Sustainable Supramolecular Extraction of Phytocomplexes from Microgreens and Their Eco-Loading in Nutriosomes: Physicochemical Characterization, Stability, and In Vitro Release Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Extraction from Microgreens
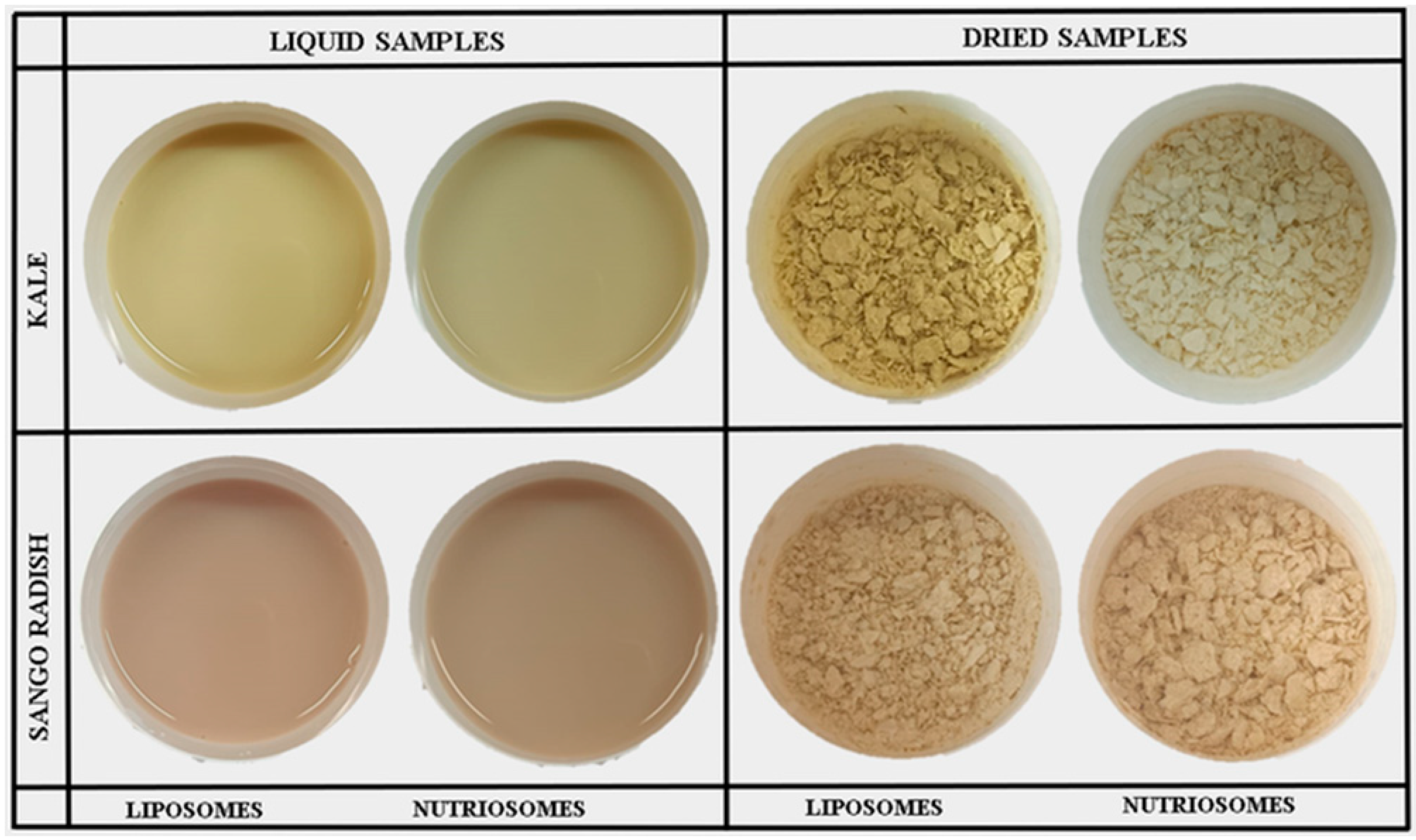
2.2. Characterization of Vesicles
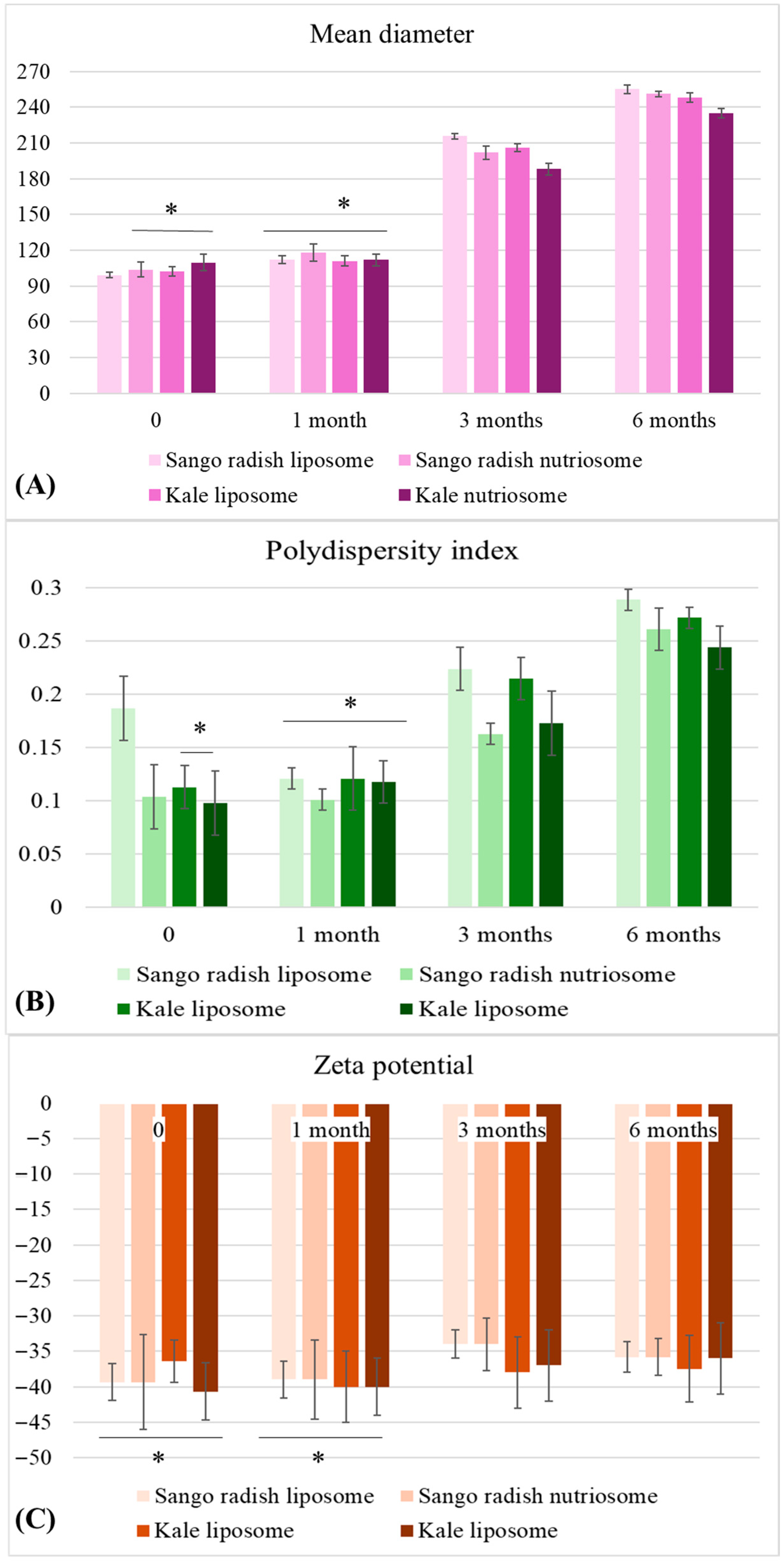
2.3. Stability of Vesicles over 6 Months
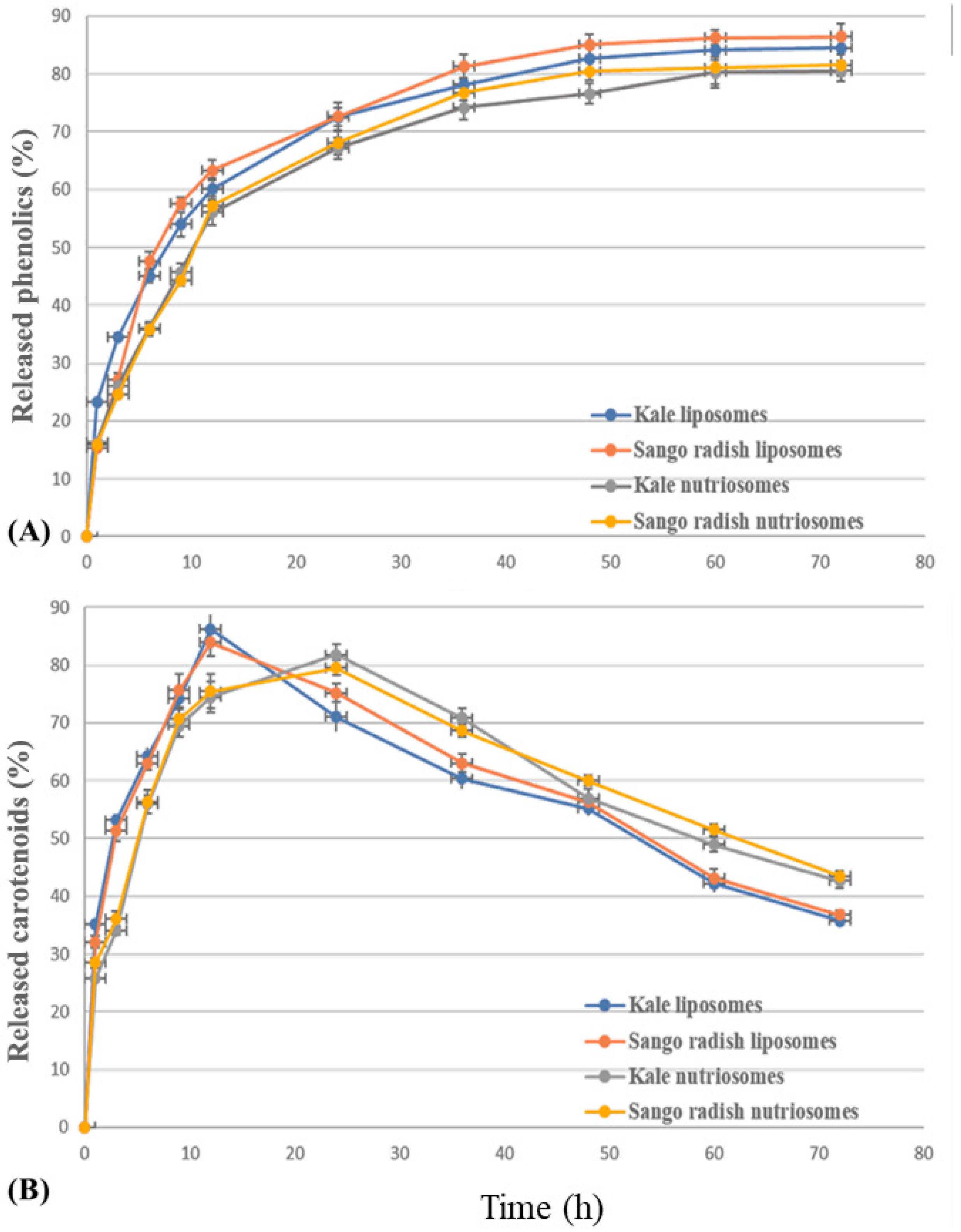
2.4. In Vitro Release of Phenolics and Carotenoids from Vesicles
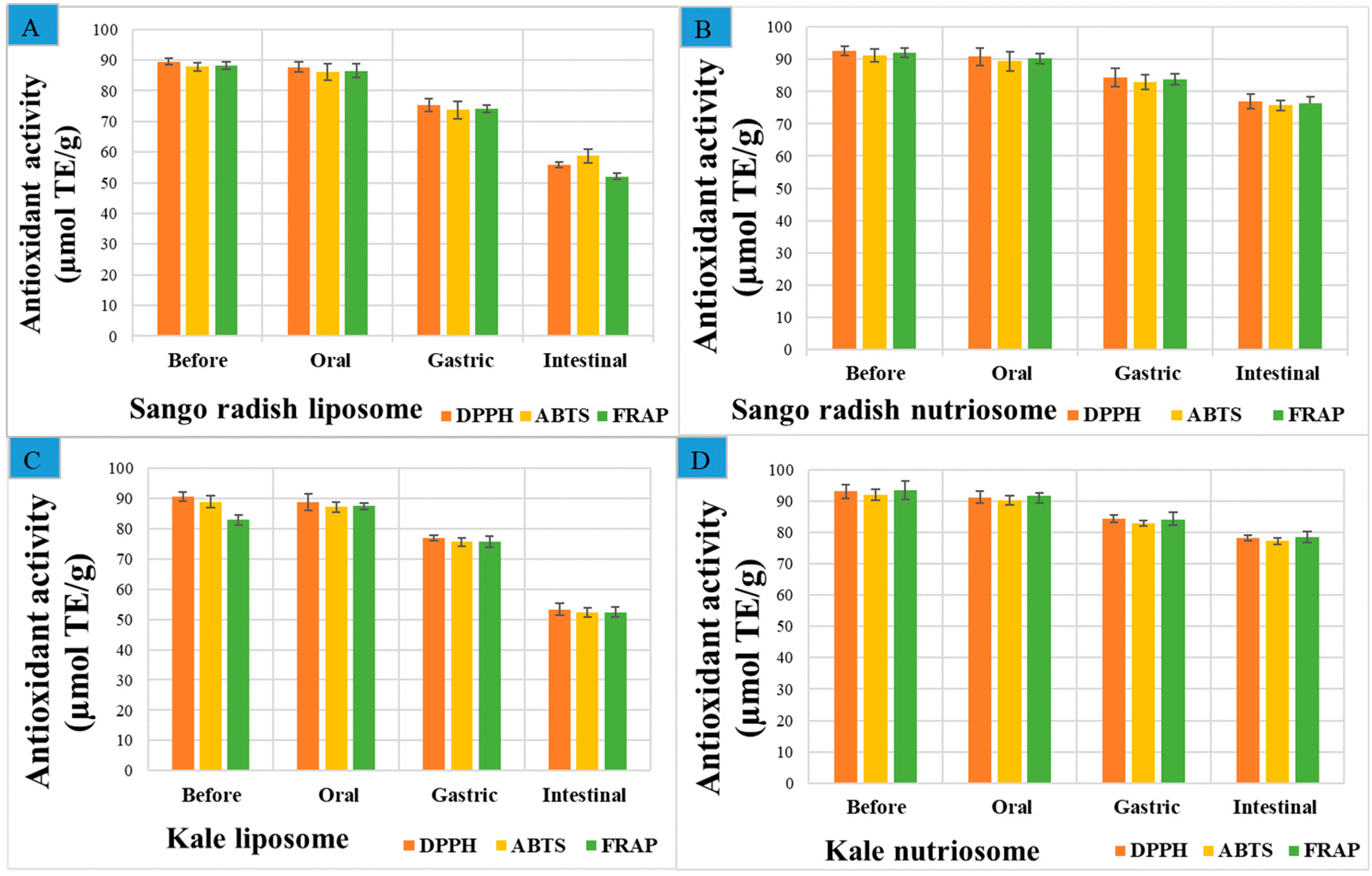
2.5. Antioxidant Capacity of Vesicles in Simulated In Vitro Digestion
2.6. Microbiological Content of Vesicles
3. Discussion
3.1. Extraction from Microgreens
3.2. Characterization of Vesicles
3.3. Stability of Vesicles over 6 Months
3.4. In Vitro Release of Phenolics and Carotenoids from Vesicles
3.5. Antioxidant Capacity of Vesicles in Simulated In Vitro Digestion
3.6. Microbiological Content of Vesicles
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microgreens, Chemicals, and Equipment
4.2. Supramolecular Extraction of Phytocomplex from Microgreens
4.3. HPLC Analysis of Phytocomplexes
4.4. Quantification of Carotenoids, Phenols, and Antioxidants of Phytocomplexes
4.5. Preparation of Nutriosomes Loading Phytocomplexes
4.6. Characterization of Vesicles
4.7. Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of Freezer-Dried Vesicles
4.8. Evaluation of In Vitro Digestibility and Bioaccessibility of Vesicles
4.9. In Vitro Release of Carotenoids and Phenols from Vesicles
4.10. Measurement of Microbiological Content of Vesicles
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alloggia, F.P.; Bafumo, R.F.; Ramirez, D.A.; Maza, M.A.; Camargo, A.B. Brassicaceae microgreens: A novel and promissory source of sustainable bioactive compounds. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaswant, M.; Shanmugam, D.K.; Miyazawa, T.; Abe, C.; Miyazawa, T. Microgreens—A Comprehensive Review of Bioactive Molecules and Health Benefits. Molecules 2023, 28, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vučetić, A.; Šovljanski, O.; Pezo, L.; Gligorijević, N.; Kostić, S.; Vulić, J.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J. A Comprehensive Antioxidant and Nutritional Profiling of Brassicaceae Microgreens. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgari, R.; Baldi, A.; Ferrante, A.; Lenzi, A. Yield and quality of basil, Swiss chard, and rocket microgreens grown in a hydroponic system. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2016, 45, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.; Abellán-Victorio, A.; Beretta, V.; Camargo, A.; Moreno, D.A. Functional ingredients from Brassicaceae species: Overview and perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas-Agustí, A.; Martín-Belloso, O.; Soliva-Fortuny, R.; Elez-Martínez, P. Food processing strategies to enhance phenolic compounds bioaccessibility and bioavailability in plant-based foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2531–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.; Castro-Puyana, M.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibanez, E. Compressed fluids for the extraction of bioactive compounds. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivošija, S.; Vidović, S.; Dueñas-Mas, M.J.; Ballesteros-Gómez, A. Supramolecular biosolvent extraction of antioxidants from orange peel residues from the tea industry. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vučetić, A.; Pezo, L.; Šovljanski, O.; Vulić, J.; Travičić, V.; Lević, S. Supramolecular solvent-based extraction of microgreens: Taguchi design coupled-ANN multi-objective optimization. Processes 2024, 12, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Gómez, A.; Lunar, L.; Sicilia, M.D.; Rubio, S. Hyphenating supramolecular solvents and liquid chromatography: Tips for efficient extraction and reliable determination of organics. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, E.; Yaşar, V. Supramolecular Solvent Based Microextraction with Sugaring-out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction for the Determination of Fungicides in Honey. Anal. Lett. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradiso, V.M.; Castellino, M.; Renna, M.; Santamaria, P.; Caponio, F. Setup of an Extraction Method for the Analysis of Carotenoids in Microgreens. Foods 2020, 9, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezagholizade-Shirvan, A.; Soltani, M.; Shokri, S.; Radfar, R.; Arab, M.; Shamloo, E. Bioactive compound encapsulation: Characteristics, applications in food systems, and implications for human health. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalkar, S.V.; Hatwar, P.R.; Bakal, R.L.; Mendake, R.A.; Rathod, G.J. Liposomes: A Versatile Drug Delivery System. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2025, 85, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán-Latorre, A.; Pleguezuelos-Villa, M.; Castangia, I.; Manca, M.L.; Caddeo, C.; Nácher, A.; Díez-Sales, O.; Peris, J.E.; Pons, R.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; et al. Nutriosomes: Prebiotic delivery systems combining phospholipids, a soluble dextrin and curcumin to counteract intestinal oxidative stress and inflammation. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1957–1969. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fathi, M.; Martín, Á.; McClements, D.J. Nanoencapsulation of food ingredients using carbohydrate based delivery systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 39, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpf, J.; Burger, R.; Schulze, M. Statistical evaluation of DPPH, ABTS, FRAP, and Folin-Ciocalteu assays to assess the antioxidant capacity of lignins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada, J.; Aguilera, J.M. Food microstructure affects the bioavailability of several nutrients. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, R21–R32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holban, A.M.; Grumezescu, A.M. (Eds.) Microbial Contamination and Food Degradation; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Álvarez-Rivera, G.; Valdés, A.; Ibáñez, E.; Cifuentes, A. Food by-products and food wastes: Are they safe enough for their valorization? TIFS 2021, 114, 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros-Gómez, A.; Sicilia, M.D.; Rubio, S. Supramolecular solvents in the extraction of organic compounds. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 677, 108–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Z.; Subbiah, V.; Suleria, H.A.R. Extraction and characterization of phenolic compounds and their potential antioxidant activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 81112–81129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, B.H.; Yu, Z.L.; Lu, Y.A.; Liu, S.J.; Li, Y.M.; Xie, M.X.; Lin, L.M. Green and efficient extraction of phenolic components from plants with supramolecular solvents: Experimental and theoretical studies. Molecules 2024, 29, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travičić, V.; Cvanić, T.; Vučetić, A.; Kostić, M.; Perović, M.; Pezo, L.; Ćetković, G. Green Extraction Technologies for Carotenoid Recovery from Citrus Peel: Comparative Study and Encapsulation for Stability Enhancement. Processes 2025, 13, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Rausch, S.R.; Luo, Y.; Sun, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, P.; Yu, L.; Stommel, J.R. Microgreens of Brassicaceae: Genetic diversity of phytochemical concentrations and antioxidant capacity. LWT 2019, 101, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, B.; López-García, G.; Máñez, V.; Alegría, A.; Barberá, R.; Cilla, A. Evaluation of the bioaccessibility of antioxidant bioactive compounds and minerals of four genotypes of Brassicaceae microgreens. Foods 2019, 8, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šola, I.; Vujčić Bok, V.; Popović, M.; Gagić, S. Phytochemical composition and functional properties of Brassicaceae microgreens: Impact of in vitro digestion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Fröhlich, K.; Böhm, V. Comparative antioxidant activities of carotenoids measured by ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), ABTS bleaching assay (αTEAC), DPPH assay and peroxyl radical scavenging assay. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; de Freitas, V.; Mateus, N.; Fernandes, I.; Oliveira, J. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers of Natural Phenolic Compounds. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMuhaysh, K.A.; Sergis, A.; Hardalupas, Y. Effects of pH and Nanoparticle Concentration on Al2O3–H2O Nanofluid Stability. Int. J. Thermophys. 2025, 46, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, Z.; Csóka, I.; Semnani Jazani, R.; Sipos, B.; Haspel, H.; Kozma, G.; Kónya, Z.; Dobó, D.G. Quality by design-driven zeta potential optimisation study of liposomes with charge imparting membrane additives. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadalinejhad, S.; Kurek, M.A. Microencapsulation of anthocyanins—Critical review of techniques and wall materials. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teli, D.; Satasia, R.; Patel, V.; Nair, R.; Khatri, R.; Gala, D.; Balar, P.C.; Patel, K.; Sharma, A.; Vadodariya, P.; et al. Nature meets technology: Harnessing nanotechnology to unleash the power of phytochemicals. Clin. Tradit. Med. Pharmacol. 2024, 5, 200139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaw, M.; Perra, M.; Parekh, P.; Serra, M.; Marongiu, J.; Castangia, I.; Fulgheri, F.; Caboni, P.; Tolle, G.; Corrias, F.; et al. Antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of nutriosomes and grape pomace phytochemicals in a cell model of oxidative stress and mouse model of Parkinson disease. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, P.; Serra, M.; Allaw, M.; Perra, M.; Pinna, A.; Manconi, M.; Morelli, M. Extract from Nasco pomace loaded in nutriosomes exerts anti-inflammatory effects in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 382, 114958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manconi, M.; Manca, M.L.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Coma-Cros, E.M.; Biosca, A.; Lantero, E.; Fernàndez-Busquets, X.; Fadda, A.M.; Caddeo, C. Nanoformulation of curcumin-loaded eudragit-nutriosomes to counteract malaria infection by a dual strategy: Improving antioxidant intestinal activity and systemic efficacy. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 556, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V. Liposome: A novel carrier for targeting drug delivery system. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 2020, 8, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, B.; Han, Q.; Xie, L.; Rashwan, A.K.; Yahia, Z.O.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W. Development and evaluation of guar gum-coated nano-nutriosomes for cyanidin-3-O-glucoside encapsulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahia, Z.O.; Xie, L.; Rashwan, A.K.; Paul, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, W. Gum Arabic modified nano-nutriosomes for curcumin encapsulation: Characterization, influence on physicochemical, microstructural and microbial properties of integrated yogurt. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, M.; Manca, M.L.; Caddeo, C.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Carbone, C.; Peris, J.E.; Usach, I.; Diez-Sales, O.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Co-loading of ascorbic acid and tocopherol in eudragit-nutriosomes to counteract intestinal oxidative stress. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, C.S.; McClements, D.J.; Weiss, J.; Decker, E.A. Factors influencing the chemical stability of carotenoids in foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Medina-Pastor, P.; Triacchini, G. The 2018 European Union report on pesticide residues in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, C.; Chung, M.M.S.; dos Santos, C.; Mayer, C.R.M.; Moraes, I.C.F.; Branco, I.G. Microencapsulation of an anthocyanin-rich blackberry (Rubus spp.) by-product extract by freeze-drying. LWT 2017, 84, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. Ferric Reducing/Antioxidant Power Assay: Direct Measure of Total Antioxidant capacity of Biological Fluids and Modified Version for Simultaneous Measurement of Total Antioxidant Power and Ascorbic Acid Concentration. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Castangia, I.; Fulgheri, F.; Leyva-Jimenez, F.J.; Alañón, M.E.; Cádiz-Gurrea, M.D.L.L.; Marongiu, F.; Meloni, M.C.; Aroffu, M.; Perra, M.; Allaw, M.; et al. From grape by-products to enriched yogurt containing pomace extract loaded in nanotechnological nutriosomes tailored for promoting gastro-intestinal wellness. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulić, J.; Šeregelj, V.; Tumbas Šaponjac, V.; Karadžić Banjac, M.; Kovačević, S.; Šovljanski, O.; Ćetković, G.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.; Jevrić, L.; Podunavac-Kuzmanović, S. From Sweet Corn By-Products to Carotenoid-Rich Encapsulates for Food Applications. Processes 2022, 10, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, T.; Kasoju, N.; Bora, U. Encapsulation of curcumin in alginate-chitosan-pluronic composite nanoparticles for delivery to cancer cells. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 4833-1:2013; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 1: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Pour Plate Technique. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 21528-2:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Enterobacteriaceae—Part 2: Colony-Count Technique. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 21527-1:2008; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Yeasts and Molds—Part 1: Colony Count Technique in Products with Water Activity Greater than 0. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 7937:2004; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Clostridium Perfringens—Colony-Count Technique. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.


| Nutriosome | Liposome | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sango radish | Kale | Sango radish | Kale | |
| Mean diameter (nm) | 110 ± 4 a | 104 ± 3 ab | 102 ± 2 b | 99 ± 2 b |
| Polydispersity index (au) | 0.10 ± 0.01 b | 0.10 ± 0.01 b | 0.11 ± 0.02 b | 0.19 ± 0.03 a |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −41 ± 2 ab | −42 ± 3 a | −36 ± 2 b | −39 ± 3 ab |
| Retention of antioxidant activity (%) | 96 ± 1 ab | 99 ± 1 a | 91 ± 1 c | 94 ± 1 b |
| Type of Nanovesicles | Nutriosome | Liposome | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Sango radish | Kale | Sango radish | Kale |
| Moisture content (g/100 g) | 8.3 ± 0.0 a | 7.5 ± 0.0 c | 7.9 ± 0.0 b | 7.1 ± 0.0 d |
| Solubility (g/100 g) | 50 ± 0 d | 74 ± 0 b | 62 ± 0 c | 77 ± 0 a |
| Hygroscopicity (g/100 g) | 12 ± 0.00 a | 12 ± 0 a | 12 ± 0 c | 12 ± 0 b |
| Bulk density (g/mL) | 0.17 ± 0.00 ab | 0.17 ± 0.01 ab | 0.17 ± 0.00 ab | 0.16 ± 0.00 b |
| Tapped density (g/mL) | 0.22 ± 0.00 b | 0.21 ± 0.00 c | 0.31 ± 0.01 a | 0.29 ± 0.01 a |
| Carr Index (%) | 21 ± 0.1 b | 19 ± 0.1 c | 47 ± 0.3 a | 47 ± 0.5 a |
| Hausner ratio | 1.3 ± 0.0 b | 1.2 ± 0.0 c | 1.9 ± 0.0 a | 1.9 ± 0.0 a |
| Flowability | Fair | Good | Very bad | Very bad |
| Cohesiveness | Intermediate | Intermediate | High | High |
| Color | ||||
| L* (lightness) | 80 ± 0.0 d | 93 ± 0.0 a | 88 ± 0.0 c | 93 ± 0.0 b |
| a* (redness/greenness) | −0.7 ± 0.0 a | −4.6 ± 0.0 c | −4.4 ± 0.0 b | −4.8 ± 0.0 d |
| b* (yellowness) | 23 ± 0.1 b | 28 ± 0.1 a | 19 ± 0.1 c | 22 ± 0.1 b |
| C* (saturation) | 23 ± 0.0 b | 28 ± 0.0 a | 20 ± 0.0 c | 22 ± 0.0 b |
| Test Sample | Total Aerobic Bacteria (log CFU/g or mL) | Enterobacteriaceae (log CFU/g or mL) | Yeasts and Fungi (log CFU/g or mL) | Salmonella spp. (Presence/Absence) | Sulfite-Reducing Clostridia (log CFU/g or mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kale upper-phase | <1 | <1 | <1 | / * | / |
| Kale lower-phase | <1 | <1 | <1 | / | / |
| Sango radish upper-phase | <1 | <1 | <1 | / | / |
| Sango radish lower-phase | <1 | <1 | <1 | / | / |
| Kale liposomes | <1 | <1 | <1 | absence | <1 |
| Sango radish liposomes | <1 | <1 | <1 | absence | <1 |
| Kale nutrisomes | <1 | <1 | <1 | absence | <1 |
| Sango radish nutrisomes | <1 | <1 | <1 | absence | <1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vučetić, A.; Rached, R.A.; Manca, M.L.; Šovljanski, O.; Cvetković, D.; Manconi, M.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J. Sustainable Supramolecular Extraction of Phytocomplexes from Microgreens and Their Eco-Loading in Nutriosomes: Physicochemical Characterization, Stability, and In Vitro Release Behavior. Molecules 2025, 30, 3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183774
Vučetić A, Rached RA, Manca ML, Šovljanski O, Cvetković D, Manconi M, Čanadanović-Brunet J. Sustainable Supramolecular Extraction of Phytocomplexes from Microgreens and Their Eco-Loading in Nutriosomes: Physicochemical Characterization, Stability, and In Vitro Release Behavior. Molecules. 2025; 30(18):3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183774
Chicago/Turabian StyleVučetić, Anja, Rita Abi Rached, Maria Letizia Manca, Olja Šovljanski, Dragoljub Cvetković, Maria Manconi, and Jasna Čanadanović-Brunet. 2025. "Sustainable Supramolecular Extraction of Phytocomplexes from Microgreens and Their Eco-Loading in Nutriosomes: Physicochemical Characterization, Stability, and In Vitro Release Behavior" Molecules 30, no. 18: 3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183774
APA StyleVučetić, A., Rached, R. A., Manca, M. L., Šovljanski, O., Cvetković, D., Manconi, M., & Čanadanović-Brunet, J. (2025). Sustainable Supramolecular Extraction of Phytocomplexes from Microgreens and Their Eco-Loading in Nutriosomes: Physicochemical Characterization, Stability, and In Vitro Release Behavior. Molecules, 30(18), 3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30183774












