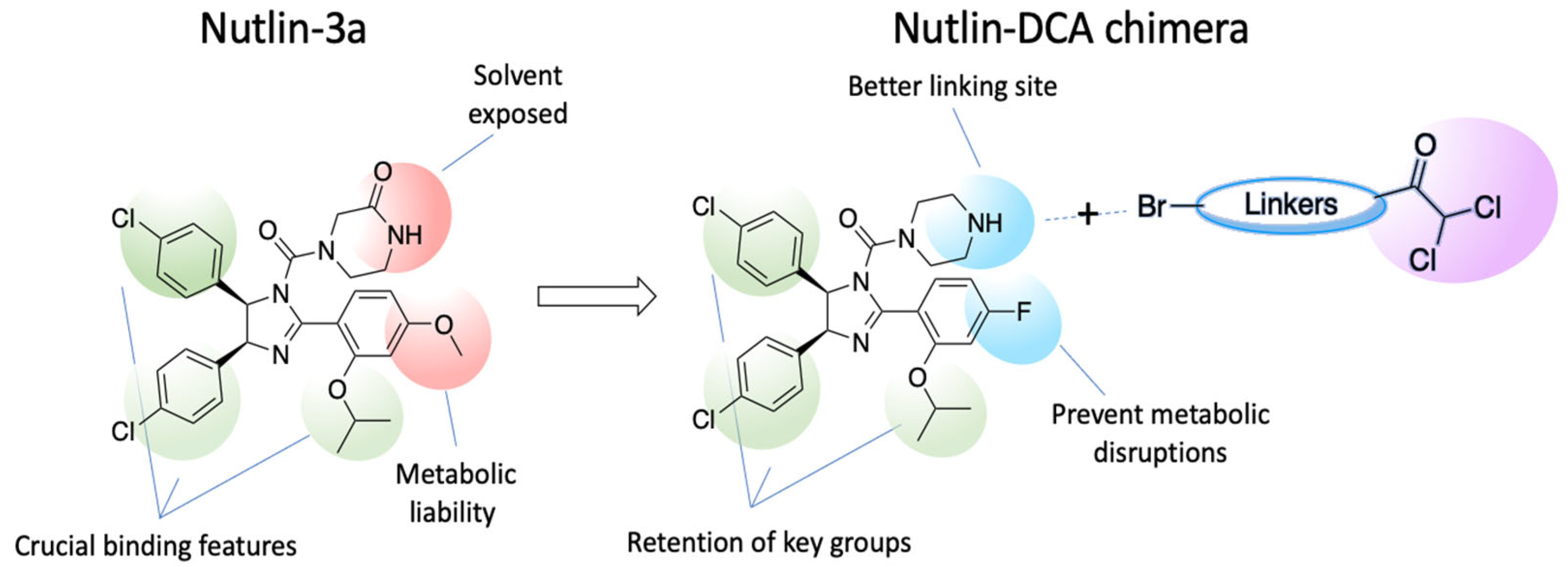
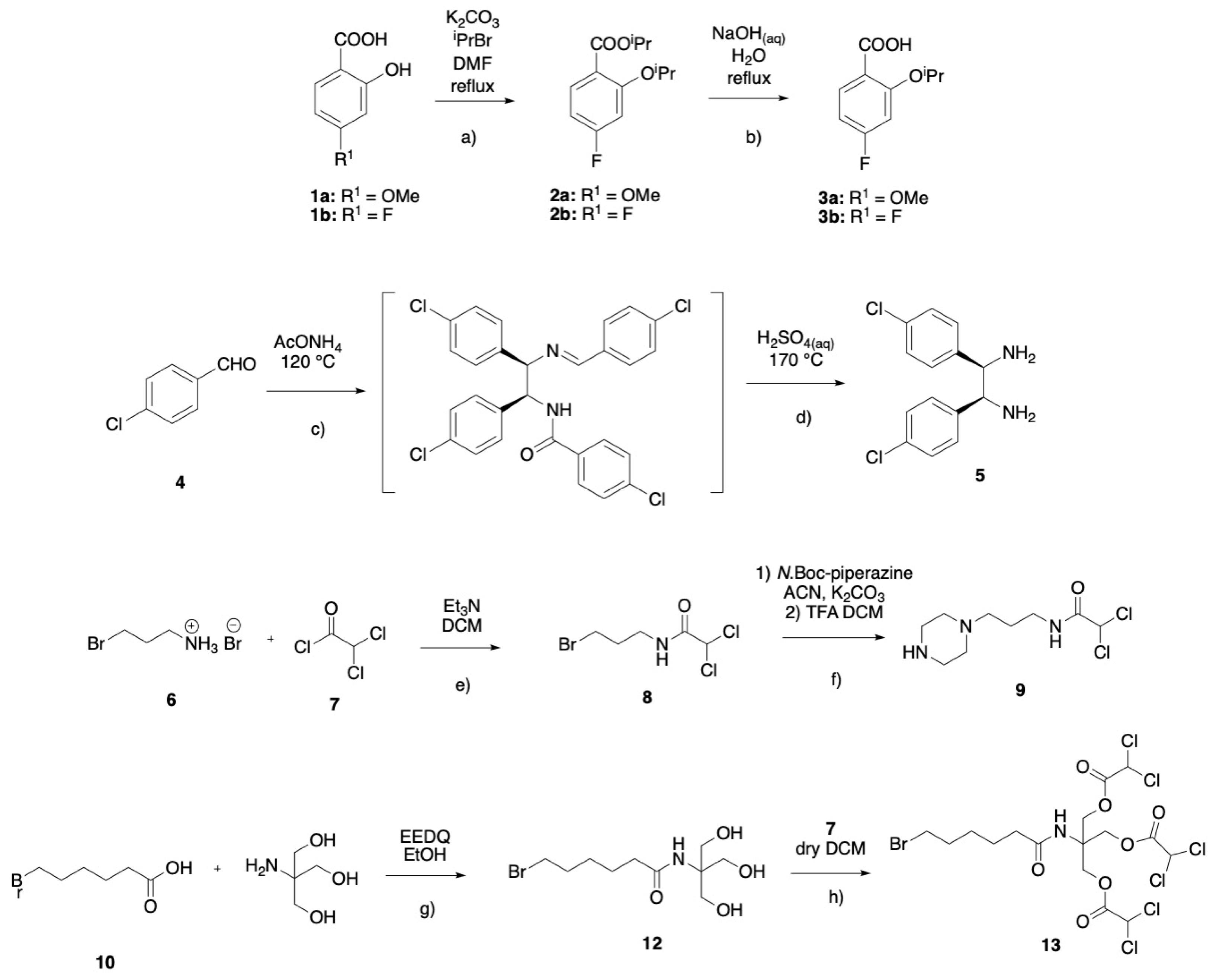
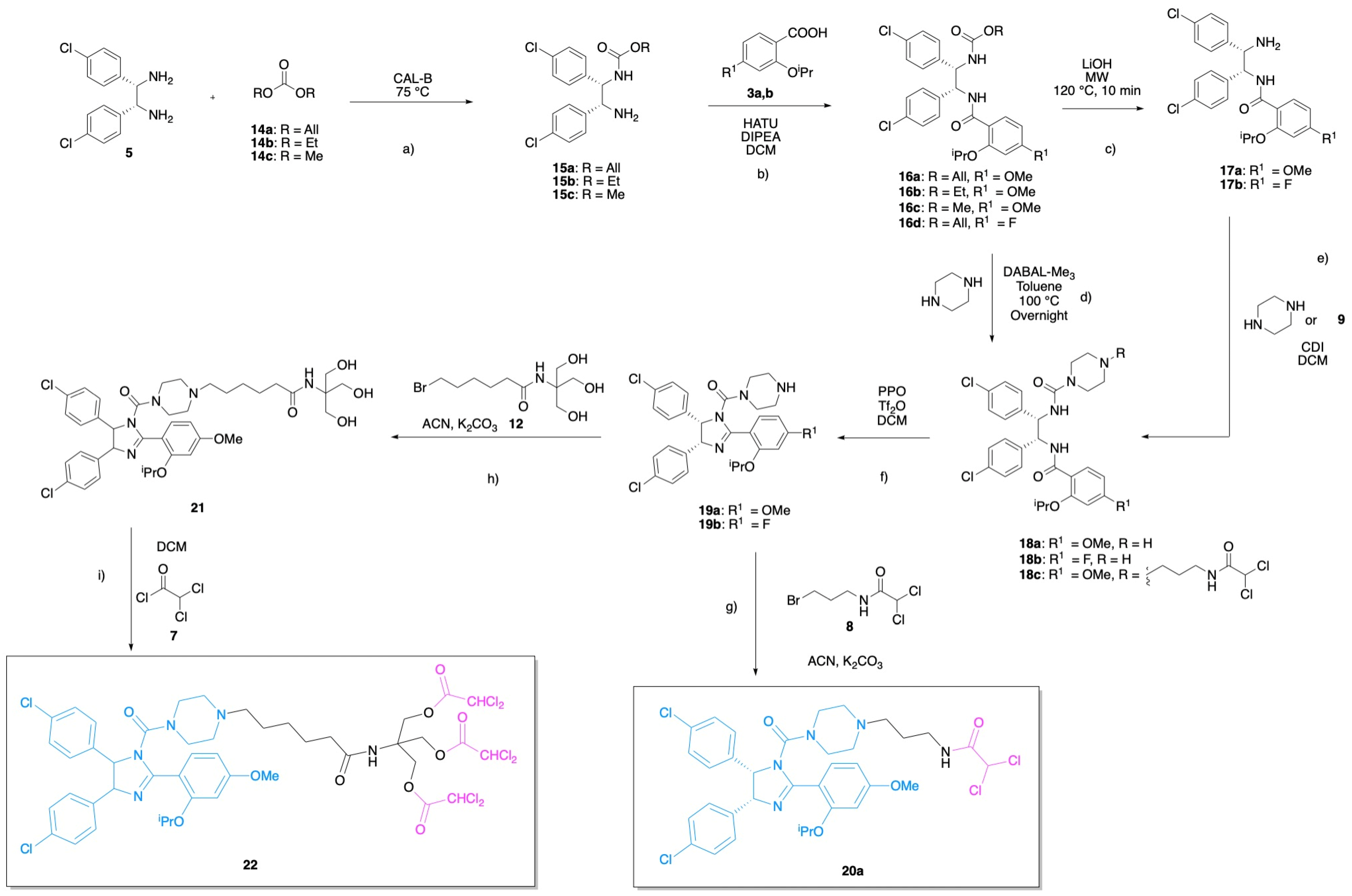
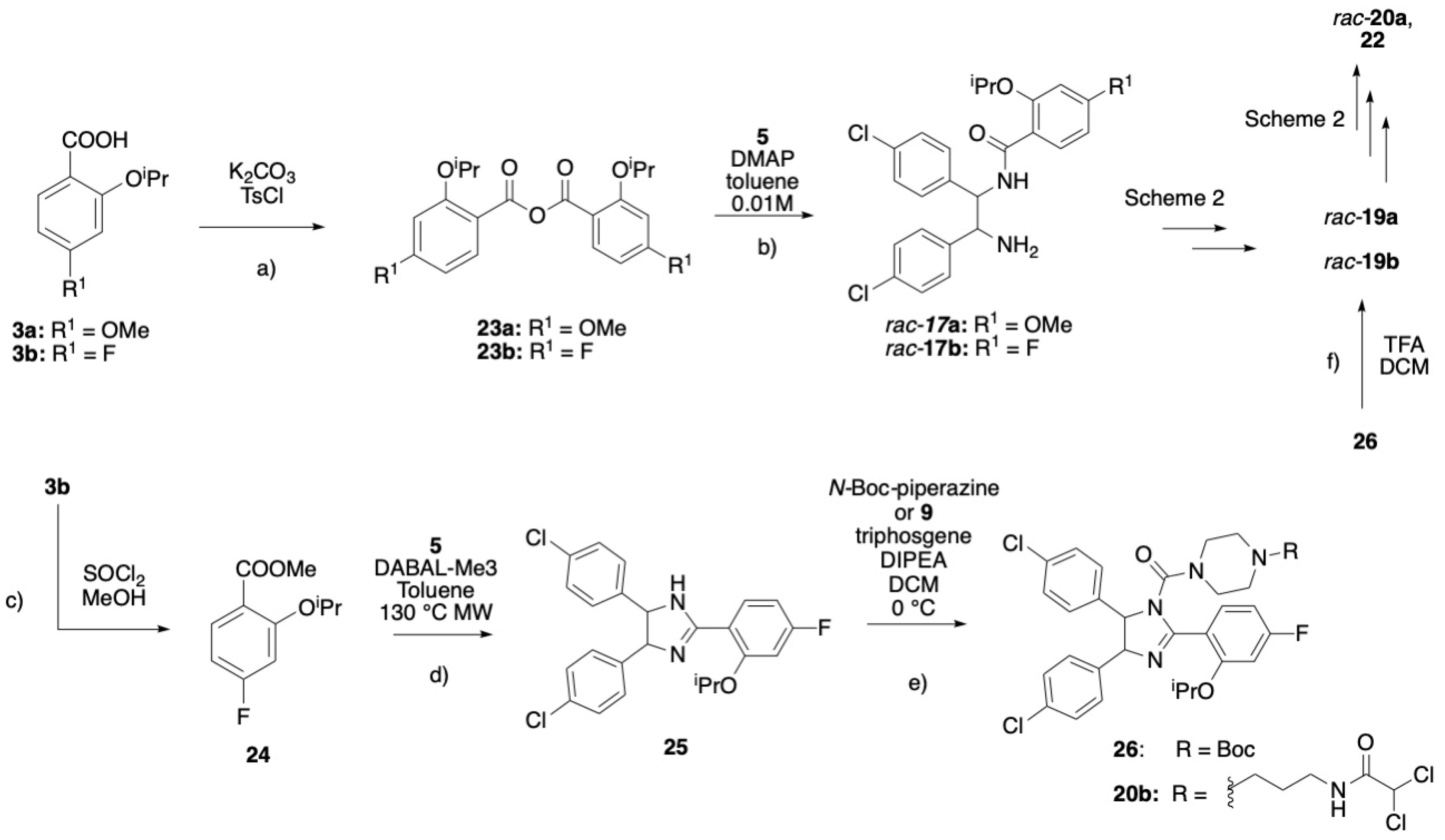
3.1. Chemistry
All the NMR spectra were elaborated using Mestre MNova 6.0.2 software.
http://www.mestrelab.com (accessed on 1 August 2025) and FID data are available on request. Analytical thin layer chromatography (TLC) was performed on silica gel Macherey-Nagel Polygram SIL/UV 254 of 0.25 mm and visualisation was achieved using UV light (254) and potassium permanganate (KMnO
4) 2% in water. Flash column chromatography was undertaken on silica gel Merck 60–200 mesh using chromatography (Isolera, Biotage, Uppsala, Sweden). Products were dried using anhydrous sodium sulphate (Carlo Erba, Milan, Italy). Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (
1H NMR) and carbon nuclear magnetic resonance (
13C NMR) were recorded using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer (VARIAN 400 MHz, Varian, Palo Alto, CA, USA). All spectra were recorded using as solvent CDCl
3, unless otherwise specified. Chemical shifts (
δ) were quoted in ppm relative to residual solvent and coupling constants (
J) were quoted in hertz (Hz). Multiplicity was reported with the following abbreviations: s = singlet; d = doublet; t = triplet; q = quartet; m = multiplet, bs = broad signal. Molecular weights were measured with a mass spectrometer ESI MICROMASS ZMD 2000 (Waters, Manchester, UK) and high-resolution spectra with an Agilent ESI-Q- TOF LC/MS 6520 system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Solvents and chemicals used for TLC, chromatographic purification, crystallisations and reactions were reported with the following abbreviations: Et
2O for diethyl ether, THF for tetrahydrofuran, AcOEt for ethyl acetate, DCM for methylene chloride, ACN for acetonitrile, TFA for trifluoroacetic acid. Preparative HPLC purifications were performed using Phenomenex Jupiter C
18 column, 15 µm, 300 Å, 250 × 30 mm (L × ID), flow rate 20 mL/min. The biocatalysts
Candida antarctica lipase type B immobilised on acrylic polymeric support (Novozyme 435
®, CAL-B, 9000 PLU/g propyl laurate unit) was provided by Novozymes (Lyngby, Denmark).
3.1.1. Isopropyl 4-Fluoro-2-isopropoxybenzoate (2b)
In a 100 mL round-bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer and a reflux condenser, 4.0 g (26 mmol) of p-fluorosalicylic acid 1b and 14.2 g (102 mmol, 4 equivalents) of K2CO3 were dissolved in 20 mL of DMF. After 15 min, 9.5 mL (102 mmol, 4 equivalents) of 2-bromopropane were added. The mixture was heated in an oil bath under reflux and stirred for 3.5 h, then it was cooled to room temperature and the solvent was removed to dry using a rotary evaporator. The residue was dissolved in AcOEt and filtered through nylon discs filter to remove K2CO3. The filtrate was washed with NaHCO3 three times. The organic phase was dried with anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered through a cotton plug and concentrated under reduced pressure. 4.1 g (17 mmol, 66% yield) of desired product 2b, was obtained as a yellow solid. Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 7:3) = 0.95. ESI [M + H]+calc = 241.12, ESI [M + H]+found = 241.22. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.8–7.7 (m, 1H), 6.7–6.5 (m, 2H), 5.2 (p, J = 6.2 Hz, 1H), 4.5 (hept, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 1.5–1.3 (m, 12H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 166.9, 165.7, 164.5, 133.5, 133.4, 118.6, 107.2, 106.9, 102.6, 102.4, 71.9, 68.3, 22.1, 22.0.
3.1.2. 4-Fluoro-2-isopropoxybenzoic Acid (3b)
In a 100 mL round-bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer and a reflux condenser, 4.1 g (17 mmol) of ester 2b were dissolved in 34 mL (68 mmol, 4 equivalents) of 2N aqueous solution of NaOH. The mixture was refluxed for 2.5 h, then the solvent was removed to dry using a rotary evaporator. The residue was resuspended in water and it was acidified with a 2M aqueous solution of HCl (pH = 2). The acidic aqueous phase was extracted with AcOEt three times. The organic phases were combined, dried with Na2SO4, filtered through a cotton plug and concentrated to dry under reduced pressure. A total of 3 g (15 mmol, 89% yield) of acid 3b, was obtained as a pale yellow solid. Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 3:7) = 0.34. ESI [M + H]+calc = 199.08, ESI [M + H]+found = 199.2. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.2 (ddt, J = 8.9, 6.9, 0.4 Hz, 1H), 6.8 (tdd, J = 7.6, 2.3, 0.7 Hz, 1H), 6.8–6.7 (m, 1H), 4.8 (hept, J = 6.1, 0.6 Hz, 1H), 1.5 (dd, J = 6.1, 0.7 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 164.6, 136.2, 136.1, 109.8, 109.6, 102.1, 101.9, 74.8, 22.0. 19F NMR (376 MHz, cdcl3) δ -101.3.
3.1.3. N-(3-Bromopropyl)-2,2-dichloroacetamide (8)
In a 100 mL round-bottom flask, with magnetic stirring immerse an ice bath, 1 g (4.6 mmol) of 3-bromopropylamine hydrobromide 6 was dissolved in freshly distilled DCM (40 mL). Then, 0.5 mL (5 mmol; 1.25 equivalents) of 2,2-dichloroacetyl chloride 7 and 1.9 mL of triethylamine (TEA) (13 mmol; 3 equivalents) were added dropwise at 0 °C. After 3 h, the reaction was quenched with 2 M HCl aqueous solution, transferred to a separatory funnel and extracted 3 times with DCM. The organic phases were combined and dried over Na2SO4, filtered with a funnel on cotton and brought to dry with a rotary evaporator to give 1.1 g of product N-(3-bromopropyl)-2,2-dichloroacetamide 8 (3.8 mmol; 97%), an orange solid. ESI [M + H]+calc = 247.92, [M + H]+found = 249.64. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 6.70 (bs, 1H, NH), 5.92 (s, 1H), 3.57–3.49 (m, 2H), 3.45 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 2.20–2.13 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 164.6, 66.5, 39.1, 31.6, 30.4.
3.1.4. tert-Butyl 4-(3-(2,2-Dichloroacetamido)propyl)piperazine-1-carboxylate, N-Boc-9
In a 100 mL flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer, 290 mg (0.83 mmol, 1.5 equivalents) of 8 and 155.45 mg (0.83 mmol, 1 equivalent) of N-Boc-piperazine were dissolved in 10 mL of ACN. The mixture was stirred for 1 h. Then, 400 mg (2.9 mmol, 4 equivalents) of K2CO3 were added and the mixture was stirred overnight. The next day, the reaction filtered through a Nylon membrane to remove excess K2CO3. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure using a rotary evaporator and the residue was washed with water and AcOEt. The organic phase was dried over Na2SO4, filtered through a cotton plug and the solvent was removed to dry using a rotary evaporator. A total of 293 mg of crude product N-Boc-9, a brown solid, was obtained and used for the following step (Quantitative yield). ESI [M + H]+calc = 354.13, [M + H]+found = 354.23. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.5 (s, 1H), 5.9 (d, J = 0.5 Hz, 1H), 3.5 (dq, J = 12.0, 6.8, 5.9 Hz, 4H), 2.6–2.5 (m, 2H), 1.8–1.7 (m, 2H), 1.4 (d, J = 1.0 Hz, 9H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 164.4, 154.6, 79.8, 66.7, 58.3, 53.2, 44.9, 41.2, 28.4, 28.3, 23.7.
3.1.5. 2,2-Dichloro-N-(3-(piperazin-1-Yl)propyl)cetamide (9)
In a 100 mL flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer, 293 mg (0.83 mmol, 1 equivalent) of compound N-Boc-9 was dissolved in 20 mL of DCM. Then, 635 µL (8.3 mmol, 10 equivalents) of TFA were added. The mixture was stirred overnight. The next day, the reaction was quenched and the solvent was removed to dry using a rotary evaporator. The residue was dissolved in a solution of NaHCO3 until a pH of 9 was reached. The product was extracted with AcOEt three times, the organic phases were combined and dried over Na2SO4, filtered through a cotton plug and concentrated under reduced pressure. Eventually, 150 mg (0.60 mmol) of product 9, a yellow solid, were obtained (71% yield). ESI [M + H]+calc = 254.08, [M + H]+found = 254.11. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.6 (s, 1H), 5.9 (s, 1H), 3.5–3.3 (m, 2H), 3.0 (t, J = 4.9 Hz, 4H), 2.7–2.4 (m, 8H), 1.8–1.6 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 164.5, 66.9, 58.9, 54.3, 45.7, 41.5, 29.8, 23.6.
3.1.6. 6-Bromo-N-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-Yl)hexanamide (12)
In a 100 mL round-bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer, 1 g (5.1 mmol, 1 equivalent) of 6-bromohexanoic acid 10 and 1.52 g (6.15 mmol, 1.2 equivalents) of EEDQ were dissolve in ethanol (50 mL). After stirring the mixture for 20 min, a solution of 0.62 g (5.13 mmol, 1:1 equivalents) of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane 11 in 40 mL of EtOH was added with a dropping funnel and the reaction was refluxed overnight. After the starting material was no longer detectable by TLC, the solvent was evaporated using a rotary evaporator. The product was purified from the crude mixture by gradient elution flash chromatography (2–15% DCM/MeOH) with dry loading on silica, obtaining 1 g of hexanamide 12 (3.3 mmol, yield 66%) as a colourless oil. TLC: (CH2Cl2/MeOH 9:1) Rf = 0,45. ESI [M + H]+calc = 298.06, ESI [M + H]+found = 298,18. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Methanol-d4) δ 5.5–5.4 (m, 1H), 3.7 (t, J = 2.9 Hz, 6H), 3.5–3.3 (m, 2H), 3.3–3.2 (m, 2H), 2.2 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 1.9–1.8 (m, 2H), 1.6 (p, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H), 1.4 (dq, J = 10.8, 7.4, 7.0 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cd3od) δ 176.9, 63.4, 62.6, 54.7, 37.2, 34.1, 33.5, 28.6, 25.9.
3.1.7. 2-(6-Bromohexanamido)-2-((1,2-dichloro-2-oxoethoxy)methyl)propane-1,3-diyl bis(2,2-Dichloroacetate) (13)
A previously dried 100 mL round-bottom flask was filled with 900 mg (3 mmol, 1 equivalent) of compound 12 and 50 mL of freshly distilled DCM. The suspension was gently heated until complete dissolution; then, 870 µL (9.05 mmol, 3 equivalents) of dichloroacetic acid chloride 7 was added to the solution. The reaction was stirred at r.t. overnight then the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. The product was purified from the crude by gradient concentration chromatography (10–40% petroleum ether/AcOEt) on silica gel. Finally, the fractions were collected to afford 267 mg (0.4 mmol, 13% yield) of product 13. TLC: (ethyl acetate/petroleum ether 2:8) Rf = 0,4. ESI [M + H]+calc = 627.86, ESI [M + H]+found = 630.01. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 6.01 (d, J = 0.6 Hz, 3H), 4.68 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 6H), 3.40 (td, J = 6.6, 1.7 Hz, 2H), 2.22 (td, J = 7.5, 1.4 Hz, 2H), 1.94–1.79 (m, 2H), 1.62 (p, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 1.54–1.39 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 174.1, 163.9, 64.7, 63.9, 58.5, 36.7, 33.7, 32.3, 27.6, 24.5.
3.1.8. General Enantioselective Biocatalytic Reaction [8]
A solution of meso-diamine 5 (200 mg, 0.7 mmol) in dialkyl carbonate 14a–c was placed in an Erlenmeyer flask, under inert atmosphere and 2 g of immobilised CAL-B was added. The mixture was gently shaken at 70 °C in orbital shaking for 2 days. The mixture was cooled to room temperature and the reaction was finished by filtering off the enzyme which was rinsed twice with DCM. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and the enantioenriched monocarbamate product 15a–c was purified by silica gel column chromatography.
Allyl 2-Amino-1,2,-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl)carbamate (15a)
A 65% yield. ESI [M + H]+calc = 365.08, ESI [M + H]+found = 365.1. TLC Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 1:1) = 0.28. Analytical Chiral HPLC Method A (Chiralpack-ID 250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm. % MP (Hex:IPA) = 90:10. Flow = 1.5 mL/min. UV: 254 nm): tR [(1S,2R)-15a] = 11.43 min (major ent in enzymatic reaction), tR [(1R,2S)-15a] = 13.47 min (minor ent in enzymatic reaction). Method B (Whelk-01 SS 100 mm × 4.6 mm, 1.8 μm. % MP (Hex:IPA) = 80:20). Flow 1 mL/min): tR [(1S,2R)-15a] = 4.68 min (major ent in enzymatic reaction), tR [(1R,2S)-15a] = 12.00 min (minor ent in enzymatic reaction). 89% ee%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Methanol-d4) δ 7.40–7.25 (m, 8H), 5.77 (ddt, J = 16.2, 10.6, 5.4 Hz, 1H), 5.16–5.02 (m, 2H), 4.77 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 4.36 (qdt, J = 13.5, 5.2, 1.6 Hz, 2H), 4.10 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CD3OD) δ 134.2, 130.5, 130.3, 129.7, 129.4, 117.3, 66.3, 62.1, 60.5. [α] = +12.5 (c 0.085, MeOH).
Ethyl 2-Amino-1,2,-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl)carbamate (15b)
A 30% yield. ESI [M + H]+calc = 352.08, ESI [M + H]+found = 353.1. TLC Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 1:1) = 0.27. Analytical chiral HPLC: (Chiralpack-ID 250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm. % MP (Hex:IPA) = 95:5. Flow = 1.5 mL/min. UV: 254 nm): tR [(1S,2R)-15b] = 6.24 min (major ent) in enzymatic reaction, tR [(1R,2S)- 15b] = 9.12 min (minor ent in enzymatic reaction). 78% ee%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.62 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 1H), 7.43–7.24 (m, 8H), 4.54 (t, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 3.98 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 3.79 (p, J = 6.7 Hz, 2H), 1.02 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, dmso) δ 219.5, 197.7, 194.3, 155.3, 143.2, 140.3, 131.5, 131.1, 129.7, 129.2, 127.8, 127.6, 60.6, 59.6, 58.8, 14.4. [α] = +14.9 (c 0.085, MeOH).
Methyl 2-Amino-1,2,-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl)carbamate (15c)
A 95% yield. ESI [M + H]+calc = 339.1, ESI [M + H]+found = 339.07. TLC Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 1:1) = 0.3. Analytical chiral HPLC Method A: (Chiralpack-ID 250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm. % MP (Hex:IPA) = 95:5. Flowrate = 1.5 mL/min. UV: 254 nm): tR [(1S,2R)-15c] = 7.95 min, tR [(1R,2S)-15c] = 10.19 min. Method B: (Whelk-01 SS 100 × 4.6 mm, 1.8 μm. % MP (Hex:IPA) = 80:20. Flowrate = 1 mL/min. UV: 228 nm): tR [(1S,2R)-15c] = 4.88 min (major ent in enzymatic reaction), tR [(1R,2S)- 15c] = 14.80 min (minor ent in enzymatic reaction). 73% ee%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.3–7.2 (m, 4H), 7.0 (m, 2H), 7.0–6.9 (m, 2H), 5.7 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 4.8 (s, 1H), 4.2 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H), 3.6 (s, 3H), 1.6–1.4 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 156.4, 140.2, 136.8, 133.7, 133.6, 128.9, 128.7, 128.5, 128.4, 59.3, 52.4. [α] = +16.0 (c 0.085, MeOH).
3.1.9. General Amidic Coupling Procedure
Benzoic acid derivatives 3a–b (1.7 mmol) were dissolved in DCM, with 5.1 mmol HATU (3 equivalents). After 30 min, a solution of monocarbamate 15a–c (1.4 mmol, 0.8 equivalents) in DCM (20 mL) and DIPEA (3.4 mmol, 2 equivalents) were added dropwise. The mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature. A white solid was filtered off through a Gooch filter and the liquid phase was transferred in a separatory funnel and washed three times with water and brine. Organic layers were combined, dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated (up to 30%) on a rotary evaporator then filtered to obtain the amido carbamate product 16a–d.
Allyl (1,2-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-isopropoxy-4-methoxybenzamido)ethyl) Carbamate (16a)
Yellowish solid, 70% yield. ESI [M + H]+calc = 557.16, ESI [M + H]+found = 557.1. Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 1:1) = 0.5. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.4 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.2 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.3 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.2 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.0 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.0–6.9 (m, 2H), 6.6 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.5 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 5.9 (dd, J = 11.0, 6.0 Hz, 1H), 5.8–5.7 (m, 1H), 5.2 (dd, J = 31.5, 13.7 Hz, 2H), 5.1 (dd, J = 7.4, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 4.7 (dp, J = 11.5, 6.0 Hz, 1H), 4.5 (td, J = 18.6, 15.5, 8.7 Hz, 2H), 3.8 (s, 3H), 1.3–1.2 (m, 9H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 157.4, 136.6, 134.6, 133.7, 129.0, 128.8, 128.6, 128.5, 118.2, 105.5, 100.4, 71.6, 66.0, 60.5, 57.0, 55.7, 22.2.
Ethyl (1,2-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-isopropoxy-4-methoxybenzamido)ethyl) Carbamate (16b)
Yellowish solid, 87% yield. ESI [M + H]+calc = 545.14, ESI [M + H]+found = 545.8. Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 7:3) = 0.28. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.3 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H), 7.8 (d, J = 9.4 Hz, 1H), 7.5–7.3 (m, 8H), 6.6–6.4 (m, 2H), 5.5 (t, J = 9.3 Hz, 1H), 5.0 (t, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H), 4.7 (p, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 3.8 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 3.8 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 3H), 2.1 (s, 2H), 1.2 (dt, J = 13.4, 6.5 Hz, 7H), 1.0 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, dmso) δ 206.5, 163.7, 162.6, 156.5, 155.4, 139.7, 139.5, 132.1, 131.9, 131.7, 129.5, 128.0, 115.6, 105.9, 100.4, 71.1, 59.8, 57.7, 55.5, 55.3, 39.9, 30.7, 21.5, 21.4, 14.4.
Methyl (1,2-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-isopropoxy-4-methoxybenzamido)ethyl) Carbamate (16c)
Yellowish solid, 98% yield. ESI [M + H]+calc = 531.14, ESI [M + H]+found = 531.1. Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 1:1) = 0.28. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.5–8.4 (m, 1H), 8.2 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.3–7.3 (m, 2H), 7.2–7.2 (m, 2H), 7.0 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.0–6.9 (m, 2H), 6.6 (dd, J = 8.9, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.5–6.4 (m, 1H), 5.8 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 5.1 (dd, J = 7.3, 3.4 Hz, 1H), 4.7 (p, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 3.8 (s, 3H), 2.8 (s, 3H), 1.3–1.2 (m, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 163.9, 157.4, 156.4, 134.6, 133.7, 129.1, 128.8, 128.6, 128.5, 114.1, 105.4, 100.4, 71.6, 60.5, 57.1, 55.7, 52.4, 38.7, 22.1, 21.7.
Allyl (1,2-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluoro-2-isopropoxybenzamido)ethyl)carbamate (16d)
Yellowish solid, 67% yield. ESI [M + H]+calc = 545.14, ESI [M + H]+found = 545.23. TLC Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 7:3) = 0.83. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.4 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 8.2 (dd, J = 8.9, 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.4–7.1 (m, 4H), 7.1–6.8 (m, 4H), 6.8 (ddd, J = 8.8, 7.5, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.7 (dd, J = 10.9, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.2 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 6.0–5.7 (m, 2H), 5.3–5.0 (m, 3H), 4.7 (dp, J = 11.1, 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.5 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 1.3 (dd, J = 14.8, 6.0 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 167.1, 165.2, 164.6, 157.5, 157.4, 155.6, 136.5, 136.3, 135.0, 134.9, 134.1, 133.9, 132.7, 128.9, 128.9, 128.6, 118.3, 117.4, 108.5, 108.3, 101.4, 101.1, 72.4, 66.1, 60.2, 57.2, 22.1, 21.7. 19F NMR (376 MHz, cdcl3) δ -104.47.
3.1.10. General Carbamate Removal Procedure
In a microwave vial, equipped with a magnetic stirrer, the enantiomerically enriched alkylcarbamate 16a–c (0.4 mmol) were dissolved in 10 mL of a 2 M solution of LiOH (20 mmol), prepared in H2O, THF and MeOH (1:1:1). The mixture was reacted for 10 min at 120 °C. After this time, the mixture was filtered through a Gooch filter. The filtrate was diluted with AcOEt and washed three times with water. The organic phase was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered over cotton and evaporated using a rotary evaporator to give the enantiomerically enriched products 17a–b.
N-(2-Amino-1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl)-2-isopropoxy-4-methoxybenzamide (17a)
Yellowish oil, 92% yield. Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 7:3 = 0.43. ESI [M + H]+calc = 473.4, ESI [M + H]+found = 473.2. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.84 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.11 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.29–7.16 (m, 5H), 7.01 (dd, J = 8.5, 3.0 Hz, 4H), 6.55 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.48 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 5.47 (dd, J = 7.9, 4.6 Hz, 1H),4.74 (p, J = 6.1Hz, 1H), 4.43 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 3.83 (d, J = 0.7 Hz, 3H), 1.41 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.1, 163.5, 157.4, 140.0, 136.8, 134.3, 133.4, 129.3, 128.6, 128.4, 114.9, 105.3, 100.5, 71.7, 59.2, 58.6, 55.7, 22.3, 22.2. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Methanol-d4) δ 7.92 (d, J = 9.4 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (m, 4H), 7.29 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.22 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 6.63 (dd, J = 4.7, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 5.83 (d, J = 5.5 Hz, 1H), 4.80 (dd, J = 8.7, 5.8 Hz, H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 1.29 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 3H), 1.19 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CD3OD) δ 165.7, 137.5, 136.3, 135.5, 134.5, 130.7, 130.2, 130.1, 107.1, 101.4, 73.2, 59.9, 57.0, 56.1, 22.2, 22.2.
N-(2-Amino-1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl)-4-fluoro-2-isopropoxybenzamide (17b)
Light-yellow oil, 81% yield. Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 7:3 = 0.33. ESI [M + H]+calc = 461.12, ESI [M + H]+found = 461.26. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.8 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.1 (dd, J = 8.8, 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.2 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.0 Hz, 4H), 7.0 (tt, J = 7.2, 2.0 Hz, 4H), 6.8–6.6 (m, 2H), 5.5 (dt, J = 8.5, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 4.7 (hept, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 4.4 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 3.3 (s, 3H), 1.4 (dd, J = 10.3, 6.1 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 165.0, 164.5, 157.6, 136.2, 134.8, 134.7, 133.9, 129.1, 128.7, 128.6, 108.4, 108.2, 101.4, 101.1, 72.5, 59.3, 58.4, 22.1, 22.0.
3.1.11. General CDI Coupling Procedure
A previously dried 100 mL round bottom flask under Ar atmosphere was filled with a solution of amino amide 17a–b (0.25 mmol) in freshly distilled DCM (20 mL) and (0.3 mmol, 1.2 equivalents) CDI were added. After complete conversion to imidazoyl intermediate, which was monitored by mass spectrometry (MS ESI), piperazine or piperazine–DCA 9 (0.25 mmol, 1 equivalent) was added and the reaction was stirred overnight at room temperature. The reaction was quenched with water and transferred into a separatory funnel in order to wash the mixture three times with water and brine. The organic phase was separated, dried over Na2SO4 and the crude material was purified on silica gel chromatography with gradient elution, to give compound 18a–c.
3.1.12. General DABAL-Me3 Coupling Procedure
In a 50 mL round-bottom flask, previously dried and equipped with a magnetic stirrer and reflux condenser, three vacuum-argon cycles were performed to create an inert atmosphere. Anhydrous piperazine (0.88 mmol, 1.2 equivalents) and 226 mg (0.88 mmol, 1.2 equivalents) of DABAL-Me3 were dissolved in 10 mL of anhydrous toluene. The mixture was stirred for 1 h at 40 °C; then, desymmetrised amido carbamate 16a–c (0.74 mmol) was added. The temperature was increased to 90 °C and the mixture was stirred for additional 2 h. After this time, the reaction was stopped and the solvent was removed to dry using a rotary evaporator. The residue was dissolved in DCM and washed with water three times. The organic phase was dried over Na2SO4, filtered through cotton and concentrated using a rotary evaporator. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography on silica gel, affording pure enantioenriched products 18a–b.
N-(1,2-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-isopropoxy-4-methoxybenzamido)ethyl)piperazine-1-carboxamide (18a)
- -
CDI coupling method: 96% yield (MS ESI Imidazoyl intermediate [M + H]+found = 567.71).
- -
DABAL-Me3 coupling method: 58% yield.
Product ESI [M + H]+calc = 585.20, ESI [M + H]+found = 585.9. TLC: (CH2Cl2/MeOH 9.5:0.5) Rf = 0.45. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.4 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 8.3 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.3 (dd, J = 8.3, 1.4 Hz, 2H), 7.2–7.1 (m, 2H), 7.0–6.9 (m, 3H), 6.9–6.8 (m, 2H), 6.6 (dd, J = 8.9, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.5–6.4 (m, 1H), 5.8 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 5.1 (dd, J = 5.2, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 4.7 (p, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 3.4 (tdt, J = 18.2, 12.9, 5.8 Hz, 3H), 2.9 (t, J = 5.2 Hz, 3H), 1.2 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 4H), 1.2 (dd, J = 5.9, 2.7 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 167.1, 164.1, 157.5, 157.2, 134.5, 133.3, 129.5, 128.8, 128.6, 128.2, 113.9, 105.5, 100.5, 71.6, 61.9, 57.7, 55.8, 46.1, 44.9, 22.1, 21.7.
N-(1,2-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluoro-2-isopropoxybenzamido)ethyl)piperazine-1-carboxamide (18b)
- -
CDI coupling method: 70% yield. (MS ESI Imidazoyl intermediate [M + H]+found = 555.1).
- -
DABAL-Me3 coupling method: 40% yield.
Product ESI [M + H]+calc = 573.18, ESI [M + H]+found = 573.44. TLC: (CH2Cl2/MeOH 9:1) Rf = 0.17., 1H NMR (400 MHz, Methanol-d4) δ 7.5 (ddt, J = 8.6, 6.9, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.3–7.1 (m, 3H), 6.7 (dd, J = 11.1, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.6–6.5 (m, 1H), 5.6 (dd, J = 9.1, 1.9 Hz, 1H), 5.1 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H), 4.6 (dt, J = 12.2, 6.3 Hz, 1H), 3.5–3.3 (m, 5H), 3.0–2.9 (m, 4H), 1.1–1.0 (m, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cd3od) δ 139.9, 139.5, 134.7, 130.7, 130.4, 129.7, 129.5, 73.7, 59.7, 57.4, 44.3, 42.2, 22.1, 21.9.
N-(1,2-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-isopropoxy-4-methoxybenzamido)ethyl)-4-(3-(2,2-dichloroacetamido)propyl)piperazine-1-carboxamide (18c)
CDI coupling method: 40% yield. Imidazoyl intermediate: MS ESI [M + H]+ = 567.71. TLC (CH2Cl2/MeOH 9.5:0.5): Rf = 0.43. Product: ESI [M + H]+calc = 752.19, ESI [M + H]+found = 752.52. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.5 (s, 1H), 8.4 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.2 (dd, J = 8.8, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.5 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, 1H), 7.3–7.2 (m, 3H), 7.2–7.1 (m, 2H), 7.0 (dd, J = 8.5, 6.9 Hz, 2H), 6.9–6.8 (m, 2H), 6.6 (dd, J = 8.9, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.5 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.9 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 5.8 (dd, J = 8.0, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 5.1 (dt, J = 7.5, 3.7 Hz, 1H), 4.7 (h, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 3.8 (d, J = 1.3 Hz, 3H), 3.5 (q, J = 4.7 Hz, 4H), 3.4 (tt, J = 6.2, 2.8 Hz, 3H), 2.5 (dt, J = 17.1, 5.4 Hz, 7H), 2.4 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 1.8–1.7 (m, 4H), 1.2 (dd, J = 19.8, 6.1 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 200.8, 200.2, 167.3, 164.5, 164.1, 157.5, 156.9, 136.9, 136.7, 134.4, 133.3, 129.5, 128.8, 128.6, 128.2, 113.7, 105.5, 100.4, 77.5, 71.6, 66.9, 62.1, 58.5, 57.7, 55.8, 53.4, 43.5, 41.4, 29.8, 28.5, 23.8, 22.1, 21.6.
3.1.13. General Ring Closure Catalysed by Hendrickson’s Reagent
In a previously dried 100 mL round-bottom flask, equipped with a magnetic stirrer under inert atmosphere, Ph3PO (0.7 mmol, 4 equivalents) was dissolved in 10 mL of distilled DCM and, Tf2O (0.35 mmol, 2 equivalents) were added with a syringe. The mixture was allowed to react for 2 h. Next, amido urea 18a–b (0.2 mmol, 1 equivalent) was added and the reaction was stirred for an additional 2 h. Then the solvent was removed to dry using a rotary evaporator. The resulting residue was purified by flash chromatography on silica gel.
(4,5-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-isopropoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)(piperazin-1-yl)methanone (19a)
A 43% yield; TLC (DMC/MeOH 9:1), ESI [M + H]+calc = 567.19, ESI [M + H]+found = 567.02. Preparative RP-HPLC: (solvent A = H2O + 0.1% TFA, solvent B = H2O/ACN (40:60) + 0.1% TFA, gradient from 35% of B to 95% B in 20 min; flow 20 mL/min; tR: 21.3 min). Chiral HPLC (Whelk01 150 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm. % MP solvent system A = H2O, B = ACN: from 20% to 40% of B in 40 min. Flow = 1 mL/min. UV: 300 nm): tR[(1S,2R)-19a] = 28.2 min (minor ent), tR[(1R,2S)-19a] = 29.8 min (major ent) (ee% = 89%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.4 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.2–7.1 (m, 4H), 7.1–7.0 (m, 2H), 7.0–6.9 (m, 2H), 6.7–6.6 (m, 2H), 5.6 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H), 5.5 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H), 4.7 (p, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 3.8 (s, 3H), 3.0 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 4H), 2.2 (s, 4H), 1.8 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 1.3 (dd, J = 14.6, 6.0 Hz, 7H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, dmso) δ 162.2, 160.2, 156.8, 154.8, 137.6, 136.7, 131.7, 131.1, 129.8, 128.8, 127.5, 113.7, 104.7, 99.4, 70.7, 69.9, 67.9, 55.5, 46.6, 44.9, 21.8, 21.8.
1H NMR (400 MHz, Methanol-d4) δ 7.8–7.8 (m, 1H), 7.3–7.2 (m, 4H), 7.2–7.0 (m, 4H), 6.9–6.8 (m, 2H), 6.2 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H), 6.1 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H), 4.9 (dt, J = 12.4, 6.2 Hz, 1H), 3.5 (t, J = 5.3 Hz, 4H), 2.9 (tq, J = 13.0, 6.6, 5.3 Hz, 4H), 1.5 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H), 1.4 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cd3od) δ 168.7, 160.0, 152.2, 136.0, 134.4, 133.8, 133.1, 132.7, 132.5, 130.6, 130.4, 129.9, 129.8, 129.6, 108.2, 105.1, 101.6, 74.1, 70.8, 65.1, 56.8, 44.0, 22.1, 22.2.
(4,5-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluoro-2-isopropoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)(piperazin-1-yl)methanone (19b)
A 41% yield; TLC: (CH2Cl2/MeOH 9:1) Rf = 0.37. ESI [M + H]+calc = 555.2, ESI [M + H]+found = 555.46. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Methanol-d4) δ 8.0 (s, 1H), 7.9 (dd, J = 8.7, 6.2 Hz, 1H), 7.3–7.1 (m, 9H), 7.0 (ddd, J = 8.6, 7.8, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.3 (d, J = 11.3 Hz, 1H), 6.2 (d, J = 11.3 Hz, 1H), 5.0 (h, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 3.6 (ddd, J = 6.5, 4.3, 2.2 Hz, 4H), 3.0–2.9 (m, 7H), 2.9 (s, 2H), 1.5 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H), 1.4 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cd3od) δ 170.6, 168.1, 167.2, 160.0, 159.9, 151.7, 136.2, 136.1, 134.4, 134.3, 132.4, 132.4, 130.7, 130.6, 130.4, 129.8, 129.7, 109.8, 109.6, 103.6, 103.4, 74.8, 70.9, 65.5, 44.1, 43.8, 37.1, 31.8, 30.7, 22.2, 22.0. 19F NMR (376 MHz, cd3od) δ -80.0. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.5 (dd, J = 8.4, 6.6 Hz, 1H), 7.1–7.0 (m, 2H), 7.1–7.0 (m, 2H), 7.0–6.9 (m, 2H), 6.9–6.8 (m, 2H), 6.8–6.7 (m, 2H), 5.6 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H), 5.5 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H), 4.6 (p, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 3.1 (t, J = 4.9 Hz, 4H), 2.4 (s, 4H), 1.4 (dd, J = 18.0, 6.1 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 166.4, 163.9, 160.3, 157.5, 155.3, 136.4, 135.3, 133.3, 133.0, 132.2, 132.1, 129.4, 128.6, 128.3, 128.1, 107.4, 107.1, 101.1, 100.8, 71.9, 71.6, 69.2, 46.8, 45.5, 29.8, 22.2.19F NMR (376 MHz, cdcl3) δ −75.9.
3.1.14. N-(3-(4-(4,5-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-isopropoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole-1-carbonyl)piperazin-1-Yl)propyl)-2,2-bichloroacetamide (20a)
A previously dried 100 mL round bottom flask was filled with 146 mg (0.26 mmol) of compound 19a, 105 mg (0.78 mmol, 3 equivalents) of K2CO3 and 64 mg (0.26 mmol, 1 equivalent) of bromide 9 in 20 mL of ACN. The reaction was heated until reflux and stirred overnight. The solvent was removed to dry and the residue mixture was purified by preparative RP-HPLC: (solvent A = H2O + 0.1% TFA, solvent B = H2O/ACN (40:60) + 0.1% TFA, gradient from 30% B to 90% B in 25 min; flow 20 mL/min; Rt: 28.5 min) to give 124 mg of 20a (65% yield). MS ESI: [M + H]+calc = 734.2, [M + H]+found = 734.38; 736.38. Chiral HPLC (Whelk01 150 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm. % MP solvent system A = H2O, B = ACN: from 30% to 50% of B in 40 min. Flow = 1 mL/min. UV: 300 nm): tR[(4S,5R)-20a] = 19.1 min (minor ent), tR[(4R,5S)-20a] = 20.6 min (major ent)(ee% = 88.2%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.0 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H), 10.6 (s, 1H), 10.0–9.8 (m, 5H), 9.6–9.4 (m, 4H), 9.4–9.2 (m, 4H), 9.1–9.0 (m, 2H), 8.8 (s, 1H), 8.2 (d, J = 33.6 Hz, 2H), 7.2–7.1 (m, 1H), 6.2 (s, 3H), 5.4 (q, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 5.3–5.1 (m, 3H), 4.0 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H), 3.6 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H), 3.5 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, dmso) δ 163.9, 157.3, 133.2, 132.7, 132.0, 131.5, 131.4, 129.6, 129.0, 128.8, 128.7, 127.8, 105.8, 99.7, 79.2, 70.9, 68.1, 66.8, 55.9, 53.5, 50.5, 42.5, 36.7, 23.2, 21.7, 21.6.
3.1.15. 4-Fluoro-2-isopropoxybenzoic Anhydride (23b)
In a mortar, 581 mg (2.9 mmol) of acid 3b and 1.7 g (12,7 mmol, 4.3 equivalents) of K2CO3 were mixed with a pestle. A solution of 346 mg (1.8 mmol) of tosyl chloride (TsCl) in 4 mL of AcOEt was added dropwise and mixed for 20 min. A few drops of AcOEt were added to obtain a uniform mixture. The resulting mixture were diluted with 20 mL of DCM and filtered through a Gooch crucible. The filtrate was dried using a rotary evaporator. Then, 332 mg (0.9 mmol, 60% yield) of anhydride 23b, an amorphous compound, was obtained. Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 1:9) = 0.45.
3.1.16. General Procedure for Racemic Monoamide (17)
In a two-neck 250 mL round-bottom flask, equipped with a magnetic stirrer and previously dried, under inert atmosphere, meso-diamine 5 (1 mmol) was dissolved in 40 mL of toluene. Then, a solution of DMAP (1.5 mmol, 1.5 eq) in 20 mL of toluene was added. After 10 min, a solution of anhydride 23a–b (0.8 mmol, 0.8 equivalents) in 30 mL of toluene was slowly added via dropping funnel. The mixture was stirred for three hours then the solvent was removed to dry with rotary evaporator. The residue was dissolved in AcOEt and transferred in a separatory funnel, washed three times with water and then three times with brine. The organic phase was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered through a cotton plug and solvent was evaporated to dry with a rotary evaporator. The crude solid was purified by gradient column chromatography on silica gel, affording monoamide products as a racemic mixture. rac-17a (53% yield), rac-17b (50% yield).
3.1.17. Methyl 4-Fluoro-2-isopropoxybenzoate (24)
In a 100 mL two-neck flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer and a reflux condenser, 500 mg (2.5 mmol) of compound 3b were dissolved in MeOH and 202 µL (2.8 mmol, 1.1 equivalents) of thionyl chloride (SOCl2) were slowly added with a syringe. The flask was immersed in a silicone oil bath on a heating plate until reflux. The mixture was left to react overnight at reflux temperature. The flask was then allowed to cool to room temperature and the solvent was removed to dry using under reduced pressure. The residue was dissolved in DCM and washed with H2O three times. The organic phase was dried, filtered through a cotton plug and concentrated to dry using a rotary evaporator. A total of 525 mg (2.5 mmol, 98%) of methyl ester 24 were obtained as a brownish oil. Rf (solvent system: AcOEt/Petroleum ether 1:1) = 0.91. ESI [M + H]+calc = 213,09, ESI [M + H]+found = 213.13. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.8 (ddd, J = 8.3, 7.0, 0.6 Hz, 1H), 6.7–6.6 (m, 2H), 4.5 (hept, J = 6.1, 0.6 Hz, 1H), 3.9 (s, 3H), 1.4 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 6H).
3.1.18. 4,5-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluoro-2-isopropoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole (25)
In a microwave vial equipped with a magnetic stirrer, 500 mg (1.79 mmol) of meso-diammine 5, 406 mg (2.13 mmol, 1.1 equivalents) of methyl ester 24 and 456 mg (1.79 mmol, 1 equivalent) of DABAL-Me3 were dissolved in 20 mL of toluene. The mixture was reacted in a microwave for 90 min at 130 °C. Subsequently, the toluene was removed to dry using a rotary evaporator and the crude product was purified by flash chromatography (10–100% DCM/MeOH) on silica gel, yielding 400 mg of product 25 (yield 50%), a yellow amorphous solid. TLC: (DCM/MeOH 9.5:0.5): Rf = 0.30. MS ESI: [M + H]+calc = 443.11, [M + H]+found = 443.32. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.2 (dd, J = 8.7, 7.0 Hz, 1H), 7.1–7.0 (m, 4H), 6.9–6.8 (m, 4H), 6.8–6.6 (m, 2H), 5.4 (s, 2H), 4.7 (hept, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 1.4 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 166.6, 164.1, 163.6, 157.6, 157.5, 137.7, 133.6, 133.5, 132.7, 128.9, 128.6, 128.0, 115.2, 108.4, 108.2, 101.5, 101.3, 72.0, 69.6, 22.1. 19F NMR (376 MHz, cdcl3) δ −106.2.
3.1.19. tert-Butyl 4-(4,5-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluoro-2-isopropoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole-1-carbonyl)piperazine-1-carboxylate (26)
In a 100 mL round-bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer, an inert atmosphere was created by performing three vacuum-argon cycles. Then, 80 mg (0.180 mmol) of imidazoline 25 was dissolved in 1.6 mL of freshly distilled DCM and 283 µL (1.62 mmol, 9 equivalents) of DIPEA were added at 0 °C. To the clear solution, a solution of triphosgene (40 mg, 0.135 mmol, 0.75 equivalents) in 1.6 mL of anhydrous DCM was added at 0 °C. The mixture was stirred for 3 h at room temperature. Next, 54 mg of N-Boc-Piperazine dissolved in 0.8 mL of anhydrous DCM (0.288 mmol, 1.6 equivalents) were added. The reaction was stirred for an additional 3 h at room temperature. After quenching the reaction with water, the heterogeneous mixture was transferred into a separatory funnel and washed twice with water. The organic phase was dried over Na2SO4, filtered through a cotton plug and the solvent was removed to dry under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography (5–15% MeOH/DCM) on silica gel, yielding 80 mg of pure compound 26, a light-yellow solid (71% yield). TLC: (CH2Cl2/MeOH 9.5:0.5) Rf = 0.70. ESI [M + H]+calc = 655.22, ESI [M + H]+found = 655.63.
3.1.20. (4,5-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluoro-2-isopropoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-1-Yl)(piperazin-1-Yl)methanone (rac-19b)
In a round-bottom 100 mL flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer, 80 mg (0.122 mmol) of compound 26 were dissolved in 4 mL of DCM. After adding 280 µL (3.66 mmol, 30 equivalents) of trifluoracetic acid (TFA), the solution was allowed to react overnight at room temperature. The following day, complete consumption of starting material was detected and the reaction was quenched by adding a saturated solution of NaHCO3 to reach basic pH (9). The mixture was stirred for 30 min and transferred in a separatory funnel. The two layers were separated and organic phase was washed three times with water then dried over Na2SO4, filtered through a funnel with cotton. The solvent was removed to dry using a rotary evaporator. Finally, 80 mg of deprotected racemic product rac-19b, was obtained as a light orange solid (90% yields).
3.1.21. N-(3-(4-(4,5-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluoro-2-isopropoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole-1-carbonyl)piperazin-1-Yl)propyl)-2,2-dichloroacetamide (rac-20b)
In a previously dried 100 mL round-bottom flask, equipped with a magnetic stirrer, an inert atmosphere was created by performing three vacuum-argon cycles. A solution of 100 mg (0.226 mmol) of imidazoline 25 in 2 mL of freshly distilled DCM was mixed with 354 µL (2.034 mmol, 9 equivalents) of DIPEA at 0 °C. To the clear solution, a solution of triphosgene (50.45 mg, 0.170 mmol, 0.75 equivalents) in 2 mL of anhydrous DCM was added at 0 °C. The mixture was stirred for 3 h at room temperature. Next, 92 mg of compound 2,2-dichloro-N-(3-(piperazin-1-yl)propyl)acetamide 9 (0.362 mmol, 1.6 equivalents) were added and the reaction was stirred for an additional 2.5 h at room temperature. After quenching with water, the mixture was transferred in a separatory funnel and washed with distilled water twice. The organic phase was dried over Na2SO4, filtered through a cotton plug and the solvent was removed to dry using a rotary evaporator. The resulting residue was purified by flash chromatography (10–20% DCM/MeOH) on silica gel, yielding 60 mg of racemic product rac-20b, a pale orange solid (37% yield). TLC: (DCM/MeOH 9.5:0.5): Rf = 0,74. MS ESI: [M + H]+calc = 722.16, [M + H]+found = 724.68. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.2 (s, 1H), 7.6–7.5 (m, 1H), 7.1–7.0 (m, 4H), 7.0–6.9 (m, 2H), 6.8 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 6.8–6.7 (m, 2H), 5.9 (s, 1H), 5.6 (d, J = 9.9 Hz, 1H), 5.5 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H), 4.6 (h, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 3.4 (q, J = 5.5 Hz, 2H), 3.2–3.1 (m, 3H), 2.4 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 2H), 2.1 (d, J = 9.7 Hz, 4H), 1.7 (p, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 1.4 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 3H), 1.4 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 166.4, 164.4, 163.9, 136.3, 135.2, 133.3, 133.0, 132.2, 129.3, 128.6, 128.3, 128.1, 107.5, 107.2, 101.1, 100.9, 71.9, 71.6, 69.2, 66.8, 58.1, 52.9, 45.4, 41.1, 29.8, 23.8, 22.2, 22.1.
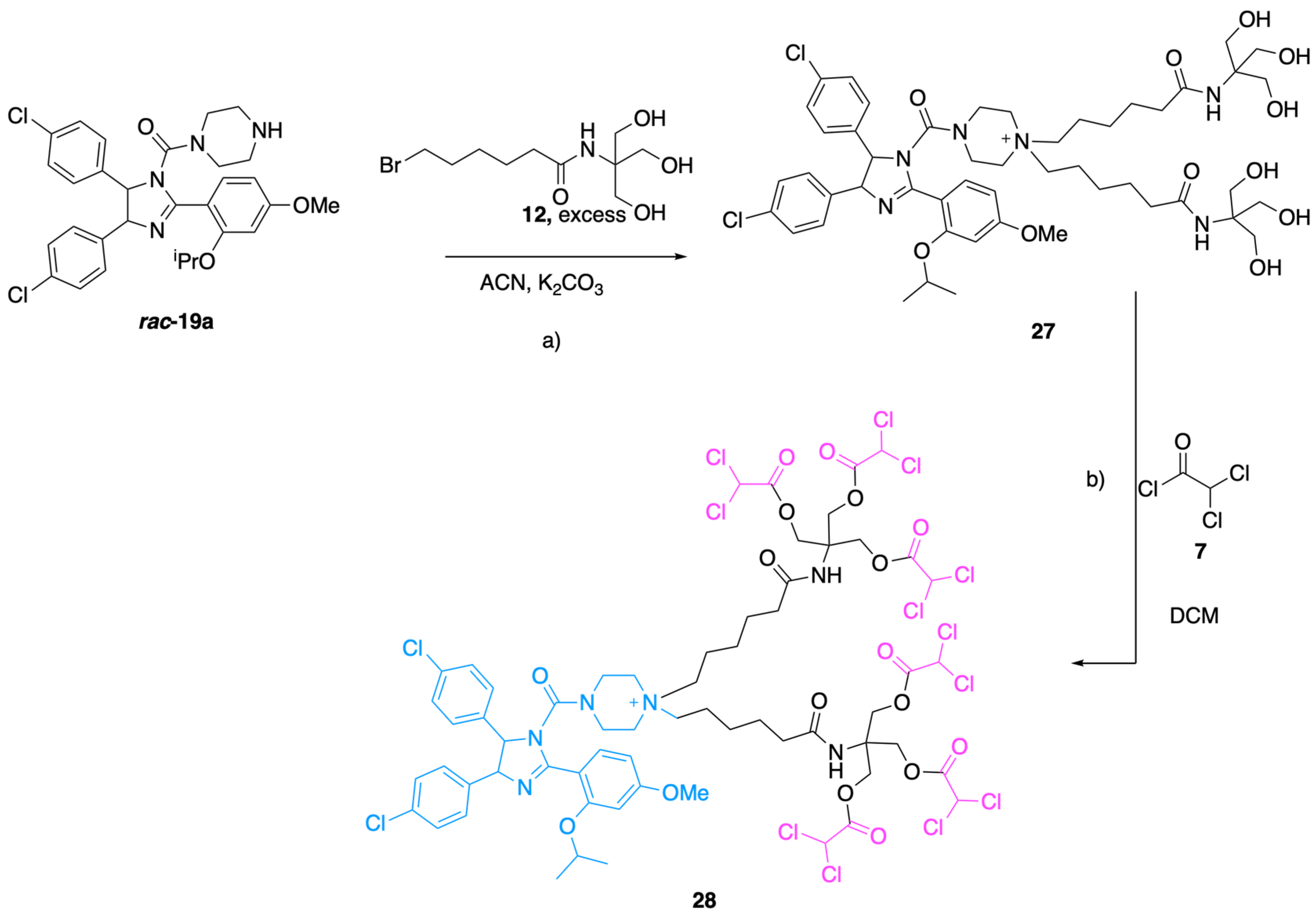
3.1.22. 6-(4-(4,5-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-isopropoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole-1-carbonyl)piperazin-1-yl)-N-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-Yl)hexanamide (21)
A previously dried 100 mL round bottom flask was filled with 100 mg (0.17 mmol) of compound 19a, 83 mg 0.6 mmol, 3 equivalents) of K2CO3 and 60 mg (0.20 mmol, 1.2 equivalents) of bromide 12 in 10 mL of ACN. The temperature of the flask was gradually increased until reflux and the reaction was stirred overnight. The solvent was removed to dry and the residue mixture was purified by isocratic chromatography (Solvent system DCM/MeOH/Toluene 17:1:2) on silica gel, to obtain 30 mg, 0.04 mmol, 23% yield) of product 21. ESI [M + H]+calc = 784.32, ESI [M + H]+found = 784.89. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Methanol-d4) δ 7.6–7.5 (m, 1H), 7.2–7.0 (m, 8H), 6.9 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 6.7–6.7 (m, 2H), 5.8 (d, J = 10.2 Hz, 1H), 5.5 (d, J = 10.3 Hz, 1H), 4.7 (p, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 3.9 (s, 3H), 3.7 (s, 7H), 3.3–3.1 (m, 4H), 2.2 (dt, J = 10.3, 7.1 Hz, 4H), 2.2–1.9 (m, 4H), 1.6 (p, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H), 1.4 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H), 1.4 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H), 1.3 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 6H), 1.0–0.8 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cd3od) δ 177.2, 165.0, 158.8, 156.4, 137.8, 136.6, 134.2, 132.9, 130.7, 130.0, 129.2, 129.0, 114.2, 106.4, 101.4, 72.4, 71.7, 70.0, 63.6, 62.7, 59.2, 56.2, 53.2, 49.9, 49.6, 49.4, 49.2, 49.0, 48.8, 48.6, 48.4, 46.6, 37.3, 27.9, 26.7, 22.5, 22.4. Dialkylated compound 27 was also isolated from crude mixture by chromatography to obtain (MS ESI [M + H]+calc = 1001.46, ESI [M + H]+found = 1002.4).
3.1.23. 2-(6-(4-(4,5-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-isopropoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole-1-carbonyl)piperazin-1-Yl)hexanamido)-2-((2,2-dichloroacetoxy)methyl)propane-1,3-diyl Bis(2,2-dichloroacetate) (22)
A previously dried 50 mL round-bottom flask was filled with 65 mg (0.08 mmol, 1 equivalent) of compound 21 and 5 mL of freshly distilled DCM. Then 24 µL (0.25 mmol, 3 equivalents) of dichloroacetic chloride 7 was added to the solution. The reaction was stirred at r.t. overnight then the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. The product was purified from the crude by gradient concentration chromatography (0–15% DCM/MeOH) on silica gel. Finally, the fractions were collected to afford 8 mg (9% yield) of finale product 22. TLC: (DCM/MeOH 9.5:0.5) Rf = 0.3. ESI [M + H]+calc = 1114.12, ESI [M + H]+found = 1118.42, 1006.42 [M–DCA], 896.55 [M–2DCA]. 1H NMR (500 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 9.84 (s, 1H), 7.53 (dd, J = 8.6, 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.44 (dd, J = 7.3, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.42–7.35 (m, 1H), 7.12–7.05 (m, 2H), 7.07–7.00 (m, 2H), 6.96–6.90 (m, 2H), 6.87–6.82 (m, 2H), 6.70 (s, 1H), 6.57 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 5.59 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 5.45 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H), 4.61 (h, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H), 3.95 (s, 1H), 3.86 (s, 2H), 3.64 (s, 4H), 3.25 (s, 4H), 2.38 (s, 2H), 2.23 (dt, J = 13.7, 7.0 Hz, 2H), 1.66 (p, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 1.51 (s, 2H), 1.40 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H), 1.34 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, cdcl3) δ 191.1, 175.1, 163.2, 157.5, 155.0, 136.2, 135.2, 133.3, 133.1, 132.2, 130.4, 129.4, 128.9, 128.6, 128.4, 128.3, 128.1, 127.3, 126.7, 113.7, 112.5, 109.5, 104.7, 100.5, 71.6, 71.3, 71.0, 69.3, 64.3, 61.5, 57.8, 56.2, 55.8, 44.4, 36.5, 29.8, 26.2, 24.8, 22.3.
3.1.24. 1,1-Bis(6-((1,3-bis(2,2-dichloroacetoxy)-2-((2,2-dichloroacetoxy)methyl)propan-2-Yl)amino)-6-oxohexyl)-4-(4,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-isopropoxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole-1-carbonyl)piperazin-1-ium (28)
A previously dried 50 mL round-bottom flask was filled with 65 mg (0.08 mmol, 1 equivalent) of compound 27 and 5 mL of freshly distilled DCM. Then 24 µL (0.25 mmol, 3 equivalents) of dichloroacetic chloride 7 was added to the solution. The reaction was stirred at r.t. overnight then the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. The product 28 was purified from the crude through Preparative RP-HPLC: (solvent A = H2O + 0.1% TFA, solvent B = H2O/ACN (40:60) + 0.1% TFA, gradient from 10% B to 80% of B in 20 min then isocratic 100% of B for 15 min; flow 20 mL/min; tR: 33 min). ESI [M]+calc = 1661.05, ESI [M]+found = 1667.1, 1556.2 [M–DCA].