Designed Reactive Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Propeties of R-NADESs
2.1.1. Thermal and Physical Properties of R-NADES Mixtures
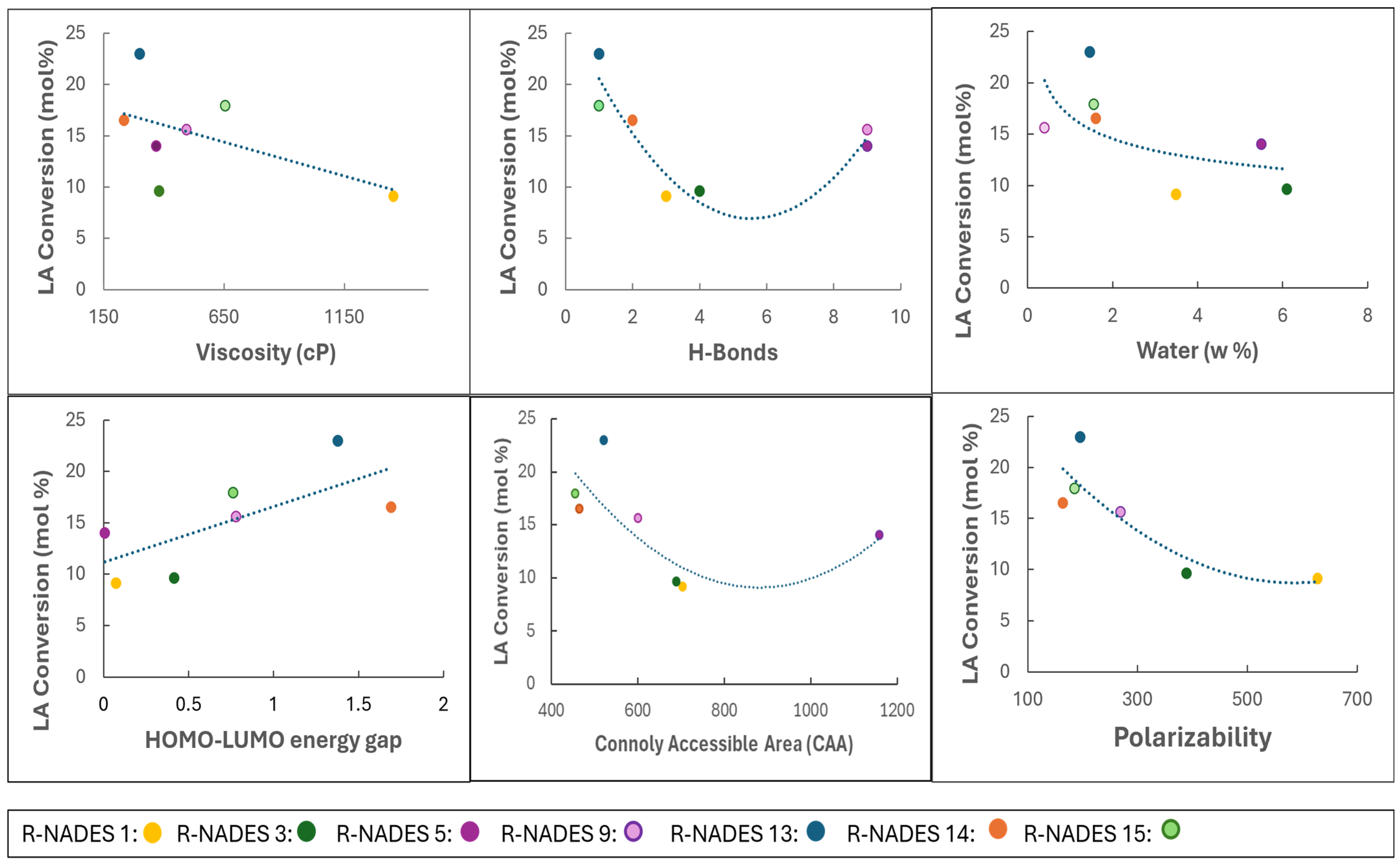
2.1.2. Computational Characterization of R-NADES
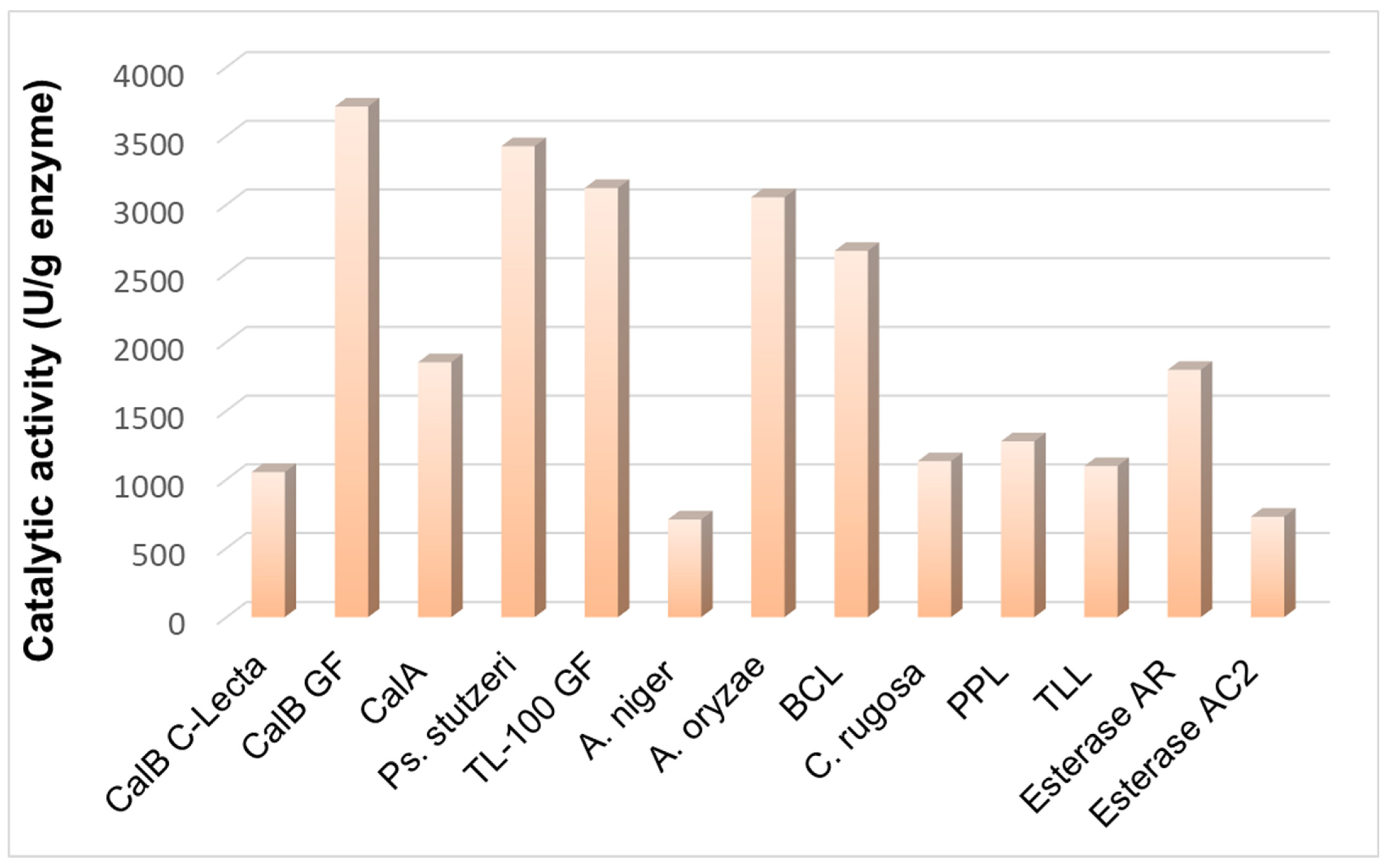
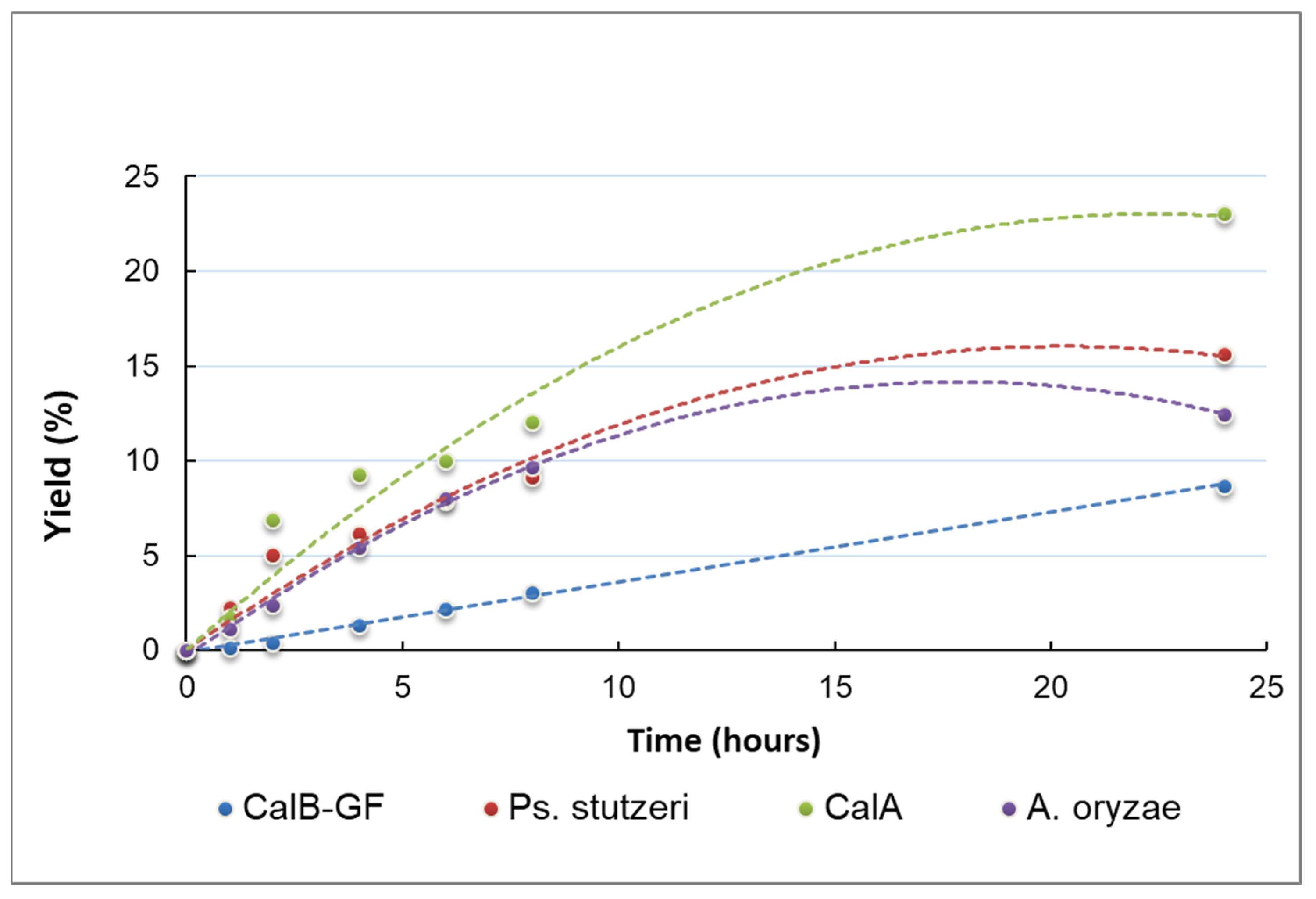
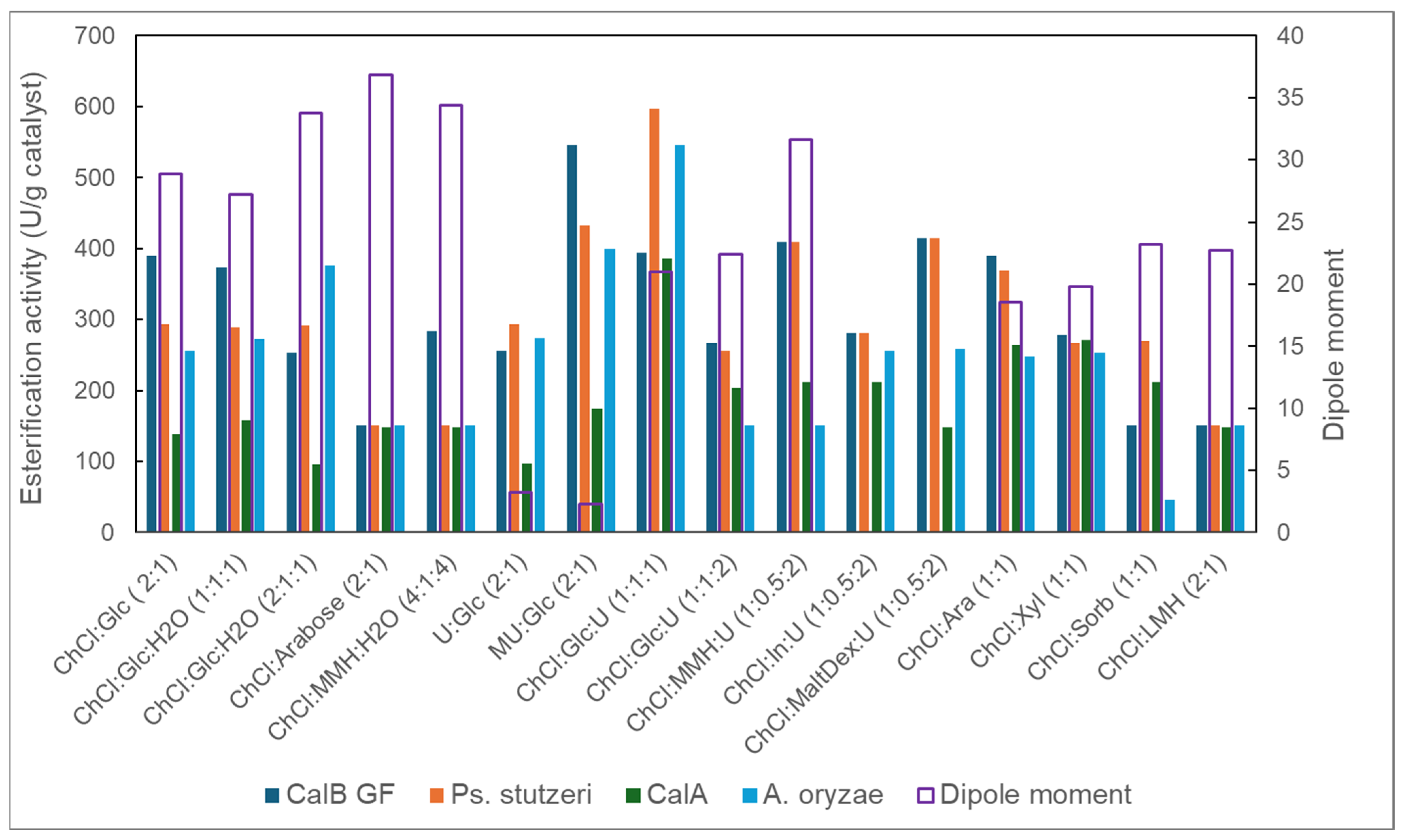
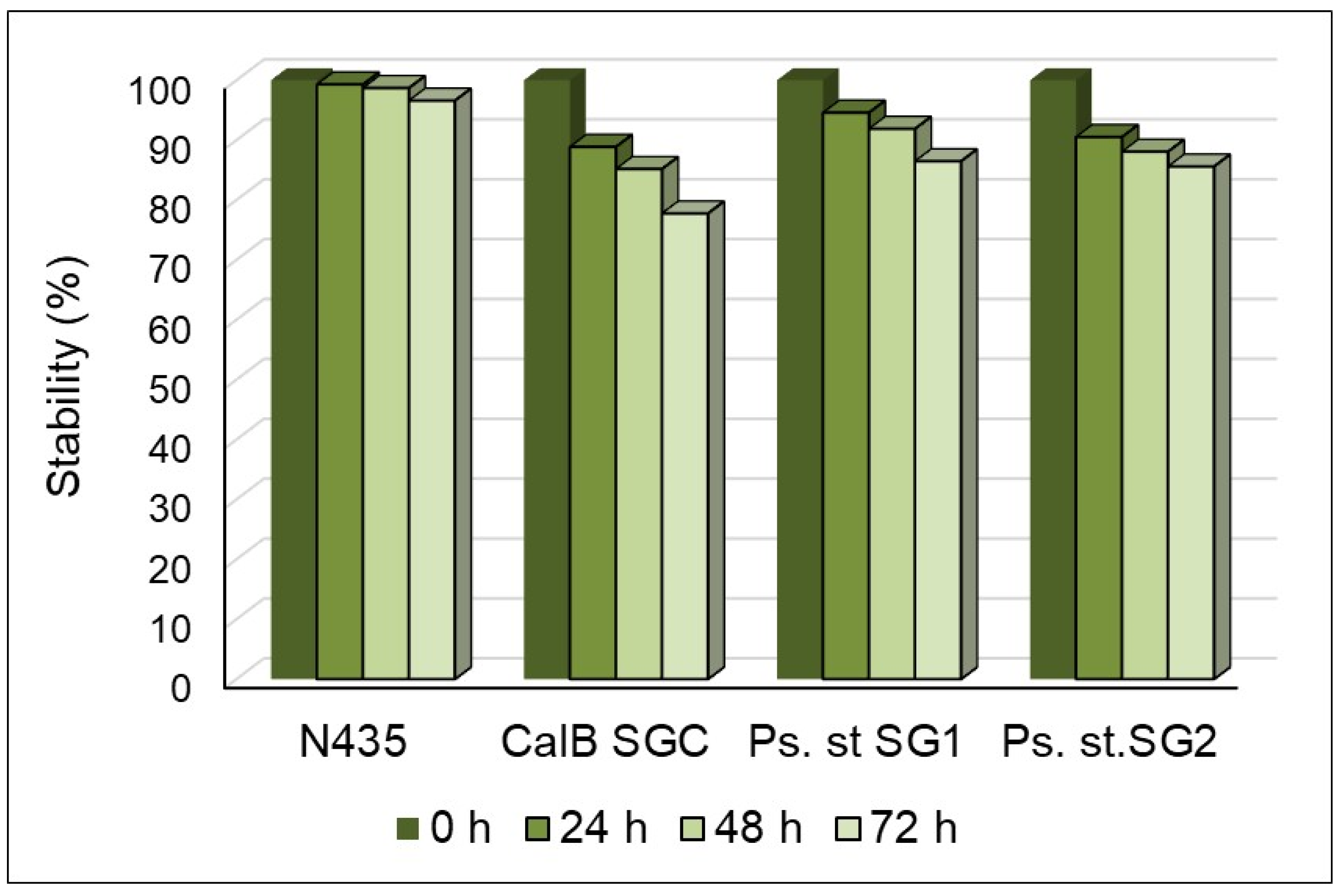
2.2. Evidence for the Performant Use of the R-NADES as a Solvent and Substrate Source for Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification Reactions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Preparation and Characterization of R-NADESs
3.2.2. Computational Details
3.2.3. Determination of the Esterification Activity of Free and Immobilized Enzymes
3.2.4. Lipase Immobilization
3.2.5. Determination of the Thermal Stability of Native and Immobilized Lipases
3.2.6. Synthesis of Lauryl Esters of Polyols and Glucose with Immobilized Lipase in R-NADESs
3.2.7. Characterization of the Esterification Products
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliviera Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jerome, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzouz, A.; Hayyan, M. Are deep eutectic solvents biodegradable? Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 176, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbous, Y.P.; Hayyan, M.; Wong, W.F.; Looi, C.Y.; Hashim, M.A. Unraveling the cytotoxicity and metabolic pathways of binary natural deep eutectic solvent systems. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents—Solvents of the 21st Century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, Z.; Sharma, M.; Tripathi, M.; Lukk, T.; Karpichev, Y.; Gathergood, N.; Singh, B.N.; Thakur, K.V.; Tabatabaei, M.; Gupta, V.K. Biobased natural deep eutectic system as versatile solvents: Structure, interaction, and advanced applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Domínguez de María, P.; Kara, S. Biocatalysis for the Synthesis of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients in Deep Eutectic Solvents: State-of-the-Art and Prospects. Catalysts 2024, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, R.; Hollmann, F.; Maccallini, C. Choline Chloride-Based DES as Solvents/Catalysts/Chemical Donors in Pharmaceutical Synthesis. Molecules 2021, 26, 6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, Ö.; Hollmann, F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as Performance Additives for Biocatalysis. In Eutectic Solvents and Stress in Plants; Verpoorte, R., Witkamp, G.-J., Choi, Y.H., Eds.; Advances in Botanical Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 97, pp. 95–132. [Google Scholar]
- Rente, D.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Panić, M.; Paiva, A.; Caprin, B.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Duarte, A.R.C. Review of deep eutectic systems from laboratory to industry, taking the application in cosmetics industry as an example. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taklimi, S.M.; Divsalar, A.; Ghalandari, B.; Ding, X.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Omar, K.A.; Saboury, A.A. Effects of deep eutectic solvents on the activity and stability of enzymes. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 377, 121562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, A.; Yusupov, M.; Cornet, I.; Billen, P.; Neyts, E.C. Effect of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents of Non-Eutectic Compositions on Enzyme Stability. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 366, 120180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Ali, S.; Li, P.; Zhang, W.; Rauch, M.C.R.; Willot, S.J.-P.; Ribitsch, D.; Choi, Y.H.; Alcalde, M.; et al. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as Performance Additives for Peroxygenase Catalysis. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, L.N.; Perna, R.F.; Vieira, A.C.; de Almeida, A.F.; Ferreira, N.R. Trends in the Use of Lipases: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Foods 2023, 12, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todea, A.; Dreavă, D.M.; Benea, I.C.; Bîtcan, I.; Peter, F.; Boeriu, C.G. Achievements and Trends in Biocatalytic Synthesis of Specialty Polymers from Biomass-Derived Monomers Using Lipases. Processes 2021, 9, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofani, G.; Petri, A.; Piccolo, O. Preparation of enantiomerically pure N -heterocyclic amino alcohols by enzymatic kinetic resolution. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2015, 26, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dhar, K.; Kanwar, S.S.; Arora, P.K. Lipase Catalysis in Organic Solvents: Advantages and Applications. Biol. Proced. Online 2016, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.R.; Silva, A.S.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Ferreira-Leitão, V.S. Solvent-Free Esterifications Mediated by Immobilized Lipases: A Review from Thermodynamic and Kinetic Perspectives. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 5696–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaks, A.; Klibanov, A.M. Enzymatic catalysis in organic media at 100 degrees C. Science 1984, 224, 1249–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Biocatalysis in ionic liquids: State-of-the-union. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 8406–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, S.; Yu, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.J.; Kan, E.; Lee, S.H. Effect of deep eutectic solvent mixtures on lipase activity and stability. J. Mol. Cat. B Enzym. 2016, 128, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.N.; Dou, Y. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Biocatalytic Transformations: Focused Lipase-Catalyzed Organic Reactions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1481–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Synthesis, Application, and Focus on Lipase-Catalyzed Reactions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2013, 115, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arıkaya, A.; Ünlü, A.E.; Takaç, S. Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Enzyme Catalysed Production of Ethyl Lactate. Process Biochem. 2019, 84, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craveiro, R.; Meneses, L.; Durazzo, L.; Rocha, Â.; Silva, J.M.; Reis, R.L.; Barreiros, S.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Paiva, A. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Enzymatic Esterification of Racemic Menthol. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 19943–19950. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Suo, H.; Zhang, G.; Xu, P.; Gao, X.; Du, S. Ultrasound-assisted enzymatic preparation of fatty acid ethyl ester in deep eutectic solvent. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, B.; Cao, C.; Liu, Y. Lipase and Metal Chloride Hydrate-Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Synergistically Catalyze Amidation Reaction via Multiple Noncovalent Bond Interactions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18174–18184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noro, J.; Cabo, J.; Freitas, D.S.; Roque, C.S.; de Castro, M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Silva, C. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Suitable Solvents for Lipase-Catalyzed Transesterification Reactions. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202300615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Wu, R.; Zhu, F.; Dong, Q.; Su, E. Enzymes in Nearly Anhydrous deep eutectic solvents: Insight into de biocompatibility and thermal stability. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 1571, 10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wu, R.; Zhu, F.; Dong, Q.; Su, E. How to improve the efficiency of biocatalysis in non-aqueous pure deep eutectic solvents: A case study on the lipase-catalyzed transesterification reaction. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 179, 108336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzatu, A.R.; Soler, M.A.; Fortuna, S.; Ozkilinc, O.; Dreavă, D.M.; Bîtcan, I.; Badea, V.; Giannozzi, P.; Fogolari, F.; Peter, P.; et al. Reactive natural deep eutectic solvents as essential reaction media for lipase catalyzed esterification of carbohydrate polyols. Catal. Today 2024, 426, 114373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenbach, R.; Ochsenreither, K.; Syldatk, C. Enzymatic synthesis of glucose monodecanoate in a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollenbach, R.; Bindereif, B.; van der Schaaf, U.S.; Ochsenreither, K.; Syldatk, C. Optimization of Glycolipid Synthesis in Hydrophilic Deep Eutectic Solvents. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzatu, A.R.; Todea, A.; Peter, F.; Boeriu, C.G. The Role of Reactive Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in Sustainable Biocatalysis. ChemCatChem 2024, 16, e202301597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgharbawy, A.A.; Hayyan, A.; Hayyan, M.; Rashid, S.N.; Nor, M.R.M.; Zulkifli, M.Y.; Alias, Y.; Mirghani, M.E.S. Shedding light on lipase stability in natural deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Biochem. Eng. 2018, 32, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos, L.V.; Ramírez, L.; Yarce, C.J.; Alvarez-Vasco, C.; Ortega, N.H.C. Sustainable production of glycolipids by biocatalyst on renewable deep eutectic solvents. Catalysts 2021, 11, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.; Gupta, M.N. Lipase promiscuity and its biochemical applications. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzatu, A.R.; Soler, M.A.; Ozkilinc, O.; Fortuna, S.; Dreavă, D.M.; Bîtcan, I.; Giannozzi, P.; Fogolari, F.; Gardossi, L.; Peter, F.; et al. Lipase-Catalysed Esterification in a Reactive Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent Leads to Lauroylcholine Chloride Rather than Glucose Ester. React. Chem. Eng. 2024, 9, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroso, I.M.; Paiva, A.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural deep eutectic solvents from choline chloride and betaine. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lenthe, E.; Baerends, E.J. Optimized Slater-type basis sets for the elements 1-118. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Te Velde, G.; Bickelhaupt, F.M.; Baerends, E.J.; Fonseca Guerra, C.; van Gisbergen, S.J.A.; Snijders, J.G.; Ziegler, T. Chemistry with ADF. J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 931–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gisbergen, S.J.A.; Snijders, J.G.; Baerends, E.J. Implementation of time-dependent density functional response equations. Comp. Phys. Commun. 1999, 118, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gisbergen, S.J.A.; Snijders, J.G.; Baerends, E.J. A Density Functional Theory study of frequency-dependent polarizabilities and van der Waals dispersion coefficients for polyatomic molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 9347–9354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.; Borza, P.; Marcu, A.; Rusu, G.; Bîrdeanu, M.; Marc Zarcula, S.; Peter, F. Influence of the physico-chemical characteristics of the hybrid matrix on the catalytic properties of sol-gel entrapped Pseudomonas fluorescens lipase. Nanomat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recker, E.A.; Hardy, D.; Anderson, G.I.; Mirjafari, A.; Wagle, D.V. Covalently linked hydrogen bond donors: The other side of molecular frustration in DES. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 155, 084502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.J.; McDaniel, J.G.; Yethiraj, A. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Molecular Simulations with First-Principles Polarizable Force Field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 7177–7186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semproli, R.; Chanquia, S.N.; Bittner, J.P.; Müller, S.; Domingues de Maria, P.; Kara, S.; Ubiali, D. Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Enzymatic Synthesis of Sugar Esters: A Generalizable Strategy? ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 5926–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

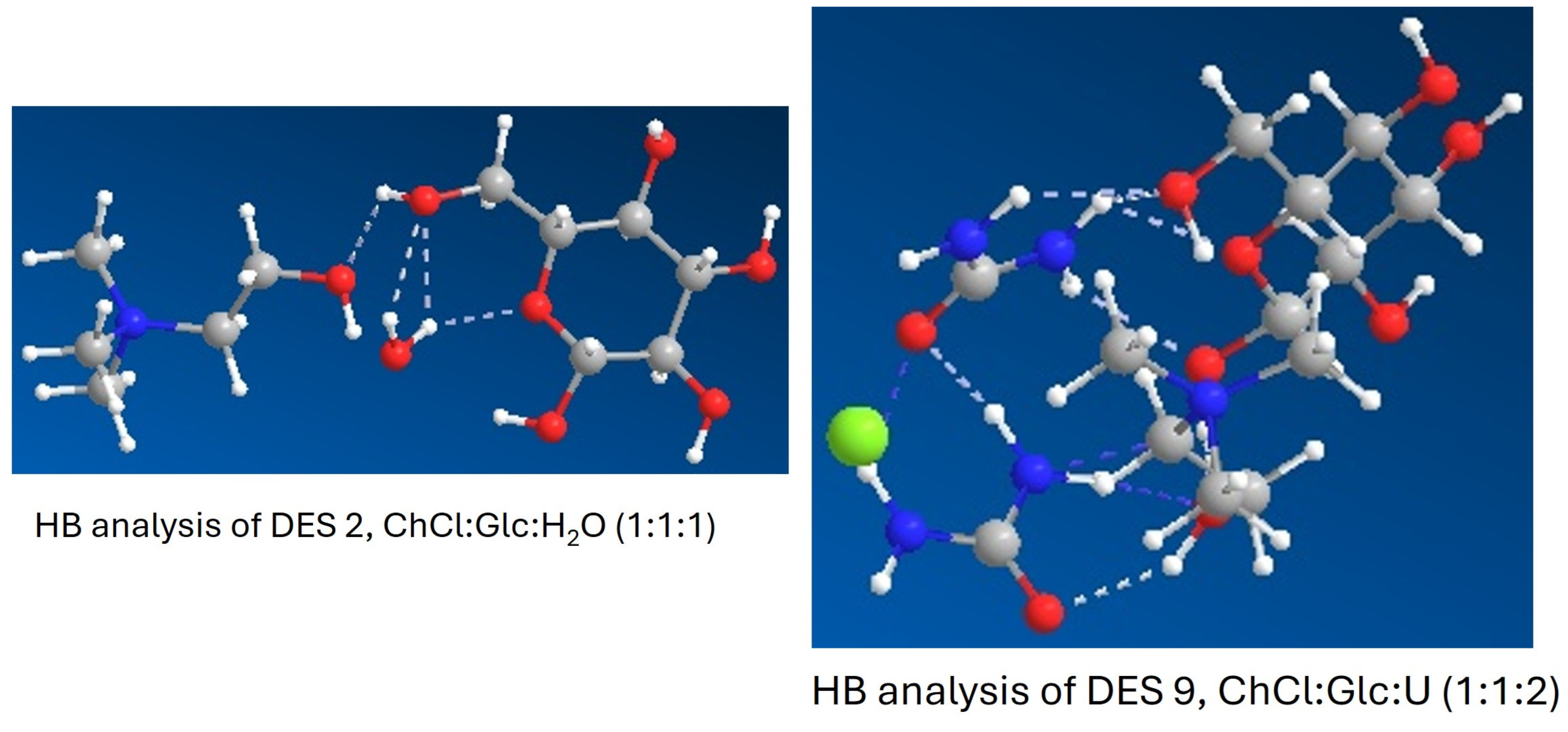

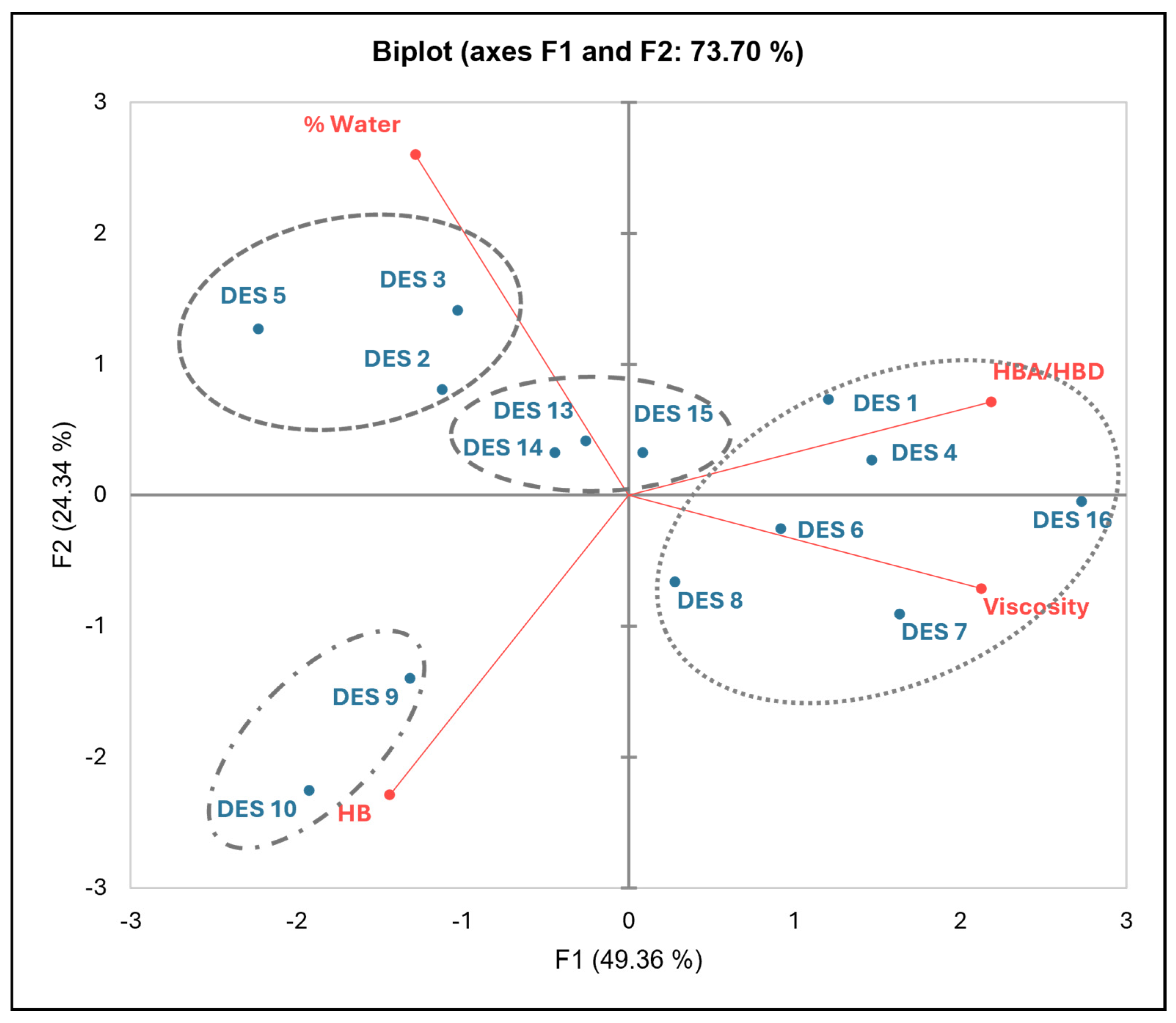



| R-NADES | TGA | DSC | Viscosity at 70 °C (cP) | HBA/HBD # | H-Bonds (HBs) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Composition | Water Loss (w%) | Tonset (°C) | Tm (°C) | Tg (°C) | (mol/mol) | ||
| 1 | ChCl:Glc (2:1) | 3.5 | 196 | 76.8 | −52.3 | 1354 | 2 | 3 |
| 2 | ChCl:Glc:H2O (1:1:1) | 5.5 | 190 | * n.o. | −44.5 | 767.5 | 0.5 | 4 |
| 3 | ChCl:Glc:H2O (2:1:1) | 6.08 | 195 | 8.7, 73.7 | −22 | 382 | 1 | 3 |
| 4 | ChCl:Arabose (2:1) | 1.46 | 195 | 79.3 | −20 | 1183 | 2 | 2 |
| 5 | ChCl:MMH:H2O (4:1:4) | 5.46 | 212 | 60.5 | * n.o. | 370 | 0.8 | 9 |
| 6 | U:Glc (2:1) | 0.86 | 142 | 89.4 | −0.3 | 845 | 2 | 5 |
| 7 | MU:Glc (2:1) | 0.72 | 141 | 62.4 | −0.4 | 1730 | 2 | 7 |
| 8 | ChCl:Glc:U (1:1:1) | 0.58 | 150 | * n.o. | −27.5 | 1370 | 0.5 | 3 |
| 9 | ChCl:Glc:U (1:1:2) | 0.40 | 145 | * n.o. | −28.5 | 495 | 0.33 | 9 |
| 10 | ChCl:MMH:U (1:0.5:2) | 1.28 | 153 | * n.o. | −51.5 | 627.5 | 0.4 | 16 |
| 11 | ChCl:In:U (1:0.5:2) | 1.73 | 153 | * n.o. | −51.5 | 350 | 0.4 | ^ n.d. |
| 12 | ChCl:MaltDex:U (1:0.5:2) | 1.80 | 150 | * n.o. | −51.5 | 487.5 | 0.4 | ^ n.d. |
| 13 | ChCl:D-Ara (1:1) | 1.46 | 276.6 | 50.2 | −62.1 | 300 | 1 | 1 |
| 14 | ChCl:Xyl (1:1) | 1.61 | 277.5 | 29.4 | −58.6 | 235 | 1 | 2 |
| 15 | ChCl:D-Sorb (1:1) | 1.56 | 278 | 44.2 | −55.7 | 655 | 1 | 1 |
| 16 | ChCl:LMH (2:1) | 1.14 | 245 | 61, 77.8, 145 | * n.o. | 2300 | 2 | 1 |
| R-NADES | E HOMO (H) | E LUMO (H) | HL Gap (eV) | Steric Parameters | Polarizability (a.u.) | Dipole Moment (D) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nr. | Composition | CAA (Å2) | CSEV (Å3) | |||||
| 1 | ChCl:Glc (2:1) | −0.0825 | −0.0798 | 0.073 | 703.831 | 489.463 | 627.690 | 28.903 |
| 2 | ChCl:Glc:H2O (1:1:1) | −0.1109 | −0.0858 | 0.682 | 578.348 | 316.263 | 192.431 | 27.248 |
| 3 | ChCl:Glc:H2O (2:1:1) | −0.1064 | −0.0911 | 0.416 | 689.734 | 488.310 | 389.509 | 33.830 |
| 4 | ChCl:Arabose (2:1) | −0.0954 | −0.0946 | 0.021 | 663.381 | 452.222 | 420.004 | 36.802 |
| 5 | ChCl:MMH:H2O (4:1:4) | −0.0855 | −0.0852 | 0.008 | 1160.43 | 1100.00 | * | 34.357 |
| 6 | U:Glc (2:1) | −0.2141 | −0.0320 | 4.953 | 484.641 | 246.967 | 168.796 | 3.204 |
| 7 | MU:Glc (2:1) | −0.1938 | −0.0275 | 4.523 | 532.677 | 288.432 | 181.260 | 2.254 |
| 8 | ChCl:Glc:U (1:1:1) | −0.1003 | −0.0774 | 0.622 | 640.500 | 358.293 | 256.863 | 21.018 |
| 9 | ChCl:Glc:U (1:1:2) | −0.1121 | −0.0834 | 0.781 | 600.765 | 419.292 | 269.003 | 22.417 |
| 10 | ChCl:MMH:U (1:0.5:2) | −0.1314 | −0.0857 | 1.243 | 957.111 | 869.306 | * | 31.588 |
| 13 | ChCl:D-Ara (1:1) | −0.1311 | −0.0804 | 1.379 | 521.383 | 288.194 | 195.500 | 18.497 |
| 14 | ChCl:Xyl (1:1) | −0.1352 | −0.0730 | 1.692 | 465.509 | 180.247 | 164.222 | 19.817 |
| 15 | ChCl:D-Sorb (1:1) | −0.1168 | −0.0888 | 0.762 | 455.295 | 214.224 | 185.314 | 23.195 |
| 16 | ChCl:LMH (2:1) | −0.1128 | −0.0817 | 0.846 | 657.739 | 458.275 | 288.993 | 22.689 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buzatu, A.R.; Todea, A.; Pop, R.; Dreavă, D.M.; Paul, C.; Bîtcan, I.; Motoc, M.; Peter, F.; Boeriu, C.G. Designed Reactive Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification. Molecules 2025, 30, 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040778
Buzatu AR, Todea A, Pop R, Dreavă DM, Paul C, Bîtcan I, Motoc M, Peter F, Boeriu CG. Designed Reactive Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification. Molecules. 2025; 30(4):778. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040778
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuzatu, Alina Ramona, Anamaria Todea, Raluca Pop, Diana Maria Dreavă, Cristina Paul, Ioan Bîtcan, Marilena Motoc, Francisc Peter, and Carmen Gabriela Boeriu. 2025. "Designed Reactive Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification" Molecules 30, no. 4: 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040778
APA StyleBuzatu, A. R., Todea, A., Pop, R., Dreavă, D. M., Paul, C., Bîtcan, I., Motoc, M., Peter, F., & Boeriu, C. G. (2025). Designed Reactive Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification. Molecules, 30(4), 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040778









