Groomed Fingerprint Sebum Sampling: Reproducibility and Variability According to Anatomical Collection Region and Biological Sex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
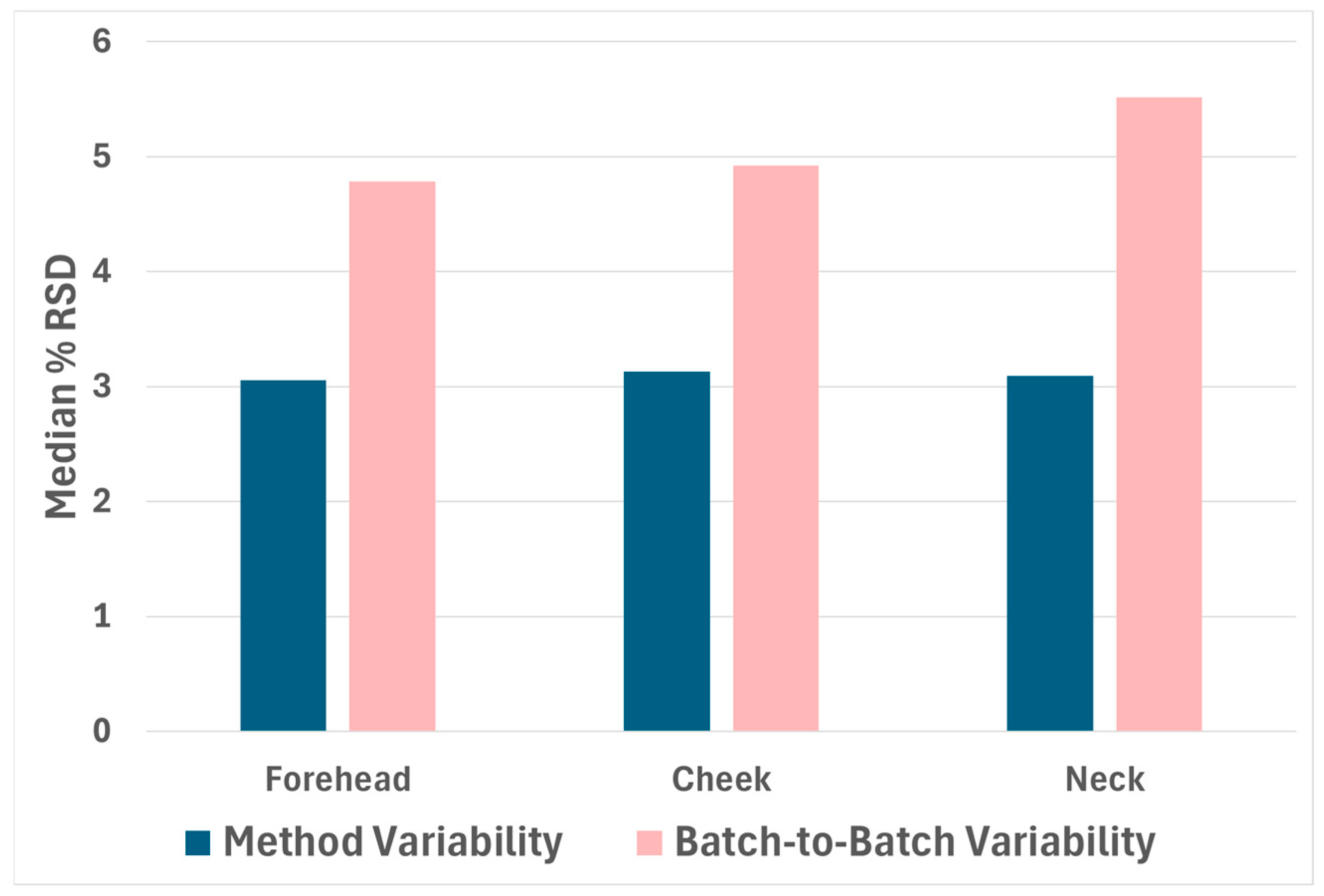
2.1. Reproducibility
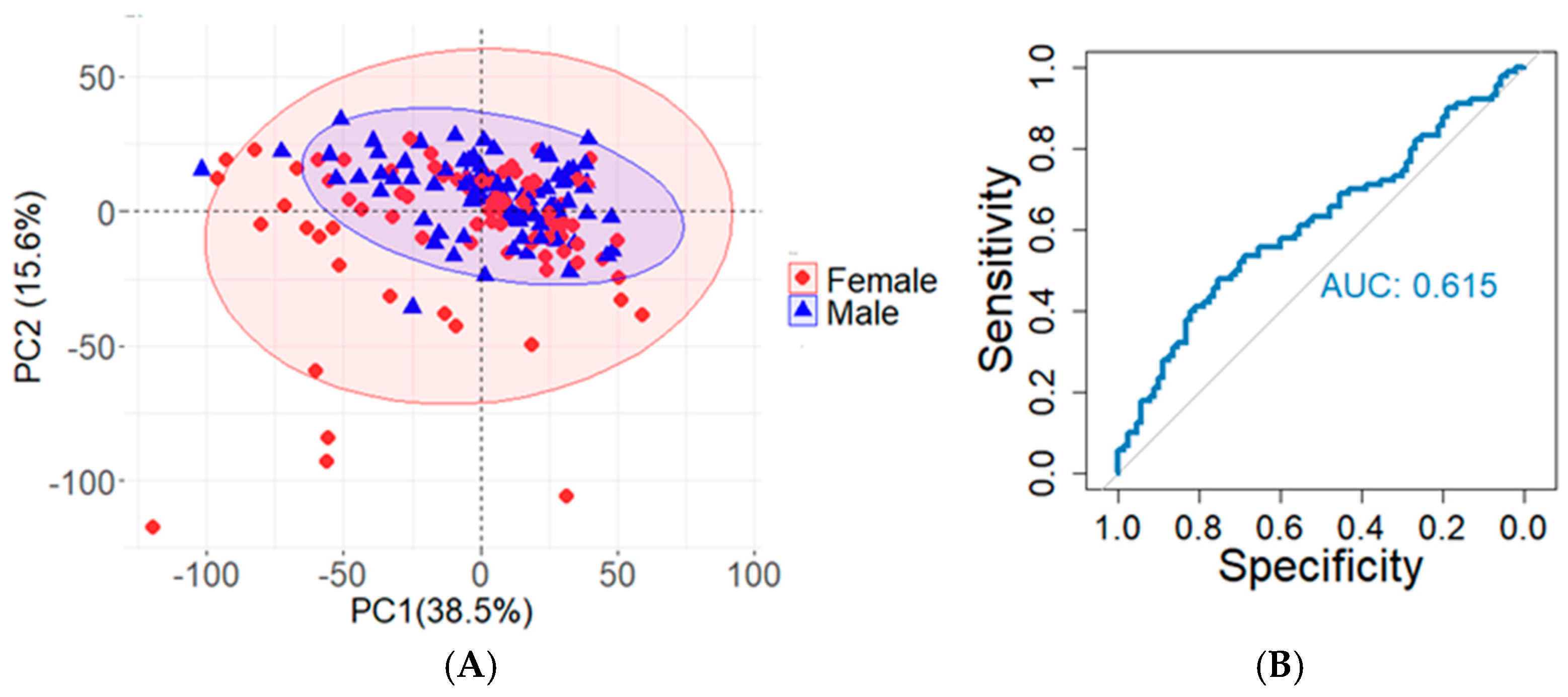
2.2. Sex-Based Differences
2.3. Anatomical Region Variability
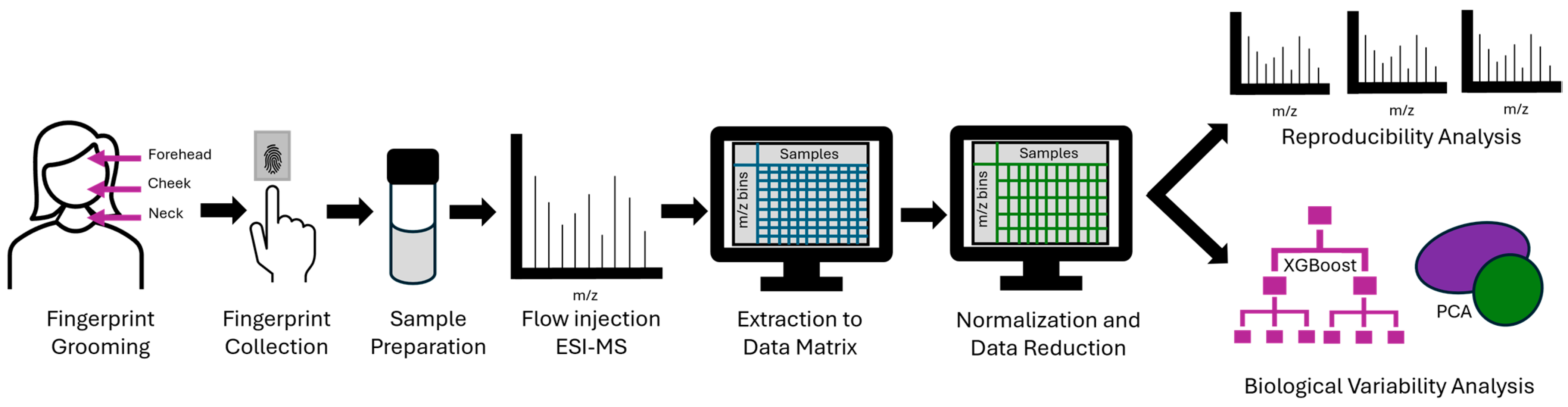
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Flow Injection ESI-MS
3.4. Data Processing
3.5. Data Analysis: Sample Reproducibility
3.6. Data Analysis: Sample Variability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Isom, M.; Desaire, H. Skin Surface Sebum Analysis by ESI-MS. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xia, Y. Shotgun Lipidomic Profiling of Sebum Lipids via Photocatalyzed Paternò-Büchi Reaction and Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 5589–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, S.; O’Boyle, N.M. Skin lipids in health and disease: A review. Chem. Phys. Lip. 2021, 236, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxton, R.S.; Baron, M.G.; Butler, D.; Kent, T.; Sears, V.G. Variation in amino acid and lipid composition of latent fingerprints. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 199, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, E.; Trivedi, D.K.; Sarkar, D.; Walton-Doyle, C.; Milne, J.; Kunath, T.; Rijs, A.M.; de Bie, R.M.A.; Goodacre, R.; Silverdale, M.; et al. Metabolomics of sebum reveals lipid dysregulation in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, S.; Truglio, M.; Angiolillo, A.; Lombardo, S.; Leccese, D.; Camera, E.; Picardo, M.; Di Costanzo, A. Application of Sebum Lipidomics to Biomarkers Discovery in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Metabolites 2021, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Sinclair, E.; Lim, S.H.; Walton-Doyle, C.; Jafri, K.; Milne, J.; Vissers, J.P.C.; Richardson, K.; Trivedi, D.K.; Silverdale, M.; et al. Paper Spray Ionization Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry of Sebum Classifies Biomarker Classes for the Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease. JACS Au 2022, 2, 2013–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spick, M.; Lewis, H.M.; Frampas, C.F.; Longman, K.; Costa, C.; Stewart, A.; Dunn-Walters, D.; Greener, D.; Evetts, G.; Wilde, M.J.; et al. An integrated analysis and comparison of serum, saliva and sebum for COVID-19 metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spick, M.; Longman, K.; Frampas, C.; Lewis, H.; Costa, C.; Walters, D.D.; Stewart, A.; Wilde, M.; Greener, D.; Evetts, G.; et al. Changes to the sebum lipidome upon COVID-19 infection observed via rapid sampling from the skin. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 33, 100786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Qiu, Z.; Zhu, R.; Wang, S.; Gu, C.; Yao, X.; Li, W. Dysregulated lipidome of sebum in patients with atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2023, 78, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallo, A.; Camera, E.; Bottillo, G.; Maiellaro, M.; Truglio, M.; Marini, F.; Chavagnac-Bonneville, M.; Fauger, A.; Perrier, E.; Pigliacelli, F.; et al. Biosignatures of defective sebaceous gland activity in sebum-rich and sebum-poor skin areas in adult atopic dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e15066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetage, S.S.; Traynor, M.J.; Brown, M.B.; Galliford, T.M.; Chilcott, R.P. Application of sebomics for the analysis of residual skin surface components to detect potential biomarkers of type-1 diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Géhin, C.; Tokarska, J.; Fowler, S.J.; Barran, P.E.; Trivedi, D.K. No skin off your back: The sampling and extraction of sebum for metabolomics. Metabolomics 2023, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shores, D.R.; Everett, A.D. Children as Biomarker Orphans: Progress in the Field of Pediatric Biomarkers. J. Pediatr. 2018, 193, 14–20.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedrak, M.S.; Freedman, R.A.; Cohen, H.J.; Muss, H.B.; Jatoi, A.; Klepin, H.D.; Wildes, T.M.; Le-Rademacher, J.G.; Kimmick, G.G.; Tew, W.P.; et al. Older adult participation in cancer clinical trials: A systematic review of barriers and interventions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ní Raghallaigh, S.; Bender, K.; Lacey, N.; Brennan, L.; Powell, F.C. The fatty acid profile of the skin surface lipid layer in papulopustular rosacea. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, K.; Hassoun, L.A.; Foolad, N.; Borkowski, K.; Pedersen, T.L.; Sivamani, R.K.; Newman, J.W. Effects of atopic dermatitis and gender on sebum lipid mediator and fatty acid profiles. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2018, 134, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zare, R.N. Personal Information from Latent Fingerprints Using Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry and Machine Learning. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1369–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, K.C.; Hinners, P.; Jin Lee, Y. Potential of triacylglycerol profiles in latent fingerprints to reveal individual diet, exercise, or health information for forensic evidence. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleik, S.; Spengler, B.; Ram Bhandari, D.; Luhn, S.; Schäfer, T.; Urbach, D.; Kirsch, D. Ambient-air ozonolysis of triglycerides in aged fingerprint residues. Analyst 2018, 143, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girod, A.; Weyermann, C. Lipid composition of fingermark residue and donor classification using GC/MS. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 238, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleik, S.; Spengler, B.; Schäfer, T.; Urbach, D.; Luhn, S.; Kirsch, D. Fatty Acid Structure and Degradation Analysis in Fingerprint Residues. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 27, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, N.E.; Charles, Y.; Elliott, J.A.; Jickells, S. Changes in the lipid composition of latent fingerprint residue with time after deposition on a surface. Forensic Sci. Int. 2005, 154, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolstenholme, R.; Bradshaw, R.; Clench, M.R.; Francese, S. Study of latent fingermarks by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometry imaging of endogenous lipids. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 3031–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlo, A.B.M.; Roux, C.; Bécue, A.; Weyermann, C. A comparison of the natural and groomed fingermark lipid composition of different donors using GC/MS. Forensic Sci. Int. 2023, 348, 111709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girod, A.; Ramotowski, R.; Weyermann, C. Composition of fingermark residue: A qualitative and quantitative review. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 223, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetage, S.S.; Traynor, M.J.; Brown, M.B.; Raji, M.; Graham-Kalio, D.; Chilcott, R.P. Effect of ethnicity, gender and age on the amount and composition of residual skin surface components derived from sebum, sweat and epidermal lipids. Skin Res. Technol. 2014, 20, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, M.Q.; Xin, S.J.; Song, S.P.; Cho, S.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Tu, C.X.; Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M. Variation of skin surface pH, sebum content and stratum corneum hydration with age and gender in a large Chinese population. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2009, 22, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, M.; Han, M.; Kim, D.; Chung, K. Sebum output as a factor contributing to the size of facial pores. Br. J. Dermatol. 2006, 155, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetage, S.S.; Traynor, M.J.; Brown, M.B.; Chilcott, R.P. Sebomic identification of sex- and ethnicity-specific variations in residual skin surface components (RSSC) for bio-monitoring or forensic applications. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, U.; Gautier, J.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Gender-related differences in the physiology of the stratum corneum. Dermatology 2005, 211, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, K.P.; Cua, A.B.; Maibach, H.I. Skin aging. Effect on transepidermal water loss, stratum corneum hydration, skin surface pH, and casual sebum content. Arch. Dermatol. 1991, 127, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akutsu, N.; Ooguri, M.; Onodera, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Katsuyama, M.; Kunizawa, N.; Hirao, T.; Hosoi, J.; Masuda, Y.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Functional characteristics of the skin surface of children approaching puberty: Age and seasonal influences. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2009, 89, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowski, T.; Klose, C.; Gerl, M.J.; Wójcik-Maciejewicz, A.; Herzog, R.; Simons, K.; Reich, A.; Surma, M.A. Large-scale human skin lipidomics by quantitative, high-throughput shotgun mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, B.; Gidden, J.; Lay, J.O.; Durham, B. Laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry of triacylglycerols and other components in fingermark samples. J. Forensic Sci. 2011, 56, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrakchi, S.; Maibach, H.I. Biophysical parameters of skin: Map of human face, regional, and age-related differences. Contact Dermat. 2007, 57, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isom, M.; Go, E.P.; Desaire, H. Enabling Lipidomic Biomarker Studies for Protected Populations by Combining Noninvasive Fingerprint Sampling with MS Analysis and Machine Learning. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 2805–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Diedrich, J.; Chu, Y.-Y.; Yates, J.R. Extracting accurate precursor information for tandem mass spectra by RawConverter. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 11361–11367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, A.E.; Pfeifer, L.D.; Sekera, E.R.; Hummon, A.B.; Desaire, H. Workflow for Evaluating Normalization Tools for Omics Data Using Supervised and Unsupervised Machine Learning. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2023, 34, 2775–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses, R Package Version 1.0.7. 2020.
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Desaire, H. How (Not) to Generate a Highly Predictive Biomarker Panel Using Machine Learning. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 2071–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Isom, M.; Go, E.P.; Desaire, H. Groomed Fingerprint Sebum Sampling: Reproducibility and Variability According to Anatomical Collection Region and Biological Sex. Molecules 2025, 30, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030726
Isom M, Go EP, Desaire H. Groomed Fingerprint Sebum Sampling: Reproducibility and Variability According to Anatomical Collection Region and Biological Sex. Molecules. 2025; 30(3):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030726
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsom, Madeline, Eden P. Go, and Heather Desaire. 2025. "Groomed Fingerprint Sebum Sampling: Reproducibility and Variability According to Anatomical Collection Region and Biological Sex" Molecules 30, no. 3: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030726
APA StyleIsom, M., Go, E. P., & Desaire, H. (2025). Groomed Fingerprint Sebum Sampling: Reproducibility and Variability According to Anatomical Collection Region and Biological Sex. Molecules, 30(3), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030726






