A Novel Aptamer Selection Strategy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Application as a Detecting Probe in a Hybrid Lateral Flow Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Methods
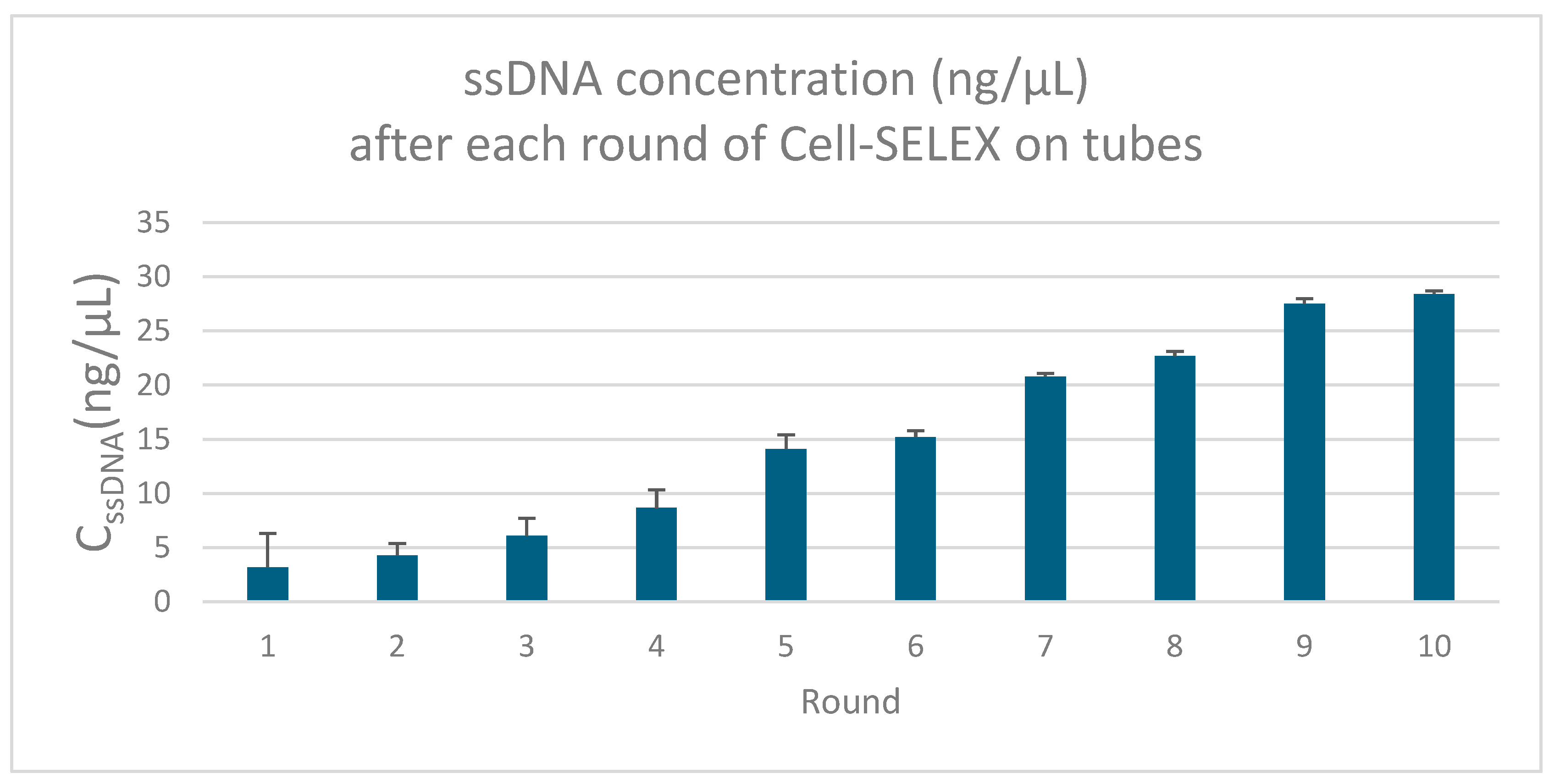
2.2.1. SELEX Procedure
Target Binding and Washing
Elution and Amplification
Asymmetric PCR and Iterative Selection
2.2.2. Cloning and Sequence Analysis
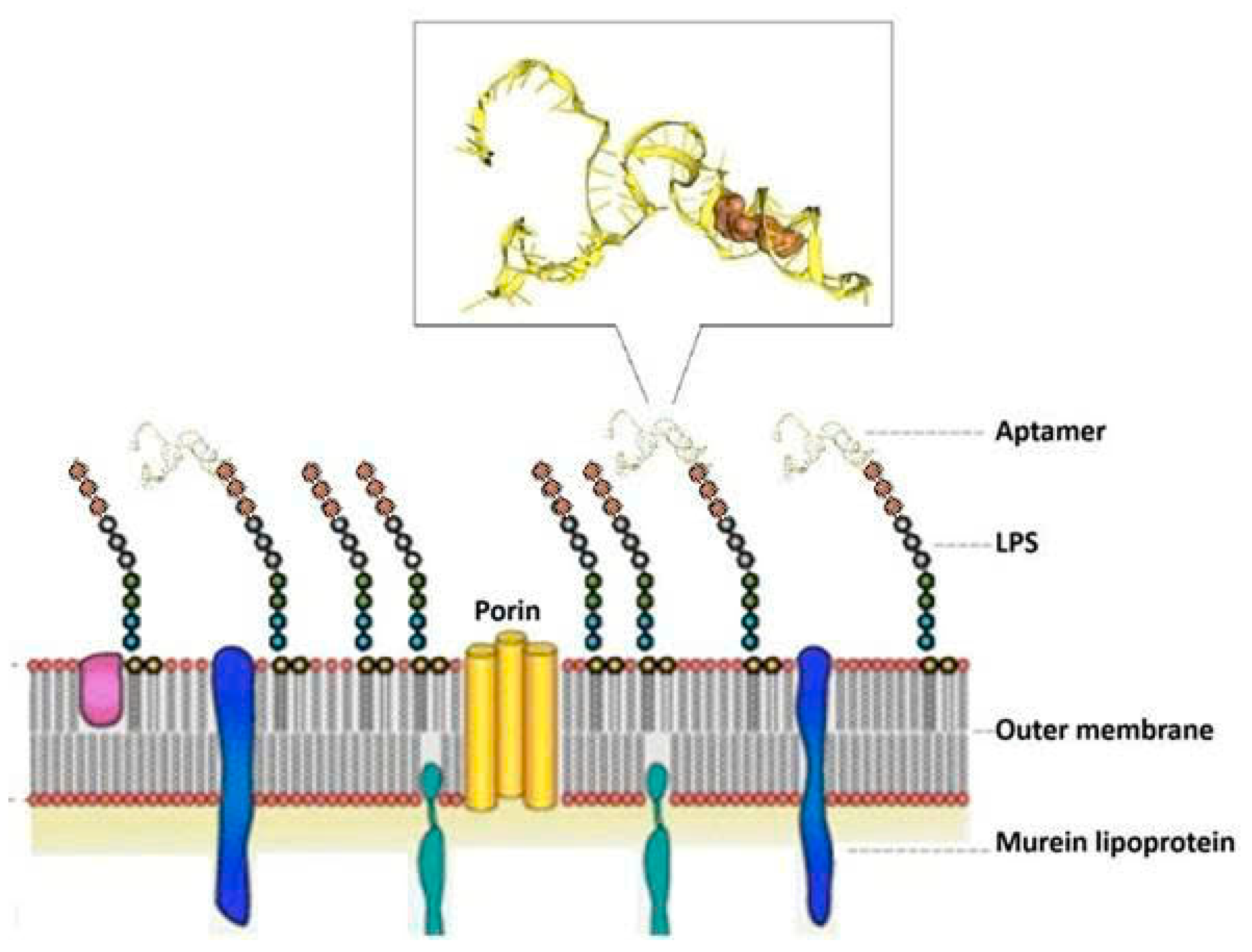
2.2.3. Docking and Structure Modeling
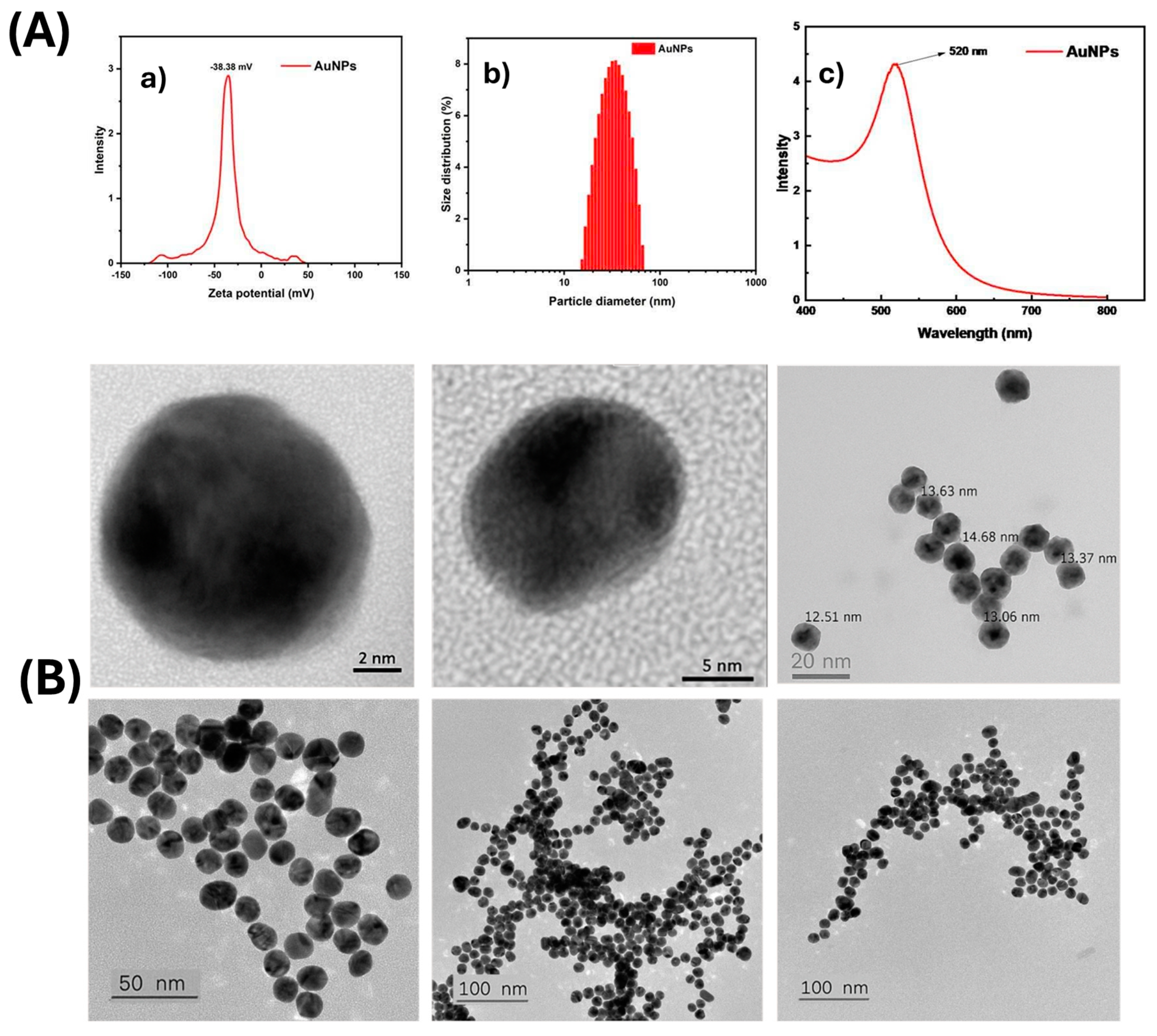
2.2.4. Synthesis and Characterization of AuNPs
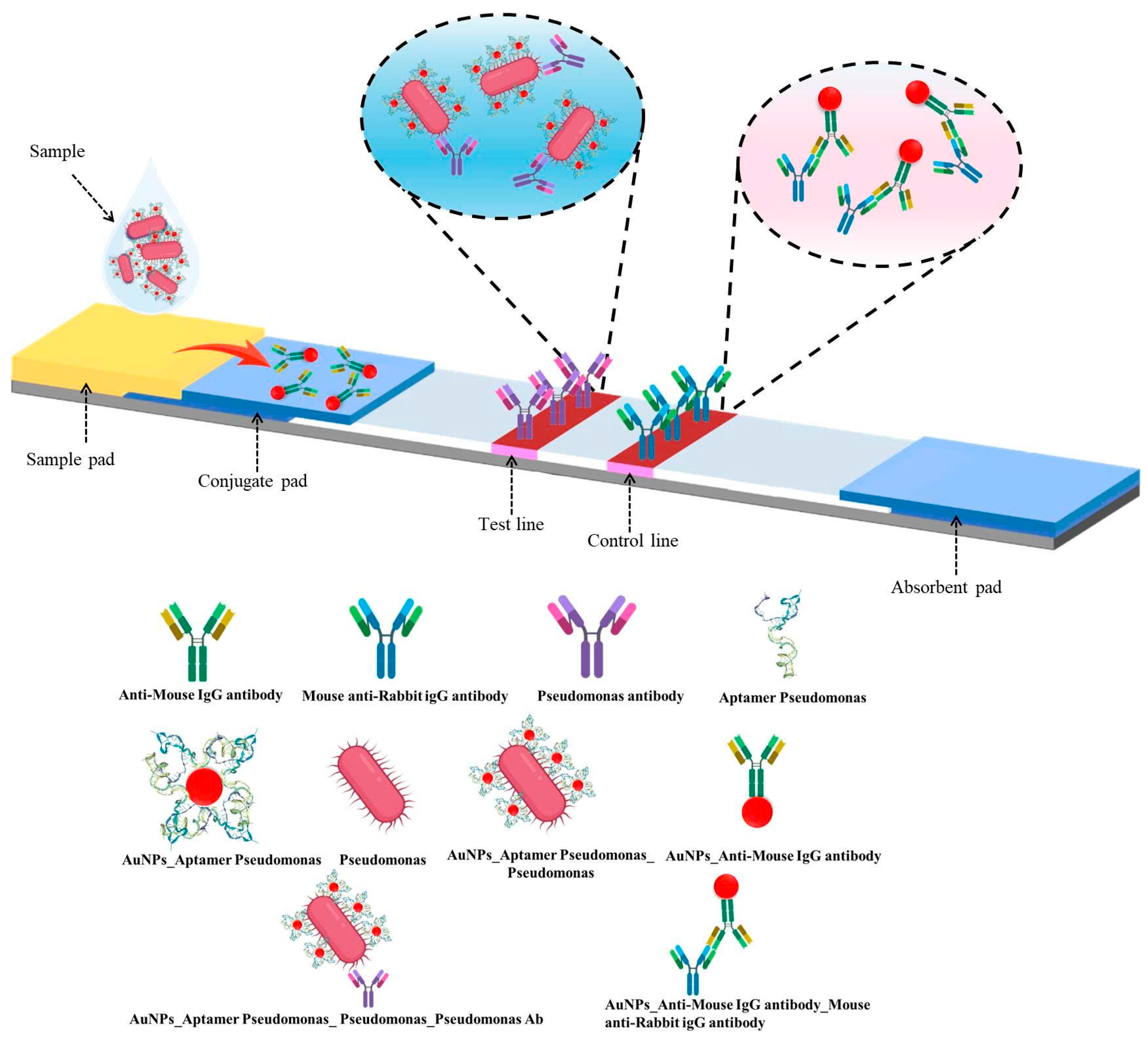
2.2.5. Fabrication of LFIA
Aptamer–AuNP Conjugation
IgG Antibody–AuNP Conjugation
Assembly and Processing of Test Strip Components
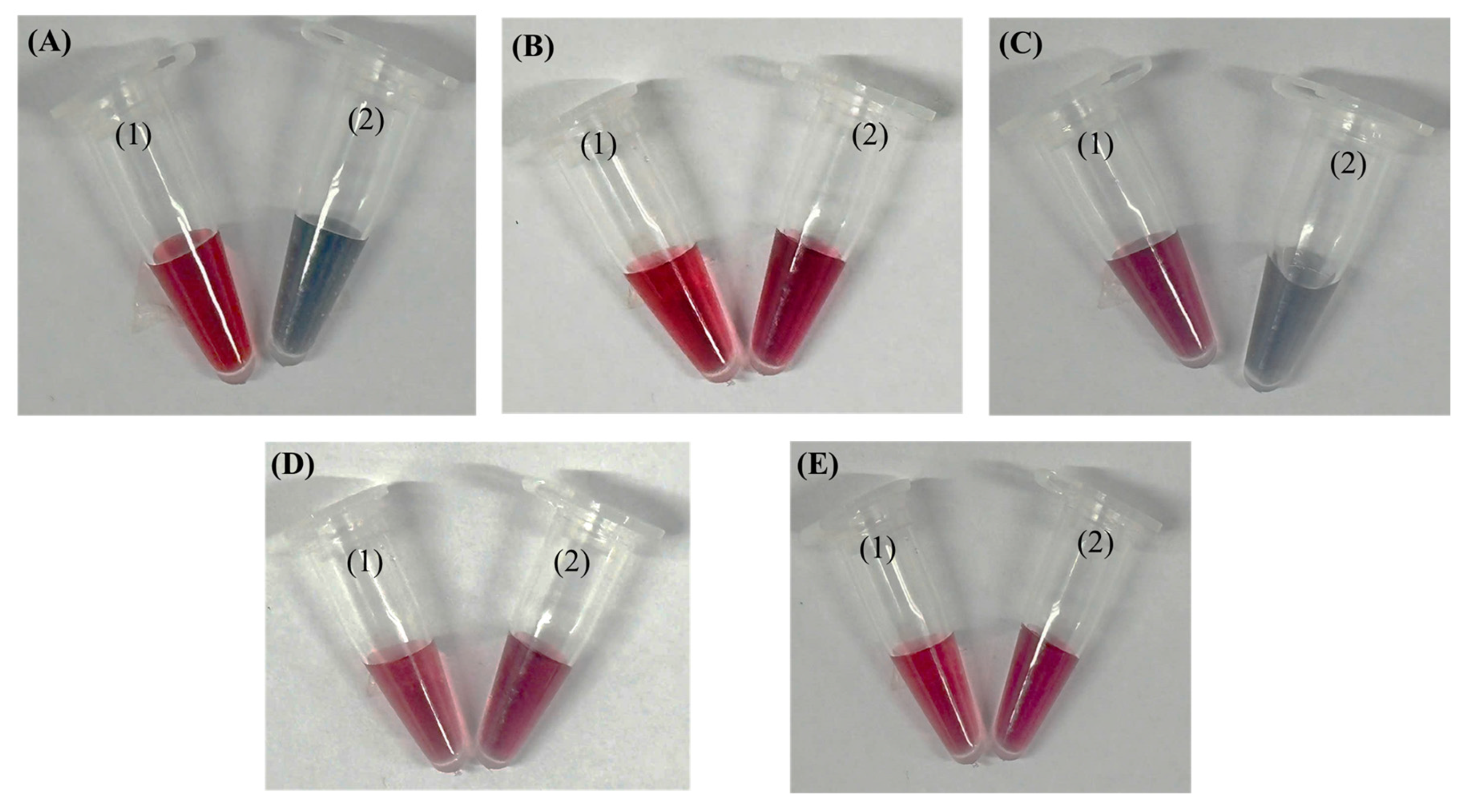
2.2.6. Evaluation of Colloidal Stability of AuNP–Aptamer Conjugates via Salt-Induced Aggregation
2.2.7. Sample Detection Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
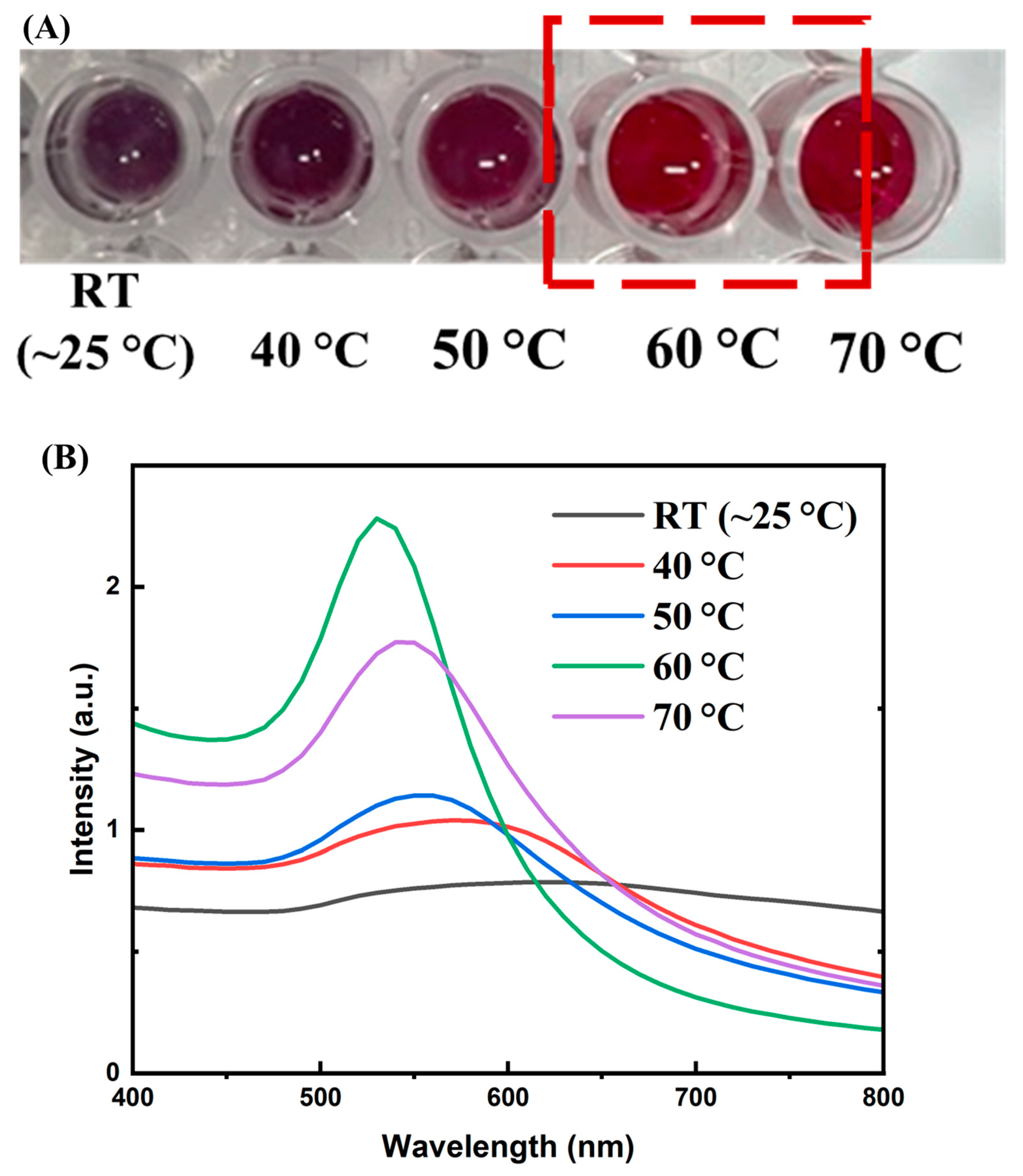
3.1. Aptamer Enrichment and Characterization
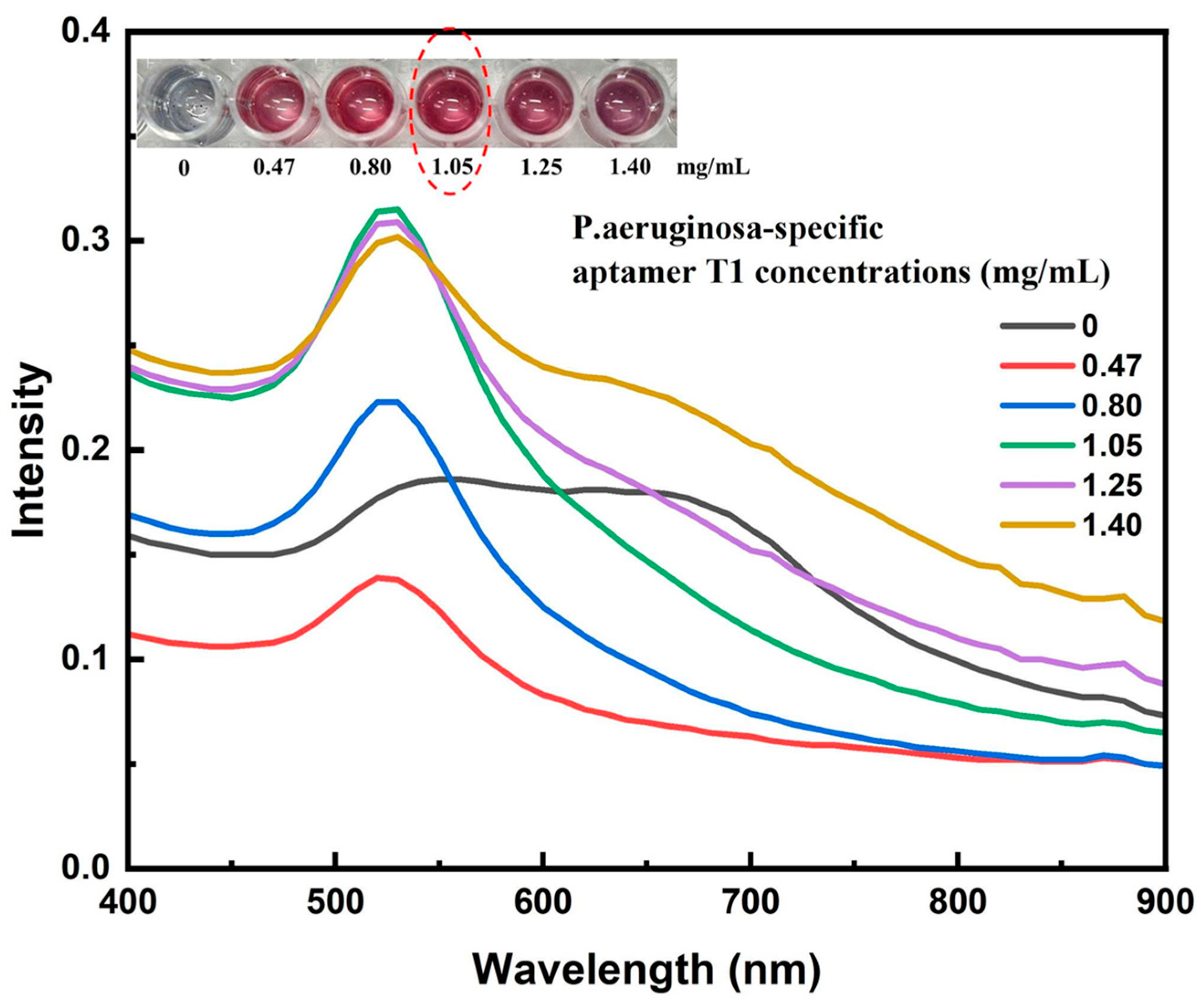
3.2. Aptamer T1–AuNP Conjugation and Optimization
3.3. Evaluation of the Hybrid LFIA Strip for P. aeruginosa Detection
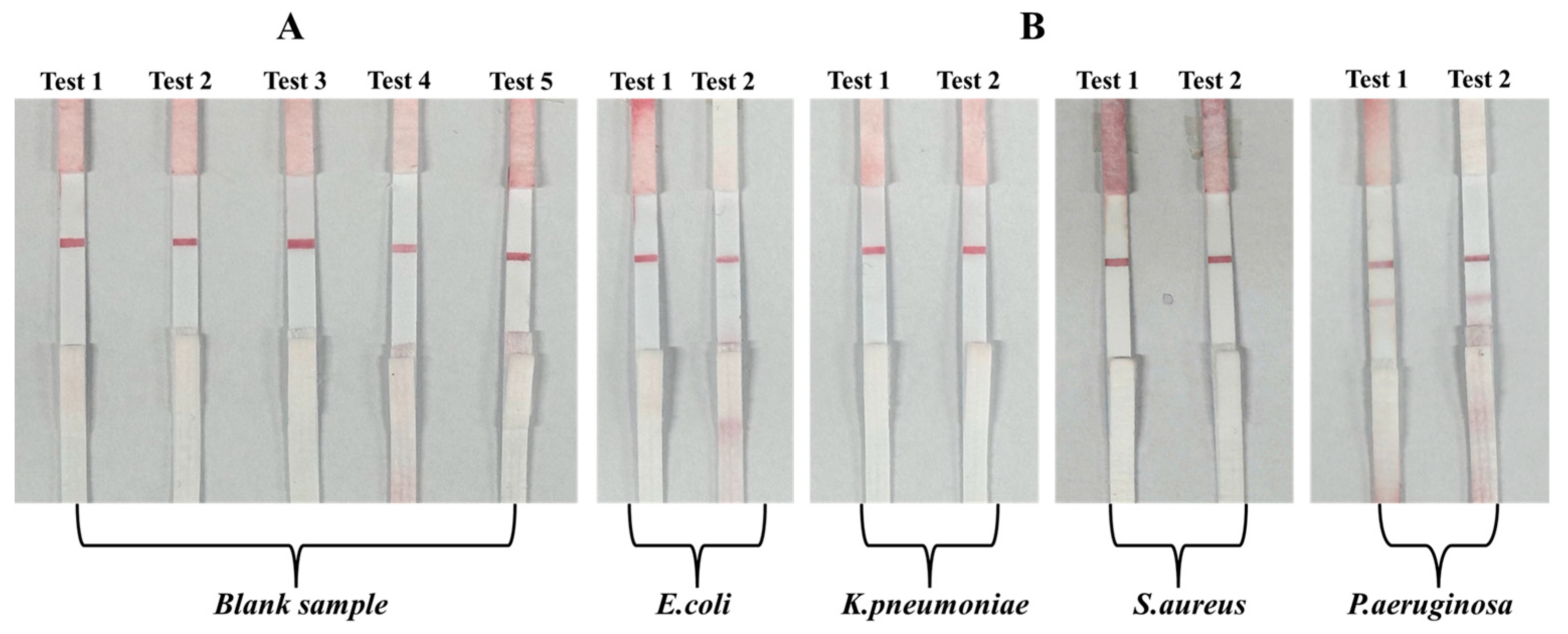
3.3.1. Specificity Assessment Using Blank and Non-Target Bacteria
3.3.2. Sensitivity Evaluation with Spiked P. aeruginosa Samples
3.3.3. Demonstrating Clinical Readiness Using Simulated Positive Samples in Authentic Matrices
3.4. Advantages, Limitations, and Perspectives of Aptamer-Based LFIA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aldona, B.; Raymond, S. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa: Infections and Treatment; Informa Health Care: London, UK, 1994; pp. 83–84. ISBN 0-8247-9210-6. [Google Scholar]
- Alariqi, R.; Almansoob, S.; Senan, A.M.; Raj, A.K.; Shah, R.; Shrewastwa, M.K.; Kumal, J.P.P. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and related antibiotic resistance genes as indicators for wastewater treatment. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.M.; Lee, S.; Ban, C. Aptamers and their biological applications. Sensors 2012, 8, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Yang, C.Y.; Sun, R.L.; Cheng, Y.F.; Kao, W.C.; Yang, P.C. Rapid single cell detection of Staphylococcus aureus by aptamer-conjugated gold nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bruno, J.G. A review of therapeutic aptamer conjugates with emphasis on new approaches. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larry, G. SELEX: How It Happened and Where It will Go. J. Mol. Evol. 2015, 81, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.Y.; Nguyen, D.; Hong, S.W.; Kim, B.C. Broadly reactive aptamers targeting bacteria belonging to different genera using a sequential toggle cell-SELEX. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerpedjiev, P.; Hammer, S.; Hofacker, I.L. Forna (force-directed RNA): Simple and effective online RNA secondary structure diagrams. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3377–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeddi, I.; Saiz, L. Three-dimensional modeling of single stranded DNA hairpins for aptamer-based biosensors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Tao, H.; He, J.; Huang, S.-Y. The HDOCK server for integrated protein–protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1829–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.S.; Liu, H.; Chen, B.B.; Zhang, H.Z.; Huang, C.Z.; Wang, J. Stable gold nanoparticles as a novel peroxidase mimic for colorimetric detection of cysteine. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2494–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.T.; Le, T.-K.; Huyen, N.T.T.; Van, N.L.; Nguy, T.P.; Tran, D.L.; N, L.T.T. Staining-Enhanced Peroxidase-Mimicking Gold Nanoparticles in NanoELISA for Highly Sensitive Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 49211–49217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrashoudi, A.A.; Albalawi, H.I.; Aldoukhi, A.H.; Moretti, M.; Bilalis, P.; Abedalthagafi, M.; Hauser, C.A.E. Fabrication of a Lateral Flow Assay for Rapid In-Field Detection of COVID-19 Antibodies Using Additive Manufacturing Printing Technologies. Int. J. Bioprinting 2021, 7, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Siederdissen, C.H.Z.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. ViennaRNA package 2.0. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2021, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, J.; Salena, B.J.; Li, Y. Aptamer and DNAzyme Based Colorimetric Biosensors for Pathogen Detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 64, e202418725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Lai, Y.; Bougouffa, S.; Xu, Z.; Yan, A. Comparative genome and transcriptome analysis reveals distinctive surface characteristics and unique physiological potentials of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ding, X.; Xu, C.; Zheng, B.; Yu, H.; Zheng, P. Molecular Mechanism of Interaction between DNA Aptamer and Receptor-Binding Domain of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Variants Revealed by Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Molecules 2024, 29, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Lv, C.; Li, Z.H.; Jiang, S.; Cai, D.; Liu, S.S.; Wang, T.; Zhang, K.H. Analysis of aptamer-target binding and molecular mechanisms by thermofluorimetric analysis and molecular dynamics simulation. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1144347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisold, A.; Labudde, D. Detailed Analysis of 17β-Estradiol-Aptamer Interactions: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Molecules 2018, 23, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.F.R.; Hsing, I.-M. Prediction of Aptamer-Small-Molecule Interactions Using Metastable States from Multiple Independent Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 4799–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Y. Preparation of aptamer-linked gold nanoparticle purple aggregates for colorimetric sensing of analytes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehara, R.; Tonouchi, A.; Konno, K.; Hashimoto, M. Cyclohumulanoid Sesquiterpenes from the Culture Broth of the Basidiomycetous Fungus Daedaleopsis tricolor. Molecules 2021, 26, 4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Bar-Sagi, D. Modulation of signalling by Sprouty: A developing story. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- António, M.; Ferreira, R.; Vitorino, R.; Daniel-da-Silva, A.L. A simple aptamer-based colorimetric assay for rapid detection of C-reactive protein using gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2020, 214, 120868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, T.A.; Narovec, C.M.; Whelan, R.J. Effects of Cationic Proteins on Gold Nanoparticle/Aptamer Assays. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8222–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi-Coll, S.; Marín, M.J.; Sule, O.; Hutchinson, P.J.; Carpenter, K.L.H. Aptamer-modified gold nanoparticles for rapid aggregation-based detection of inflammation: An optical assay for interleukin-6. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, A.; Meganathan, Y. Aptamer-based assay for rapid detection, surveillance, and screening of pathogenic Leptospira in water samples. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolm, C.; Cervenka, I.; Aschl, U.J.; Baumann, N.; Jakwerth, S.; Krska, R.; Mach, R.L.; Sommer, R.; DeRosa, M.C.; Kirschner, A.K.T.; et al. DNA aptamers against bacterial cells can be efficiently selected by a SELEX process using state-of-the art qPCR and ultra-deep sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Fan, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhao, P.; Wu, H.; et al. A Rapid and Sensitive Detection Method for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Using Visualized Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Lateral Flow Strip Technology. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 698929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, F.; Niu, L.; Nong, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, N.; Zhu, X.; Wu, L.; Hu, S. Rapid and sensitive detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa using multiple cross displacement amplification and gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor visualization. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Z.; Yang, X.; Dong, H.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, S.; Cheng, X.; Wang, C.; Rong, Z.; Wang, S. Ultrasensitive Fluorescence Lateral Flow Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium via Wheat Germ Agglutinin-Functionalized Magnetic Quantum Dot Nanoprobe. Biosensors 2022, 12, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dong, K.; Kang, Z.; Ji, X.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, P.; Sun, B. A Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification with a Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor Assay to Detect Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Endophthalmitis. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Aptamer Name | Aptamer DNA Sequence | Docking Score | MFE (kcal/mol) | Frequency (%) | Diversity Score | Predicted Secondary Structure (2D) Based on MFE Model | Predicted Tertiary Structure (3D) Based on MFE Model | Molecular Docking with CPA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | ATCCGTCACACCTGCTCTGTAAACACCTACGGTCTTAGCATACGGTATAAGCCGTAACCGGTTTTACCTAAACTGGTGTTGGCTCCCGTAT | −453.85 | −27.10 | 24.98 | 4.64 | 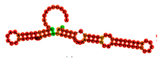 |  | 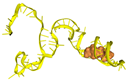 |
| T2 | ATCCGTCACACCTGCTCTCAAAGGTCATAGGGGCTTCTTGGCAGCGTAATGCCTTGCTCGCATTTTTCCCTCATGGTGTTGGCTCCCGTAT | −366.23 | −22.11 | 3.82 | 28.74 |  | 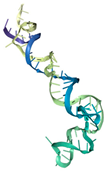 |  |
| T3 | ATCCGTCACACCTGCTCTCATCATGCCCGCGTTCTAATAACTGCTATATCCTTTATCGCCTCTATCCCTCCGTTGGTGTTGGCTCCCGTAT | −409.72 | −12.20 | 8.83 | 13.74 |  | 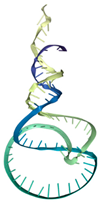 | 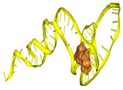 |
| T4 | ATCCGTCACACCTGCTCTGAGACTAGCAGTTTTTAACCAGAGTAAATAACTCCCCTCTTCCTAAAATTTCCCCTGGTGTTGGCTCCCGTAT | −427.08 | −15.86 | 21.23 | 8.54 |  | 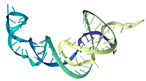 | 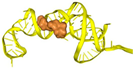 |
| T5 | ATCCGTCACACCTGCTCTCGGTGGTCAGCATCTCACTTGCCTTCTGTCCTGACCTATCCATCCCTCGTCGTCATGGTGTTGGCTCCCGTAT | −373.65 | −18.11 | 1.15 | 19.52 |  |  |  |
| T6 | ATCCGTCACACCTGCTCTCAGTATACACCCGTTCTCCGTCTGGTCTACAGTCCCCCGGCTGAGCCCCTATTCGTGGTGTTGGCTCCCGTAT | −378.06 | −18.83 | 5.12 | 22.07 |  | 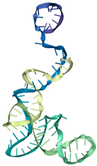 |  |
| Blank Sample | Test Line Intensity (Mean Gray Value, Inverted 8-Bit Image) (a.u.) | Mean Value | STDEV |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 81.029 | 80.771 | 1.109 |
| 2 | 79.317 | ||
| 3 | 79.656 | ||
| 4 | 79.456 | ||
| 5 | 81.370 | ||
| 6 | 81.357 | ||
| 7 | 82.507 | ||
| 8 | 81.368 | ||
| 9 | 81.024 | ||
| 10 | 81.924 |
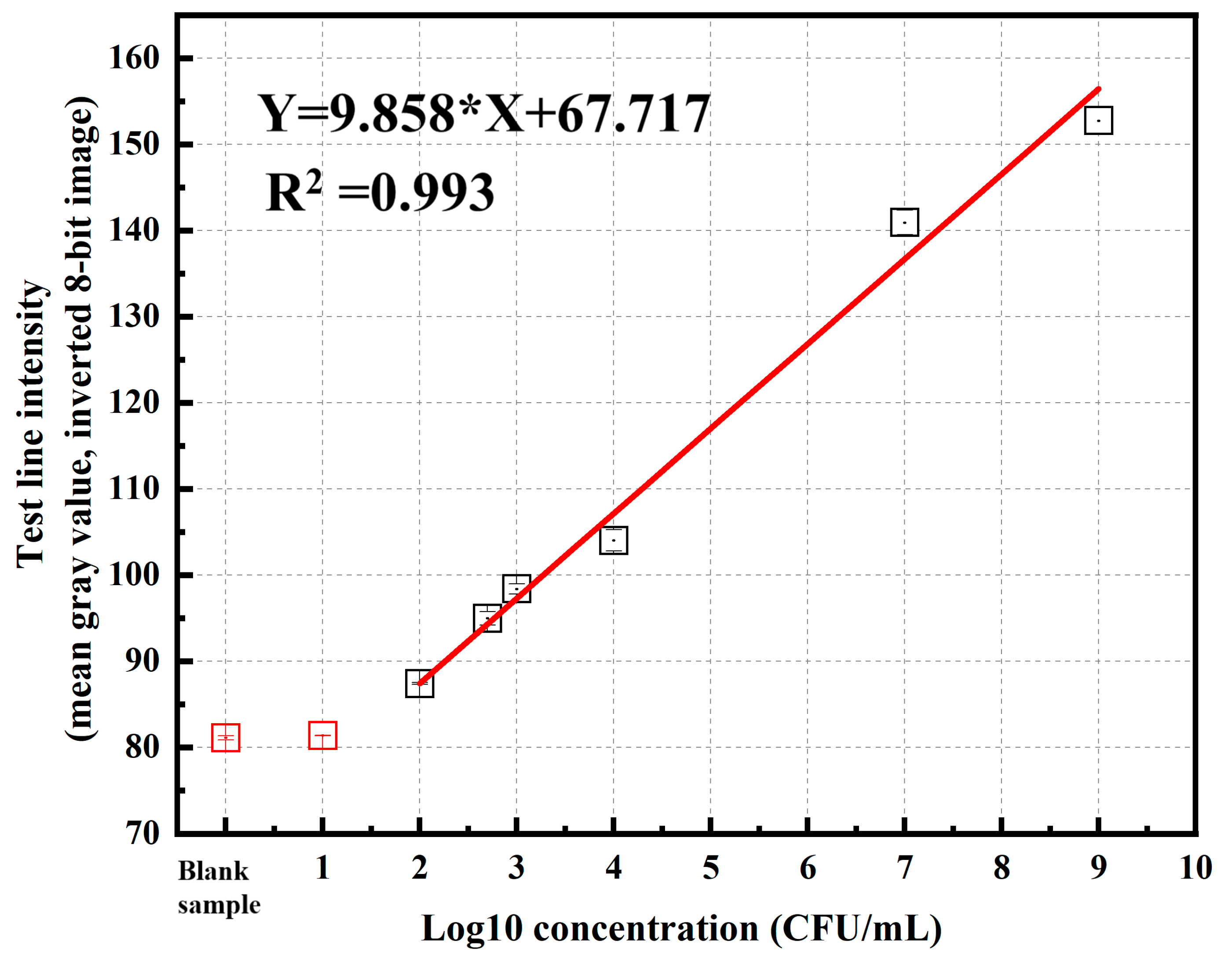
| P. aeruginosa Concentration (CFU/mL) | Log10 Value | Test-Line Intensity (Mean Gray Value, Inverted 8-Bit Image) (a.u.) | Mean Value | STDEV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 109 | 9.00 | Test 1 | 154.499 | 152.766 | 1.609 |
| Test 2 | 151.320 | ||||
| Test 3 | 152.479 | ||||
| 107 | 7.00 | Test 1 | 139.736 | 140.934 | 1.428 |
| Test 2 | 140.552 | ||||
| Test 3 | 142.515 | ||||
| 104 | 4.00 | Test 1 | 103.569 | 104.022 | 1.239 |
| Test 2 | 105.424 | ||||
| Test 3 | 103.074 | ||||
| 103 | 3.00 | Test 1 | 98.232 | 98.383 | 0.604 |
| Test 2 | 99.048 | ||||
| Test 3 | 97.887 | ||||
| 5 × 102 | 2.70 | Test 1 | 95.887 | 94.974 | 0.792 |
| Test 2 | 94.569 | ||||
| Test 3 | 94.468 | ||||
| 102 | 2.00 | Test 1 | 87.526 | 87.405 | 0.106 |
| Test 2 | 87.331 | ||||
| Test 3 | 87.357 | ||||
| 101 | 1.00 | Test 1 | 81.368 | 81.370 | 0.014 |
| Test 2 | 81.357 | ||||
| Test 3 | 81.370 | ||||
| Blank sample | 0.00 | Test 1 | 81.357 | 81.102 | 0.227 |
| Test 2 | 81.024 | ||||
| Test 3 | 81.940 |
| No. | Code | Type of Sample | Province /City | IBV-Positive Sample Confirmed by Real-Time PCR | Ct Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 230713.2 | Feces swab | Bắc Ninh | positive | 25.75 |
| 2 | 230716.1 | Mouth swab | Bắc Ninh | positive | 27.66 |
| 3 | 240227.1 | Oral swab | Lai Châu | positive | 30.00 |
| 4 | 240227.2 | Rectal swab | Lai Châu | positive | 24.50 |
| 5 | 240228.1 | Oral swab | Gia Lai | positive | 35.20 |
| Method | Signal Type | LOD | Assay Time | Sample Type | Advantages | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPA-LFS LasB gene | AuNP Colorimetric | 103 CFU/mL | 1 h | DNA from bacteria (culture/clinical) | High sensitivity and specificity, no PCR instrument required | [31] |
| MCDA-LFB (MCDA+AuNP-LFA) | AuNP Colorimetric | 10 fg DNA | 40 min | DNA from bacteria | Rapid, visual, no instrument required | [32] |
| Mag@QDs-WGA LFA | Fluorescent LFA | 101–102 CFU/mL | 35 min | Food/environmental samples | Very high sensitivity, multiplexing capability, broad-spectrum | [33] |
| LAMP-LFB (ophthalmic P. aeruginosa) | AuNP Colorimetric | 102 CFU/mL | 1 h | Biological DNA samples | Simple, suitable for clinical use | [34] |
| Hybrid AuNP–aptamer + antibody LFIA | AuNP Colorimetric | 102 CFU/mL | 15 min | Whole bacterial cells | Sensitive, rapid, simple operation at point-of-care | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pham, T.T.; T. T. Huyen, N.; Hong Oanh, L.; Dai Tran, L.; Tran, H.V.; Truong, T.N.L.; Thi Phuong Trang, N. A Novel Aptamer Selection Strategy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Application as a Detecting Probe in a Hybrid Lateral Flow Assay. Molecules 2025, 30, 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173499
Pham TT, T. T. Huyen N, Hong Oanh L, Dai Tran L, Tran HV, Truong TNL, Thi Phuong Trang N. A Novel Aptamer Selection Strategy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Application as a Detecting Probe in a Hybrid Lateral Flow Assay. Molecules. 2025; 30(17):3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173499
Chicago/Turabian StylePham, Thu Thao, Nguyen T. T. Huyen, Le Hong Oanh, Lam Dai Tran, Hiep V. Tran, T. N. Lien Truong, and Nguyen Thi Phuong Trang. 2025. "A Novel Aptamer Selection Strategy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Application as a Detecting Probe in a Hybrid Lateral Flow Assay" Molecules 30, no. 17: 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173499
APA StylePham, T. T., T. T. Huyen, N., Hong Oanh, L., Dai Tran, L., Tran, H. V., Truong, T. N. L., & Thi Phuong Trang, N. (2025). A Novel Aptamer Selection Strategy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Application as a Detecting Probe in a Hybrid Lateral Flow Assay. Molecules, 30(17), 3499. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173499






