Highly Efficient Enrichment of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines in Meat Products Using the Magnetic Metal—Organic Framework Fe3O4@MOF-545-AMSA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
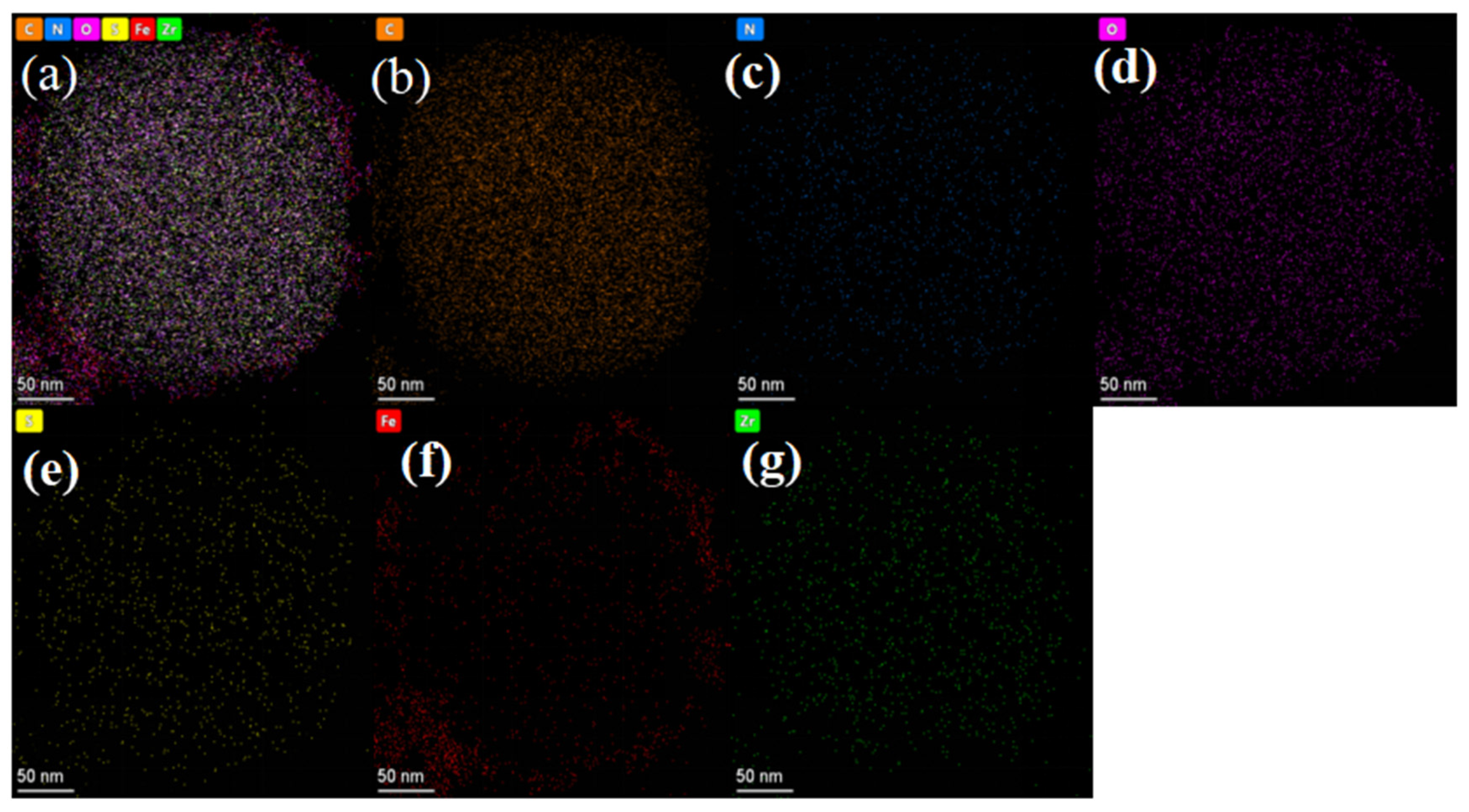
2.1. Fe3O4@MOF-545 and Fe3O4@MOF-545-AMSA Characterization
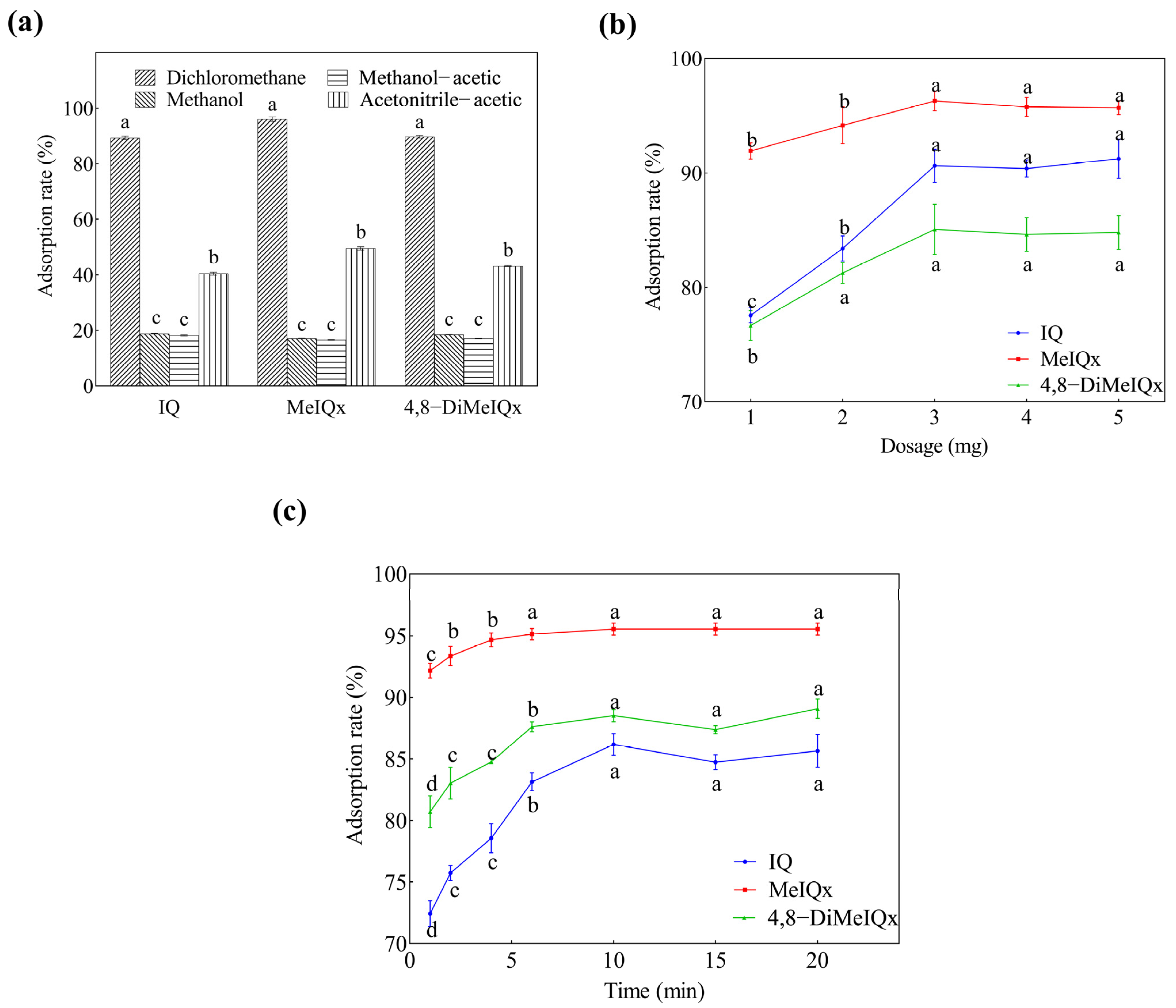
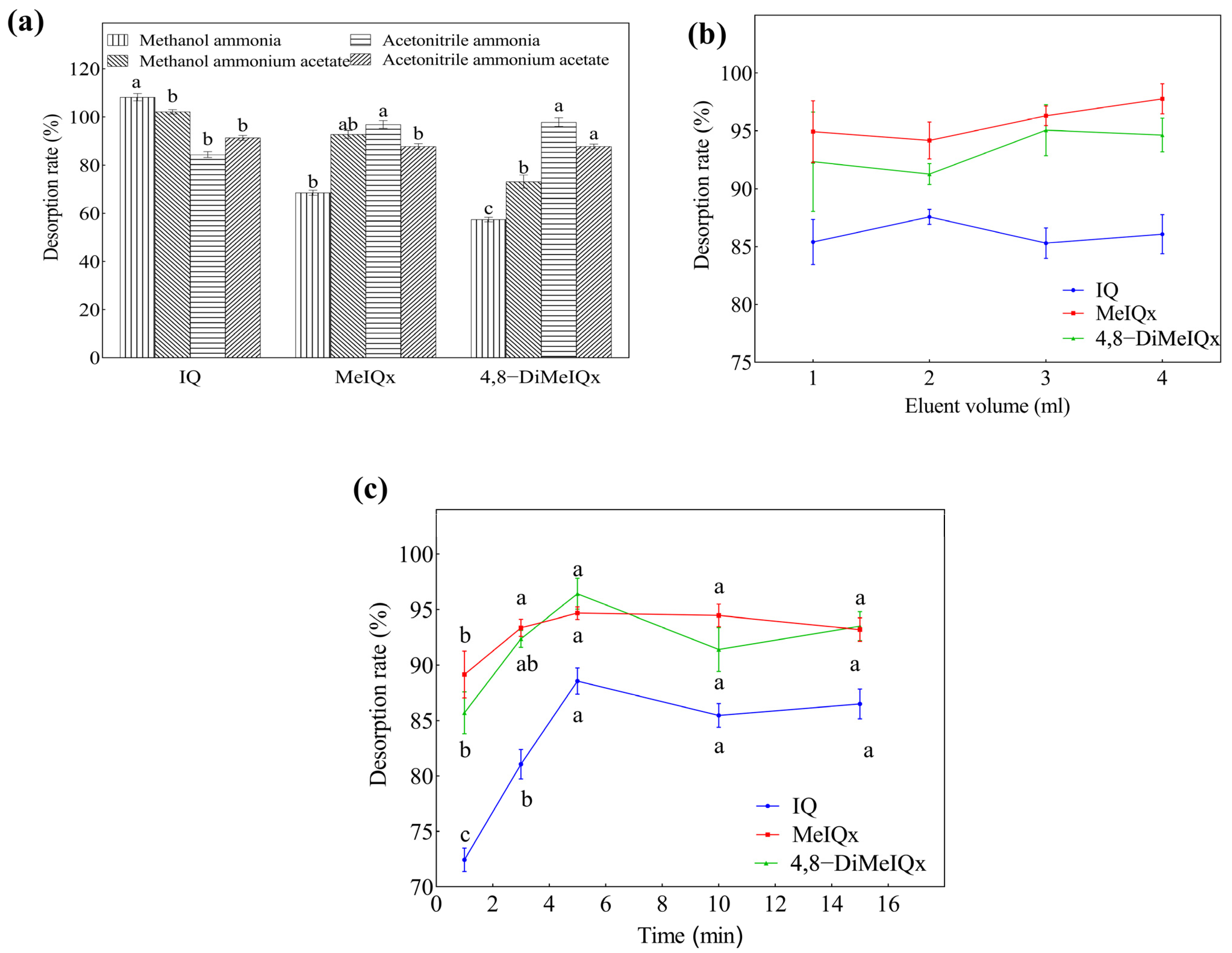
2.2. Optimization of the MSPE Conditions
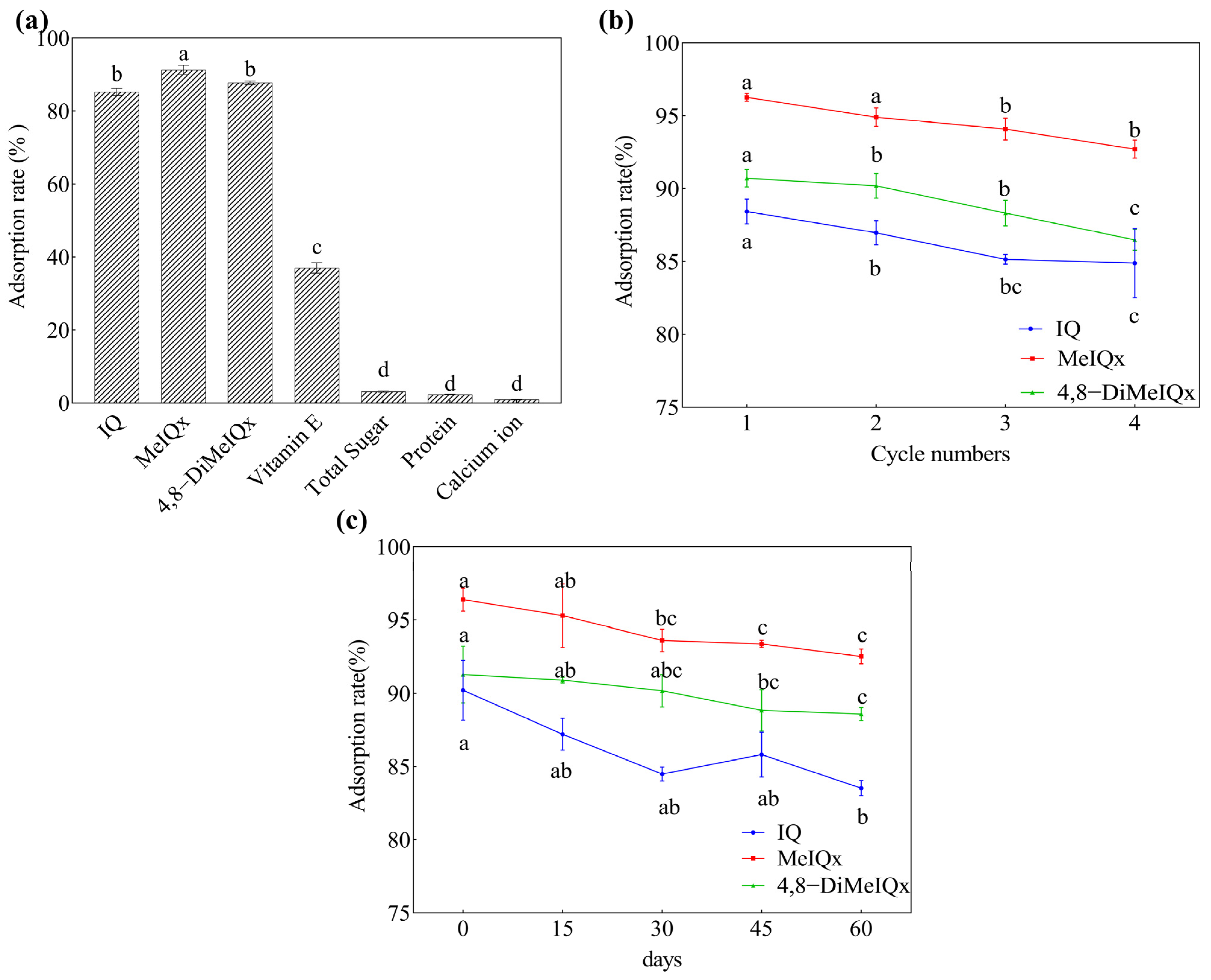
2.3. Selectivity, Reproducibility, and Stability of Fe3O4@MOF-545-AMSA
2.4. Method Validation
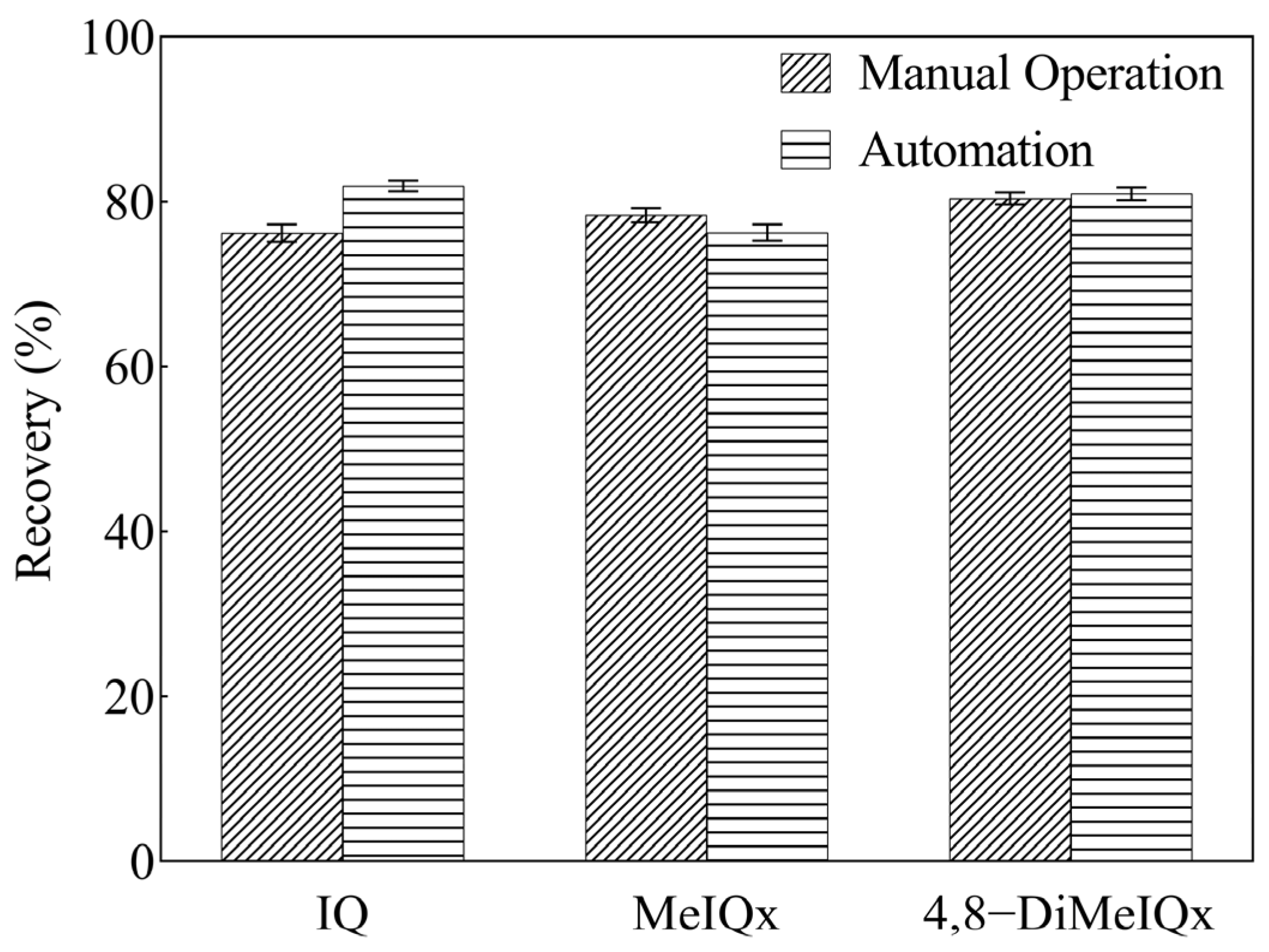
2.5. Comparison Between Fe3O4@MOF-545-AMSA and SPE
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Equipment
3.3. Synthesis of Fe3O4@MOF-545-AMSA
3.4. IQ, MeIQx and 4,8-DiMeIQx Separation Fe3O4@MOF-545-AMSA
3.5. MSPE Pretreatment
3.6. Analysis Using UPLC-MS/MS
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Su, Z.; Xi, L.; Li, G. Improved enrichment and analysis of heterocyclic aromatic amines in thermally processed Foods by magnetic solid phase extraction combined with HPLC-MS/MS. Food Control 2022, 137, 108929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, F.; Kamankesh, M.; Mohammadi, A. Heterocyclic aromatic amines in cooked food: A review on formation, health risk-toxicology and their analytical techniques. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, R.; Hidalgo, F.J. Formation of heterocyclic aromatic amines with the structure of aminoimidazoazarenes in food products. Food Chem. 2020, 313, 126128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Li, C. Effects of turmeric on reducing heterocyclic aromatic amines in Chinese tradition braised meat products and the underlying mechanism. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5575–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agim, Z.S.; Cannon, J.R. Dietary Factors in the Etiology of Parkinson’s Disease. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 672838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, L.; Grant, W.B. Observational and Ecological Studies of Dietary Advanced Glycation End Products in National Diets and Alzheimer’s Disease Incidence and Prevalence. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 45, 965–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawana, V.; Um, S.Y.; Rochet, J.; Turesky, R.J.; Shannahan, J.H.; Cannon, J.R. Neuromelanin Modulates Heterocyclic Aromatic Amine-Induced Dopaminergic Neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 173, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeda, T.; Foguth, R.M.; Llewellyn, E.; Cannon, J.R. PhIP exposure in rodents produces neuropathology potentially relevant to Alzheimer’s disease. Toxicology 2020, 437, 152436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janoszka, B.; Blaszczyk, U.; Warzecha, L.; Strózyk, M.; Damasiewicz-Bodzek, A.; Bodzek, D. Clean-up procedures for the analysis of heterocyclic aromatic amines (aminoazaarenes) from heat-treated meat samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 938, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinap, S.; Hasnol, N.D.S.; Sanny, M.; Jahurul, M.H.A. Effect of organic acid ingredients in marinades containing different types of sugar on the formation of heterocyclic amines in grilled chicken. Food Control 2018, 84, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeenehvand, S.; Toudehrousta, Z.; Kamankesh, M.; Mashayekh, M.; Tavakoli, H.R.; Mohammadi, A. Evaluation and application of microwave-assisted extraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of polar heterocyclic aromatic amines in hamburger patties. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruebo, M.; Fernandez-Pacheco, R.; Ibarra, M.R.; Santamaria, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today 2007, 2, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Pan, M.; Xie, X.; Liu, K.; Hong, L.; Wang, S. Synthesis of Magnetic Metal-Organic Frame Material and Its Application in Food Sample Preparation. Foods 2020, 9, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Mondol, M.M.H.; Jung, M.; Lee, G.H.; Jhung, S.H. MOFs with bridging or terminal hydroxo ligands: Applications in adsorption, catalysis, and functionalization. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 475, 214912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, X.; Kim, K.; Wang, S.; Liu, M. Exploration of coordination polymer as sorbent for flow injection solid-phase extraction on-line coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental materials. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1116, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, N.; Chen, T.; Ma, Y.; Li, Q. A green cyclodextrin metal-organic framework as solid-phase extraction medium for enrichment of sulfonamides before their HPLC determination. Microchem. J. 2018, 138, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Qin, N.; Pan, A.; Wu, X.; Peng, C.; Ke, F.; Iqbal, M.; Ramachandraiah, K.; Zhu, J. Magnetic Nanoparticles@Metal-Organic Framework Composites as Sustainable Environment Adsorbents. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 1454358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghayi-Anaraki, M.; Safarifard, V. Fe3O4@MOF Magnetic Nanocomposites: Synthesis and Applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 2020, 1916–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, F.; Cabello, C.P.; Frizzarin, R.M.; Estela, J.M.; Palomino, G.T.; Cerda, V. Magnetic solid-phase extraction using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and their derived carbons. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Dixit, R.; Sharma, S.; Dutta, S.; Solanki, K.; Sharma, R.K. Magnetic metal-organic framework composites: Structurally advanced catalytic materials for organic transformations. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 2153–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Qin, X.F.; Meng, Y.F.; Guo, Z.L.; Yang, L.X.; Ming, Y.F. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2013, 16, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.; Sai, N.; You, L.; Yin, X.; Ni, J. Zirconium-Porphyrin PCN-222: pH-responsive Controlled Anticancer Drug Oridonin. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 3249023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Shun, Y.C.; Zheng, X.; Phillips, D.L. Resonance Raman spectroscopy and density functional theory calculation study of photodecay dynamics of tetra(4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 10183–10190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Hasan, Z.; Khan, N.A.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive denitrogenation of model fuels with porous metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Effect of acidity and basicity of MOFs. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 129, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabbaghi, E.K.; Mokhtari, J.; Naimi-Jamal, M.R.; Khosravi, A. Zn-MOF: An efficient drug delivery platform for the encapsulation and releasing of Imatinib Mesylate. J. Porous Mater. 2021, 28, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Li, L.; You, S.; Liu, Y.; Cui, H.; Chen, K.; Zhang, S. A Solvent-Stable Zinc(II)-Gadolinium(III) Metal-Organic Framework Assembled with Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid: Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Magnetic Property. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2019, 29, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.D.; Hu, X.F.; Qin, S.L.; Chu, H.T.; Zhao, X.; Wang, B.B. L-Cysteine modified metal-organic framework as a chiral stationary phase for enantioseparation by capillary electrochromatography. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 6063–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaraguru, S.; Pavulraj, R.; Mohan, S. Influence of cobalt, nickel and copper-based metal-organic frameworks on the corrosion protection of mild steel. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish 2017, 95, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Huang, R.; Cao, Q.; Liu, N.; Li, P.; Sun, M.; Qin, H.; Wu, L. Magnetic metal-organic frameworks as adsorbents for the detection of azo pigments in food matrices. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrani, S.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K.; Ostovan, A.; Mansoorkhani, M.J.K.; Salehi, A. MOF-5(Zn)-Fe2O4 nanocomposite based magnetic solid-phase microextraction followed by HPLC-UV for efficient enrichment of colchicine in root of colchicium extracts and plasma samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1067, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chen, K.; Li, S.; He, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, N.; Du, M. Impedimetric aptasensor based on zirconium-cobalt metal-organic framework for detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Mikrochim. Acta 2022, 338, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatami, Z.; Jalali, F.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Shamsipur, M. Application of metal-organic framework as redox probe in an electrochemical aptasensor for sensitive detection of MUC1. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Ye, B. An efficient electrochemical glucose sensor based on porous nickel-based metal organic framework/carbon nanotubes composite (Ni-MOF/CNTs). J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 767, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Hou, H.M.; Zhang, G.L.; Hao, H.; Zhu, B.W.; Bi, J. Defective UiO-66/Cellulose Nanocomposite Aerogel for the Adsorption of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Huang, R.; Wang, P.; Li, G. Simultaneous Detection of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Acrylamide in Thermally Processed Foods by Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction Combined with HPLC-MS/MS Based on Cysteine-Functionalized Covalent Organic Frameworks. Food Chem. 2023, 424, 136349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Li, X. A Magnetic Carboxyl-Functionalized Covalent Organic Framework for the Efficient Enrichment of Foodborne Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines prior to UPLC-MS Analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 461, 140852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Analytes | Found (ng/g) | Spiked Level (μg/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 25 | 50 | ||||||
| Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | |||
| Dezhou braised chicken | IQ | 0.98 | 93.40 | 1.48 | 92.80 | 3.67 | 90.00 | 5.49 |
| MeIQx | N.D. | 91.70 | 1.03 | 88.70 | 4.35 | 93.20 | 2.72 | |
| 4,8-DiMeIQx | N.D. | 85.50 | 4.29 | 85.30 | 2.77 | 84.60 | 2.87 | |
| Spiced beef | IQ | 1.50 | 89.70 | 1.58 | 93.00 | 2.17 | 90.60 | 2.56 |
| MeIQx | N.D. | 99.30 | 2.13 | 93.40 | 1.44 | 99.10 | 3.87 | |
| 4,8-DiMeIQx | N.D. | 83.70 | 1.43 | 88.40 | 4.81 | 86.80 | 3.03 | |
| Fried pork | IQ | 1.66 | 93.70 | 3.04 | 98.60 | 2.11 | 87.90 | 3.21 |
| MeIQx | 0.58 | 103.80 | 1.49 | 95.10 | 3.07 | 111.00 | 3.85 | |
| 4,8-DiMeIQx | N.D. | 89.60 | 4.76 | 93.50 | 3.32 | 98.90 | 3.25 | |
| Crispy yellow croaker | IQ | 2.40 | 91.10 | 4.21 | 97.10 | 2.70 | 96.40 | 3.36 |
| MeIQx | N.D. | 92.20 | 1.87 | 84.80 | 4.24 | 107.30 | 4.26 | |
| 4,8-DiMeIQx | 0.44 | 87.30 | 2.41 | 88.50 | 4.33 | 89.40 | 3.08 | |
| Sample Name | Dezhou Braised Chicken | Spiced Beef | Fried Pork | Crispy Yellow Croaker |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IQ (ng/g) | 1.142 | 1.463 | 1.591 | 2.448 |
| MeIQx (ng/g) | N.D. | N.D. | 0.551 | N.D. |
| 4,8-DiMeIQx (ng/g) | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.482 |
| HAAs | Fe3O4@MOF-545-AMSA | Bond Elut PPL | QuEChERS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery | RSD | Recovery | RSD | Recovery | RSD | |
| IQ | 78.77 | 1.44 | 48.87 | 1.50 | 81.47 | 1.47 |
| MeIQx | 81.35 | 2.05 | 39.09 | 1.80 | 87.96 | 0.76 |
| 4,8-DiMeIQx | 80.16 | 1.39 | 57.47 | 1.93 | 79.42 | 1.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liang, S. Highly Efficient Enrichment of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines in Meat Products Using the Magnetic Metal—Organic Framework Fe3O4@MOF-545-AMSA. Molecules 2025, 30, 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081705
Wang Y, Liu Y, Chen Z, Liang S. Highly Efficient Enrichment of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines in Meat Products Using the Magnetic Metal—Organic Framework Fe3O4@MOF-545-AMSA. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081705
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yang, Ying Liu, Ziyan Chen, and Shan Liang. 2025. "Highly Efficient Enrichment of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines in Meat Products Using the Magnetic Metal—Organic Framework Fe3O4@MOF-545-AMSA" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081705
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, Y., Chen, Z., & Liang, S. (2025). Highly Efficient Enrichment of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines in Meat Products Using the Magnetic Metal—Organic Framework Fe3O4@MOF-545-AMSA. Molecules, 30(8), 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081705







