A Multi-Component and Multi-Functional Synergistic System for Efficient Viscosity Reduction of Extra-Heavy Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Viscosity Reduction Effect of Blending Coal Tar
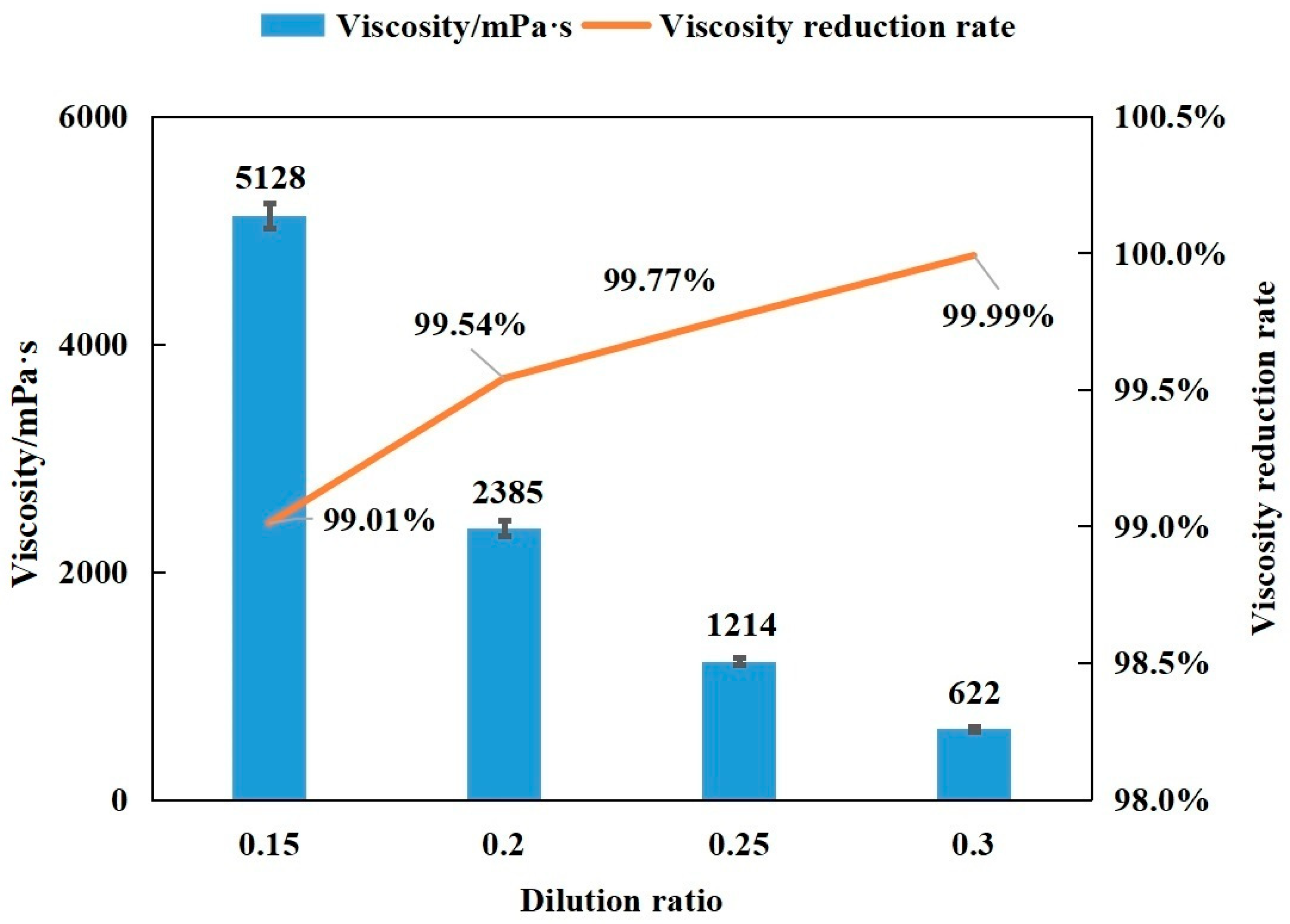
2.2. Viscosity Reduction Effect of Blending Washing Oil
2.3. Viscosity Reduction Effect of Blending Washing Oil/Light Crude Oil
2.4. Viscosity Reduction Effect of Blending Washing Oil/Aromatic Compound
2.5. Viscosity Reduction Effect of Blending Washing Oil and Surfactant
2.6. Comparison of Viscosity Reduction Effects of Different Dilute Media
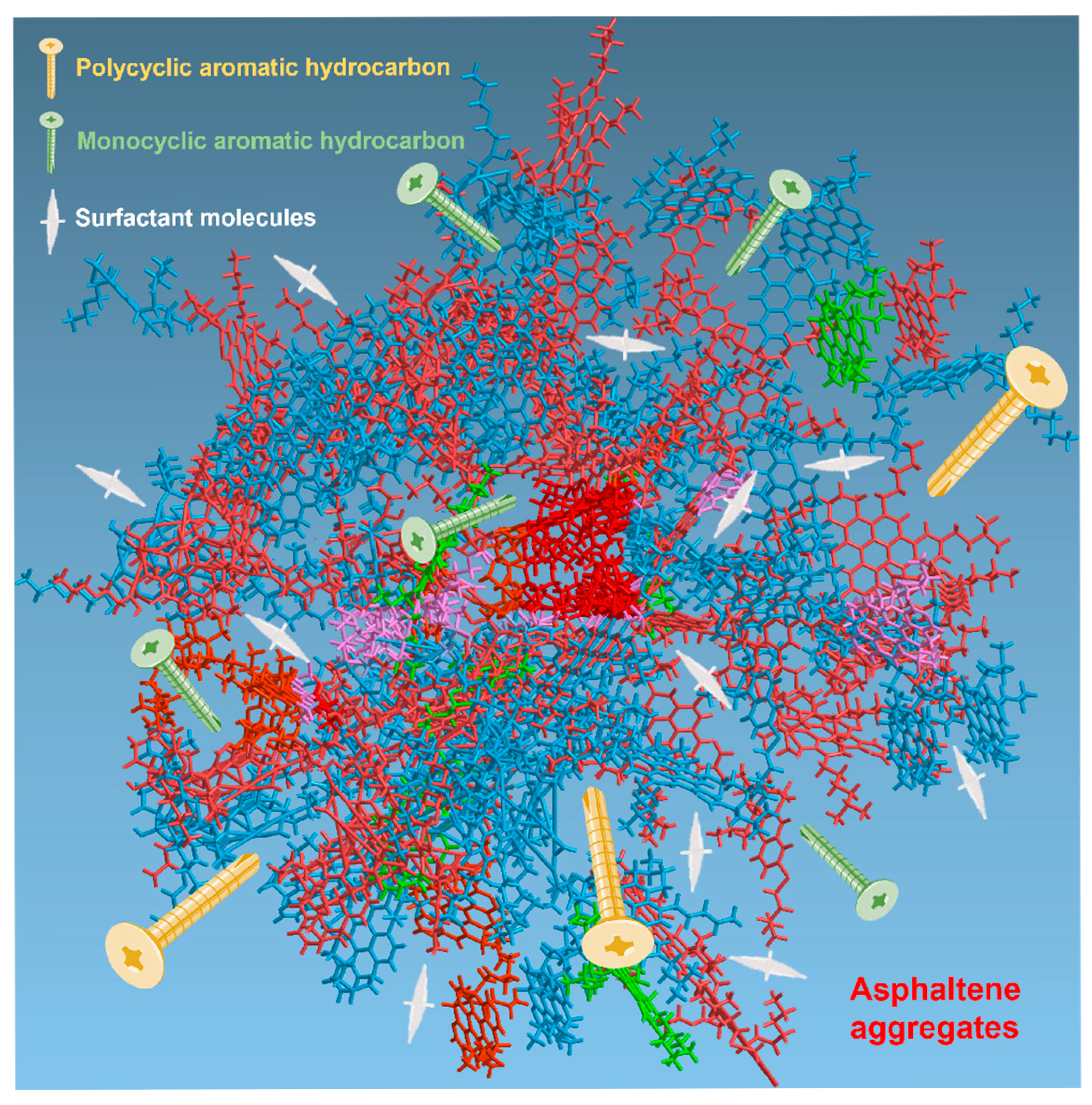
2.7. Viscosity Reduction Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experiment on Blending and Viscosity Reduction of Extra-Heavy Oil
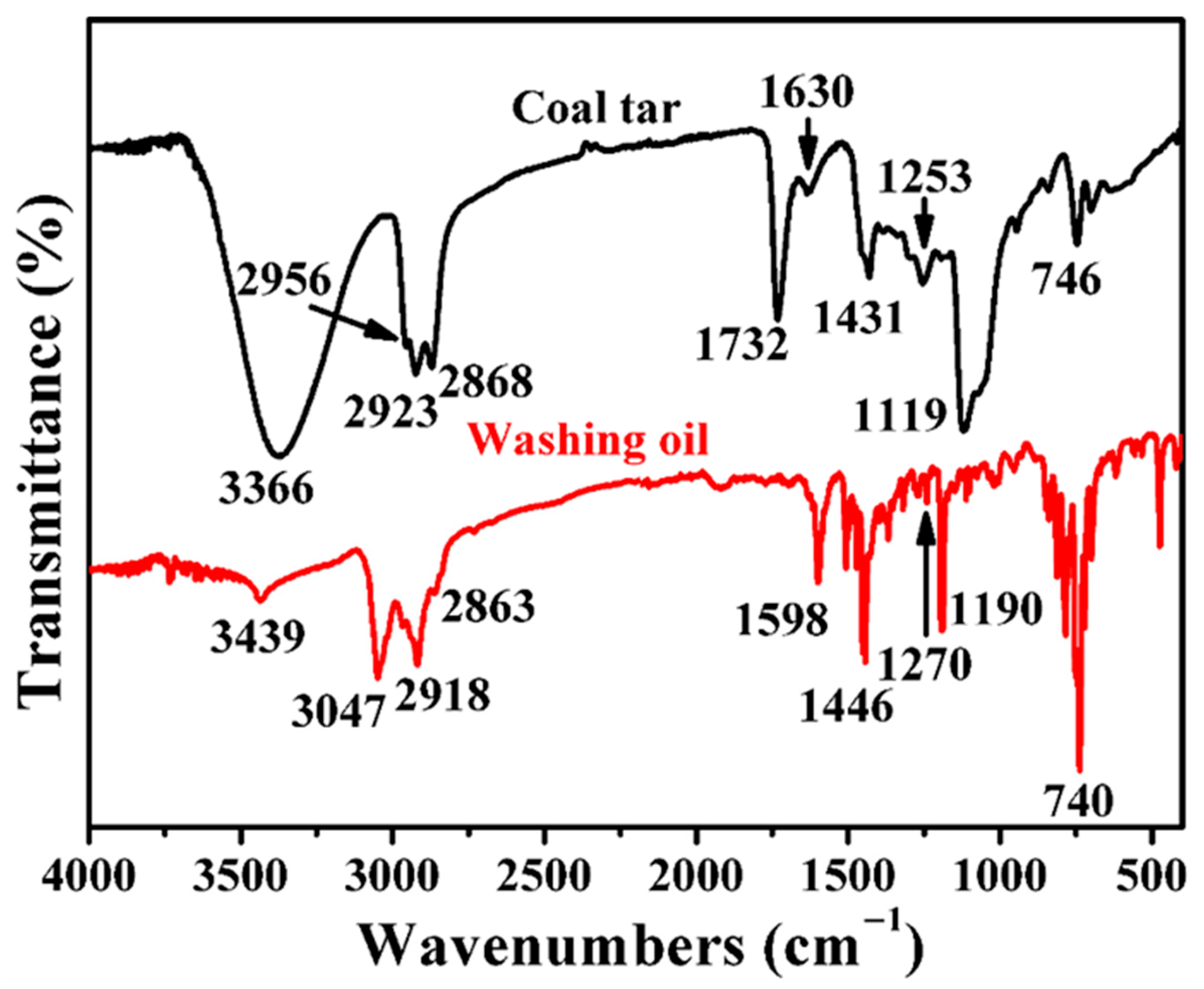
3.3. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyu, C.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Han, X.; Chen, M.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J. Core scale analysis of low viscosity oil injection in enhancing oil recovery of heavy oil reservoirs. Energy 2023, 275, 127432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, S.; Zendehboudi, S.; James, L. A comprehensive review of asphaltene deposition in petroleum reservoirs: Theory, challenges, and tips. Fuel 2019, 252, 753–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Gu, Y. Effects of asphaltene content on the heavy oil viscosity at different temperatures. Fuel 2007, 86, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Li, H.; Yu, Z. In-situ heavy and extra-heavy oil recovery: A review. Fuel 2016, 185, 886–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y. Analysis of the microstructure of high viscosity components in Tahe ultra heavy oil based on the combination of ESI (±) FT-ICR/MS. Fuel 2024, 368, 131594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, J.A.; Jafari, A.; Sabet, S.A.; Karami, F. Kinetic studies on extra heavy crude oil upgrading using nanocatalysts by applying CFD techniques. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Jiang, T.; Yuan, C.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Wan, F.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X. An improved viscosity prediction model of extra heavy oil for high temperature and high pressure. Fuel 2022, 319, 123852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Guo, J.; Kiyingi, W.; Gao, C.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.; Song, H.; Wang, X. Technical transformation of heavy/ultra-heavy oil production in China driven by low carbon goals: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 458, 142531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, B.; Yuan, H.; Peng, H.; Zhong, J.; Yan, Y.; Li, Z. Nonlinear relationship between heavy oil viscosity and asphaltene dispersion: A molecular dynamics simulation study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 295, 120173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minale, M.; Merola, M.C.; Carotenuto, C. Effect of solvents on the microstructure aggregation of a heavy crude oil. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 177, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.; An, N.; Cao, J. The influence of separated fractions on crude oil viscosity. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2012, 30, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Microstructure of heavy oil components and mechanism of influence on viscosity of heavy oil. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 10980–10990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.D.; Dong, P.C.; Cui, J.W.; Gao, Q.C. Prediction model for the viscosity of heavy oil diluted with light oil using machine learning techniques. Energies 2022, 15, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Arinina, M.P.; Polyakova, M.Y.; Kulichikhin, V.G.; Malkin, A.Y. Rheological comparison of light and heavy crude oils. Fuel 2016, 186, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baikenov, M.; Izbastenova, D.; Sarsenbekova, A.; Balpanova, N.; Tusipkhan, A.; Khalikova, Z.; Rakhimzhanova, N.; Kochegina, E.; Tulebaeva, B.; Taurbaeva, G. Determination of the kinetic parameters of thermal degradation and hydrodemetallization of a mixture of the heavy fraction of low-temperature coal tar and coal shale. Energies 2024, 17, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiatowski, M.; Kapusta, K.; Muzyka, R. Study of properties of tar obtained from underground coal gasification trials. Fuel 2018, 228, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Zhu, J.; Wei, B.; Hu, H.; Jin, L. Catalytic upgrading of ex-situ heavy coal tar over modified activated carbon. Fuel 2022, 312, 122912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, T.; Xu, G.; Ding, X. Multiscale study on aging process and mechanism of high viscosity Asphalt: Macro-micro experiments and quantum chemical molecular simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 402, 133059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Xia, Q.; Yan, J.; Shui, H. Synergistic effect on co-hydrogenation of coal-petroleum co-processing oil and washing oil from coal tar distillate. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 170, 105921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, M.M.; Rabeea, M.A.; Muslim, R.F.; Zidan, T.A. Chemical composition (saturate fraction) of western Iraq natural bitumen. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 2527–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibiryaev, A.M.; Kozhevnikov, I.V.; Shalygin, A.S.; Martyanov, O.N. Transformation of petroleum asphaltenes in supercritical alcohols studied via FTIR and NMR techniques. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tian, F.; Liu, Y.; Cui, L.; Dan, Y.; Du, C.; Li, D. Comparison of the composition and structure for coal-derived and petroleum heavy subfraction by an improved separation method. Fuel 2021, 292, 120362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, M.; Ren, G.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Sun, D. Viscosity reduction of extra-heavy oil using toluene in water emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 560, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam-Maldonado, M.; Aranda-Jiménez, Y.G.; Arvizu-Sanchez, E.; Melo-Banda, J.A.; Díaz-Zavala, N.P.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.F.; Suarez-Dominguez, E.J. Extra heavy crude oil viscosity and surface tension behavior using a flow enhancer and water at different temperatures conditions. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, M.Z.; Zhang, R.; Ma, C.; Ma, D.S.; Jiang, L.X.; Xue, R.R.; Liu, K.E.D.; Huang, J.B. Viscosity reduction of heavy oils of different viscosities based on general cationic/anionic surfactant systems. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2017, 33, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headen, T.F.; Boek, E.S.; Jackson, G.; Totton, T.S.; Müller, E.A. Simulation of asphaltene aggregation through molecular dynamics: Insights and limitations. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 1108–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barré, L.; Simon, S.; Palermo, T. Solution properties of asphaltenes. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3709–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedghi, M.; Goual, L.; Welch, W.; Kubelka, J. Effect of asphaltene structure on association and aggregation using molecular dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 5765–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
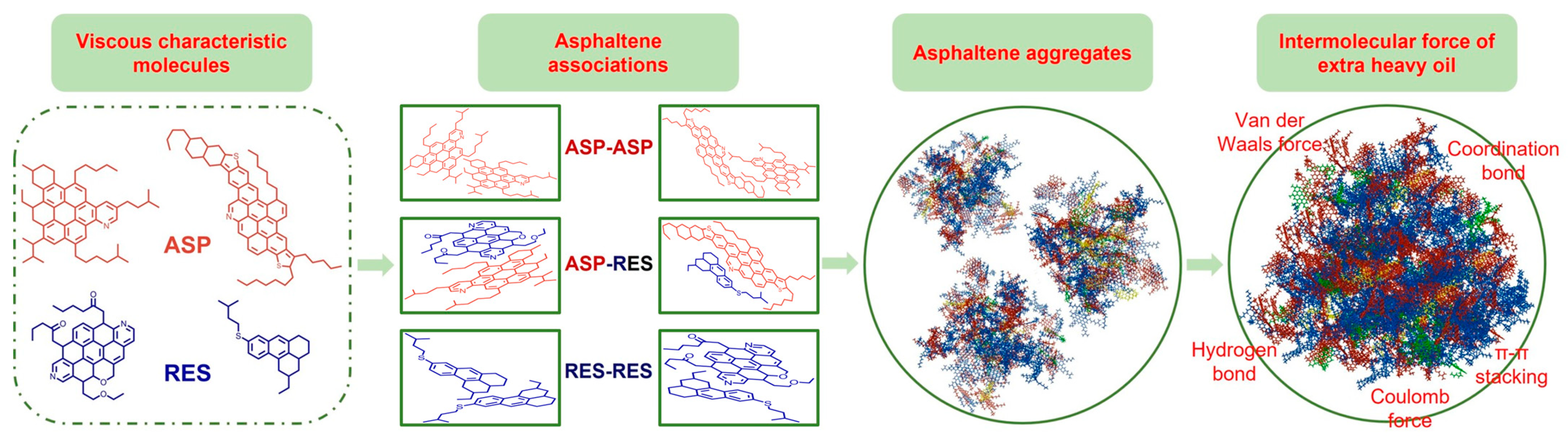


| Extra-Heavy Oil | Coal Tar | Coal Tar–Extra-Heavy Oil (Mass Ratio) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5 | |||
| Viscosity/mPa·s | 520,350 ± 1381 | 1834 ± 55 | 4283 ± 119 | 1900 ± 41 |
| Viscosity reduction rate/% | - | - | 99.18 | 99.63 |
| Extra-Heavy Oil | Washing Oil | Washing Oil–Extra-Heavy Oil (Mass Ratio) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.3 | |||
| Viscosity/mPa·s | 520,350 ± 1381 | <10 | 5128 ± 107 | 2385 ± 36 | 1214 ± 27 | 622 ± 19 |
| Viscosity reduction rate/% | - | - | 99.01 | 99.54 | 99.77 | 99.99 |
| Extra-Heavy Oil | Washing Oil | Light Crude Oil | Blending Medium (Washing Oil–Light Crude Oil)–Extra-Heavy Oil (Mass Ratio) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.6 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.4 | 0.3 | ||||
| (0:1.6) | (0:1.4) | (0.1:0.6) | (0.15:0.4) | (0.15:0.3) | (0.2:0.2) | (0.2:0.1) | ||||
| Viscosity/mPa·s | 520,350 ± 1381 | <10 | 220 ± 5 | 1556 ± 26 | 1838 ± 34 | 2097 ± 48 | 1409 ± 27 | 1974 ± 34 | 1486 ± 20 | 1775 ± 13 |
| Viscosity reduction rate/% | - | - | - | 99.70 | 99.65 | 99.60 | 99.73 | 99.62 | 99.71 | 99.66 |
| Extra-Heavy Oil | Washing Oil | Light Crude Oil | Blending Medium (Light Crude Oil)–Extra-Heavy Oil (Mass Ratio) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 | 1 | 0.8 | |||||||||
| Additive amount of washing oil/% | - | - | - | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 10 |
| Viscosity/mPa·s | 520,350 ± 1381 | <10 | 220 ± 5 | 2101 ± 39 | 1572 ± 23 | 2742 ± 29 | 2523 ± 42 | 1619 ± 22 | 5193 ± 103 | 3841 ± 75 | 1838 ± 28 |
| Viscosity reduction rate/% | - | - | - | 99.60 | 99.70 | 99.47 | 99.52 | 99.69 | 99.00 | 99.26 | 99.65 |
| Washing Oil–Aromatic Compounds–Extra-Heavy Oil (Mass Ratio) | Toluene | Xylene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity/mPa·s | Viscosity Reduction Rate/% | Viscosity/mPa·s | Viscosity Reduction Rate/% | |
| Extra-heavy oil (0:0:1) | 520,350 ± 1381 | - | 520,350 ± 1381 | - |
| Washing oil (1:0:0) | <10 | - | <10 | - |
| 0.2:0:1 | 2385 ± 36 | 99.54 | 2385 ± 36 | 99.54 |
| 0.16:0.04:1 | 2324 ± 38 | 99.55 | 2350 ± 61 | 99.55 |
| 0.14:0.06:1 | 1763 ± 33 | 99.66 | 1714 ± 34 | 99.67 |
| 0.12:0.08:1 | 1486 ± 23 | 99.71 | 1470 ± 19 | 99.72 |
| Surfactant Solution Concentration | SDBS | OP-10 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity /mPa·s | Viscosity Reduction Rate/% | Viscosity /mPa·s | Viscosity Reduction Rate/% | |
| 2% | 4111 ± 125. | 99.21 | 7510 ± 128 | 98.56 |
| 3% | 2689 ± 49 | 99.48 | 6185 ± 89 | 98.81 |
| 4% | 1541 ± 23 | 99.70 | 5133 ± 128 | 99.01 |
| Blending Medium–Extra-Heavy Oil (Mass Ratio) | Washing Oil–Another Medium–Extra-Heavy Oil (Mass Ratio) | Viscosity/mPa·s | Viscosity Reduction Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | 0:0.4 (diesel oil):1 | 1861 ± 29 | >99.62 |
| 0.25 | 0.25:0:1 | 1214 ± 27 | 99.77 |
| 0.3 | 0.2:0.1 (light crude oil):1 | 1775 ± 13 | 99.66 |
| 0.2 | 0.12:0.08 (toluene):1 | 1486 ± 23 | 99.71 |
| 0.2 | 0.12:0.08 (xylene):1 | 1470 ± 19 | 99.72 |
| 0.36 | 0.16:0.2 (4% SDBS):1 | 1541 ± 23 | 99.70 |
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Naphthalene content | 12.1% |
| Toluene insoluble content | 12.1% |
| Quinoline insoluble content | 3.1% |
| Water content | 2.8% |
| Ash content | 0.06% |
| Density | 1.2998 g·cm−3 |
| Carbon residue | 13.58% |
| Condensation point | −6 °C |
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Organochlorine content | 0.0055% |
| Naphthalene content | 1.03% |
| Phenol content | 0.6% |
| Water content | 0.9% |
| Density | 1.056 g·cm−3 |
| Open cup flash point | 75 °C |
| Initial boiling point | 193 °C |
| Distillate before 200 °C (volume fraction) | 17% |
| Distillate before 220 °C (volume fraction) | 67% |
| Distillate before 257 °C (volume fraction) | 93% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Pan, L.; Wei, D.; Feng, X.; He, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y. A Multi-Component and Multi-Functional Synergistic System for Efficient Viscosity Reduction of Extra-Heavy Oil. Molecules 2025, 30, 4446. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224446
Yang Z, Liu Y, Jiang J, Pan L, Wei D, Feng X, He L, Guo J, Zhang Y. A Multi-Component and Multi-Functional Synergistic System for Efficient Viscosity Reduction of Extra-Heavy Oil. Molecules. 2025; 30(22):4446. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224446
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zuguo, Yanxia Liu, Jing Jiang, Lijuan Pan, Dandi Wei, Xingen Feng, Long He, Jixiang Guo, and Yagang Zhang. 2025. "A Multi-Component and Multi-Functional Synergistic System for Efficient Viscosity Reduction of Extra-Heavy Oil" Molecules 30, no. 22: 4446. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224446
APA StyleYang, Z., Liu, Y., Jiang, J., Pan, L., Wei, D., Feng, X., He, L., Guo, J., & Zhang, Y. (2025). A Multi-Component and Multi-Functional Synergistic System for Efficient Viscosity Reduction of Extra-Heavy Oil. Molecules, 30(22), 4446. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224446







