Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Material via In Situ Solid–Liquid Host–Guest Composite Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
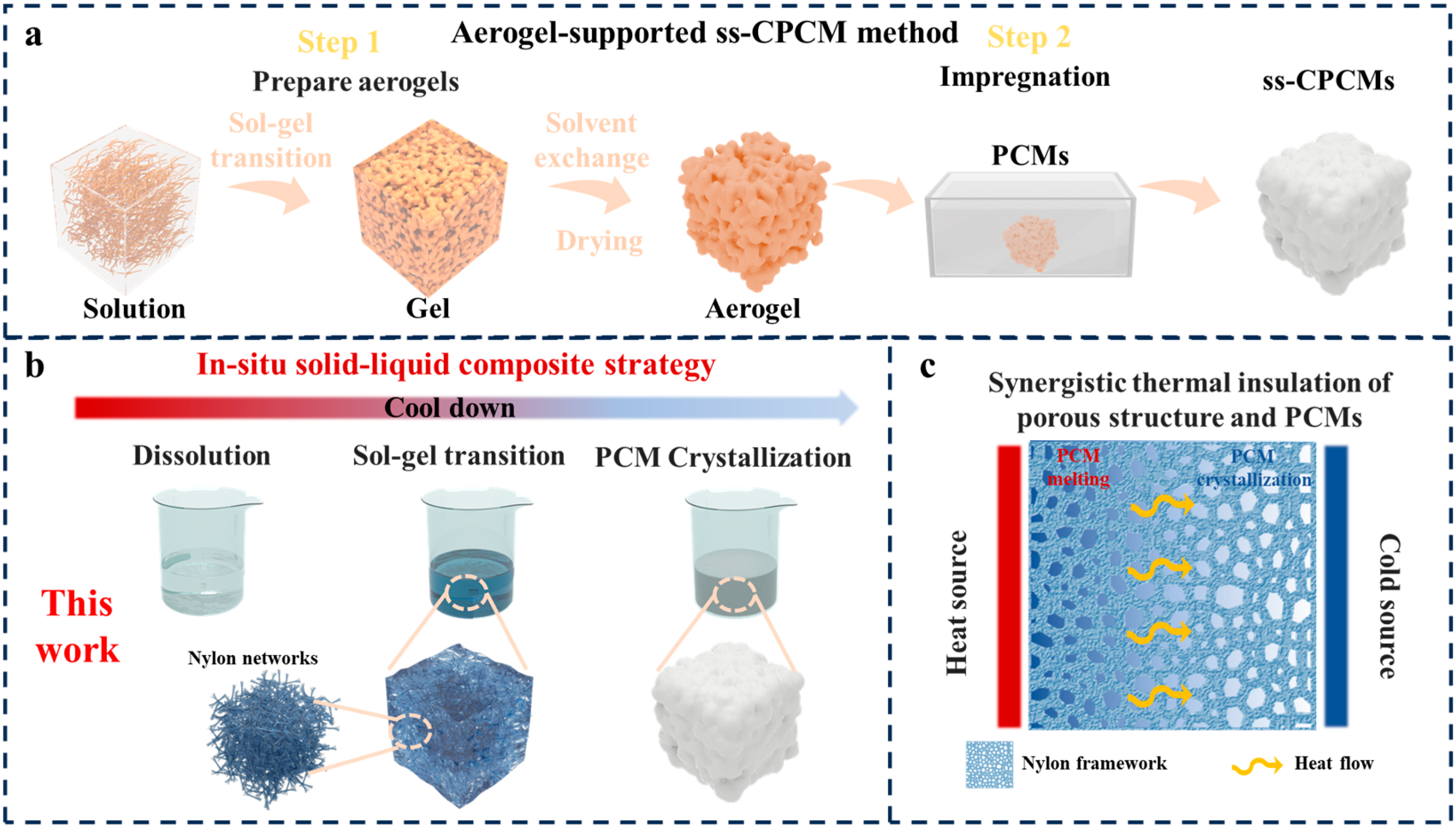
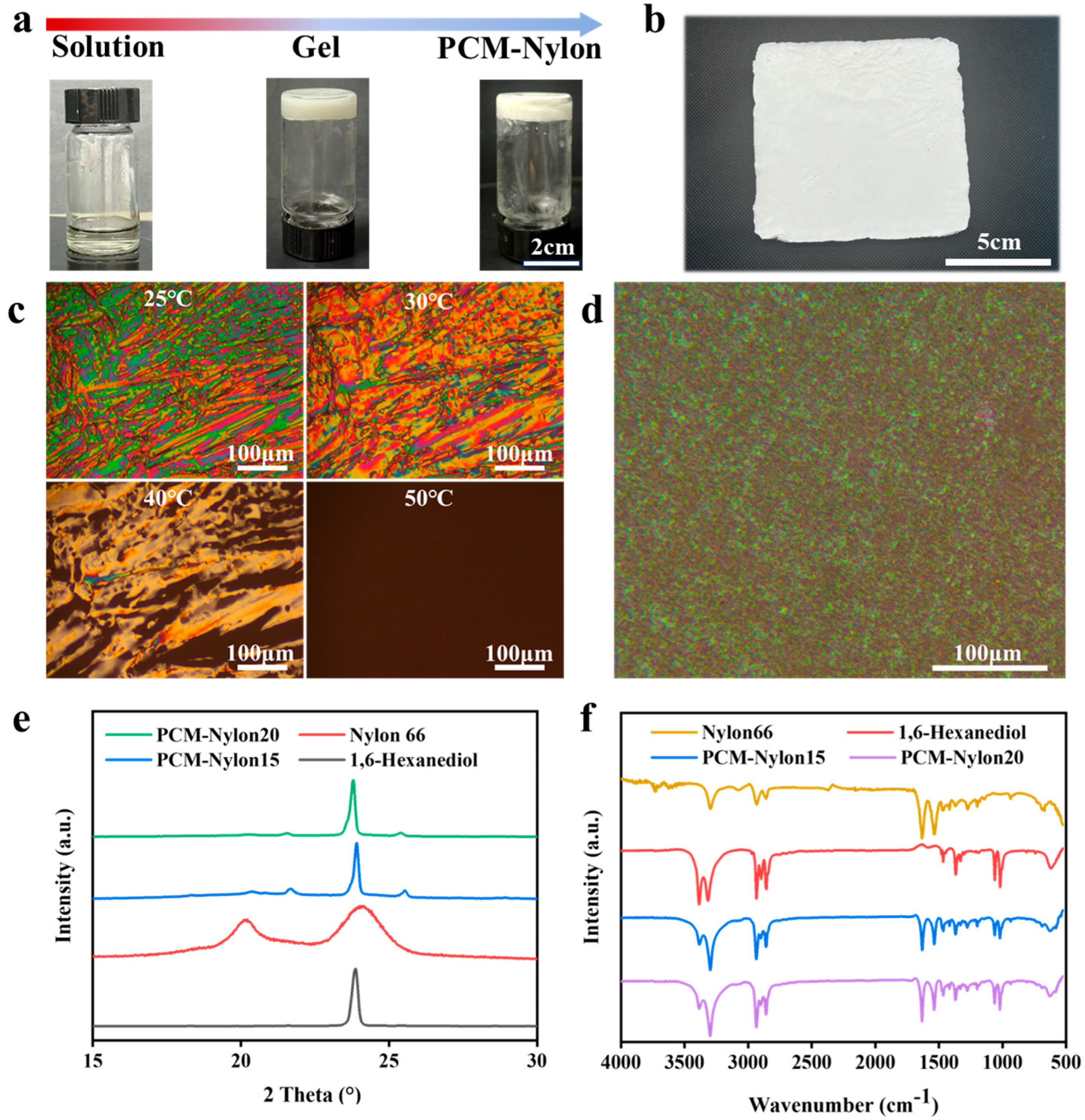
2.1. In Situ Formation of Porous Networks
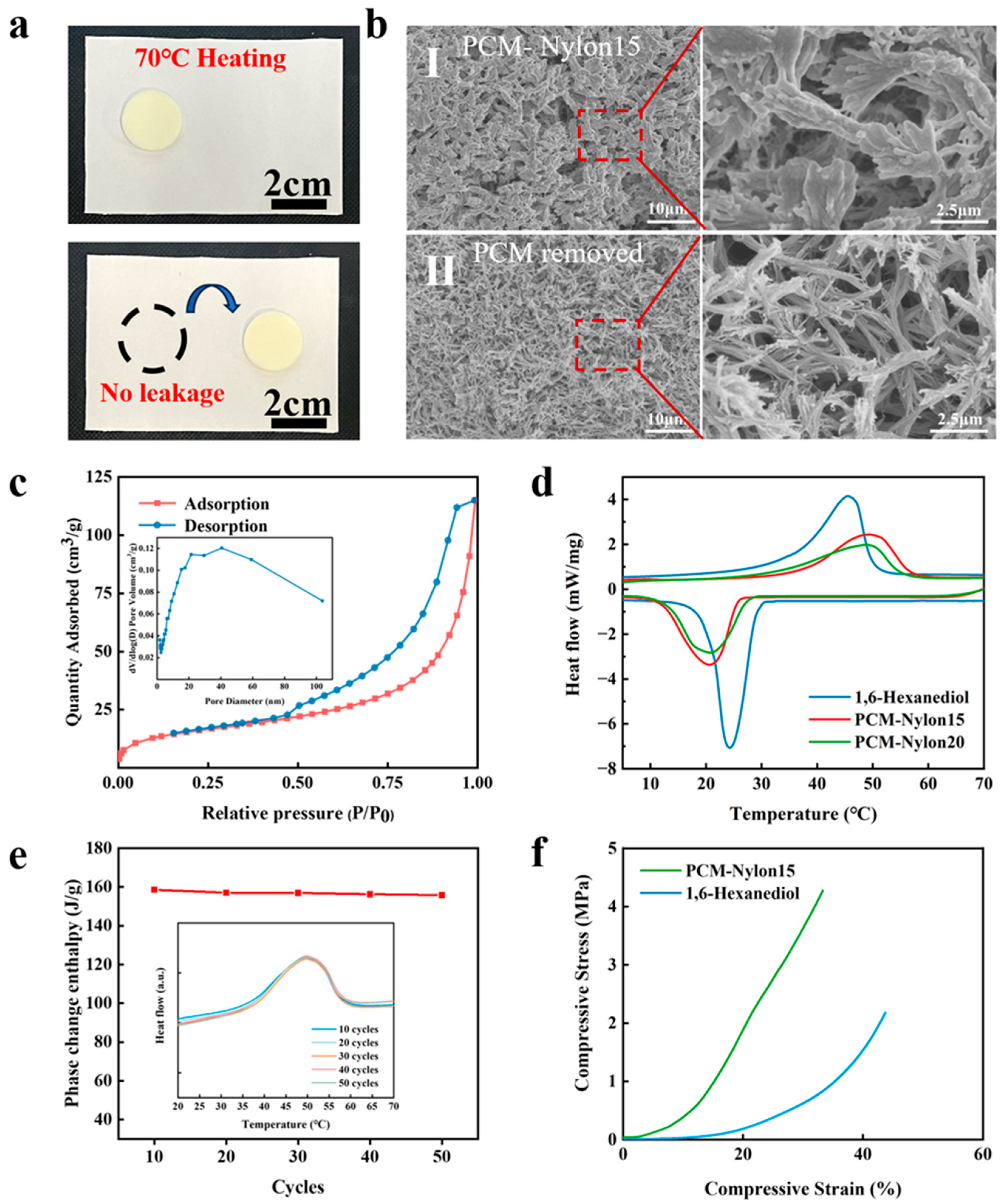
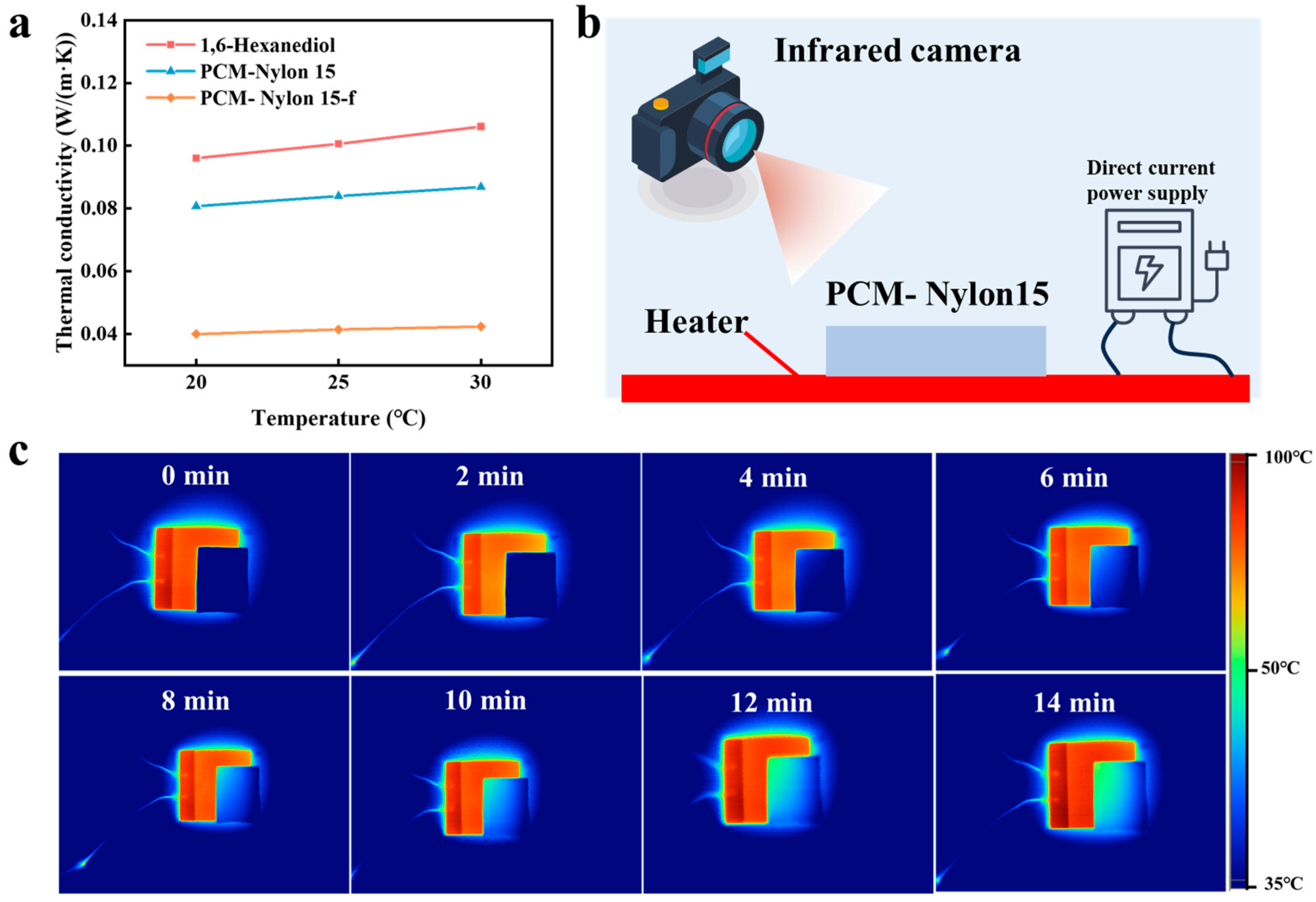
2.2. Pore Structure-Dictated Performance
2.3. Multifunctional Applications
2.3.1. Infrared Stealth
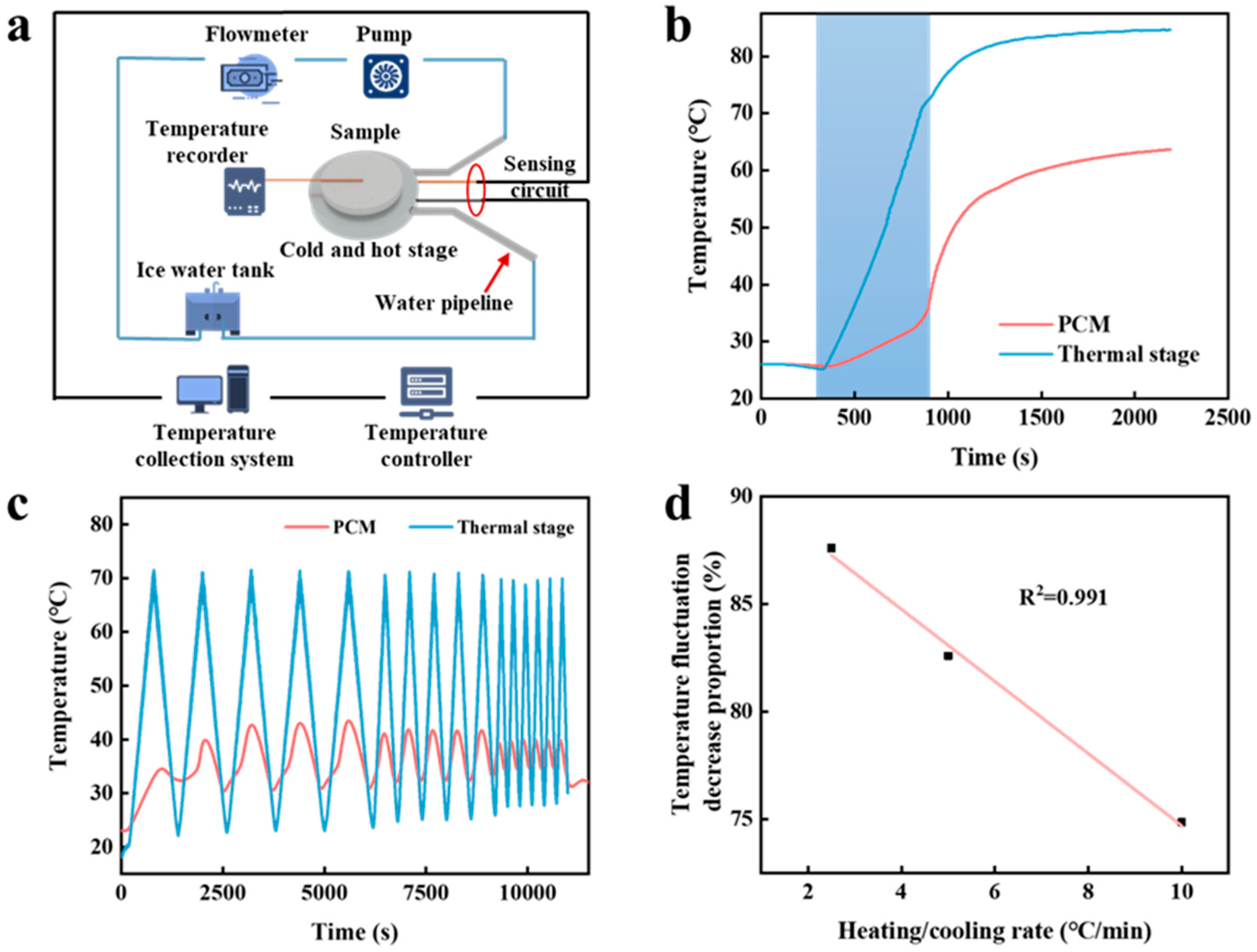
2.3.2. Thermal Buffering
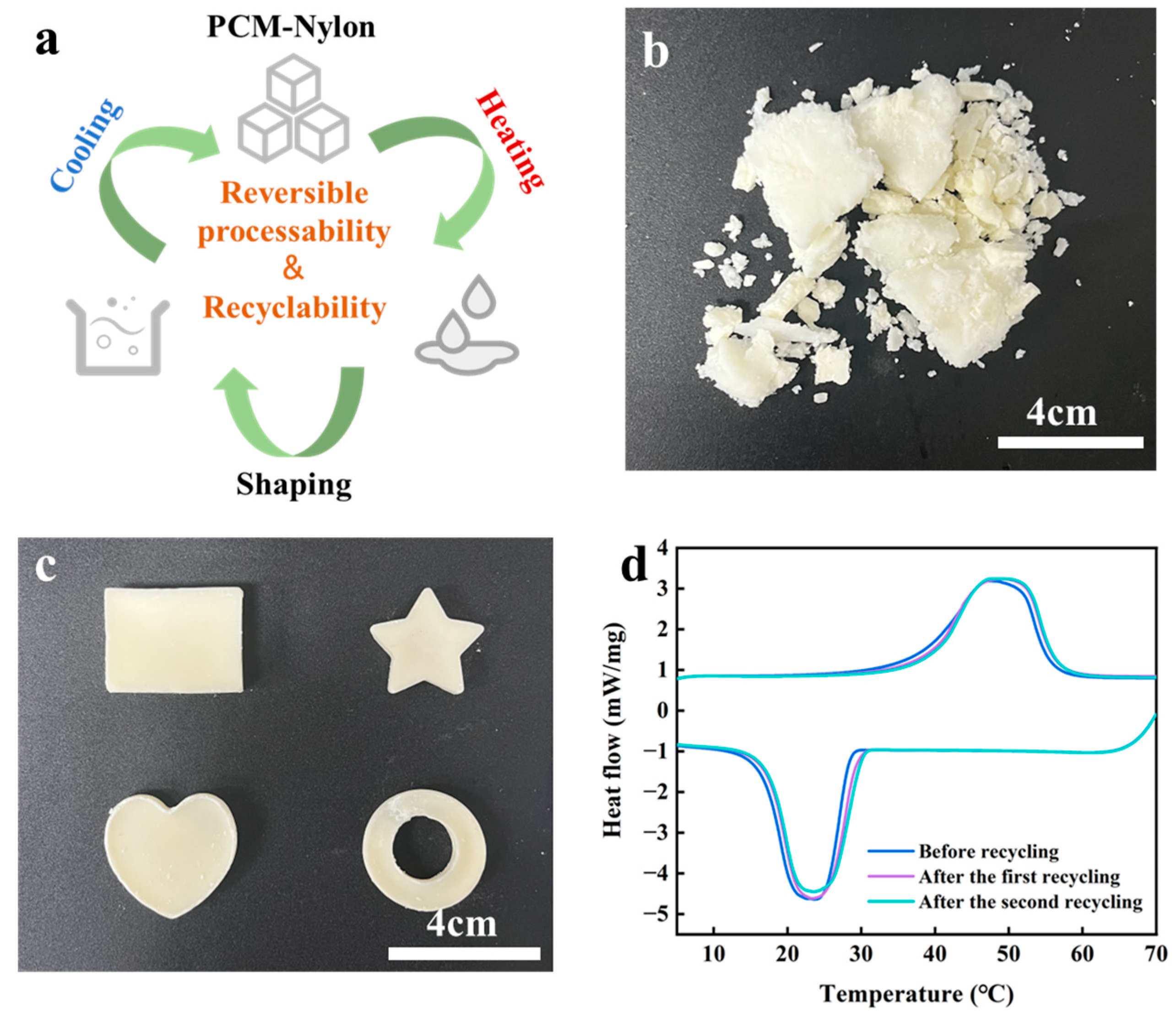
2.4. Recyclability and Reversible Processability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of PCM-Nylon
3.3. Preparation of PCM-Nylon 15 Framework (PCM-Nylon 15-f)
3.4. Polarizing Microscope Images
3.5. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.6. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR)
3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.8. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.9. Nitrogen Adsorption–Desorption
3.10. Compressive Strength
3.11. IR Images
3.12. Thermal Conductivity
3.13. Temperature Recording
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCM | Phase change material |
| ss-CPCMs | Shape-stabilized composite PCMs |
| TES | Thermal energy storage |
References
- Chen, X.; Gao, H.; Tang, Z.; Dong, W.; Li, A.; Wang, G. Optimization strategies of composite phase change materials for thermal energy storage, transfer, conversion and utilization. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 4498–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Li, A.; Chen, X. Phase change thermal storage materials for interdisciplinary applications. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 6953–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Huang, X.; Li, A.; Dong, W. Nanoconfinement effects on thermal properties of nanoporous shape-stabilized composite PCMs: A review. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 769–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Feng, D.; Shi, L.; Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Tian, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhao, L.; Yan, Y. A review of phase change heat transfer in shape-stabilized phase change materials (ss-PCMs) based on porous supports for thermal energy storage. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Q.; Wu, S.; Cai, Y.F.; Wang, R.Z.; Li, T.X. Form-stable phase change composites: Preparation, performance, and applications for thermal energy conversion, storage and management. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 42, 380–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, A.C.; Pajonk, G.M. Chemistry of aerogels and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4243–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Cheng, P.; Tang, Z.; Lv, J.; Aftab, W.; Wang, G. Aerogels meet phase change materials: Fundamentals, advances, and beyond. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 15586–15626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Sun, L.; Zou, Y.; Chu, H.; Yan, E. Synthesis of three-dimensional graphene aerogel encapsulated n-octadecane for enhancing phase-change behavior and thermal conductivity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 15191–15199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Luo, W.; Kim, J.-K.; Yang, J. Graphene oxide aerogel beads filled with phase change material for latent heat storage and release. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 3657–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, X.; Han, S.; Yang, R.; Min, P.; Yu, Z.-Z. High quality graphene aerogels for thermally conductive phase change composites with excellent shape stability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 5880–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Lu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Tan, L.; Gao, H.; Fan, S.; Dong, W.; Wang, G. Surface functionalization engineering driven crystallization behavior of polyethylene glycol confined in mesoporous silica for shape-stabilized phase change materials. Nano Energy 2016, 19, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Peng, X. Preparation of paraffin/SiO2 aerogel stable-stabilized phase change composites for high-humidity environment. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 1511–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Deng, Y.; Wu, F.; Jin, H.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J. Facile in-situ fabrication of latent heat enhanced cellulose aerogel-based form-stable composite phase change materials based on dopamine modification strategy. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2021, 230, 111236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, Z.; Ren, X.; Jiang, F. Lightweight, strong, and form-stable cellulose nanofibrils phase change aerogel with high latent heat. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 272, 118460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Tang, L.-S.; Feng, C.-P.; Bai, L.; Bao, R.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Yang, M.-B.; Yang, W. Hierarchically porous PVA aerogel for leakage-proof phase change materials with superior energy storage capacity. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Shao, Z.; Gao, W.; Fan, W.; Liu, T.; Bai, H. Multifunctional polyimide aerogel textile inspired by polar bear hair for thermoregulation in extreme environments. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Xie, J.; He, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, W.; Fang, J.; Yan, S.; Zhang, L.; Sheng, X.; Chen, Y. MXene aerogel-based phase change materials toward solar energy conversion. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 206, 110229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, G.; Xu, L.; Liao, J.; Zhang, X. Nanoporous boron nitride aerogel film and its smart composite with phase change materials. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16590–16599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Nie, R.; Yuan, J. A review of shape stabilized aerogel-based phase change materials for preparation, classification and applications. Energy Built Environ. 2025, 6, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molefi, J.A.; Luyt, A.S.; Krupa, I. Comparison of LDPE, LLDPE and HDPE as matrices for phase change materials based on a soft Fischer–Tropsch paraffin wax. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 500, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa, I.; Miková, G.; Luyt, A.S. Phase change materials based on low-density polyethylene/paraffin wax blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 4695–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarı, A. Form-stable paraffin/high density polyethylene composites as solid–liquid phase change material for thermal energy storage: Preparation and thermal properties. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zou, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Shi, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Guo, J.; et al. Phase change and aerogel dual functionalized composites materials with double network structure through one-step preparation of polyacrylamide/calcium alginate/polyethylene glycol. Polymer 2021, 223, 123710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Xie, R.; Shen, J.; Song, L.; Chen, L. One-step strategy to construct GA/PEG shape-stabilized phase change material with excellent thermophysical properties. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 103, 107716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gao, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, D.; Lv, J.; Han, M.; Cheng, P.; Wang, G. In situ one-step construction of monolithic silica aerogel-based composite phase change materials for thermal protection. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 195, 108072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Ma, G.; Xie, S.; Sun, J.; Jia, Y.; Jing, Y. Thermal properties and stabilities of the eutectic mixture: 1,6-hexanediol/lauric acid as a phase change material for thermal energy storage. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 116, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, N.S.; Curran, S.A.; Aharoni, S.M.; Minor, H. Premelting crystalline relaxations and phase transitions in Nylon 6 and 6,6. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 3215–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyotani, M. Solution crystallization of Nylon 6. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1979, 17, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, T.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, H.; Huang, T. In-Situ Polymerization of High-Molecular Weight Nylon 66 Modified Clay Nanocomposites with Low Apparent Viscosity. Polymers 2019, 11, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Zhou, M.; Ji, G. Broadband multispectral compatible absorbers for radar, infrared and visible stealth applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 135, 101088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochetov, R.; Andritsch, T.; Lafont, U.; Morshuis, P.H.F.; Picken, S.J.; Smit, J.J. Thermal behaviour of epoxy resin filled with high thermal conductivity nanopowders. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference, Virginia Beach, VA, USA, 18–21 October 2009; IEEE: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2009; pp. 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Zhang, A. Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Material via In Situ Solid–Liquid Host–Guest Composite Strategy. Molecules 2025, 30, 3376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163376
Chen J, Zhang A. Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Material via In Situ Solid–Liquid Host–Guest Composite Strategy. Molecules. 2025; 30(16):3376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163376
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jian, and Afang Zhang. 2025. "Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Material via In Situ Solid–Liquid Host–Guest Composite Strategy" Molecules 30, no. 16: 3376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163376
APA StyleChen, J., & Zhang, A. (2025). Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Material via In Situ Solid–Liquid Host–Guest Composite Strategy. Molecules, 30(16), 3376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163376






