Molecular Properties of Phosphodiesterase 4 and Its Inhibition by Roflumilast and Cilomilast
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Disease-Related Biological Functions of PDE4
2.1. Inflammatory Diseases
2.2. Neurodegenerative Disorders
2.3. Hepatic Pathophysiology
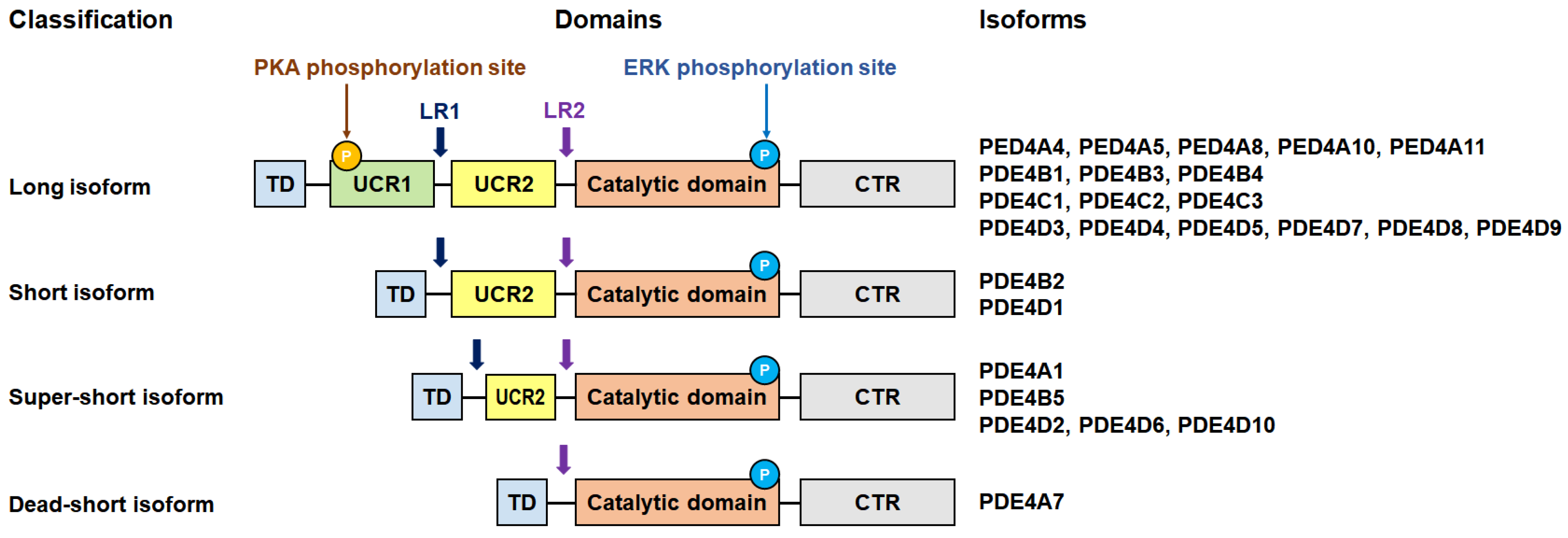
3. PDE4 Subfamily
4. Structure of the PDE4s
4.1. Overall Structure of PDE4
4.2. Metal Binding Site and Substrate Recognition of PDE4B and PDE4D
5. Biological Roles of PDE4 Inhibitors in Disease
5.1. Inflammatory Diseases and Immune Regulation
5.2. Neuroprotective Effects
5.3. Dermatological Diseases
5.4. Cardiovascular Effects
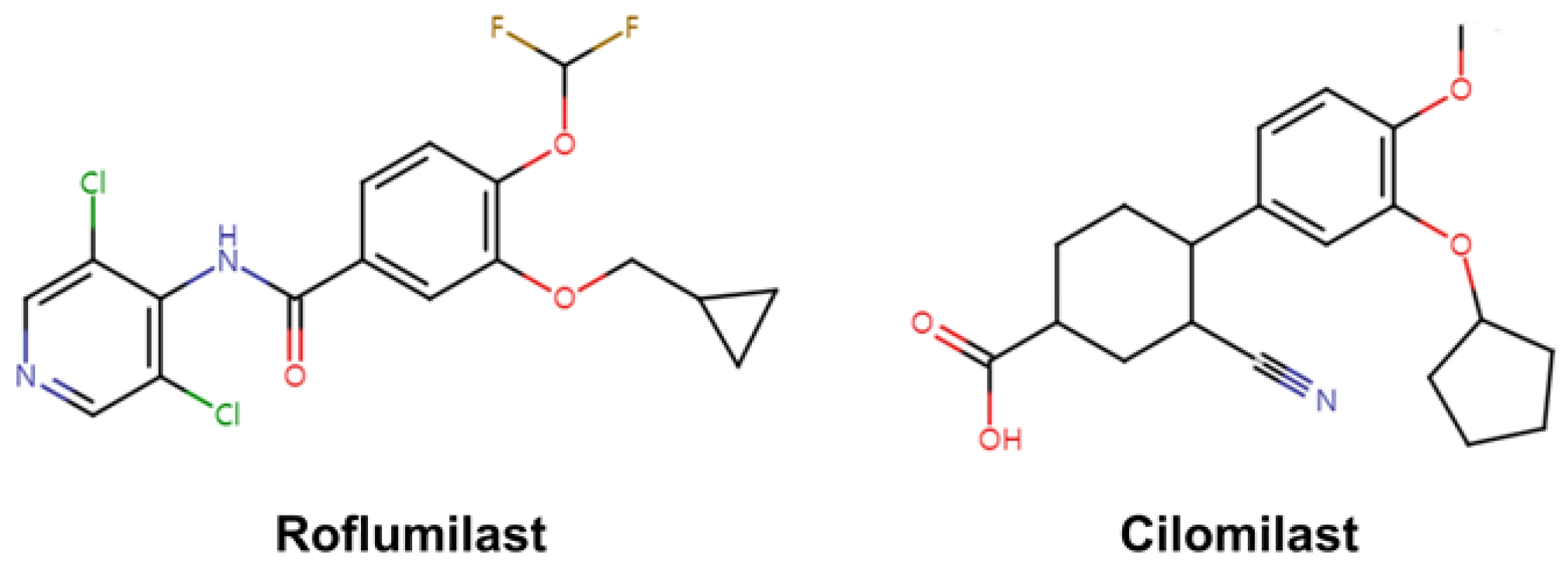
6. Crystal Structure of PDE4 Complexed with Roflumilast and Cilomilast
6.1. Roflumilast-Bound State of PDE4B and PDE4D
6.2. Cilomilast-Bound State of PDE4B and PDE4D
7. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stratakis, C.A.; Manganiello, V.; Ahmad, F.; de Alexandre, R.B.; Levy, I.; Horvath, A.; Bimpaki, E.; Faucz, F.R.; Azevedo, M.F. Clinical and Molecular Genetics of the Phosphodiesterases (PDEs). Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 195–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Murata, T.; Shimizu, K.; Degerman, E.; Maurice, D.; Manganiello, V. Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterases: Important signaling modulators and therapeutic targets. Oral Dis. 2014, 21, e25–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillie, G.S.; Tejeda, G.S.; Kelly, M.P. Therapeutic targeting of 3′,5′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: Inhibition and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 770–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keravis, T.; Lugnier, C. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) isozymes as targets of the intracellular signalling network: Benefits of PDE inhibitors in various diseases and perspectives for future therapeutic developments. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 1288–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, A.T.; Beavo, J.A. Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterases: Molecular Regulation to Clinical Use. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 488–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhaye, S.; Bardoni, B. Role of phosphodiesterases in the pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4570–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongthombam, P.D.; Haobam, R. Targeting phosphodiesterase 4 as a potential therapy for Parkinson’s disease: A review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schick, M.A.; Schlegel, N. Clinical Implication of Phosphodiesterase-4-Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houslay, M.D. Underpinning compartmentalised cAMP signalling through targeted cAMP breakdown. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zuo, J.; Tang, W. Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puertas-Umbert, L.; Alonso, J.; Hove-Madsen, L.; Martínez-González, J.; Rodríguez, C. PDE4 Phosphodiesterases in Cardiovascular Diseases: Key Pathophysiological Players and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusardi, M.; Rapetti, F.; Spallarossa, A.; Brullo, C. PDE4D: A Multipurpose Pharmacological Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.R.; Belder, N.; Ansari, S.A.; Kayhan, M.; Bal, H.; Raza, U.; Ersan, P.G.; Tokat, Ü.M.; Eyüpoğlu, E.; Saatci, Ö.; et al. Reactivation of cAMP Pathway by PDE4D Inhibition Represents a Novel Druggable Axis for Overcoming Tamoxifen Resistance in ER-positive Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1987–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, F.; Panera, N.; Cardarelli, S.; Scarsella, M.; Bianchi, M.; Biagioni, S.; Giorgi, M.; Alisi, A.; Massimi, M. Phosphodiesterase 4D Depletion/Inhibition Exerts Anti-Oncogenic Properties in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Rocha, E.; Rusiñol, L.; Puig, L. Exploring the Therapeutic Landscape: A Narrative Review on Topical and Oral Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors in Dermatology. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, R.; Nambiar, A.M. Potential of phosphodiesterase 4B inhibition in the treatment of progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2025, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, V.A.; Martins, F.R.B.; Martins, D.G.; Queiroz-Junior, C.M.; Félix, F.B.; Resende, L.C.; Santos, F.R.d.S.; Lacerda, L.d.S.B.; Costa, V.R.d.M.; da Silva, W.N.; et al. Selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor roflumilast reduces inflammation and lung injury in models of betacoronavirus infection in mice. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 74, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, A.; Bhattacharya, A.; Bera, A.; Basak, D.; Chatterji, U.; Biswas, A. PDE4 inhibitor rolipram represses hedgehog signaling via ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of GLI transcription factors to regress breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 2025, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, A.Y.; Sakamoto, K.M.; Miller, L.S. The Role of the Transcription Factor CREB in Immune Function. J. Immun. 2010, 185, 6413–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, H.J.; Nam, J.Y.; Song, J.S.; No, Z.; Yang, S.D.; Cheon, H.G. Discovery of a novel orally active PDE-4 inhibitor effective in an ovalbumin-induced asthma murine model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 685, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.-J.; Park, K.-M.; Choi, H.-E.; Chung, K.-S.; Lim, H.-J.; Park, H.-Y. PDE4 inhibitor, roflumilast protects cardiomyocytes against NO-induced apoptosis via activation of PKA and Epac dual pathways. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, W.; Menniti, F.S.; Zhang, H.-T.; Conti, M. PDE4 as a target for cognition enhancement. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 1011–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refaie, M.M.M.; Fouli Gaber Ibrahim, M.; Fawzy, M.A.; Abdel-Hakeem, E.A.; Shaaban Mahmoud Abd El Rahman, E.; Zenhom, N.M.; Shehata, S. Molecular mechanisms mediate roflumilast protective effect against isoprenaline-induced myocardial injury. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2023, 45, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essam, R.M.; Kandil, E.A. p-CREB and p-DARPP-32 orchestrating the modulatory role of cAMP/PKA signaling pathway enhanced by Roflumilast in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 372, 110366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.M.; Gerard-O’Riley, R.L.; Acton, D.; Alam, I.; Econs, M.J.; Bruzzaniti, A. The PDE4 Inhibitors Roflumilast and Rolipram Rescue ADO2 Osteoclast Resorption Dysfunction. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2024, 114, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, N.; Rafique, S.; Naveed, Z.; Nadeem, J.; Waqas, M.; Ali, A.; Shah, M.; Idrees, M. Regulatory pathways and therapeutic potential of PDE4 in liver pathophysiology. Life Sci. 2024, 345, 122565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingham, J.; Sudarsanam, S.; Srinivasan, S. Profiling human phosphodiesterase genes and splice isoforms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 350, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori, K.; Kotera, J. Overview of PDEs and Their Regulation. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Peng, M.S.; Chen, Y.; Geng, J.; Robinson, H.; Houslay, M.D.; Cai, J.; Ke, H. Structures of the four subfamilies of phosphodiesterase-4 provide insight into the selectivity of their inhibitors. Biochem. J. 2007, 408, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.T.; Gurney, M.E.; O’Donnell, J.M. Comparison of the Pharmacological Profiles of Selective PDE4B and PDE4D Inhibitors in the Central Nervous System. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.R.; Nicodemus-Johnson, J.; Danziger, R.S. An evolutionary analysis of cAMP-specific Phosphodiesterase 4 alternative splicing. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, L.; Vicini, E.; Conti, M. Structure of two rat genes coding for closely related rolipram-sensitive cAMP phosphodiesterases. Multiple mRNA variants originate from alternative splicing and multiple start sites. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurney, M.E.; D’Amato, E.C.; Burgin, A.B. Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) Molecular Pharmacology and Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, W.; Jin, S.L.C.; Conti, M. Splice variants of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase PDE4D are differentially expressed and regulated in rat tissue. Biochem. J. 2005, 388, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, X.; Pérez-Torres, S.; Puigdomènech, P.; Palacios, J.M.; Mengod, G. Differential distribution of PDE4D splice variant mRNAs in rat brain suggests association with specific pathways and presynaptical localization. Synapse 2002, 45, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, P.; Ohleth, K.M.; Egan, R.W.; Billah, M.M. Phosphodiesterase 4B2 Is the Predominant Phosphodiesterase Species and Undergoes Differential Regulation of Gene Expression in Human Monocytes and Neutrophils. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 56, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillie, G.S.; Kyurkchieva, E. Short PDE4 Isoforms as Drug Targets in Disease. Front. Biosci. 2023, 28, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houslay, M.D.; Schafer, P.; Zhang, K.Y.J. Keynote review: Phosphodiesterase-4 as a therapeutic target. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 1503–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, D.; Schepers, M.; Rombaut, B.; van den Hove, D.; Vanmierlo, T.; Prickaerts, J.; Michel, M. The Molecular Biology of Phosphodiesterase 4 Enzymes as Pharmacological Targets: An Interplay of Isoforms, Conformational States, and Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 1016–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Card, G.L.; England, B.P.; Suzuki, Y.; Fong, D.; Powell, B.; Lee, B.; Luu, C.; Tabrizizad, M.; Gillette, S.; Ibrahim, P.N.; et al. Structural Basis for the Activity of Drugs that Inhibit Phosphodiesterases. Structure 2004, 12, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.X.; Hassell, A.M.; Vanderwall, D.; Lambert, M.H.; Holmes, W.D.; Luther, M.A.; Rocque, W.J.; Milburn, M.V.; Zhao, Y.; Ke, H.; et al. Atomic Structure of PDE4: Insights into Phosphodiesterase Mechanism and Specificity. Science 2000, 288, 1822–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Y.J.; Card, G.L.; Suzuki, Y.; Artis, D.R.; Fong, D.; Gillette, S.; Hsieh, D.; Neiman, J.; West, B.L.; Zhang, C.; et al. A Glutamine Switch Mechanism for Nucleotide Selectivity by Phosphodiesterases. Mol. Cell. 2004, 15, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L. PDE4 inhibitors: Potential protective effects in inflammation and vascular diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1407871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocetti, L.; Floresta, G.; Cilibrizzi, A.; Giovannoni, M.P. An Overview of PDE4 Inhibitors in Clinical Trials: 2010 to Early 2022. Molecules 2022, 27, 4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamatawong, T. Roles of roflumilast, a selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in airway diseases. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanova, A.; Medvedova, I.; Kertys, M.; Mikolka, P.; Kosutova, P.; Mokra, D.; Mokrý, J. Dose dependent effects of tadalafil and roflumilast on ovalbumin-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in guinea pigs. Exp. Lung Res. 2017, 43, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakkas, L.I.; Mavropoulos, A.; Bogdanos, D.P. Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors in Immune-mediated Diseases: Mode of Action, Clinical Applications, Current and Future Perspectives. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3054–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crilly, A.; Robertson, S.E.; Reilly, J.H.; Gracie, J.A.; Lai, W.-Q.; Leung, B.P.; Life, P.F.; McInnes, I.B. Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) regulation of proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine release from rheumatoid synovial membrane. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.; Ray, B.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Tuladhar, S.; Nandakumar, D.N.; Srinivasan, M.; Essa, M.M.; Chidambaram, S.B.; Guillemin, G.J.; Sakharkar, M.K. Phosphodiesterase-4 enzyme as a therapeutic target in neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milara, J.; Ribera, P.; Marín, S.; Montero, P.; Roger, I.; Tenor, H.; Cortijo, J. Phosphodiesterase 4 is overexpressed in human keloids and its inhibition reduces fibroblast activation and skin fibrosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2024, 402, 111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira Alves, G.; Oliveira, J.G.; Nakashima, M.A.; Delfrate, G.; Sordi, R.; Assreuy, J.; da Silva-Santos, J.E.; Collino, M.; Fernandes, D. Cardiovascular effects of Roflumilast during sepsis: Risks or benefits? Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 983, 177015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, E.S.; Sayed, R.H.; Saad, M.A.; El-Yamany, M.F. Roflumilast ameliorates ovariectomy-induced depressive-like behavior in rats via activation of AMPK/mTOR/ULK1-dependent autophagy pathway. Life Sci. 2023, 327, 121806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Luo, M.; Ren, C.; Zhang, J. PDE4 Inhibitors for Disease Therapy: Advances and Future Perspective. Future Med. Chem. 2023, 15, 1185–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Mazzacuva, F.; Crocetti, L.; Giovannoni, M.P.; Cilibrizzi, A. PDE4 Inhibitors: Profiling Hits through the Multitude of Structural Classes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, Y.; Araya, J.; Tanaka, Y.; Kumanogoh, A. Pathological mechanisms and novel drug targets in fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Inflamm. Regen. 2024, 44, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Patel, S.; Patel, Y.; Chudasama, P.; Soni, S.; Patel, S.; Raval, M. Roflumilast mitigates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by regulating TNF-α/TNFR1/TNFR2/Fas/Caspase mediated apoptosis and inflammatory signals. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2024, 77, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.J.; Song, J.S.; No, Z.S.; Song, J.H.; Yang, S.D.; Cheon, H.G. The inhibitory effects of roflumilast on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in RAW264.7 cells are mediated by heme oxygenase-1 and its product carbon monoxide. Inflamm. Res. 2005, 54, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, H.J.; Song, J.S.; Heo, J.Y.; Yang, S.D.; Nam, J.-Y.; Cheon, H.G. Roflumilast Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Mediators via Suppression of Nuclear Factor-κB, p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase, and c-Jun NH2-Terminal Kinase Activation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. 2005, 315, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yu, X.; Meng, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Jia, Z. Inhibition of PDE4/PDE4B improves renal function and ameliorates inflammation in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2020, 318, F576–F588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-C.; Yu, H.-P.; Lin, C.-Y.; Elzoghby, A.O.; Hwang, T.-L.; Fang, J.-Y. Use of cilomilast-loaded phosphatiosomes to suppress neutrophilic inflammation for attenuating acute lung injury: The effect of nanovesicular surface charge. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.; Tan, V.; Heng, B.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Essa, M.M.; Chidambaram, S.B.; Guillemin, G.J. Roflumilast, a cAMP-Specific Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitor, Reduces Oxidative Stress and Improves Synapse Functions in Human Cortical Neurons Exposed to the Excitotoxin Quinolinic Acid. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 4405–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzelmann, A.; Schudt, C. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory potential of the novel PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in vitro. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, K.F. Update on roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgin, A.B.; Magnusson, O.T.; Singh, J.; Witte, P.; Staker, B.L.; Bjornsson, J.M.; Thorsteinsdottir, M.; Hrafnsdottir, S.; Hagen, T.; Kiselyov, A.S.; et al. Design of phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) allosteric modulators for enhancing cognition with improved safety. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugnier, C. The Complexity and Multiplicity of the Specific cAMP Phosphodiesterase Family: PDE4, Open New Adapted Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, W.; Conti, M. The Oligomerization State Determines Regulatory Properties and Inhibitor Sensitivity of Type 4 cAMP-specific Phosphodiesterases. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30338–30348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Protein | Inhibitor | PDB Code | Resolution (Å) | Residues | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDE4B | Roflumilast | 1XMU | 2.30 | 324–700 | [41] |
| Cilomilast | 1XLX | 2.19 | 324–700 | [41] | |
| PDE4D | Roflumilast | 1XOQ | 1.83 | 388–715 | [41] |
| Roflumilast | 3G4L | 2.50 | 380–753 | [65] | |
| Cilomilast | 1XOM | 1.55 | 388–715 | [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwak, H.J.; Nam, K.H. Molecular Properties of Phosphodiesterase 4 and Its Inhibition by Roflumilast and Cilomilast. Molecules 2025, 30, 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030692
Kwak HJ, Nam KH. Molecular Properties of Phosphodiesterase 4 and Its Inhibition by Roflumilast and Cilomilast. Molecules. 2025; 30(3):692. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030692
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwak, Hyun Jeong, and Ki Hyun Nam. 2025. "Molecular Properties of Phosphodiesterase 4 and Its Inhibition by Roflumilast and Cilomilast" Molecules 30, no. 3: 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030692
APA StyleKwak, H. J., & Nam, K. H. (2025). Molecular Properties of Phosphodiesterase 4 and Its Inhibition by Roflumilast and Cilomilast. Molecules, 30(3), 692. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030692







