Response to Salt Stress of the Halotolerant Filamentous Fungus Penicillium chrysogenum P13
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
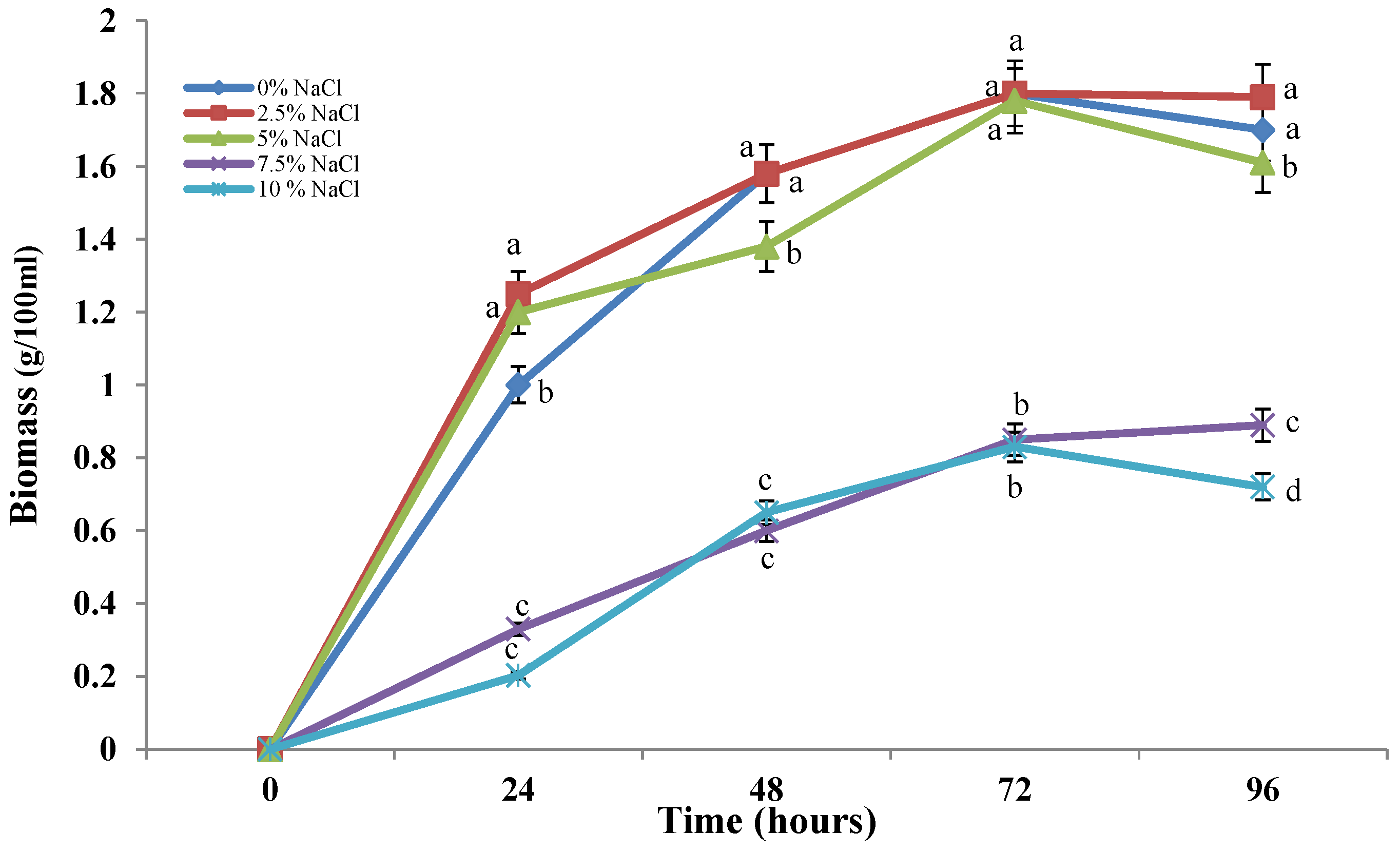
2.1. Effect of Different Salt Concentrations on Growth and Glucose Consumption of the Halotolerant Fungal Strain
2.2. Determination of the Oxidatively Damaged Proteins Level by the Amount of Carbonyl Groups
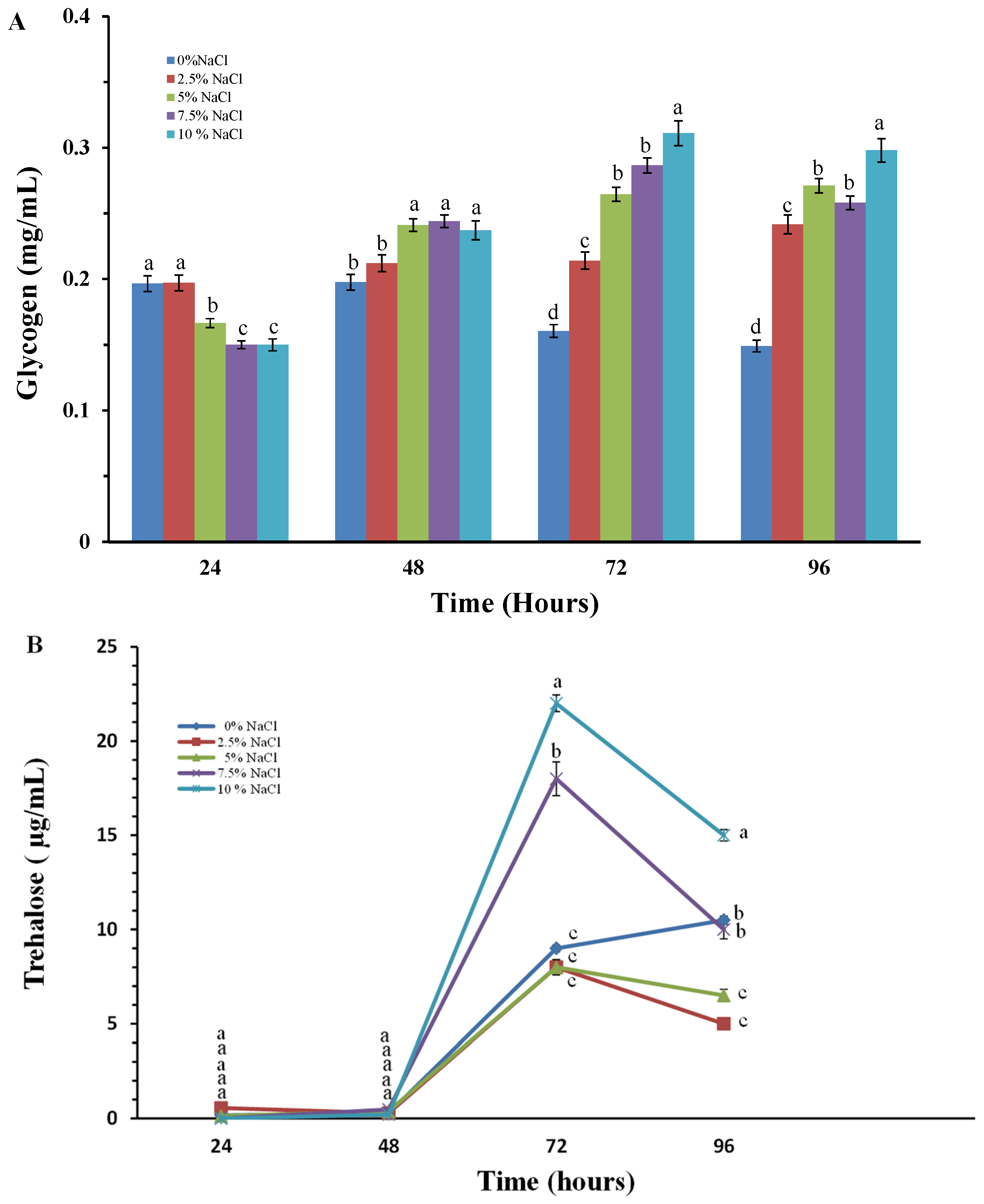
2.3. Study of Changes in the Level of Reserve Carbohydrates–Glycogen and Trehalose
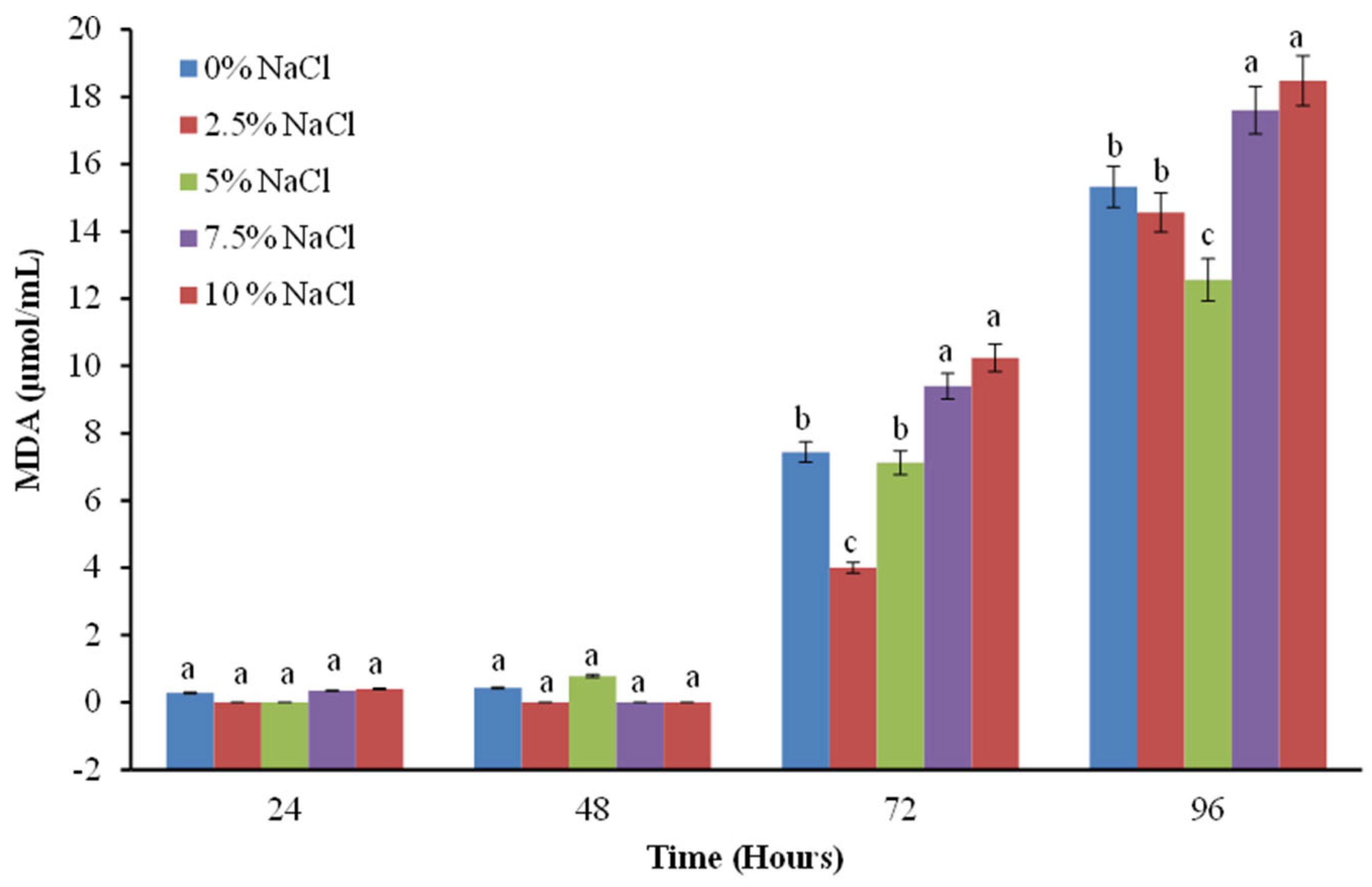
2.4. Study of Lipid Peroxidation as a Marker for the Degree of Membrane Integrity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Material
4.2. Molecular Genetic Identification of the Species Level of the Isolates
4.3. Nutrient Media and Culture Conditions
4.3.1. Solid Nutrient Media
4.3.2. Liquid Culture Media
4.4. Analytical Methods
4.4.1. Morphological and Physiological Measurements
4.4.2. Cell-Free Extract Preparation
4.5. Enzyme Activities Determination
4.6. Other Determinations
4.6.1. Soluble Reducing Sugars Determination
4.6.2. Total Protein Determination
4.6.3. Determination of the Content of Oxidatively Modified Proteins
4.6.4. Determination of the Content of Reserve Carbohydrates
4.6.5. Determination of the Lipid Peroxidation Level
4.7. Statistical Evaluation of the Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seckbach, J.; Oren, A. Polyextremophiles: Life Under Multiple Forms of Stress; Stan-Lotter, H., Ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Bowers, K.J.; Mesbah, N.M.; Wiegel, J. Biodiversity of poly-extremophilic Bacteria: Does combining the extremes of high salt, alkaline pH, and elevated temperature approach a physico-chemical boundary for life? Saline Syst. 2009, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Borgne, S.; Paniagua, D.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Biodegradation of organic pollutants by halophilic bacteria and Archaea. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 15, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventosa, A.; Nieto, J.J.; Oren, A. Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 504–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Zalar, P. Extremely halotolerant and halophilic fungi inhabit brine in solar salterns around the globe. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 52, 170–179. [Google Scholar]
- Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Plemenitaš, A.; Oren, A. Strategies of adaptation of microorganisms of the three domains of life to high salt concentrations. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plemenitaš, A.; Konte, T.; Gostinčar, C.; Cimerman, N.G. Transport systems in halophilic fungi. In Yeast Membrane Transport; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 307–325. [Google Scholar]
- Bremer, E.; Krämer, R. Responses of microorganisms to osmotic stress. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanek, L. Proteomic responses to environmentally induced oxidative stress. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1867–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovič, U. Role of oxidative stress in the extremely salt-tolerant yeast Hortaea werneckii. FEMS Yeast Res. 2006, 6, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yovchevska, L.; Gocheva, Y.; Stoyancheva, G.; Miteva-Staleva, J.; Dishliyska, V.; Abrashev, R.; Stamenova, T.; Angelova, M.; Krumova, E. Halophilic Fungi—Features and Potential Applications. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onofri, S.; de Vera, J.P.; Zucconi, L.; Selbmann, L.; Scalzi, G.; Venkateswaran, K.J.; Horneck, G. Survival of Antarctic cryptoendolithic fungi in simulated Martian conditions on board the International Space Station. Astrobiology 2015, 15, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacelli, C.; Selbmann, L.; Zucconi, L.; Coleine, C.; de Vera, J.P.; Rabbow, E.; Onofri, S. Responses of the black fungus Cryomyces antarcticus to simulated Mars and space conditions on rock analogs. Astrobiology 2019, 19, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.K.; Roy, I. Trehalose and protein stability. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2010, 59, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotayo, T.I.; Akinyemi, G.S.; Omololu, P.A.; Ajayi, B.O.; Akindahunsi, A.A.; Rocha, J.B.T.; Kade, I.J. Possible involvement of membrane lipids peroxidation and oxidation of catalytically essential thiols of the cerebral transmembrane sodium pump as component mechanisms of iron-mediated oxidative stress-linked dysfunction of the pump’s activity. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamakhi, L.; Zibaee, A.; Karimi-Malati, A.; Hoda, H. Simultaneous effects of thermal stress and fungal infection on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant system of rice-striped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis Walker (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Biol. Rhythm. Res. 2020, 51, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingfield, L.K.; Jitprasitporn, N.; Che-Alee, N. Isolation and characterization of halophilic and halotolerant fungi from man-made solar salterns in Pattani Province, Thailand. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazareth, S.; Gonsalves, V.; Nayak, S. A first record of obligate halophilic Aspergilli from the Dead Sea. Indian J. Microbiol. 2012, 52, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.N.; Kaur, T.; Kour, D.; Rana, K.L.; Yadav, N.; Rastegari, A.A.; Saxena, A.K. Saline microbiome: Biodiversity, ecological significance, and potential role in amelioration of salt stress. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 283–309. [Google Scholar]
- Kopytina, N. Fungi of the Black Sea reservoir: Directions and perspectives of research. Mar. Biol. J. 2019, 4, 15–33. [Google Scholar]
- Haldar, S.; Nazareth, S.W. Diversity of fungi from mangrove sediments of Goa, India, obtained by metagenomic analysis using Illumina sequencing. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Raihan, M.H.; Masud, A.C.; Rahman, K.; Nowroz, F.; Rahman, M.; Fujita, M. Regulation of reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under salinity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.A.; Jiménez, A.; Mullineaux, P.; Sevilia, F. Tolerance of pea (Pisum sativum L.) to long-term salt stress is associated with induction of antioxidant defenses. Plant Cell Environ. 2000, 23, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feofilova, E.P.; Tereshina, V.M.; Khokhlova, N.S.; Memorskaya, A.S. Different mechanisms of the biochemical adaptation of mycelial fungi to temperature stress: Changes in the cytosol carbohydrate composition. Microbiology 2000, 69, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, S.; Saharan, R.K.; Mahmood, A.; Sharma, S.C. Effect of reserve carbohydrates on oxidative stress in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae Y6210. Curr. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 3, 633–636. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Dai, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, F.; Tang, X.; Feng, W.; Zhang, J. Molecular and functional analysis of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase genes enhancing salt tolerance in Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. Molecules 2023, 28, 5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Y.; Bakpa, E.P. Trehalose alleviates salt tolerance by improving photosynthetic performance and maintaining mineral ion homeostasis in tomato plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 974507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumova, E.; Andreyinski, N.; Abrashev, R.; Stoyancheva, G.; Kostadinova, N.; Miteva-Staleva, J.; Angelova, M. Comparison of the oxidative stress response of two aspergillus fumigatus strains isolated from polluted soils against combined heavy metal toxicity. Geomicrobiol. J. 2021, 38, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumova, E.; Koeva, E.; Stoitsova, S.; Paunova-Krasteva, T.; Stoyancheva, G.; Angelova, M. Cell response of Antarctic strain Penicillium griseofulvum against low temperature stress. Pol. Pol. Res. 2022, 43, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Gómez, I.; Valdés-Muñoz, G.; Moreno-Ulloa, A.; Pérez-Llano, Y.; Moreno-Perlín, T.; Silva-Jiménez, H.; Batista-García, R.A. Surviving in the brine: A multi-omics approach for understanding the physiology of the halophile fungus Aspergillus sydowii saturated NaCl concentration. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 840408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostiňcar, C.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Overview of oxidative stress response genes in selected halophilic fungi. Genes 2018, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y. Material composition characteristics of Aspergillus cristatus under high salt stress through LC–MS Metabolomics. Molecules 2024, 29, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martínez, S.; Portillo-López, A.; López-Landavery, E.A. Response of the obligate halophile fungus Aspergillus loretoensis to stress salinity. J. Microbiol. Exp. 2023, 11, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Saad-Allah, K.M.; Ragab, G.A. Sulfur nanoparticles mediated improvement of salt tolerance in wheat relates to decreasing oxidative stress and regulating metabolic activity. PMBP 2020, 26, 2209–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakkammal, K.; Pandian, S.; Maharajan, T.; Antony Ceasar, S.; Sohn, S.I.; Ramesh, M. Humic acid regulates gene expression and activity of antioxidant enzymes to inhibit the salt-induced oxidative stress in finger millet. Cereal Res. Commun. 2024, 52, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyancheva, G.; Krumova, E.; Kostadinova, N.; Miteva-Staleva, J.; Grozdanov, P.; Ghaly, M.F.; Angelova, M. Biodiversity of contaminant fungi at different coloured materials in ancient Egypt Tombs and Mosques. Comptes Rendus De L’académie Bulg. Des. Sci. 2018, 71, 907–915. [Google Scholar]
- Angelova, M.; Genova, L.; Pashova, S.; Slokoska, L.; Dolashka, P. Effect of cultural conditions on the synthesis of superoxide dismutase by Humicola lutea 110. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1996, 82, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase: Improved assay and an assay applicable to polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, R.F.; Sizer, I.W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 195, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somogyi, M. Notes on sugar determination. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 195, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, H.J.; Faar, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, H.; Ishii, N. Effects of tocotrienols on life span and protein carbonylation in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2000, 55, B280–B285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A. A method for glycogen determination in whole yeast cells. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandercammen, A.; Francois, J.; Her, H. Characterization of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 182, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrou, J.L.; Teste, M.A.; François, J. Effects of various types of stress on the metabolism of reserve carbohydrates in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Genetic evidence for a stress-induced recycling of glycogen and trehalose. Microbiology 1997, 143, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yovchevska, L.; Miteva-Staleva, J.; Dishliyska, V.; Stoyancheva, G.; Gocheva, Y.; Abrashev, R.; Spasova, B.; Angelova, M.; Krumova, E. Response to Salt Stress of the Halotolerant Filamentous Fungus Penicillium chrysogenum P13. Molecules 2025, 30, 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061196
Yovchevska L, Miteva-Staleva J, Dishliyska V, Stoyancheva G, Gocheva Y, Abrashev R, Spasova B, Angelova M, Krumova E. Response to Salt Stress of the Halotolerant Filamentous Fungus Penicillium chrysogenum P13. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061196
Chicago/Turabian StyleYovchevska, Lyudmila, Jeny Miteva-Staleva, Vladislava Dishliyska, Galina Stoyancheva, Yana Gocheva, Radoslav Abrashev, Boryana Spasova, Maria Angelova, and Ekaterina Krumova. 2025. "Response to Salt Stress of the Halotolerant Filamentous Fungus Penicillium chrysogenum P13" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061196
APA StyleYovchevska, L., Miteva-Staleva, J., Dishliyska, V., Stoyancheva, G., Gocheva, Y., Abrashev, R., Spasova, B., Angelova, M., & Krumova, E. (2025). Response to Salt Stress of the Halotolerant Filamentous Fungus Penicillium chrysogenum P13. Molecules, 30(6), 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061196




