Supramolecular Detoxification Approach of Endotoxin Through Host–Guest Complexation by a Giant Macrocycle
Abstract
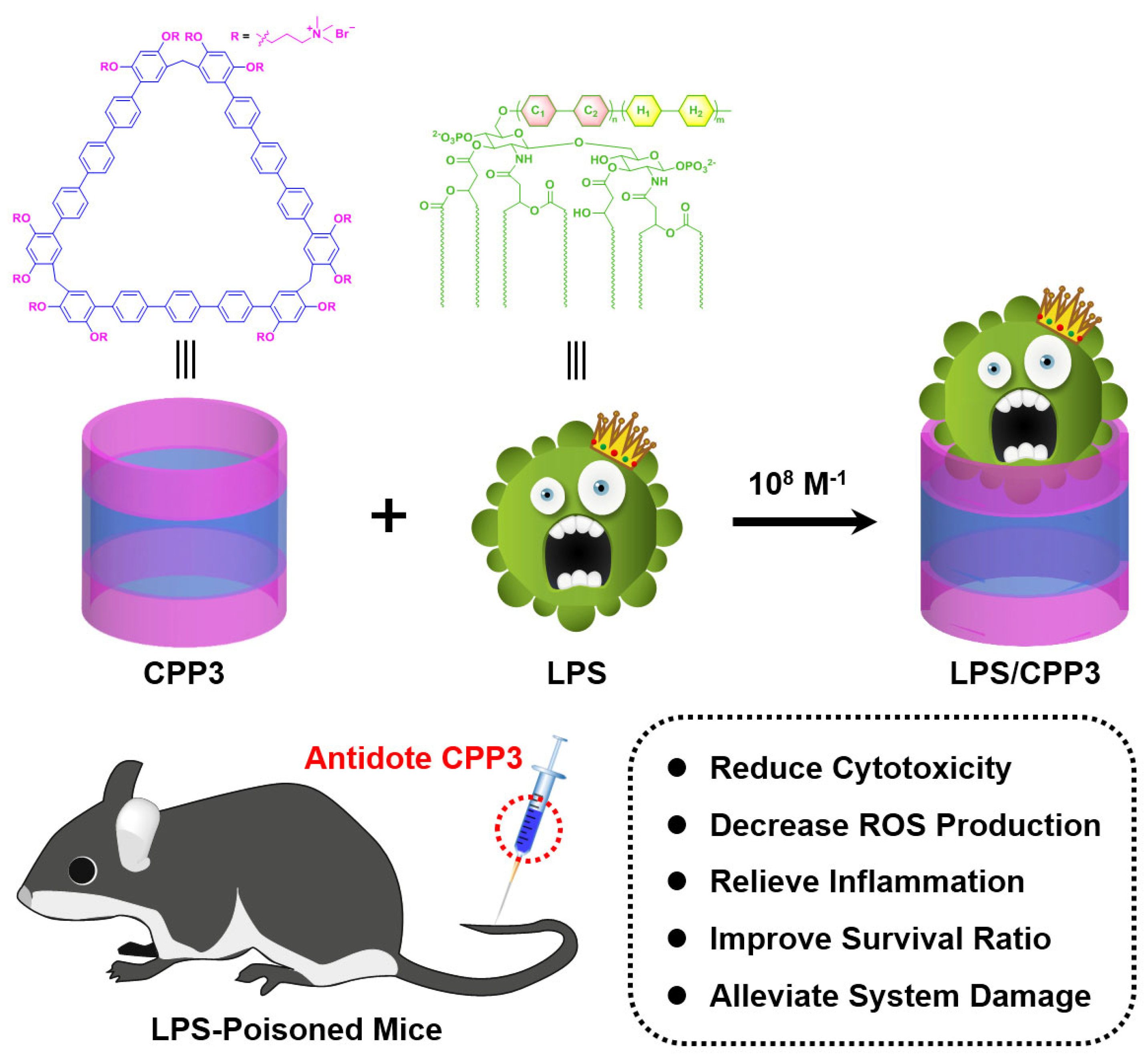
1. Introduction
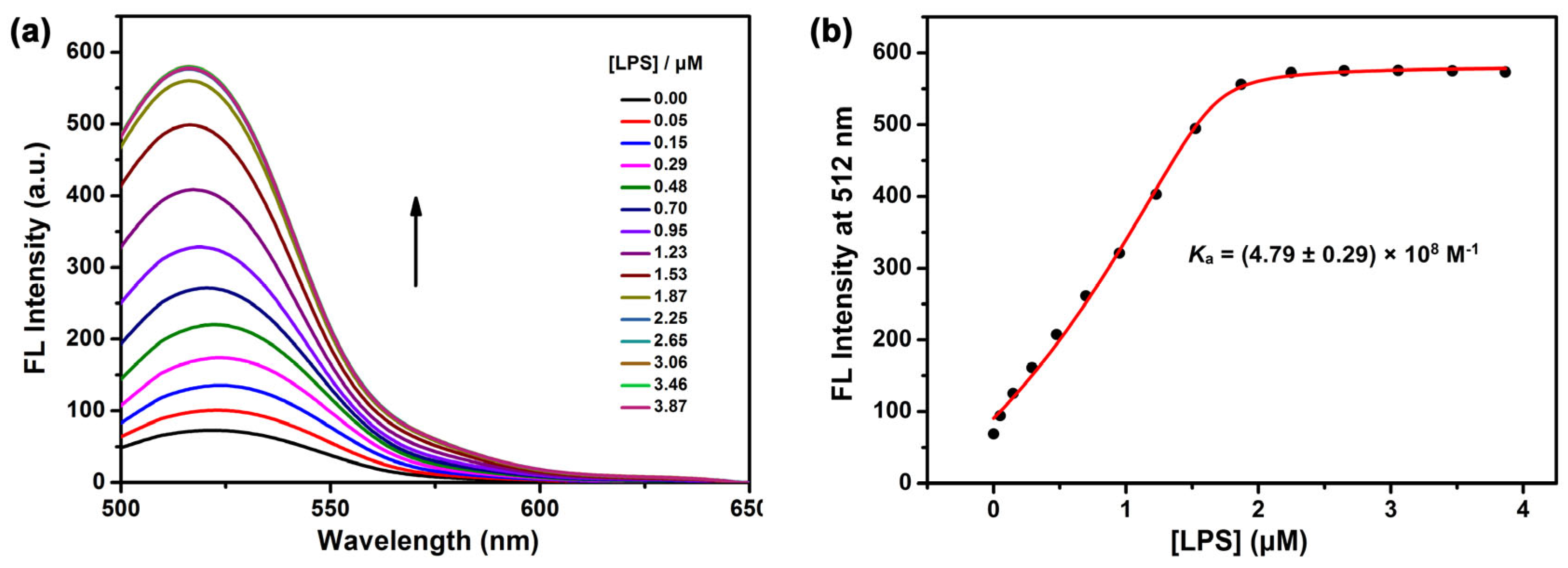
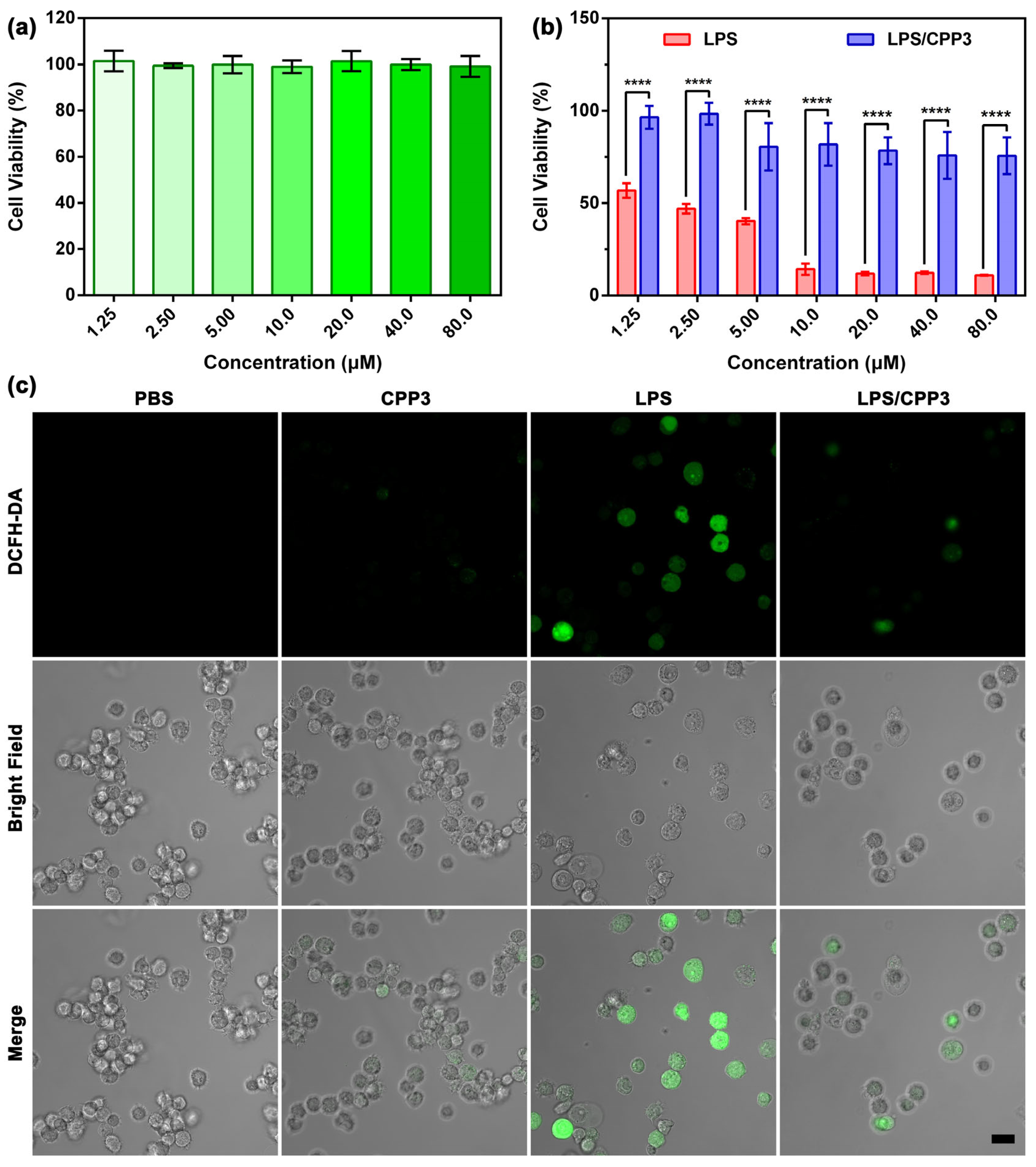
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature 2002, 420, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-I.; Lee, C.J.; Jin, M.S.; Lee, C.-H.; Paik, S.-G.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.-O. Crystal structure of CD14 and its implications for lipopolysaccharide signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11347–11351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raetz, C.R.H.; Whitfield, C. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 635–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinbockel, L.; Weindl, G.; Martinez-de-Tejada, G.; Correa, W.; Sanchez-Gomez, S.; Bárcena-Varela, S.; Goldman, T.; Garidel, P.; Gutsmann, T.; Brandenburg, K. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide− and lipoprotein−induced inflammation by antitoxin peptide Pep19-2.5. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, K.U.; Nygaard, R.; Vickery, O.N.; Erramilli, S.K.; Herrera, C.M.; McConvile, T.H.; Petrou, V.I.; Giacometti, S.I.; Dufrisne, M.B.; Nosol, K.; et al. Structural basis of lipopolysaccharide maturation by the O−antigen ligase. Nature 2022, 604, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, C.; Trent, M.S. Biosynthesis and export of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014, 83, 99–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raetz, C.R.H.; Reynolds, C.M.; Trent, M.S.; Bishop, R.E. Lipid A modification systems in gram-negative bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 295–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaniuk, N.A.; Vinogradov, E.; Whitfield, C. Investigation of the structural requirements in the lipopolysaccharide core acceptor for ligation of O antigens in the GenusSalmonella. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 36470–36480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarin, R.S.; Li, M.-S.; Zimmel, P.A.; Marshall, J.C.; Li, Y.-M.; Zhang, H.-B. Intracellular and extracellular lipopolysaccharide signaling in sepsis: Avenues for novel therapeutic strategies. J. Innate. Immun. 2021, 13, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.-D.; Liang, Y.-Q.; Shao, F.; Wang, X.-D. Toll−like receptors activate programmed necrosis in macrophages through a receptor−interacting kinase−3−mediated pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20054–20059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Feng, J.; Zhou, D.-X.; Wang, J.-S. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide−induced endothelial activation and dysfunction: A new predictive and therapeutic paradigm for sepsis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Ning, B.-T. Signaling pathways and intervention therapies in sepsis. Sig. Trans. Tar. Ther. 2021, 6, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Monneret, G.; Payen, D. Sepsis−induced immunosuppression: From cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, G.M.; Mattiotti, M.; de Cal, M.; Ronco, C.; Zanella, M.; de Rose, S. Endotoxin in sepsis: Methods for LPS detection and the use of omics techniques. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, I.; Lukšić, I.; Rafnsson, S.B. Assessing available information on the burden of sepsis: Global estimates of incidence, prevalence and mortality. J. Glob. Health 2012, 2, 010404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relouw, F.J.A.; Kox, M.; Taal, H.R.; Koch, B.C.P.; Prins, M.W.J.; van Riel, N.A.W. Mathematical model of the in fl amatory response to acute and prolonged lipopolysaccharide exposure in humans. NPG. Syst. Biol. Appl. 2024, 10, 146. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, J.-L. Current sepsis therapeutics. eBioMedicine 2022, 86, 104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Han, F.; Yuan, A.-R.; Wu, L.; Cao, J.; Qian, J.; Qi, X.-Y.; Yan, Y.-S.; Ge, Y.-R. Engineered nanoparticles disguised as macrophages for trapping lipopolysaccharide and preventing endotoxemia. Biomaterials 2019, 189, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconi, M.; Evans, L.; Levy, M.; Rhodes, A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 2018, 392, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Langeveled, P.; Kwappenberg, K.M.C.; Groeneveld, P.H.P.; Mattle, H.; van Dissel, J.T. Antibiotic−induced lipopolysaccharide (LPS) release from Salmonella typhi: Delay between killing by ceftazidime and imipenem and release of LPS. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 1998, 42, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shang, D.-J. Inhibitory effects of antimicrobial peptides on lipopolysaccharide−induced inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 167572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna, R.C.S.; Gomes, R.N.; Bozza, F.A.; Amâncio, R.T.; Bozza, P.T.; David, C.M.N.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C. Antibotic treatment in a murine model of sepsis: Impact on cytokines and endotoxin release. Shock 2004, 21, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, F.D.; Duda, K.A.; Lanzetta, R.; Silipo, A.; De Castro, C.; Molinaro, A. A journey from structure to function of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 15767–15821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietschel, E.T. Chemical structure and biological activity of endotoxins (lipopolysaccharides) and lipid A. Naunyun-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1975, 287, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckoff, T.J.O.; Raetz, C.R.H.; Jackman, J.E. Antibacterial and anti−inflammatory agents that target endotoxin. Trends Microbiol. 1998, 6, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanOtterloo, L.M.; Trent, M.S. Microbial Primer: Lipopolysaccharide−a remarkable component of the Gram−negative bacterial surface. Microbiology 2024, 170, 001439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, A.; Bhattacharjya, S. Mapping residue−specific contacts of polymyxin B with lipopolysaccharide by saturation transfer difference NMR: Insights into outer−membrane disruption and exdotoxin neutralization. Pept. Sci. 2010, 96, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kasiakou, S.K. Colistin: The revival of polymyxins for the management of multidrug−resistant gram−negative bacterial infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustici, A.; Velucchi, M.; Faggioni, R.; Sironi, M.; Ghezzi, P.; Quataert, S.; Green, B.; Porro, M. Molecular mapping and detoxification of the lipid A binding site by synthetic peptides. Science 1993, 259, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-L.; Teng, D.; Mao, R.-Y.; Hao, Y.; Yang, N.; Wang, X.-M.; Wang, J.-H. A cleavable chimeric peptide with targeting and killing domains enhances LPS neutralization and antibacterial properties against multi-drug resistant E. coli. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.-L.; Murkli, S.L.; Isaacs, L.D. Supramolecular hosts as in vivo sequestration agents for pharmaceuticals and toxins. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7516–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Li, C.-J.; Meng, Q.-B. Chemical warfare agent countermeasures based on macrocycle supramolecular chemistry. Sci. China Chem. 2025, 68, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockett, A.T.; Xue, W.-J.; King, D.; Deng, C.-L.; Zhai, C.-J.; Shuster, M.; Rastogi, S.; Briken, V.; Roesch, M.R.; Isaacs, L. Pillar[6]MaxQ: A potent supramolecular host for in vivo sequestration of methamphetamine and fentanyl. Chem 2023, 9, 881–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Yu, X.; Gao, D.; Chen, L.-M.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Zheng, Z.-B.; Chen, J.-Y.; Li, C.-J.; Meng, Q.-B. Macrocyclic neutralizer to polybrene via direct host−guest complexation. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 10425–10435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.-D.; Li, Q.; Haoyang, W.-W.; Zhang, D.-W.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Ma, D.; Hou, J.-L.; Li, Z.-T. Adsorption-based detoxifi cation of endotoxins by porous flexible organic frameworks. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, J.-Y.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Chen, L.-M.; Du, X.-B.; Ma, M.-K.; Li, J.; Meng, Q.-B.; Li, C.-J. Supramolecular detoxification of macromolecular biotoxin through the complexation by a large−sized macrocycle. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2200270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.-C.; Yue, Y.-X.; Hu, X.-Y.; Li, H.-B.; Guo, D.-S. A supramolecular antidote to macromolecular toxins prepared through coassembly of macrocyclic amphiphiles. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-Y.; Chen, L.-M.; Zhao, L.; Ma, M.-K.; Du, X.-B.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Z.-B.; Wang, Y.-A.; et al. Supramolecular liquid barrier for sulfur mustard utilizing host-guest complexation of pillar[5]arene with triethylene oxide substituents. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bom, A.; Bradley, M.; Cameron, K.; Clark, J.K.; van Egmond, J.; Feilden, H.; MacLean, E.J.; Muir, A.W.; Palin, R.; Rees, D.C.; et al. A novel concept of reversing neuromuscular block: Chemical encapsulation of rocuronium bromide by a cyclodextrin−based synthetic host. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Takashima, Y.; Nakahata, M. Supramolecular polymeric materials via cyclodextrin−guest interactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2128–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-J.; Liang, L.-L.; Chen, K.; Ji, N.-N.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, J.-X.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Xue, S.-F.; Zhu, Q.-J.; Ni, X.-L.; et al. Twisted cucurbit[14]uril. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7252–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, A.; Shinkai, S. Novel cavity design using calix[n]arene skeletons: Toward molecular recognition and metal binding. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 1713–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-B.; Chen, Z.-X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Hou, J.-L.; Li, Z.-T. Pillar[n]arenes (n = 8−10) with two cavities: Synthesis, structures and complexing properties. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10999–11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Li, C.-J. Biphen[n]arenes: Modular synthesis, customizable cavity sizes, and diverse skeletons. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.-D.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Yu, C.-M.; Wang, B.; Dong, M.; Zeng, X.-Q.; Gou, R.; Cui, L.; Li, C.-J. A modular synthetic strategy for functional macrocycles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7214–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Meng, Q. Heparin reversal through an entire encapsulation strategy by giant macrocycles. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2024, 5, 102044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.-Q.; Yu, W.-F.; Liu, J.-B.; Tang, D.-L.; Yang, L.; Chen, X. Oxidative cell death in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Li, Z.-Y.; Du, J.; Sun, J.; Feng, W.; Li, D.-F.; Liu, S.-S.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.-R.; Amizuka, N.; et al. Dual function of peroxiredoxin I in lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoblast apoptosis via reactive oxygen species and the apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-J.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-Y.; Li, C.-J.; Meng, Q.-B. A giant macrocycle overcomes the post-treatment phototoxicity of photofrin through host−guest complexation. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 13686–13689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, A.; Bakirci, H.; Nau, W.M. Label−free continuous enzyme assays with macrocycle-fluorescent dye complexes. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Yu, X.; Lin, S.; Fang, Z.; Li, S.; Xie, L.; Zheng, Z.; Meng, Q. Supramolecular Detoxification Approach of Endotoxin Through Host–Guest Complexation by a Giant Macrocycle. Molecules 2025, 30, 3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153188
Chen J, Yu X, Lin S, Fang Z, Li S, Xie L, Zheng Z, Meng Q. Supramolecular Detoxification Approach of Endotoxin Through Host–Guest Complexation by a Giant Macrocycle. Molecules. 2025; 30(15):3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153188
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Junyi, Xiang Yu, Shujie Lin, Zihan Fang, Shenghui Li, Liguo Xie, Zhibing Zheng, and Qingbin Meng. 2025. "Supramolecular Detoxification Approach of Endotoxin Through Host–Guest Complexation by a Giant Macrocycle" Molecules 30, no. 15: 3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153188
APA StyleChen, J., Yu, X., Lin, S., Fang, Z., Li, S., Xie, L., Zheng, Z., & Meng, Q. (2025). Supramolecular Detoxification Approach of Endotoxin Through Host–Guest Complexation by a Giant Macrocycle. Molecules, 30(15), 3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153188





