Preparation and Properties of F-Doped PrBa0.8Sr0.2Co2O5+δ Perovskite Cathode Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
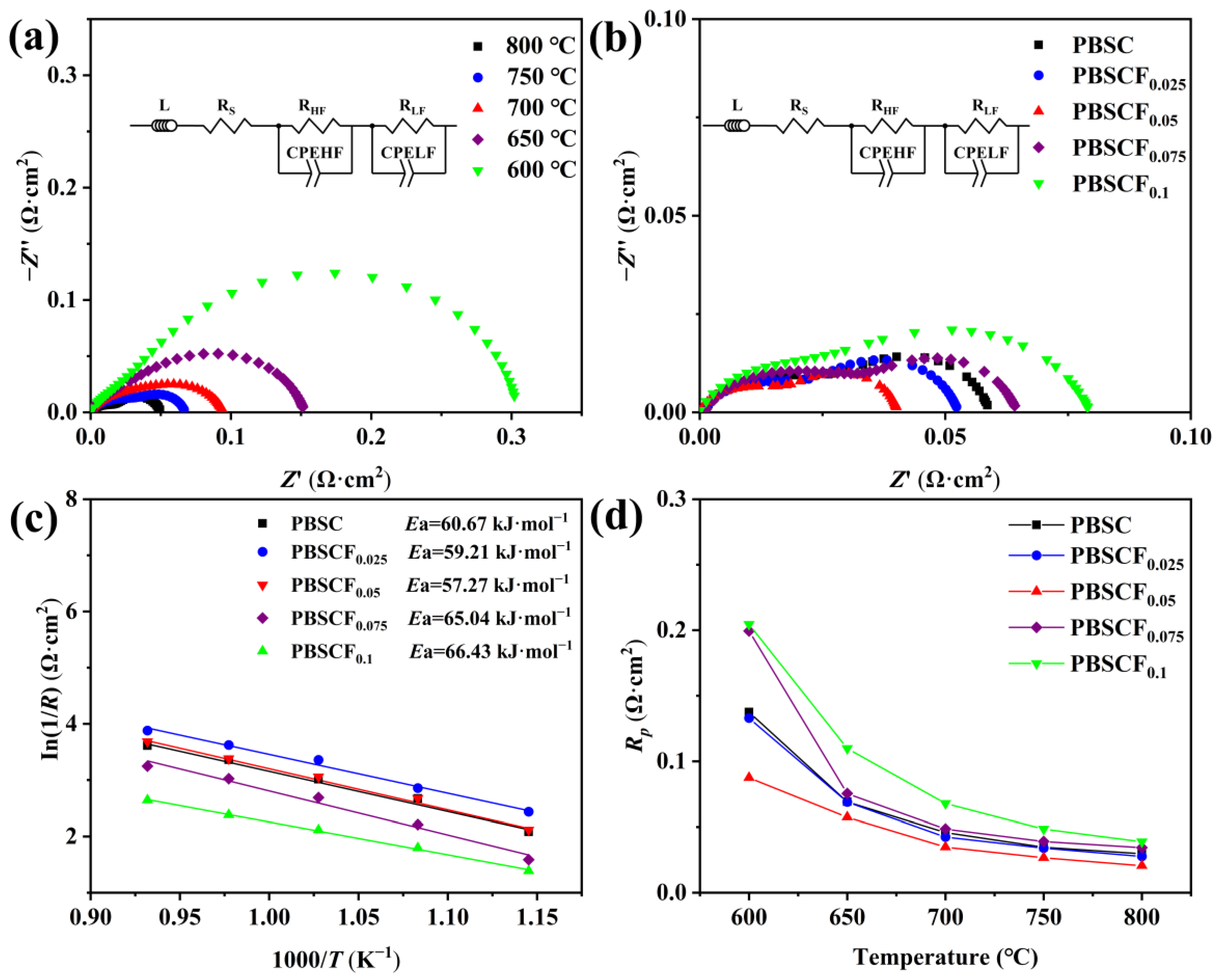
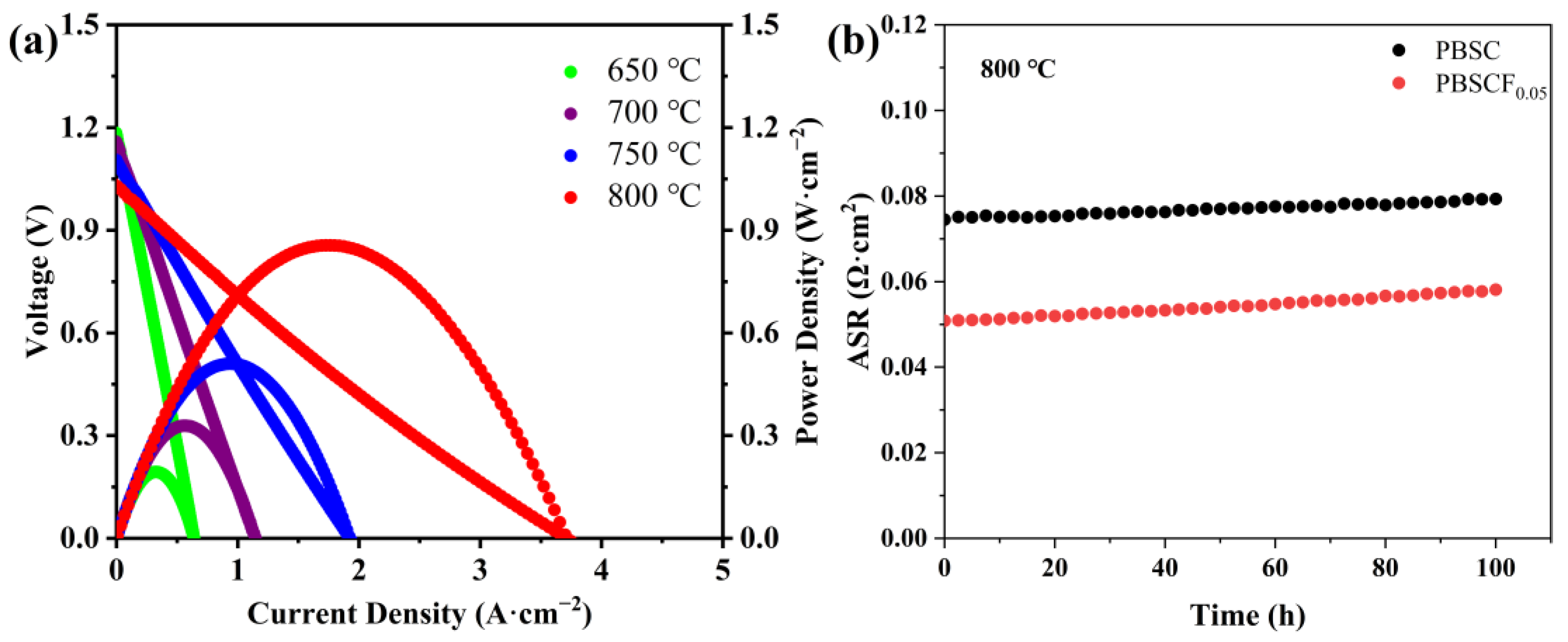
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Material Preparation
3.2. Cell Preparation
3.3. Sample Characterization and Performance Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, W.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Huang, J.B.; Li, M.R.; Xiang, B.L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Zheng, L.; Ge, L. Alternative B–site–doped La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8−xMxO3 (M = Ni, Cu, Nb; x = 0, 0.1, 0.2) as innovative cathode material for LT–SOFC with enhanced charge transfer and oxygen ion diffusion. Appl. Energy 2024, 353, 122096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.K.; Zhao, A.; Liu, F.S.; Zheng, K.; Jin, F.J.; Ling, Y.H. Designing highly active and CO2 tolerant heterostructure electrode materials by a facile A–site deficiency strategy in Pr1−xBaCo2O5+δ double perovskite. J. Power Sources 2024, 602, 234344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.H.; Baek, S.; Kim, Y. Investigation of the properties of layered perovskite materials with varying constituent elements as SOFC cathodes. Mater. Lett. 2024, 370, 136868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N.; Jiang, X.N.; Xu, H.X.; Xu, Q.L.; Jiang, L.; Shi, Y.C.; Zhang, Q.Y. Scandium–doped PrBaCo2−xScxO6−δ oxides as cathode material for intermediate–temperaturesolid oxide fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 12035–12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Du, D.; Gu, Y.Y.; Bi, L. Sc–doping strategy for LaNi0.5Fe0.5O3–δ cathode to boost the performance of proton–conducting solid oxide fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.N.; Xu, X.M.; Song, Y.F.; Shao, Z.P. Recent progress in Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5O6–δ–based multifunctional materials for energy conversion and storage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 51, 2411622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Zhong, Y.J.; Shao, Z.P. Double Perovskites in Catalysis, Electrocatalysis, and Photo(electro)catalysis. Trends Chem. 2019, 4, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.B.; Feng, J.; Abdellatif, H.R.S.; Zou, J.; Zhang, G.; Ni, C.S. Electrochemical evaluation of double perovskite PrBaCo2−xMnxO5+δ (x = 0, 0.5, 1) as promising cathodes for IT–SOFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 8962–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, Y.; Yeyongchaiwat, J.; Chaianansutcharit, S.J. Oxygen permeability and electrochemical performance of Ca–doped NdBaCo2O5+δ in IT–SOFC. Alloys Compd. 2024, 991, 174468. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.S.; Cai, H.D.; Hao, G.D.; Zhang, L.L.; Song, Z.Y.; Long, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.J. Characterization of high–valence Mo–doped PrBaCo2O5+δ cathodes for IT–SOFCs. Alloys Compd. 2020, 842, 155600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.Z.; Zhou, D.C.; Xiong, X.Q.; Pan, J.T.; Cai, D.L.; Wei, Z.; Chen, X.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Luo, N.N.; Yan, J.L.; et al. Doping strategy on improving the overall cathodic performance of double perovskite LnBaCo2O5+δ (Ln = Pr, Gd) as potential SOFC cathode materials. J. Mater. 2023, 9, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.J.; Li, J.X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Tian, Y.F.; Liu, F.S.; Wang, X.X.; Zhai, C.; Ling, Y.H. Boosting the electrocatalytic activity of NdBaCo2O5+δ via calcium co–doping as bifunctional oxygen electrodes for reversible solid oxide cells. Fuel 2024, 368, 131625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Xiong, X.Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Pan, J.T.; Cai, D.L.; Huang, X.M.; Han, G.; Liu, Y.H.; Jiang, Z.Z.; Fujita, T. The effect of Sr doping at the A–sites on the performance of La0.5Gd0.5Ba1–xSrxCo2O5+δ materials for intermediate–temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 996, 174860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Liu, X.L.; Wang, P.C.; Teng, Y.K.; Che, X.Y.; Li, J.H.; Jin, F.J. Effective calcium co–doping in Sm0.8Ca0.2Ba1–xCaxCo2O5+δ cathode materials for intermediate–temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 40358–40365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.W.; Xia, T.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.P.; Li, S.; Sun, L.P.; Huo, L.H.; Zhao, H. Addressing the origin of highly catalytic activity of A–site Sr–doped perovskite cathodes for intermediate–temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2022, 140, 107341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Sun, L.P.; Xia, T.; Huo, L.H.; Zhao, H.; Rougier, A.; Grenier, J.C. Effect of Sr doping on the electrochemical properties of bi–functional oxygen electrode PrBa1−xSrxCo2O5+δ. J. Power Sources 2016, 334, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, Q.Y.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, J.; Liu, F.; Yan, F.; Li, Z.K.; Gan, T.; Tong, X.F. Improving Electrochemical Oxidation/Reduction Kinetics in Single–Component Solid Oxide Cells through Synergistic A–Site Defects and Anion Doping. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 16050–16061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zuo, L.W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, K.P.; Zheng, D.; Afzal, M.; Xia, C.; Wang, B.Y. F–doped LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2−δ cathodes with enhanced ORR catalytic activity for LT–SOFCs. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 940, 168837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.H.; Qiu, H.; Jiang, S.S.; Jiang, J.J.; Wang, W.; Xu, X.M.; Kong, W.; Chivurugwi, T.D.; Proskurin, A.; Chen, D.F.; et al. New strategy for boosting cathodic performance of low temperature solid oxide fuel cells via chlorine doping. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 8086–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Sun, W.; Xu, C.M.; Ren, R.Z.; Yang, X.X.; Qiao, J.S.; Wang, Z.H.; Sun, K.N. Attenuating a metal–oxygen bond of double perovskite oxide via anion doping to enhance its catalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 14091–14098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Zhu, Y.L.; Zhong, Y.J.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z.P. Anion Doping: A New Strategy for Developing High–Performance Perovskite–Type Cathode Materials of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.J.; Wang, J.K.; Fan, W.W.; Wan, Y.H.; Zhang, X.W.; Li, G.J.; Wu, K.; Cheng, Y.H.; Zhou, J. Porous YFe0.5Co0.5O3 thin sheets as cathode for intermediate–temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 20164–20175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Tian, D.; Liu, R.; Wu, H.D.; Chen, Y.H.; Ding, Y.Z.; Lu, X.Y.; Lin, B. Exploiting rare–earth–abundant layered perovskite cathodes of LnBa0.5Sr0.5Co1.5Fe0.5O5+δ (Ln = La and Nd) for SOFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 46, 5630–5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Deng, G.B.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, K.T.; Wang, C. A high performance La2NiO4+δ impregnated PrBaCo2O5+δ cathode for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 2023, 403, 116387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Sun, N.; Shen, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, J.H.; Shi, K.X.; Jin, F.J. Investigation on Nd1–xCaxBaCo2O5+δ double perovskite as new oxygen electrode materials for reversible solid oxide cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 913, 165245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.M.; Su, X.G.; Wang, S.B.; Pan, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.L.; Song, Z.Y.; Long, W.; Li, C.L. Effects of Bi–doping on structure and properties of YBaCo2O5+δ layered perovskite cathode for intermediate–temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 965, 171391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Zhang, H.X.; Yao, C.G.; Lou, H.; Xia, B.X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.X.; Lang, X.S.; Cai, K.D. Ca and Fe co–doped NdBaCo2O5+δ double perovskites as high–performance cathodes for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 172084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.W.; Jin, F.J.; He, T.M. A–site calcium–doped Pr1−xCaxBaCo2O5+δ double perovskites as cathodes for intermediate–temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2016, 313, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.B.; Xie, H.P.; Liu, Z.P.; Shen, S.L.; Teng, Y.; Guan, D.Q.; Zhai, S.; Song, Y.F.; Zhou, W.; et al. CO2–induced reconstruction for ORR–enhanced solid oxide fuel cell cathode. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 462, 142216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costilla, S.U.; Escudero, M.J.; Cienfuegos, R.F.; Aguilar, J.A. Double perovskite La1.8Sr0.2CoFeO5+δ as a cathode material for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 862, 158025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Jin, F.J.; Liu, X.W.; Sun, N.; Li, J.X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, L.; Chu, X.Y.; Xu, M.Z.; et al. Effect of calcium doping on Sm1–xCaxBaCo2O5+δ cathode materials for intermediate–temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 390, 138830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.G.; Zhang, H.X.; Liu, X.J.; Meng, J.L.; Zhang, X.; Meng, F.Z.; Meng, J. Characterization of layered double perovskite LaBa0.5Sr0.25Ca0.25Co2O5+δ as cathode material for intermediate–temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 265, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.F.; Xia, T.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.P.; Huo, L.H.; Zhao, H. Heterostructured simple perovskite nanorod–decorated double perovskite cathode for solid oxide fuel cells Highly catalytic activity, stability and CO2–durability for oxygen reduction reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 249, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Tian, D.; Lu, X.Y.; Ding, Y.Z.; Yu, W.L.; Lin, B. A new A–site excessive strategy to improve performance of layered perovskite cathode for intermediate–temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 231, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
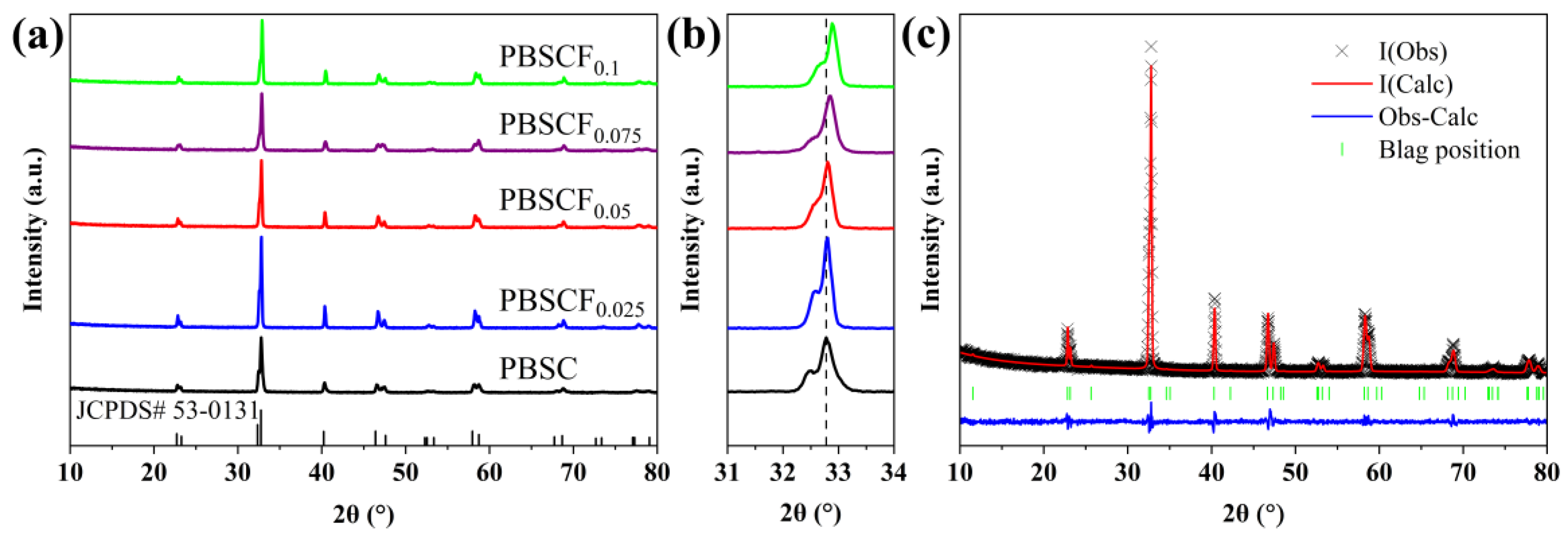
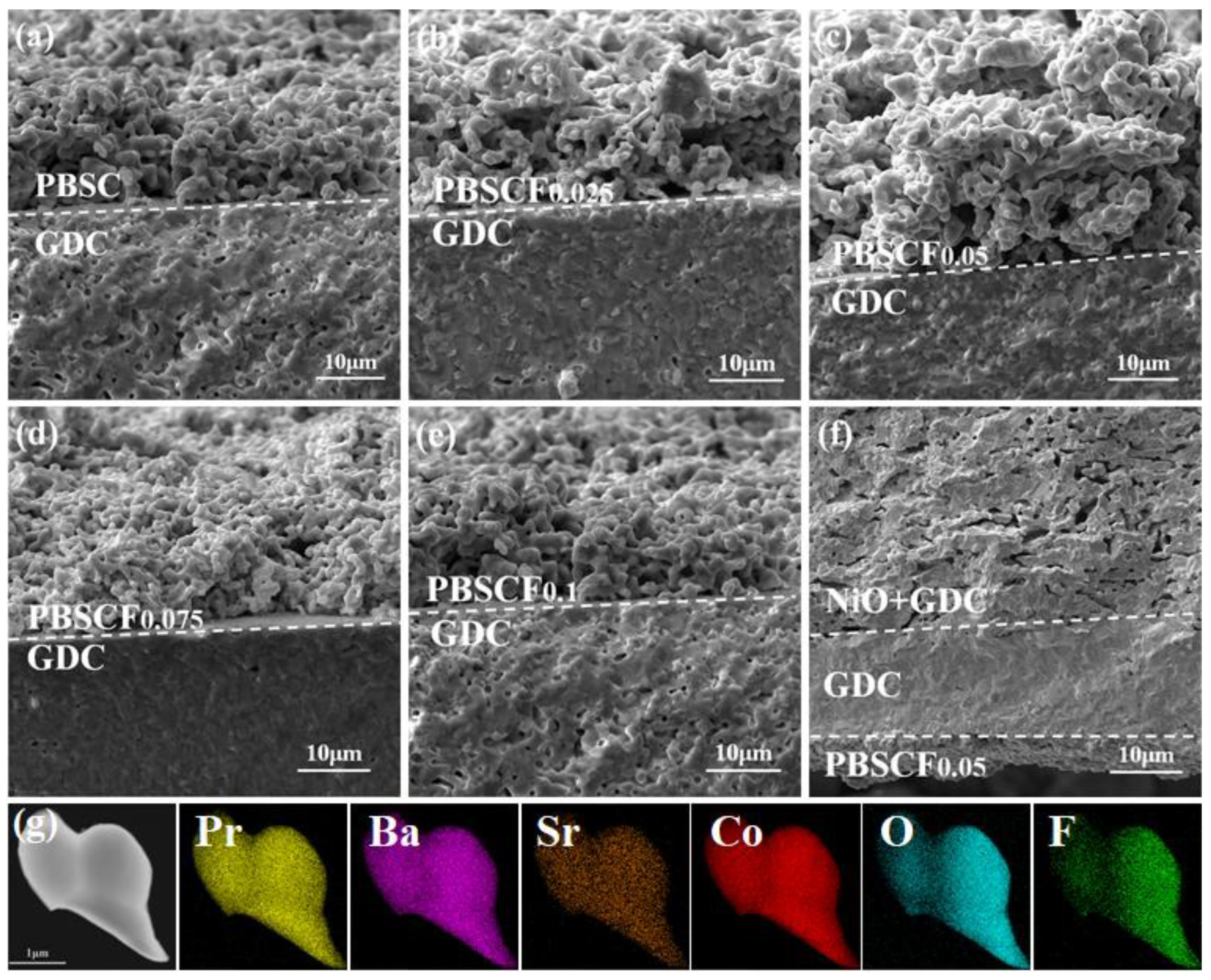

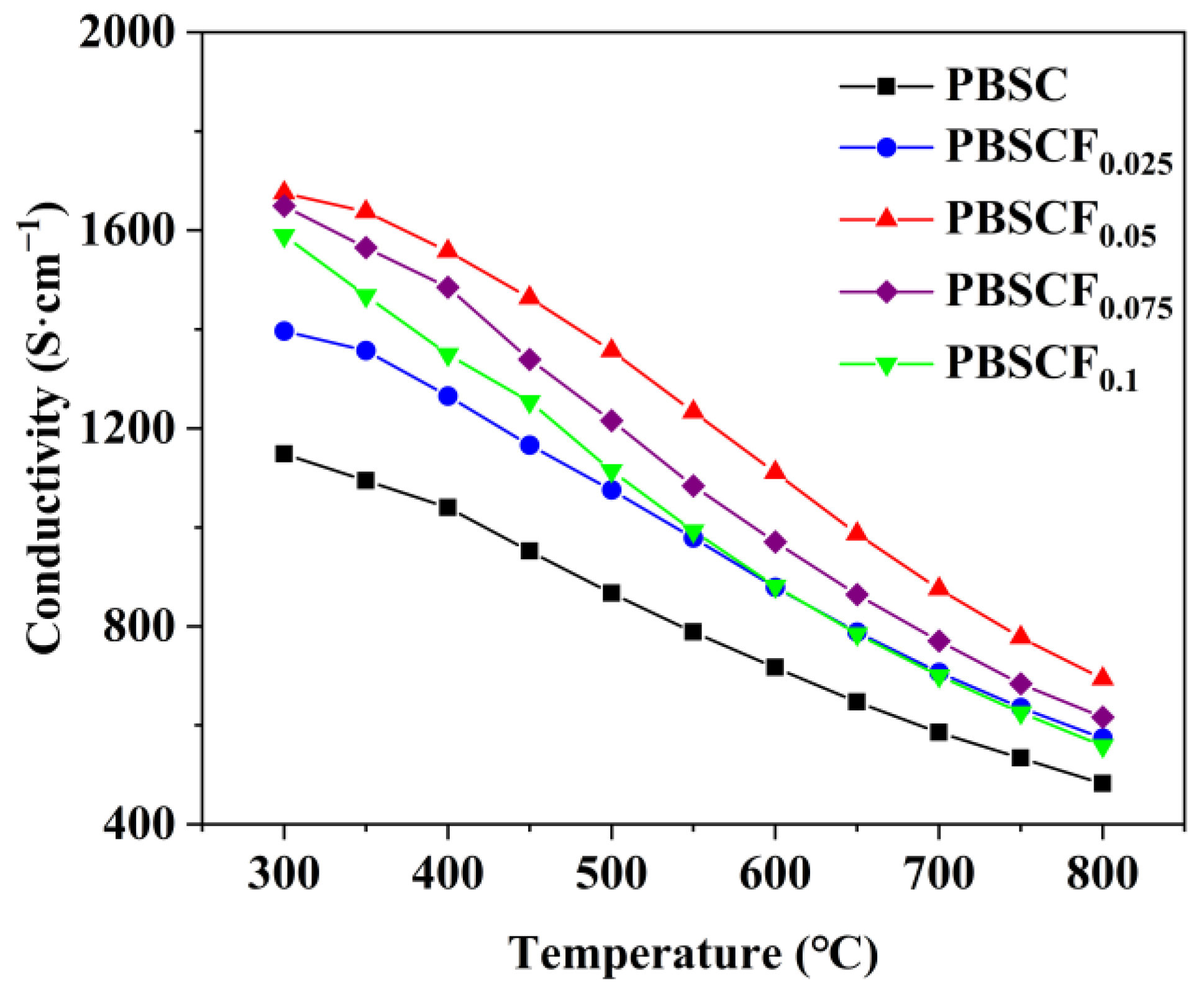
| PBSCFx | Space Group | a (Å) | c (Å) | V (Å) | χ2 | Rwp (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x = 0 | P4/mmm | 3.91980 | 7.73349 | 118.824 | 1.24 | 7.532 |
| x = 0.025 | P4/mmm | 3.91566 | 7.72752 | 118.481 | 1.36 | 7.596 |
| x = 0.05 | P4/mmm | 3.91282 | 7.71982 | 118.192 | 1.26 | 7.389 |
| x = 0.075 | P4/mmm | 3.91050 | 7.70556 | 117.834 | 1.25 | 7.973 |
| x = 0.1 | P4/mmm | 3.90391 | 7.69884 | 117.334 | 1.32 | 8.117 |
| Atom | Atomic Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| O | 55.07 |
| Co | 23.27 |
| Pr | 10.52 |
| Ba | 8.29 |
| Sr | 2.23 |
| F | 0.62 |
| Sample | O1s (eV (%)) | Ba3d (eV (%)) | Co2p1/2 (eV (%)) | Co2p3/2 (eV (%)) | Sr3d (eV (%)) | F1s (eV (%)) | Pr3d (eV (%)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBSC | 531.11 | 779.33 | 794.65 | 779.28 | 133.15 | 0(0) | 932 |
| (33.96) | (3.56) | (7.97) | (6.49) | (1.83) | (7.23) | ||
| PBSCF0.025 | 530.59 | 779.34 | 794.69 | 779.30 | 132.83 | 683 | 931.62 |
| (33.79) | (4.02) | (9.86) | (7.63) | (2.53) | (0.17) | (6.45) | |
| PBSCF0.05 | 530.95 | 779.54 | 794.79 | 779.50 | 133.11 | 684.56 | 932 |
| (33.42) | (3.48) | (8.53) | (7.80) | (3.66) | (0.34) | (6.52) | |
| PBSCF0.075 | 531.19 | 779.39 | 794.78 | 779.35 | 133 | 684.66 | 931.28 |
| (32.89) | (3.29) | (9.67) | (8.30) | (3) | (0.5) | (6.35) | |
| PBSCF0.1 | 531.81 | 779.32 | 794.78 | 779.26 | 133.59 | 684.74 | 929.09 |
| (32.49) | (3.20) | (8.35) | (6.43) | (3.45) | (0.66) | (6.65) |
| Sample | Lattice Oxygen (eV (%)) | Adsorbed Oxygen (eV (%)) |
|---|---|---|
| PBSC | 528.48 (5.90) | 531.54 (23.50) |
| PBSCF0.025 | 528.30 (7.90) | 531.12 (23.04) |
| PBSCF0.05 | 528.32 (5.46) | 531.32 (25.07) |
| PBSCF0.075 | 528.22 (5.93) | 531.40 (27.75) |
| PBSCF0.1 | 528.01 (5.64) | 531.44 (25.74) |
| Sample | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBSC | 795.27 (9.31) | 793.44 (1.69) | 780.14 (9.78) | 778.18 (1.66) |
| PBSCF0.025 | 794.95 (8.65) | 792.96 (2.22) | 779.90 (8.71) | 777.71 (2.22) |
| PBSCF0.05 | 794.78 (6.58) | 792.81 (3.28) | 780.09 (6.11) | 777.52 (3.04) |
| PBSCF0.075 | 794.86 (7.63) | 792.70 (2.54) | 779.84 (8.11) | 777.52 (1.85) |
| PBSCF0.1 | 794.64 (7.86) | 792.62 (2.43) | 779.59 (8.32) | 777.40 (1.19) |
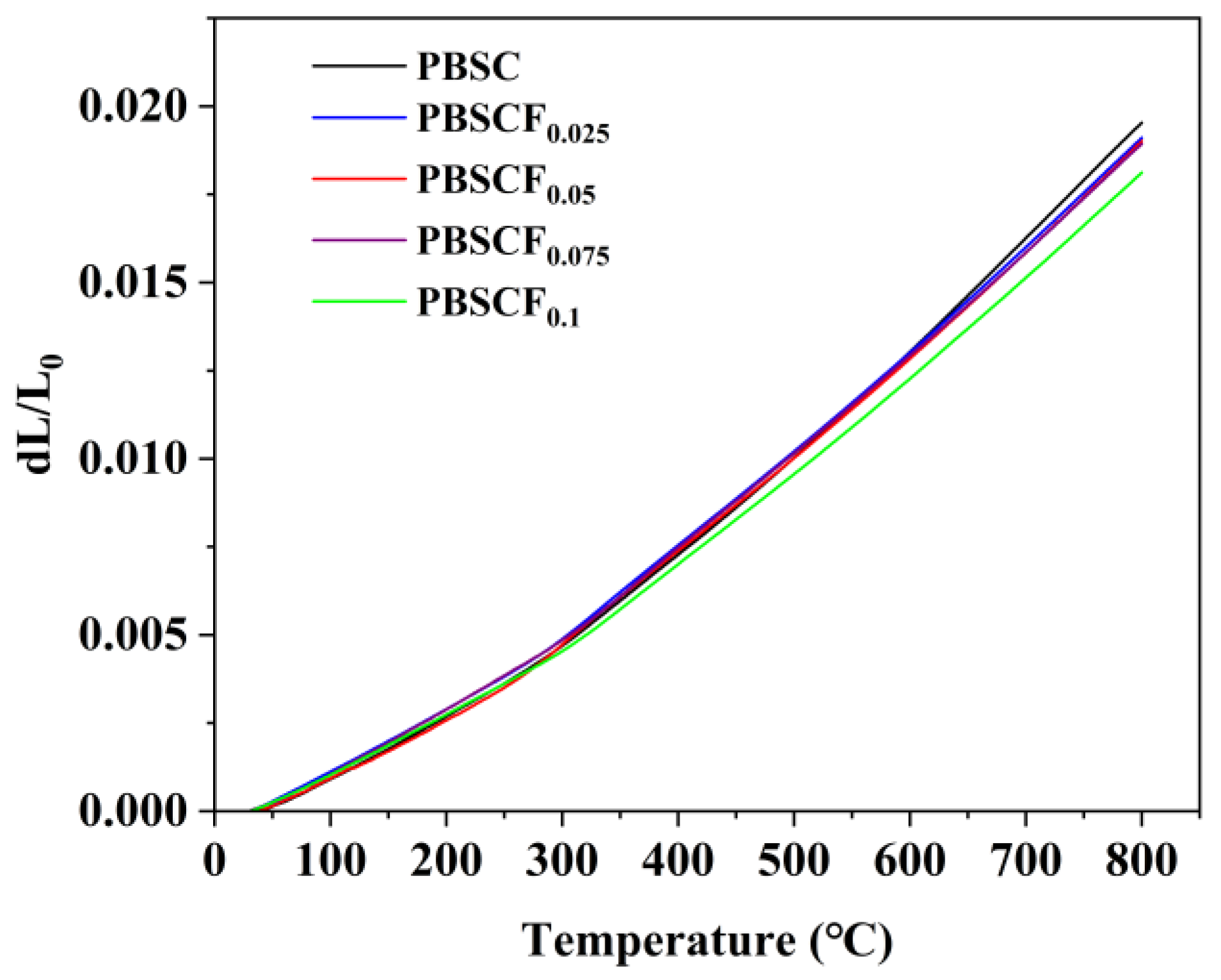
| Sample | TEC (×10−6 K−1) |
|---|---|
| PBSC | 25.3699 |
| PBSCF0.025 | 24.8132 |
| PBSCF0.05 | 24.6866 |
| PBSCF0.075 | 24.5928 |
| PBSCF0.1 | 23.5295 |
| Sample | Electrode | Temperature (°C) | ASR (Ω·cm2) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sm0.7Ca0.3BaCo2O5+δ | SDC | 700 | 0.075 | [31] |
| LaBa0.5Sr0.25Ca0.25Co2O5+δ | SDC | 800 | 0.075 | [32] |
| PrBa0.94Co2O5+δ | GDC | 700 | 0.025 | [33] |
| Gd1.05Ba1.05Co2O5+δ | GDC | 800 | 0.146 | [34] |
| Pr0.94Ba0.7Sr0.3Co2O5+δ | GDC | 700 | 0.031 | [15] |
| PrBa0.8Sr0.2Co2O4.95+δF0.05 | GDC | 800 | 0.0207 | this work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Li, S.; An, S.; Li, N.; Sun, R.; Ma, Y.; Qiao, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Preparation and Properties of F-Doped PrBa0.8Sr0.2Co2O5+δ Perovskite Cathode Materials. Molecules 2025, 30, 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051140
Li M, Li S, An S, Li N, Sun R, Ma Y, Qiao H, Liu Y, Zhang X. Preparation and Properties of F-Doped PrBa0.8Sr0.2Co2O5+δ Perovskite Cathode Materials. Molecules. 2025; 30(5):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051140
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mengxin, Songbo Li, Shengli An, Ning Li, Runze Sun, Yuanyuan Ma, Hongli Qiao, Yanpeng Liu, and Xu Zhang. 2025. "Preparation and Properties of F-Doped PrBa0.8Sr0.2Co2O5+δ Perovskite Cathode Materials" Molecules 30, no. 5: 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051140
APA StyleLi, M., Li, S., An, S., Li, N., Sun, R., Ma, Y., Qiao, H., Liu, Y., & Zhang, X. (2025). Preparation and Properties of F-Doped PrBa0.8Sr0.2Co2O5+δ Perovskite Cathode Materials. Molecules, 30(5), 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051140






