Ionizing Radiation-Induced Structural Modification of Isoegomaketone and Its Anti-Inflammatory Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
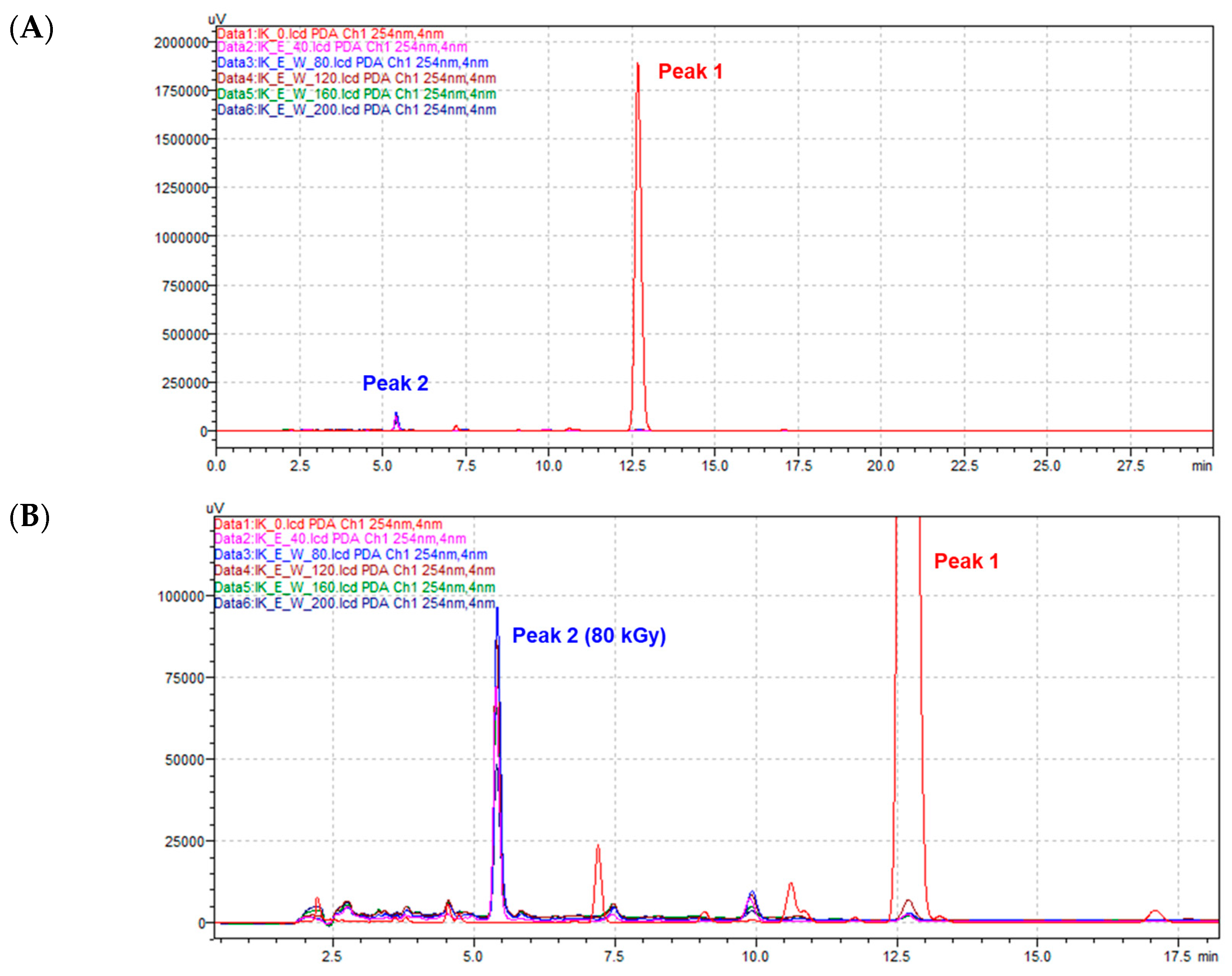
2.1. Structural Identification of Radiolysis Product Derived from Isoegomaketone (1)
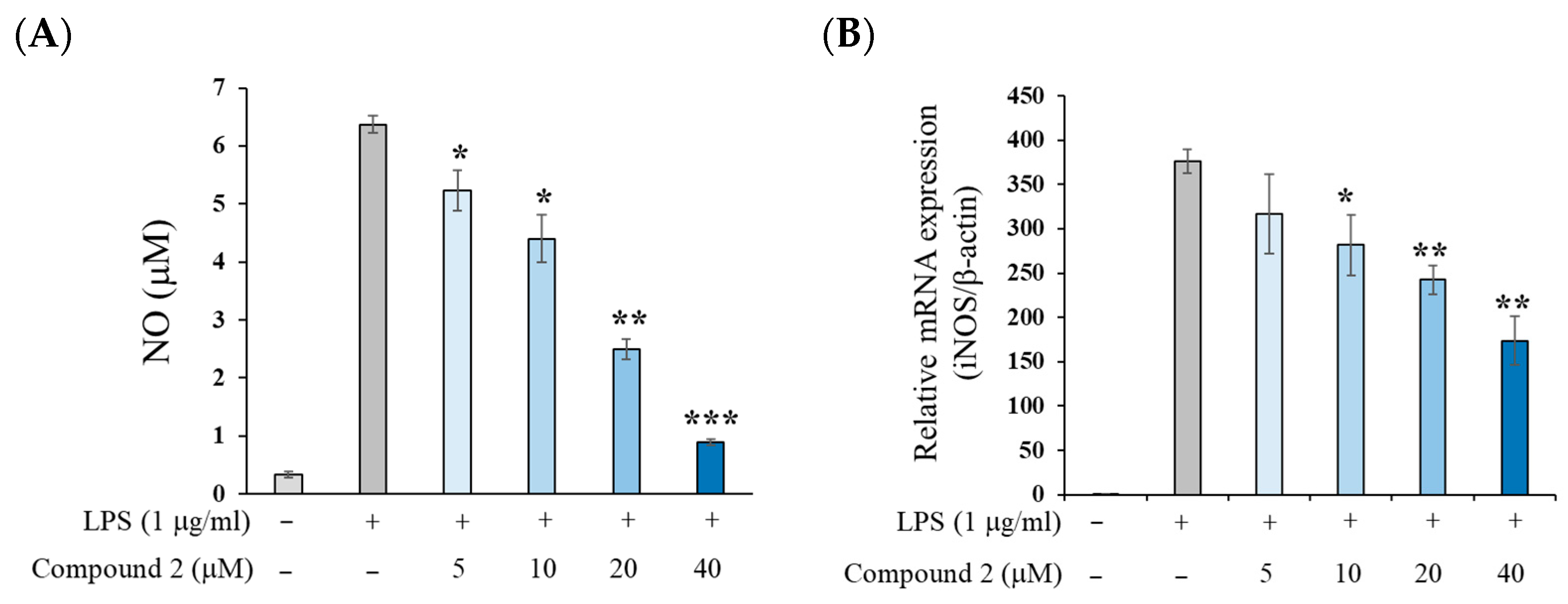
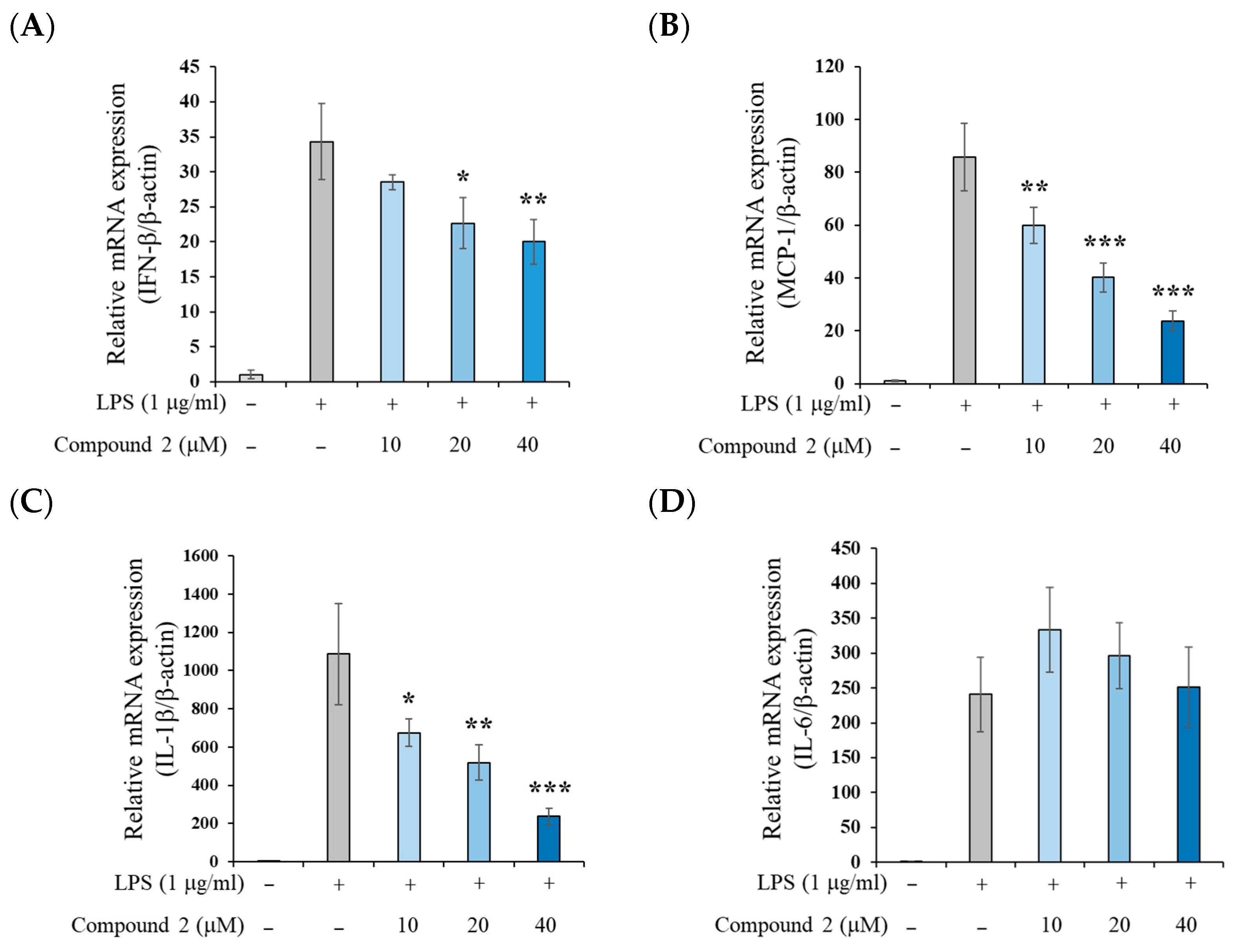
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of (±)-8-Methoxy-Perilla Ketone (2)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. HPLC PDA Analysis
3.4. Isolation of Isoegomaketone Derivative
3.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.6. Measurement of LPS-Induced NO Production on RAW 264.7 Cells
3.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
3.8. Measurement of TNF-α, IL-6, and MCP-1 by ELISA
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, C.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Meng, L. Advances in the Pharmacological Activities and Effects of Perilla Ketone and Isoegomaketone. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, 2022, 8809792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, K.D.; Jeong, I.Y.; Ahn, D.U.; Lee, M.K.; Seo, K.I. Induction of Apoptosis by Isoegomaketone from Perilla frutescens L. in B16 Melanoma Cells Is Mediated through ROS Generation and Mitochondrial-Dependent, -Independent Pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, K.D.; Jeong, I.Y.; Yee, S.T.; Lee, M.K.; Seo, K.I. Isoegomaketone Induces Apoptosis in SK-MEL-2 Human Melanoma Cells through Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway via Activating the PI3K/Akt Pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Cho, H.D.; Jeong, I.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Seo, K.I. Sensitization of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL)-Resistant Primary Prostate Cancer Cells by Isoegomaketone from Perilla frutescens. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2438–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Han, J.; Zheng, W.; Ma, W. Extract of Perilla frutescens Inhibits Tumor Proliferation of HCC via PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 10, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R.; Nam, B.; Han, A.R.; Kim, J.B.; Jin, C.H. Isoegomaketone from Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt Stimulates MAPK/ERK Pathway in Human Keratinocyte to Promote Skin Wound Healing. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 6642606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Lee, J.W.; Yu, A.R.; Yoon, H.S.; Kang, M.; Lee, B.S.; Park, H.W.; Lee, S.K.; Whang, J.; Kim, J.S. Isoegomaketone Exhibits Potential as a New Mycobacterium abscessus Inhibitor. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1344914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Lin, H.; Rao, H.; Rao, Y.; Tang, X.; Zuo, H.; Wang, Y. Isoegomaketone Alleviates Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress in Sepsis Lung Injury. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2024, 52, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, Y.D.; Choi, D.S.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, S.Y.; Seo, K.I.; Jeong, I.Y. Isoegomaketone inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the heme oxygenase-1 induction and inhibition of the interferon-beta-STAT-1 pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.H.; So, Y.K.; Han, S.N.; Kim, J.B. Isoegomaketone Upregulates Heme Oxygenase-1 in RAW264.7 Cells via ROS/p38 MAPK/Nrf2 Pathway. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2016, 24, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.H.; So, Y.; Nam, B.; Han, S.N.; Kim, J.B. Isoegomaketone Alleviates the Development of Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis in Male Balb/c Mice. Molecules 2017, 22, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abernathy, V.; Roselli, R.; Parker, R.; Pou, N. Effects of Perilla Ketone on the In Situ Sheep Lung. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 72, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, L.A.; Johnson, B.J.; Ge, B. Intoxication of Cattle by Perilla frutescens (Purple Mint). Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1986, 28, 412–416. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.-X.; Guan, J.; Tian, Y.-H.; Su, G.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q. Acute and Sub-Chronic 90-Day Oral Toxicity Study of Perilla Seed Oil in Rodents and Beagle Dogs. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 103, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, S.; Luo, D. Ultrasound Pre-Treatment Combined with Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation of Essential Oils from Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Leaves and Its Chemical Composition and Biological Activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 143, 111908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattò, C.; de Vincenti, L.; Borgonovo, G.; Bassoli, A.; Marai, S.; Villa, F.; Cappitelli, F.; Saracchi, M. Sub-Lethal Concentrations of Perilla frutescens Essential Oils Affect Phytopathogenic Fungal Biofilms. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roellecke, K.; Virts, E.; Einholz, R.; Edson, K.Z.; Altvater, B.; Rossig, C.; von Laer, D.; Scheckenbach, K.; Wagenmann, M.; Reinhardt, D. Optimized Human CYP4B1 in Combination with the Alkylator Prodrug 4-Ipomeanol Serves as a Novel Suicide Gene System for Adoptive T-Cell Therapies. Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.Y.; Kim, K.I.; Han, J.M.; Park, W.Y.; Seom, H.S.; Lim, S.; Byun, E.-B. Ionizing Radiation Technology to Improve the Physicochemical and Biological Properties of Natural Compounds by Molecular Modification: A Review. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 194, 110013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Uchihori, Y.; Yasuda, N.; Takada, M.; Kitamura, H. Estimation of Yields of OH Radicals in Water Irradiated by Ionizing Radiation. J. Radiat. Res. 2005, 46, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getoff, N.; Ritter, A.; Schwörer, F.; Bayer, P. Primary Yields of CH3•O and •CH2OH Radicals Resulting in the Radiolysis of High Purity Methanol. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1993, 41, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.H.; Lee, H.; Chung, B.Y.; Bai, H.W. A New Class of Hybrid Anti-inflammatory Agents of Silibinin A Modified Using Gamma Irradiation. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2025, 73, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, M.; Jang, S.; Kim, S.; Bai, H.; Jeong, G.; Kim, B.C.; Jeong, H.S. Rotenone and Its Derivative, Rotenoisin A, Induce Neurodegeneration Differentially in SH-SY5Y Cells. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ina, K.; Suzuki, Y. Components of perilla essential oil. II. Furan derivatives in neutral essential oil. Nippon. Nogei Kagaku Kaishi 1971, 45, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garst, J.E.; Wilson, B.J. Synthesis and Analysis of Various 3-Furyl Ketones from Perilla frutescens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1984, 32, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, B.; So, Y.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, J.-B.; Jin, C.H.; Han, A.-R. A New Monoterpene from the Leaves of a Radiation Mutant Cultivar of Perilla frutescens var. crispa with Inhibitory Activity on LPS-Induced NO Production. Molecules 2017, 22, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.J.; Jun, D.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.S.; Woo, M.H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S.C.; Yang, C.H.; Kim, Y.H. Anti-Inflammatory Action of 2-Carbomethoxy-2,3-Epoxy-3-Prenyl-1,4-Naphthoquinone (CMEP-NQ) Suppresses Both the MyD88-Dependent and TRIF-Dependent Pathways of TLR4 Signaling in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 205, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Shen, W.-W.; Zhong, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. Lipopolysaccharide/Adenosine Triphosphate Induces IL-1β and IL-18 Secretion through the NLRP3 Inflammasome in RAW264.7 Murine Macrophage Cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkbacka, H.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Huet, F.; Li, X.; Gregory, J.A.; Lee, M.A.; Ordija, C.M.; Dowley, N.E.; Golenbock, D.T.; Freeman, M.W. The induction of macrophage gene expression by LPS predominantly utilizes Myd88-independent signaling cascades. Physiol. Genomics 2004, 19, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, M.O.; Sweet, M.J.; Mansell, A.; Kelli, S.; Kobe, B. TRIF-dependent TLR signaling, its functions in host defense and inflammation, and its potential as a therapeutic target. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, B.; Paudel, S.B.; Kim, J.-B.; Jin, C.H.; Lee, D.; Nam, J.-W.; Han, A.-R. Preparative Separation of Three Monoterpenes from Perilla frutescens var. crispa Using Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 2019, 8751345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Position | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δH, mult 1 | δH, mult 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 8.18, dd (1.2, 0.8) | 8.00, s | 8.14, s |
| 4 | 6.83, dd (1.8, 1.2) | 6.65, s | 6.78, s |
| 5 | 7.51, dd (1.8, 0.8) | 7.40, s | 7.49, s |
| 7a | 3.48, dd (18.6, 7.1) | 2.72, d | 2.5–3.1, m |
| 7b | 3.03, dd (18.6, 3.4) | 2.72, d | 2.5–3.1, m |
| 8 | 3.84, dt (7.1, 3.4) | 3.50, m | 3.66, m |
| 9 | 2.72, qqd (7.1, 3.4) | 1.45, m | - |
| 10 (Me) | 1.1, d (7.1) | 0.95, s | 0.94, s |
| 11 (Me) | 1.06, d (7.1) | 0.85, s | 0.94, s |
| 12 (OMe) | 2.87, s | 3.19, s | 3.24, s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, E.; Jin, C.H.; Huy Ngo, T.; Park, J.; Nam, J.-W.; Han, A.-R. Ionizing Radiation-Induced Structural Modification of Isoegomaketone and Its Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Molecules 2025, 30, 3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173466
Choi E, Jin CH, Huy Ngo T, Park J, Nam J-W, Han A-R. Ionizing Radiation-Induced Structural Modification of Isoegomaketone and Its Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Molecules. 2025; 30(17):3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173466
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Euna, Chang Hyun Jin, Trung Huy Ngo, Jisu Park, Joo-Won Nam, and Ah-Reum Han. 2025. "Ionizing Radiation-Induced Structural Modification of Isoegomaketone and Its Anti-Inflammatory Activity" Molecules 30, no. 17: 3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173466
APA StyleChoi, E., Jin, C. H., Huy Ngo, T., Park, J., Nam, J.-W., & Han, A.-R. (2025). Ionizing Radiation-Induced Structural Modification of Isoegomaketone and Its Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Molecules, 30(17), 3466. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30173466








