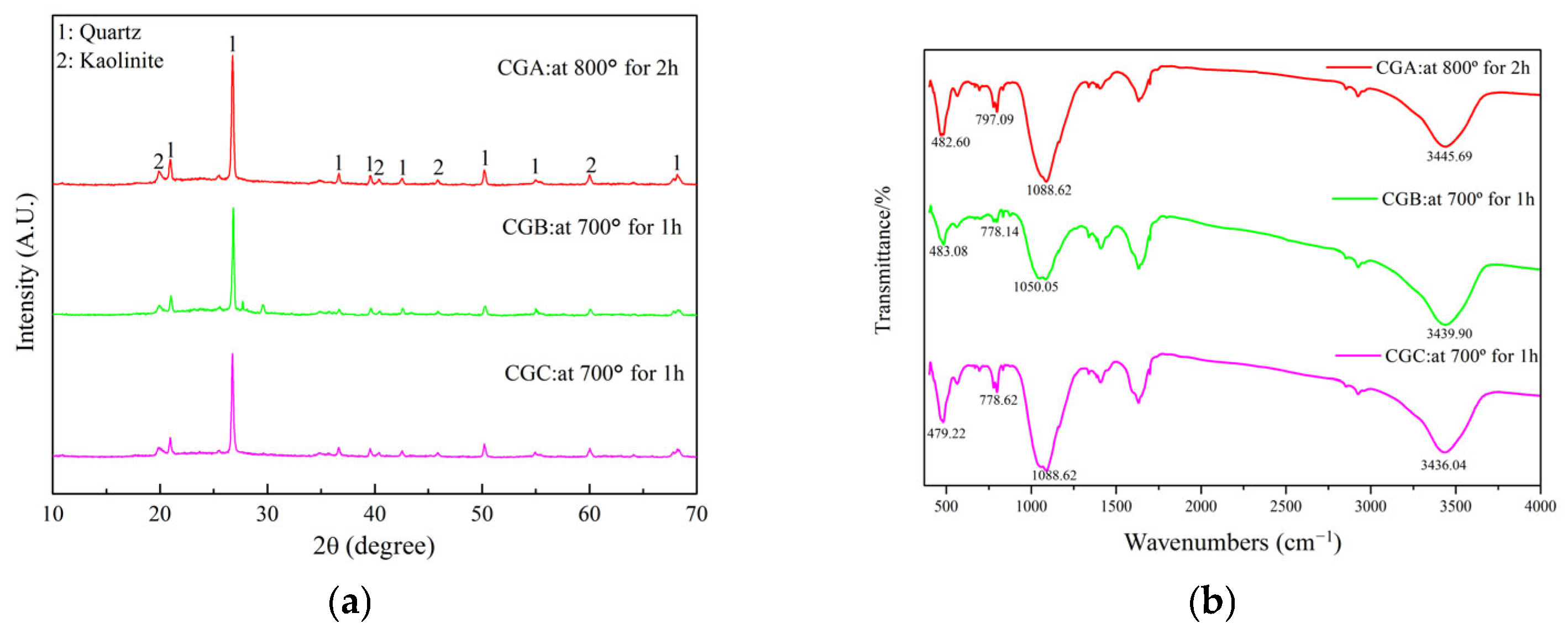
2.2.2. XRD Analysis of Thermally Treated Coal Gangue
2.2.3. FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis of Thermally Treated Coal Gangue
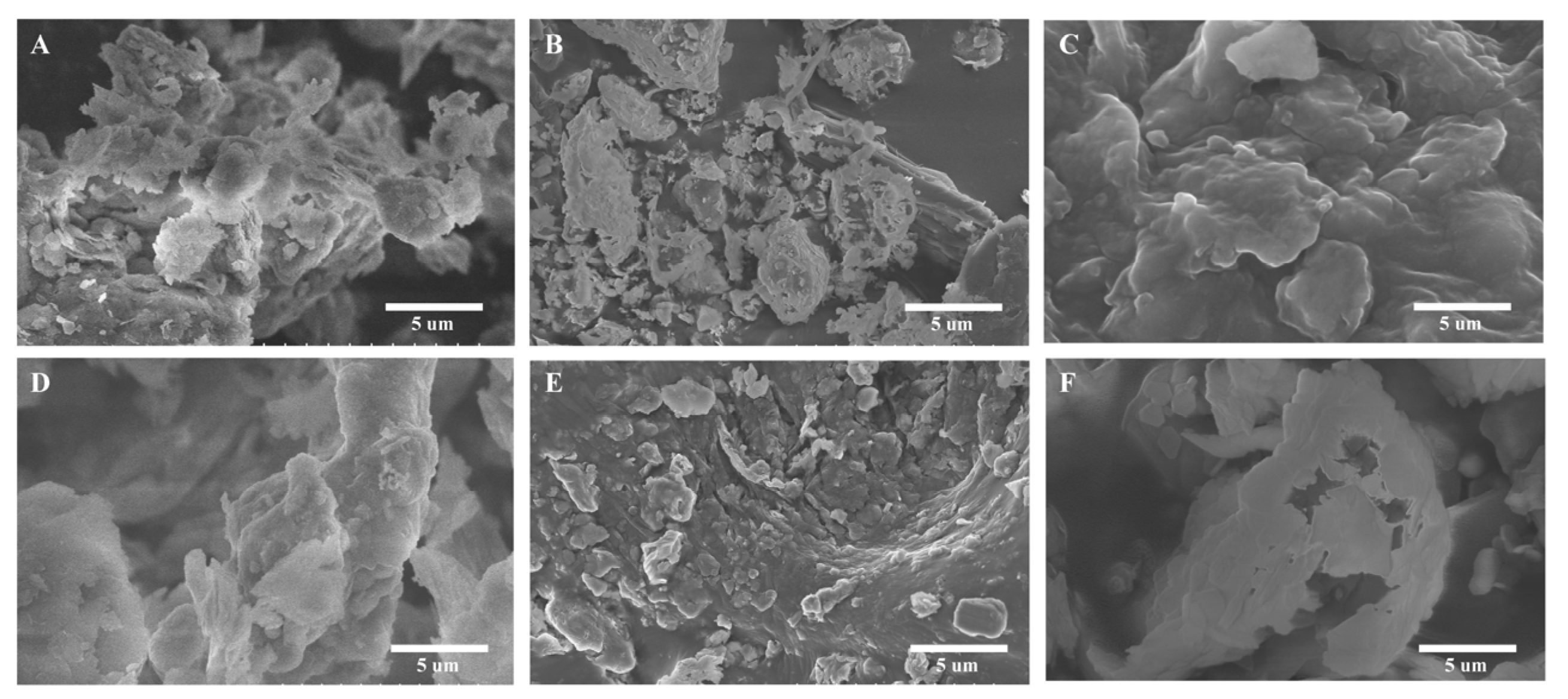
2.2.4. SEM Observations of Raw and Thermally Treated Coal Gangue
2.2.5. Calcination Mechanism
2.3. Synthesis and Characterization of C-S-H and M-S-H
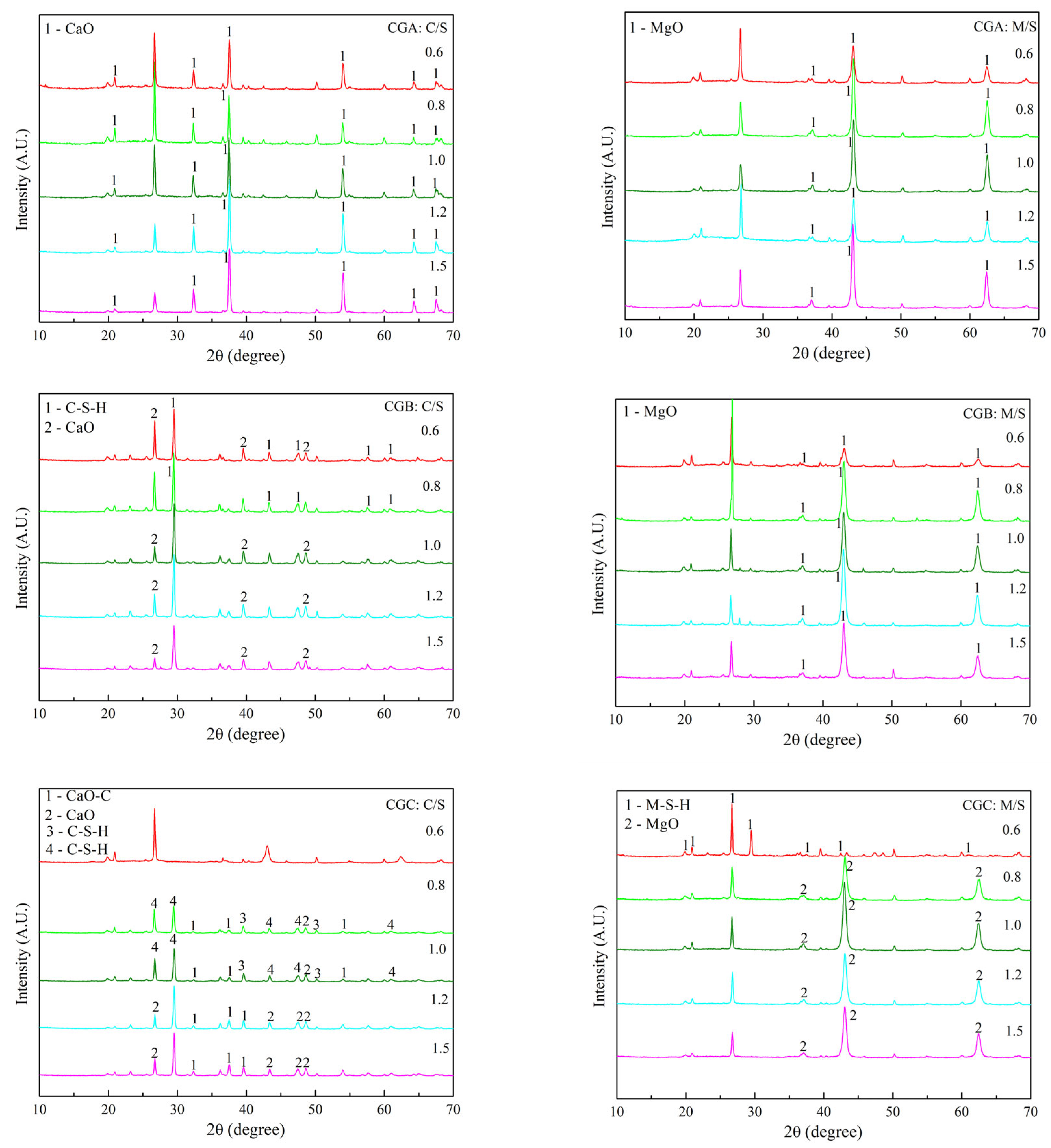
2.3.1. XRD Analysis of C-S-H and M-S-H
2.3.2. FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis of C-S-H and M-S-H
2.3.3. SEM Observations of C-S-H and M-S-H
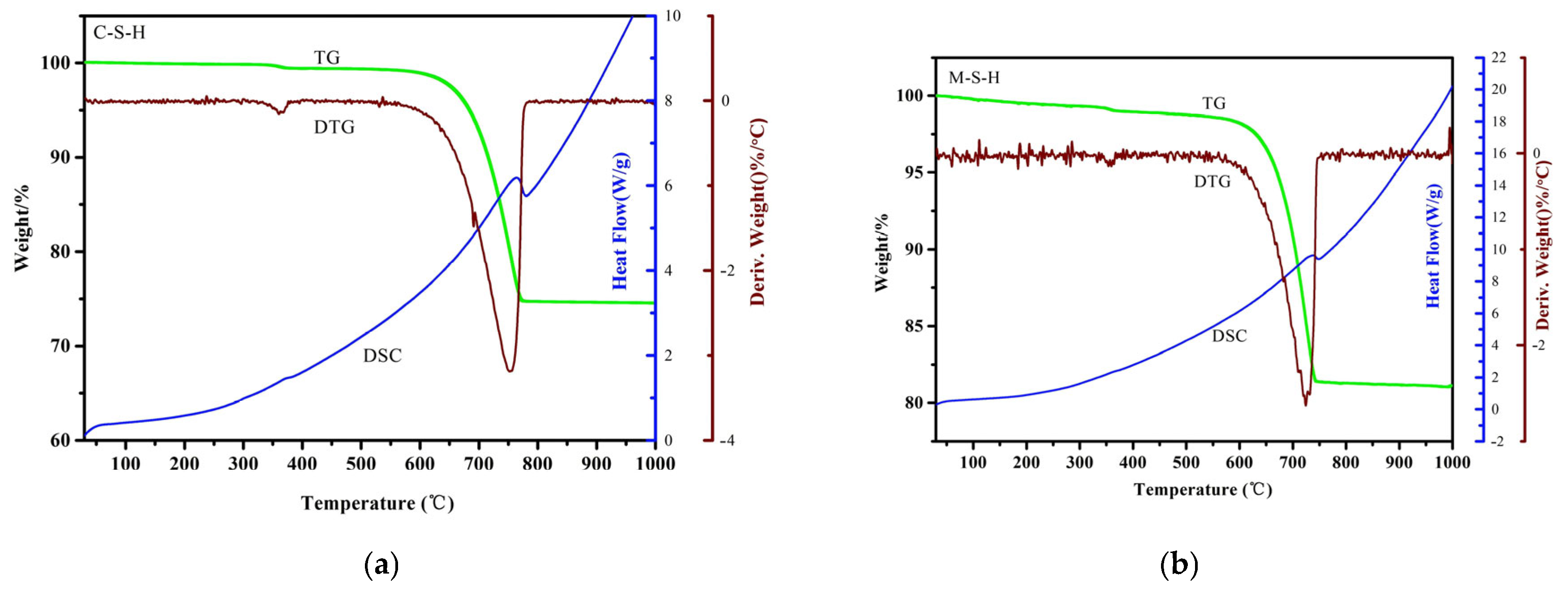
2.3.4. TG-DSC Analysis of C-S-H and M-S-H
2.3.5. Mechanical Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experimental Methods
3.2.1. Specimen Preparation
3.2.2. Mechanical Property Testing
3.2.3. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C-S-H | calcium silicate hydrate |
| M-S-H | magnesium silicate hydrate |
| CGA | coal gangue-A |
| CGB | coal gangue-B |
| CGC | coal gangue-C |
References
- Wang, A.G.; Pan, Y.H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.M.; Liu, K.W.; Sun, D.S. Research progress of resourceful and efficient utilization of coal gangue in the field of building materials. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 99, 111526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, X.J.; Yang, P.; Feng, G.R.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhu, C.Q.; Cheng, X. Layered re-breaking behavior of gangue backfilling materials and inspirations for protecting mined ecological environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wen, Q.; Hu, L.; Gong, M.; Tang, Z. Feasibility study on the application of coal gangue as landfill liner material. Waste Manag. 2017, 63, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, J.X.; Li, A.L.; Zhou, N. Reutilisation of coal gangue and fly ash as underground backfill materials for surface subsidence control. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, B.; Kityk, A.V.; Busch, M.; Huber, P. The structural and surface properties of natural and modified coal gangue. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 190, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qin, Q.; Hu, S.; Wu, K. A concrete material with waste coal gangue and fly ash used for farmland drainage in high groundwater level areas. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C. Effect of calcination condition on the microstructure and pozzolanic activity of calcined coal gangue. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 146, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raquel, V.; Garcia, R.; Martinez-Ramirez, S.; Frias, M. Effects of calcination temperature and the addition of ZnO on coal waste activation: A mineralogical and morphological evolution. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 150, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.K.; Ge, K.Y.; Sun, T.; Shui, Z.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Lu, J.X. Pozzolanic activity of mechanochemically and thermally activated coal-series kaolin in cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrović, A.; Zdujić, M. Preparation of pozzolanic addition by mechanical treatment of kaolin clay. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 132, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.L.; Zhang, L.L.; Ren, X.H.; Xu, B.H.; Hong, Z.; Ma, F.S. The characteristics of mechanical grinding on kaolinite structure and thermal behavior. Energy Procedia 2012, 16, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Song, X.; Gong, C.; Pan, Z. Research on cementitious behavior and mechanism of pozzolanic cement with coal gangue. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1752–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Dai, S.; Jian, S.; Huang, J.; Tan, H.; Li, B. Utilization of solid waste high-volume calcium coal gangue in autoclaved aerated concrete: Physico-mechanical properties, hydration products and economic costs. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, A.; Sun, D.; Chu, Y. Valorization of calcined coal gangue as coarse aggregate in concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 121, 104057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, C. Effect of particle size and thermal activation on the coal gangue based geopolymer. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 267, 124657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, I.G. The calcium silicate hydrates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.E.; Provis, J.L.; Proffen, T.; Riley, D.P.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Density functional modeling of the local structure of kaolinite subjected to thermal dehydroxylation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 4988–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhuang, R.L.; Muhammad, F.; Yu, L.; Shiau, Y.C.; Li, D.W. Solidification/stabilization of chromite ore processing residue using alkali-activated composite cementitious materials. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitos, M.; Badogiannis, E.G.; Tsivilis, S.G.; Perraki, M. Pozzolanic activity of thermally and mechanically treated kaolins of hydrothermal origin. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 116-117, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptáček, P.; Soukal, F.; Opravil, T.; Havlica, J.; Brandstetr, J. The kinetic analysis of the thermal decomposition of kaolin by DTG technique. Powder Technol. 2011, 208, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.J.; Peng, S.C.; Zhou, C.C. Synthesis of Calcium Silicate Hydrate from Coal Gangue for Cr(VI) and Cu(II) Removal from Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2021, 26, 6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.M.; Han, S.; Liu, Y.C.; Quan, S.C. On experimental study of activation coal gangue-Portland cement by microwave technology. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 838-841, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Nied, D.; L‘Hôpital, E.; Achiedo, G.; Dauzères, A. Magnesium and calcium silicate hydrates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 77, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nied, D.; Enemark-Rasmussen, K.; L‘Hopital, E.; Skibsted, J.; Lothenbach, B. Properties of magnesium silicate hydrates (M-S-H). Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.X.; Dong, J.L.; Yu, L.H.; Xu, C.j.; Jiao, X.K.; Wang, M.Y. Effect of Activated Coal Gangue in North China on the Compressive Strength and Hydration Process of Cement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.Y.; Zheng, Q.; Maboudian, R.; Monteiro, P.J.M.; Li, S.F. Electron energy loss spectroscopy of nanoscale local structures in calcium silicate hydrate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2025, 192, 107840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.Y.; Zhou, J.H.; Su, Q.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.C.; Wang, Q.; Bian, H.G.; Dong, F.X. Hydration kinetics for alkaline activation of slag from color variation data. Molecules 2021, 26, 3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapeluszna, E.; Kotwica, L.; Rozycka, A.; Golek, L. Incorporation of Al in C-A-S-H gels with various Ca/Si and Al/Si ratio: Microstructural and structural characteristics with DTA/TG, XRD, FTIR and TEM analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Redondo, E.; Yamada, K.; López-Arbeloa, I.; Manzano, H. Cs retention and diffusion in C-S-H at different Ca/Si ratios. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 140, 106294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.L.; Wang, H.L.; Li, H.; Xue, H.J.; Wei, L.S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Li, Q.F.; Dong, H.W. Comparison of performance, hydration behavior, and environmental benefits of coal gangue cementitious materials prepared by wet and dry grinding methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 471, 140665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.W.; Li, Z.J.; Yang, B.H.; Hu, Z.Y.; Hu, Z.H.; Liu, J.P.; Zhang, Y.N.; Nehdi, M.L. Spontaneous combustion coal gangue-based composite cement: Compressive performance and environmental benefits under grinding kinetics control. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.B.; Yang, C.Q.; Li, K.F.; Qu, F.; Yan, C.Y.; Wu, Z.R. Toward understanding the activation and hydration mechanisms of composite activated coal gangue geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 125999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | SO3 | K2O | Na2O | MgO | CaO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CGA | 16.87 | 35.83 | 1.10 | 0.85 | 0.76 | 0.56 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.12 |
| CGB | 12.90 | 33.77 | 2.99 | 0.88 | 1.13 | 1.48 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 2.56 |
| CGC | 18.10 | 51.60 | 2.57 | 0.91 | 0.66 | 1.81 | 0.33 | 0.54 | 0.55 |
| Sample | Curing Time (Days) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C-S-H | 3 | 15.6 | 3.2 |
| 7 | 28.5 | 4.5 | |
| 28 | 45.8 | 5.7 | |
| M-S-H | 3 | 17.4 | 3.6 |
| 7 | 30.8 | 4.8 | |
| 28 | 48.1 | 5.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S. Synthesis, Characterization, and Cementitious Activity of the Magnesium Silicate Hydrate and Calcium Silicate Hydrate from Coal Gangue. Molecules 2025, 30, 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081725
Zhang Q, Zhang X, Wang L, Zhang S. Synthesis, Characterization, and Cementitious Activity of the Magnesium Silicate Hydrate and Calcium Silicate Hydrate from Coal Gangue. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081725
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qing, Xianglin Zhang, Lulu Wang, and Shizhen Zhang. 2025. "Synthesis, Characterization, and Cementitious Activity of the Magnesium Silicate Hydrate and Calcium Silicate Hydrate from Coal Gangue" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081725
APA StyleZhang, Q., Zhang, X., Wang, L., & Zhang, S. (2025). Synthesis, Characterization, and Cementitious Activity of the Magnesium Silicate Hydrate and Calcium Silicate Hydrate from Coal Gangue. Molecules, 30(8), 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081725




