Synthesis of 1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinoline Derivatives as Ligands Targeting Haspin Kinase
Abstract
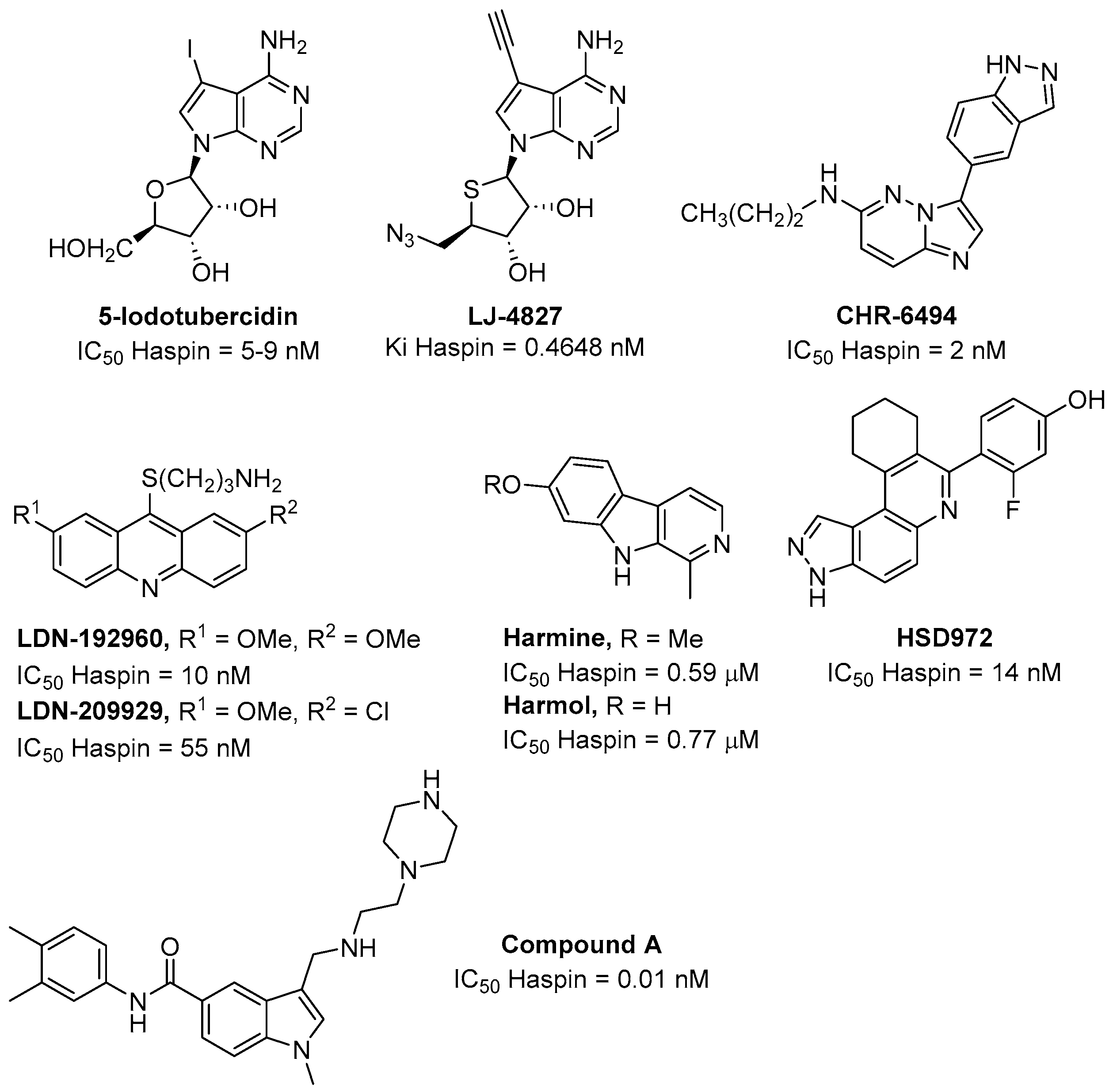
1. Introduction
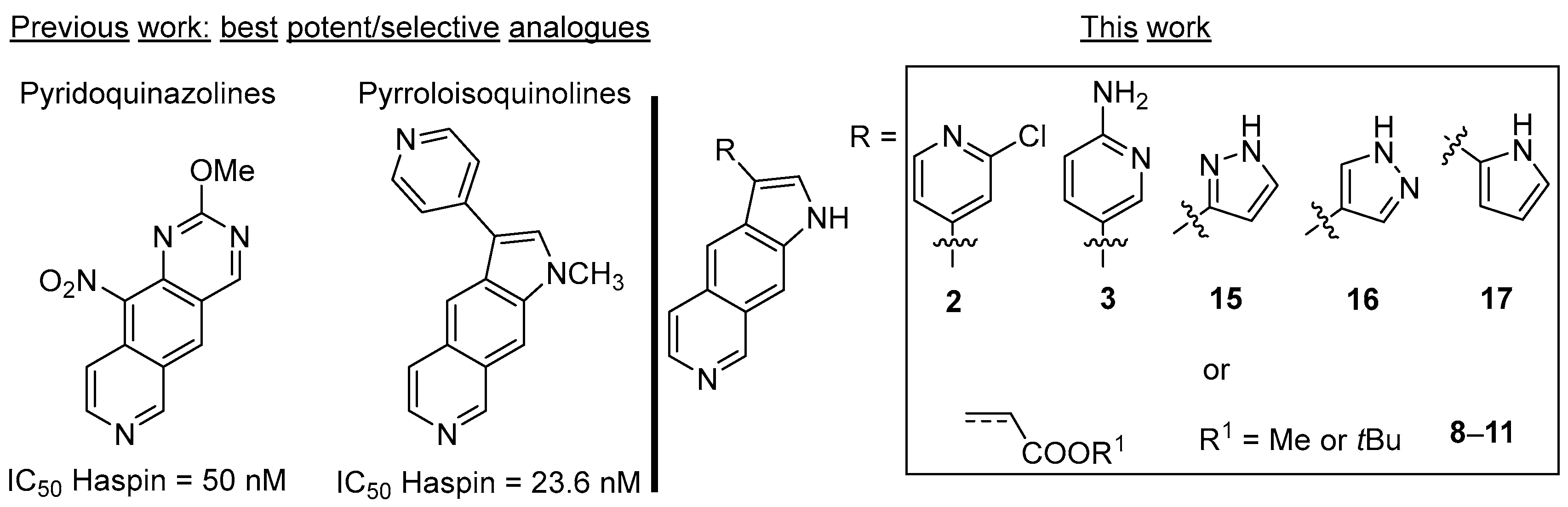
2. Synthesis and Biological Activity of New Pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinolines
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.1.1. General
4.1.2. General Synthetic Procedures
General Procedure A (Suzuki Coupling)
General Procedure B (Phosphorus Ylide)
General Procedure C (Wittig)
General Procedure D (Alkene Reduction)
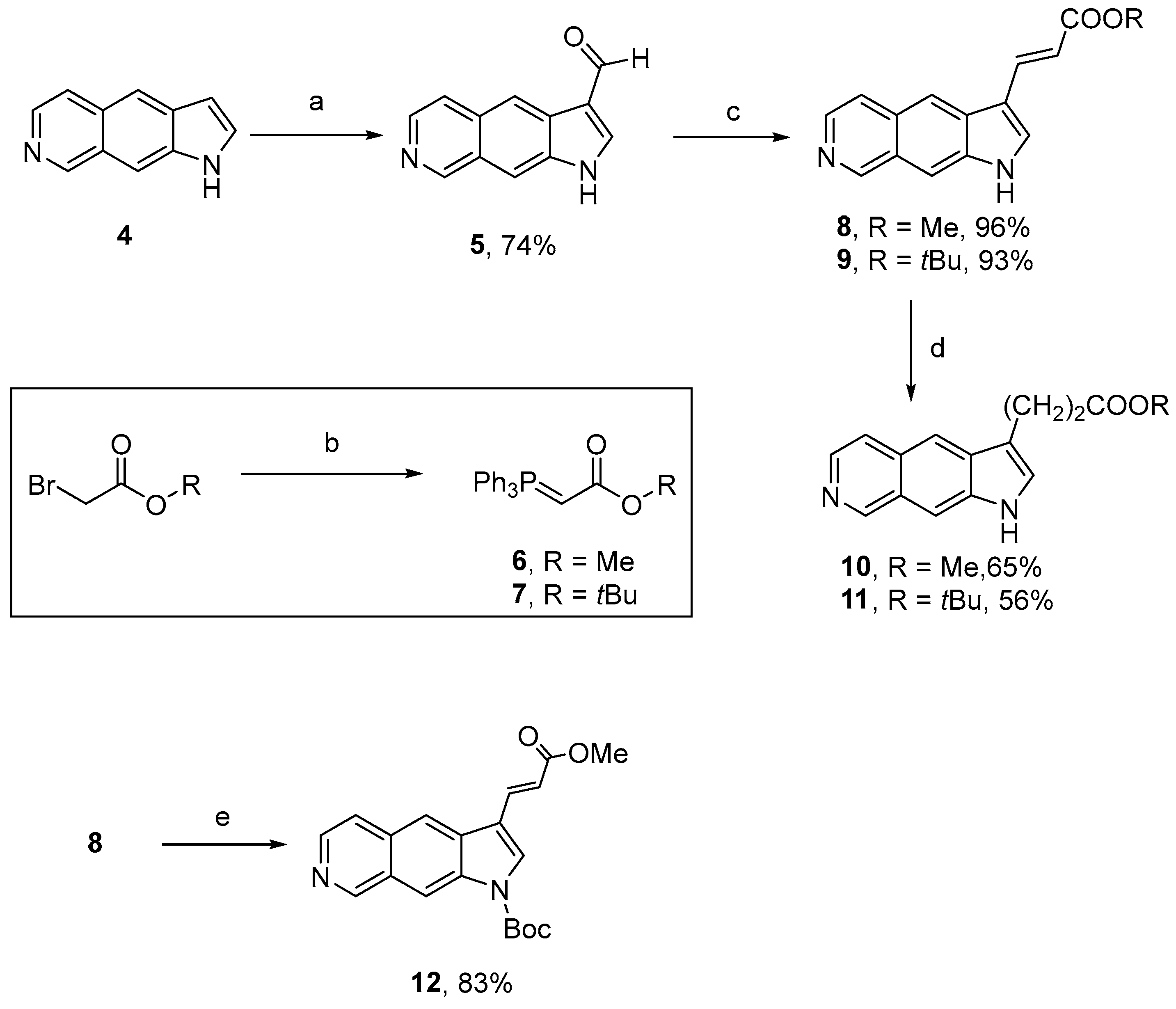
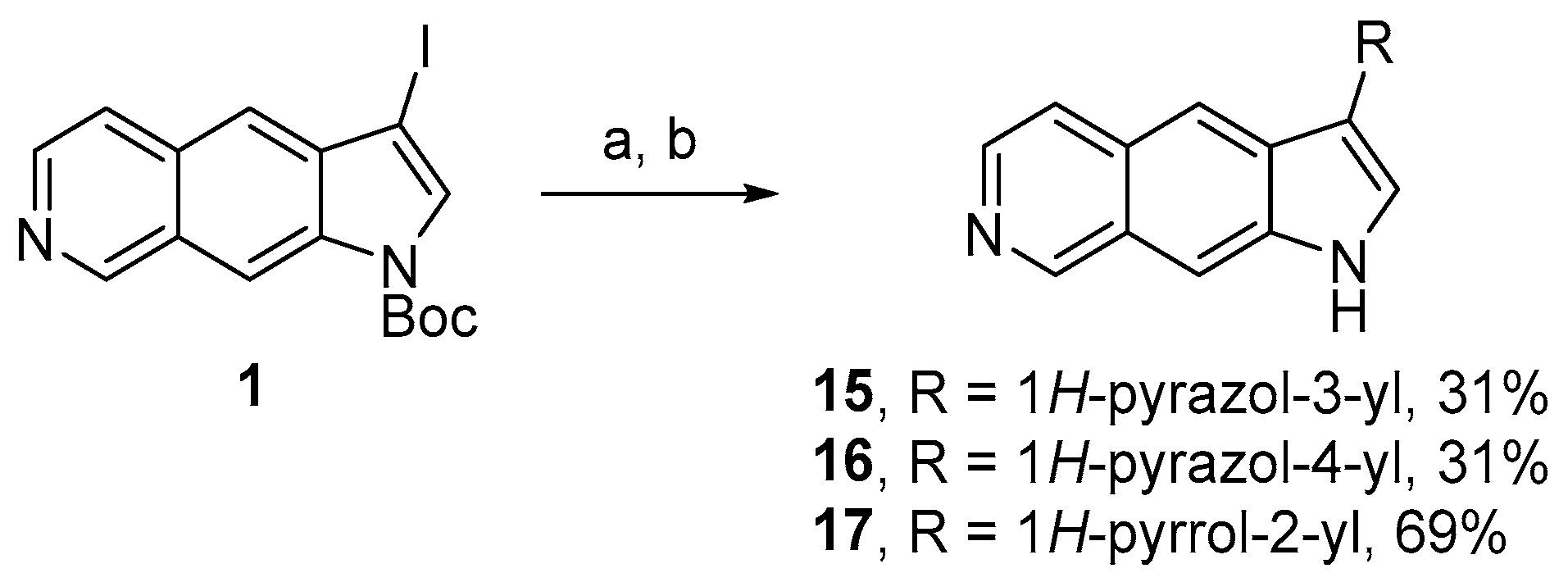
4.1.3. Synthesis of Compounds 2, 3, 6–12, and 15–17
3-(2-Chloro-pyridin-4-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinoline (2)
5-(1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinolin-3-yl)pyridin-2-amine (3)
Methyl (Triphenylphosphoranylidene)acetate (6)
tert-Butyl (Triphenylphosphoranylidene)acetate (7)
Methyl (E)-3-(1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinolin-3-yl)prop-2-enoate (8)
tert-Butyl (E)-3-(1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinolin-3-yl)prop-2-enoate (9)
Methyl 3-(1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinolin-3-yl)propanoate (10)
tert-Butyl 3-(1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinolin-3-yl)propanoate (11)
tert-Butyl (E)-3-(3-Methoxy-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinoline-1-carboxylate (12)
3-(1H-Pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinoline (15)
3-(1H-Pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinoline (16)
3-(1H-Pyrrol-2-yl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinoline (17)
4.2. In Vitro Kinase Inhibition Assays
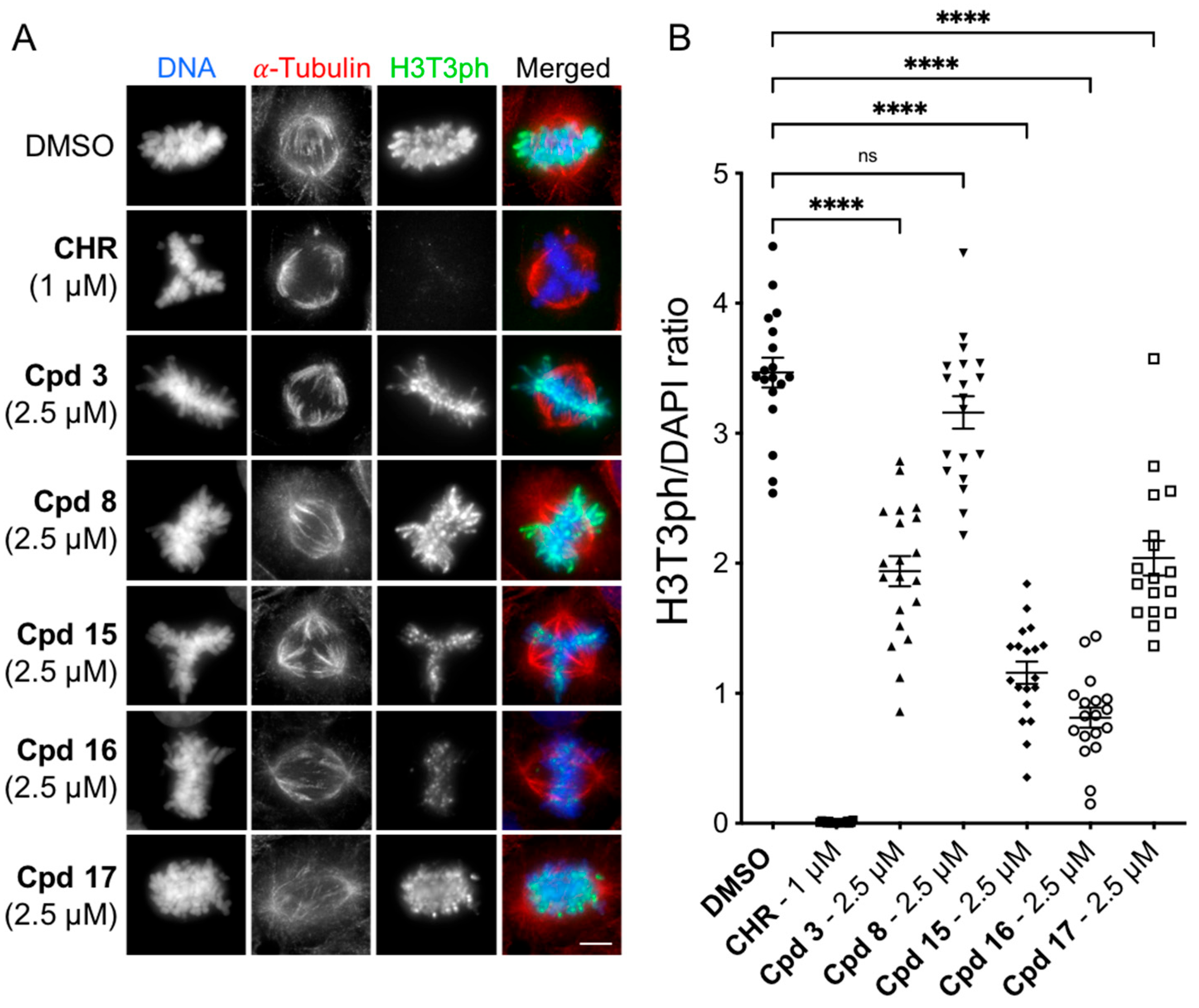
4.3. Cellular Evaluation: H3T3ph Immunofluorescence Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayala-Aguilera, C.C.; Valero, T.; Lorente-Macías, Á.; Baillache, D.J.; Croke, S.; Unciti-Broceta, A. Small molecule kinase inhibitor drugs (1995-2021): Medical indication, pharmacology, and synthesis. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 1047–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdeville, R.; Buchdunger, E.; Zimmermann, J.; Matter, A. Glivec (STI571, IMATINIB), a rationally developed, targeted anticancer drug. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors: A 2024 update. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 200, 107059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeinyeh, W.; Esvan, Y.J.; Josselin, B.; Defois, M.; Baratte, B.; Knapp, S.; Chaikuad, A.; Anizon, F.; Giraud, F.; Ruchaud, S.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of Haspin inhibitors: Kinase inhibitory potency and cellular activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 236, 114369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defois, M.; Josselin, B.; Brindeau, P.; Krämer, A.; Knapp, S.; Anizon, F.; Giraud, F.; Ruchaud, S.; Moreau, P. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1H-pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinolines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2024, 100, 117619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malosse, K.; Doula, M.B.; Josselin, B.; Robert, T.; Anizon, F.; Ruchaud, S.; Giraud, F.; Moreau, P. Synthesis and biological activity of 1H-pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinolines as Haspin kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2025, 123, 118157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feizbakhsh, O.; Place, M.; Fant, X.; Buron, F.; Routier, S.; Ruchaud, S. The mitotic kinase haspin and its inhibitors. In Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology “Protein Phosphorylation”; Prigent, C., Ed.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2017; Chapter 2; pp. 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, M.M.; Abdallah, M.; Khalifa, H.; Aboushady, Y.; Abadi, A.H.; Engel, M.; Abdel-Halim, M. Synthesis and evaluation of novel N1-acylated 5-(4-pyridinyl)indazole derivatives as potent and selective Haspin inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 145, 107235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, R.; Sertic, S.; Muzi-Falconi, M. Roles and regulation of Haspin kinase and its impact on carcinogenesis. Cell. Sign. 2022, 93, 110303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Brauer, C.; Thu, K.L.; Mason, J.M.; Blaser, H.; Bray, M.R.; Mak, T.W. Targeting mitosis in cancer: Emerging strategies. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Kuang, T.; Ren, Y.; Lu, Z.; Liao, Q.; Chen, W. Haspin knockdown can inhibit progression and development of pancreatic cancer in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 385, 111605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, D.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, W.; Xu, F. GSG2 (Haspin) promotes development and progression of bladder cancer through targeting KIF15 (Kinase-12). Aging 2020, 12, 8858–8879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas, D.; Soler, M.; Moreto, J.; Villanueva, A.; Martinez, A.; Vidal, A.; Charlton, M.; Moffat, D.; Patel, S.; McDermott, J.; et al. Antitumor activity of a small-molecule inhibitor of the histone kinase Haspin. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, D.; Liu, H.; Zhu, N.; Zhang, W.; Feng, J.; Yin, J.; Hao, B.; Cui, D.; Deng, Y.; et al. Identification of 5-iodotubercidin as a genotoxic drug with anti-cancer potential. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.-J.; Mashelkar, K.K.; Seo, J.; Shin, Y.-Z.; Sung, K.; Jang, S.C.; Cheon, S.W.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, G.; et al. In Silico discovery of 5′-modified 7-deoxy-7-ethynyl-4′-thioadenosine as a Haspin inhibitor and its synergistic anticancer effect with the PLK1 inhibitor. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 9, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuny, G.D.; Robin, M.; Ulyanova, N.P.; Patnaik, D.; Pique, V.; Casano, G.; Liu, J.-F.; Lin, X.; Xian, J.; Glicksman, M.A.; et al. Structure-activity relationship study of acridine analogs as Haspin and Dyrk2 kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3491–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuny, G.D.; Ulyanova, N.P.; Patnaik, D.; Liu, J.-F.; Lin, X.; Auerbach, K.; Ray, S.S.; Xian, J.; Glicksman, M.A.; Stein, R.L.; et al. Structure-activity relationship study of beta-carboline derivatives as Haspin kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 2015–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opoku-Temeng, C.; Dayal, N.; Sooreshjani, M.A.; Sintim, H.O. 3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline Haspin kinase inhibitors and anticancer properties. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 78, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestuto, V.; Ciagla, T.; Musella, S.; Di Sarno, V.; Smaldone, G.; Di Matteo, F.; Scala, M.C.; Napolitano, V.; Miranda, M.R.; Amodio, G.; et al. A comprehensive in vitro characterization of a new class of indole-based compounds developed as selective Haspin inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 12711–12734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Békés, M.; Langley, D.R.; Crews, C.M. PROTAC targeted protein degraders: The past is prologue. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, H. The mechanism of action and clinical value of PROTACs: A graphical review. Cell. Signal. 2022, 99, 110446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboho, T.C.; Giri, S.; Popova, I.; Michael, I.C.J.P.; de Koning, C.B. Double Sonogashira reactions on dihalogenated aminopyridines for the assembly of an array of 7-azaindoles bearing triazole and quinoxaline substitutents at C-5: Inhibitory bioactivity against Giarda duodenalis trophozoites. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 4943–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.T.; Pecchi, S.; Wagman, A.; Ni, Z.-J.; Knapp, M.; Hendrickson, T.; Atallah, G.; Pfister, K.; Zhang, Y.; Bartulis, S.; et al. Identification of NVP-BKM120 as a potent, selective, orally bioavailable class I PI3 kinase inhibitor for treating cancer. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyhlén, J.; Eriksson, L.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Synthesis and optical resolution of an allenoic acid by diastereomeric salt formation induced by chiral alkaloids. Chirality 2008, 20, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.; Ryou, B.; Choi, M.; Lee, C.; Park, C.-M. Electrochemical C(sp3)-H functionalization of γ-lactams based on hydrogen atom transfer. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 4264–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavri, N.P.; Trudell, M.L. An efficient method for the synthesis of 3-arypyrroles. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 2649–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupton, J.T.; Telang, N.; Gazzo, D.F.; Barelli, P.J.; Lescalleet, K.E.; Fagan, J.W.; Mills, B.J.; Finzel, K.L.; Kanters, R.P.F.; Crocker, K.R.; et al. Preparation of indole containing building blocks for the regiospecific construction of indole appended pyrazoles and pyrroles. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 5829–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegzouti, H.; Zdanovskaia, M.; Hsiao, K.; Goueli, S.A. ADP-Glo: A bioluminescent and homogeneous ADP monitoring assay for kinases. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2009, 7, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
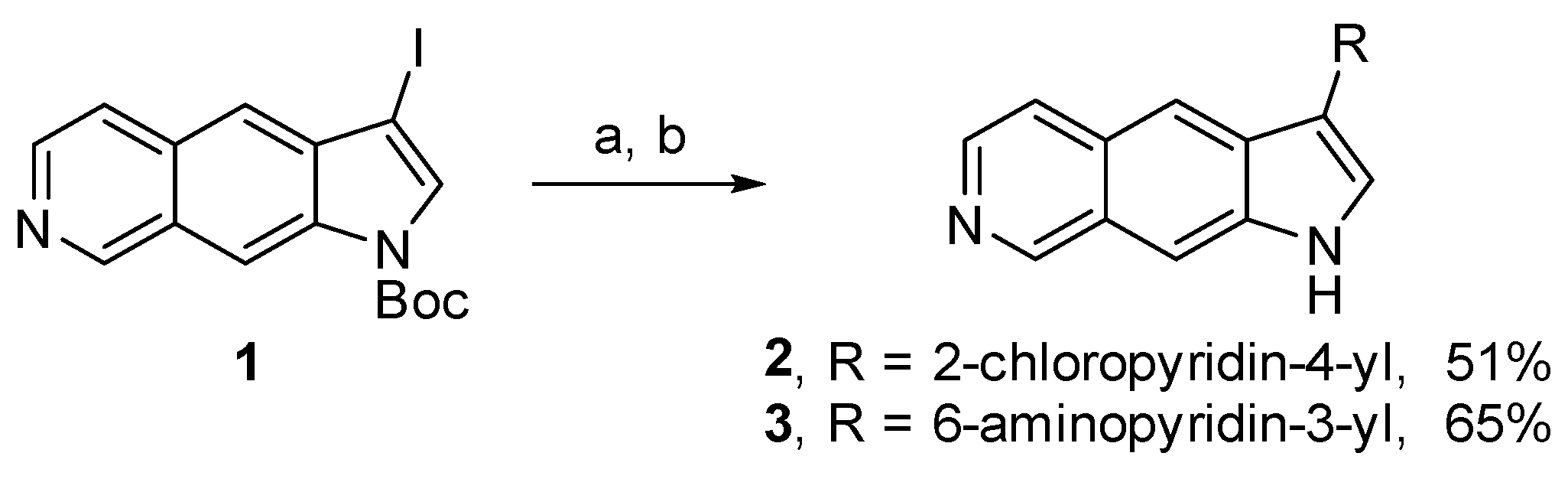

| Cpds | Kinase Inhibition (% Residual Activity at 10 μM or 1 μM (IC50 Values)) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haspin | CLK1 | DYRK1A | CDK9 | GSK3 | CK1 | CDK5 | PIM1 | SI | |||||||||
| 10 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 1 | ||
| 2 | 8 | 9 | 27 | 56 | 16 | 20 | 56 | 81 | 81 | 76 | 54 | 79 | 100 | 100 | 14 | 20 | |
| (10.1) | ND | ND | |||||||||||||||
| 3 | 1 | 7 | 18 | 59 | 0 | 15 | 44 | 83 | 58 | 80 | 63 | 78 | 100 | 100 | 7 | 17 | 8.8 |
| (10.6) | (212.5) | (93.7) | (PIM1) | ||||||||||||||
| 8 | 6 | 11 | 22 | 55 | 16 | 43 | 51 | 79 | 71 | 78 | 77 | 90 | 100 | 72 | 8 | 26 | 26.1 |
| (15.5) | (1128.0) | (404.4) | (PIM1) | ||||||||||||||
| 9 | 12 | 30 | 48 | 86 | 28 | 51 | 32 | 79 | 80 | 80 | 87 | 92 | 100 | 100 | 21 | 42 | |
| (391.8) | ND | ||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 10 | 45 | 60 | 91 | 32 | 72 | 72 | 90 | 99 | 100 | 97 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 52 | 72 | |
| (82.1) | |||||||||||||||||
| 11 | 52 | 70 | 81 | 98 | 31 | 58 | 86 | 100 | 94 | 83 | 81 | 98 | 100 | 100 | 60 | 70 | |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 32 | 1 | 39 | NE | NE | 86 | 100 | 48 | 100 | 76 | 98 | 0 | 44 | 7.4 |
| (30.6) | (503.2) | (323.8) | (221.9) | (PIM1) | |||||||||||||
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 11 | NE | NE | 17 | 94 | 12 | 77 | 10 | 91 | 0 | 20 | 8.2 |
| (12.4) | (102.0) | (163.4) | (1743) | (CLK1) | |||||||||||||
| 17 | 0 | 6 | 36 | 47 | 19 | 69 | 39 | 76 | 65 | 71 | 81 | 92 | 81 | 75 | 33 | 91 | 31.2 |
| (81.3) | (2522) | (CLK1) | |||||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malosse, K.; Josselin, B.; Ruchaud, S.; Anizon, F.; Giraud, F.; Moreau, P. Synthesis of 1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinoline Derivatives as Ligands Targeting Haspin Kinase. Molecules 2025, 30, 4388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224388
Malosse K, Josselin B, Ruchaud S, Anizon F, Giraud F, Moreau P. Synthesis of 1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinoline Derivatives as Ligands Targeting Haspin Kinase. Molecules. 2025; 30(22):4388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224388
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalosse, Killian, Béatrice Josselin, Sandrine Ruchaud, Fabrice Anizon, Francis Giraud, and Pascale Moreau. 2025. "Synthesis of 1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinoline Derivatives as Ligands Targeting Haspin Kinase" Molecules 30, no. 22: 4388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224388
APA StyleMalosse, K., Josselin, B., Ruchaud, S., Anizon, F., Giraud, F., & Moreau, P. (2025). Synthesis of 1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-g]isoquinoline Derivatives as Ligands Targeting Haspin Kinase. Molecules, 30(22), 4388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30224388








