Influencing Factors of Hexavalent Chromium Speciation Transformation in Soil from a Northern China Chromium Slag Site
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Pollution Status of Chromium (VI) in the Chromium Slag Site in North China
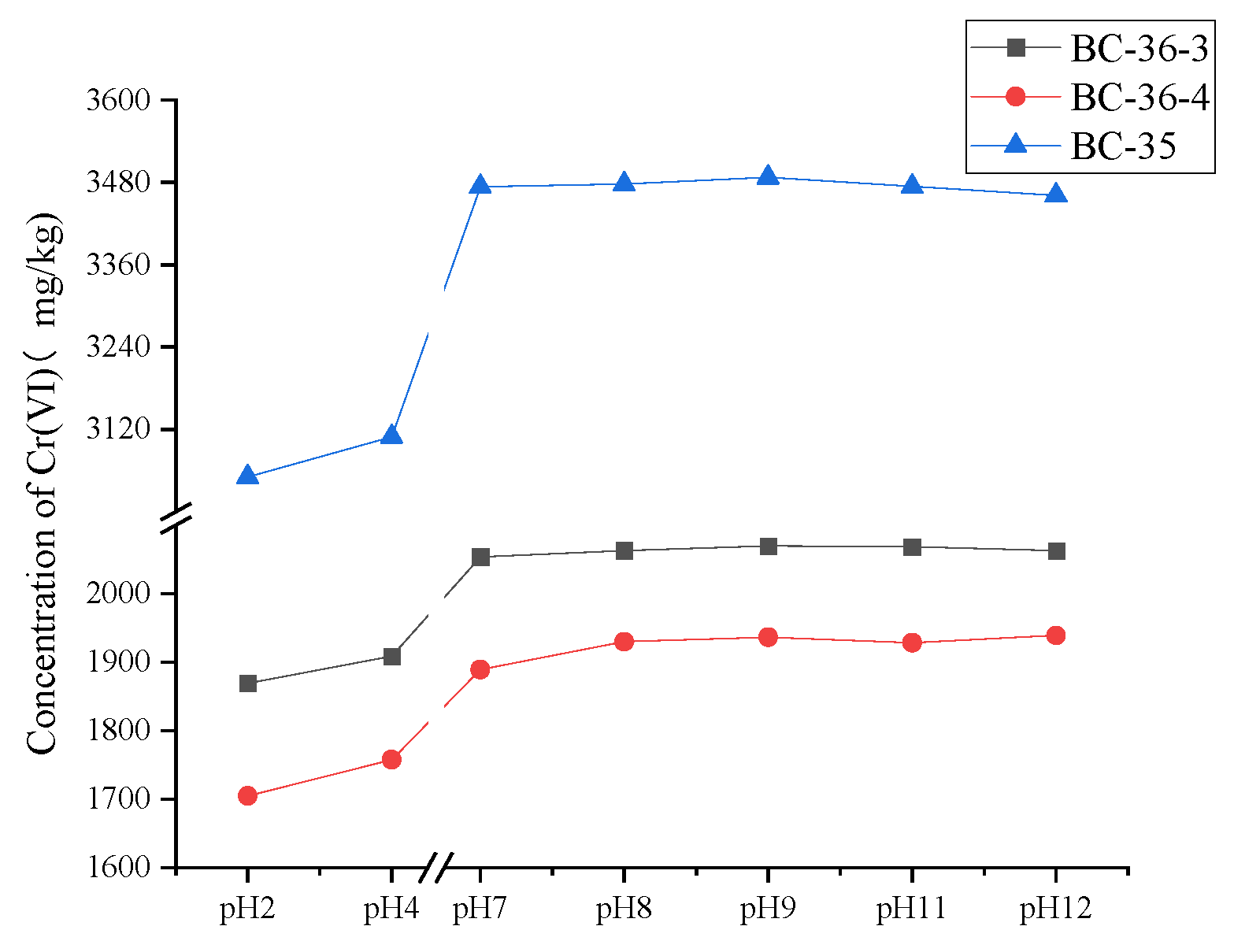
2.2. Influence of PH on Cr(VI)
2.3. Influence of Organic Matter on Cr(VI) Behavior
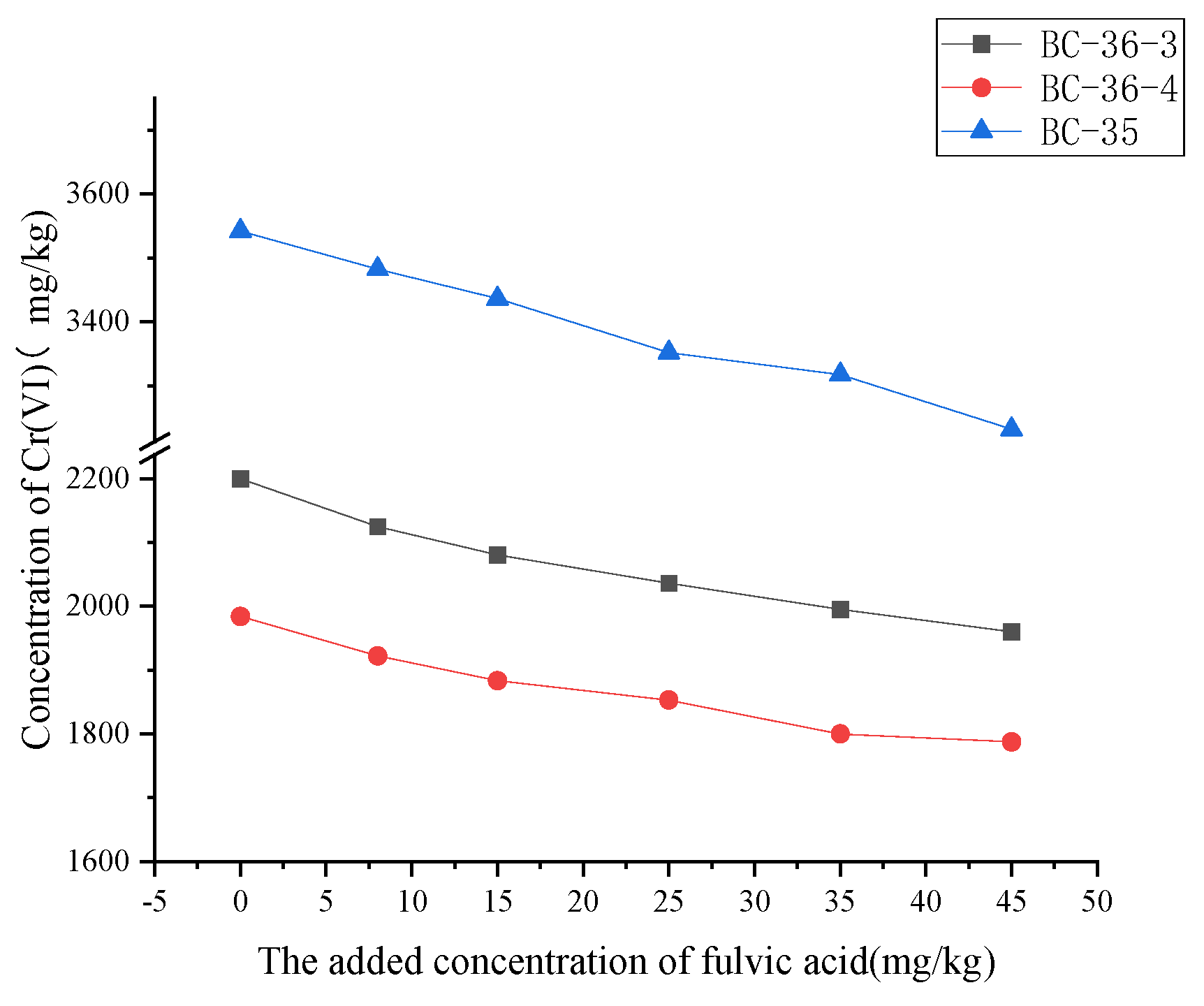
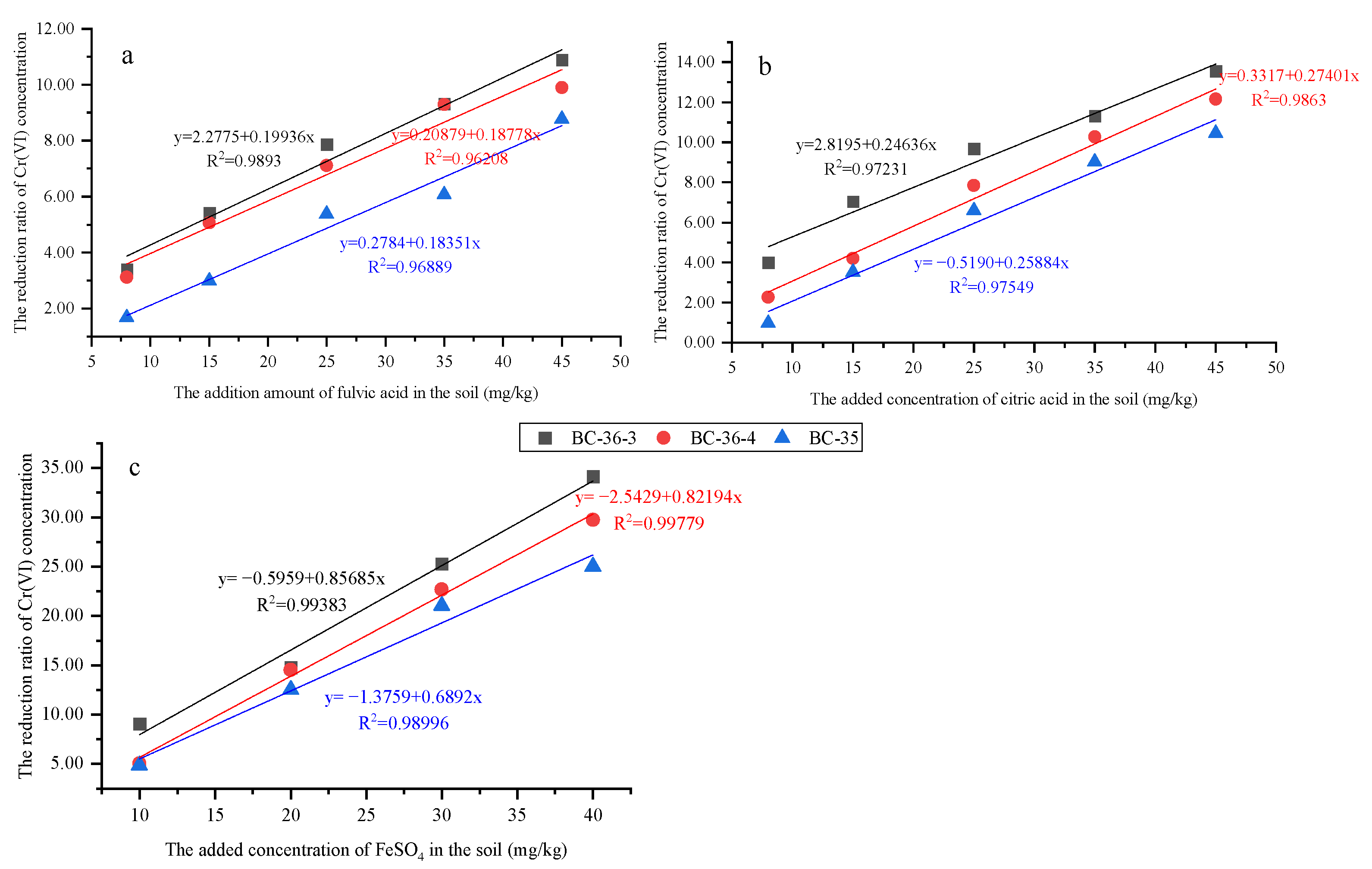
2.3.1. Influence of Fulvic Acid on Cr(VI)
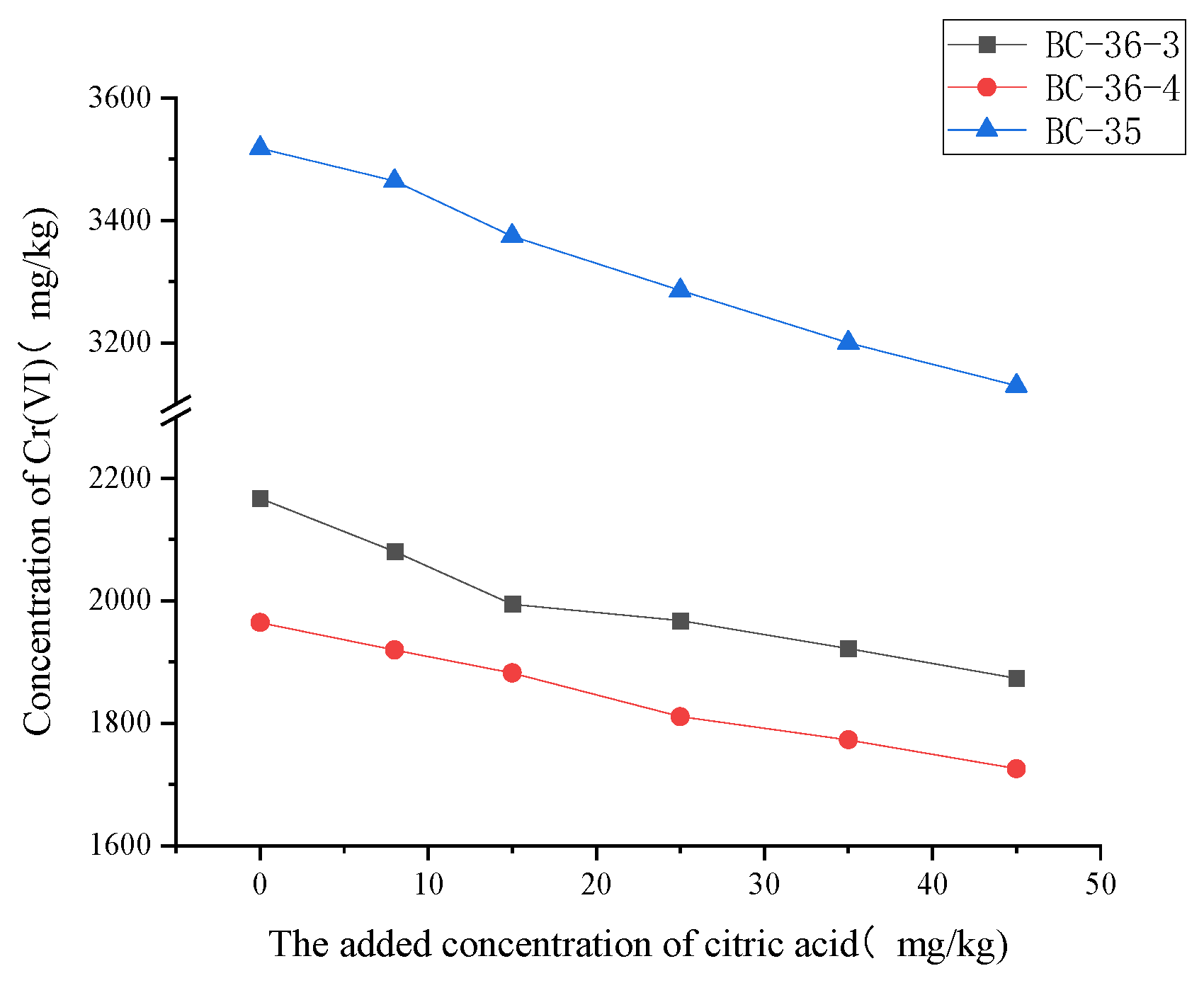
2.3.2. Influence of Citric Acid on Cr(VI)
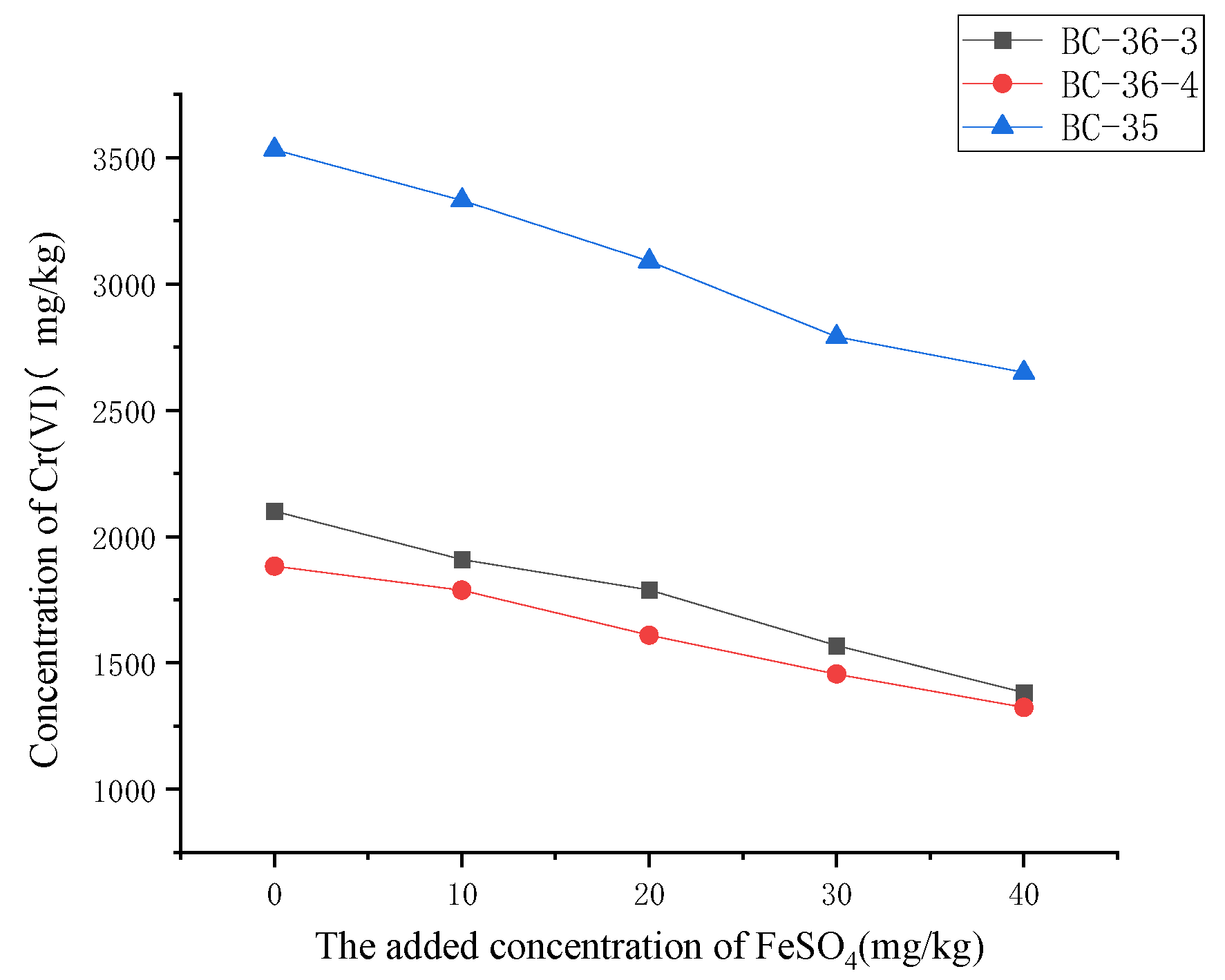
2.4. Influence of FeSO4 on Cr(VI)
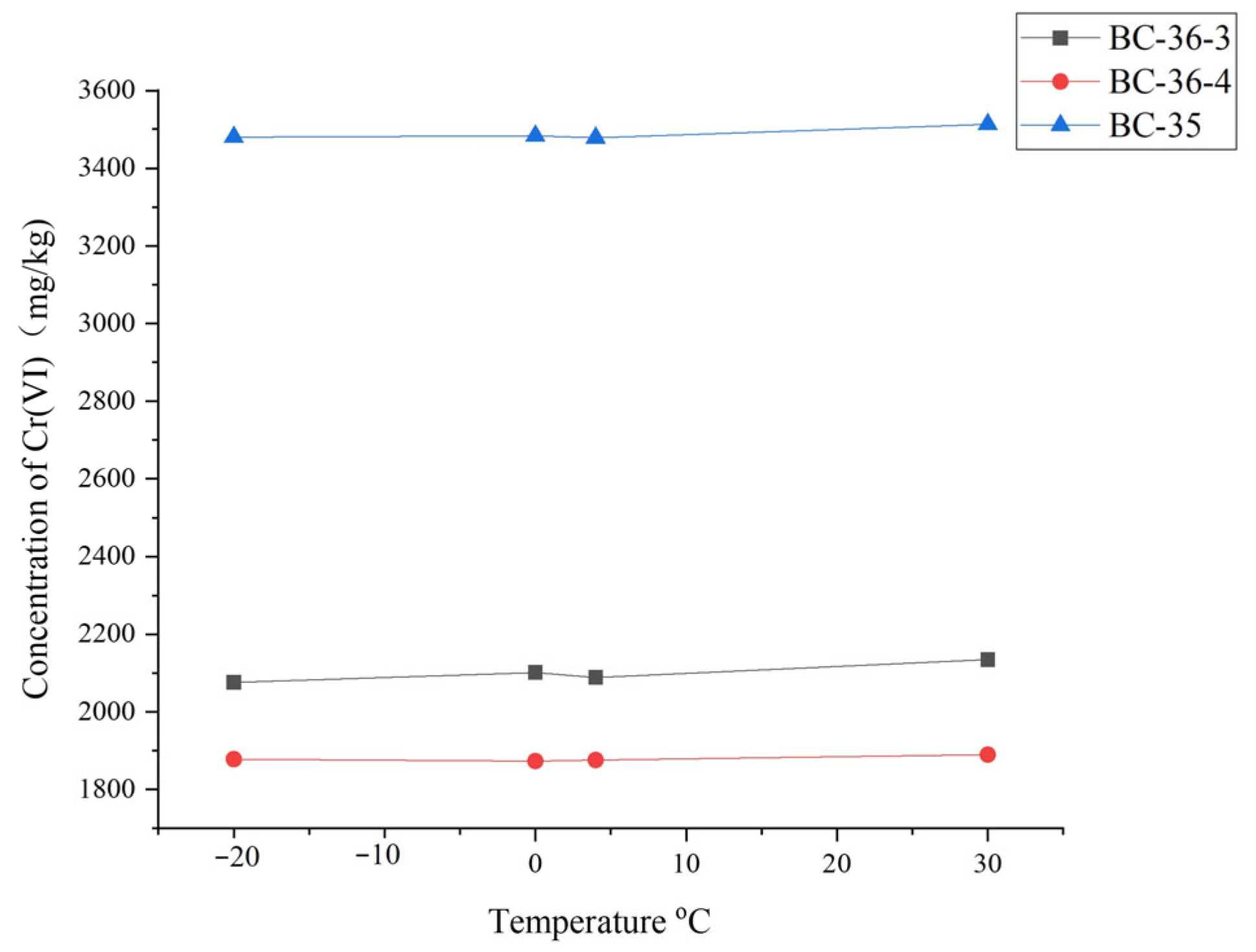
2.5. Influence of Temperature on Cr(VI)
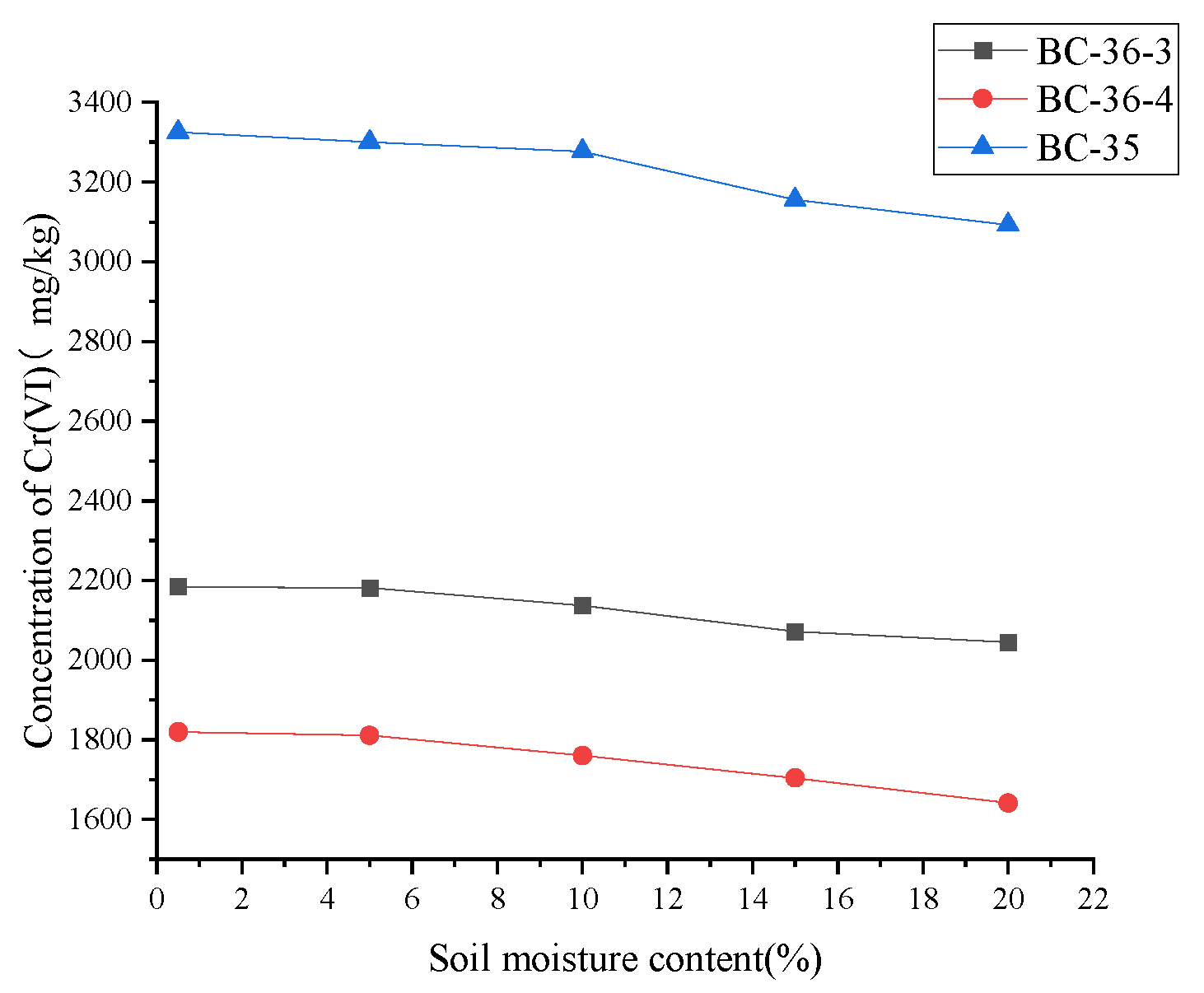
2.6. Influence of Soil Moisture on Cr(VI)
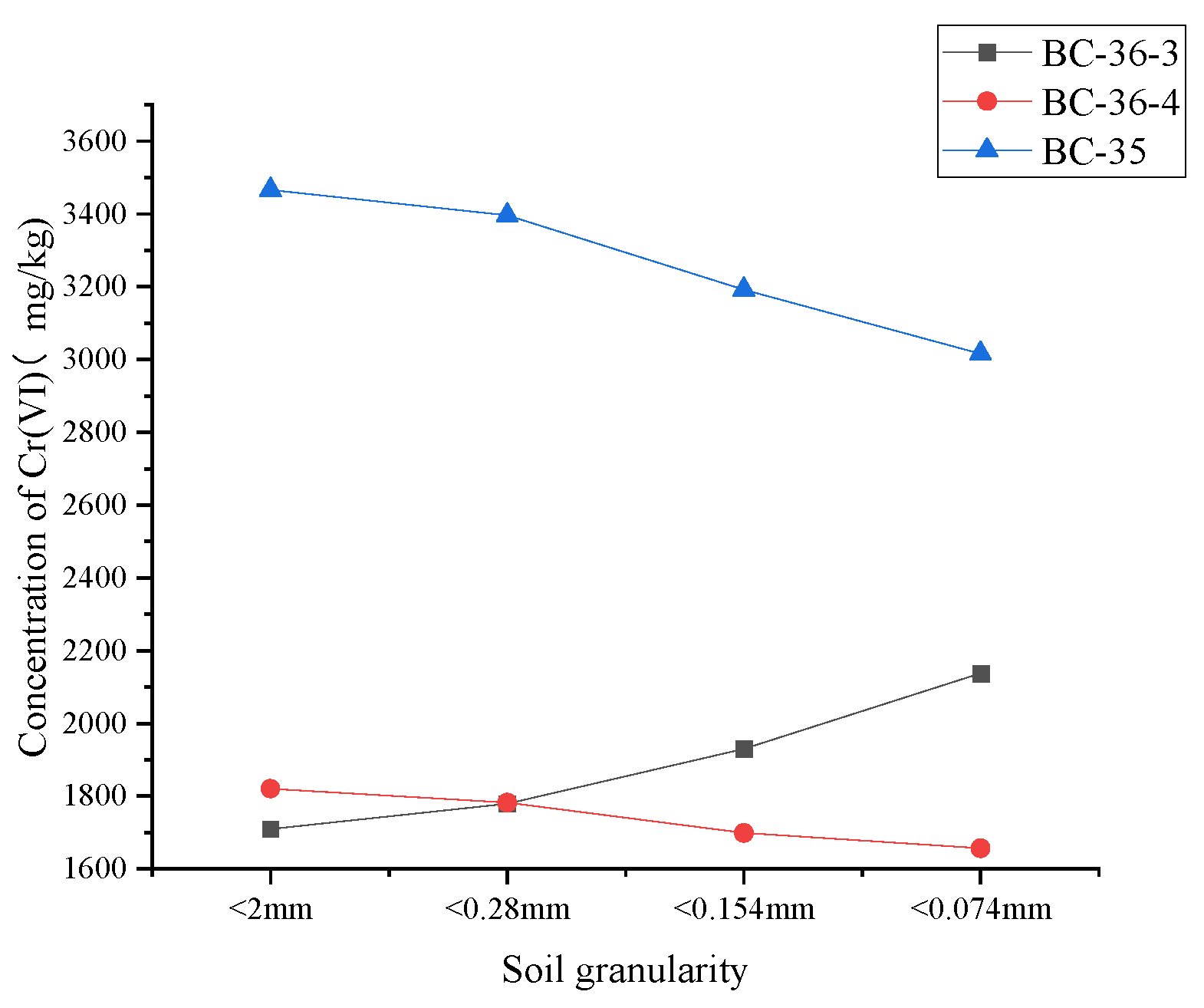
2.7. Influence of Soil Grain-Size Composition on Cr(VI)
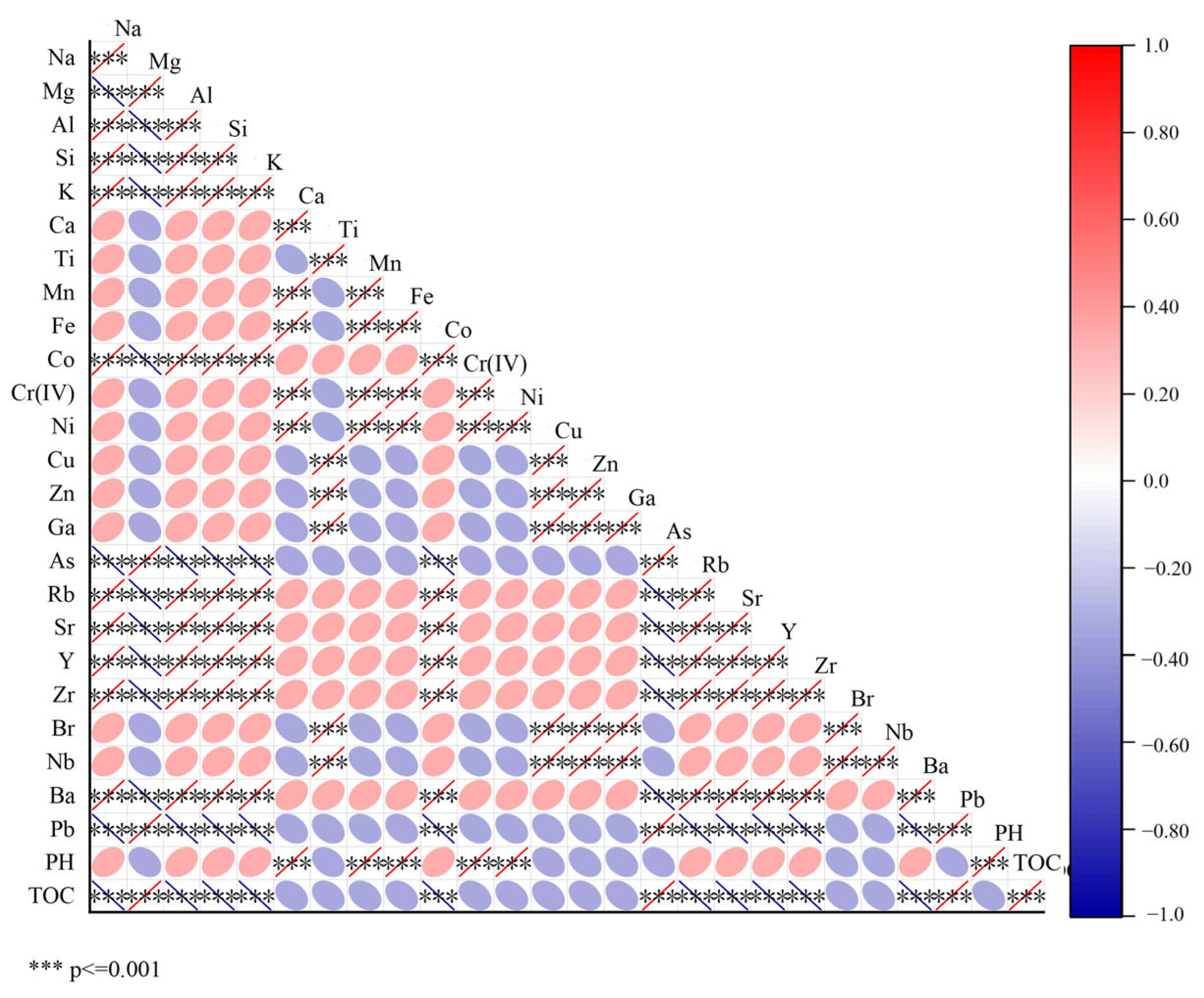
2.8. Correlation Between Chromium and Other Elements
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Soil Sample Collection
3.2. Instruments and Reagents
3.3. Determination of Basic Soil Properties
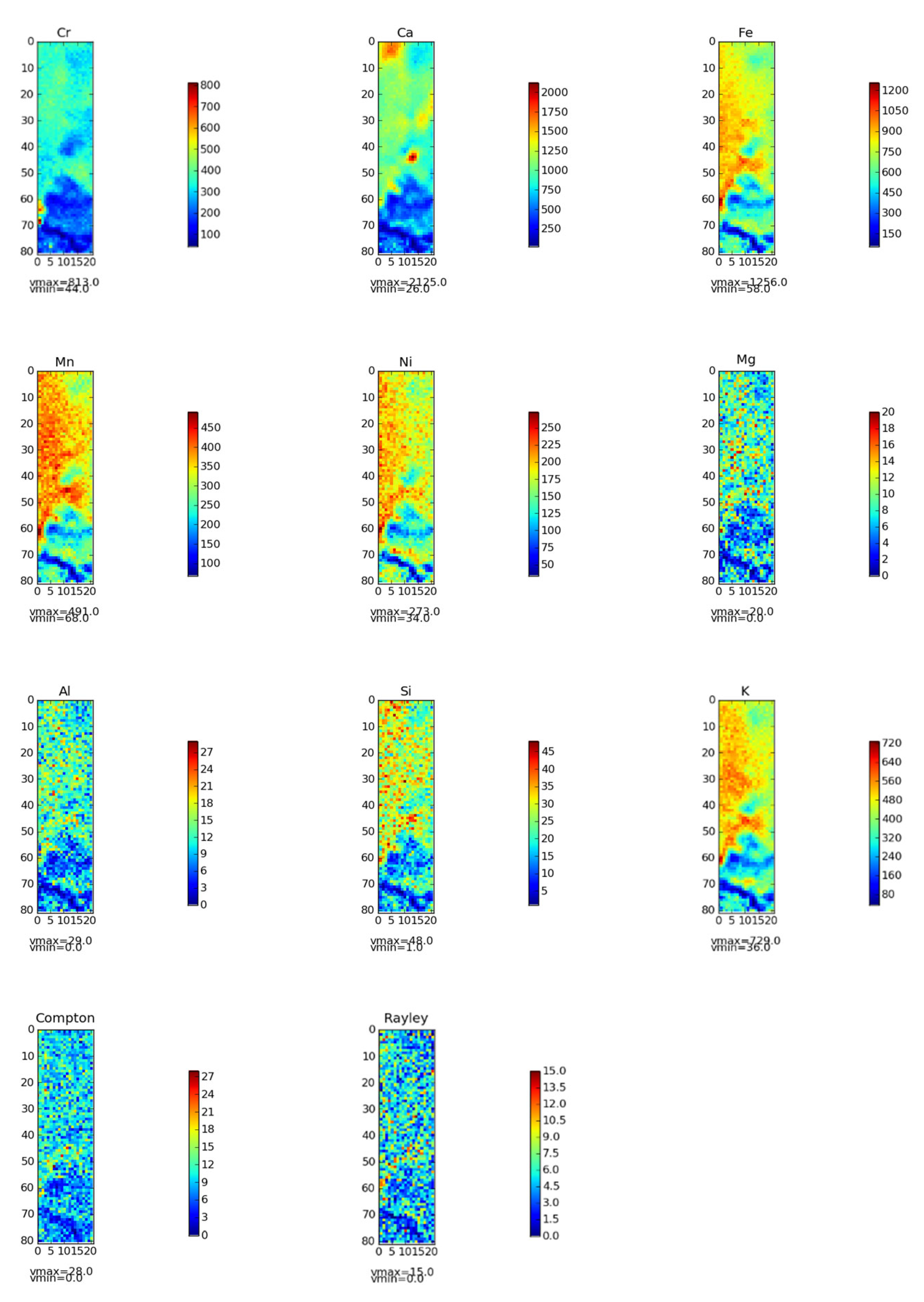
3.4. Soil Element Distribution Determination
3.5. Setting of Experimental Conditions for Controlled Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ardila, P.A.R.; Alonso, R.Á.; Valsero, J.J.D.; García, R.M.; Cabrera, F.Á.; Cosío, E.L.; Laforet, S.D. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in marine sediments from southwest of Mallorca island, Spain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 16852–16866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, L.; Li, D.; Yin, Y.; Li, D.; Xu, G.; Zhao, Z.; Li, S. Characterization of chromium waste form based on biocementation by microbacterium sp. GM-1. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 56, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.K.; Nair, V.K.; Dalvi, V.; Dhali, S.; Malik, A.; Pant, K.K. Field-scale assessment of soil, water, plant, and soil microbiome in and around Rania-Khan Chandpur Chromium contaminated site, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 467, 133747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L.; Chen, X.; Qiu, H.; Gao, B.; Cao, X. Migration and transformation of chromium in unsaturated soil during groundwater table fluctuations induced by rainfall. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y. Research on speciation and bioavailability of chromium in environment and analysis techniques: A review. Rock Miner. Anal. 2025, 44, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, D.M.; Shay, E.C.; Scott, P.K. Health-based soil action levels for trivalent and hexavalent chromium: A comparison with state and federal standards. J. Soil Contam. 1997, 6, 595–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hou, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, L. Estimation of heavy metal soil contamination distribution, hazard probability, and population at risk by machine learning prediction modeling in Guangxi, China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 330, 121607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, C.; Zang, X.; Li, B. Quantifying the influence of soil factors on the migration of chromium (VI). Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 155, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Huang, X.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; Wei, Y. A review of the formation of Cr(VI) via Cr(III) oxidation in soils and groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-C.; Chen, K.-Y.; Ahmed, M.M.M.; Syu, C.H.; Liu, Y.T.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Jien, S.H.; Tzou, Y.M. Photochemical oxidation of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) in the presence of Fe(III): Influence of Fe(III) concentration and UV wavelength. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 485, 136852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Mondal, D.; Mukherjee, D.; Chakraborty, N. Hexavalent chromium induced bioaccumulation, oxidative responses and histological anomalies in freshwater carp Labeo rohita (Hamilton, 1822). BioMetals 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, M.; Anand, U.; Thiruvenkataswamy, S.; Babu, H.W.S.; Narayanasamy, A.; Prajapati, V.K.; Tiwari, C.K.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V.; Bontempi, E.; Sonne, C.; et al. A review of chromium (Cr) epigenetic toxicity and health hazards. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renu, K.; Chakraborty, R.; Myakala, H.; Koti, R.; Famurewa, A.C.; Madhyastha, H.; Vellingiri, B.; George, A.; Valsala Gopalakrishnan, A. Molecular mechanism of heavy metals (Lead, Chromium, Arsenic, Mercury, Nickel and Cadmium)—Induced hepatotoxicity—A review. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.H.; Liu, W.J.; Wang, W.; Yang, J.H.; He, M.L.; Qiu, J.G.; Jiang, B.H. m6A RNA methyltransferase METTL16 induces Cr(VI) carcinogenesis and lung cancer development through glutamine biosynthesis and GLUL expression. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Braver-Sewradj, S.P.; van Benthem, J.; Staal, Y.C.M.; Ezendam, J.; Piersma, A.H.; Hessel, E.V.S. Occupational exposure to hexavalent chromium. Part II. Hazard assessment of carcinogenic effects. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 126, 105045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, C.; Yan, S.; Yin, J.; Shan, J. Source, distribution, and geochemical processes of geogenic high chromium groundwater around the world: A critical review. J. Hydrol. 2024, 638, 131480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molz, P.; Molz, W.A.; Dallemole, D.R.; Weber, A.F.; Salvador, M.; Prá, D.; Franke, S.I.R. Potential ameliorative effects of chromium supplementation on glucose metabolism, obesity, and genomic stability in prediabetic rat model. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 1893–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniek, H.Z.; Król, E.; Wójciak, R.W. The Interactive Effect of high doses of chromium(III) and different iron(III) levels on the carbohydrate status, lipid profile, and selected biochemical parameters in female wistar rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Mei, L.; Yang, D.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Trivalent chromium ameliorates lipid accumulation and enhances glucose metabolism in the high-NEFA environment of bovine hepatocytes by regulating PI3K/AKT pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 26898–26914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ohgami, N.; Al Hossain, M.M.A.; Tazaki, A.; Tsuchiyama, T.; He, T.; Aoki, M.; Ahsan, N.; Akhand, A.A.; Kato, M. Decreased hearing levels at frequencies for understanding speech in tannery workers exposed to a high level of trivalent chromium in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Sun, K.; Xu, D.; Gao, B. Kinetic process of Cr(III) in contaminated soils characterized by diffusive gradients in thin films technique. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Fang, W.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.; Gu, X.; Chen, H.; Luo, J. Effects of nZVI on the migration and availability of Cr(VI) in soils under simulated acid rain leaching conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 134985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Tan, X.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Ding, C. The interaction of ZnO nanoparticles, Cr(VI), and microorganisms triggers a novel ROS scavenging strategy to inhibit microbial Cr(VI) reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvoynenko, O.; Lo, S.L.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, G.W.; Tsai, H.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, J.K. Speciation analysis of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) in water with surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Samuel, B.; Tan, W.; Xi, B.; Chen, H. Crucial role of humic substance type in Cr(VI) reduction by humic substance-Fe(III) coprecipitates but not in adsorption. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Song, Z.; Jeyakumar, P.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H. A critical review on bioremediation technologies for Cr(VI)-contaminated soils and wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1027–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Hao, R.; Shan, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Lu, A. Mechanism of Cr(VI) removal by efficient Cr(VI)-resistant bacillus mobilis CR3. World J Microb Biot. 2023, 40, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, W.; Gong, K.; Fu, M.; Saif, S.; Peng, C.; Zhang, W. Polyamide microplastics as better environmental vectors of Cr(VI) in comparison to polyethylene and polypropylene microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Si, R.; Sun, D. Research on the structure-activity relationship of Fe-Cr alloy in marine environment based on synchrotron radiation: Effect of Cr content. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 26, 101370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Huang, Q.; Lou, Z.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Y. Cr migration potential and species properties in the soil profile from a chromate production site in the groundwater depression cone area. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 109, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniewska, B.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B. Speciation of chromium in alkaline soil extracts by an ion-pair reversed phase HPLC-ICP MS method. Molecules 2019, 24, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Wei, G.; Cao, T.; Shao, B.; Guan, X.; Strathmann, T.J. Insights into the oxidation of organic cocontaminants during Cr(VI) reduction by sulfite: The overlooked significance of Cr(V). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Q.; Huang, P.; Zheng, C.; Liao, Q.; Yang, W. Reductive materials for remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittbrodt, P.R.; Palmer, C.D. Effect of temperature, ionic strength, background electrolytes, and Fe(III) on the reduction of hexavalent chromium by soil humic substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2470–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.X.X.; Cui, J.Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, K.W.; Jiang, J.; Xu, R.K. Effects of soil pH and organic carbon content on in vitro Cr bioaccessibility in Ultisol, Alfisol, and Inceptisol. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.G.; Fimmen, R.L.; Chin, Y.P. Reduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) by Fe(II) in the presence of fulvic acids and in lacustrine pore water. Chem. Geol. 2009, 262, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C. Remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil by sulfidated zero-valent iron: The effect of citric acid as eluant and modifying agent. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meichtry, J.M.; Brusa, M.; Mailhot, G.; Grela, M.A.; Litter, M.I. Heterogeneous photocatalysis of Cr(VI) in the presence of citric acid over TiO2 particles: Relevance of Cr(V)–citrate complexes. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 71, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Chen, D.; Gao, N.; Huang, M.; Ye, X. Citric acid secretion from rice roots contributes to reduction and immobilization of Cr(VI) by driving microbial sulfur and iron cycle in paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.; Yoo, J.-C.; Baek, K. Synergistic and inhibitory reduction of Cr(VI) by montmorillonite, citric acid, and Mn(II). J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.W.; Tang, Z.S.; Guo, R.F.; Chen, S.Q. Soil surface catalysis of Cr(VI) reduction by citric acid. Environ. Prog. 2008, 27, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.; Shozugawa, K.; Matsuo, M. Reduction process of Cr(VI) by Fe(II) and humic acid analyzed using high time resolution XAFS analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 285, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Palma, L.; Gueye, M.T.; Petrucci, E. Hexavalent chromium reduction in contaminated soil: A comparison between ferrous sulphate and nanoscale zero-valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 281, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, D.L.; Chan, P.G. Reduction of hexavalent chromium by ferrous iron. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Xue, Q.; Li, J.S.; Wei, M.L.; Wang, P.; Liu, L.; Wan, Y. Effect of ferrous sulfate dosage and soil particle size on leachability and species distribution of chromium in hexavalent chromium-contaminated soil stabilized by ferrous sulfate. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2019, 38, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; He, Y.; Zhu, K.F.; Zhang, Z.; Lou, W.; Zhang, K.N.; Chen, Y.G.; Wang, Q. Experimental study on injection of ferrous sulphate for remediation of a clayey soil contaminated with hexavalent chromium. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yun, E.T.; Kim, H.S.; Ham, S.Y.; Sun, P.F.; Jang, Y.S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, N.P.; Park, H.D. Chromium (VI) reduction by two-chamber bioelectrochemical system with electrically conductive wall. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 440, 141738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerge, I.J.; Hug, S.J. Influence of mineral surfaces on chromium(VI) reduction by iron(II). Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 4285–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Zhong, J.; Ma, D.; Tang, C.; Hu, X. Lab-scale evaluation of the microbial bioremediation of Cr(VI): Contributions of biosorption, bioreduction, and biomineralization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22359–22371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhou, S.; Gao, X. Adsorption mechanism of Cr(VI) on woody-activated carbons. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, S.P.; Parakh, S.K.; Tong, Y.W. Health hazards of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) and its microbial reduction. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4923–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, B.; Deng, B. Influences of water vapor on Cr(VI) reduction by gaseous hydrogen sulfide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4771–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.; Abad, S.Q.; Rodríguez-González, P.; Alonso, J.I.G.; Beone, G.M. Quantification of Cr(VI) in soil samples from a contaminated area in northern Italy by isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 17569–17576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Xiang, Q.; Wu, T.; Jiang, G.; Sun, X.; Zhu, M.; Pu, L. Progress and prospect of soil microorganisms and their influencing factors in coastalwetland ecosystem. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Yan, X.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y. Processes of chromium (VI) migration and transformation in chromate production site: A case study from the middle of China. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, G.; Zhao, H.; Wu, D. Partitioning, leachability, and speciation of chromium in the size-fractions of soil contaminated by chromate production. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Song, K.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, L.C.; Yan, X.S.; Zhang, M.M. Characteristics and mechanisms of soil structure damage under salt weathering. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 238, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 1121.3-2006; Soil Testing Part 3: Method for Determination of Soil Mechanical Composition. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Hu, Y.; Xue, Q.; Tang, J.; Fan, X.; Chen, H. New insights on Cr(VI) retention by ferrihydrite in the presence of Fe(II). Chemosphere 2019, 222, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Hu, G.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhuge, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, X. Distinct accumulation of bacterial and fungal residues along a salinity gradient in coastal salt-affected soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 158, 108266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Gao, D.; Yu, M.; Jiang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Feng, X.; Tan, W.; Liu, F.; et al. Characteristics of iron (hydr)oxides and Cr(VI) retention mechanisms in soils from tropical and subtropical areas of China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandeur, D.; Juillot, F.; Morin, G.; Olivi, L.; Cognigni, A.; Webb, S.M.; Ambrosi, J.P.; Fritsch, E.; Guyot, F.; Brown, J.G.E. XANES evidence for oxidation of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) by mn-oxides in a lateritic regolith developed on serpentinized ultramafic rocks of new caledonia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7384–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebien, D.O.P.; Bortolon, L.; Tedesco, M.J.; Bissani, C.A.; Camargo, F.A.O. Environmental factors affecting chromium-manganese oxidation-reduction reactions in soil. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Giammar, D. Interplay of transport processes and interfacial chemistry affecting chromium reduction and reoxidation with iron and manganese. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Guo, M.; Zhao, S.; Lu, T. Efficient reduction of hexavalent chromium by Fe-Mn bimetallic nanoparticles: Performance and role of manganese. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 46, 103956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, M.L.; Abernathy, M.J.; Schaefer, M.V.; Lee, I.; Ying, S.C. Inhibition of chromium(III) oxidation through manganese(IV) oxide passivation and iron(II) abiotic reduction. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2023, 7, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofie, O.O.; Pleysier, J. Ion exchange involving potassium–calcium and magnesium–calcium in soil and organic matter fractions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2004, 35, 2417–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Shen, Y.T.; Chen, J.R.; Zhang, B.K.; Pan, M.; Yang, Z.P.; Zhu, Y. Determination of high-content hexavalent chromium in chromium slag field soils by alkaline extraction-inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry. Rock Miner. Anal. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Chen, J.R.; Shen, Y.T. Analysis of major and minor elements in soil samples from cr polluted areas by powder compression X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. Rock Miner. Anal. 2025; accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.Q.; Zhan, X.C.; Li, G.H. X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.T. Determination of major, minor and trace elements in soils by polarized energy X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and the application to vertical distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2012, 32, 3117–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Chu, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Bo, Y.; Zhan, X.; et al. Determination of Pb, As, Cd and trace elements in polluted soils near a lead–zinc mine using polarized X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and the characteristics of the elemental distribution in the area. X-Ray Spectrom. 2012, 41, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.F.; Shen, Y.T. Distribution and speciation of lead in moss collected from a lead—zinc mining area by micro—x-ray fluorescence and x-ray absorption near edge structure analysis. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
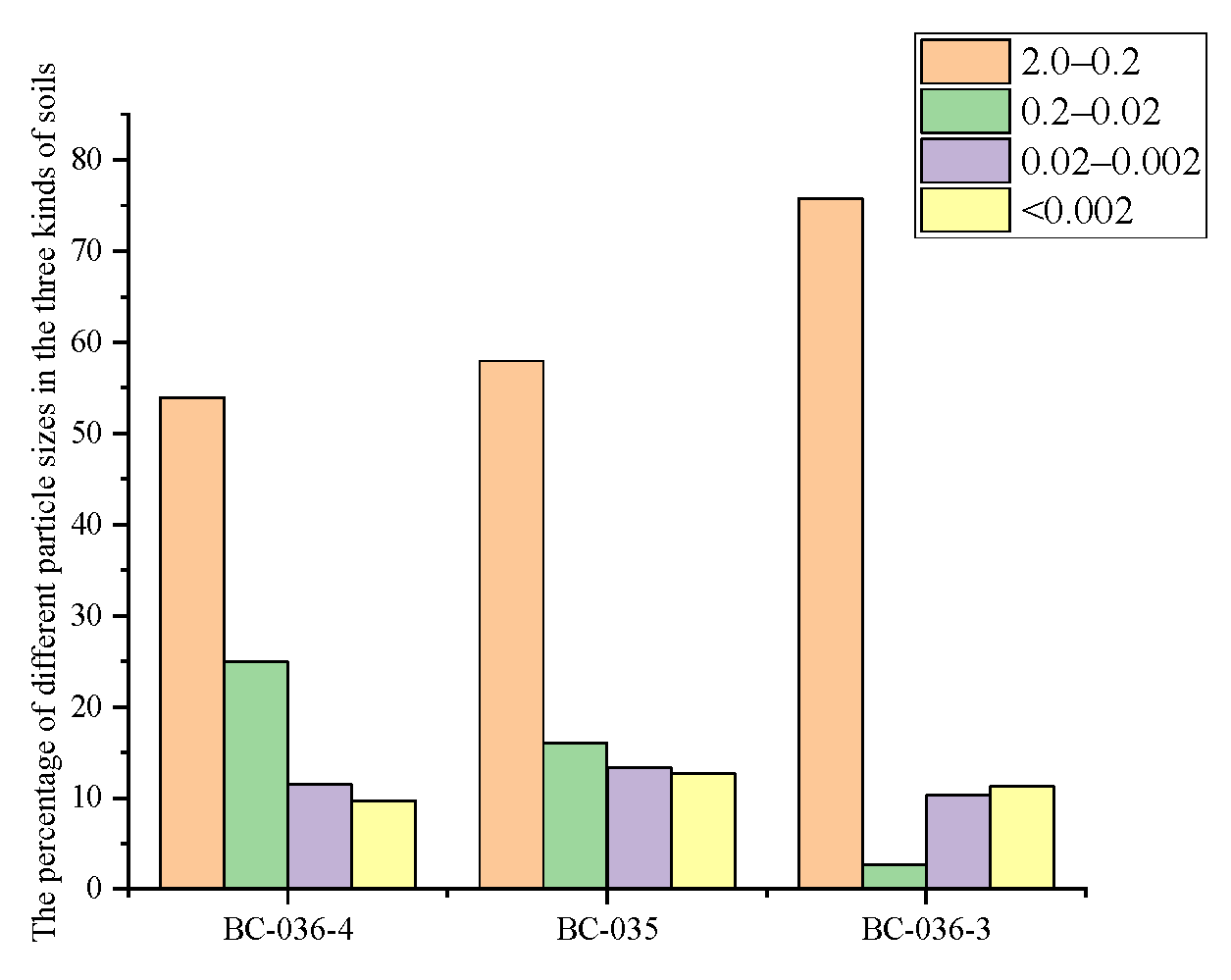
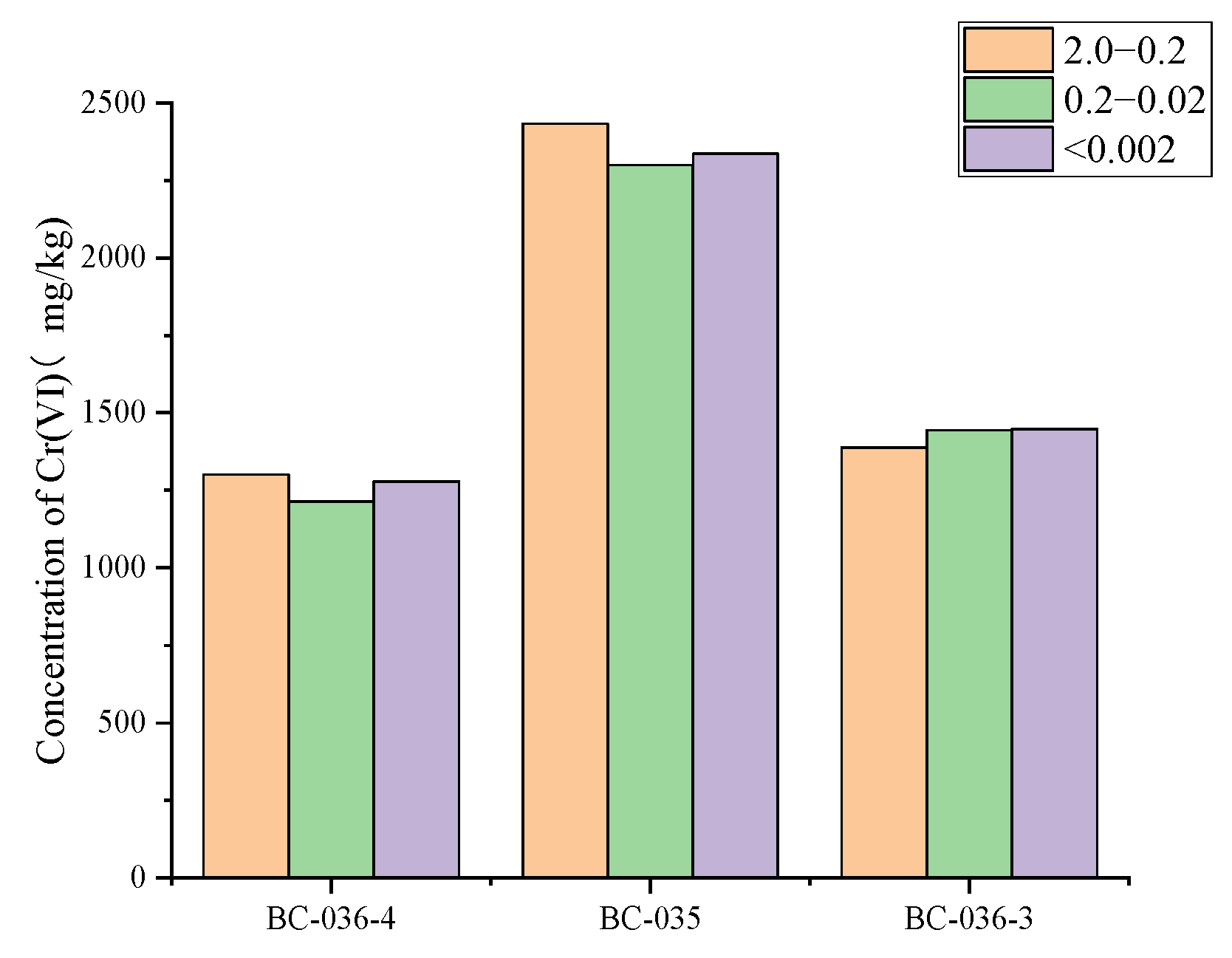
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, S.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Jia, J.; Pan, M.; Yang, Z.; Cao, J.; Shen, Y. Influencing Factors of Hexavalent Chromium Speciation Transformation in Soil from a Northern China Chromium Slag Site. Molecules 2025, 30, 3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153076
Zhu S, Chen J, Zhu Y, Zhang B, Jia J, Pan M, Yang Z, Cao J, Shen Y. Influencing Factors of Hexavalent Chromium Speciation Transformation in Soil from a Northern China Chromium Slag Site. Molecules. 2025; 30(15):3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153076
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Shuai, Junru Chen, Yun Zhu, Baoke Zhang, Jing Jia, Meng Pan, Zhipeng Yang, Jianhua Cao, and Yating Shen. 2025. "Influencing Factors of Hexavalent Chromium Speciation Transformation in Soil from a Northern China Chromium Slag Site" Molecules 30, no. 15: 3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153076
APA StyleZhu, S., Chen, J., Zhu, Y., Zhang, B., Jia, J., Pan, M., Yang, Z., Cao, J., & Shen, Y. (2025). Influencing Factors of Hexavalent Chromium Speciation Transformation in Soil from a Northern China Chromium Slag Site. Molecules, 30(15), 3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153076







