Uncovering the Metabolic Footprint of New Psychoactive Substances by Metabolomics: A Systematic Review
Abstract
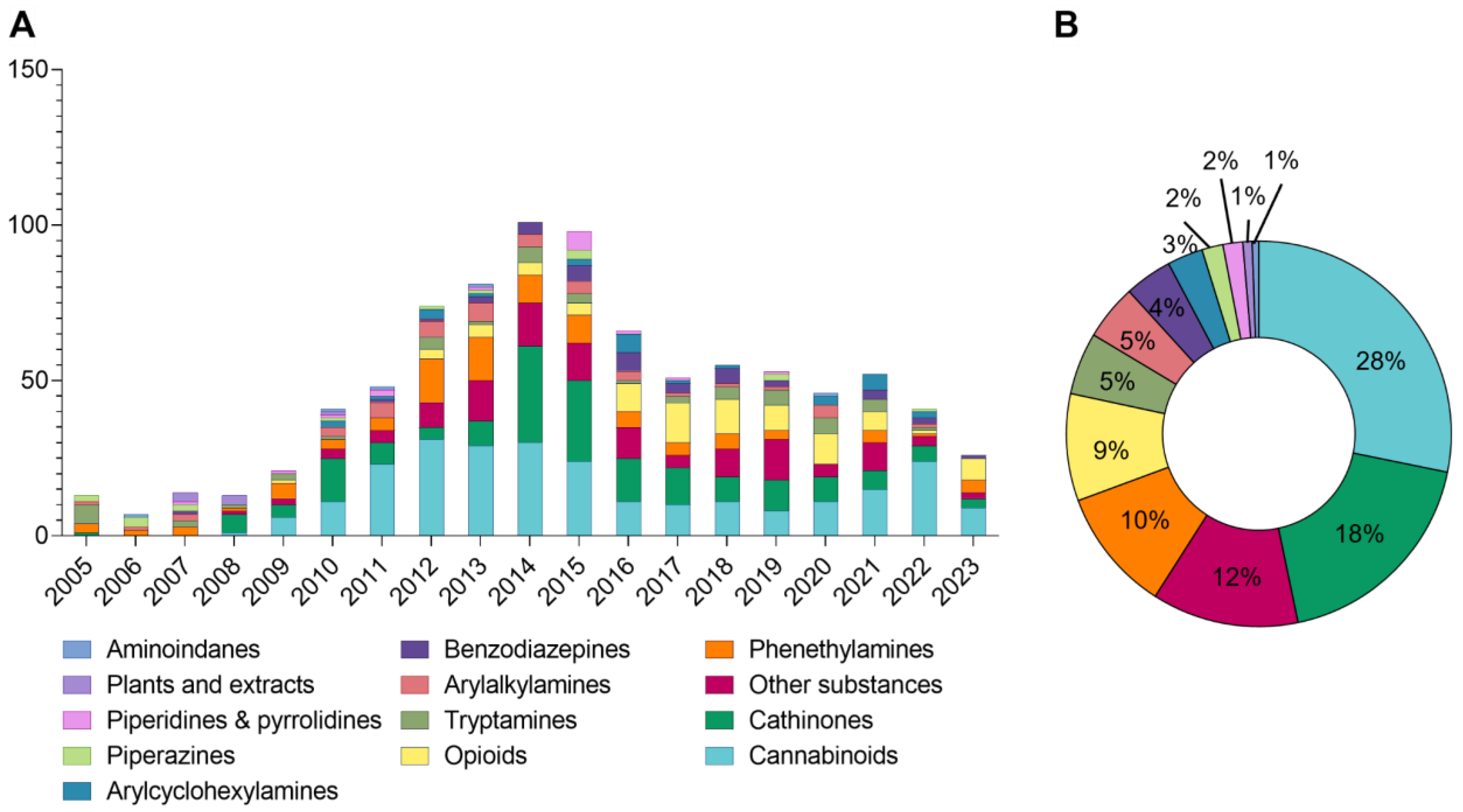
1. Introduction
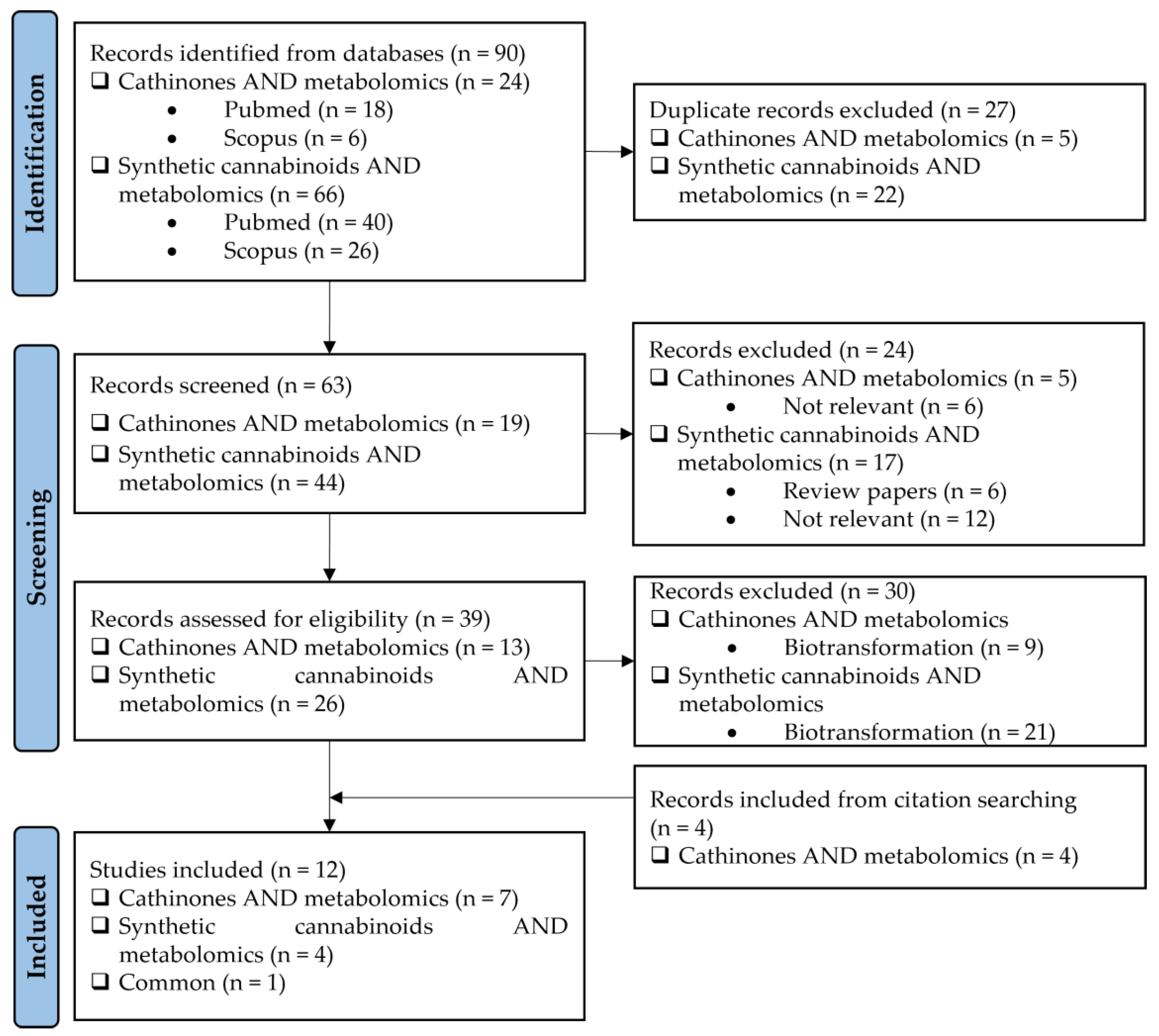
2. Literature Research Methodology
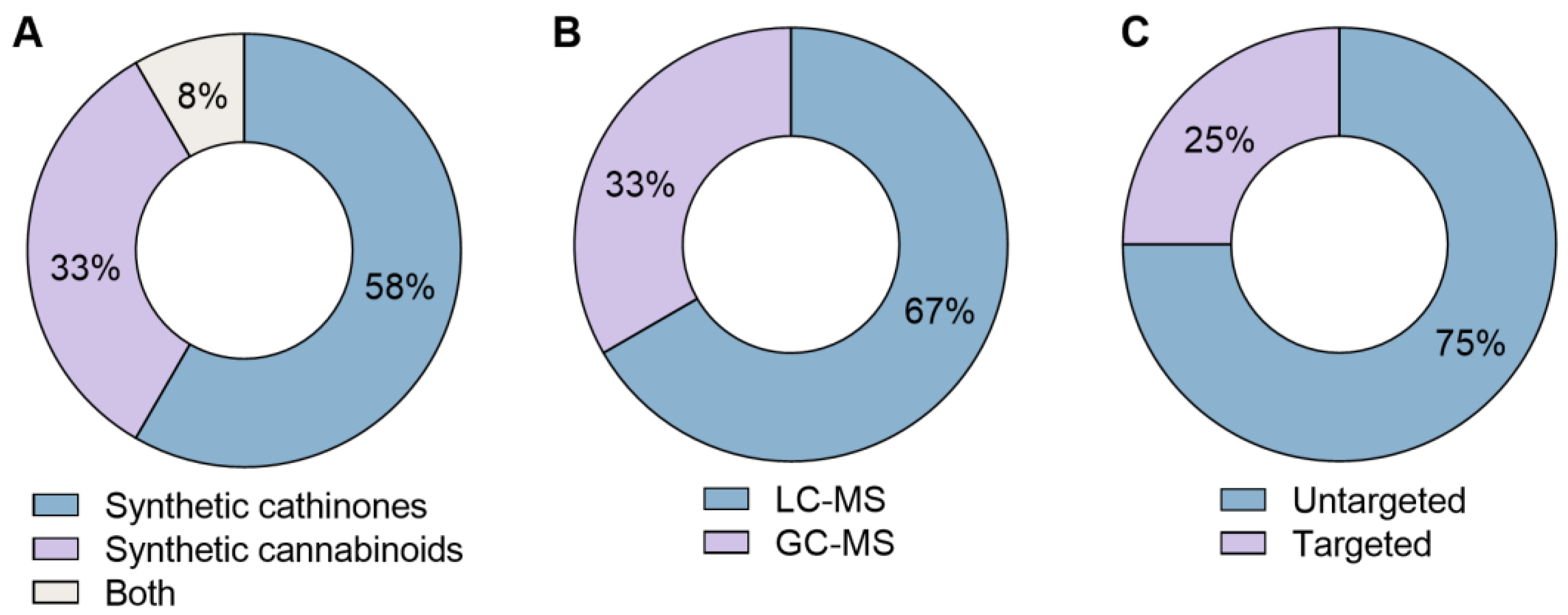
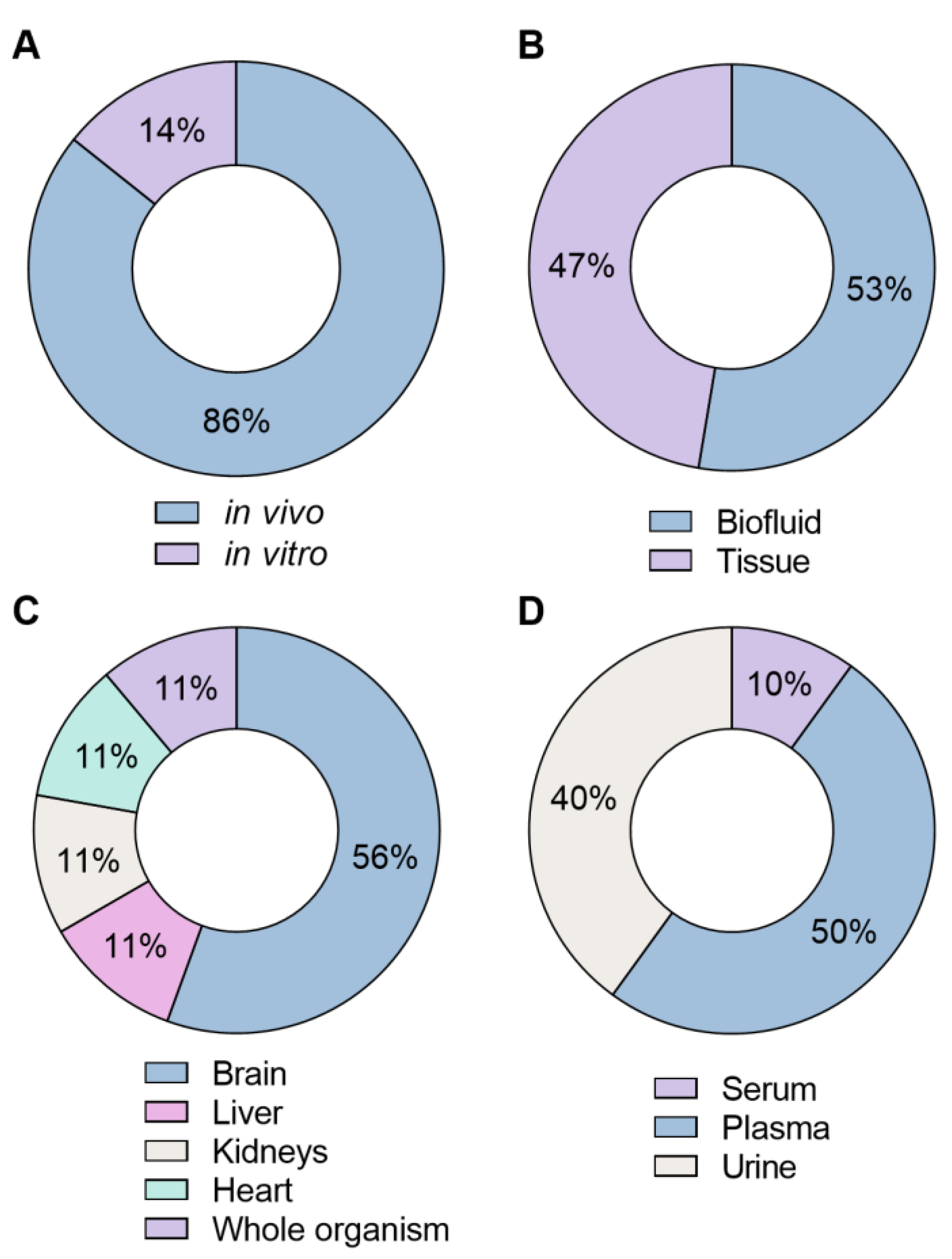
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Techniques
4.2. Metabolomic Approaches
4.3. Types of Models and Samples
4.4. Elucidation of Toxicological Effects
4.5. Comparison with Other Drugs of Abuse
4.6. Influence of Dose/Concentration
4.7. Metabolic Pathways Most Affected by Synthetic Cathinones and Synthetic Cannabinoids
4.8. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zanda, M.T.; Fattore, L. Chapter 29—Novel Psychoactive Substances: A New Behavioral and Mental Health Threat. In Addictive Substances and Neurological Disease; Watson, R.R., Zibadi, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 341–353. [Google Scholar]
- Coppola, M.; Mondola, R.; Oliva, F.; Picci, R.L.; Ascheri, D.; Trivelli, F. Chapter 63—Treating the Phenomenon of New Psychoactive Substances: Synthetic Cannabinoids and Synthetic Cathinones. In Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 679–686. [Google Scholar]
- Zawilska, J.B. Chapter Thirteen—“Legal Highs”—An Emerging Epidemic of Novel Psychoactive Substances. In International Review of Neurobiology; Taba, P., Lees, A., Sikk, K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 120, pp. 273–300. [Google Scholar]
- EMCDDA. New Psychoactive Substances—The Current Situation in Europe (European Drug Report 2024). Available online: https://www.euda.europa.eu/publications/european-drug-report/2024/new-psychoactive-substances_en (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Majchrzak, M.; Celiński, R.; Kuś, P.; Kowalska, T.; Sajewicz, M. The newest cathinone derivatives as designer drugs: An analytical and toxicological review. Forensic Toxicol. 2018, 36, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillet-Loilier, M.; Cesbron, A.; Boisselier, R.; Bourgine, J.; Debruyne, D. Emerging drugs of abuse: Current perspectives on substituted cathinones. Subst. Abus. Rehabil. 2014, 5, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.; Glennon, R.A. Cocaine-stimulus generalization to two new designer drugs: Methcathinone and 4-methylaminorex. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1993, 45, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, M.J.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Carvalho, F.; Carvalho, M. Khat and synthetic cathinones: A review. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 15–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, C.L.; Fleckenstein, A.E.; Hanson, G.R. Bath salts and synthetic cathinones: An emerging designer drug phenomenon. Life Sci. 2014, 97, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.L.; Alves, V.L.; Aguiar, J.; Teixeira, H.M.; Câmara, J.S. Synthetic cathinones: An evolving class of new psychoactive substances. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2019, 49, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debruyne, D.; Le Boisselier, R. Emerging drugs of abuse: Current perspectives on synthetic cannabinoids. Subst. Abus. Rehabil. 2015, 6, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaseit, E.; Pérez-Mañá, C.; Pérez-Acevedo, A.P.; Hladun, O.; Torres-Moreno, M.C.; Muga, R.; Torrens, M.; Farré, M. Cannabinoids: From pot to lab. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, V.L.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Aguiar, J.; Teixeira, H.M.; Câmara, J.S. The synthetic cannabinoids phenomenon: From structure to toxicological properties. A review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMCDDA. Synthetic Cannabinoids in Europe (Perspectives on Drugs). Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/topics/pods/synthetic-cannabinoids_en (accessed on 21 April 2024).
- de Oliveira, M.C.; Vides, M.C.; Lassi, D.L.S.; Torales, J.; Ventriglio, A.; Bombana, H.S.; Leyton, V.; Périco, C.A.; Negrão, A.B.; Malbergier, A.; et al. Toxicity of Synthetic Cannabinoids in K2/Spice: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.S.; Silva, B.; Pinho, P.G.; Remião, F.; Fernandes, C. Synthetic Cathinones: Recent Developments, Enantioselectivity Studies and Enantioseparation Methods. Molecules 2022, 27, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.C.; Maia, D.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Barbosa, D.J. New Psychoactive Substances: Health and Legal Challenges. Psychoactives 2024, 3, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.M.; Carvalho, F.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Carvalho, M. Toxicometabolomics: Small Molecules to Answer Big Toxicological Questions. Metabolites 2021, 11, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhifd, M.; Hartung, T.; Hogberg, H.T.; Kleensang, A.; Zhao, L. Review: Toxicometabolomics. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 1365–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, T.; Daneshian, M.; Kamp, H.; Bois, F.Y.; Clench, M.R.; Coen, M.; Donley, B.; Fischer, S.M.; Ekman, D.R.; Fabian, E.; et al. Metabolomics in toxicology and preclinical research. Altex 2013, 30, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsu, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Kusano, M.; Tsuchihashi, H.; Ishii, A. Application of metabolomics to toxicology of drugs of abuse: A mini review of metabolomics approach to acute and chronic toxicity studies. Drug. Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 31, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.M.; Carvalho, M.; Costa, V.M.; Duarte, J.A.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Bastos, M.L.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Carvalho, F. In vivo toxicometabolomics reveals multi-organ and urine metabolic changes in mice upon acute exposure to human-relevant doses of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV). Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manier, S.K.; Keller, A.; Schäper, J.; Meyer, M.R. Untargeted metabolomics by high resolution mass spectrometry coupled to normal and reversed phase liquid chromatography as a tool to study the in vitro biotransformation of new psychoactive substances. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kong, T.Y.; Moon, J.Y.; Choi, K.H.; Cho, Y.Y.; Kang, H.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, H.S. Targeted and non-targeted metabolite identification of MAM-2201 in human, mouse, and rat hepatocytes. Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 10, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhou, X.; Xu, C.; Gao, F.; Liu, J.; Wu, C.; Liu, S.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and metabolomics of the new psychoactive substance 4-chloroethylcathinone. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 105039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmer, S.; Wagmann, L.; Pulver, B.; Westphal, F.; Meyer, M.R. In Vitro and In Vivo Toxicometabolomics of the Synthetic Cathinone PCYP Studied by Means of LC-HRMS/MS. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, A.M.; Bastos, M.D.L.; Carvalho, F.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Carvalho, M. Effect of temperature on 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV)-induced metabolome disruption in primary mouse hepatic cells. Toxicology 2020, 441, 152503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, A.E.; Kaelin, D.; Boxler, M.I.; Eisenbeiss, L.; Holze, F.; Vizeli, P.; Czerwinska, J.; Dargan, P.I.; Abbate, V.; Liechti, M.E.; et al. Comparative Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of the Psychostimulants 3,4-Methylenedioxy-Methamphetamine (MDMA), Amphetamine, and the Novel Psychoactive Substance Mephedrone after Controlled Drug Administration to Humans. Metabolites 2020, 10, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesti, E.; De Toma, I.; Ramaekers, J.G.; Brunt, T.M.; Carbó, M.L.; Fernández-Avilés, C.; Robledo, P.; Farré, M.; Dierssen, M.; Pozo, Ó.J.; et al. Metabolomics predicts the pharmacological profile of new psychoactive substances. J. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 33, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manier, S.K.; Wagmann, L.; Flockerzi, V.; Meyer, M.R. Toxicometabolomics of the new psychoactive substances α-PBP and α-PEP studied in HepaRG cell incubates by means of untargeted metabolomics revealed unexpected amino acid adducts. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 2047–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, A.M.; Carvalho, M.; Bastos, M.L.; Carvalho, F.; de Pinho, P.G. Metabolic signature of methylone in primary mouse hepatocytes, at subtoxic concentrations. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 3277–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shestakova, K.M.; Mesonzhnik, N.V.; Markin, P.A.; Moskaleva, N.E.; Nedorubov, A.A.; Brito, A.; Appolonova, E.G.; Kuznetsov, R.M.; Bochkareva, N.L.; Kukharenko, A.; et al. Pharmacokinetic Properties of the Novel Synthetic Cannabinoid 5F-APINAC and Its Influence on Metabolites Associated with Neurotransmission in Rabbit Plasma. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markin, P.A.; Brito, A.; Moskaleva, N.E.; Tagliaro, F.; La Frano, M.R.; Savitskii, M.V.; Appolonova, S.A. Short- and long-term exposures of the synthetic cannabinoid 5F-APINAC induce metabolomic alterations associated with neurotransmitter systems and embryotoxicity confirmed by teratogenicity in zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 243, 109000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.S.; Fukumori, R.; Takeda, T.; Song, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Kikura-Hanajiri, R.; Yamaguchi, T.; Watanabe, K.; Aritake, K.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Elevation of endocannabinoids in the brain by synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018: Mechanism and effect on learning and memory. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaitsu, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Nakayama, H.; Hattori, N.; Takahara, R.; Kusano, M.; Tsuchihashi, H.; Ishii, A. Metabolome disruption of the rat cerebrum induced by the acute toxic effects of the synthetic cannabinoid MAM-2201. Life Sci. 2015, 137, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Raftery, D. NMR-Based Metabolomics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1280, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emwas, A.H.; Roy, R.; McKay, R.T.; Tenori, L.; Saccenti, E.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Raftery, D.; Alahmari, F.; Jaremko, L.; Jaremko, M.; et al. NMR Spectroscopy for Metabolomics Research. Metabolites 2019, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Cheng, L.L.; Copié, V.; Edison, A.S.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Hoch, J.C.; Gouveia, G.J.; Pathmasiri, W.; Powers, R.; Schock, T.B.; et al. NMR and Metabolomics-A Roadmap for the Future. Metabolites 2022, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crook, A.A.; Powers, R. Quantitative NMR-Based Biomedical Metabolomics: Current Status and Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeki, Ö.C.; Eylem, C.C.; Reçber, T.; Kır, S.; Nemutlu, E. Integration of GC-MS and LC-MS for untargeted metabolomics profiling. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 190, 113509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.W.; Li, Q.H.; Xu, Z.D.; Dou, J.J. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics in health and medical science: A systematic review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 3092–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujak, R.; Struck-Lewicka, W.; Markuszewski, M.J.; Kaliszan, R. Metabolomics for laboratory diagnostics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 113, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szeremeta, M.; Pietrowska, K.; Niemcunowicz-Janica, A.; Kretowski, A.; Ciborowski, M. Applications of Metabolomics in Forensic Toxicology and Forensic Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, M.H.; Walters, H.M.; Niello, M.; Sitte, H.H. Neuropharmacology of Synthetic Cathinones. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2018, 252, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidnia, S.; Manayi, A.; Abdollahi, M. From in vitro Experiments to in vivo and Clinical Studies; Pros and Cons. Curr. Drug. Discov. Technol. 2015, 12, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Xu, H.; Qiu, S.; Wang, X. Cell metabolomics. Omics 2013, 17, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, T.; Daston, G. Are in vitro tests suitable for regulatory use? Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 111, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.J.; Araújo, A.M.; Silva, R.; Bastos, M.d.L.; Carvalho, F.; Guedes de Pinho, P.; Carvalho, M. 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV): In vitro mechanisms of hepatotoxicity under normothermic and hyperthermic conditions. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1959–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luethi, D.; Liechti, M.E.; Krähenbühl, S. Mechanisms of hepatocellular toxicity associated with new psychoactive synthetic cathinones. Toxicology 2017, 387, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetwynd, A.J.; Dunn, W.B.; Rodriguez-Blanco, G. Collection and Preparation of Clinical Samples for Metabolomics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 965, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Villaret-Cazadamont, J.; Claus, S.P.; Canlet, C.; Guillou, H.; Cabaton, N.J.; Ellero-Simatos, S. Important Considerations for Sample Collection in Metabolomics Studies with a Special Focus on Applications to Liver Functions. Metabolites 2020, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibotto, G.; Sofia, A.; Saffioti, S.; Bonanni, A.; Mannucci, I.; Verzola, D. Amino acid and protein metabolism in the human kidney and in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Maejima, T.; Kano, M. Endogenous cannabinoids mediate retrograde signals from depolarized postsynaptic neurons to presynaptic terminals. Neuron 2001, 29, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, M.; Ossato, A.; Canazza, I.; Trapella, C.; Borelli, A.C.; Beggiato, S.; Rimondo, C.; Serpelloni, G.; Ferraro, L.; Marti, M. Synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018 and its halogenated derivatives JWH-018-Cl and JWH-018-Br impair Novel Object Recognition in mice: Behavioral, electrophysiological and neurochemical evidence. Neuropharmacology 2016, 109, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, L. Cannabis and the brain. Brain 2003, 126, 1252–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, E.; Baur, R.; Rácz, I.; Marazzi, J.; Smart, T.G.; Zimmer, A.; Gertsch, J. The major central endocannabinoid directly acts at GABA(A) receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18150–18155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altun, B.; Çok, İ. Psychoactive Bath Salts and Neurotoxicity Risk. Turk. J. Pharma. Sci. 2020, 17, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, A.M.; Bastos, M.L.; Fernandes, E.; Carvalho, F.; Carvalho, M.; Guedes de Pinho, P. GC-MS metabolomics reveals disturbed metabolic pathways in primary mouse hepatocytes exposed to subtoxic levels of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 3307–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrine, S.A.; Michaels, M.S.; Ghoddoussi, F.; Hyde, E.M.; Tancer, M.E.; Galloway, M.P. Cardiac effects of MDMA on the metabolic profile determined with 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the rat. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomfield, M.A.; Ashok, A.H.; Volkow, N.D.; Howes, O.D. The effects of Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol on the dopamine system. Nature 2016, 539, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moranta, D.; Esteban, S.; García-Sevilla, J.A. Differential effects of acute cannabinoid drug treatment, mediated by CB1 receptors, on the in vivo activity of tyrosine and tryptophan hydroxylase in the rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2004, 369, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dando, I.; Donadelli, M.; Costanzo, C.; Dalla Pozza, E.; D’Alessandro, A.; Zolla, L.; Palmieri, M. Cannabinoids inhibit energetic metabolism and induce AMPK-dependent autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compound | Experimental Conditions | Main Results | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
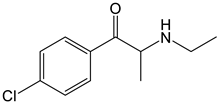 4-CEC | Approach: Untargeted Sample: Mouse serum Dose: 40 mg/kg Exposure time: 2 h or 7 days Replicates: 7 Technique: UHPLC-MS/MS |
| [26] |
 PCYP | Approach: Untargeted Sample: Rat urine and plasma Dose: 2 mg/kg body weight Exposure time: 1 h for plasma and 24 h for urine Replicates: 5 Technique: LC-HRMS | Rat plasma samples:
| [27] |
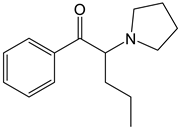 MDPV | Approach: Untargeted Sample: Mouse liver, kidneys, brain, heart tissues, and urine Dose: 2.5 mg/kg or 5 mg/kg every 2 h Exposure time: 24 h Replicates: 10 Technique: GC-MS | Metabolites and metabolic pathways affected in each sample: Liver:
| [22] |
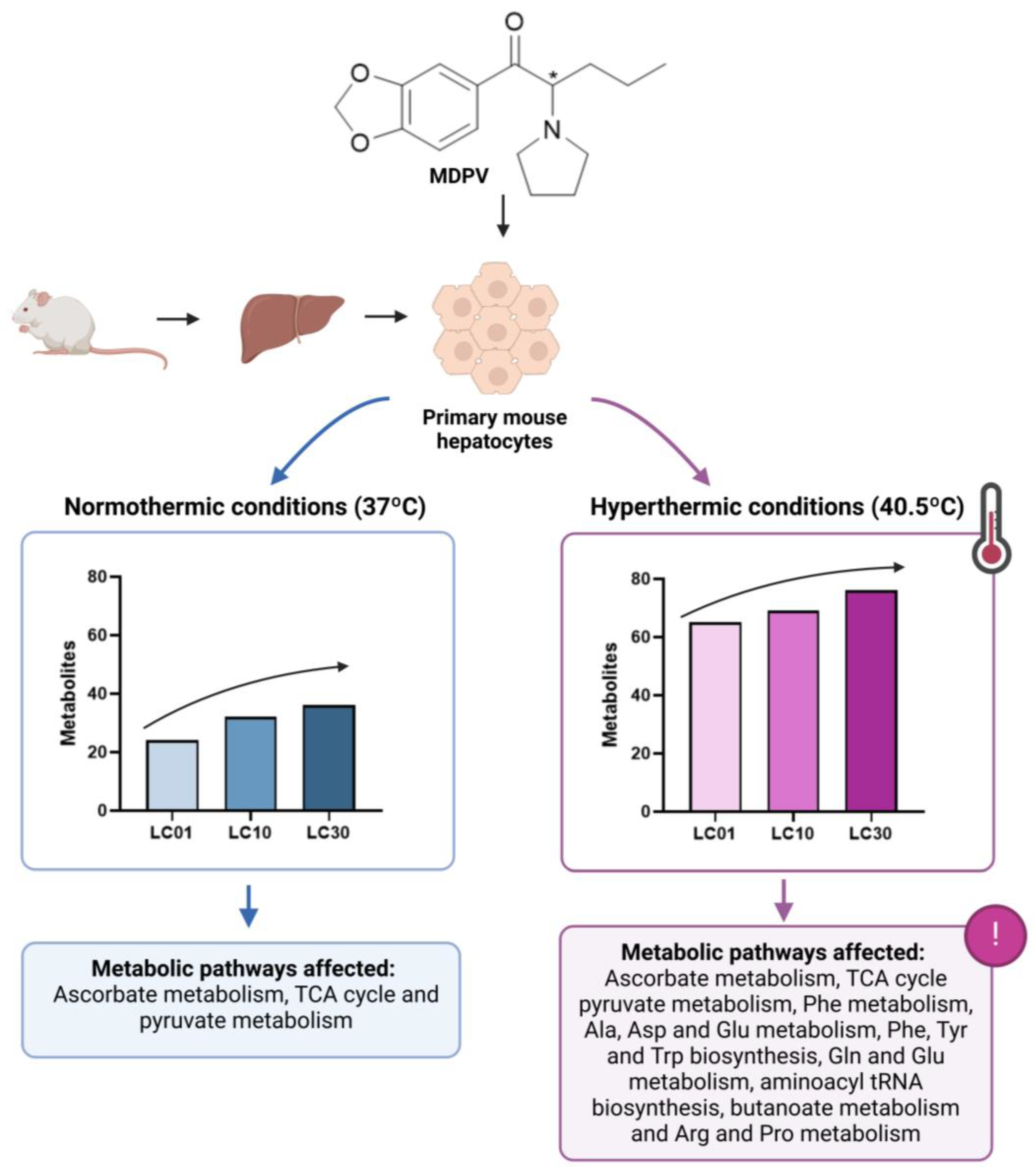
| Approach: Untargeted Sample: Primary mouse hepatocytes Concentration: 70, 240, and 477 μM Exposure time: 24 h Replicates: 10 Technique: GC-MS | Normothermic conditions (37 °C)
| [28] | |
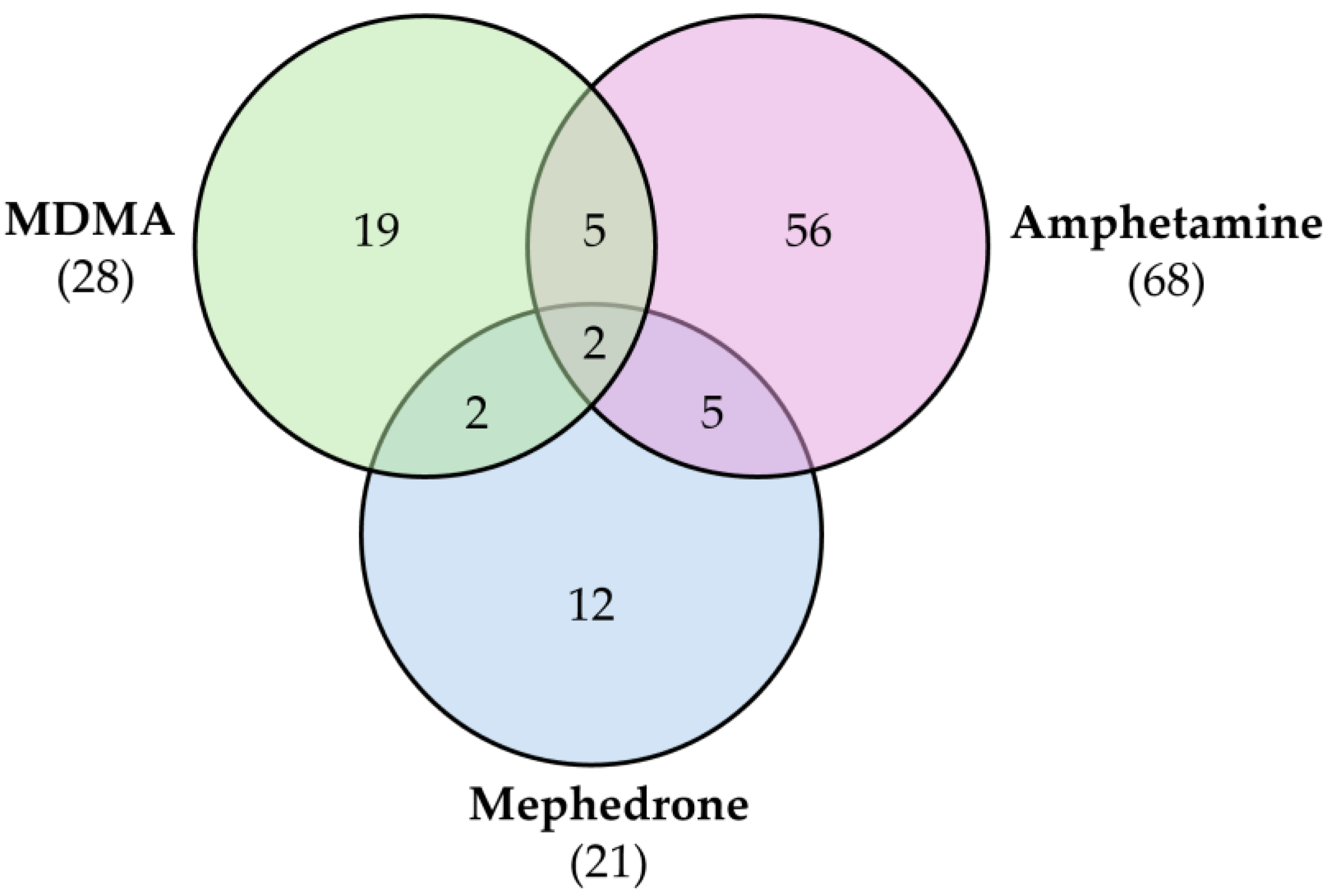
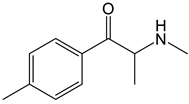 Mephedrone | Approach: Untargeted Sample: Human plasma Dose: 1.4 ± 0.2 mg/kg bodyweight Exposure time: 3 and 6 h Replicates: 5 Technique: UHPLC-TOF-MS |
| [29] |
| Approach: Targeted Sample: Rat urine, plasma and brain Dose: 30 mg/kg Exposure time: 1 or 4 h Replicates: 6 Technique: UHPLC-TQ-MS |
| [30] | |
 α-PBP | Approach: Untargeted Sample: HepaRG cells Concentration: 12.5 or 25 µM Exposure time: 24 h Replicates: - Technique: HPLC-HRMS/MS |
| [31] |
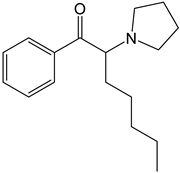 α-PEP (PV8) |
| ||
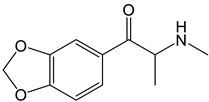 Methylone | Approach: Untargeted Sample: Primary mouse hepatocytes Concentration: 0.184 mM and 0.390 mM Exposure time: 24 h Replicates: 10 Technique: GC-MS | Metabolic pathways affected:
| [32] |
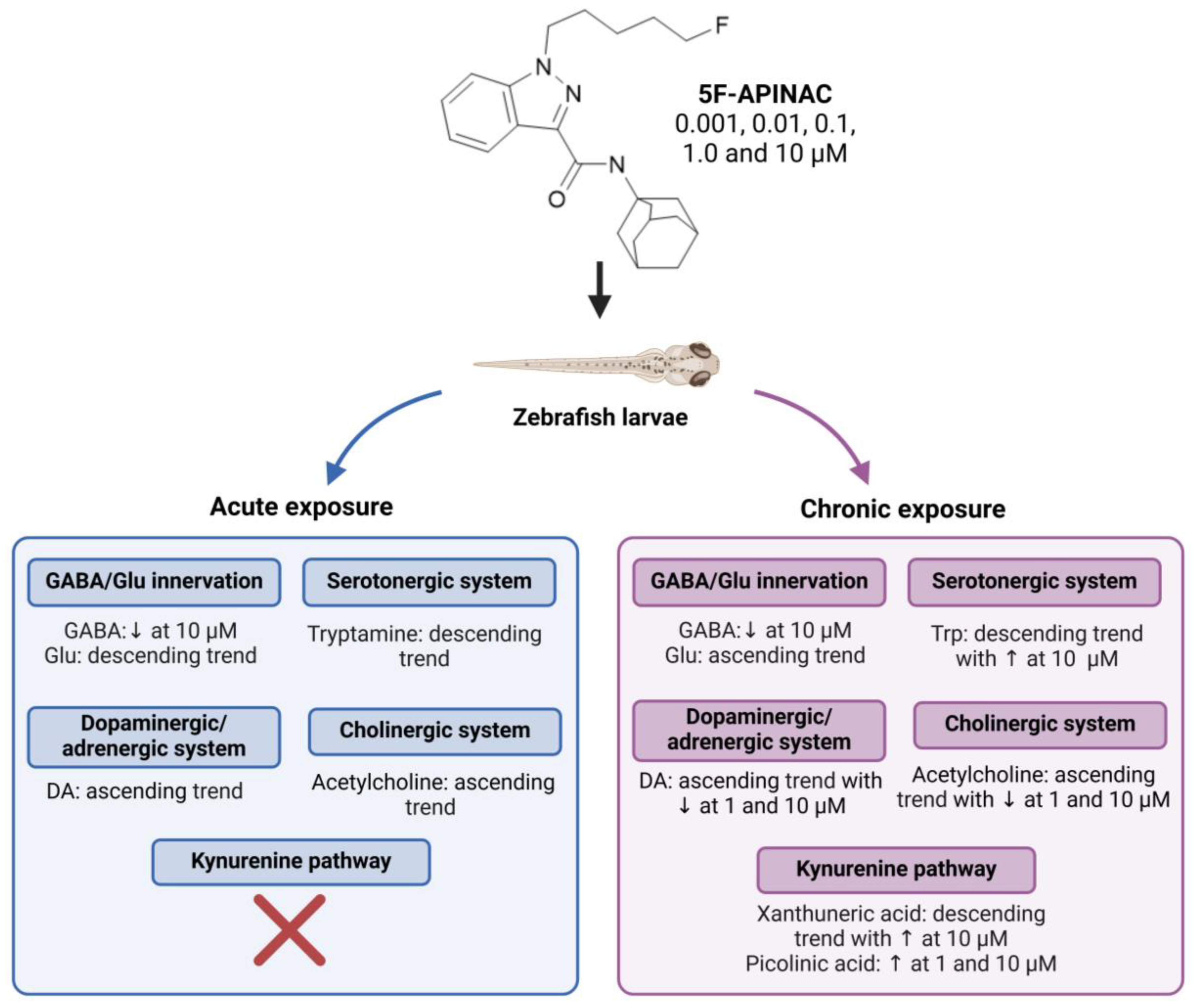
 5F-APINAC | Approach: Targeted Sample: Rabbit plasma Concentration: 0.1, 1 and 2 mg/kg Exposure time: Nine time points (0–24 h) Replicates: 4 Technique: UHPLC-MS | Serotonergic system/SER pathway
| [33] |
| Approach: Targeted Sample: Zebrafish eggs/ larvae Concentration: 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1.0 and 10 μM Exposure time: 4 or 96 h Replicates: 20 Technique: UHPLC-MS/MS | GABA/Glu innervation
| [34] | |
 JWH-018 | Approach: Untargeted Sample: Mice hippocamp Concentration: 1 mg/kg Exposure time: 2 h Replicates: 10 Technique: UHPLC-TOF/MS |
| [35] |
| Approach: Targeted Sample: Rat urine, plasma, and brain Dose: 10 mg/kg Exposure time: 1 and 4 h Replicates: 6 Technique: UHPLC-TQ-MS |
| [30] | |
 MAM-2201 | Approach: Untargeted Sample: Rat cerebrum Dose: 5 or 15 mg/kg Exposure time: 2 h Replicates: 5 Technique: GC-MS/MS |
| [36] |
| Neurotransmitter System and Metabolite Pathways | Metabolites |
|---|---|
| GABA/Glu innervation | GABA, Glu, Gln |
| Serotonergic system/SER pathway | Trp, 5-hydroytryptophan, SER, 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid, tryptamine |
| Dopaminergic/adrenergic system | Phe, Tyr, L-DOPA, DA, NE, normetanephrine, epinephrine, metanephrine |
| Asp innervation system | Asp, Asn |
| Cholinergic system | Acetylcholine, choline |
| Kynurenine pathway | Kynurenine, kynurenic acid, anthranilic acid, xanthurenic acid, quinolinic acid, picolinic acid |
| Microbial Trp catabolism | Indole-3-carboxaldehyde, indole-3-acetic acid, indole-3-butyric acid, indole-3-lactic acid, indole-3-acrylic acid, indole-3-propionic acid |
| Others | Cortisol, citrulline, biopterin, neopterin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeida, A.S.; Pinho, P.G.d.; Remião, F.; Fernandes, C. Uncovering the Metabolic Footprint of New Psychoactive Substances by Metabolomics: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020290
Almeida AS, Pinho PGd, Remião F, Fernandes C. Uncovering the Metabolic Footprint of New Psychoactive Substances by Metabolomics: A Systematic Review. Molecules. 2025; 30(2):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020290
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeida, Ana Sofia, Paula Guedes de Pinho, Fernando Remião, and Carla Fernandes. 2025. "Uncovering the Metabolic Footprint of New Psychoactive Substances by Metabolomics: A Systematic Review" Molecules 30, no. 2: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020290
APA StyleAlmeida, A. S., Pinho, P. G. d., Remião, F., & Fernandes, C. (2025). Uncovering the Metabolic Footprint of New Psychoactive Substances by Metabolomics: A Systematic Review. Molecules, 30(2), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020290









