Structural Insights into the Nonmutagenicity of 2-Haloacetophenone
Abstract
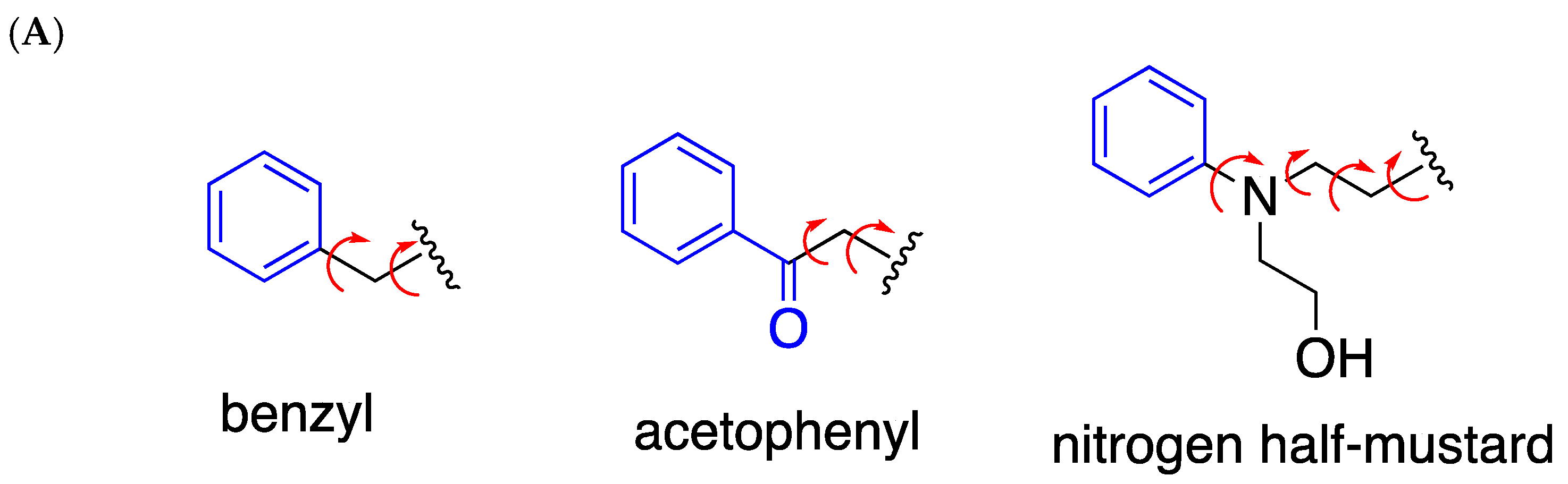
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
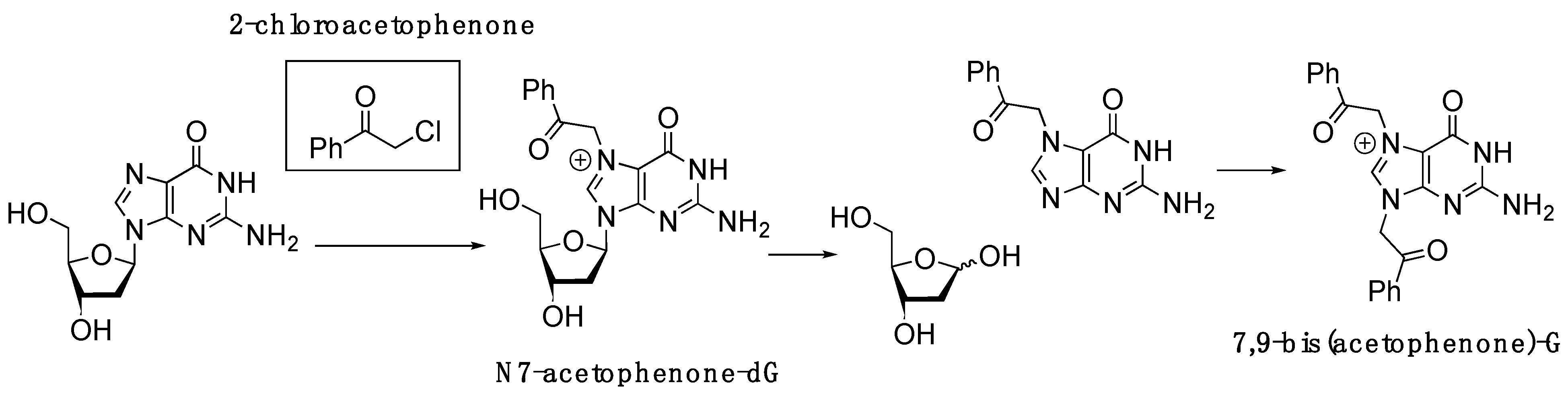
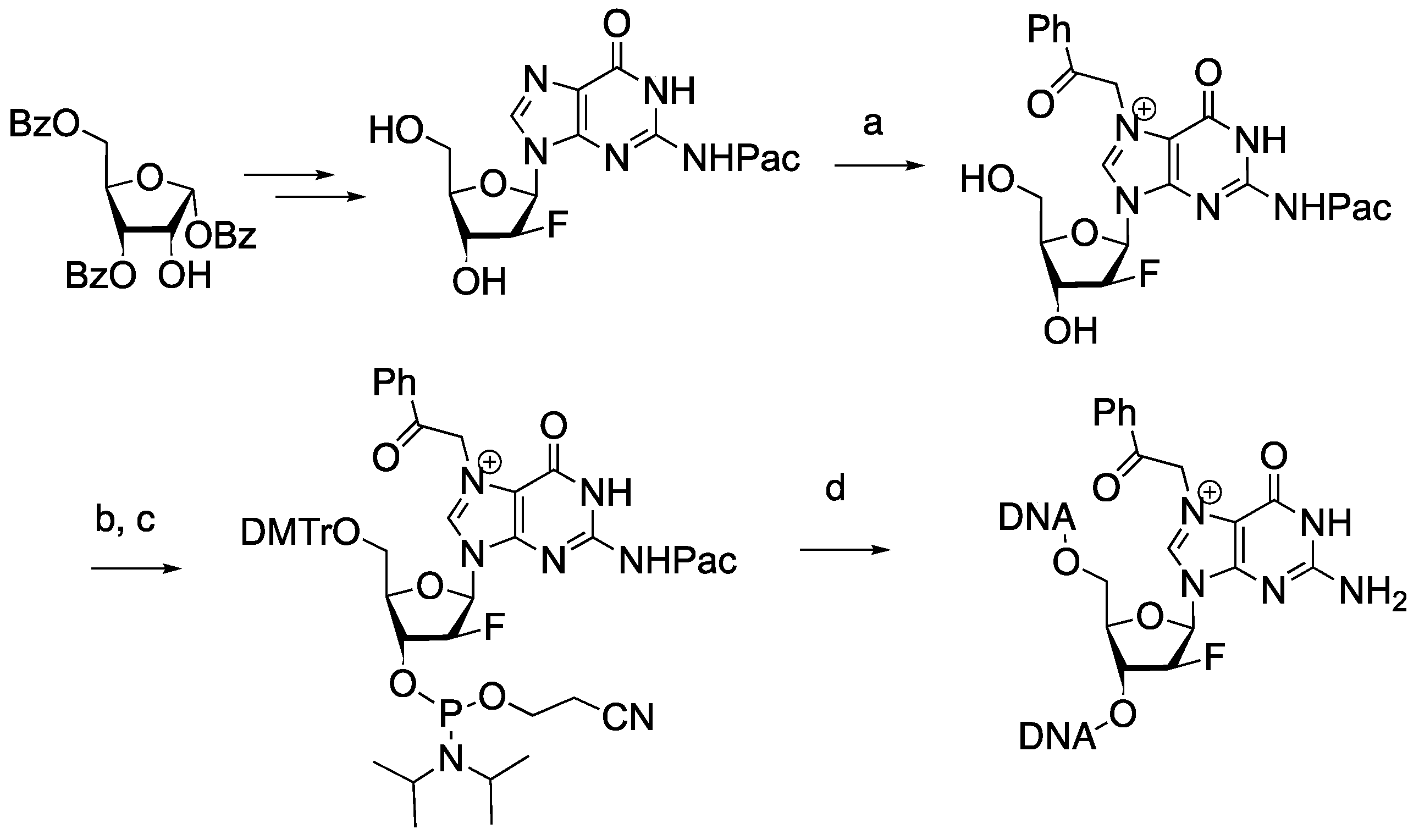
2.1. Synthesis of 2′-Deoxy-2′-F-N7-Acetophenone-dG-Containing Oligonucleotide
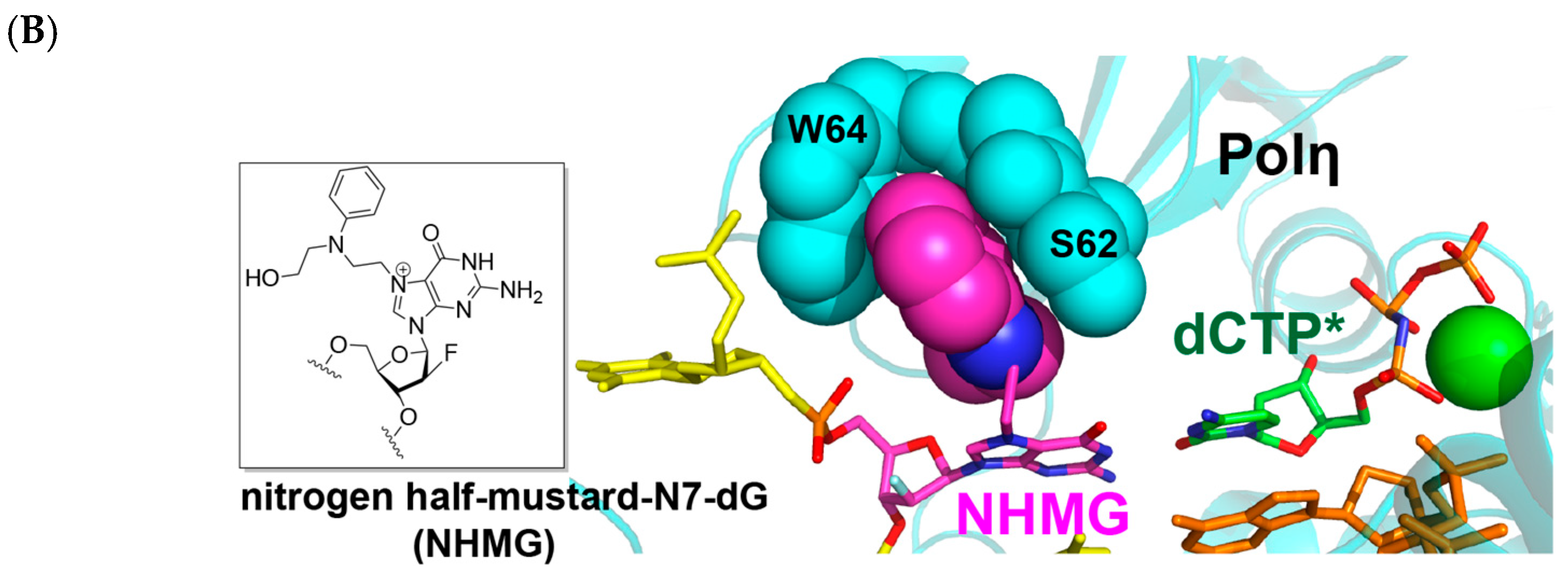
2.2. Polη Bypasses N7AcPhG Lesion with Low Efficiency
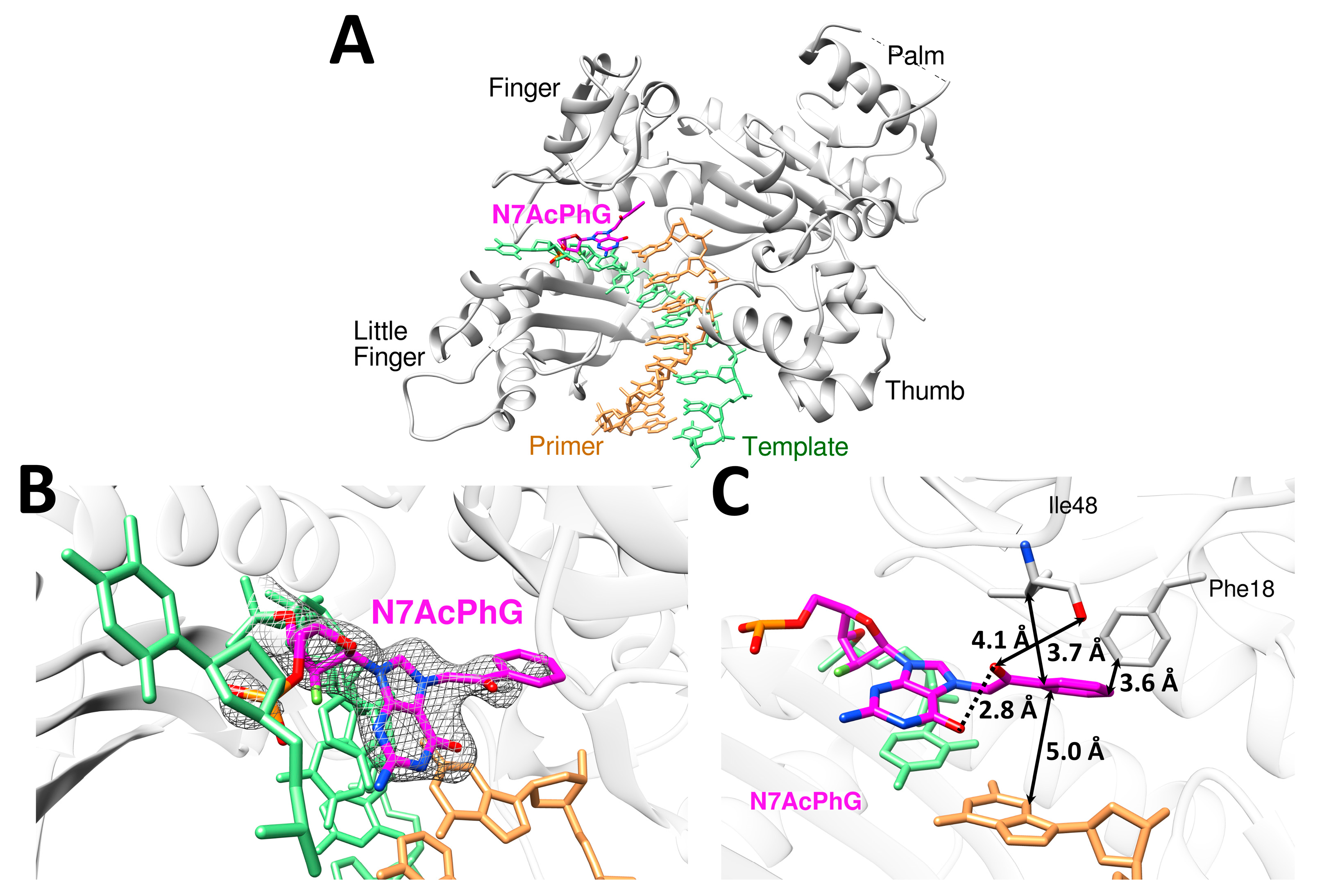
2.3. N7AcPhG at the Templating Position Preferentially Adopts a Syn Base Conformation
3. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Povirk, L.F.; Shuker, D.E. DNA damage and mutagenesis induced by nitrogen mustards. Mutat. Res. 1994, 318, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koag, M.C.; Kou, Y.; Ouzon-Shubeita, H.; Lee, S. Transition-state destabilization reveals how human DNA polymerase beta proceeds across the chemically unstable lesion N7-methylguanine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8755–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lin, Y.C.; Li, L.; Makarova, A.V.; Burgers, P.M.; Stone, M.P.; Lloyd, R.S. Molecular basis of aflatoxin-induced mutagenesis-role of the aflatoxin B1-formamidopyrimidine adduct. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, A.K.; Lloyd, R.S. Mechanisms underlying aflatoxin-associated mutagenesis—Implications in carcinogenesis. DNA Repair 2019, 77, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, E.A.; Iyer, R.S.; Stone, M.P.; Harris, T.M.; Essigmann, J.M. Mutational properties of the primary aflatoxin B1-DNA adduct. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidwell, R.D.; Wills, B.K. Tear Gas and Pepper Spray Toxicity. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Olajos, E.J.; Salem, H. Riot control agents: Pharmacology, toxicology, biochemistry and chemistry. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2001, 21, 355–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Toxicology, P. NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of 2-Chloroacetophenone (CAS No. 532-27-4) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Inhalation Studies). Natl. Toxicol. Program Tech. Rep. Ser. 1990, 379, 1–191. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, K.S.; Nooner, T.; Dutta, S. Biologically relevant chemical reactions of N7-alkylguanine residues in DNA. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 839–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Koag, M.C.; Lee, S. N7 methylation alters hydrogen-bonding patterns of guanine in duplex DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14067–14070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Verdine, G.L. Atomic substitution reveals the structural basis for substrate adenine recognition and removal by adenine DNA glycosylase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18497–18502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummat, A.; Rechkoblit, O.; Jain, R.; Roy Choudhury, J.; Johnson, R.E.; Silverstein, T.D.; Buku, A.; Lone, S.; Prakash, L.; Prakash, S.; et al. Structural basis for cisplatin DNA damage tolerance by human polymerase eta during cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, G.W.; Ober, M.; Carell, T.; Beese, L.S. Error-prone replication of oxidatively damaged DNA by a high-fidelity DNA polymerase. Nature 2004, 431, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masutani, C.; Kusumoto, R.; Yamada, A.; Dohmae, N.; Yokoi, M.; Yuasa, M.; Araki, M.; Iwai, S.; Takio, K.; Hanaoka, F. The XPV (xeroderma pigmentosum variant) gene encodes human DNA polymerase eta. Nature 1999, 399, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W. An overview of Y-Family DNA polymerases and a case study of human DNA polymerase eta. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 2793–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koag, M.C.; Jung, H.; Kou, Y.; Lee, S. Bypass of the Major Alkylative DNA Lesion by Human DNA Polymerase eta. Molecules 2019, 24, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Rayala, N.K.; Lee, S. Effects of N7-Alkylguanine Conformation and Metal Cofactors on the Translesion Synthesis by Human DNA Polymerase eta. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Rayala, N.K.; Lee, S. Translesion synthesis of the major nitrogen mustard-induced DNA lesion by human DNA polymerase eta. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 4543–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenthal, B.D.; Beard, W.A.; Wilson, S.H. Structures of dNTP intermediate states during DNA polymerase active site assembly. Structure 2012, 20, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biertumpfel, C.; Zhao, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Ramon-Maiques, S.; Gregory, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Masutani, C.; Lehmann, A.R.; Hanaoka, F.; Yang, W. Structure and mechanism of human DNA polymerase eta. Nature 2010, 465, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Lee, S. Promutagenic bypass of 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoadenine by translesion synthesis DNA polymerase Dpo4. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 2859–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 1997, 276, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vagin, A.; Teplyakov, A. Molecular replacement with MOLREP. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebschner, D.; Afonine, P.V.; Baker, M.L.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Croll, T.I.; Hintze, B.; Hung, L.W.; Jain, S.; McCoy, A.J.; et al. Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: Recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2019, 75, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B.; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. MolProbity: All-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzon-Shubeita, H.; Vilas, C.K.; Lee, S. Structural insights into the promutagenic bypass of the major cisplatin-induced DNA lesion. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Template:dNTP | Km (μM) | kcat (10−3 s−1) | kcat/Km (10−3 s−1μM−1) | f a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dG:dCTP | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 120.6 ± 6.0 | 45.6 | 1 |
| dG:dTTP | 159.3 ± 2.7 | 74.8 ± 0.9 | 0.47 | 1.0 × 10−2 |
| N7mG:dCTP [16] | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 56.4 ± 2.7 | 13.2 | 0.29 |
| N7mG:dTTP | 52.5 ± 1.7 | 49.3 ± 0.1 | 0.94 | 2.1 × 10−2 |
| N7BnG:dCTP [17] | 10.2 ± 2.3 | 20.6 ± 3.6 | 2.07 | 4.5 × 10−2 |
| N7BnG:dTTP | 51.7 ± 5.3 | 11.5 ± 0.3 | 0.22 | 4.8 × 10−3 |
| N7AcPhG:dCTP | 83.8 ± 6.5 | 5.7 ± 0.3 | 0.068 | 1.5 × 10−3 |
| N7AcPhG:dTTP | 551.0 ± 9.7 | 3.6 ± 0.3 | 0.0065 | 1.4 × 10−4 |
| PDB CODE | Polη: N7-AcPhG (7LCD) |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | |
| space group | P61 |
| Cell Constants | |
| a (Å) | 98.785 |
| b | 98.785 |
| c | 81.876 |
| α (°) | 90.00 |
| β | 90.00 |
| γ | 120.00 |
| resolution (Å) a | 50–1.98 (2.05–1.98) |
| Rmerge b (%) | 0.057 (0.427) |
| <I/σ> | 24.2 (2.5) |
| CC1/2 (2.05–1.98) | 0.755 |
| completeness (%) | 99.9 (100.0) |
| redundancy | 6.1 (5.9) |
| Refinement | |
| Rwork c/Rfree d (%) | 18.2/21.2 |
| unique reflections | 31,450 |
| Mean B Factor (Å2) | |
| protein | 32.39 |
| ligand | 40.55 |
| solvent | 36.56 |
| Ramachandran Plot | |
| most favored (%) | 97.9 |
| add. allowed (%) | 1.4 |
| RMSD | |
| bond lengths (Å) | 0.008 |
| bond angles (degree) | 0.968 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, H.; Rayala, N.K.; Pal, R.; Lee, S. Structural Insights into the Nonmutagenicity of 2-Haloacetophenone. Molecules 2025, 30, 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061264
Jung H, Rayala NK, Pal R, Lee S. Structural Insights into the Nonmutagenicity of 2-Haloacetophenone. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061264
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Hunmin, Naveen Kumar Rayala, Ritesh Pal, and Seongmin Lee. 2025. "Structural Insights into the Nonmutagenicity of 2-Haloacetophenone" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061264
APA StyleJung, H., Rayala, N. K., Pal, R., & Lee, S. (2025). Structural Insights into the Nonmutagenicity of 2-Haloacetophenone. Molecules, 30(6), 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061264







