Multifaceted Approaches in Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-Mediated Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. EpCAM-Based CTC Enrichment
Integration of Other Biomarkers into EpCAM-Based CTC Enrichment
3. EpCAM-Independent Circulating Tumor Cell Enrichment Strategies
3.1. Negative Selection
3.2. Label-Free CTC Enrichment: A Challenger of Immune-Affinity-Based Methods
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joosse, S.A.; Beyer, B.; Gasch, C.; Nastały, P.; Kuske, A.; Isbarn, H.; Horst, L.J.; Hille, C.; Gorges, T.M.; Cayrefourcq, L.; et al. Tumor-Associated Release of Prostatic Cells into the Blood after Transrectal Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy in Patients with Histologically Confirmed Prostate Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Liquid Biopsy: From Discovery to Clinical Application. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 858–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Peeters, D.J.; Fehm, T.; Nolé, F.; Gisbert-Criado, R.; Mavroudis, D.; Grisanti, S.; Generali, D.; Garcia-Saenz, J.A.; Stebbing, J.; et al. Clinical validity of circulating tumour cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer: A pooled analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strati, A.; Zavridou, M.; Kallergi, G.; Politaki, E.; Kuske, A.; Gorges, T.M.; Riethdorf, S.; Joosse, S.A.; Koch, C.; Bohnen, A.-L.; et al. A Comprehensive Molecular Analysis of in Vivo Isolated EpCAM-Positive Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, D.J.; Pantel, K. Circulating tumor cells as liquid biopsy markers in cancer patients. Mol. Asp. Med. 2024, 96, 101258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, A.; Kraemer, A.; Sicking, A.; Watolla, M.; Rivandi, M.; Yang, L.; Warfsmann, J.; Polzer, B.M.; Friedl, T.W.P.; Meier-Stiegen, F.; et al. Comparative analysis of EpCAM high-expressing and low-expressing circulating tumour cells with regard to their clonal relationship and clinical value. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 1742–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Fatima, K.; Malik, F. Understanding the cell survival mechanism of anoikis-resistant cancer cells during different steps of metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2022, 39, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.; Luo, B.; Yu, P.; Qi, D.; Shangguan, W.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Ke, R.; et al. Polyphyllin VII induces CTC anoikis to inhibit lung cancer metastasis through EGFR pathway regulation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 5204–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Hissa, B.; Győrffy, B.; Jann, J.-C.; Yang, C.; Reissfelder, C.; Schölch, S. Characterization of Stem-like Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Cancer. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi-Wen, W.; Long-Long, L.; Ming, L.; Hao, L.; Kong-Wang, H. Stem cell-like circulating tumor cells indicate poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Arch. Med. Sci. 2022, 18, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, C.; Xie, M.; Zhu, C.; Shu, Y.; Tang, J.; Guan, X. Heterogeneity of CTC contributes to the organotropism of breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Wei, S.; Lv, X. Circulating tumor cells: From new biological insights to clinical practice. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakir, B.; Chiarella, A.M.; Pitarresi, J.R.; Rustgi, A.K. EMT, MET, Plasticity, and Tumor Metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, D.; Vialaret, J.; Hirtz, C.; Alix-Panabières, C. Surfaceome: A new era in the discovery of immune evasion mechanisms of circulating tumor cells. Mol. Oncol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amintas, S.; Bedel, A.; Moreau-Gaudry, F.; Boutin, J.; Buscail, L.; Merlio, J.-P.; Vendrely, V.; Dabernat, S.; Buscail, E. Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters: United We Stand Divided We Fall. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harouaka, R.A.; Nisic, M.; Zheng, S.Y. Circulating tumor cell enrichment based on physical properties. J. Lab Autom. 2013, 18, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyailo, M.E.; Tretyakova, M.S.; Denisov, E.V. Heterogeneity of Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer: Identifying Metastatic Seeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Jafferji, I.; Garza, M.; Melnikova, V.O.; Hasegawa, D.K.; Pethig, R.; Davis, D.W. ApoStream™, a new dielectrophoretic device for antibody independent isolation and recovery of viable cancer cells from blood. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 024133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.I.; Musso, N.; Romano, A.; Caruso, G.; Petralia, S.; Lanzanò, L.; Broggi, G.; Camarda, M. The Role of Dielectrophoresis for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cancers 2022, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Hou, Y. Mechanical properties of CTCs in patients with diagnosed ovarian cancer. J. Biomech. 2023, 160, 111831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Mezencev, R.; Kim, B.; Wang, L.; McDonald, J.; Sulchek, T. Cell stiffness is a biomarker of the metastatic potential of ovarian cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, I.; Morawetz, E.W.; Tschodu, D.; Käs, J.A.; Aktas, B. The Mechanical Fingerprint of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Xu, F.; Tian, J.; Gao, K.; Wan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; Chong, T. The prognostic value of circulating tumour cells (CTCs) and CTC white blood cell clusters in patients with renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.J.; Jana, J.A.; Kaehr, A.; Purcell, E.; Opdycke, T.; Paoletti, C.; Cooling, L.; Thamm, D.H.; Hayes, D.F.; Nagrath, S. Inertial focusing of circulating tumor cells in whole blood at high flow rates using the microfluidic CTCKey™ device for CTC enrichment. Lab A Chip 2021, 21, 3559–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Veiga, T.; Schneegans, S.; Pantel, K.; Wikman, H. Circulating tumor cell-blood cell crosstalk: Biology and clinical relevance. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boya, M.; Chu, C.-H.; Liu, R.; Ozkaya-Ahmadov, T.; Sarioglu, A.F. Circulating Tumor Cell Enrichment Technologies. In Tumor Liquid Biopsies; Schaffner, F., Merlin, J.-L., von Bubnoff, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 25–55. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, M.; Mohamed, B.M.; Ward, M.P.; Kelly, T.E.; O’Connor, R.; Malone, V.; Brooks, R.; Brooks, D.; Selemidis, S.; Martin, C.; et al. Circulating tumour cells: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, C.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Ou, L. Greatly isolated heterogeneous circulating tumor cells using hybrid engineered cell membrane-camouflaged magnetic nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieng, F.Y.F.; Abu, N.; Nasir, S.N.; Lee, L.-H.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S. Liquid Biopsy-Based Colorectal Cancer Screening via Surface Markers of Circulating Tumor Cells. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gires, O.; Pan, M.; Schinke, H.; Canis, M.; Baeuerle, P.A. Expression and function of epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM: Where are we after 40 years? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 969–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami-S, Z.; Cortés-Hernández, L.E.; Alix-Panabières, C. Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule: An Anchor to Isolate Clinically Relevant Circulating Tumor Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.C.; Sankpal, N.V.; Gillanders, W.E. Functional Implications of the Dynamic Regulation of EpCAM during Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitz, J.; Goodale, D.; Postenka, C.; Lowes, L.E.; Allan, A.L. EMT-independent detection of circulating tumor cells in human blood samples and pre-clinical mouse models of metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2021, 38, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinsgaard, E.M.B.; Korsnes, M.S.; Korsnes, R.; Moestue, S.A. Single-cell tracking as a tool for studying EMT-phenotypes. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 437, 113993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüönd, F.; Sugiyama, N.; Bill, R.; Bornes, L.; Hager, C.; Tang, F.; Santacroce, N.; Beisel, C.; Ivanek, R.; Bürglin, T.; et al. Distinct contributions of partial and full EMT to breast cancer malignancy. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 3203–3221.e3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlyn, M.; Steplewski, Z.; Herlyn, D.; Koprowski, H. Colorectal carcinoma-specific antigen: Detection by means of monoclonal antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 1438–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugli, A.; Iezzi, G.; Hostettler, I.; Muraro, M.G.; Mele, V.; Tornillo, L.; Carafa, V.; Spagnoli, G.; Terracciano, L.; Zlobec, I. Prognostic impact of the expression of putative cancer stem cell markers CD133, CD166, CD44s, EpCAM, and ALDH1 in colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maetzel, D.; Denzel, S.; Mack, B.; Canis, M.; Went, P.; Benk, M.; Kieu, C.; Papior, P.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Munz, M.; et al. Nuclear signalling by tumour-associated antigen EpCAM. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Went, P.T.H.; Lugli, A.; Meier, S.; Bundi, M.; Mirlacher, M.; Sauter, G.; Dirnhofer, S. Frequent EpCam protein expression in human carcinomas. Hum. Pathol. 2004, 35, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombolan, L.; Rossi, E.; Zin, A.; Santoro, L.; Bonvini, P.; Zamarchi, R.; Bisogno, G. Pediatric sarcomas display a variable EpCAM expression in a histology-dependent manner. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentink, A.; Isebia, K.T.; Kraan, J.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; Stevens, M. Measuring antigen expression of cancer cell lines and circulating tumour cells. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, S.; Ding, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, B. Understanding the versatile roles and applications of EpCAM in cancers: From bench to bedside. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malani, R.; Fleisher, M.; Kumthekar, P.; Lin, X.; Omuro, A.; Groves, M.D.; Lin, N.U.; Melisko, M.; Lassman, A.B.; Jeyapalan, S.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid circulating tumor cells as a quantifiable measurement of leptomeningeal metastases in patients with HER2 positive cancer. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2020, 148, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.; Piairo, P.; Chícharo, A.; Abalde-Cela, S.; Pires, L.R.; Corredeira, P.; Alves, P.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; Costa, L.; Diéguez, L. HER2 Expression in Circulating Tumour Cells Isolated from Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Using a Size-Based Microfluidic Device. Cancers 2021, 13, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Shen, H.; Zhu, H.; Liang, X.; Shen, Z. Tracking of trastuzumab resistance in patients with HER2-positive metastatic gastric cancer by CTC liquid biopsy. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 5684–5697. [Google Scholar]
- Cetin, D.; Okan, M.; Bat, E.; Kulah, H. A comparative study on EpCAM antibody immobilization on gold surfaces and microfluidic channels for the detection of circulating tumor cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.; Zacharowski, K.; Meybohm, P.; Schnitzbauer, A.; Ruf, P.; Kellermann, C.; Lindhofer, H. Removal of EpCAM-positive tumor cells from blood collected during major oncological surgery using the Catuvab device- a pilot study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021, 21, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelmuter, V.M.; Grigoryeva, E.S.; Savelieva, O.E.; Alifanov, V.V.; Andruhova, E.S.; Zavyalova, M.V.; Bragina, O.D.; Garbukov, E.Y.; Menyailo, M.E.; Khozyainova, A.A.; et al. EpCAM-CD24+ circulating cells associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onukwugha, N.-E.; Nagrath, S.; McEacheron, H. Abstract 2131: Immunoaffinity isolation of EpCAM expressing exosomes utilizing high throughput microfluidic chip with IEDDA chemistry (EpCAM-TCOOncoBean Chip). Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Shafiee, S.; Vafaei, R.; Salehi, M.; Jalili, N.; Nazerian, Z.; Muhammadnajad, A.; Yadegari, F.; Reza Esmailinejad, M.; Farahmand, L. Production of novel recombinant anti-EpCAM antibody as targeted therapy for breast cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 122, 110656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Tan, S.; Wu, M.; Ju, H.; Liang, X.; Li, P. Evaluation of a new magnetic bead as an integrated platform for systematic CTC recognition, capture and clinical analysis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 199, 111542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ding, H.; Qu, X.; Shi, X.; Yang, J.; Huang, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Song, J.; Zhu, L.; et al. Fluidic Multivalent Membrane Nanointerface Enables Synergetic Enrichment of Circulating Tumor Cells with High Efficiency and Viability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4800–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzani, P.; D’Argenio, V.; Re, M.D.; Pellegrini, C.; Cucchiara, F.; Salvianti, F.; Galbiati, S. Updates on liquid biopsy: Current trends and future perspectives for clinical application in solid tumors. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2021, 59, 1181–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zang, X.; Lv, Y. Detection of circulating tumor cells: Advances and critical concerns (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüstmann, N.; Humberg, V.; Vieler, J.; Seitzer, K.; von Rüden, S.; Juratli, M.A.; Pascher, A.; Kemper, M.; Bleckmann, A.; Franken, A.; et al. Enhancing Biomarker Detection in Cancer: A Comparative Analysis of Preanalytical Reverse Transcription Enzymes for Liquid Biopsy Application. Lab. Investig. 2024, 104, 102142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasseur, A.; Kiavue, N.; Bidard, F.-C.; Pierga, J.-Y.; Cabel, L. Clinical utility of circulating tumor cells: An update. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1647–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Tumor Cells Circulate in the Peripheral Blood of All Major Carcinomas but not in Healthy Subjects or Patients with Nonmalignant Diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecklein, N.H.; Fluegen, G.; Guglielmi, R.; Neves, R.P.L.; Hackert, T.; Birgin, E.; Cieslik, S.A.; Sudarsanam, M.; Driemel, C.; van Dalum, G.; et al. Ultra-sensitive CTC-based liquid biopsy for pancreatic cancer enabled by large blood volume analysis. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andree, K.C.; van Dalum, G.; Terstappen, L.W. Challenges in circulating tumor cell detection by the CellSearch system. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.N.; Nisar, S.; Masoodi, T.; Singh, M.; Rizwan, A.; Hashem, S.; El-Rifai, W.; Bedognetti, D.; Batra, S.K.; Haris, M.; et al. Liquid biopsy: A step closer to transform diagnosis, prognosis and future of cancer treatments. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, W.; Fan, A.; Tran, T.; Danila, D.C.; Keys, D.; Schwartz, M.; Ionescu-Zanetti, C. Mutational Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells Using a Novel Microfluidic Collection Device and qPCR Assay. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo-Cruz, M.L.; González-Rubio, S.; Espejo, J.J.; Zamora-Olaya, J.M.; Alejandre-Altamirano, R.M.; Prieto-Torre, M.; Linares, C.I.; Guerrero-Misas, M.; Barrera-Baena, P.; Poyato-González, A.; et al. Enumeration and Characterization of Circulating Tumor Cells in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Transarterial Chemoembolization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Rodríguez, A.J.; Molina-Vallejo, M.P.; Aznar-Peralta, I.; González Puga, C.; Cañas García, I.; González, E.; Lorente, J.A.; Serrano, M.J.; Garrido-Navas, M.C. Deep Phenotypic Characterisation of CTCs by Combination of Microfluidic Isolation (IsoFlux) and Imaging Flow Cytometry (ImageStream). Cancers 2021, 13, 6386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas-Camarero, S.; Orden-García, V.D.l.; Veganzones-de-Castro, S.; Mediero-Valeros, B.; Fuentes-Ferrer, M.E.; Ruiz, A.C.S.; Provencio, M.; Aranda, E.; Valera, J.S.; Diaz-Rubio, E. Performance of two immunoafinity-based methods for CTC detection and molecular characterization in advanced colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, e15648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Dávila-Ibáñez, A.B. Methodology for the Isolation and Analysis of CTCs. In Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer Metastatic Disease; Piñeiro, R., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Gorges, T.M.; Penkalla, N.; Schalk, T.; Joosse, S.A.; Riethdorf, S.; Tucholski, J.; Lücke, K.; Wikman, H.; Jackson, S.; Brychta, N.; et al. Enumeration and Molecular Characterization of Tumor Cells in Lung Cancer Patients Using a Novel In Vivo Device for Capturing Circulating Tumor Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandair, D.; Vesely, C.; Ensell, L.; Lowe, H.; Spanswick, V.; Hartley, J.A.; Caplin, M.E.; Meyer, T. A comparison of CellCollector with CellSearch in patients with neuroendocrine tumours. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, L29–L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, G.; Boehm, C.; Fischer, K.; Bialek, J.; Hoda, R.; Weber, E.; Schönburg, S.; Kawan, F.; Fornara, P. In vivo isolation of circulating tumor cells in patients with different stages of prostate cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Oh, D.-Y. HER2-targeted therapies beyond breast cancer—An update. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 675–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, P.; Viale, G.; Press, M.F.; Hu, X.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Bardia, A.; Batistatou, A.; Burstein, H.J.; Carey, L.A.; Cortes, J.; et al. ESMO expert consensus statements (ECS) on the definition, diagnosis, and management of HER2-low breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulukcuoglu Guneri, E.; Lakis, E.; Hajji, I.; Martin, E.; Champ, J.; Rampanou, A.; Pierga, J.-Y.; Viovy, J.-L.; Proudhon, C.; Bidard, F.-C.; et al. Deciphering HER2-HER3 Dimerization at the Single CTC Level: A Microfluidic Approach. Cancers 2022, 14, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, M.L.; Marrocco, I.; Yarden, Y. EGFR in Cancer: Signaling Mechanisms, Drugs, and Acquired Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.M.; Shastry, M.; Hamilton, E. Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer: Advances and future directions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miglietta, F.; Griguolo, G.; Bottosso, M.; Giarratano, T.; Lo Mele, M.; Fassan, M.; Cacciatore, M.; Genovesi, E.; De Bartolo, D.; Vernaci, G.; et al. Evolution of HER2-low expression from primary to recurrent breast cancer. Npj Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhussein, M.M.; Mokbel, A.; Cosman, T.; Aghel, N.; Yang, E.H.; Mukherjee, S.D.; Dent, S.; Ellis, P.M.; Dhesy-Thind, S.; Leong, D.P. Pertuzumab Cardiotoxicity in Patients with HER2-Positive Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. CJC Open 2021, 3, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, P.; Gupta, H.; Hughes, M.E.; Files, J.; Strauss, S.; Kirkner, G.; Feeney, A.-M.; Li, Y.; Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; et al. Comprehensive genomic characterization of HER2-low and HER2-0 breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinetto, E.; Rediti, M.; Fimereli, D.; Debien, V.; Piccart, M.; Aftimos, P.; Sotiriou, C.; de Azambuja, E. HER2-Low Breast Cancer: Molecular Characteristics and Prognosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbeck, N.; Ciruelos, E.; Jerusalem, G.; Müller, V.; Niikura, N.; Viale, G.; Bartsch, R.; Kurzeder, C.; Higgins, M.J.; Connolly, R.M.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in HER2-positive advanced breast cancer with or without brain metastases: A phase 3b/4 trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 3717–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schettini, F.; Chic, N.; Brasó-Maristany, F.; Paré, L.; Pascual, T.; Conte, B.; Martínez-Sáez, O.; Adamo, B.; Vidal, M.; Barnadas, E.; et al. Clinical, pathological, and PAM50 gene expression features of HER2-low breast cancer. Npj Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, C.; Liang, J.; Yi, J.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Y. Preliminary Clinical Validation of a Filtration-Based CTC Assay for Tumor Burden and HER2 Status Monitoring in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2022, 45, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefayat, A.; Sartipzadeh, O.; Molaabasi, F.; Amiri, M.; Gholami, R.; Mirzadeh, M.; Shokati, F.; Khandaei, M.; Ghahremani, F.; Poursamar, S.A.; et al. Microfluidic System Consisting of a Magnetic 3D-Printed Microchannel Filter for Isolation and Enrichment of Circulating Tumor Cells Targeted by Anti-HER2/MOF@Ferrite Core–Shell Nanostructures: A Theranostic CTC Dialysis System. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 4377–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levantini, E.; Maroni, G.; Del Re, M.; Tenen, D.G. EGFR signaling pathway as therapeutic target in human cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.d.S.; Nogueira, K.A.B.; Fernandes, L.C.C.; Martins, J.R.P.; Reis, A.V.F.; Neto, J.d.B.V.; Júnior, I.J.d.S.; Pessoa, C.; Petrilli, R.; Eloy, J.O. EGFR targeting for cancer therapy: Pharmacology and immunoconjugates with drugs and nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orofiamma, L.A.; Vural, D.; Antonescu, C.N. Control of cell metabolism by the epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robichaux, J.P.; Le, X.; Vijayan, R.S.K.; Hicks, J.K.; Heeke, S.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Udagawa, H.; Skoulidis, F.; Tran, H.; et al. Structure-based classification predicts drug response in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Nature 2021, 597, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, S.; Bonner, J.A.; Bredel, M. EGFR Mutations in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehmani, H.S.; Issaeva, N. EGFR in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Exploring possibilities of novel drug combinations. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, S.; Martini, G.; Ciardiello, D.; Del Tufo, S.; Martinelli, E.; Troiani, T.; Ciardiello, F. Targeting the EGFR signalling pathway in metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlaender, A.; Subbiah, V.; Russo, A.; Banna, G.L.; Malapelle, U.; Rolfo, C.; Addeo, A. EGFR and HER2 exon 20 insertions in solid tumours: From biology to treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doleschal, B.; Petzer, A.; Rumpold, H. Current concepts of anti-EGFR targeting in metastatic colorectal cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1048166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, S.; Salib, S.; Balasubramaniam, M.; Aboud, O. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors in Glioblastoma: Current Status and Future Possibilities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Jänne, P.A.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yanagitani, N.; Kim, S.-W.; Sugawara, S.; Yu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Geater, S.L.; et al. Osimertinib with or without Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Lin, J.J. Third-generation EGFR and ALK inhibitors: Mechanisms of resistance and management. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, K.; Xie, F.; Wang, F.; Fu, L. Therapeutic strategies for EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with osimertinib resistance. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fina, E.; Cleris, L.; Dugo, M.; Lecchi, M.; Ciniselli, C.M.; Lecis, D.; Bianchi, G.V.; Verderio, P.; Daidone, M.G.; Cappelletti, V. Gene signatures of circulating breast cancer cell models are a source of novel molecular determinants of metastasis and improve circulating tumor cell detection in patients. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Teng, X.; Liu, A.; Yang, W. Novel Isolating Approaches to Circulating Tumor Cell Enrichment Based on Microfluidics: A Review. Micromachines 2024, 15, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiò, C.; Criscitiello, C.; Scatena, C.; Santinelli, A.; Graziano, P.; Malapelle, U.; Cursano, G.; Venetis, K.; Fanelli, G.N.; Pepe, F.; et al. Think “HER2” different: Integrative diagnostic approaches for HER2-low breast cancer. Pathologica 2023, 115, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetis, K.; Crimini, E.; Sajjadi, E.; Corti, C.; Guerini-Rocco, E.; Viale, G.; Curigliano, G.; Criscitiello, C.; Fusco, N. HER2 Low, Ultra-low, and Novel Complementary Biomarkers: Expanding the Spectrum of HER2 Positivity in Breast Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 834651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wuethrich, A.; Wang, J.; Korbie, D.; Lin, L.L.; Trau, M. Dynamic Monitoring of EMT in CTCs as an Indicator of Cancer Metastasis. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16787–16795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Po, J.W.; Roohullah, A.; Lynch, D.; DeFazio, A.; Harrison, M.; Harnett, P.R.; Kennedy, C.; de Souza, P.; Becker, T.M. Improved ovarian cancer EMT-CTC isolation by immunomagnetic targeting of epithelial EpCAM and mesenchymal N-cadherin. J. Circ. Biomark. 2018, 7, 1849454418782617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Ding, S.; Huang, C.; Pan, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Liang, X.; Wang, X.; Song, P. Distribution and Clinical Analysis of EpCAM+/Vimentin+ Circulating Tumor Cells in High-Risk Population and Cancer Patients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 642971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Xu, L.; Han, T.; Luan, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Kong, X.; et al. Exploring new frontiers: Cell surface vimentin as an emerging marker for circulating tumor cells and a promising therapeutic target in advanced gastric Cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satelli, A.; Mitra, A.; Brownlee, Z.; Xia, X.; Bellister, S.; Overman, M.J.; Kopetz, S.; Ellis, L.M.; Meng, Q.H.; Li, S. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transitioned Circulating Tumor Cells Capture for Detecting Tumor Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xie, T.; Yang, J.; Lin, X.; Huang, L.; Su, S.; Deng, J. Feasibility study of expressing epcam + /vimentin + CTC in prostate cancer diagnosis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 8699–8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, R.; Watters, M.; Davies, C.R.; Pantel, K.; Lu, Y.-J. Circulating tumour cells for early detection of clinically relevant cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Meng, Q.H.; Noh, H.; Somaiah, N.; Torres, K.E.; Xia, X.; Batth, I.S.; Joseph, C.P.; Liu, M.; Wang, R.; et al. Cell-surface vimentin–positive macrophage-like circulating tumor cells as a novel biomarker of metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. OncoImmunology 2018, 7, e1420450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Meng, Q.H.; Noh, H.; Batth, I.S.; Somaiah, N.; Torres, K.E.; Xia, X.; Wang, R.; Li, S. Detection of circulating tumor cells from cryopreserved human sarcoma peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cancer Lett. 2017, 403, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satelli, A.; Brownlee, Z.; Mitra, A.; Meng, Q.H.; Li, S. Circulating Tumor Cell Enumeration with a Combination of Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule– and Cell-Surface Vimentin–Based Methods for Monitoring Breast Cancer Therapeutic Response. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liao, Y.; Ran, Y.; Wang, G.; Wu, W.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wen, N.; Jing, T.; Wang, H.; et al. Evaluation of sensitivity and specificity of CanPatrol™ technology for detection of circulating tumor cells in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Shen, L.; Luo, M.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Circulating tumor cells: Biology and clinical significance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Ryu, J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Shin, S.-W.; Shin, Y.K.; Ko, S.; Lee, H.S. Abstract 1356: GENOCTC, a highly efficient system for enrichment of circulating tumor cells and its clinical application. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IKEDA, M.; KOH, Y.; OYANAGI, J.; TERAOKA, S.; ISHIGE, M.; FUJIMURA, Y.; TAKEDA, K.; TOKUDOME, N.; OZAWA, Y.; UEDA, H.; et al. High-purity Isolation for Genotyping Rare Cancer Cells from Blood Using a Microfluidic Chip Cell Sorter. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, G.; Miyaoka, Y. Large-scale single-cell cloning of genome-edited cultured human cells by On-chip SPiS. STAR Protoc. 2023, 4, 102364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Serizawa, M.; Sawada, T.; Takeda, K.; Takahashi, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Koizumi, F.; Koh, Y. A novel flow cytometry-based cell capture platform for the detection, capture and molecular characterization of rare tumor cells in blood. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisotto, G.; Biscontin, E.; Rossi, E.; Bulfoni, M.; Piruska, A.; Spazzapan, S.; Poggiana, C.; Vidotto, R.; Steffan, A.; Colombatti, A.; et al. Dysmetabolic Circulating Tumor Cells Are Prognostic in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, E.; Basso, U.; Celadin, R.; Zilio, F.; Pucciarelli, S.; Aieta, M.; Barile, C.; Sava, T.; Bonciarelli, G.; Tumolo, S.; et al. M30 neoepitope expression in epithelial cancer: Quantification of apoptosis in circulating tumor cells by CellSearch analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5233–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisencu, L.A.; Trancă, S.; Bonci, E.-A.; Pașca, A.; Mihu, C.; Irimie, A.; Tudoran, O.; Balacescu, O.; Lisencu, I.C. The Role of Circulating Tumor Cells in the Prognosis of Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancers: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Fassan, M.; Aieta, M.; Zilio, F.; Celadin, R.; Borin, M.; Grassi, A.; Troiani, L.; Basso, U.; Barile, C.; et al. Dynamic changes of live/apoptotic circulating tumour cells as predictive marker of response to Sunitinib in metastatic renal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOON, S.M.; KIM, J.-H.; KIM, S.K.; KIM, S.; KWON, H.-J.; BAE, J.-S.; LEE, S.; LEE, H.S.; CHOI, M.-Y.; JEON, B.H.; et al. Clinical Utility of Combined Circulating Tumor Cell and Circulating Tumor DNA Assays for Diagnosis of Primary Lung Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 3435–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Wang, C.; Wan, S.; Mu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Abu-Khalaf, M.M.; Fellin, F.M.; Silver, D.P.; Neupane, M.; Jaslow, R.J.; et al. Association of clinical outcomes in metastatic breast cancer patients with circulating tumour cell and circulating cell-free DNA. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 106, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, A.; Piairo, P.; Matos, B.; Santos, D.A.R.; Palmeira, C.; Santos, L.L.; Lima, L.; Diéguez, L. Minimizing false positives for CTC identification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1288, 342165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, K.; Taubenberger, A.; Werner, C.; Fischer-Friedrich, E. EMT-Induced Cell-Mechanical Changes Enhance Mitotic Rounding Strength. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Sudo, T.; Akamatsu, S.; Sunada, T.; Myomoto, A.; Okano, K.; Shimizu, K. Cell Lines of Circulating Tumor Cells: What Is Known and What Needs to Be Resolved. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridrichova, I.; Kalinkova, L.; Ciernikova, S. Clinical Relevancy of Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer: Epithelial or Mesenchymal Characteristics, Single Cells or Clusters? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Otero, N.; Marshall, J.R.; Glenn, A.; Matloubieh, J.; Joseph, J.; Sahasrabudhe, D.M.; Messing, E.M.; King, M.R. TRAIL-coated leukocytes to kill circulating tumor cells in the flowing blood from prostate cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K.; Cohen, E.N.; Reuben, J.M.; Khoury, J.D. Circulating Tumor Cells: State-of-the-art Update on Technologies and Clinical Applications. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2019, 14, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, R.; Edd, J.F.; Chirn, B.; Mishra, A.; Haber, D.A.; Toner, M.; Maheswaran, S. Negative-Selection Enrichment of Circulating Tumor Cells from Peripheral Blood Using the Microfluidic CTC-iChip. In Mammary Stem Cells: Methods and Protocols; Vivanco, M.d., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 309–321. [Google Scholar]
- Topa, J.; Grešner, P.; Żaczek, A.J.; Markiewicz, A. Breast cancer circulating tumor cells with mesenchymal features—An unreachable target? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Cen, C.; Tang, S.; Dique, M.R.; Cai, L.; Luis, M.A.; Smollar, J.; et al. Detection Methods and Clinical Applications of Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 652253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallergi, G.; Politaki, E.; Alkahtani, S.; Stournaras, C.; Georgoulias, V. Evaluation of Isolation Methods for Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs). Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Shi, D. Circulating tumor cell isolation for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. eBioMedicine 2022, 83, 104237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapeleris, J.; Kulasinghe, A.; Warkiani, M.E.; Oleary, C.; Vela, I.; Leo, P.; Sternes, P.; O’Byrne, K.; Punyadeera, C. Ex vivo culture of circulating tumour cells derived from non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomka, A.; Wang, B.; Mocan, T.; Horhat, A.; Willms, A.G.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.G.H.; Strassburg, C.P.; Gonzalez-Carmona, M.A.; Lukacs-Kornek, V.; Kornek, M.T. Extracellular Vesicles and Circulating Tumour Cells—Complementary liquid biopsies or standalone concepts? Theranostics 2022, 12, 5836–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, A.J.; Nteliopoulos, G.; Shaw, J.A.; Coombes, R.C. A Review of Circulating Tumour Cell Enrichment Technologies. Cancers 2021, 13, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, P.-Y.; Nguyen, T.N.A.; Wu, A.-Y.; Huang, P.-S.; Huang, K.-L.; Liao, C.-J.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Wu, M.-H. The Utilization of Optically Induced Dielectrophoresis (ODEP)-Based Cell Manipulation in a Microfluidic System for the Purification and Sorting of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) with Different Sizes. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-B.; Wu, M.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Yang, C.-L.; Lin, H.-C.; Tseng, C.-P.; Lee, G.-B. High-purity and label-free isolation of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in a microfluidic platform by using optically-induced-dielectrophoretic (ODEP) force. Lab A Chip 2013, 13, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwizera, E.A.; Sun, M.; White, A.M.; Li, J.; He, X. Methods of Generating Dielectrophoretic Force for Microfluidic Manipulation of Bioparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 2043–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Wu, M.-H. The Combination of Immunomagnetic Bead-Based Cell Isolation and Optically Induced Dielectrophoresis (ODEP)-Based Microfluidic Device for the Negative Selection-Based Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çağlayan, Z.; Demircan Yalçın, Y.; Külah, H. Examination of the dielectrophoretic spectra of MCF7 breast cancer cells and leukocytes. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretyakova, M.S.; Menyailo, M.E.; Schegoleva, A.A.; Bokova, U.A.; Larionova, I.V.; Denisov, E.V. Technologies for Viable Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkumur, E.; Shah, A.M.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Emmink, B.L.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Brachtel, E.; Yu, M.; Chen, P.-i.; Morgan, B.; Trautwein, J.; et al. Inertial focusing for tumor antigen-dependent and -independent sorting of rare circulating tumor cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 179ra147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirone, D.; Montella, A.; Sirico, D.G.; Mugnano, M.; Villone, M.M.; Bianco, V.; Miccio, L.; Porcelli, A.M.; Kurelac, I.; Capasso, M.; et al. Label-free liquid biopsy through the identification of tumor cells by machine learning-powered tomographic phase imaging flow cytometry. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franses, J.W.; Philipp, J.; Missios, P.; Bhan, I.; Liu, A.; Yashaswini, C.; Tai, E.; Zhu, H.; Ligorio, M.; Nicholson, B.; et al. Pancreatic circulating tumor cell profiling identifies LIN28B as a metastasis driver and drug target. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, Y.; Konik, A.; Otani, K.; Pittie, R.; Chung, E.; Rodden, D.J.; Kelly, J.P.; Shan, M.; Xu, K.H.; Otani, Y.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell-Based Molecular Biomarkers of 177Lu-PSMA-617 Treatment Efficacy in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 120, S70–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, Y.; Konik, A.; Otani, K.; Pittie, R.; Rodden, D.; Kelly, J.; Chung, E.; Ohtani, Y.; Badusi, P.; Pompa, I.; et al. Circulating tumor cell molecular signatures of response to 177Lu-PSMA-617 therapy in metastatic prostate cancer patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65, 241193. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Guo, G.; Wu, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Shi, N.; Guan, Y. Advances in Integration, Wearable Applications, and Artificial Intelligence of Biomedical Microfluidics Systems. Micromachines 2023, 14, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccioli, M.; Kim, K.; Khazan, N.; Khoury, J.D.; Cooke, M.J.; Miller, M.C.; O’Shannessy, D.J.; Pailhes-Jimenez, A.-S.; Moore, R.G. Identification of circulating tumor cells captured by the FDA-cleared Parsortix® PC1 system from the peripheral blood of metastatic breast cancer patients using immunofluorescence and cytopathological evaluations. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.N.; Jayachandran, G.; Moore, R.G.; Cristofanilli, M.; Lang, J.E.; Khoury, J.D.; Press, M.F.; Kim, K.K.; Khazan, N.; Zhang, Q.; et al. A Multi-Center Clinical Study to Harvest and Characterize Circulating Tumor Cells from Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer Using the Parsortix® PC1 System. Cancers 2022, 14, 5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeman, A.; Miller, M.C.; Cooke, M.J.; O’Shannessy, D.J.; Gurung, Y.; Pereira, T.; Peters, S.G.; Piano, M.; Teo, M.; Khazan, N.; et al. Analytical performance of the FDA-cleared Parsortix(®) PC1 system. J. Circ. Biomark. 2023, 12, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, G.; Templeman, A.; Hendry, F.; Miller, K.; Pailhes-Jimenez, A.-S. Molecular Profiling of Circulating Tumour Cells and Circulating Tumour DNA: Complementary Insights from a Single Blood Sample Utilising the Parsortix® System. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Vlietinck, L.; Greaves, D.; Ciccioli, M.; Pailhes-Jimenez, A.S. Interrogating HER2 status in Circulating Tumor Cells isolated using the Parsortix® System from Metastatic Breast Cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 200, 113873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, A.; Mograbi, B.; Romeo, B.; Gastaud, L.; Lalvee, S.; Zahaf, K.; Fayada, J.; Nahon-Esteve, S.; Bonnetaud, C.; Salah, M.; et al. Assessment of Different Circulating Tumor Cell Platforms for Uveal Melanoma: Potential Impact for Future Routine Clinical Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alwis, R.; Hansson, J.; Lindgren, D.; Schoch, S.; Tejera, A.; Scholtz, B.; Elfving, P.; Möller, C.; Nilsson, H.; Johansson, M.; et al. Size-based isolation and detection of renal carcinoma cells from whole blood. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 16, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.K.; Menon, N.V.; Tan, P.S.; Pan, T.L.; Bonney, G.K.; Shridhar, I.G.; Madhavan, K.; Lim, C.T.; Kow, A.W. Presence of tumor cells in intra-operative blood salvage autotransfusion samples from hepatocellular carcinoma liver transplantation: Analysis using highly sensitive microfluidics technology. HPB 2021, 23, 1700–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, L.; Yang, J.; Zhai, C.; Chai, S.; Dong, Z.; Li, M. Survival, Chemotherapy and Chemosensitivity Predicted by CTC Cultured In Vitro of SCLC Patients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 683318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Shirai, K.; Ijiri, Y.; Morita, E.; Yoshida, T.; Iwanaga, S.; Yanagida, M. Integrated system for detection and molecular characterization of circulating tumor cells. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
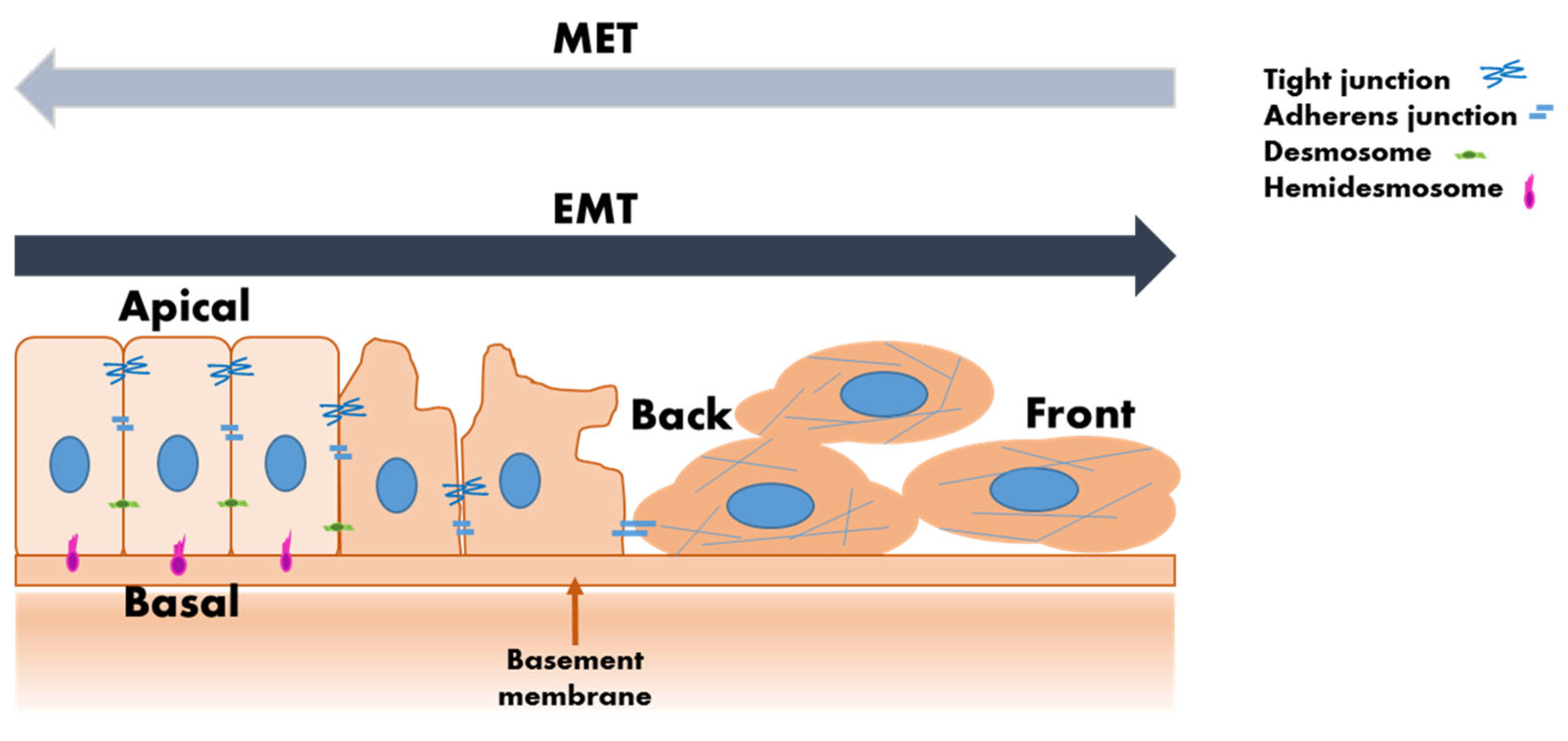
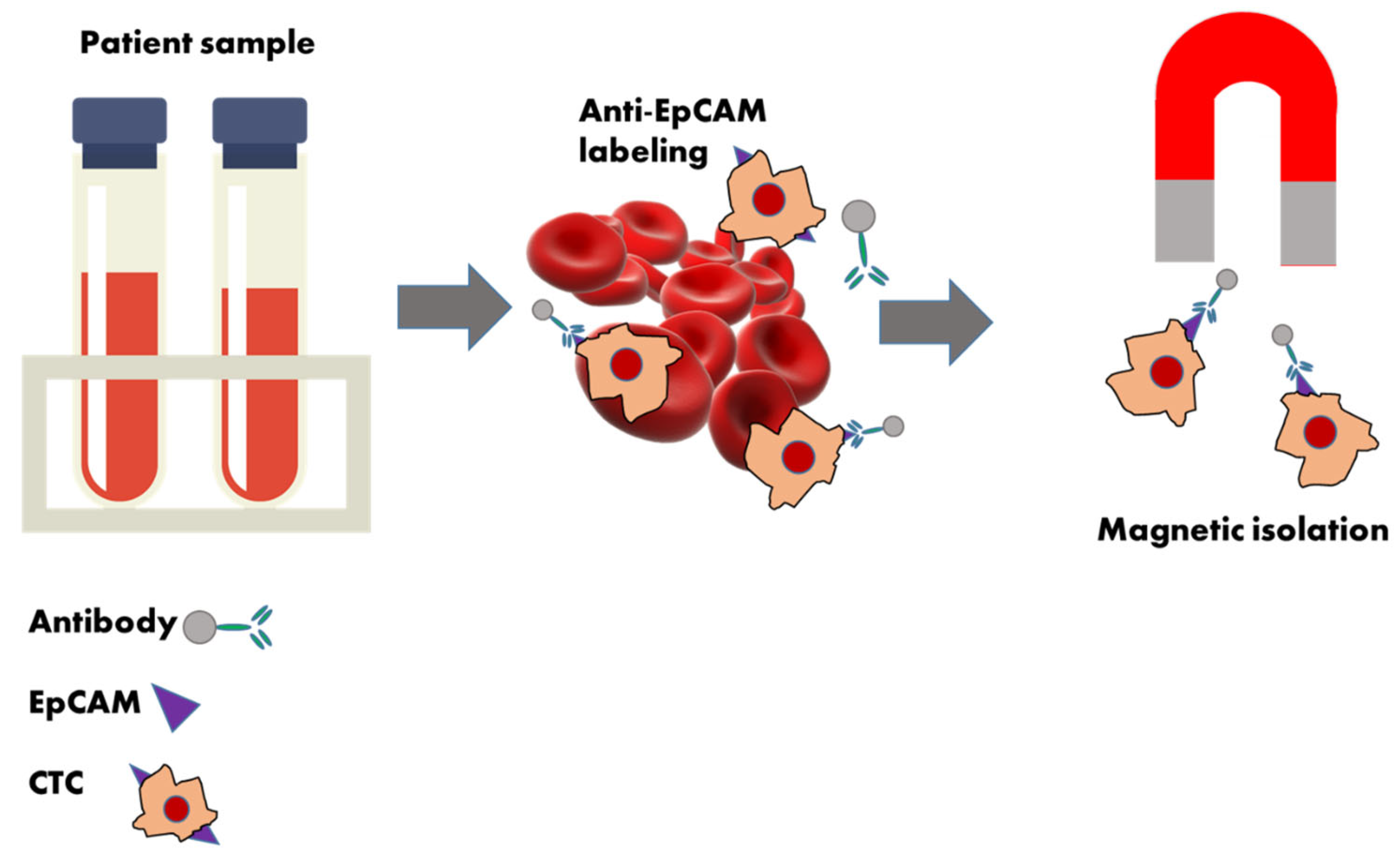
| Early cancer detection [36] | Detecting CTCs in blood samples can facilitate early diagnosis of cancers, potentially before symptoms arise. This non-invasive approach allows for timely intervention, which is crucial for improving patient outcomes. |
| Prognosis prediction [18] | The number and characteristics of CTCs correlate with disease stage and aggressiveness. Elevated CTC counts are often associated with a higher risk of metastasis and poorer prognosis. Monitoring CTC levels can help to predict disease progression and informed treatment decisions. |
| Monitoring treatment response [37] | CTC analysis enables real-time assessment of tumor response to therapy. A decrease in CTC count during treatment may indicate a positive response, while an increase could suggest resistance or disease progression. This dynamic monitoring can aid in adjusting treatment plans promptly. |
| Detecting minimal residual disease [38] | After surgical removal of tumors, CTCs can persist in the bloodstream, leading to recurrence. Identifying these residual cells through CTC analysis allows for early intervention to prevent relapse. |
| Assessing metastatic potential [39] | CTCs are essential for understanding the metastatic process. Their presence and characteristics can provide insights into the likelihood of cancer spreading to other parts of the body, guiding surveillance and preventive strategies. |
| Personalized medicine [40] | Analyzing CTCs allows for molecular profiling of tumors, identifying specific mutations and alterations. This information is crucial for selecting targeted therapies tailored to the individual patient’s cancer, enhancing treatment efficacy. |
| EpCAM-dependent CTC enrichment | Positive selection | CELLSEARCH® [59] | The first FDA-approved system for isolating and enumerating circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in patients with metastatic breast, prostate, or colorectal cancer. |
| IsoFlux™ CTC System [61] | A microfluidic-based system that captures CTCs using immunomagnetic beads targeting the EpCAM, enabling high-purity isolation for downstream analysis. | ||
| GILUPI CellCollector® [65] | An anti-EpCAM coated medical-grade catheter, which is inserted into a vein, allowing for in vivo isolation. | ||
| GenoCTC [111] | The device utilizes microfluidic magnetophoresis and a specialized isolation chip with optimized ferromagnetic wire patterns to enrich CTCs, targeting both epithelial and mesenchymal markers. | ||
| EpCAM-independent CTC enrichment | Positive selection | On-chip Sort [114] | The device utilizes fluorescence-based cell sorting for the positive selection of different cell types in the samples. |
| Negative selection | Dynabeads™ [131] | Magnetic beads coated with antibodies against CD45, enabling the depletion of leukocytes from blood samples to enrich CTCs. | |
| RosetteSep™ [132] | A negative selection method that uses tetrameric antibody complexes to remove unwanted blood cells, facilitating the isolation of CTCs. | ||
| CTC-iCHIP [127] | A microfluidic device that combines inertial focusing and magnetic separation to isolate CTCs from whole blood without the need for labeling. | ||
| Label-free enrichment | Parsortix® [147] | A microfluidic system that separates CTCs from blood based on size and deformability, allowing for label-free isolation. | |
| ClearCell® FX1 System [152] | A microfluidic device that captures CTCs using size-based filtration, enabling label-free isolation for subsequent analysis. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szerenyi, D.; Jarvas, G.; Guttman, A. Multifaceted Approaches in Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-Mediated Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation. Molecules 2025, 30, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050976
Szerenyi D, Jarvas G, Guttman A. Multifaceted Approaches in Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-Mediated Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation. Molecules. 2025; 30(5):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050976
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzerenyi, Dora, Gabor Jarvas, and Andras Guttman. 2025. "Multifaceted Approaches in Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-Mediated Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation" Molecules 30, no. 5: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050976
APA StyleSzerenyi, D., Jarvas, G., & Guttman, A. (2025). Multifaceted Approaches in Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-Mediated Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation. Molecules, 30(5), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30050976








