Salvianolic Acid A Activates Nrf2-Related Signaling Pathways to Inhibit Ferroptosis to Improve Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Salvianolic Acid A Reduced Ischemic Brain Injury in PTS Mice
2.2. Salvianolic Acid A Exerted Antioxidative Stress Effect in PTS Mice
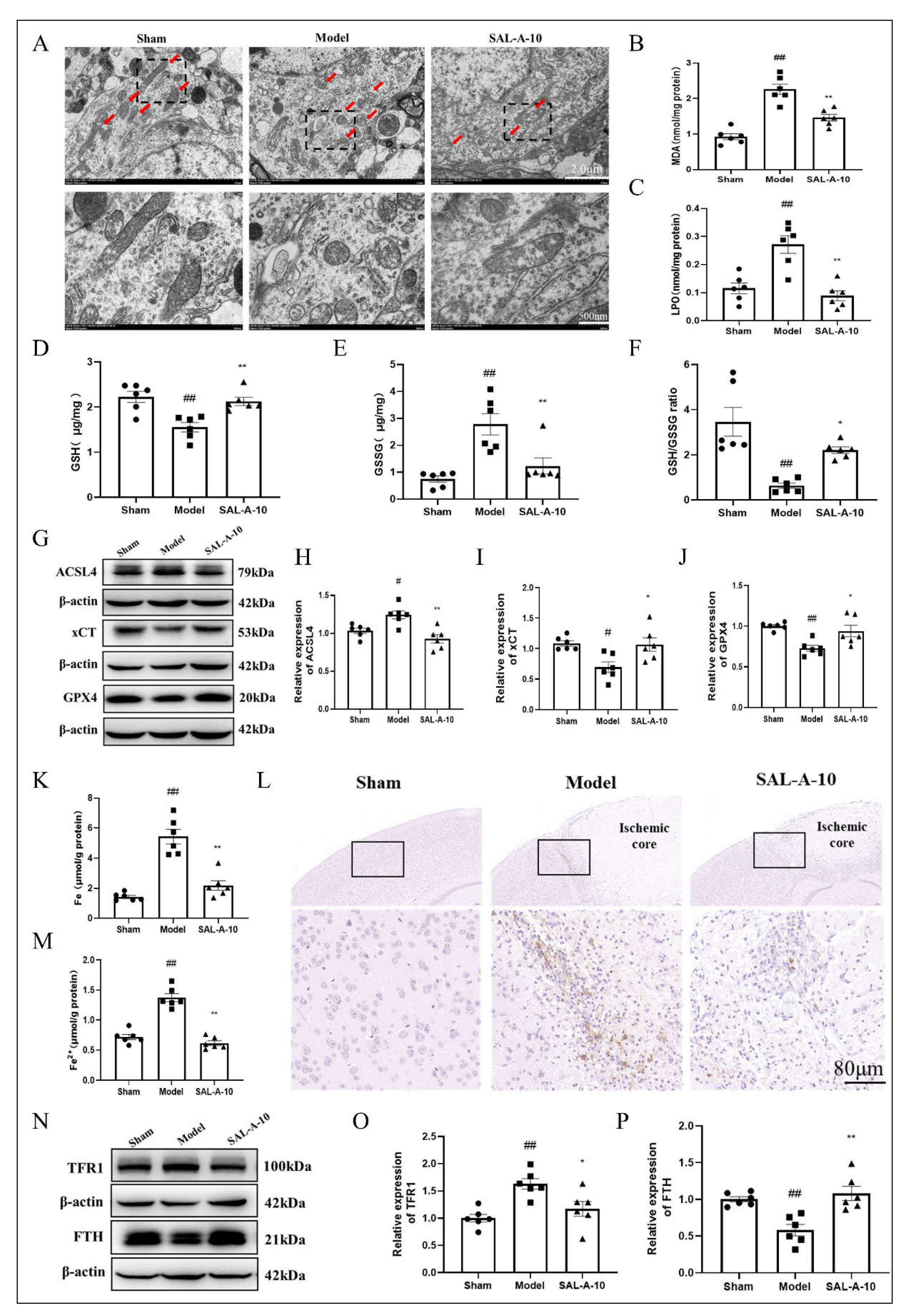
2.3. Salvianolic Acid A Protected from Ferroptosis by Inhibiting Lipid Peroxidation and Iron Overload in PTS Mice
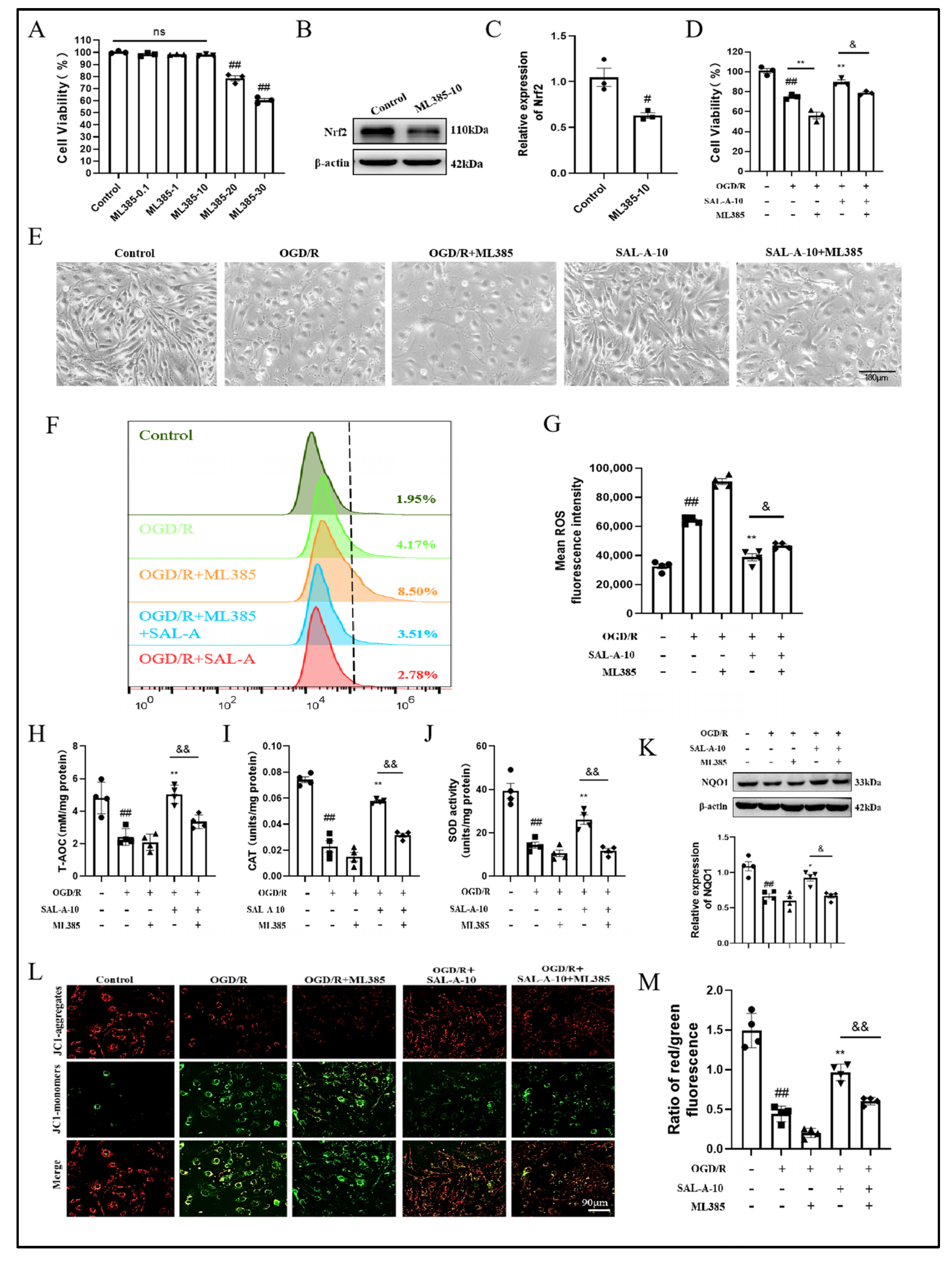
2.4. Salvianolic Acid A Attenuates OGD/R-Induced Oxidative Stress in b.End.3 Cells via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway
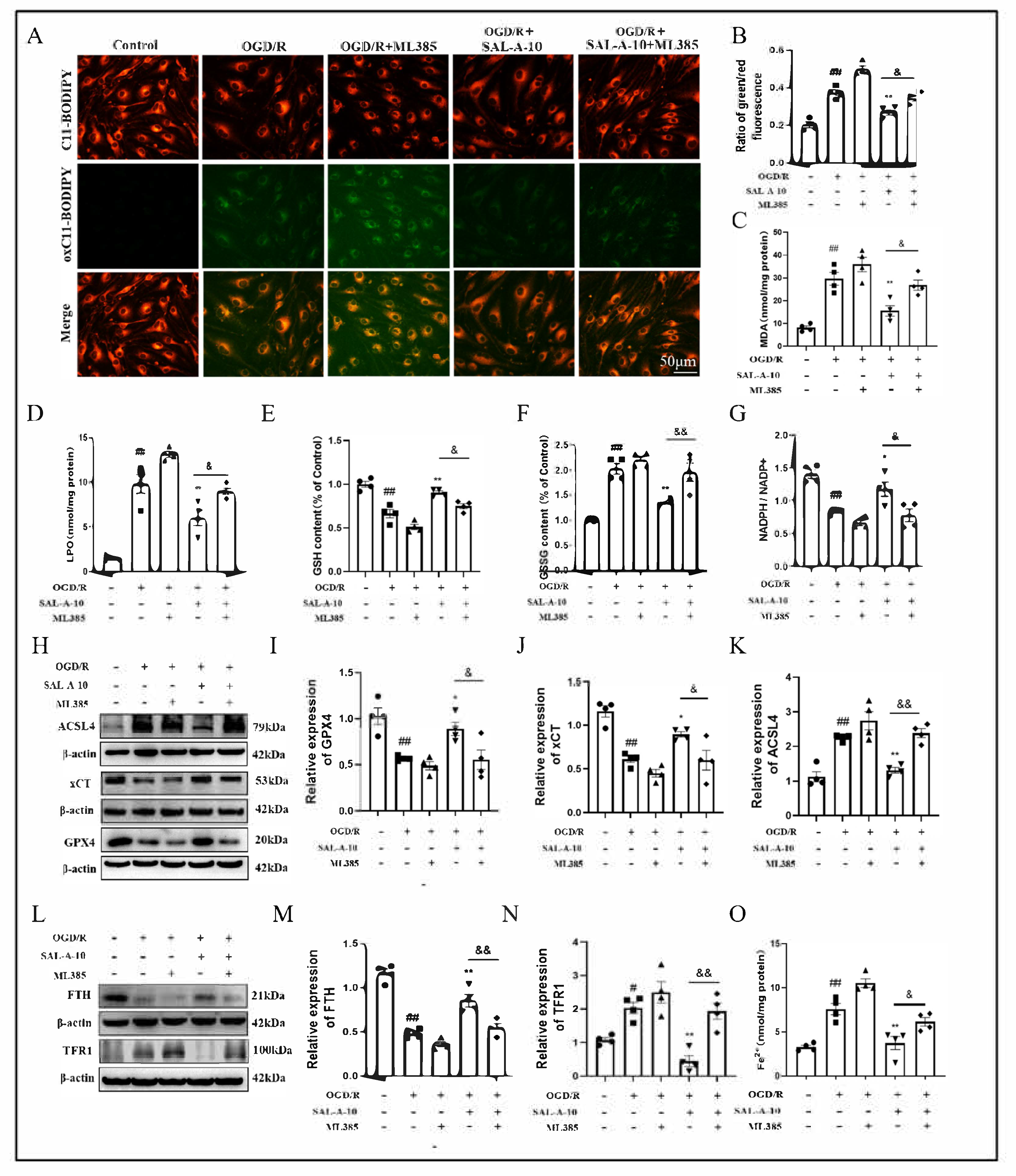
2.5. Salvianolic Acid A Attenuates OGD/R-Induced Ferroptosis via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in b.End.3 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. PTS Mice Model and SAL-A Treatment
4.3. Behavior Tests
4.3.1. Neurological Deficit Scoring (mNSS) and Zea Longa Scoring
4.3.2. Corner Test
4.3.3. Grip Strength Test
4.4. Infarct Volume Assessments
4.5. Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) Staining
4.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Assay of Mitochondrial Morphology
4.7. DAB Enhanced Prussian Blue Stain
4.8. Content Assay of T-AOC, CAT, SOD, GSH, GSSG, NADPH, Fe and Fe2+
4.9. Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation (OGD/R) Modeling and Grouping
4.10. Cell Viability Assay with CCK-8
4.11. ROS Analysis
4.12. MMP Analysis with JC-1 Staining
4.13. Lipid Peroxidation Analysis with BODIPY 581/581 C11 Staining
4.14. Western Blotting Analysis
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AREs | antioxidant response elements |
| ACSL4 | long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 4 |
| b.End.3 | brain microvascular endothelial cells |
| CAT | catalase |
| Dr2 | dopamine receptors D2 |
| DCFH-DA | 2,7-dichlorodi-hydrofluorescein diacetate |
| FTH | ferritin heavy chain |
| GPX4 | glutathione peroxidase 4 |
| GSH | glutathione |
| GSSG | oxidized glutathione |
| HO-1 | heme oxygenase 1 |
| HE | Hematoxylin-Eosin |
| IS | Ischemic stroke |
| Keap1 | kelch-like ech-associated protein 1 |
| LPO | lipid peroxidation |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| MMP | mitochondrial membrane potential |
| mNSS | neurological deficit scoring |
| NADPH | reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-B |
| NQO1 | NADPH quinone oxidoreductase 1 |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| NOX | NADPH oxidases |
| OGD/R | oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation |
| PTS | photochemical induction of stroke |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors γ |
| PUFAs | polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| PKA | protein kinase A |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SAL-A | salvianolic acid A |
| SLC7A11/xCT | solute carrier family 7 member 11 |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| TFR1 | transferrin receptor 1 |
| TTC | 2, 3, 5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride |
| T-AOC | total antioxidant capacity |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
References
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2023 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 147, e93–e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpich, F.; Rincon, F. Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Ospel, J.M.; Menon, B.; Almekhlafi, M.; Jayaraman, M.; Fiehler, J.; Psychogios, M.; Chapot, R.; van der Lugt, A.; Liu, J.; et al. Challenging the Ischemic Core Concept in Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging. Stroke 2020, 51, 3147–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, A.; Su, E.J.; Muthusamy, A.; Zeitelhofer, M.; Torrente, D.; Nilsson, I.; Protzmann, J.; Fredriksson, L.; Eriksson, U.; Antonetti, D.A.; et al. Thrombolytic tPA-Induced Hemorrhagic Transformation of Ischemic Stroke Is Mediated by PKCβ Phosphorylation of Occludin. Blood 2022, 140, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzdensky, A.B. Photothrombotic Stroke as a Model of Ischemic Stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2018, 9, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluri, F.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Kleinschnitz, C. Animal Models of Ischemic Stroke and Their Application in Clinical Research. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2015, 9, 3445–3454. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An Iron-Dependent Form of Nonapoptotic Cell Death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Smith, M.J. Metal Profiling in Coronary Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Implications for KEAP1/NRF2 Regulated Redox Signaling. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 210, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, J.; Cai, N.; Cheng, K.; Liang, H.; Zhang, W. The Molecular Mechanisms of Regulating Oxidative Stress-Induced Ferroptosis and Therapeutic Strategy in Tumors. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8810785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hu, S.; Bian, Y.; Yao, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, S.; Peng, L. Targeting Cell Death: Pyroptosis, Ferroptosis, Apoptosis and Necroptosis in Osteoarthritis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 789948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.X.; Li, C.; Yan, X.L.; Qu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Z.N. Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Ferroptosis/Oxytosis in Ischemic Stroke: Possible Targets and Molecular Mechanisms. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6643382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloska, A.; Malinowska, M.; Gabig-Cimińska, M.; Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka, J. Lipids and Lipid Mediators Associated with the Risk and Pathology of Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Feng, S.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, X.; Gu, L. Ferroptosis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Ischemic Stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.; Duennwald, M.L. Nrf2 and Oxidative Stress: A General Overview of Mechanisms and Implications in Human Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, L.; Yamamoto, M. The Molecular Mechanisms Regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 Pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 40, e00099-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vriend, J.; Reiter, R.J. The Keap1-Nrf2-Antioxidant Response Element Pathway: A Review of Its Regulation by Melatonin and the Proteasome. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 401, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.-Y.; Gladwell, W.; Wang, X.; Chorley, B.; Bell, D.; Reddy, S.P.; Kleeberger, S.R. Nrf2-Regulated PPAR{gamma} Expression Is Critical to Protection against Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Sato, H.; Kuriyama-Matsumura, K.; Sato, K.; Maebara, K.; Wang, H.; Tamba, M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Bannai, S. Electrophile Response Element-Mediated Induction of the Cystine/Glutamate Exchange Transporter Gene Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 44765–44771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerins, M.J.; Ooi, A. The Roles of NRF2 in Modulating Cellular Iron Homeostasis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1756–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.N.; Zhao, H.C.; Huang, J.Y.; Wang, H.L.; Li, J.S.; Lu, Y.; Di, L.Q. Challenges and Strategies in Progress of Drug Delivery System for Traditional Chinese Medicine Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma (Danshen). Chin. Herb. Med. 2021, 13, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wei, K.; Zhang, G.; Lei, L.; Yang, D.; Wang, W.; Han, Q.; Xia, Y.; Bi, Y.; Yang, M.; et al. Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of Chinese Salvia Species: A Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 225, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Kong, D.W.; Ma, G.D.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.J.; Liu, S.; Jiang, N.; Pan, Z.R.; Zhang, W.; Kong, L.L.; et al. Long-Term Administration of Salvianolic Acid A Promotes Endogenous Neurogenesis in Ischemic Stroke Rats through Activating Wnt3a/GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2212–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.D.; Liu, N.N.; Zhang, S.; Ma, G.D.; Yang, H.G.; Kong, L.L.; Du, G.H. Salvianolic Acid A Prevented Cerebrovascular Endothelial Injury Caused by Acute Ischemic Stroke through Inhibiting the Src Signaling Pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, S.J.; Prabhakaran, S. Diagnosis and Management of Transient Ischemic Attack and Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Kim, J.S. Ischemic Stroke Subtype Classification: An Asian Viewpoint. J. Stroke. 2014, 16, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimbrone, M.A.; García-Cardeña, G. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellariou, X.M.; Papafaklis, M.I.; Domouzoglou, E.M.; Katsouras, C.S.; Michalis, L.K.; Naka, K.K. Exercise-Mediated Adaptations in Vascular Function and Structure: Beneficial Effects in Coronary Artery Disease. World J. Cardiol. 2021, 13, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labatgest, V.; Tomasi, S. Photothrombotic Ischemia: A Minimally Invasive and Reproducible Photochemical Cortical Lesion Model for Mouse Stroke Studies. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 76, 50370. [Google Scholar]
- Barayeu, U.; Schilling, D.; Eid, M.; da Silva, T.N.X.; Schlicker, L.; Mitreska, N.; Zapp, C.; Gräter, F.; Miller, A.K.; Kappl, R.; et al. Hydropersulfides Inhibit Lipid Peroxidation and Ferroptosis by Scavenging Radicals. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesterman, C.N. Vascular Endothelium, Haemostasis and Thrombosis. Blood Rev. 1988, 2, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Hu, N.; Liu, T.Y.; Qu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.H.; Yang, B.F.; Li, C.L. Salvianolic Acid A Provides Neuroprotective Effects on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats via PKA/CREB/c-Fos Signaling Pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 124, 155326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, J.; Liu, N.; Wei, G.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, N.; Yang, H.; Du, G. Salvianolic Acid A Relieves Cognitive Disorder after Chronic Cerebral Ischemia: Involvement of Drd2/Cryab/NF-κB Pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 105989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Aa, N.; Geng, J.; Huang, J.; Sun, R.; Ge, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Aa, J.; Wang, G. Pharmacokinetic and Metabolomic Analyses of the Neuroprotective Effects of Salvianolic Acid a in a Rat Ischemic Stroke Model. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Niu, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Su, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Qian, L.; Liu, P.; et al. Ferroptosis: A Cell Death Connecting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Cardiovascular Diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, Y.; Okazaki, R.; Sato, M.; Oh-Hashi, K.; Takemori, H.; Furuta, K. Effect of Ferroptosis Inhibitors Oxindole-Curcumin Hybrid Compound and N,N-Dimethylaniline Derivatives on Rotenone-Induced Oxidative Stress. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 928, 175119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Mao, G.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Han, R.; She, J.; Zhang, R.; Sheng, R.; Chen, Z.; et al. NADPH Is Superior to NADH or Edaravone in Ameliorating Metabolic Disturbance and Brain Injury in Ischemic Stroke. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.N.; Shang, N.Y.; Kang, Y.Y.; Sheng, N.; Lan, J.Q.; Tang, J.S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.L.; Peng, Y. Caffeic Acid Alleviates Cerebral Ischemic Injury in Rats by Resisting Ferroptosis via Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Bao, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Chen, C. The Role of Ferroptosis and Its Mechanism in Ischemic Stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 372, 114630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yan, M.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, T.; Xue, J. Calycosin Decreases Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing ACSL4-Dependent Ferroptosis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 734, 109488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, F.; Maiorino, M. Lipid Peroxidation and Ferroptosis: The Role of GSH and GPx4. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Duan, H.; Li, R.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling: An Important Molecular Mechanism of Herbal Medicine in the Treatment of Atherosclerosis via the Protection of Vascular Endothelial Cells from Oxidative Stress. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 34, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Roh, J.-L. Targeting Nrf2 for Ferroptosis-Based Therapy: Implications for Overcoming Ferroptosis Evasion and Therapy Resistance in Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Xia, J.; Liang, L.; Lei, C.; Hu, Y.; Cai, X.; et al. SLC27A5 Deficiency Activates NRF2/TXNRD1 Pathway by Increased Lipid Peroxidation in HCC. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 1086–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, M.; Castro-Portuguez, R.; Zhang, D.D. NRF2 Plays a Critical Role in Mitigating Lipid Peroxidation and Ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2019, 23, 101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, K.; Hirt, H. Reactive Oxygen Species: Metabolism, Oxidative Stress, and Signal Transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Cai, C.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q. Parthenolide Ameliorates Neurological Deficits and Neuroinflammation in Mice with Traumatic Brain Injury by Suppressing STAT3/NF-κB and Inflammasome Activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 108, 108913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Tang, T.; Lin, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, W.; Liang, S. Functional Connectivity of Ipsilateral Striatum in Rats with Ischemic Stroke Increased by Electroacupuncture. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 21, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.; Wen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; Li, R.; et al. Lipocalin-2 May Produce Damaging Effect after Cerebral Ischemia by Inducing Astrocytes Classical Activation. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Hua, Y.; Fan, Y. Minocycline Promotes Functional Recovery in Ischemic Stroke by Modulating Microglia Polarization through STAT1/STAT6 Pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 186, 114464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, N.W.; Ho, C.S.; Chiu, Y.S.; Huang, W.C.; Chen, P.Y.; Tung, Y.T.; Huang, C.C. Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation and Exercise Training on Exercise Performance in Middle-Aged Mice. Molecules 2016, 21, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.-L.; Li, W.-H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, S.-S.; Wang, Y.-H.; Du, G.-H. Dynamic Alterations of Brain Injury, Functional Recovery, and Metabolites Profile after Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion in Rats Contributes to Potential Biomarkers. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 70, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-H.; Yang, Y.-L.; Cheng, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, S.-S.; Wang, Y.-H.; Du, G.-H. Baicalein Attenuates Caspase-Independent Cells Death via Inhibiting PARP-1 Activation and AIF Nuclear Translocation in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Rats. Apoptosis 2020, 25, 354–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Gao, W.; Wang, Z.; Jian, H.; Peng, L.; Yu, X.; Xue, P.; Peng, W.; Li, K.; Zeng, P. Polyphyllin I Induced Ferroptosis to Suppress the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Activation of the Mitochondrial Dysfunction via Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 Axis. Phytomedicine 2024, 122, 155135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wang, B.-Y.; Yang, Y.-F.; Kuai, L.-Y.; Wan, J.; Zhang, M.; Xia, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Meng, X.-W.; et al. Ciprofol Ameliorates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Ferroptosis Through Upregulating HIF-1α. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2024, 18, 6115–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Wei, M.; Wang, J.; Zeng, J.; Liu, D.; Du, Q.; Ge, J.; Mei, Z. Naotaifang Formula Attenuates OGD/R-Induced Inflammation and Ferroptosis by Regulating Microglial M1/M2 Polarization through BMP6/SMADs Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, Q. Herceptin Induces Ferroptosis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in H9c2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Tie, H.; Tian, W.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, L.; Guo, S.; Li, Q.; Bao, C. Eriodictyol Regulated Ferroptosis, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Cell Viability via Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 Signaling Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.M.; Kim, A.; Yang, W.S. Detection of Ferroptosis by BODIPYTM 581/591 C11. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2108, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, S.-S.; Liu, D.-N.; Yang, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-H.; Du, G.-H. Chrysomycin A Attenuates Neuroinflammation by Down-Regulating NLRP3/Cleaved Caspase-1 Signaling Pathway in LPS-Stimulated Mice and BV2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, Y.-F.; Feng, W.-D.; Liu, D.-N.; Zhang, W.-F.; Xu, S.; Feng, D.-H.; Du, G.-H.; Wang, Y.-H. Salvianolic Acid A Activates Nrf2-Related Signaling Pathways to Inhibit Ferroptosis to Improve Ischemic Stroke. Molecules 2025, 30, 3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153266
Shang Y-F, Feng W-D, Liu D-N, Zhang W-F, Xu S, Feng D-H, Du G-H, Wang Y-H. Salvianolic Acid A Activates Nrf2-Related Signaling Pathways to Inhibit Ferroptosis to Improve Ischemic Stroke. Molecules. 2025; 30(15):3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153266
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Yu-Fu, Wan-Di Feng, Dong-Ni Liu, Wen-Fang Zhang, Shuang Xu, Dan-Hong Feng, Guan-Hua Du, and Yue-Hua Wang. 2025. "Salvianolic Acid A Activates Nrf2-Related Signaling Pathways to Inhibit Ferroptosis to Improve Ischemic Stroke" Molecules 30, no. 15: 3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153266
APA StyleShang, Y.-F., Feng, W.-D., Liu, D.-N., Zhang, W.-F., Xu, S., Feng, D.-H., Du, G.-H., & Wang, Y.-H. (2025). Salvianolic Acid A Activates Nrf2-Related Signaling Pathways to Inhibit Ferroptosis to Improve Ischemic Stroke. Molecules, 30(15), 3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153266





