The Impact of Proinflammatory M1 Macrophages on the Proliferation and Expression of Cyclin E2, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases 4 and 7 in Hepatocytes Isolated from a Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Body Weight and Blood Biochemical Analyses
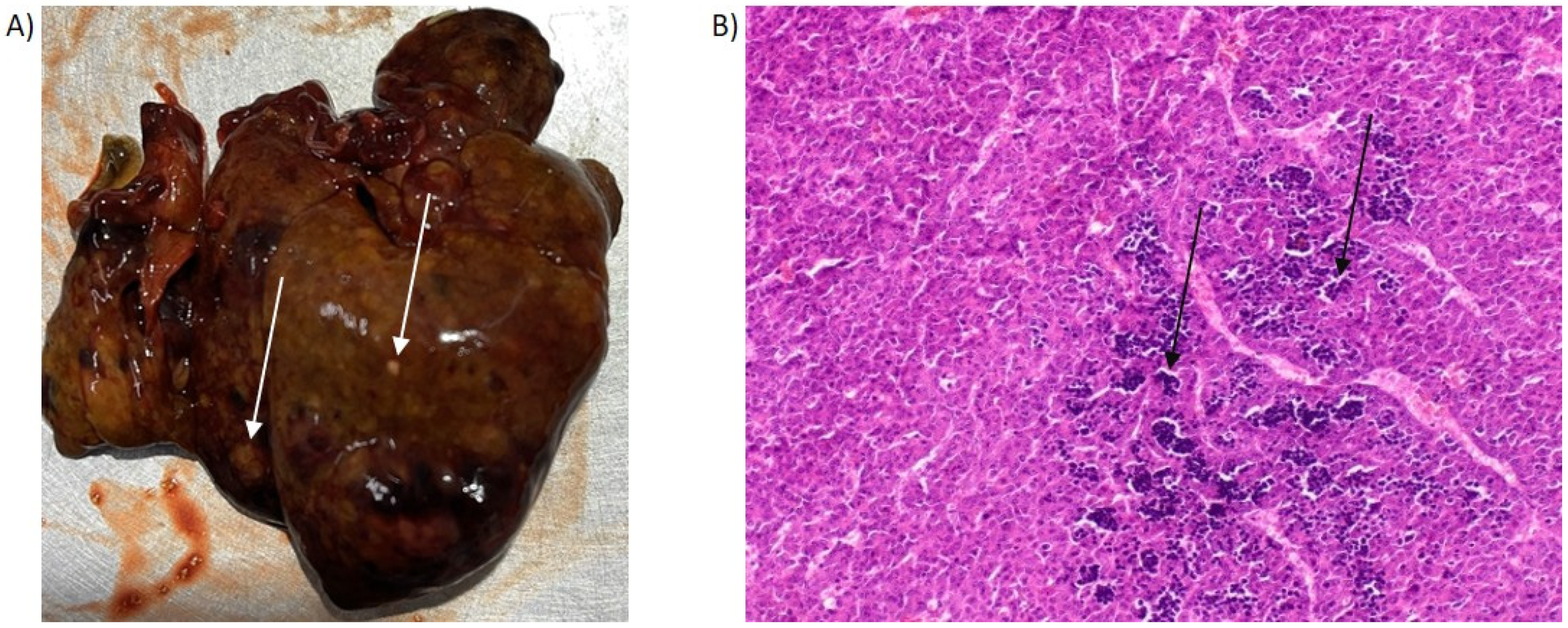
2.2. Histological Examination of PH/DEN-Induced Livers
2.3. Alpha-Fetoprotein Levels in PH- and PH/DEN-Derived Hepatocytes
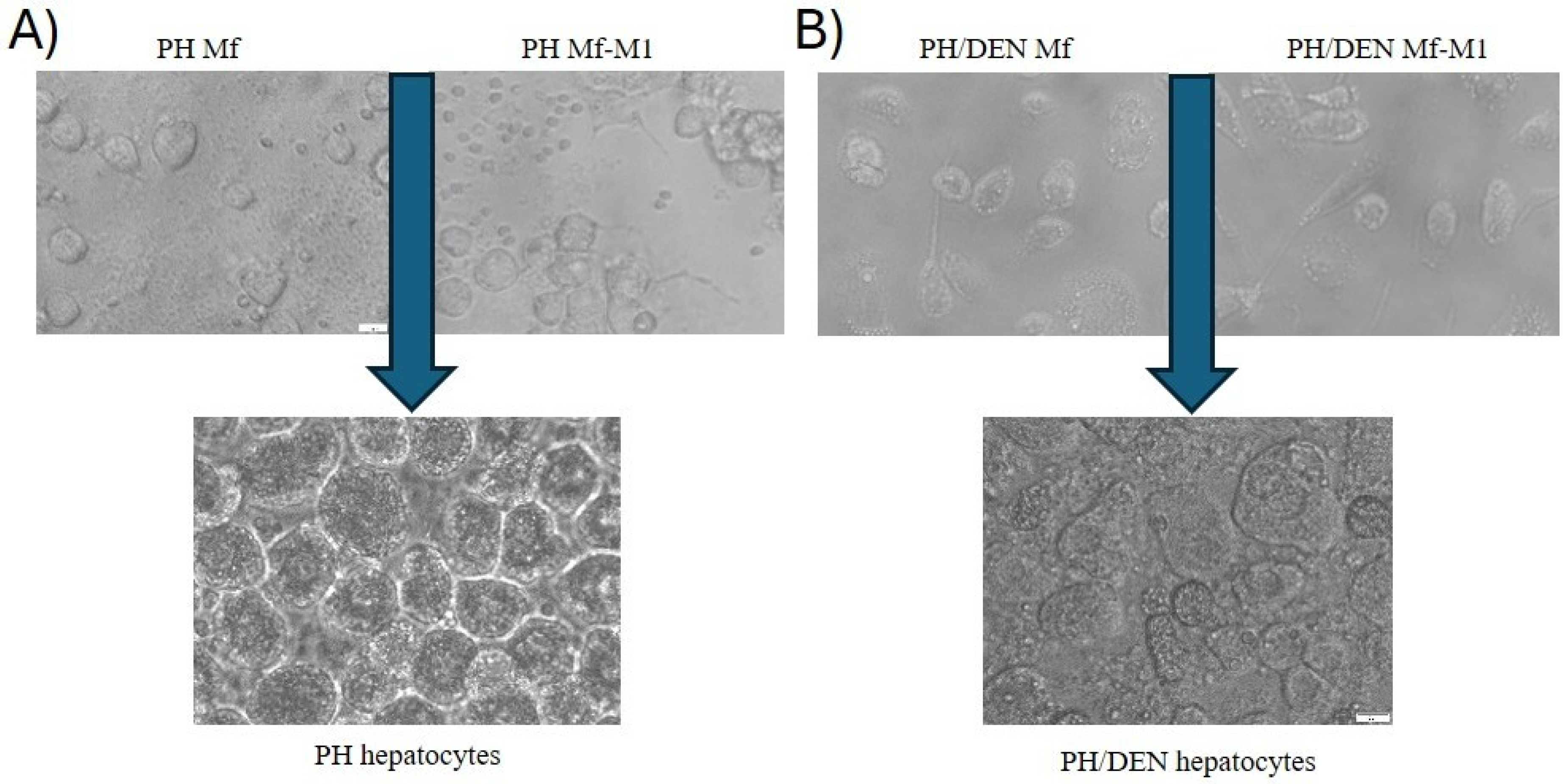
2.4. Phenotypes of Primary PH- and PH/DEN-Derived Hepatocyte Cultures
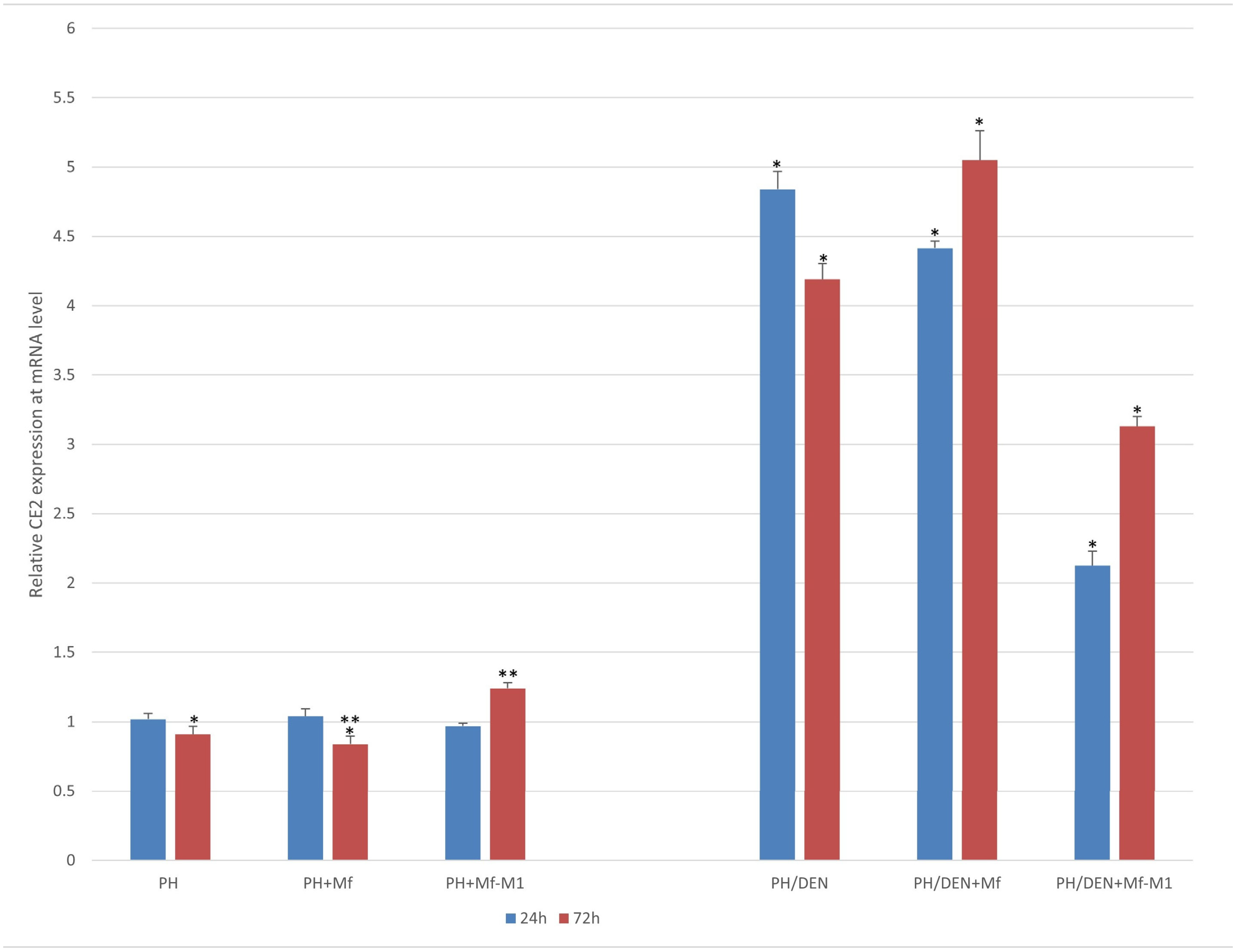
2.5. CE2 Expression Under Nonneoplastic and Neoplastic Conditions
2.6. Mapk4 Expression Under Nonneoplastic and Neoplastic Conditions
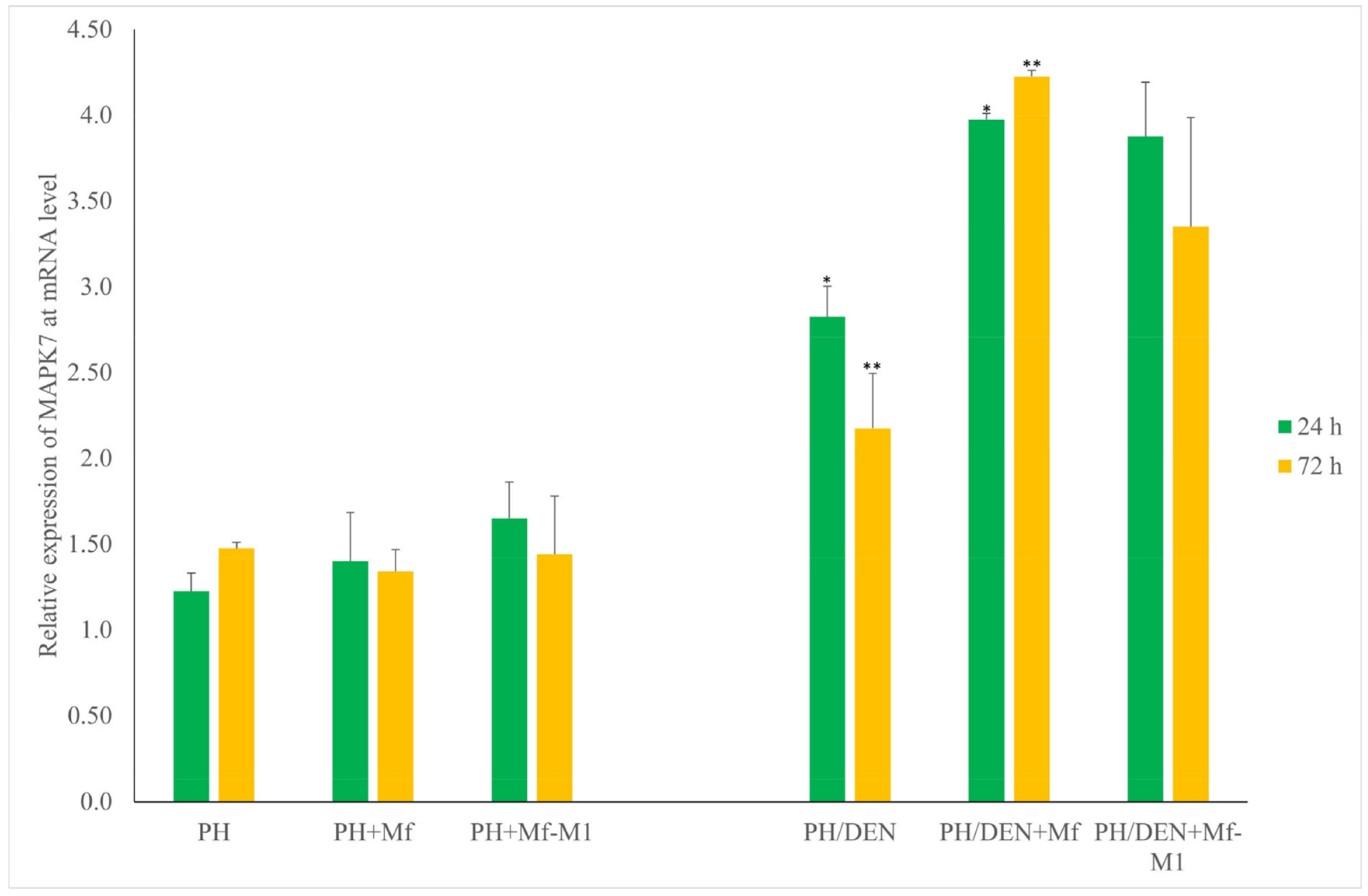
2.7. Mapk7 Expression Under Nonneoplastic and Neoplastic Conditions
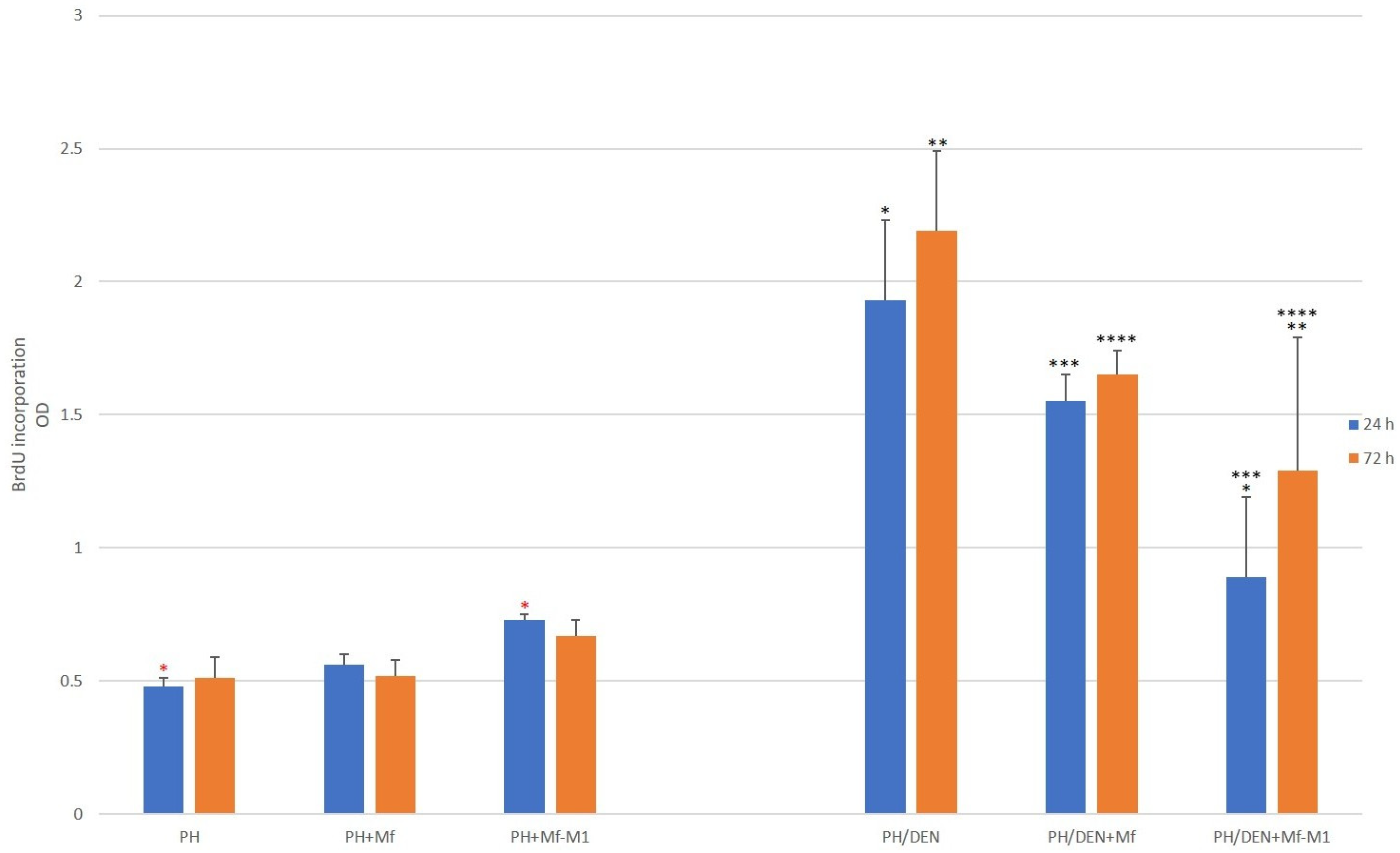
2.8. Hepatocyte Proliferation Analysis
2.9. Apoptosis Analysis
2.10. Correlation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animal Model
4.3. Hepatocyte Isolation and Treatment
4.4. Isolation of Rat Blood-Derived Monocytes
4.5. Microenvironment Culture of Hepatocytes and Blood-Derived Monocytes
4.6. Biochemical Analysis of Liver Function
4.7. Histopathological Examination
4.8. Isolation of Total RNA from PH and PH/DEN Cells Cultured In Vitro
4.9. Reverse Transcription
4.10. Analysis of CE2 and Mapk4/7 Expression at the mRNA Level Using Real-Time PCR
4.11. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.12. Apoptosis Detection
4.13. Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) ELISA
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFP | alpha-fetoprotein |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AP | alkaline phosphatase |
| BBG | barley β-glucan |
| BrdU | 5-Bromo-2′-deoxyuridine |
| CDK2 | cyclin-dependent kinase 2 |
| CE2 | cyclin E2 |
| DEN | diethylnitrosamine |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| Mf | macrophages (control macrophages) |
| Mf-M1 | M1 macrophages (cells with M1 phenotype) |
| Mf-M2 | M2 macrophages (cells with M2 phenotype) |
| NFkB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of activated B cells |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PH | partial hepatectomy |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
| TNF | tumor necrosis alpha |
References
- Singal, A.G.; Lampertico, P.; Nahon, P. Epidemiology and Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: New Trends. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Vos, T.; Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Flaxman, A.D.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; et al. Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) for 291 Diseases and Injuries in 21 Regions, 1990–2010: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2197–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Pikarsky, E.; Sangro, B.; Schwartz, M.; Sherman, M.; Gores, G. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Kuk, D.; Gönen, M.; Balachandran, V.P.; Kingham, T.P.; Allen, P.J.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Jarnagin, W.R.; DeMatteo, R.P. Actual 10-Year Survivors After Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Visser, K.E.; Joyce, J.A. The Evolving Tumor Microenvironment: From Cancer Initiation to Metastatic Outgrowth. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 374–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Dai, B.; Li, J.; Shang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, X. Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Derived Exosomal MiRNA-21 Contributes to Tumor Progression by Converting Hepatocyte Stellate Cells to Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Amaro, R.; García-Monzón, C.; García-Buey, L.; Moreno-Otero, R.; Alonso, J.L.; Yagüe, E.; Pivel, J.P.; López-Cabrera, M.; Fernández-Ruiz, E.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Induction of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Production by Human Hepatocytes in Chronic Viral Hepatitis. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichner, J.S. Interleukin-6 Production by Rat Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Is Associated with Metastatic Potential but Not with Tumorigenicity. JAMA Surg. 1996, 131, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWaal, D.; Nogueira, V.; Terry, A.R.; Patra, K.C.; Jeon, S.-M.; Guzman, G.; Au, J.; Long, C.P.; Antoniewicz, M.R.; Hay, N. Hexokinase-2 Depletion Inhibits Glycolysis and Induces Oxidative Phosphorylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Sensitizes to Metformin. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K.; Sica, A.; Lewis, C.E. Plasticity of Macrophage Function during Tumor Progression: Regulation by Distinct Molecular Mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Zhao, E.; Kryczek, I.; Vatan, L.; Sadovskaya, A.; Ludema, G.; Simeone, D.M.; Zou, W.; Welling, T.H. Tumor-Associated Macrophages Produce Interleukin 6 and Signal via STAT3 to Promote Expansion of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Stem Cells. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Giraud, F.; Hafner, M.; Ries, C.H. In Vitro Generation of Monocyte-Derived Macrophages under Serum-Free Conditions Improves Their Tumor Promoting Functions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Zou, J.; Mao, R.; Ma, C.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y. M1 Macrophages Induce PD-L1 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Through IL-1β Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 01643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, M.; Wessely-Szponder, J.; Cichoż-Lach, H.; Celiński, K.; Bobowiec, R. In Vitro Proinflammatory Polarization of Macrophages Isolated from Hepatocarcinogenic Stage in Humans and Rats. In Vivo 2016, 30, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Ge, W.; Zhou, J.; Gao, B.; Qian, X.; Wang, W. The Role of Tumor Associated Macrophages in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbath, I.; Leclercq, I.A.; Abarca-Quinones, J.; Desaeger, C.; Lebrun, V.; Moulin, P.; Sempoux, C.; Horsmans, Y. Inhibition of Early Preneoplastic Events in the Rat Liver by the Somatostatin Analog Lanreotide. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, J.M.; Pearson, G.; Hockenberry, T.; Shivakumar, L.; White, M.A.; Cobb, M.H. Contribution of the ERK5/MEK5 Pathway to Ras/Raf Signaling and Growth Control. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31588–31592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Shen, T.; Dong, B.; Creighton, C.J.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Moore, D.D.; et al. MAPK4 Overexpression Promotes Tumor Progression via Noncanonical Activation of AKT/MTOR Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 129, 1015–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudas, J.M.; Payton, M.; Thukral, S.; Chen, E.; Bass, M.; Robinson, M.O.; Coats, S. Cyclin E2, a Novel G 1 Cyclin That Binds Cdk2 and Is Aberrantly Expressed in Human Cancers. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.C.; Clurman, B.E. Cyclin E in Normal and Neoplastic Cell Cycles. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2776–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiariello, M.; Gomez, E.; Gutkind, J.S. Regulation of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (Cdk) 2 Thr-160 Phosphorylation and Activity by Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Late G1 Phase. Biochem. J. 2000, 349, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Ro, S.W. MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Bai, L.; Wang, D.; Ding, W.; Cao, Z.; Yan, P.; Li, Y.; Xi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X.; et al. SIRT3-dependent Delactylation of Cyclin E2 Prevents Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth. EMBO Rep. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farra, R.; Dapas, B.; Pozzato, G.; Scaggiante, B.; Agostini, F.; Zennaro, C.; Grassi, M.; Rosso, N.; Giansante, C.; Fiotti, N.; et al. Effects of E2F1–Cyclin E1–E2 Circuit down Regulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Dig. Liver Dis. 2011, 43, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonntag, R.; Giebeler, N.; Nevzorova, Y.A.; Bangen, J.-M.; Fahrenkamp, D.; Lambertz, D.; Haas, U.; Hu, W.; Gassler, N.; Cubero, F.J.; et al. Cyclin E1 and Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 2 Are Critical for Initiation, but Not for Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9282–9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Michowski, W.; Chick, J.M.; Wang, Y.E.; Jecrois, M.E.; Sweeney, K.E.; Liu, L.; Han, R.C.; Ke, N.; Zagozdzon, A.; et al. Kinase-Independent Function of E-Type Cyclins in Liver Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotty, J.; Bablon, P.; Weiss, P.-H.; Soussan, P. Diethylnitrosamine Induction of Hepatocarcinogenesis in Mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2769, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Meza, J.; Campos-Valdez, M.; Domínguez-Rosales, J.A.; Godínez-Rubí, J.M.; Rodríguez-Reyes, S.C.; Martínez-López, E.; Zúñiga-González, G.M.; Sánchez-Orozco, L.V. Chronic Administration of Diethylnitrosamine and 2-Acetylaminofluorene Induces Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Wistar Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; Li, J.; Lin, W.; Lou, L.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Jiang, Y. Proteomic Analysis of DEN and CCl4-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Mouse Model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, R.; Sijtsema, H.P.; Tlali, M.; Marais, A.D.; Hall, P.d.l.M. Effects of Iron Overload in a Rat Nutritional Model of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Liver Int. 2006, 26, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, D.; Łukomska, A.; Dec, K.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Gutowska, I.; Skórka-Majewicz, M.; Styburski, D.; Misiakiewicz-Has, K.; Pilutin, A.; Palma, J.; et al. Diet-Induced Rat Model of Gradual Development of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) with Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) Secretion. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aassouani, F.; Lkharrat, F.-Z.; Charifi, Y.; Attar, A.; Lahlali, M.; El Bouardi, N.; Abid, H.; Haloua, M.; Alami, B.; Boubbou, M.; et al. Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma Developed within Dysplastic Nodule as Nodule-within-Nodule Appearance: Case Report with Literature Review. Radiol. Case Rep. 2022, 17, 4087–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Tang, C.; Luo, R.; Gu, X.; Zhou, J.; Gao, J. Current Concepts of Precancerous Lesions of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Recent Progress in Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.J.; Rodrigues, G.; Bona, S.; Cerski, C.T.; Marroni, C.A.; Mauriz, J.L.; González-Gallego, J.; Marroni, N.P. Oxidative Stress and Cell Damage in a Model of Precancerous Lesions and Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurma, K.; Manches, O.; Chuffart, F.; Sturm, N.; Gharzeddine, K.; Zhang, J.; Mercey-Ressejac, M.; Rousseaux, S.; Millet, A.; Lerat, H.; et al. DEN-Induced Rat Model Reproduces Key Features of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-F.; Zha, B.-S.; Zhang, H.-L.; Zhu, X.-J.; Li, Y.-H.; Zhu, J.; Guan, X.-H.; Feng, Z.-Q.; Zhang, J.-P. Characteristic Gene Expression Profiles in the Progression from Liver Cirrhosis to Carcinoma Induced by Diethylnitrosamine in a Rat Model. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 28, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggi, F.; Pelassa, S.; Pierobon, D.; Penco, F.; Gattorno, M.; Novelli, F.; Eva, A.; Varesio, L.; Giovarelli, M.; Bosco, M.C. Regulation of Human Macrophage M1–M2 Polarization Balance by Hypoxia and the Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-1. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 01097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, H.; Ye, Y.; Chen, X.; Zou, Y.; Duan, J.; Xiang, D. Β-glucan, a Dectin-1 Ligand, Promotes Macrophage M1 Polarization via NF-κB/Autophagy Pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 54, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Luo, F.; Ding, C.; Albeituni, S.; Hu, X.; Ma, Y.; Cai, Y.; McNally, L.; Sanders, M.A.; Jain, D.; et al. Dectin-1 Activation by a Natural Product β-Glucan Converts Immunosuppressive Macrophages into an M1-like Phenotype. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 5055–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerriero, J.L. Macrophages: The Road Less Traveled, Changing Anticancer Therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 472–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.E.; Pollard, J.W. Distinct Role of Macrophages in Different Tumor Microenvironments. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. RIG-I Promotes Cell Death in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Inducing M1 Polarization of Perineal Macrophages Through the RIG-I/MAVS/NF-ΚB Pathway. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2020, 13, 8783–8794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.; Ge, Y.; Ma, H.; Gao, X.; Pan, J.; Liu, D.; Xu, G.; Ma, J.; Jia, W. Prognostic Value of Polarized Macrophages in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Resection. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Dahl, E.; Luedde, T.; Neumann, U.P.; Bednarsch, J. The Role of Macrophage Polarization-Associated Gene Expression in the Oncological Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterol. Insights 2024, 15, 764–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J. Promotion of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transformation by Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Educated Macrophages through Wnt2b/β-Catenin/c-Myc Signaling and Reprogramming Glycolysis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Fan, Y.; Li, G.; Guo, C.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y. CD68+HLA-DR+ M1-like Macrophages Promote Motility of HCC Cells via NF-ΚB/FAK Pathway. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P. The Interaction of Anticancer Therapies with Tumor-Associated Macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-Related Inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage Plasticity and Interaction with Lymphocyte Subsets: Cancer as a Paradigm. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, C.; Ding, A. Nonresolving Inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, L.; Han, L.; Yao, X.; Hu, Y.; Wu, F. Cyclin D1b Induces Changes in the Macrophage Phenotype Resulting in Promotion of Tumor Metastasis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 2559–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, F.; Tan, K.W.; Schöpf, B.; Santos, M.M.; Zegerman, P. Dephosphorylation of the Pre-Initiation Complex Is Critical for Origin Firing. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 12–25.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagundes, R.; Teixeira, L.K. Cyclin E/CDK2: DNA Replication, Replication Stress and Genomic Instability. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 774845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varallo, G.; Gelaleti, G.; Maschio-Signorini, L.; Moschetta, M.; Lopes, J.; De Nardi, A.; Tinucci-Costa, M.; Rocha, R.; de Campos Zuccari, D. Prognostic Phenotypic Classification for Canine Mammary Tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Beers Gibson, T.; Xu, B.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) Kinase Pathways: Regulation and Physiological Functions. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, L.; Liu, S.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, J.; Guo, M.; Chen, C.; He, Z.; et al. Identification of Atypical Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase MAPK4 as a Novel Regulator in Acute Lung Injury. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. NF-ΚB: Linking Inflammation and Immunity to Cancer Development and Progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, J.W. Tumour-Educated Macrophages Promote Tumour Progression and Metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerneur, C.; Cano, C.E.; Olive, D. Major Pathways Involved in Macrophage Polarization in Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1026954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, U.; Sarkar, T.; Mukherjee, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, S.; Nayak, D.; Kaushik, S.; Das, T.; Sa, G. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: An Effective Player of the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1295257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisitpongpun, P.; Potup, P.; Usuwanthim, K. Oleamide-Mediated Polarization of M1 Macrophages and IL-1β Production by Regulating NLRP3-Inflammasome Activation in Primary Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 856296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degroote, H.; Lefere, S.; Vandierendonck, A.; Vanderborght, B.; Meese, T.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Verhelst, X.; Geerts, A.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; Devisscher, L. Characterization of the Inflammatory Microenvironment and Hepatic Macrophage Subsets in Experimental Hepatocellular Carcinoma Models. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 562–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Hao, Y.; Gao, D.; Gao, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z. Phenotype and Function of Macrophage Polarization in Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Rat Model. Physiol. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, A.; Ali, M.A.; Newmai, K.; Madhuri, P.; Azyu, R.Z.; Malsawmsangi. Effective Management of Wistar Rats in Laboratory Research: A Brief Review. Int. J. Adv. Biochem. Res. 2024, 8, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solt, D.B.; Medline, A.; Farber, E. Rapid Emergence of Carcinogen-Induced Hyperplastic Lesions in a New Model for the Sequential Analysis of Liver Carcinogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 1977, 88, 595–618. [Google Scholar]
- Wójcik, M.; Bobowiec, R.; Martelli, F. Effect of Carotenoids on in Vitro Proliferation and Differentiation of Oval Cells during Neoplastic and Non-Neoplastic Liver Injuries in Rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008, 59 (Suppl. S2), 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Wójcik, M.; Wessely-Szponder, J.; Kosior-Korzecka, U. Proliferative and Oxidative Response of Hepatocytes (Hep) and Hepatic Stellate Cells (HSC) Isolated from Rats Exposed to Ketogenic Diet. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 17, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacalone, A.G.; Merritt, M.E.; Ragavan, M. <Em>Ex Vivo</Em> Hepatic Perfusion Through the Portal Vein in Mouse. J. Vis. Exp. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, M.; Bobowiec, R.; Lisiecka, U.; Śmiech, A. Expression of Receptor Interacting Protein 1 and Receptor Interacting Protein 3 Oval Cells in a Rat Model of Hepatocarcinogenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 4448–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomczynski P A Reagent for the Single-Step Simultaneous Isolation of RNA, DNA and Proteins from Cell and Tissue Samples. Biotechniques 1993, 15, 536–537.
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Pang, Z. Stability of Methods for Differential Expression Analysis of RNA-Seq Data. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, S.; García-Alcalde, F.; Dopazo, J.; Ferrer, A.; Conesa, A. Differential Expression in RNA-Seq: A Matter of Depth. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, W.D.; Peschke, P. Hepatic Progenitor Cells, Stem Cells, and AFP Expression in Models of Liver Injury. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2006, 87, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Feature | PH-Rats (mean, ±SD) | PH/DEN Rats (mean, ±SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial weight (g) | 203 ± 2.18 | 202 ± 8.2 |
| Final weight (g) | 312 ± 1.93 | 258 ± 9.2 * |
| AST (U/L) | 105 ± 3.88 | 210.25 ± 19.04 * |
| ALT (U/L) | 47.15 ± 1.09 | 77.65 ± 5.15 * |
| AP (U/L) | 72.85 ± 1.34 | 142.75 ± 2.1 * |
| GGT (U/L) | 5.15 ± 0.65 | 61.65 ± 9.08 * |
| Hepatocytes | 24 h (%, ±SD) | p Value | 72 h (%, ±SD) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | 13.14 ± 1.2 | - | 16.86 ± 3.5 | - |
| PH and Mf | 12.7 ± 1.8 | p = 0.89 * | 15.44 ± 2.5 | p = 0.31 * |
| PH and Mf-M1 | 19.2 ± 2.9 | p < 0.001 ** | 17.9 ± 3.1 | p = 0.49 ** |
| PH/DEN | 1.5 ± 0.2 | - | 2.9 ± 0.7 | - |
| PH/DEN and Mf | 3.08 ± 0.5 | p < 0.001 *** | 5.94 ± 0.8 | p < 0.001 *** |
| PH/DEN and Mf-M1 | 10.8 ± 1.4 | p < 0.001 **** | 15.8 ± 2.1 | p < 0.001 **** |
| After 24 h | |||||
| Apoptosis | CE2 | Mapk4 | Mapk7 | Proliferative activity | |
| Apoptosis | |||||
| CE2 | −0.94 * | ||||
| Mapk4 | −0.39 | 0.33 | |||
| Mapk7 | −0.64 | 0.71 | 0.36 | ||
| Proliferative activity | −0.88 * | 0.98 * | 0.37 | 0.36 | |
| After 72 h | |||||
| Apoptosis | |||||
| CE2 | −0.71 | ||||
| Mapk4 | −0.31 | 0.32 | |||
| Mapk7 | −0.41 | 0.80 | 0.18 | ||
| Proliferative activity | −0.91 * | 0.92 * | 0.68 * | 0.61 | |
| Gene Name | Assay ID of Primer/Probe Set | References/Source |
|---|---|---|
| CE2 (rat) Primers/probe set (FAM-MGB) | Rn01442731_m1 | Life Technologies Poland LTD (Warszawa, Poland) |
| Mapk4 (rat) Primers/probe set (FAM-MGB) | Rn01461524_m1 | Life Technologies Poland LTD (Warszawa, Poland) |
| Mapk7 (rat) Primers/probe set (FAM-MGB) | Rn01403106_m1 | Life Technologies Poland LTD (Warszawa, Poland) |
| Gadph (rat) Primers/probe set (FAM-MGB) | Rn01775763_g1 | Life Technologies Poland LTD (Warszawa, Poland) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wójcik, M.; Pozzo, L.; Vornoli, A.; Longo, V.; Śmiech, A.; Czerwik-Marcinkowska, J.; Rozempolska-Rucińska, I.; Chrapko, A.; Zmorzynski, S. The Impact of Proinflammatory M1 Macrophages on the Proliferation and Expression of Cyclin E2, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases 4 and 7 in Hepatocytes Isolated from a Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Rat Model. Molecules 2025, 30, 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173657
Wójcik M, Pozzo L, Vornoli A, Longo V, Śmiech A, Czerwik-Marcinkowska J, Rozempolska-Rucińska I, Chrapko A, Zmorzynski S. The Impact of Proinflammatory M1 Macrophages on the Proliferation and Expression of Cyclin E2, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases 4 and 7 in Hepatocytes Isolated from a Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Rat Model. Molecules. 2025; 30(17):3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173657
Chicago/Turabian StyleWójcik, Marta, Luisa Pozzo, Andrea Vornoli, Vincenzo Longo, Anna Śmiech, Joanna Czerwik-Marcinkowska, Iwona Rozempolska-Rucińska, Agnieszka Chrapko, and Szymon Zmorzynski. 2025. "The Impact of Proinflammatory M1 Macrophages on the Proliferation and Expression of Cyclin E2, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases 4 and 7 in Hepatocytes Isolated from a Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Rat Model" Molecules 30, no. 17: 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173657
APA StyleWójcik, M., Pozzo, L., Vornoli, A., Longo, V., Śmiech, A., Czerwik-Marcinkowska, J., Rozempolska-Rucińska, I., Chrapko, A., & Zmorzynski, S. (2025). The Impact of Proinflammatory M1 Macrophages on the Proliferation and Expression of Cyclin E2, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases 4 and 7 in Hepatocytes Isolated from a Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Rat Model. Molecules, 30(17), 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173657








