Synthesis of S- and N,S-Heterocycle–Dipeptide Conjugates for Supramolecular Hydrogel Formation
Abstract
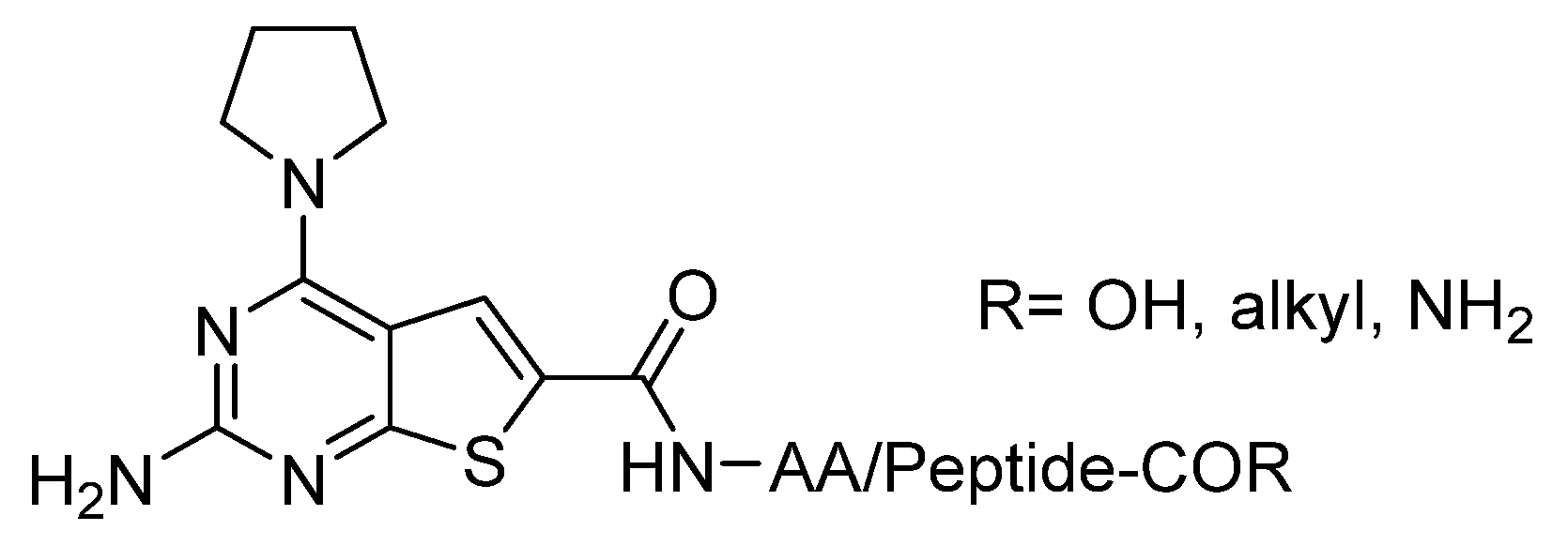
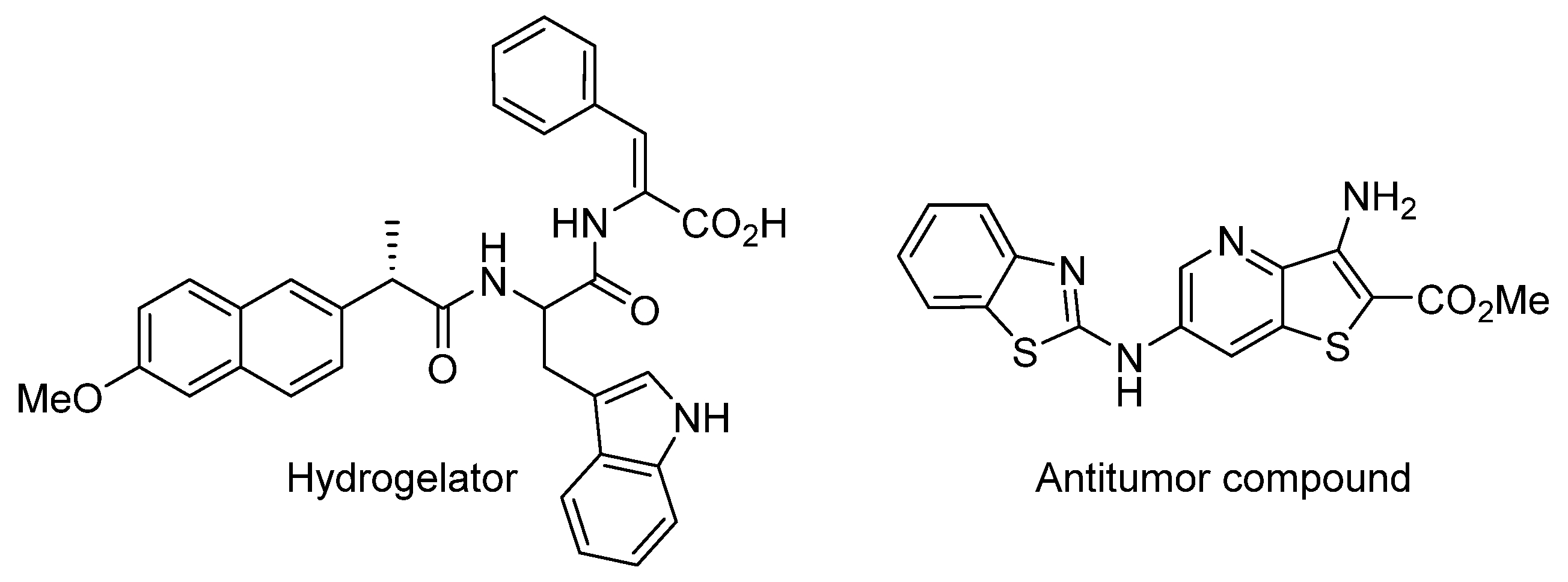
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
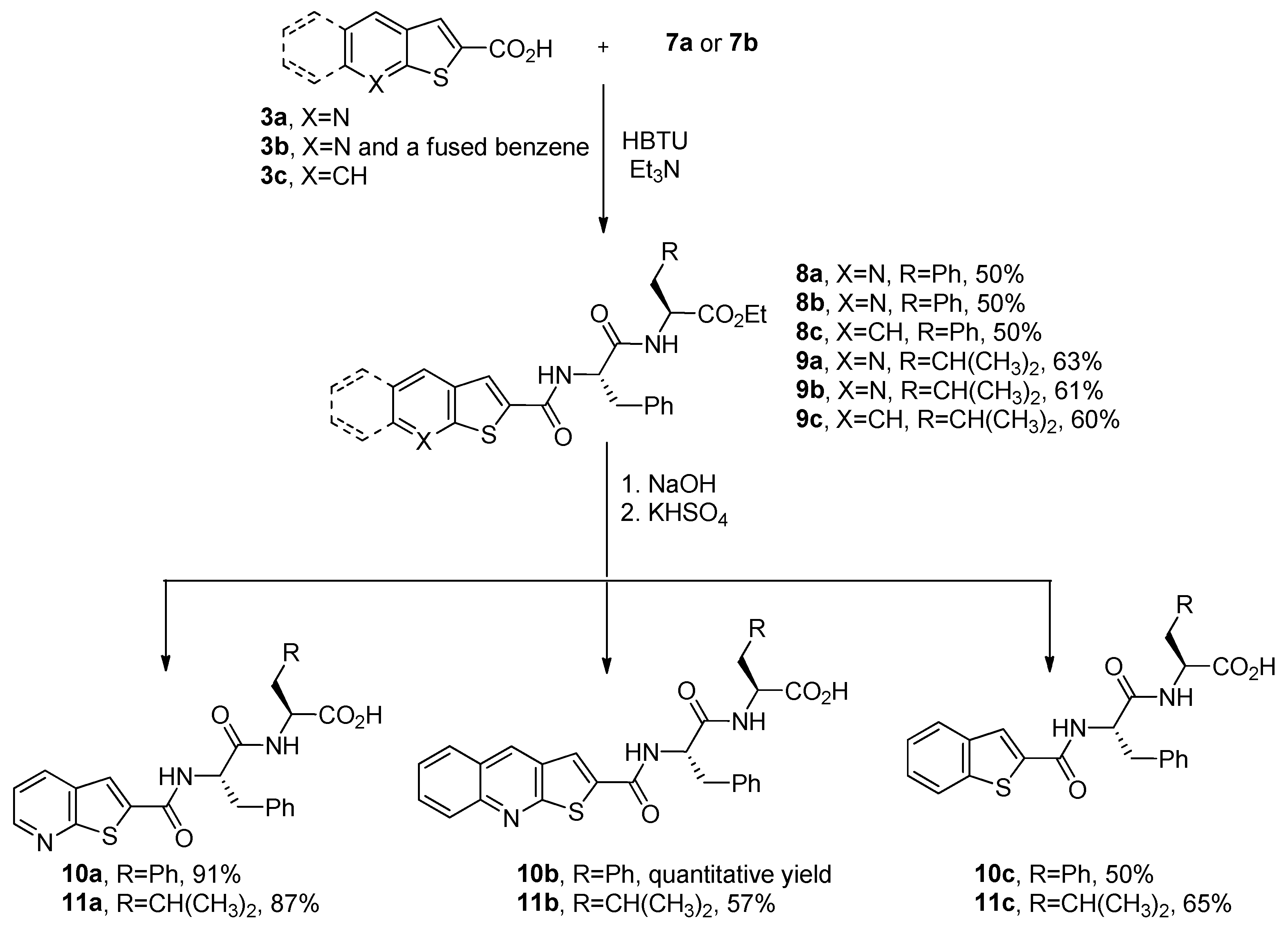
2.1. Synthesis of Dipeptides N-Capped with Benzo[b]Thiophene, Thieno[2,3-b]Pyridine, or Thieno[2,3-b]Quinoline
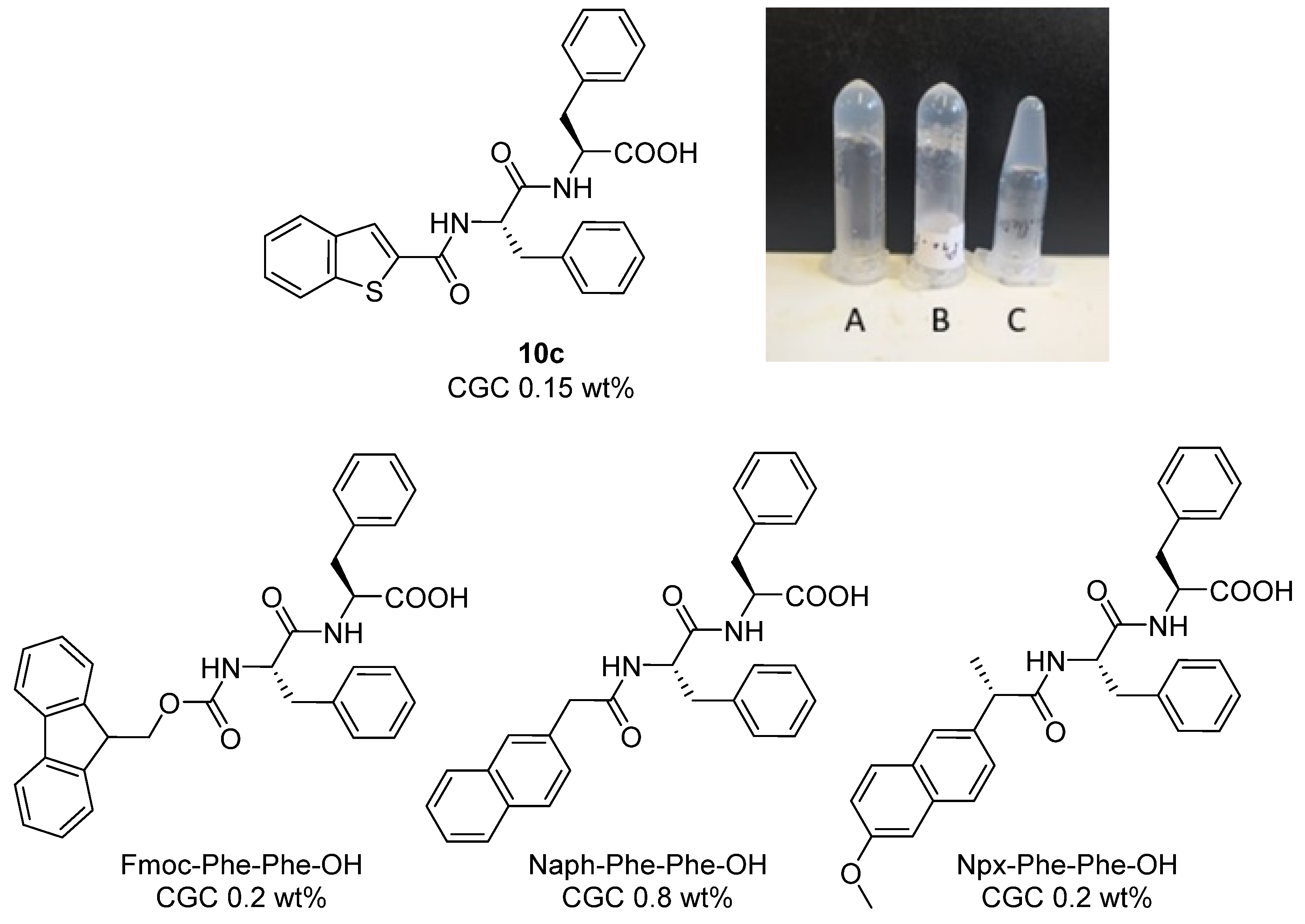
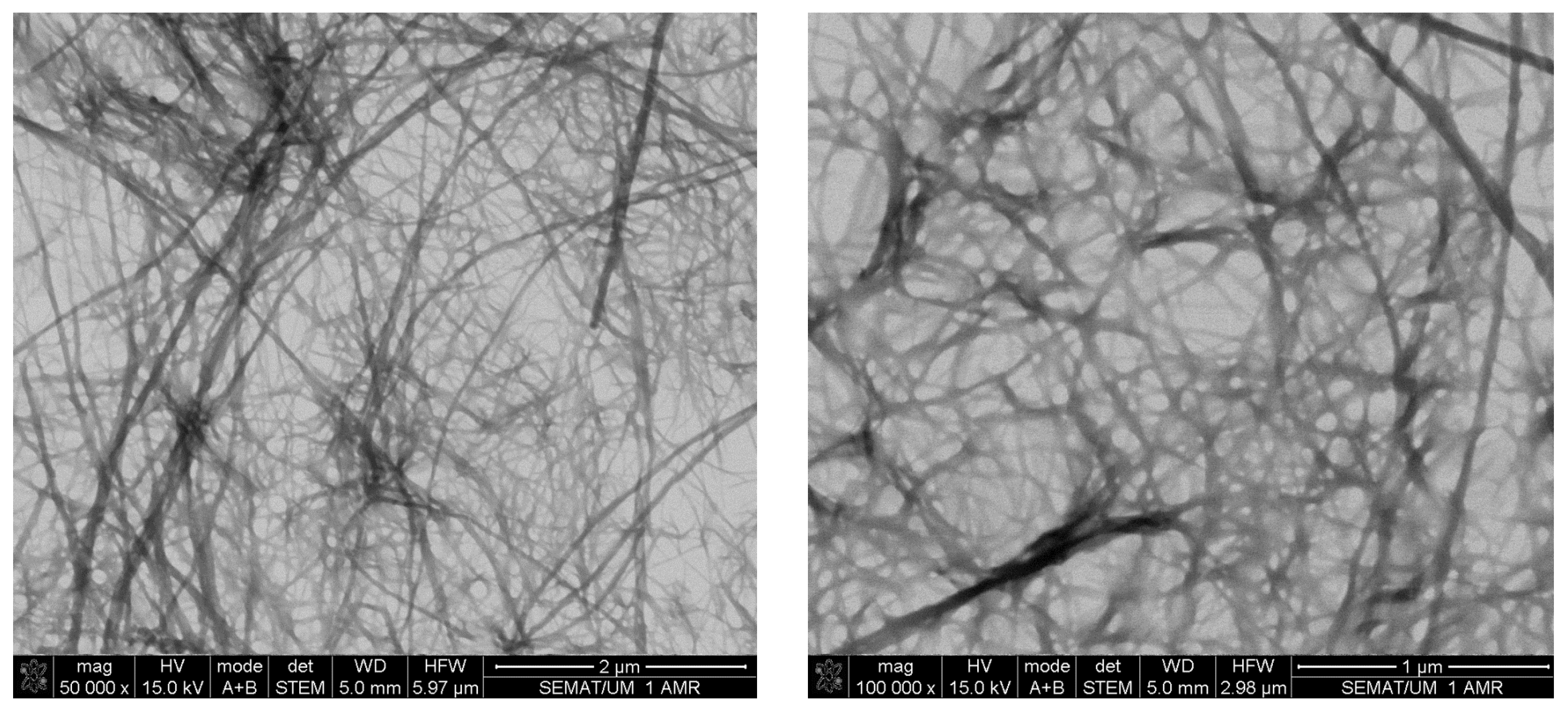
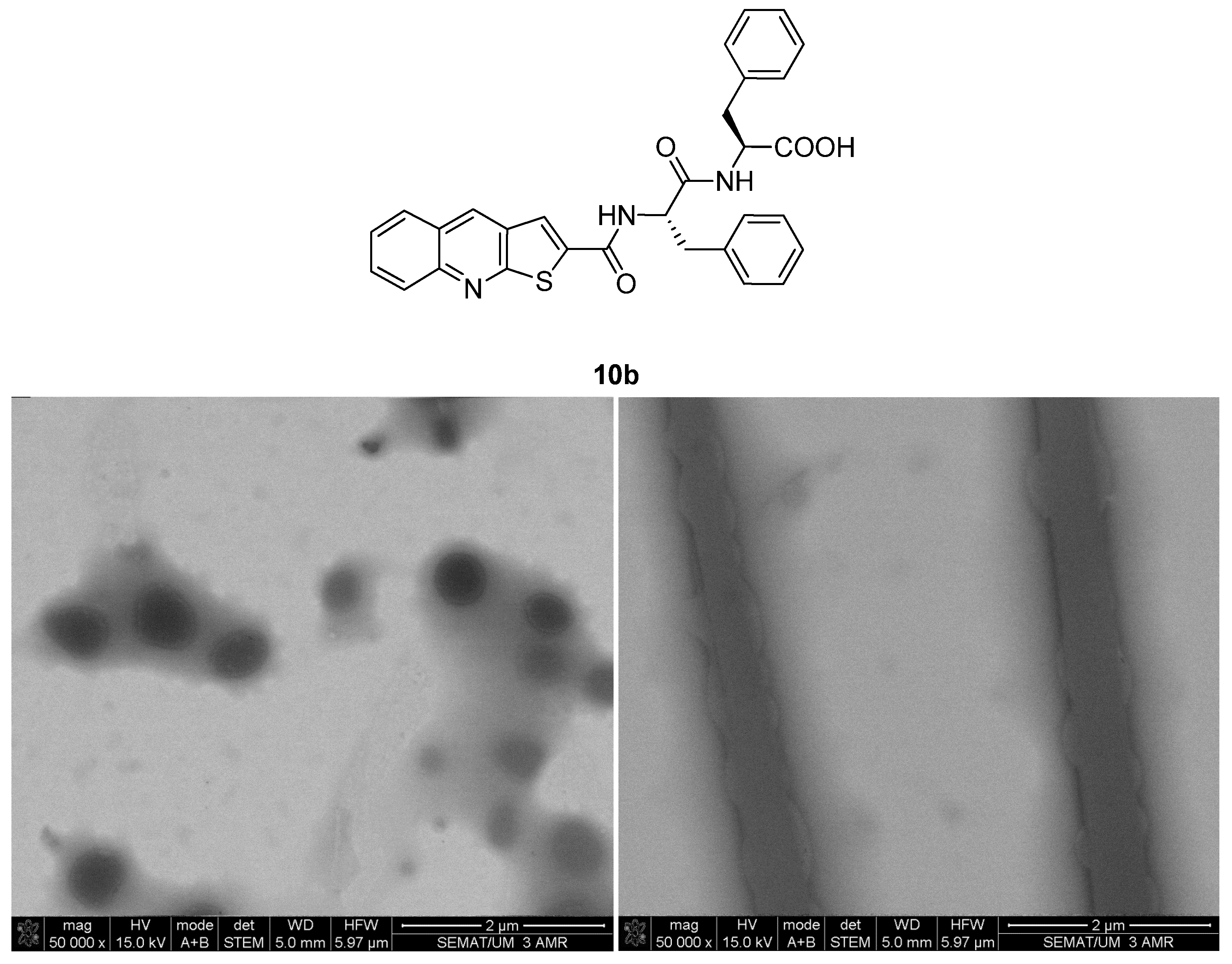
2.2. Hydrogelation
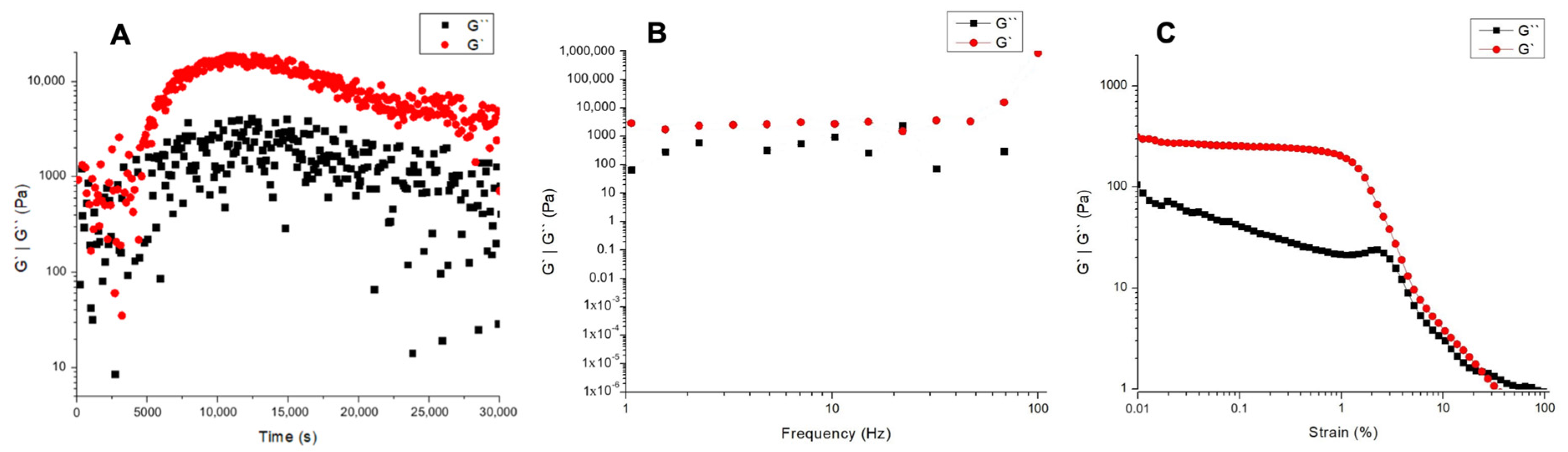
2.3. Rheology
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
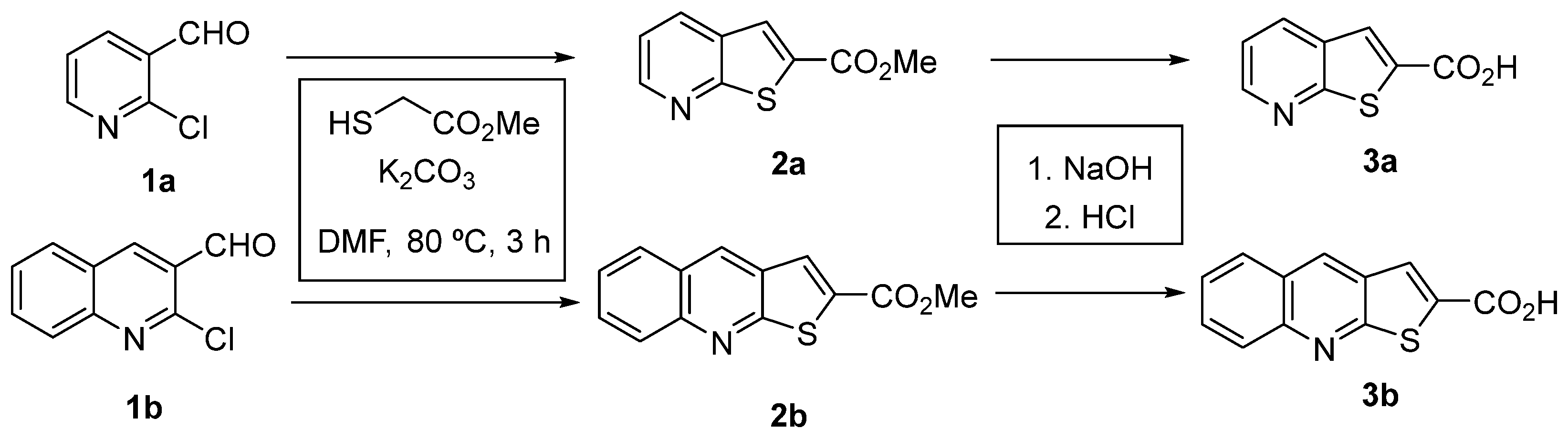
3.1.1. Synthesis of Heterocyclic Precursors
Methyl Thieno[2,3-b]Pyridine-2-Carboxylate (2a)
Methyl Thieno[2,3-b]Quinoline-2-Carboxylate (2b)
Thieno[2,3-b]Pyridine-2-Carboxylic Acid (3a)
Thieno[2,3-b]Quinoline-2-Carboxylic Acid (3b)
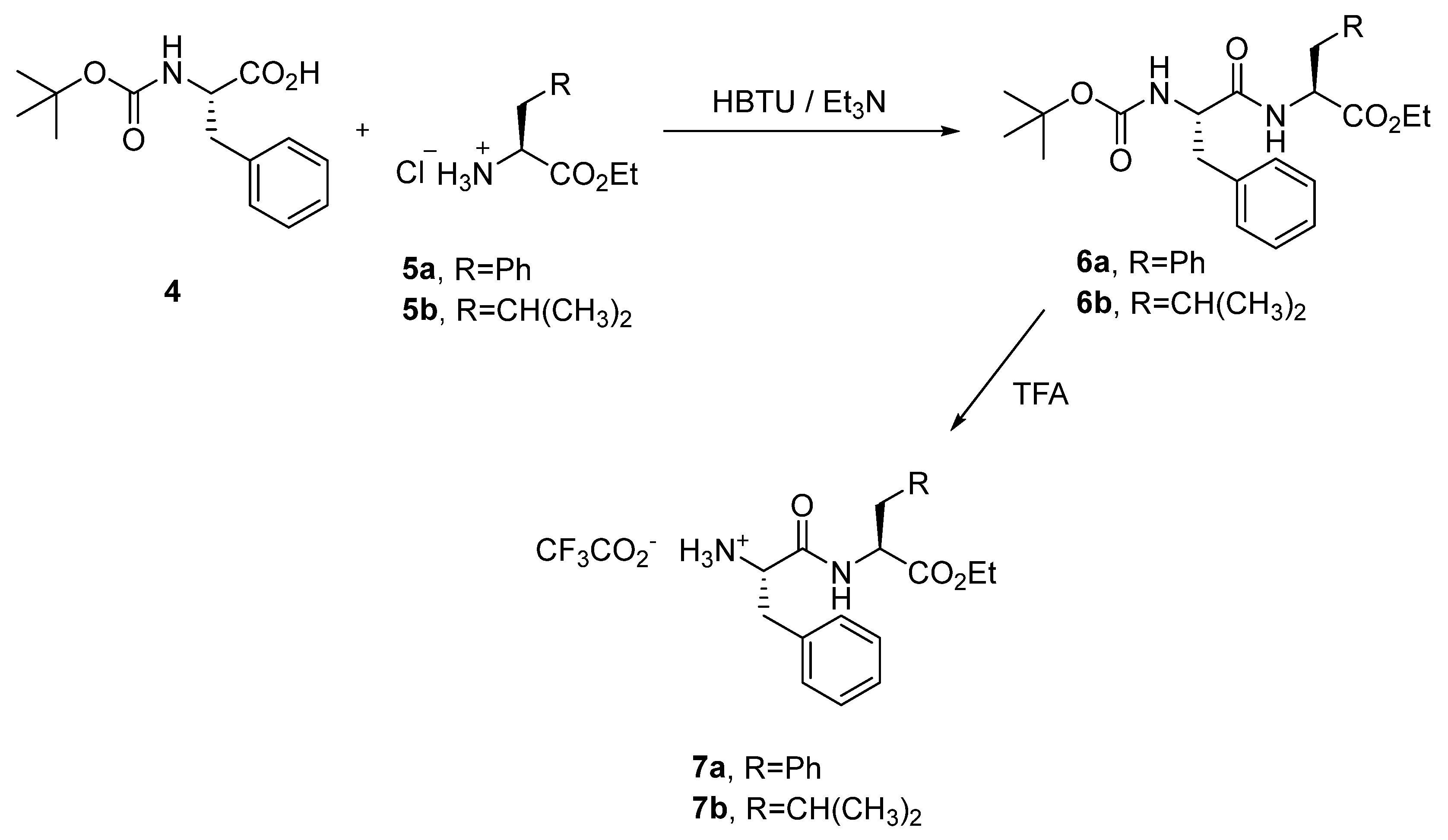
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Ethyl N-(Tert-Butoxicarbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-pheylalaninate (6a) and Ethyl N-(Tert-Butoxicarbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-leucinate (6b)
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Trifluoroacetate Salt of Dipeptides 7a or 7b
3.1.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Ethyl N-Heterocycle Dipeptide Esters 8a–c and 9a–c
Ethyl N-(Thieno[2,3-b]Pyridine-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-phenylalaninate (8a)
Ethyl N-(Thieno[2,3-b]Quinoline-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-phenylalaninate (8b)
Ethyl N-(Benzo[b]Thiophene-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-phenylalaninate (8c)
Ethyl N-(Thieno [2,3-b]Pyridine-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-leucinate (9a)
Ethyl N-(Thieno [2,3-b]Quinoline-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-leucinate (9b)
Ethyl N-(Benzo[b]Thiophene-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-leucinate (9c)
3.1.5. General Procedure for the Ethyl Ester Hydrolysis of Conjugates 8a–c and 9a–c to the Corresponding Carboxylic Acids 10a–c and 11a–c
N-(Thieno[2,3-b]Pyridine-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-phenylalanine (10a)
N-(Thieno[2,3-b]Quinoline-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-phenylalanine (10b)
N-(Benzo[b]Thiophene-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-phenylalanine (10c)
N-(Thieno[2,3-b]Pyridine-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-leucine (11a)
N-(Thieno[2,3-b]Quinoline-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-leucine (11b)
N-(Benzo[b]Thiophene-2-Carbonyl)-l-phenylalanyl-l-leucine (11c)
3.2. Hydrogel Preparation
3.3. Rheology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vigata, M.; Meinert, C.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Bock, N. Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of Current Characterization and Evaluation Techniques. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, J.; Pei, R. Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 14976–14995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiraja, C.; Ning, X.; Cui, M.; Xu, C. Hydrogel-Based Technologies for the Diagnosis of Skin Pathology. Technologies 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Chauhan, M.K.; Chauhan, V.S. Short to Ultrashort Peptide-Based Hydrogels as a Platform for Biomedical Applications. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xing, R.; Bai, S.; Yan, X. Recent Advances of Self-Assembling Peptide-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 1704–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheetham, A.G.; Chakroun, R.W.; Ma, W.; Cui, H. Self-Assembling Prodrugs. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6638–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, S.; Liu, H.; Chen, J. Preparation and Applications of Peptide-Based Injectable Hydrogels. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 28299–28311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.D.; Wojciechowski, J.P.; Warren, H.; In Het Panhuis, M.; Thordarson, P. Effect of Heterocyclic Capping Groups on the Self-Assembly of a Dipeptide Hydrogel. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, S.; Ulijn, R.V. Design of Nanostructures Based on Aromatic Peptide Amphiphiles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8150–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Pang, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhu, X. Supramolecular Hydrogels: Synthesis, Properties and Their Biomedical Applications. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajareh Haghighi, F.; Binaymotlagh, R.; Fratoddi, I.; Chronopoulou, L.; Palocci, C. Peptide-Hydrogel Nanocomposites for Anti-Cancer Drug Delivery. Gels 2023, 9, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abell, A.D. Heterocyclic-based peptidomimetics. Lett. Pept. Sci. 2001, 8, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagner, J.; Qu, H.; Hruby, V.J. Peptidomimetics, a Synthetic Tool of Drug Discovery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissyris, E.E.; Belekos, D.; Magafa, V.; Tsoungas, P.G.; Varvounis, G.; Cordopatis, P. 2-Amino-4-Pyrrolidinothieno[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-6-Carboxylic Acid as an N-Terminal Surrogate in Amino Acid and Peptide Analogues. Synthesis 2005, 18, 3159–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaça, H.; Hortelão, A.C.L.; Castanheira, E.M.S.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Hilliou, L.; Hamley, I.W.; Martins, J.A.; Ferreira, P.M.T. Dehydrodipeptide Hydrogelators Containing Naproxen N-Capped Tryptophan: Self-Assembly, Hydrogel Characterization, and Evaluation as Potential Drug Nanocarriers. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3562–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Calhelha, R.C.; Vale-Silva, L.A.; Pinto, E.; São-José Nascimento, M. Novel 6-[(Hetero)Arylamino]Thieno[3,2-b]Pyridines: Synthesis and Antitumoral Activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5732–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branum, S.T.; Coldburn, R.W.; Dax, S.L.; Flores, C.M.; Jetter, M.C.; Liu, Y.; Ludovici, D.; Macielag, M.J.; Matthews, J.M.; Mcnally, J.J.; et al. Sulfonamides as TRPM8 Modulators. WO 2009/012430A1, 22 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, B.; Bhaduri, A.P. A Novel One-Step Synthesis of 2-Methoxycarbonylthieno[2,3-b]quinolines and 3-Hydroxy-2-Methoxycarbonyl-2,3-Dihydrothieno[2,3-b]quinolines. Synthesis 1984, 1984, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, P.; Nikam, M.; Asrondkar, A.; Bobade, A.; Gill, C. Synthesis, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Evaluation of Novel Thiophene-Fused Quinoline Based β-Diketones and Derivatives. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2017, 54, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeur, E.; Bradley, M. PS-IIDQ: An Efficient Polymer-Supported Amide Coupling Reagent. Chem. Commun. 2005, 9, 1164–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.P.; Singh, N.; Sasselli, I.R.; Escuder, B.; Ulijn, R.V. Metastable Hydrogels from Aromatic Dipeptides. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 13889–13892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, S.; Bellotto, O.; Parisi, E.; Garcia, A.M.; Iglesias, D.; Semeraro, S.; Deganutti, C.; D’Andrea, P.; Vargiu, A.V.; Geremia, S.; et al. Heterochirality and Halogenation Control Phe-Phe Hierarchical Assembly. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16951–16961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Zhou, J.; Shi, J.; Xu, B. Supramolecular Hydrogelators and Hydrogels: From Soft Matter to Molecular Biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13165–13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayawarna, V.; Ali, M.; Jowitt, T.A.; Miller, A.F.; Saiani, A.; Gough, J.E.; Ulijn, R.V. Nanostructured Hydrogels for Three-Dimensional Cell Culture through Self-Assembly of Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-Dipeptides. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Williams, R.J.; Tang, C.; Coppo, P.; Collins, R.F.; Turner, M.L.; Saiani, A.; Ulijn, R.V. Fmoc-Diphenylalanine Self Assembles to a Hydrogel via a Novel Architecture Based on π-π Interlocked β-Sheets. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, A.D.; Martin, A.D.; Iranmanesh, H.; Bhadbhade, M.M.; Beves, J.E.; Thordarson, P. Gel- and Solid-State-Structure of Dialanine and Diphenylalanine Amphiphiles: Importance of C-H Interactions in Gelation. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2019, 20, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kuang, Y.; Shi, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, B. The Conjugation of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAID) to Small Peptides for Generating Multifunctional Supramolecular Nanofibers/Hydrogels. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, A.-M.G.P.; Martins, M.F.; Oliveira, C.B.P.; Martins, J.A.; Ferreira, P.M.T.; Queiroz, M.-J.R.P. Synthesis of S- and N,S-Heterocycle–Dipeptide Conjugates for Supramolecular Hydrogel Formation. Molecules 2025, 30, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040869
Silva A-MGP, Martins MF, Oliveira CBP, Martins JA, Ferreira PMT, Queiroz M-JRP. Synthesis of S- and N,S-Heterocycle–Dipeptide Conjugates for Supramolecular Hydrogel Formation. Molecules. 2025; 30(4):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040869
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Ana-Morgana G. P., Maria F. Martins, Carlos B. P. Oliveira, José A. Martins, Paula M. T. Ferreira, and Maria-João R. P. Queiroz. 2025. "Synthesis of S- and N,S-Heterocycle–Dipeptide Conjugates for Supramolecular Hydrogel Formation" Molecules 30, no. 4: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040869
APA StyleSilva, A.-M. G. P., Martins, M. F., Oliveira, C. B. P., Martins, J. A., Ferreira, P. M. T., & Queiroz, M.-J. R. P. (2025). Synthesis of S- and N,S-Heterocycle–Dipeptide Conjugates for Supramolecular Hydrogel Formation. Molecules, 30(4), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040869






