A Study on the Mechanism of Cellulose Nanocrystals to Enhance the Stability of Hydrophobic Phthalocyanine Green in Water and the Functional Characteristics of Colour Pastes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
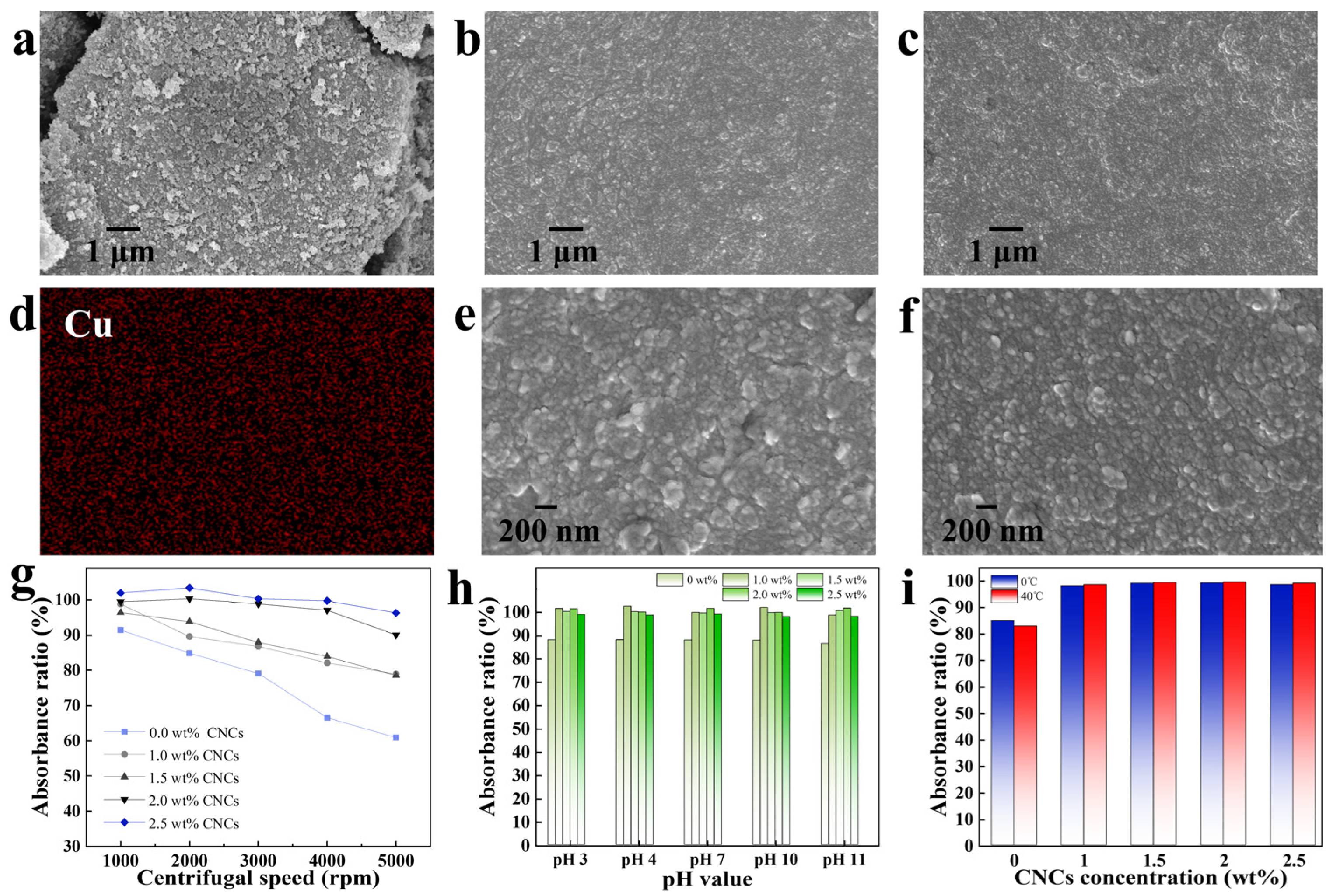
2.1. The Effect of CNCs on the Dispersion and Stability of Phthalocyanine Green in Water
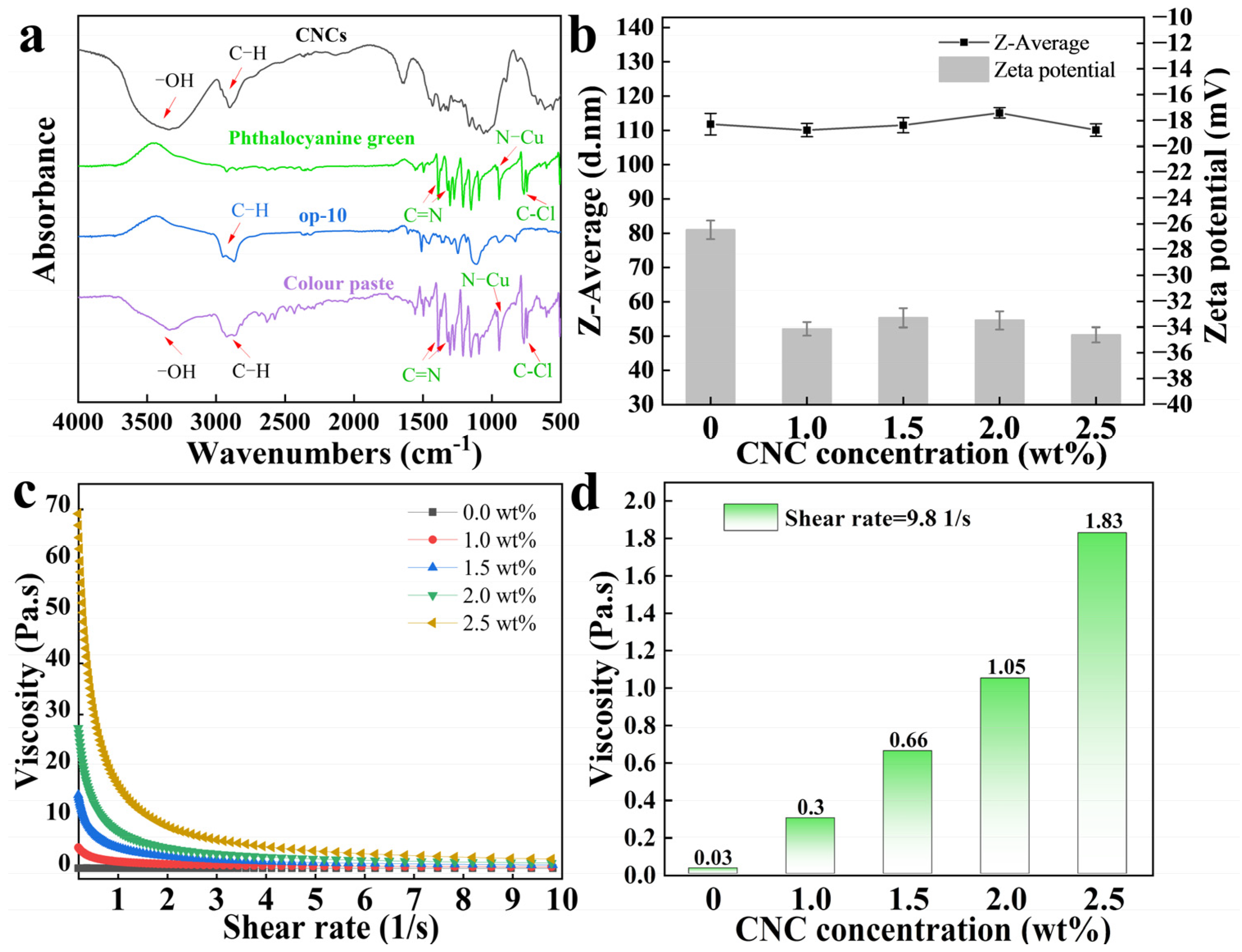
2.2. An Analysis of the Ability of CNCs to Enhance the Stability of Hydrophobic Phthalocyanine Green in Water
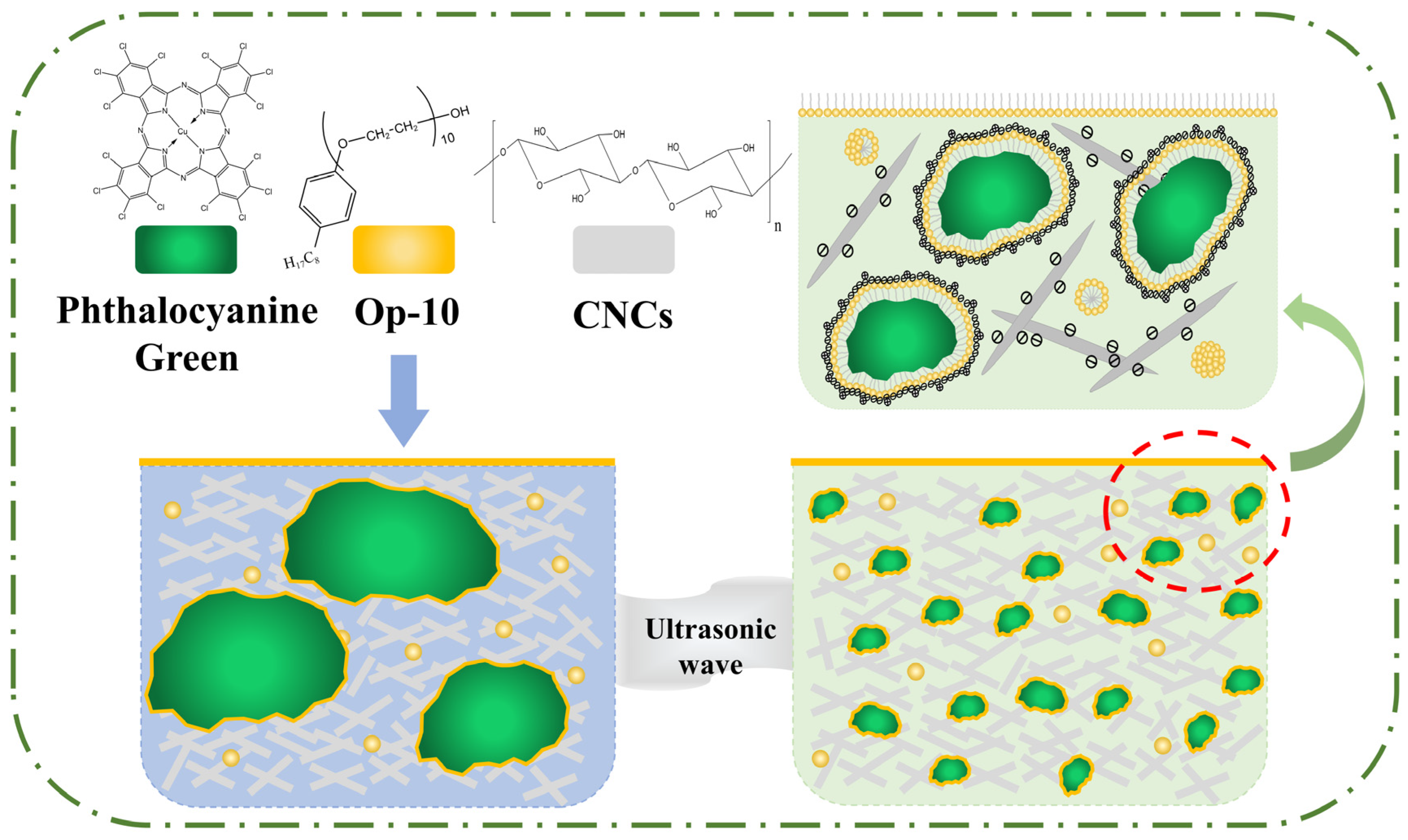
2.3. The Mechanism of CNCs to Enhance the Stability of Hydrophobic Phthalocyanine Green in Water
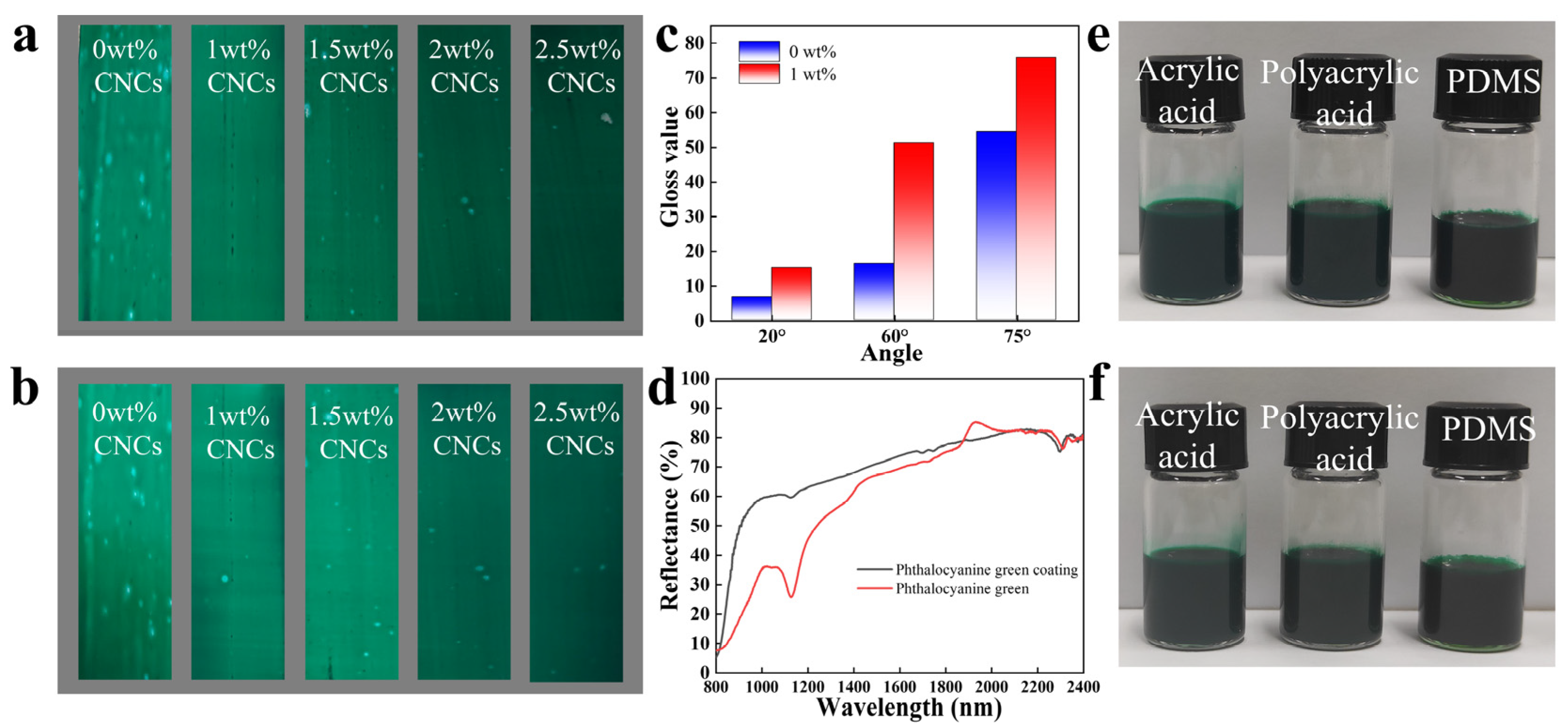
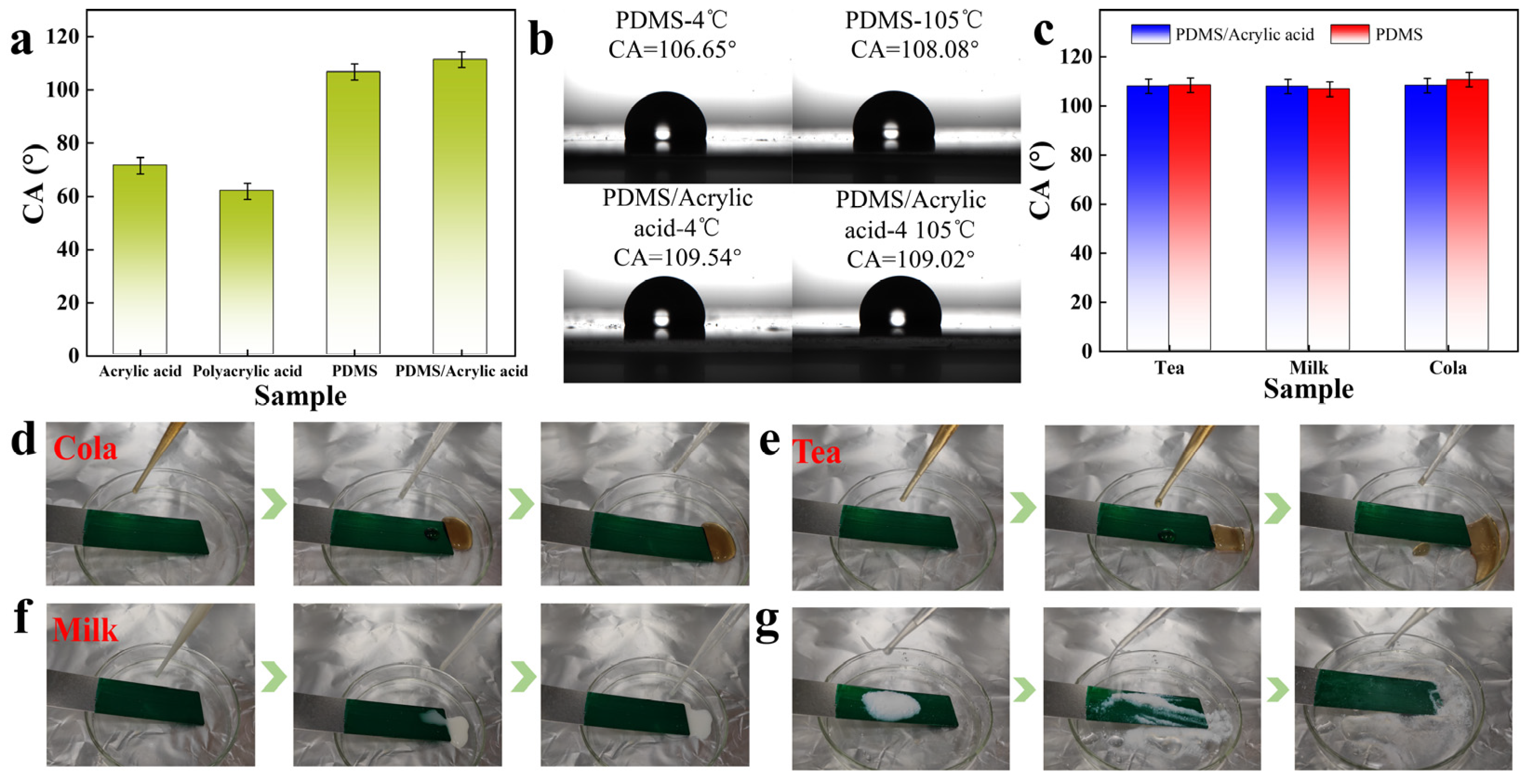
2.4. Functional Characteristics of Phthalocyanine Green Colour Pastes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Preparation of CNCs Colloid
3.3. Preparation of Phthalocyanine Green Colour Pastes and Paint
3.4. Morphology of Phthalocyanine Green Colour Pastes
3.5. Measurement of Dispersibility and Stability of Phthalocyanine Green Colour Pastes
3.5.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
3.5.2. Viscosity
3.5.3. Absorbance
3.6. Functional Measurement of Phthalocyanine Green Colour Pastes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stillman, M.J.; Thomson, A.J. Assignment of the charge-transfer bands in some metal phthalocyanines. Evidence for the S=1 state of iron (II) phthalocyanine in solution. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. II 1974, 70, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedi, B.; Edrisi, M.; Seyyedi, M.; Mahdavinia, G. A new single step synthesis of copper phthalocyanine green using microwave irradiation effects in functionalisation of C-H bonds in aromatic rings. Pigment. Resin Technol. 2014, 43, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Xie, J.; Li, G.; Li, X. Dispersion of phthalocyanine green G in nonaqueous medium using hyperdispersants and application in E-ink. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2006, 27, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.Y.; Wang, C.X.; Wang, C.X.; Zhang, K.R.; Fu, S.H. The electric response behavior and microencapsulation of the pigment phthalocyanine green G using interfacial polymerization. Polym. Bull. 2011, 67, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckler, L.C.; Phelps, D.K. Liver disease secondary to tetrachloroethylene exposure. A case report. JAMA 1966, 197, 662–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Hutcheon, D.E.; Regan, J. Cardiopulmonary toxicity of tetrachloroethylene. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1982, 10, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenschmid, D.S.; Cassin, B.J.; Hepler, B.R.; Kanluen, S. Tetrachloroethylene intoxication in an autoerotic fatality. J. Forensic Sci. 1998, 43, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emara, A.M.; El-Noor, M.M.A.; Hassan, N.A.; Wagih, A.A. Immunotoxicity and hematotoxicity induced by tetrachloroethylene in egyptian dry cleaning workers. Inhal. Toxicol. 2010, 22, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikmet, S.; Mustafa, B. Wetting and rheological characteristics of hydrophobic organic pigments in water in the presence of non-ionic surfactants. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 455, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haramagatti, C.R.; Dhande, P.; Bhavsar, R.; Umbarkar, A.; Joshi, A. Role of surfactants on stability of iron oxide yellow pigment dispersions. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 120, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musselman, S.W.; Chander, S. Wetting and adsorption of acetylenic diol based nonionic surfactants on heterogeneous surfaces. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 206, 497–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Yao, C.P.; Xue, F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Huettmann, G. Brownian diffusion of gold nanoparticles in an optical trap studied by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Laser Phys. 2011, 21, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libchaber, A. From Biology to Physics and back: The problem of Brownian movement. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2019, 10, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.T.; Wu, J.C. Organic nano-particle capping with polymeric surfactant dispersed by supercritical carbon dioxide in the binary solvent. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2013, 66, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.K.; Ambade, A.V.; Weck, M. Supramolecular ABC triblock copolymers via one-pot, orthogonal self-assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankova, K.; Chen, X.Y.; Kops, J.; Batsberg, W. Synthesis of amphiphilic PS-b-PEG-b-PS by atom transfer radical polymerization. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, S.; Peinado, S.; Morillas-Gutierrez, F.; La Rubia, M.D.; Moya, A.J. Nanocellulose from agricultural wastes: Products and applications-a review. Processes 2021, 9, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechyporchuk, O.; Belgacem, M.N.; Bras, J. Production of cellulose nanofibrils: A review of recent advances. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 93, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yu, H.; Abdalkarim, S.Y.H.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L. A comprehensive investigation on cellulose nanocrystals with different crystal structures from cotton via an efficient route. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 276, 118766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, D.; Purkait, M.K. Micro and nanocrystalline cellulose derivatives of lignocellulosic biomass: A review on synthesis, applications and advancements. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, T.; Ashraf, M.S.; Rajesh, A.S.; Ahalya, N.; Rawat, M.S.; Uma, B.; Sharma, R.; Subbiah, R.; Sida, S. Study of progress on nanocrystalline cellulose and natural fiber reinforcement biocomposites. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 6519480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Qiu, C.B.; Li, J.B.; Cao, Z.X.; Ma, C.S.; Zheng, J.; Huang, G.S. Self-recovery magnetic hydrogel with high strength and toughness using nanofibrillated cellulose as a dispersing agent and filler. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajian, A.; Lindstrom, S.B.; Pettersson, T.; Hamedi, M.M.; Wagberg, L. Understanding the dispersive action of nanocellulose for carbon nanomaterials. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.M.; Lu, S.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, F.S.; Cha, R.T. Nanocrystalline cellulose-dispersed AKD emulsion for enhancing the mechanical and multiple barrier properties of surface-sized paper. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noremylia, M.B.; Hassan, M.Z.; Ismail, Z. Recent advancement in isolation, processing, characterization and applications of emerging nanocellulose: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 954–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, K.L.; Venditti, R.A.; Rojas, O.J.; Habibi, Y.; Pawlak, J.J. A comparative study of energy consumption and physical properties of microfibrillated cellulose produced by different processing methods. Cellulose 2011, 18, 1097–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, O.; Syverud, K.; Gregersen, O. The use of microfibrillated cellulose produced from kraft pulp as strength enhancer in TMP paper. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 2008, 23, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Song, S.; Lopez-Valdivieso, A.; Shen, J.; Lu, S. Dispersion of silica fines in water-ethanol suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 238, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.A. Colloidal processing of ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 83, 2341–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, R.G. Surface forces and their action in ceramic materials. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1990, 73, 1117–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fu, S. Strategy for Manufacturing a deep-red ink based on nanocellulose and reactive red 120. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7233–7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, K. Study on mechanism of cellulose nanocrystals on hydrophobic phthalocyanine green in aqueous phase. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 324, 121505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Somasundaran, P.; Maltesh, C. Adsorption of n-dodecyl-beta-D-maltoside on solids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 191, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, I.; Levitz, P.; Zemb, T. SANS structural determination of a nonionic surfactant layer adsorbed on clay particles. Eur. Phys. J. B 1999, 10, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhu, S.; Yu, W.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, K. A design with natural polysaccharide particles and cationic conditioning agent as efficient emulsifier for hair care. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 286, 119311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 2409:2020 (en); Paints and Varnishes—Cross-Cut Test. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
| Sample | Wood | Polypropylene | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 wt% CNCs | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1.0 wt% CNCs | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1.5 wt% CNCs | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 2.0 wt% CNCs | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 2.5 wt% CNCs | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Sample | Peeling | Blistering | Loss of Light |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 wt% CNCs | NO | NO | NO |
| 1.0 wt% CNCs | NO | NO | NO |
| 1.5 wt% CNCs | NO | NO | NO |
| 2.0 wt% CNCs | NO | NO | NO |
| 2.5 wt% CNCs | NO | NO | NO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, K. A Study on the Mechanism of Cellulose Nanocrystals to Enhance the Stability of Hydrophobic Phthalocyanine Green in Water and the Functional Characteristics of Colour Pastes. Molecules 2025, 30, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020327
Lu J, Xu J, Zhou Z, Zhang Z, Li J, Zhang W, Chen K. A Study on the Mechanism of Cellulose Nanocrystals to Enhance the Stability of Hydrophobic Phthalocyanine Green in Water and the Functional Characteristics of Colour Pastes. Molecules. 2025; 30(2):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020327
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Junliang, Jun Xu, Ziyong Zhou, Zhaohui Zhang, Jun Li, Wei Zhang, and Kefu Chen. 2025. "A Study on the Mechanism of Cellulose Nanocrystals to Enhance the Stability of Hydrophobic Phthalocyanine Green in Water and the Functional Characteristics of Colour Pastes" Molecules 30, no. 2: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020327
APA StyleLu, J., Xu, J., Zhou, Z., Zhang, Z., Li, J., Zhang, W., & Chen, K. (2025). A Study on the Mechanism of Cellulose Nanocrystals to Enhance the Stability of Hydrophobic Phthalocyanine Green in Water and the Functional Characteristics of Colour Pastes. Molecules, 30(2), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020327





