Influence of Deep Eutectic Solvent Composition on Micelle Properties: A Molecular Dynamics Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
2.1. Simulation Setup
2.2. Validation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Free Energy of Solvation
3.2. Shape and Radius
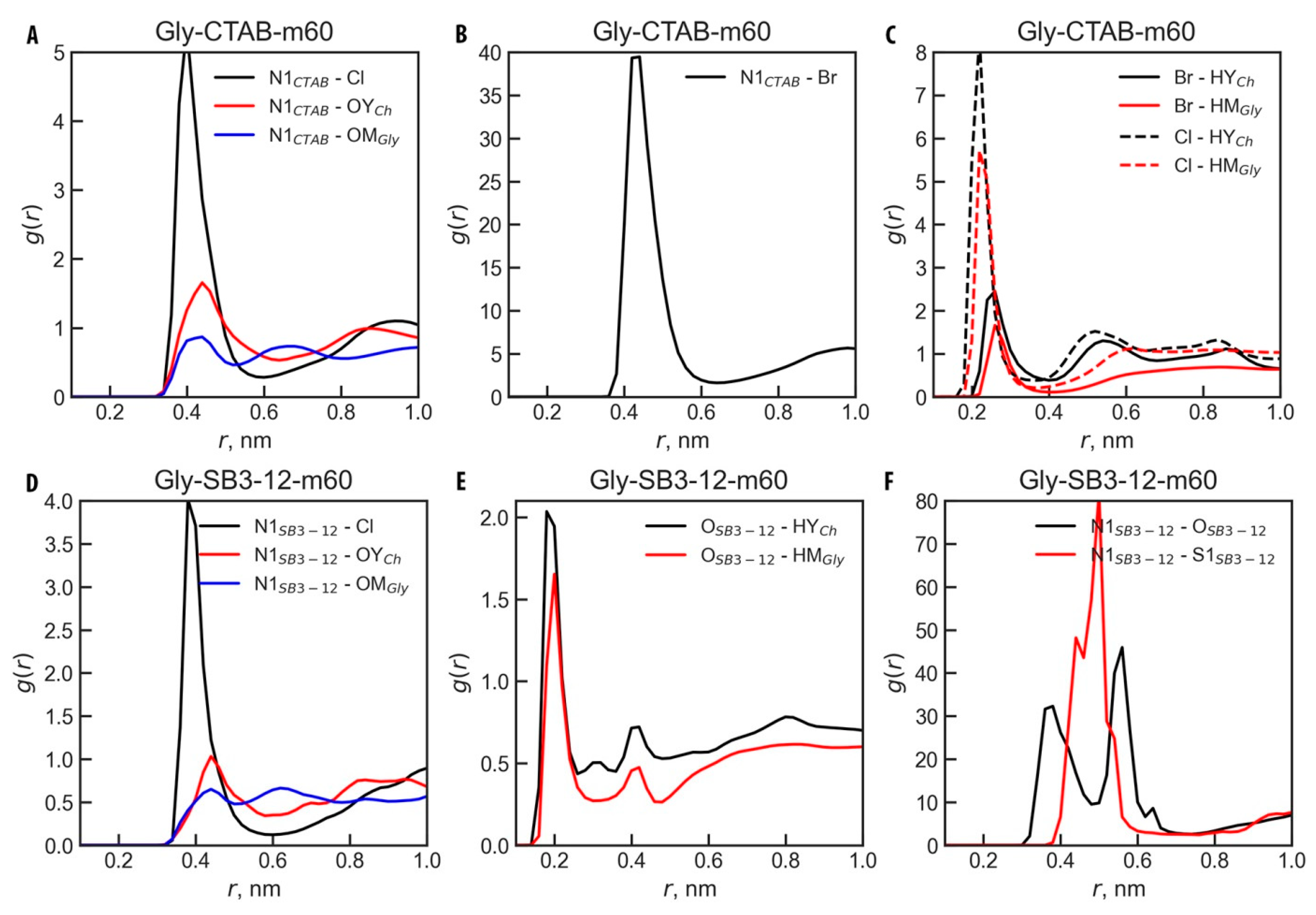
3.3. Micelle Structure and Conformations
3.4. Micelle–Solvent and Intra-Micellar Interaction
3.5. Transport Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voroshylova, I.V.; Ferreira, E.S.C.; Koverga, V.A.; Pereira, C.M.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Chapter 4—Structure and Noncovalent Interactions in Ionic Liquids Mixtures and Deep Eutectic Solvents. In Theoretical and Computational Approaches to Predicting Ionic Liquid Properties; Joseph, A., Mathew, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 105–157. ISBN 978-0-12-820280-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, E.S.C.; Voroshylova, I.V.; Pereira, C.M.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Improved Force Field Model for the Deep Eutectic Solvent Ethaline: Reliable Physicochemical Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 10124–10137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negi, T.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Rawat, N.; Saini, D.; Sirohi, R.; Prakash, O.; Dubey, A.; Dutta, A.; Shahi, N.C. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Preparation, Properties, and Food Applications. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.S.C.; Voroshylova, I.V.; Figueiredo, N.M.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Molecular Dynamic Study of Alcohol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 155, 064506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, S.; Koudahi, M.F.; Frackowiak, E. Reline Deep Eutectic Solvent as a Green Electrolyte for Electrochemical Energy Storage Applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 1156–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voroshylova, I.V.; Ferreira, E.S.C.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Electrical Double Layer in Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents. In Encyclopedia of Solid-Liquid Interfaces, 1st ed.; Wandelt, K., Bussetti, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2024; pp. 29–39. ISBN 978-0-323-85670-6. [Google Scholar]
- Francisco, M.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Kroon, M.C. Low-Transition-Temperature Mixtures (LTTMs): A New Generation of Designer Solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3074–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza, A.; Song, K.; Soltero-Martínez, J.F.A.; Wu, K.; Pojman, J.A.; Mota-Morales, J.D. On the Stability and Chemorheology of a Urea Choline Chloride Deep-Eutectic Solvent as an Internal Phase in Acrylic High Internal Phase Emulsions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 81694–81702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, O.S.; Bowron, D.T.; Jackson, A.J.; Arnold, T.; Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Tsapatsaris, N.; Garcia Sakai, V.; Edler, K.J. Resilience of Malic Acid Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent Nanostructure to Solidification and Hydration. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 7473–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.J.; Tu, W.-C.; Levers, O.; Bröhl, A.; Hallett, J.P. Green and Sustainable Solvents in Chemical Processes. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 747–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.S.C.; Voroshylova, I.V.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Probing the Interface of Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent Ethaline with Gold Surfaces: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 46, 104051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents—Solvents for the 21st Century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Edler, K.J.; Arnold, T.; Venero, D.A.; Jackson, A.J. Protein Conformation in Pure and Hydrated Deep Eutectic Solvents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 8667–8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, S.J.; Atkin, R.; Warr, G.G. Spontaneous Vesicle Formation in a Deep Eutectic Solvent. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.A.; Chavda, V.; Hirpara, D.; Sharma, V.S.; Shrivastav, P.S.; Kumar, S. Exploring the Potential of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Pharmaceuticals: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 390, 123171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eterno Fileti, E.; Voroshylova, I.V.; Ferreira, E.S.C.; Natália, D.S.; Cordeiro, M.; Malaspina, T. Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Study of Hydroxyl Positioning in Butanediol and Its Impact on Deep Eutectic Solvent Structure. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 409, 125548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusas, J.R.B.; Dela Pena, E.M.B. An Environment-Friendly Chromium Electrodeposition Process Using Additive-Laden Deep Eutectic Solvent. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P. Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Application in Electrochemistry. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 36, 100649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.S.C.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, A.F. Electrochemical Studies of Metallic Chromium Electrodeposition from a Cr(III) Bath. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 707, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotor-Fernández, V.; Paul, C.E. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Redox Biocatalysis. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 293, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długosz, O. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Synthesis of Inorganic Nanoparticles. Materials 2023, 16, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Park, Y.R.; Garg, A.; Lee, B.-S. Deep Eutectic Solvents Enhancing Drug Solubility and Its Delivery. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 14807–14819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangre, P.V.; Korekar, P.P.; Borkar, M.R.; Chaturvedi, K.K.; Borikar, S.P.; Pethe, A.M. Tailoring Deep Eutectic Solvents to Provoke Solubility and Bioavailability of Naringin: Implications of a Computational Approach. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 12820–12829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pileni, M.-P. The Role of Soft Colloidal Templates in Controlling the Size and Shape of Inorganic Nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Hammond, O.S.; Jackson, A.J.; Arnold, T.; Doutch, J.; Edler, K.J. Surfactant–Solvent Interaction Effects on the Micellization of Cationic Surfactants in a Carboxylic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. Langmuir 2017, 33, 14304–14314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Moody, G.L.; Murfin, L.C.; Arnold, T.; Jackson, A.J.; King, S.M.; Lewis, S.E.; Edler, K.J. Self-Assembly and Surface Behaviour of Pure and Mixed Zwitterionic Amphiphiles in a Deep Eutectic Solvent. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 5525–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häckl, K.; Li, H.; Aldous, I.M.; Tsui, T.; Kunz, W.; Abbott, A.P.; Warr, G.G.; Atkin, R. Potential Dependence of Surfactant Adsorption at the Graphite Electrode/Deep Eutectic Solvent Interface. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 5331–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-T.; Liu, Y.-R. Micelle Structure in a Deep Eutectic Solvent for the Electrochemical Preparation of Nanomaterials. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10270–10275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, B.; Sau, A.; Guerrero, J.D.M.; Das, S.; Das, K. Multifaceted Insights into Au Coatings Electrodeposited from a ChCl-EG Based Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES): Unravelling the Effect of Surfactant Polarity and Current Density on the Morphology, Mechanical Properties, and Anti-Tarnishing Efficacy. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 49, 104484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.N.; Do, H.D.K.; Trinh, K.T.L.; Lee, N.Y. Design Strategy and Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents for Green Synthesis of Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medoš, Ž.; Plechkova, N.V.; Friesen, S.; Buchner, R.; Bešter-Rogač, M. Insight into the Hydration of Cationic Surfactants: A Thermodynamic and Dielectric Study of Functionalized Quaternary Ammonium Chlorides. Langmuir 2019, 35, 3759–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.A.; Rankin, B.M.; Ben-Amotz, D. Micelle Structure and Hydrophobic Hydration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10809–10815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Hammond, O.S.; Edler, K.J.; Arnold, T.; Doutch, J.; Dalgliesh, R.M.; Li, P.; Ma, K.; Jackson, A.J. Counterion Binding Alters Surfactant Self-Assembly in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 13952–13961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atri, R.S.; Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Hammond, O.S.; Manasi, I.; Doutch, J.; Tellam, J.P.; Edler, K.J. Morphology Modulation of Ionic Surfactant Micelles in Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 6004–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Arnold, T.; Jackson, A.J.; Fussell, S.L.; Heenan, R.K.; Campbell, R.A.; Edler, K.J. Micellization of Alkyltrimethylammonium Bromide Surfactants in Choline Chloride:Glycerol Deep Eutectic Solvent. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 33240–33249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Singh, R.K.; Pandey, S. Evidence of Self-Aggregation of Cationic Surfactants in a Choline Chloride+Glycerol Deep Eutectic Solvent. ChemPhysChem 2015, 16, 2538–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, T.; Jackson, A.J.; Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Magnone, D.; Terry, A.E.; Edler, K.J. Surfactant Behavior of Sodium Dodecylsulfate in Deep Eutectic Solvent Choline Chloride/Urea. Langmuir 2015, 31, 12894–12902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, O.S.; Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Tyte, R.; Dalgliesh, R.; Smith, A.J.; Edler, K.J. Mix-and-Match Diols: Adjusting Self-Assembly of Micellar Phases in Choline Chloride Eutectics. Crystals 2022, 12, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirpara, D.; Patel, B.; Chavda, V.; Kumar, S. Micellization of Conventional and Gemini Surfactants in Aquoline: A Case of Exclusively Water Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 362, 119672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasquevici, R.; Bernardino, K. Counter-Ion Adsorption and Electrostatic Potential in Sodium and Choline Dodecyl Sulfate Micelles—A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. J. Mol. Model. 2024, 30, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrankó-Rideg, N.; Darvas, M.; Horvai, G.; Jedlovszky, P. Immersion Depth of Surfactants at the Free Water Surface: A Computer Simulation and ITIM Analysis Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 8733–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.T.; Saaka, Y.; Lawrence, M.J.; Lorenz, C.D. Atomistic Description of the Solubilisation of Testosterone Propionate in a Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Micelle. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 13192–13201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoun, B.; Sharma, V.K.; Pellegrini, E.; Mitra, S.; Johnson, M.; Mukhopadhyay, R. Structure and Dynamics of Ionic Micelles: MD Simulation and Neutron Scattering Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 5079–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aray, Y.; Parra, J.G.; Jiménez, D.M.; Paredes, R.; Martiz, A.; Samaniego, S.; Cornejo, M.; Ludena, E.V.; Paredes, C. Exploring the Effect of the O-(1-Heptylnonyl) Benzene Sulfonate Surfactant on the Nature of the Linear Hydrocarbons/Water Interface by Means of an Atomistic Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Comput. Methods Sci. Eng. 2017, 17, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, N.S.; Abu Bakar, N.F.; Tengku Mohd, T.A.; Azizi, A. Molecular Dynamics Simulation on CO2 Foam System with Addition of SiO2 Nanoparticles at Various Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) Concentrations and Elevated Temperatures for Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) Application. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2020, 184, 109937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, B.J.; Choi, J.I.; Jang, S.S. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Micelle: Water Penetration and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Dissociation. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 474, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergin, G.; Lbadaoui-Darvas, M.; Takahama, S. Molecular Structure Inhibiting Synergism in Charged Surfactant Mixtures: An Atomistic Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Langmuir 2017, 33, 14093–14104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerdt, G.; Tranca, I.; Markvoort, A.J.; Szyja, B.M.; Morgon, N.H.; Hensen, E.J.M. Photoisomerization Induced Scission of Rod-like Micelles Unravelled with Multiscale Modeling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 510, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Huang, P.; Han, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wei, X.; Huang, W.; Dai, J.; Song, J.; Yan, H.; Liu, D. Synergistic Effects of Janus Graphene Oxide and Surfactants on the Heavy Oil/Water Interfacial Tension and Their Application to Enhance Heavy Oil Recovery. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 314, 113791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Singh, G.; Kaura, A. Understanding the Formation of Nanorods on Hematite (α-Fe2O3) in the Presence of Surfactants: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 316, 113882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Yoshii, N.; Okazaki, S. Molecular Dynamics Study of the Potential of Mean Force of SDS Aggregates. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 084903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Marchi, M.; Guo, C.; Dang, Z.; Abel, S. Atomistic Simulation of Solubilization of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in a Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Micelle. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3645–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Guo, C.; Liu, S.; Dang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Yi, X.; Abel, S. Cosolubilization of Phenanthrene and Pyrene in Surfactant Micelles: Experimental and Atomistic Simulations Studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hoopes, M.I.; Karttunen, M. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of DPPC/CTAB Monolayers at the Air/Water Interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 11723–11737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Lee, M.-T.; Vishnyakov, A.; Neimark, A.V. Modeling Aggregation of Ionic Surfactants Using a Smeared Charge Approximation in Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 11673–11683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, S.K.; Sulpizi, M. Understanding the Microscopic Origin of Gold Nanoparticle Anisotropic Growth from Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Langmuir 2013, 29, 14954–14961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Ghosh, S.; De, S. Atomistic Level Molecular Dynamics Simulation on the Solubilization Mechanism of Aromatic Molecules in Anionic Micelles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 104493–104501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peredo-Mancilla, D.; Dominguez, H. Adsorption of Phenol Molecules by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) Surfactants Deposited on Solid Surfaces: A Computer Simulation Study. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2016, 65, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rideg, N.A.; Darvas, M.; Varga, I.; Jedlovszky, P. Lateral Dynamics of Surfactants at the Free Water Surface: A Computer Simulation Study. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14944–14953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-López, M.; Mendez-Bermúdez, J.G.; Domínguez, H. New Force Field Parameters for the Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate and Alpha Olefin Sulfonate Anionic Surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 4558–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-López, M.; Mendez-Bermúdez, J.G.; Vázquez-Sánchez, M.I.; Domínguez, H. Surface Tension Calculations of the Cationic (CTAB) and the Zwitterionic (SB3-12) Surfactants Using New Force Field Models: A Computational Study. Mol. Phys. 2019, 117, 3632–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, E.; Yordanova, D.; Gerlach, T.; Smirnova, I.; Jakobtorweihen, S. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Various Micelles to Predict Micelle Water Partition Equilibria with COSMOmic: Influence of Micelle Size and Structure. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 422, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Morales, Y.; Romero-Martínez, A. Coarse-Grain Molecular Dynamics Simulations To Investigate the Bulk Viscosity and Critical Micelle Concentration of the Ionic Surfactant Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) in Aqueous Solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 3931–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Arriaga, A.B.; Dominguez, H. Decane Structure on a Graphite Surface with Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate and Betaine Surfactant Mixtures: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Chem. Phys. 2020, 539, 110945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storm, S.; Jakobtorweihen, S.; Smirnova, I.; Panagiotopoulos, A.Z. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of SDS and CTAB Micellization and Prediction of Partition Equilibria with COSMOmic. Langmuir 2013, 29, 11582–11592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Li, W.; Jin, Z. Molecular Dynamics Studies on Effective Surface-Active Additives: Toward Hard Water-Resistant Chemical Flooding for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Langmuir 2022, 38, 4802–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Koenig, P.H.; Larson, R.G. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Micelles in Water—The Effect of the Force Field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 3864–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Larson, R.G. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Threadlike Cetyltrimethylammonium Chloride Micelles: Effects of Sodium Chloride and Sodium Salicylate Salts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 13697–13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Liu, M.; Hu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, Y. Spreading Behavior and Wetting Characteristics of Anionic Surfactant Droplets Impacting Bituminous Coal. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 46241–46249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, M.; Ünlü, A.; Iglesias-Fernández, J.; Osuna, S.; Sezerman, O.U.; Timucin, E. Brave New Surfactant World Revisited by Thermoalkalophilic Lipases: Computational Insights into the Role of SDS as a Substrate Analog. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 2234–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Jin, H.; Wu, T.; Huang, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, T.; Yan, Y. Physical Insight into the Conditions Required in the Solid-Phase Molecular Self-Assembly of SDS Revealed by Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 6345–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Effect of Surfactant on the Attachment between Coal Particles and Bubbles: An Experimental and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Fuel 2023, 337, 127272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalipillai, P.; Raghuram, E.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Mani, E. Self-Assembly of a CTAB Surfactant on Gold Nanoparticles: A United-Atom Molecular Dynamics Study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 28353–28361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmonem, A.; Zhang, Y.; Braunschweig, B.; Glikman, D.; Rumpel, A.; Peukert, W.; Begović, T.; Liu, X.; Lützenkirchen, J. Adsorption of CTAB on Sapphire-c at High pH: Surface and Zeta Potential Measurements Combined with Sum-Frequency and Second-Harmonic Generation. Langmuir 2022, 38, 3380–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Mitchell-Koch, K.R.; Marapureddy, S.G.; Verma, R.; Thareja, P.; Kuperkar, K.; Bahadur, P. Self-Assembly and Micellar Transition in CTAB Solutions Triggered by 1-Octanol. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 8102–8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.A.; Dias, R.P.; Hora, G.C.A.; Soares, T.A.; Meneghetti, M.R. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide (CTAB) Micelles and Their Interactions with a Gold Surface in Aqueous Solution. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2018, 29, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, B.; Acevedo, O. OPLS Force Field for Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 9982–9993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Maxwell, D.S.; Tirado-Rives, J. Development and Testing of the OPLS All-Atom Force Field on Conformational Energetics and Properties of Organic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11225–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, N.M.; Voroshylova, I.V.; Koverga, V.A.; Ferreira, E.S.C.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Influence of Alcohols on the Inter-Ion Interactions in Ionic Liquids: A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 294, 111538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.-M.; Liu, H.; Qian, H.-J.; Jiao, G.-S.; Lu, Z.-Y. Multiscale Simulations of Ligand Adsorption and Exchange on Gold Nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 16; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, L.; Andrade, R.; Birgin, E.G.; Martínez, J.M. PACKMOL: A Package for Building Initial Configurations for Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banjare, R.K.; Banjare, M.K.; Behera, K.; Pandey, S.; Ghosh, K.K. Micellization Behavior of Conventional Cationic Surfactants within Glycerol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 19350–19362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, R.; Ruckenstein, E. Theory of Surfactant Self-Assembly: A Predictive Molecular Thermodynamic Approach. Langmuir 1991, 7, 2934–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. LINCS: A Linear Constraint Solver for Molecular Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical Sampling through Velocity Rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular Dynamics with Coupling to an External Bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosé, S. A Molecular Dynamics Method for Simulations in the Canonical Ensemble. Mol. Phys. 1984, 52, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, W.G. Canonical Dynamics: Equilibrium Phase-Space Distributions. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 31, 1695–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic Transitions in Single Crystals: A New Molecular Dynamics Method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockney, R.W.; Goel, S.P.; Eastwood, J.W. Quiet High-Resolution Computer Models of a Plasma. J. Comput. Phys. 1974, 14, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; van der Spoel, D. GROMACS 3.0: A Package for Molecular Simulation and Trajectory Analysis. Mol. Model. Annu. 2001, 7, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirts, M.R.; Pitera, J.W.; Swope, W.C.; Pande, V.S. Extremely Precise Free Energy Calculations of Amino Acid Side Chain Analogs: Comparison of Common Molecular Mechanics Force Fields for Proteins. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 5740–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, E.P.; Paul, T.J.; Hayes, R.L.; Brooks, C.L.I. Automated, Accurate, and Scalable Relative Protein–Ligand Binding Free-Energy Calculations Using Lambda Dynamics. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2020, 16, 7895–7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumbri, K.; Micaelo, N.M.; Abdul Rahman, M.B. Solvation Free Energies of Nucleic Acid Bases in Ionic Liquids. Mol. Simul. 2017, 43, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.A.M.; Micaêlo, N.; Abdul Rahman, M.B. Solvation Free Energies in [Bmim]-Based Ionic Liquids: Anion Effect toward Solvation of Amino Acid Side Chain Analogues. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 615, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voroshylova, I.V.; Ferreira, E.S.C.; Malček, M.; Costa, R.; Pereira, C.M.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Influence of the Anion on the Properties of Ionic Liquid Mixtures: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 14899–14918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.S.C.; Voroshylova, I.V.; Koverga, V.A.; Pereira, C.M.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. New Force Field Model for Propylene Glycol: Insight to Local Structure and Dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 10906–10921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, K.; Baroutian, S.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Densities of Ammonium and Phosphonium Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Prediction Using Artificial Intelligence and Group Contribution Techniques. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 527, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leron, R.B.; Soriano, A.N.; Li, M.-H. Densities and Refractive Indices of the Deep Eutectic Solvents (Choline Chloride+ethylene Glycol or Glycerol) and Their Aqueous Mixtures at the Temperature Ranging from 298.15 to 333.15K. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2012, 43, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agieienko, V.; Buchner, R. Densities, Viscosities, and Electrical Conductivities of Pure Anhydrous Reline and Its Mixtures with Water in the Temperature Range (293.15 to 338.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 4763–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, C.; Harris, R.C.; Abbott, A.P.; Gladden, L.F.; Mantle, M.D. Molecular Motion and Ion Diffusion in Choline Chloride Based Deep Eutectic Solvents Studied by 1H Pulsed Field Gradient NMR Spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 21383–21391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Zhao, B.; Chen, X.-B.; Birbilis, N.; Yang, H. Effect of Water Presence on Choline Chloride-2urea Ionic Liquid and Coating Platings from the Hydrated Ionic Liquid. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, S.; Benito, C.; Alcalde, R.; Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. Insights on the Water Effect on Deep Eutectic Solvents Properties and Structuring: The Archetypical Case of Choline Chloride + Ethylene Glycol. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.S.C.; Voroshylova, I.V.; Figueiredo, N.M.; Pereira, C.M.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Computational and Experimental Study of Propeline: A Choline Chloride Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 298, 111978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VandeVondele, J.; Krack, M.; Mohamed, F.; Parrinello, M.; Chassaing, T.; Hutter, J. Quickstep: Fast and Accurate Density Functional Calculations Using a Mixed Gaussian and Plane Waves Approach. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2005, 167, 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, J.; Iannuzzi, M.; Schiffmann, F.; VandeVondele, J. Cp2k: Atomistic Simulations of Condensed Matter Systems. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2014, 4, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-Functional Exchange-Energy Approximation with Correct Asymptotic Behavior. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti Correlation-Energy Formula into a Functional of the Electron Density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VandeVondele, J.; Hutter, J. Gaussian Basis Sets for Accurate Calculations on Molecular Systems in Gas and Condensed Phases. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-L.; Chen, K.; Rossomme, E.; Head-Gordon, M.; Head-Gordon, T. Optimized Pseudopotentials and Basis Sets for Semiempirical Density Functional Theory for Electrocatalysis Applications. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 10304–10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedecker, S.; Teter, M.; Hutter, J. Separable Dual-Space Gaussian Pseudopotentials. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brehm, M.; Thomas, M.; Gehrke, S.; Kirchner, B. TRAVIS-A Free Analyzer for Trajectories from Molecular Simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 164105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.; Alekseenko, A.; Bergh, C.; Blau, C.; Briand, E.; Doijade, M.; Fleischmann, S.; Gapsys, V.; Garg, G.; Gorelov, S.; et al. GROMACS 2023.2 Manual; Zenodo: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzesi, F.; Calvaresi, M.; Zerbetto, F. A Molecular Dynamics Investigation of Structure and Dynamics of SDS and SDBS Micelles. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9148–9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, S.; Akhavan, M. A Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation of a Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Micelle in Aqueous Solution. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 352, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Su, T.M.; Mou, C.Y. Size of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Micelle in Concentrated Salt Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1986, 90, 2418–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKerell, A.D., Jr. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Analysis of a Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Micelle in Aqueous Solution: Decreased Fluidity of the Micelle Hydrocarbon Interior. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzar, A.; Chandler, D. Effect of Environment on Hydrogen Bond Dynamics in Liquid Water. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 76, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maginn, E.J.; Messerly, R.A.; Carlson, D.J.; Roe, D.R.; Elliot, J.R. Best Practices for Computing Transport Properties 1. Self-Diffusivity and Viscosity from Equilibrium Molecular Dynamics [Article v1.0]. Living J. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2019, 1, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Mitra, S.; Verma, G.; Hassan, P.A.; Garcia Sakai, V.; Mukhopadhyay, R. Internal Dynamics in SDS Micelles: Neutron Scattering Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 17049–17056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Mitra, S.; Sakai, V.G.; Mukhopadhyay, R. Dynamical Features in Cationic Micelles of Varied Chain Length. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 9007–9015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| System Name | DES Name | HBD | Surfactant | Number of Surfactants in the Micelle | Total Number of Interaction Sites | Final Simulation Box Length, nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eth-SDS-m60 | Ethaline | Eg | SDS | 60 | 45,588 | 7.745 |
| Gly-CTAB-m60 | Glyceline | Gly | CTAB | 60 | 54,980 | 7.978 |
| Gly-SB3-12-m60 | Glyceline | Gly | SB3-12 | 60 | 54,740 | 7.922 |
| Gly-SDS-m60 | Glyceline | Gly | SDS | 60 | 53,780 | 7.904 |
| Rel-SDS-m60 | Reline | Ure | SDS | 60 | 41,492 | 7.546 |
| Eth-SDS-m120 | Ethaline | Eg | SDS | 120 | 48,168 | 7.893 |
| Gly-CTAB-m120 | Glyceline | Gly | CTAB | 120 | 58,760 | 8.132 |
| Gly-SB3-12-m120 | Glyceline | Gly | SB3-12 | 120 | 58,280 | 8.064 |
| Gly-SDS-m120 | Glyceline | Gly | SDS | 120 | 56,360 | 8.028 |
| Rel-SDS-m120 | Reline | Ure | SDS | 120 | 44,072 | 7.577 |
| DES | d, kg m−3 | D, 10−11 m2 s−1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choline Cation | HBD | ||||||||
| Sim | Exp | Error, % | Sim | Exp | Error, % | Sim | Exp | Error, % | |
| Glyceline | 1183.7 (0.1) | 1180 [2] | 0.3 | 0.17 (0.01) | 0.38 [2] | 55 | 0.30 (0.01) | 0.52 [2] | 42 |
| 1192 [103] | 0.7 | ||||||||
| 1191.2 [104] | 0.6 | ||||||||
| Reline | 1135.6 (0.2) | 1240 [2] | 8 | * 0.52 (0.03) | 0.35 [2] | * 0.94 (0.03) | 0.66 [2] | ||
| 1196.55 [105] | 4 | ||||||||
| 1198 [80] | 5 | ||||||||
| DES | Surfactant | ΔG, kJ mol−1 |
|---|---|---|
| Ethaline | SDS | −21 (3) |
| Glyceline | SDS | −36 (1) |
| CTAB | −27.6 (0.7) | |
| SB3-12 | −59 (1) | |
| Reline | SDS | −32.0 (0.4) |
| Ethaline | Glyceline | Reline | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDS-m60 | 0.114 | 0.09 | 0.066 |
| CTAB-m60 | 0.12 | ||
| SB3-12-m60 | 0.05 | ||
| SDS-m120 | 0.202 | 0.07 | 0.134 |
| CTAB-m120 | 0.107 | ||
| SB3-12-m120 | 0.07 |
| Micelle | Ethaline | Glyceline | Reline | Ethaline | Glyceline | Reline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs, Å | Rg, Å | |||||
| SDS-m60 | 19.9 | 21.0 | 22.6 | 15.4 | 16.2 | 17.5 |
| CTAB-m60 | 24.3 | 18.8 | ||||
| SB3-12-m60 | 19.7 | 15.3 | ||||
| SDS-m120 | 26.3 | 26.0 | 25.8 | 20.4 | 20.1 | 20.0 |
| CTAB-m120 | 29.3 | 22.7 | ||||
| SB3-12-m120 | 25.0 | 19.4 | ||||
| System | Atoms Forming Head–Tail Distance | Distance, Å | Atoms Forming Angle | Angle, Degrees |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eth-SDS-m60 | S1-C12 | 14.1 (0.2) | S1-C1-C12 | 143 (2) |
| Eth-SDS-m120 | 14.5 (0.1) | 148 (1) | ||
| Gly-SDS-m60 | S1-C12 | 14.0 (0.1) | S1-C1-C12 | 142 (2) |
| Gly-SDS-m120 | 14.3 (0.1) | 146 (2) | ||
| Gly-SB3-12-m60 | S1-C17 | 9.9 (0.2) | S1-C6-C17 | 118 (2) |
| Gly-SB3-12-m120 | 9.9 (0.1) | 119 (1) | ||
| Gly-CTAB-m60 | N1-C19 | 17.7 (0.2) | N1-C8-C19 | 146 (2) |
| Gly-CTAB-m120 | 17.8 (0.2) | 148 (3) | ||
| Rel-SDS-m60 | S1-C12 | 13.7 (0.2) | S1-C1-C12 | 138 (3) |
| Rel-SDS-m120 | 14.2 (0.1) | 143 (2) |
| System | Hbonds | Hbonds Involving Surfactant | Hbond Involving Only DES Components | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surf–Surf | Surf–Ch | Surf–HBD | Surf–Cl | Ch–Ch | Ch–HBD | Ch–Cl | Cl–HBD | HBD–HBD | |||
| Eth-SDS- m60 | Number | 1 (1) | 27 (5) | 36 (5) | 0 | 33 (8) | 591 (1) | 313 (14) | 727 (18) | 1373 (47) | 3101 |
| % | 0.0 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 19.1 | 10.1 | 23.4 | 44.3 | 100 | |
| 2.1 | 97.9 | ||||||||||
| Eth-SDS- m120 | Number | 2 (2) | 54 (7) | 66 (7) | 0 | 32 (8) | 583 (21) | 302 (15) | 704 (21) | 1375 (53) | 3118 |
| % | 0.1 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 18.7 | 9.7 | 22.6 | 44.1 | 100 | |
| 3.9 | 96.1 | ||||||||||
| Gly-SDS- m60 | Number | 0.6 (1) | 19 (4) | 70 (7) | 0 | 52 (11) | 328 (19) | 383 (18) | 1584 (30) | 1012 (42) | 3449 |
| % | 0.0 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 9.5 | 11.1 | 45.9 | 29.3 | 100 | |
| 2.6 | 97.4 | ||||||||||
| Gly-SDS-m120 | Number | 3 (2) | 41 (6) | 98 (8) | 0 | 55 (10) | 350 (17) | 359 (14) | 1616 (34) | 1006 (43) | 3528 |
| % | 0.1 | 1.2 | 2.8 | 0.0 | 1.6 | 9.9 | 10.2 | 45.8 | 28.5 | 100 | |
| 4.0 | 96.0 | ||||||||||
| Gly-SB3-12-m60 | Number | 163 (17) | 24 (4) | 75 (7) | 24 (4) | 54 (11) | 320 (18) | 390 (15) | 1650 (29) | 1003 (42) | 3703 |
| % | 4.4 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 8.6 | 10.5 | 44.6 | 27.1 | 100 | |
| 7.7 | 92.3 | ||||||||||
| Gly-SB3-12-m120 | Number | 352 (28) | 36 (5) | 145 (11) | 35 (5) | 55 (10) | 332 (19) | 378 (15) | 1695 (38) | 967 (45) | 3995 |
| % | 8.8 | 0.9 | 3.6 | 0.9 | 1.4 | 8.3 | 9.5 | 42.4 | 24.2 | 100 | |
| 14.2 | 85.8 | ||||||||||
| Gly-CTAB-m60 | Number | 0.4 (0.8) | 5 (2) | 21 (4) | 25 (5) | 50 (10) | 316 (17) | 382 (15) | 1649 (35) | 1013 (46) | 3461 |
| % | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 9.1 | 11.0 | 47.6 | 29.3 | 100 | |
| 1.5 | 98.5 | ||||||||||
| Gly-CTAB-m120 | Number | 1 (2) | 8 (3) | 36 (6) | 37 (6) | 55 (11) | 343 (18) | 370 (17) | 1711 (60) | 979 (42) | 3540 |
| % | 0.0 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 48.3 | 27.7 | 100 | |
| 2.3 | 97.7 | ||||||||||
| Rel-SDS- m60 | Number | 0.6 (1) | 21 (5) | 76 (10) | 0 | 50 (10) | 360 (21) | 386 (15) | 1121 (29) | 774 (39) | 2789 |
| % | 0.0 | 0.8 | 2.7 | 0.0 | 1.8 | 12.9 | 13.8 | 40.2 | 27.8 | 100 | |
| 3.5 | 96.5 | ||||||||||
| Rel-SDS- m120 | Number | 3 (2) | 36 (6) | 104 (10) | 0 | 53 (10) | 396 (19) | 378 (25) | 1167 (71) | 838 (49) | 2975 |
| % | 0.1 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 0.0 | 1.8 | 13.3 | 12.7 | 39.2 | 28.2 | 100 | |
| 4.8 | 95.2 | ||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voroshylova, I.V.; Ferreira, E.S.C.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Influence of Deep Eutectic Solvent Composition on Micelle Properties: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Molecules 2025, 30, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030574
Voroshylova IV, Ferreira ESC, Cordeiro MNDS. Influence of Deep Eutectic Solvent Composition on Micelle Properties: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Molecules. 2025; 30(3):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030574
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoroshylova, Iuliia V., Elisabete S. C. Ferreira, and M. Natália D. S. Cordeiro. 2025. "Influence of Deep Eutectic Solvent Composition on Micelle Properties: A Molecular Dynamics Study" Molecules 30, no. 3: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030574
APA StyleVoroshylova, I. V., Ferreira, E. S. C., & Cordeiro, M. N. D. S. (2025). Influence of Deep Eutectic Solvent Composition on Micelle Properties: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Molecules, 30(3), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030574








