Unveiling the ESIPT Luminescence Mechanism of 4′-N,N-Diethylamino-3-Hydroxyflavone in Ionic Liquid: A Computational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of DEAHF Structure
2.2. Absorption and Fluorescence Spectra
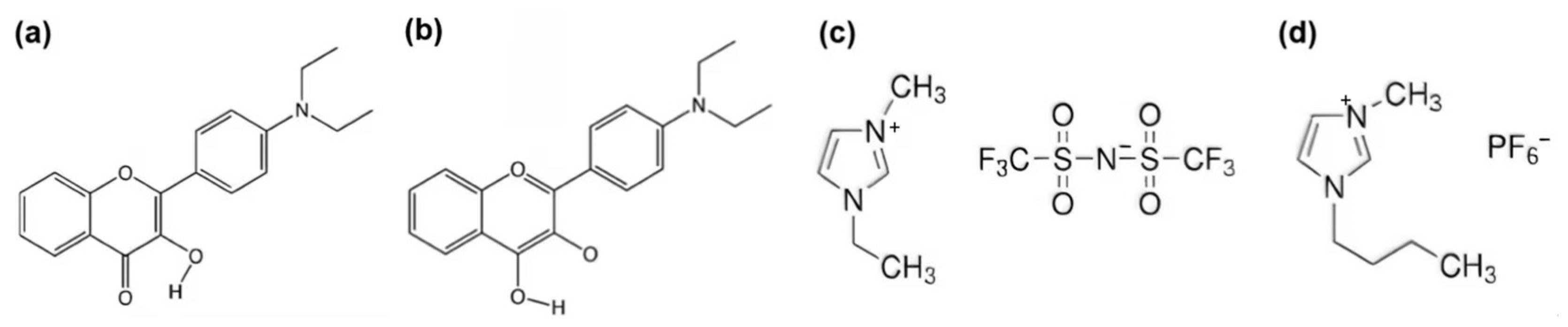
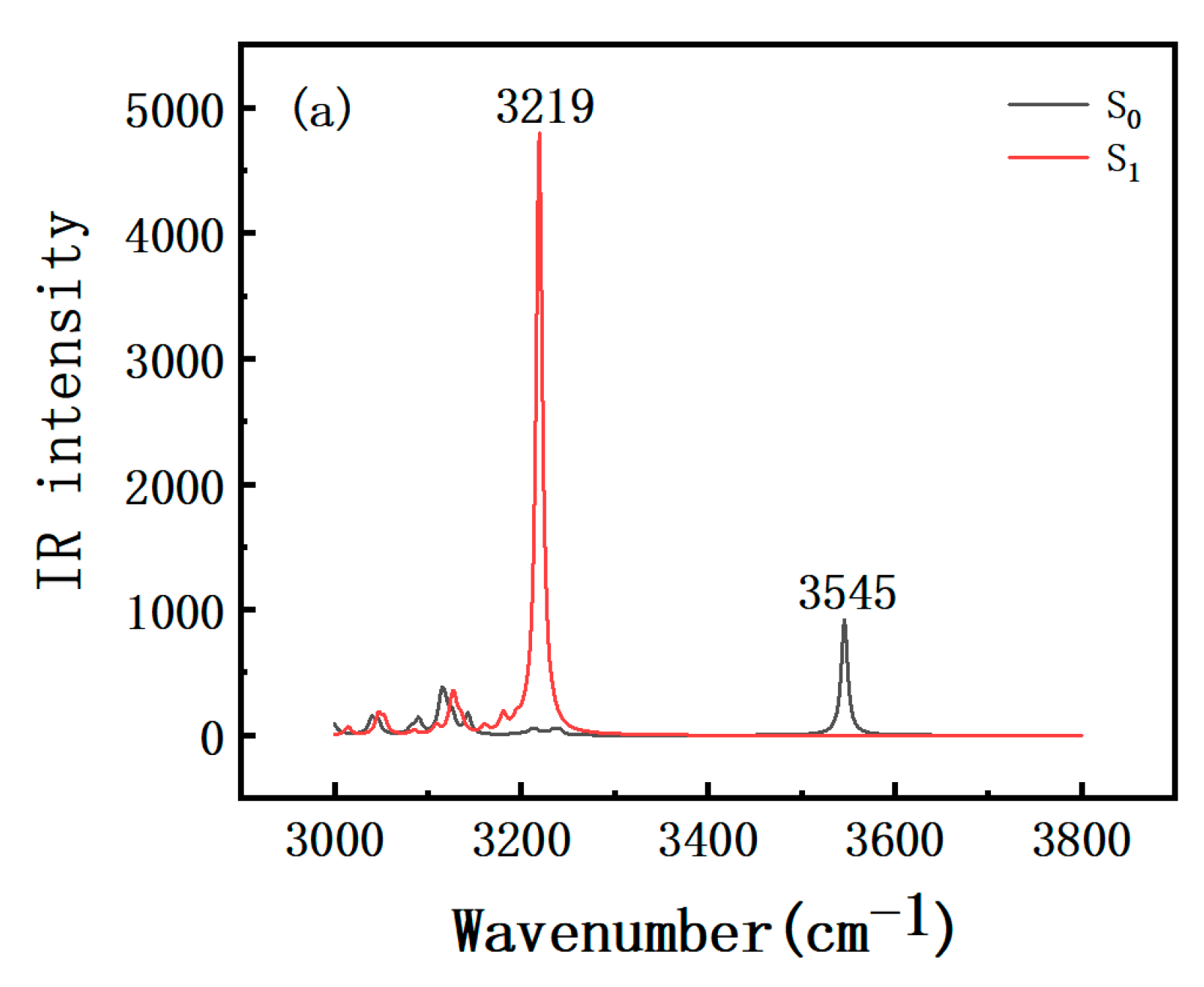
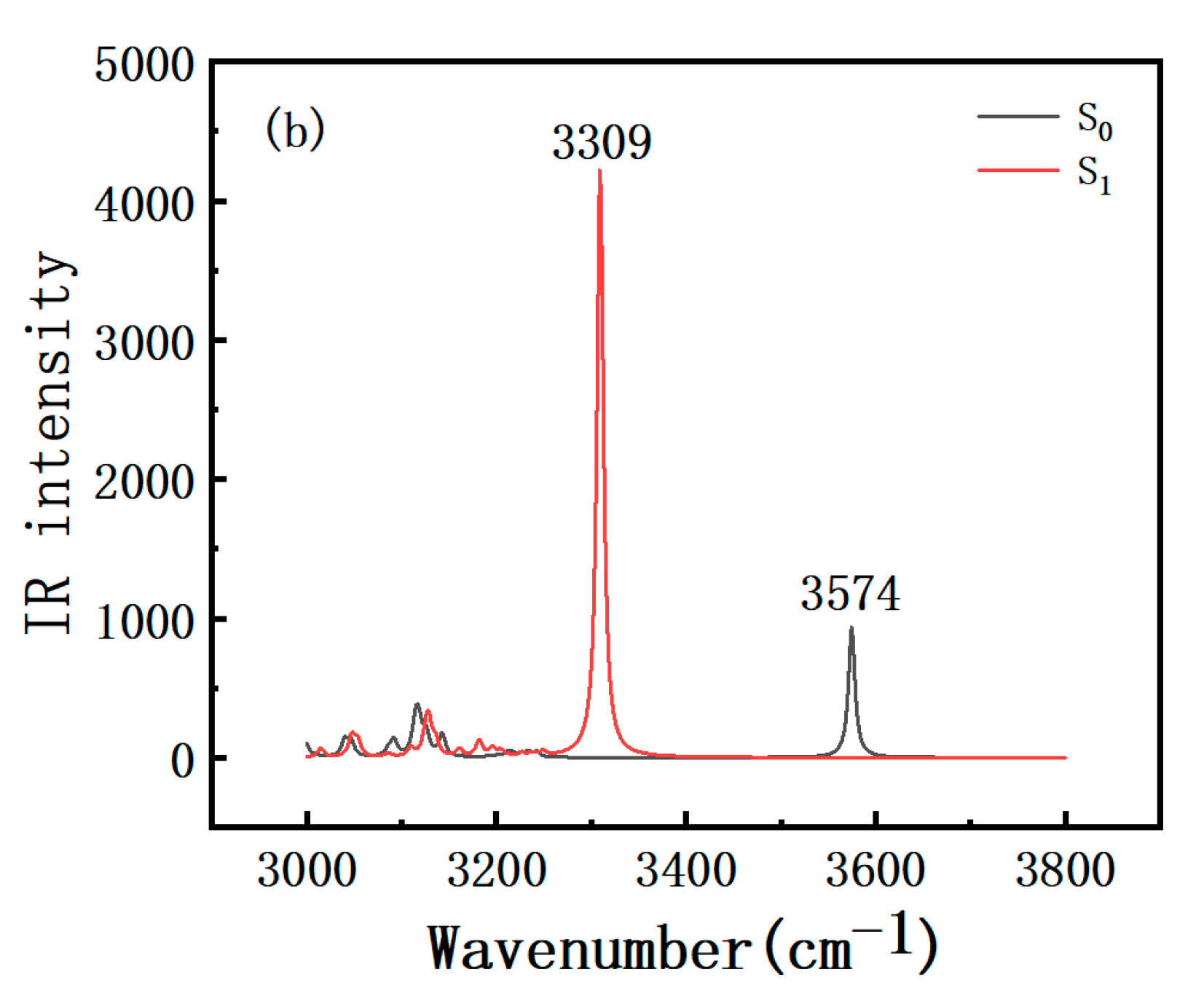
2.3. Infrared (IR) Spectra Analysis
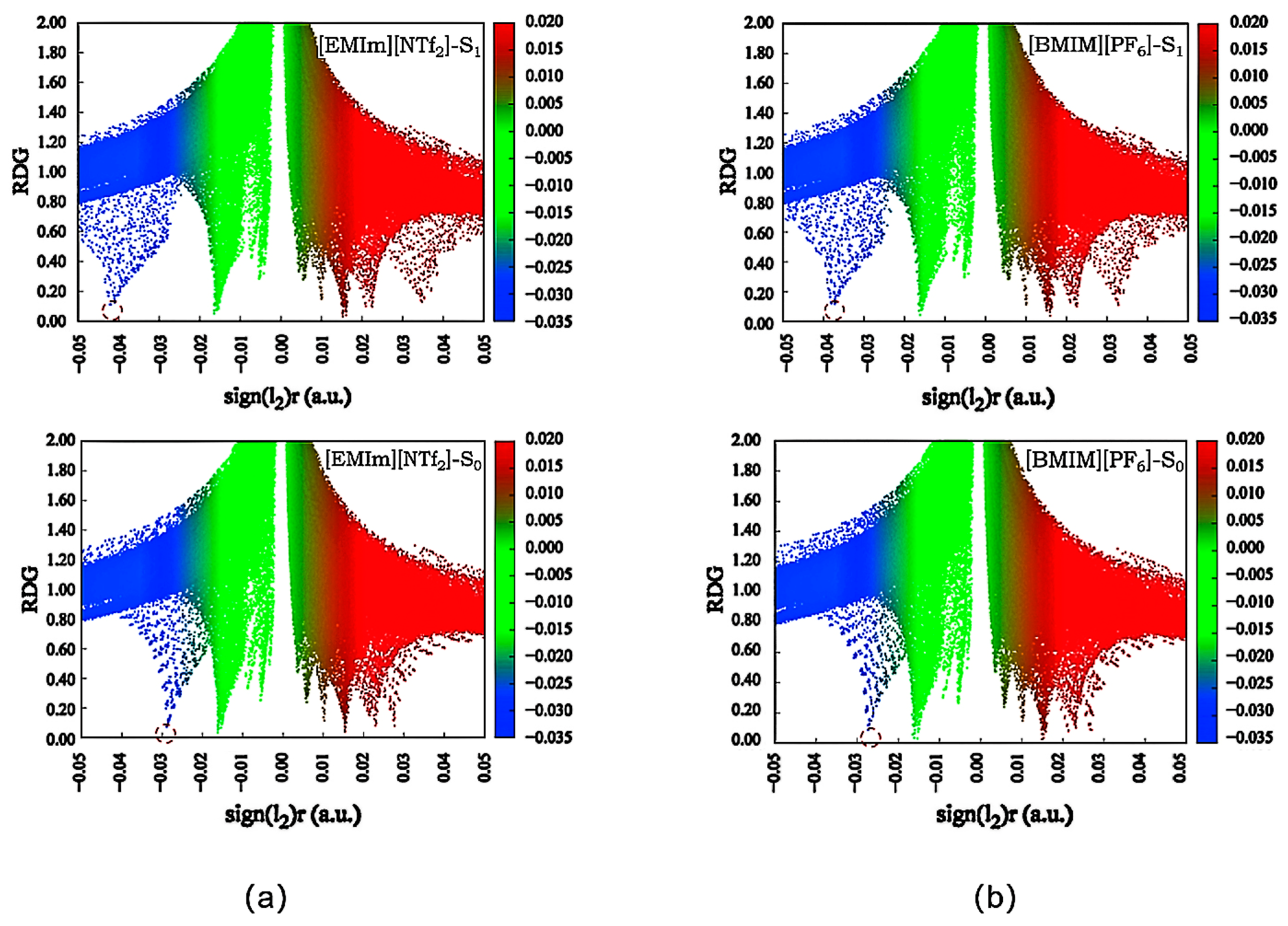
2.4. Non-Covalent Interaction (NCI) Analysis
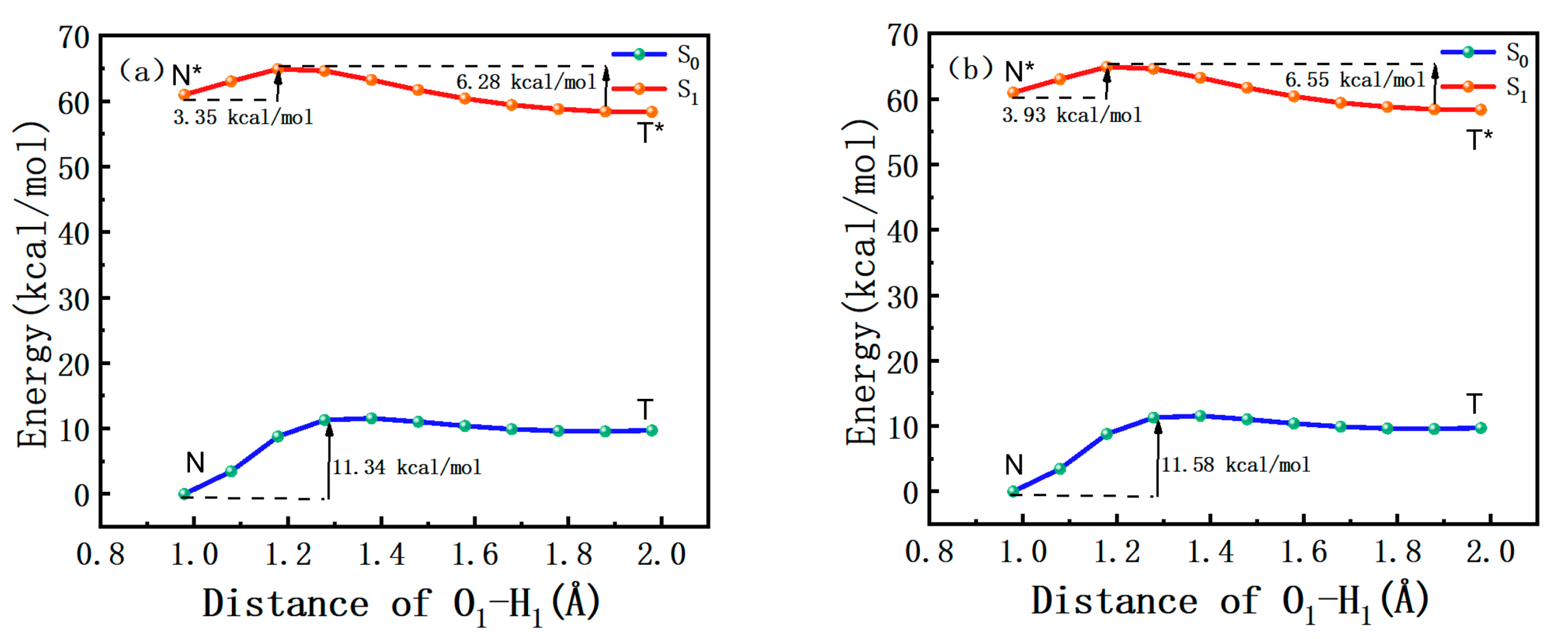
2.5. Potential Energy Curves
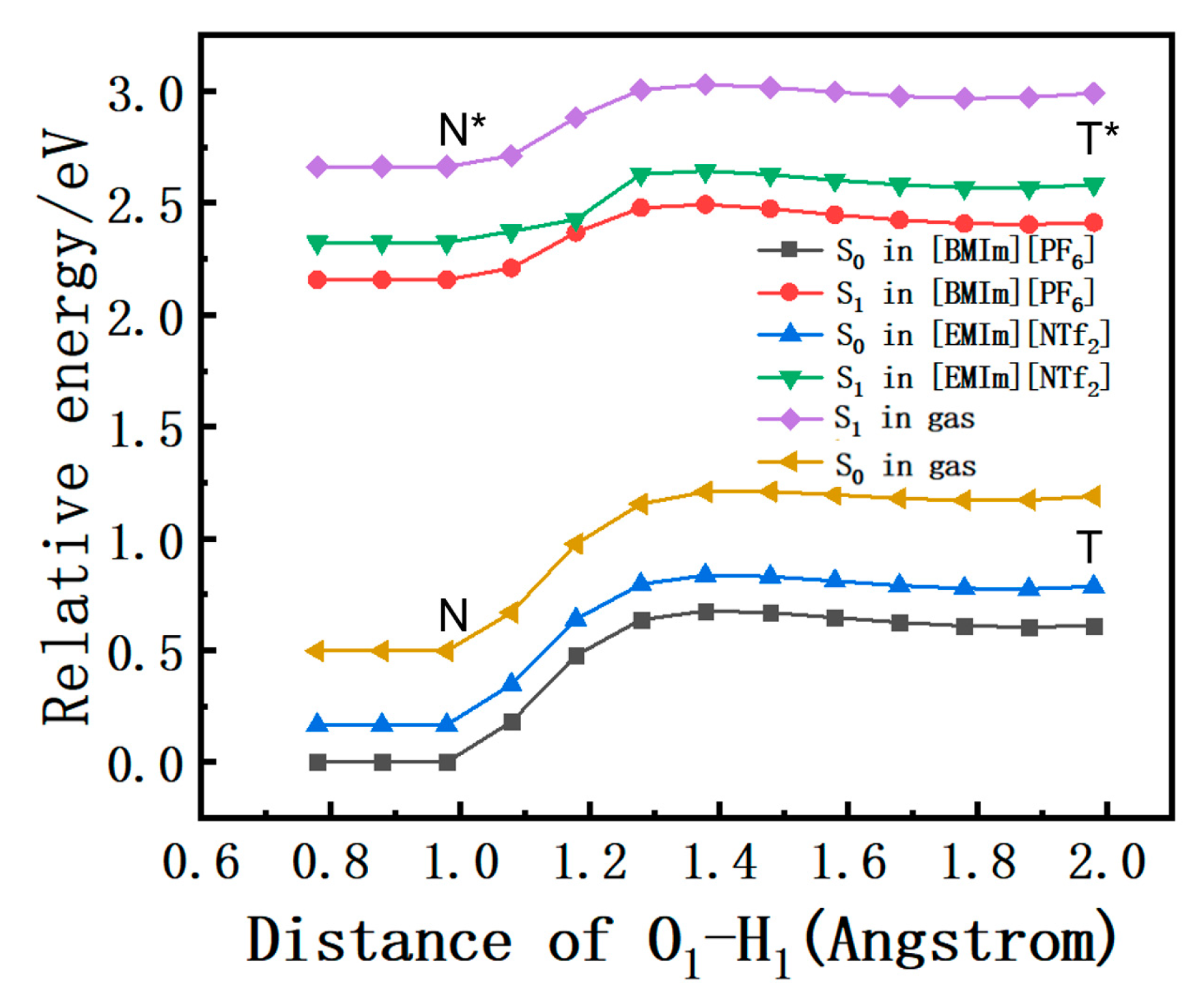
2.6. Free Energy
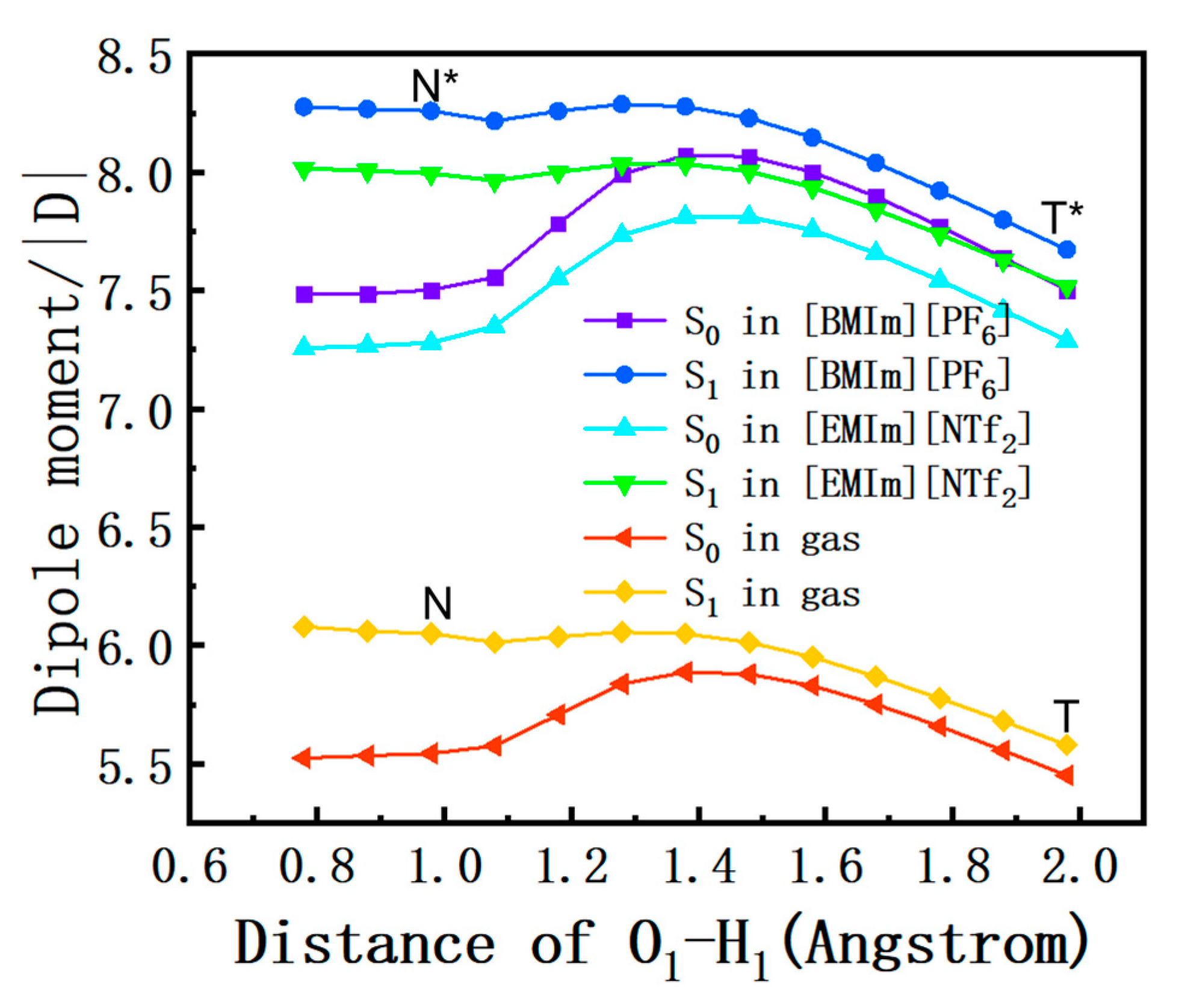
2.7. Dipole Moment
3. Computational Methods and Details
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Mu, H.; Sun, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, H. Modulating the ESIPT Mechanism and Luminescence Characteristics of Two Reversible Fluorescent Probes by Solvent Polarity: A Novel Perspective. Molecules 2024, 29, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamola, A.A.; Mittal, J.P. Solution Photochemistry of Thymine and Uracil. Science 1996, 154, 1560–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, P.T.; Huang, C.H.; Pu, S.C.; Cheng, Y.M.; Yu, W.S.; Yu, Y.C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.T. Tuning ExcitedState Charge/Proton Transfer Coupled Reaction via the Dipolar Functionality. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 6452–6454. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, P.T.; Pu, S.C.; Cheng, Y.M.; Yu, W.S.; Yu, Y.C.; Hung, F.T.; Hu, W.P. Femtosecond Dynamics on the Excited-State Proton/Charge Transfer Coupled Reaction in 4′-N,N-Diethylamino-3-hydroxy flavones. The Role of Dipolar Vectors in Constructing a Rational Mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 3777–3787. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.M.; Pu, S.C.; Yu, Y.C.; Chou, P.T.; Huang, C.H.; Chen, C.T.; Li, T.H.; Hu, W.P. Spectroscopy and Femtosecond Dynamics of 7-N,N-Diethylamino-3-hydroxyflavone. The Correlation of Dipole Moments among Various States to Rationalize the Excited-State Proton Transfer Reaction. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 11696–11706. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Yu, A.; Lu, R. Fluorescence quenching of coumarin 153 by hydroxyl-functionalized room temperature ionic liquid. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 165, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, C.; Ghosh, S.; Mandal, S.; Kuchlyan, J.; Kundu, N.; Sarkar, N. Exploring the Photophysics of Curcumin in Zwitterionic Micellar System: An Approach to Control ESIPT Process in the Presence of Room Temperature Ionic liquid (RTILs) and Anionic Surfactant. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 3669–3681. [Google Scholar]
- Miyabayashi, H.; Fujii, K.; Watanabe, T.; Matano, Y.; Endo, T.; Kimura, Y. Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer Reaction and Ground State Hole Dynamics of 4′-N,N-Dialkylamino-3-hydroxyflavone in Ionic liquid Studied by Transient Absorption Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 5373–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, A.; Sayed, M.; Kumar, A.; Pal, H. Atypical Energetic and Kinetic Course of Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer (ESIPT) in Room-Temperature Protic Ionic liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, Y.; Chakraborty, S.; Ghosh, S. Exploration and modulation of the photophysical properties of bromelain in a bioamphiphilic micellar system: Comparative studies on the basis of room temperature ionic liquids, anionic surfactants, drugs and salts. New J. Chem. 2024, 48, 12553–12564. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, M.; Vallet, P.; Teijeira, T.; Santiago-Alonso, A.; Amigo, A.; Tojo, E.; Varela, L.M.; Parajó, J.J.; Salgado, J. Effect of alkyl chain length on the thermal properties and toxicity of n-alkyl-ammonium nitrate ionic liquids (n = 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8) for energy applications. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2024, 9, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessz, D.; Bojtár, M.; Mester, D.; Szakács, Z.; Bitter, I.; Kállay, M.; Kubinyi, M. Hydrogen bonding effects on the fluorescence properties of 4′-diethylamino-3-hydroxyflavone in water and water-acetone mixtures. Spectrochim. Acta A 2018, 203, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, P.T.; Martinez, M.L.; Clements, J.H. Reversal of Excitation Behavior of Proton-Transfer vs Charge-Transfer by Dielectric Perturbation of Electronic Manifolds. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 2618–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinney, T.C.; Kelley, D.F. Proton transfer dynamics in substituted 3-hydroxyflavones: Solvent polarization effects. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalani, D.V.; Nutan, B.; Kumar, A.; Chandel, A.K.S. Bioavailability Enhancement Techniques for Poorly Aqueous Soluble Drugs and Therapeutics. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2045–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, S.; Fujii, K.; Sugihara, H.; Endo, T.; Kimura, Y. Anion Effect on the Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer of 4′-N,N-Diethylamino-3-hydroxyflavone in Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 128, 6549–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, S.M.; Perera, G.S.; Jiang, D.P.; Holler, R.A.; Zhang, D.M. Organothiols self-assembled onto gold: Evidence for deprotonation of the sulfur-bound hydrogen and charge transfer from thiolate. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 8793–8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Piao, Y.; Feng, X.; Yu, X.; Jin, X.; Zhao, G.J. Excited State Intramolecular Proton Transfer (ESIPT) Luminescence Mechanism for 4-N,N-diethylamino-3-hydroxyflavone in Propylene Carbonate, Acetonitrile and the Mixed Solvents. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2020, 224, 1386–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Batuta, S.; Das, S.; Begum, N.A.; Mandal, D. Proton Transfer Dynamics of 4′-N,N-Dimethylamino-3-hydroxyflavone Observed in Hydrogen-Bonding Solvents and Aqueous Micelles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 5650–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Suda, K.; Terazima, M.T. Excited State Intramolecular Proton Transfer Reaction of 4′-N,N-Diethylamino-3-hydroxyflavone and Solvation Dynamics in Room Temperature Ionic liquid Studied by Optical Kerr Gate Fluorescence Measurement. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 11847–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Han, J.H.; Li, Y.; Sun, C.F.; Su, X.; Shi, Y.; Yin, H. Theoretical Study on the Relationship Between the Position of the Substituent and the ESIPT Fluorescence Characteristic of HPIP. Chin. Phys. B 2020, 29, 178–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakovskaya, Y.V.; Tokarev, K.L.; Izmalkova, E.S.; Kuznetsov, V.V. High-frequency hydrogen-bond stretching vibrations as indicators of the character of molecular aggregation in solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 416, 126530. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras-García, J.; Johnson, E.R.; Keinan, S.; Chaudret, R.; Piquemal, J.P.; Beratan, D.N.; Yang, W. NCIPLOT: A Program for Plotting Non-covalent Interaction Regions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 625–632. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.R.; Keinan, S.; Mori-Sánchez, P.; Contreras-García, J.; Cohen, A.J.; Yang, W. Revealing Noncovalent Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 18, 6498–6506. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Sanville, E.; Henkelman, G. A Grid-based Bader Analysis Algorithm Without Lattice Bias. J. Phys. Condens. Mat. 2009, 21, 184–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Via-Nadall, M.; Rodríguez-Mayorga, M.; Matito, E. Salient signature of van der Waals interactions. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 050501. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A Multifunctional Wavefunction Analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar]
- Guevara-Vela, J.M.; Gallegos, M.; Valentín-Rodríguez, M.A.; Costales, A.; Rocha-Rinza, T.; Pendás, Á.M. On the Relationship between Hydrogen Bond Strength and the Formation Energy in Resonance-Assisted Hydrogen Bonds. Molecules 2021, 26, 4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushmarinov, I.S.; Lyssenko, K.A.; Yu, M. Antipin Atomic energy in the ‘Atoms in Molecules’ theoryand its use for solving chemical problems. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2009, 78, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.J. A DFT insight into structure, NBO, NCI, QTAIM, vibrational, and NLO properties of cationic amino acid ionic liquid [Pro-H]+BF4−. Struct. Chem. 2024, 35, 471–483. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, C.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Wu, J. Hunting ionic liquids with large electrochemical potential windows. AIChE J. 2019, 65, 804–810. [Google Scholar]
- Hayaki, S.; Kimura, Y.; Sato, H. Ab Initio Study on an Excited-State Intramolecular Proton-Transfer Reaction in Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 6759–6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izairi, R.; Kamberaj, H. Comparison Study of Polar and Nonpolar Contributions to Solvation Free Energy. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 2539–2553. [Google Scholar]
- Geethanjali, H.S.; Nagaraja, D.; Melavanki, R.M. Estimation of Dipole Moments and Quantum Yield of 5-chloro-2-methoxyphenyl Boronic Acid in Different Solvents Environment. J. Fluoresc. 2015, 25, 745–753. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16; Revision B.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, A.; Horn, H.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully Optimized Contracted Gaussian-basis Sets for Atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Yanai, T.; Tew, D.P.; Handy, N.C. A New Hybrid Exchange-correlation Functional Using the Coulomb-attenuating Method (CAM-B3LYP). Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 393, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional Exchange-energy Approximation with Correct Asymptotic Behavior. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, J.D.; Head-Gordon, M. Long-range Corrected Hybrid Density Functionals with Damped Atom–atom Dispersion Corrections. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 6615–6620. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density—Functional Thermochemistry. III. The Role of Exact Exchange. J. Phys. Chem. B 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, C.; Barone, V. Exchange Functionals with Improved Long-range Behavior and Adiabatic Connection Methods Without Adjustable Parameters: The mPW and mPW1PW Models. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 108, 664–675. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, N.M.; Deglmann, P.; Pliego, J.R. CMIRS Solvation Model for Methanol: Parametrization, Testing, and Comparison with SMD, SM8, and COSMO-RS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 12660–12668. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernales, V.S.; Marenich, A.V.; Contreras, R.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Quantum Mechanical Continuum Solvation Models for Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 9122–9129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weber, I.; Tsuge, M.; Sundararajan, P.; Baba, M.; Sakurai, H.; Lee, Y.P. Infrared and Laser-Induced Fluorescence Spectra of Sumanene Isolated in Solid para-Hydrogen. J. Phys. Chem. A 2022, 126, 5283–5293. [Google Scholar]
| N | T | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | S1 | S0 | S1 | ||
| DEAHF in [EMIm][NTf2] | O1-H1 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.81 | 1.95 |
| O2-H1 | 1.98 | 1.80 | 1.00 | 0.98 | |
| δ(O1-H1⋯O2) | 119.87 | 126.37 | 125.03 | 120.16 | |
| DEAHF in [BMIm][PF6] | O1-H1 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 1.86 | 1.97 |
| O2-H1 | 2.00 | 1.84 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |
| δ(O1-H1⋯O2) | 119.03 | 124.68 | 123.14 | 119.16 | |
| Structures | mPW1PW91 | CAM-B3LYP | WB97XD | PBEPBE | B1B95 | B3PW91 | Exp. a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [EMIm][NTf2] | absorption | N | 407 | 364 | 342 | 400 | 400 | 426 | ~411 |
| T | 501 | 457 | 449 | 513 | 503 | 522 | - | ||
| fluorescence | N | 460 | 443 | 476 | 469 | 464 | 488 | ~530 | |
| T | 604 | 591 | 593 | 600 | 596 | 612 | ~589 | ||
| [BMIm][PF6] | absorption | N | 407 | 353 | 341 | 408 | 402 | 427 | ~411 |
| T | 502 | 453 | 449 | 519 | 502 | 519 | - | ||
| fluorescence | N | 470 | 450 | 481 | 471 | 466 | 490 | ~524 | |
| T | 602 | 589 | 589 | 596 | 591 | 608 | ~578 |
| [EMIM][NTf2] | N | T |
|---|---|---|
| S0 | 7.28 | 7.29 |
| S1 | 7.99 | 7.51 |
| △1 | 0.71 | 0.22 |
| [BMIM][PF6] | N | T |
| S0 | 7.50 | 7.50 |
| S1 | 8.26 | 7.67 |
| △2 | 0.76 | 0.17 |
| △1 − △2 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Li, Q.; Guo, M.; Yan, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, G.; Yin, H.; Shi, Y. Unveiling the ESIPT Luminescence Mechanism of 4′-N,N-Diethylamino-3-Hydroxyflavone in Ionic Liquid: A Computational Study. Molecules 2025, 30, 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061381
Yang J, Li Q, Guo M, Yan L, Zhu L, Zhao J, Hu G, Yin H, Shi Y. Unveiling the ESIPT Luminescence Mechanism of 4′-N,N-Diethylamino-3-Hydroxyflavone in Ionic Liquid: A Computational Study. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061381
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jin, Qi Li, Meilin Guo, Lu Yan, Lixia Zhu, Jing Zhao, Guangxiong Hu, Hang Yin, and Ying Shi. 2025. "Unveiling the ESIPT Luminescence Mechanism of 4′-N,N-Diethylamino-3-Hydroxyflavone in Ionic Liquid: A Computational Study" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061381
APA StyleYang, J., Li, Q., Guo, M., Yan, L., Zhu, L., Zhao, J., Hu, G., Yin, H., & Shi, Y. (2025). Unveiling the ESIPT Luminescence Mechanism of 4′-N,N-Diethylamino-3-Hydroxyflavone in Ionic Liquid: A Computational Study. Molecules, 30(6), 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061381






