One-Pot Synthesis of Phenylboronic Acid-Based Microgels for Tunable Gate of Glucose-Responsive Insulin Release at Physiological pH
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
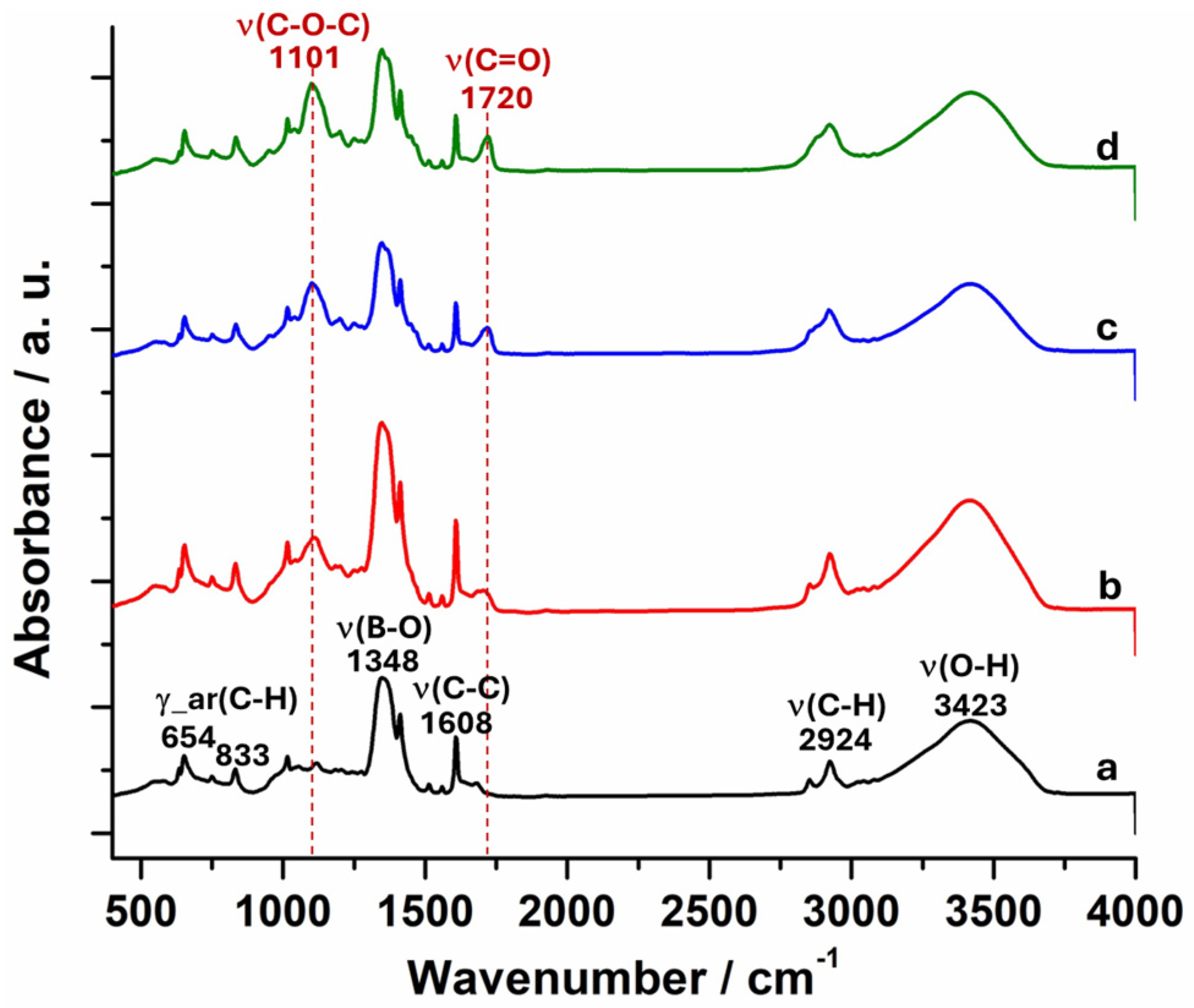
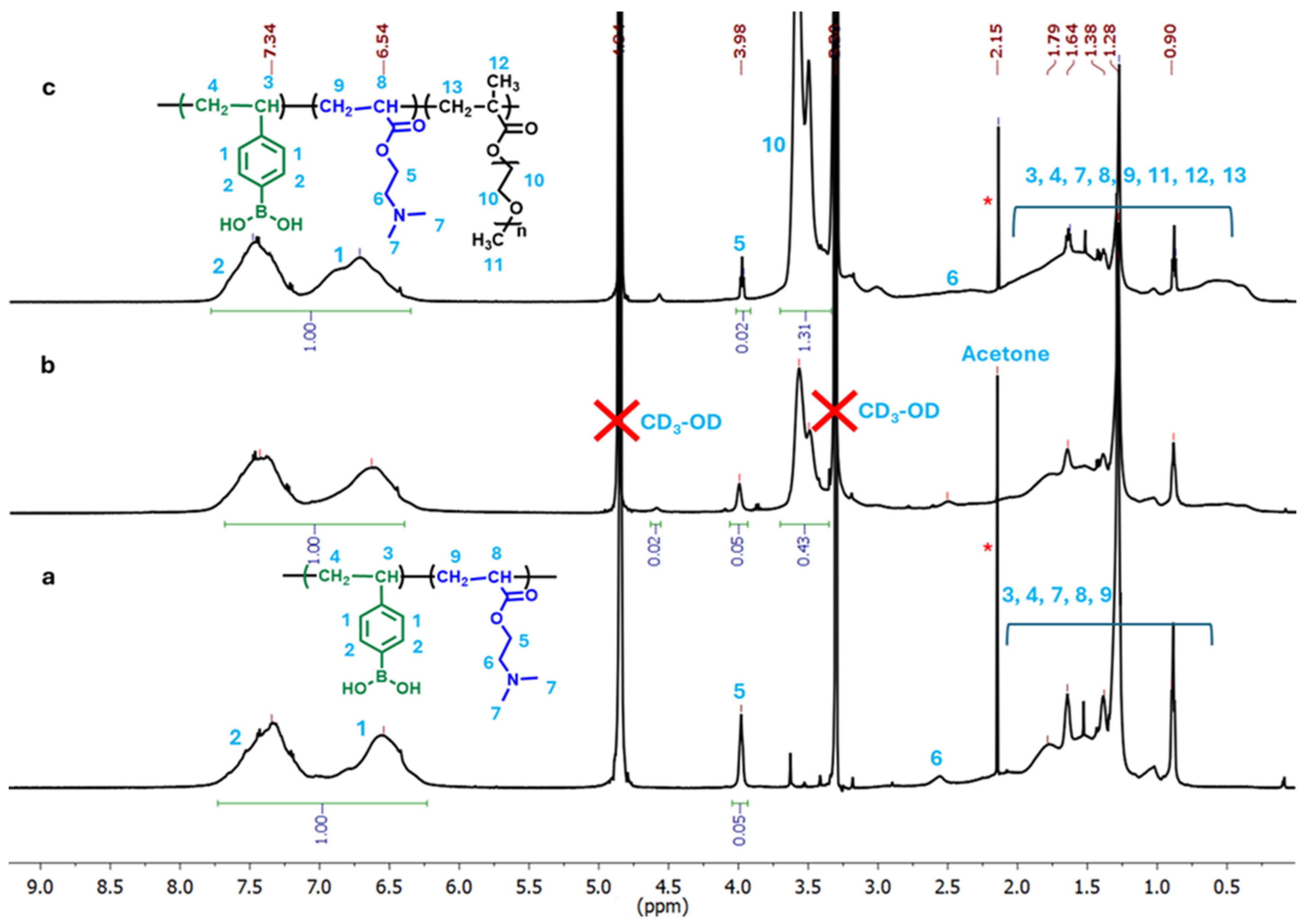
2.1. Synthesis and Compositions of p(VPBA-DMAEA-MEO5MA) Microgels
2.2. Size and Morphology of p(VPBA-DMAEA-MEO5MA) Microgels
2.3. pH-Responsive Volume Phase Transition of Microgels
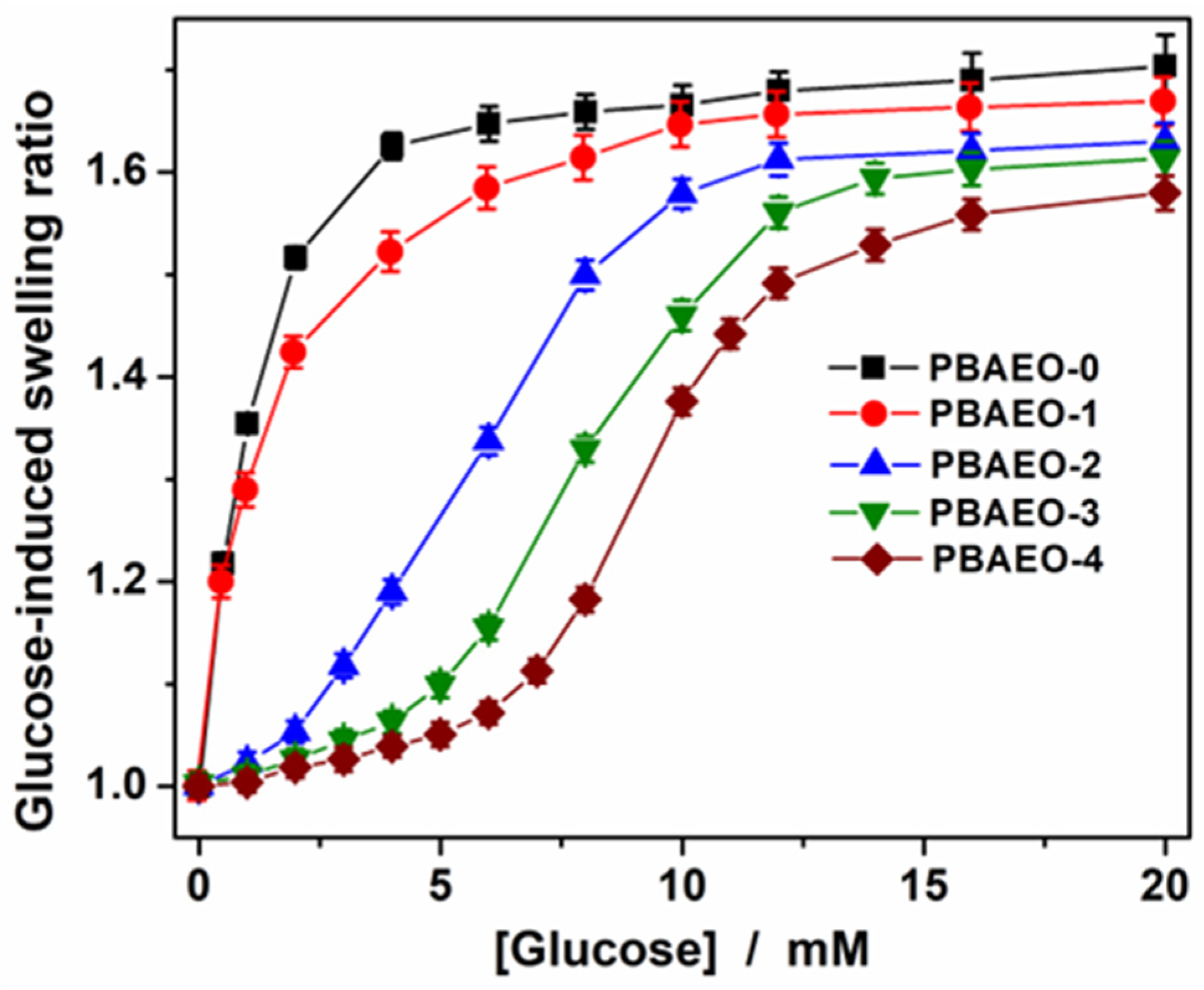
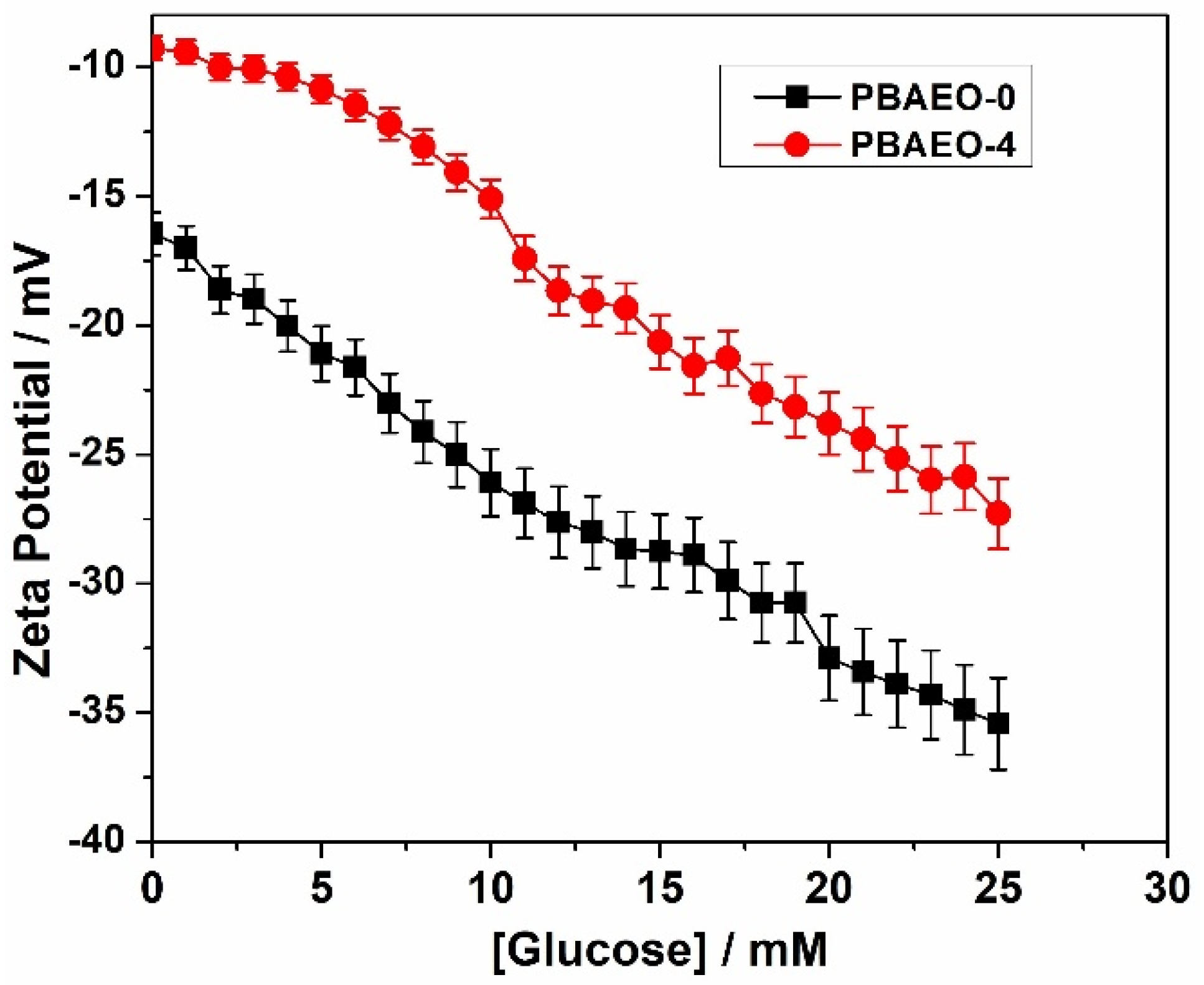
2.4. Tuning the Glucose-Responsive Volume Phase Transitions
2.5. Insulin Loading and In Vitro Glucose-Regulated Insulin Release
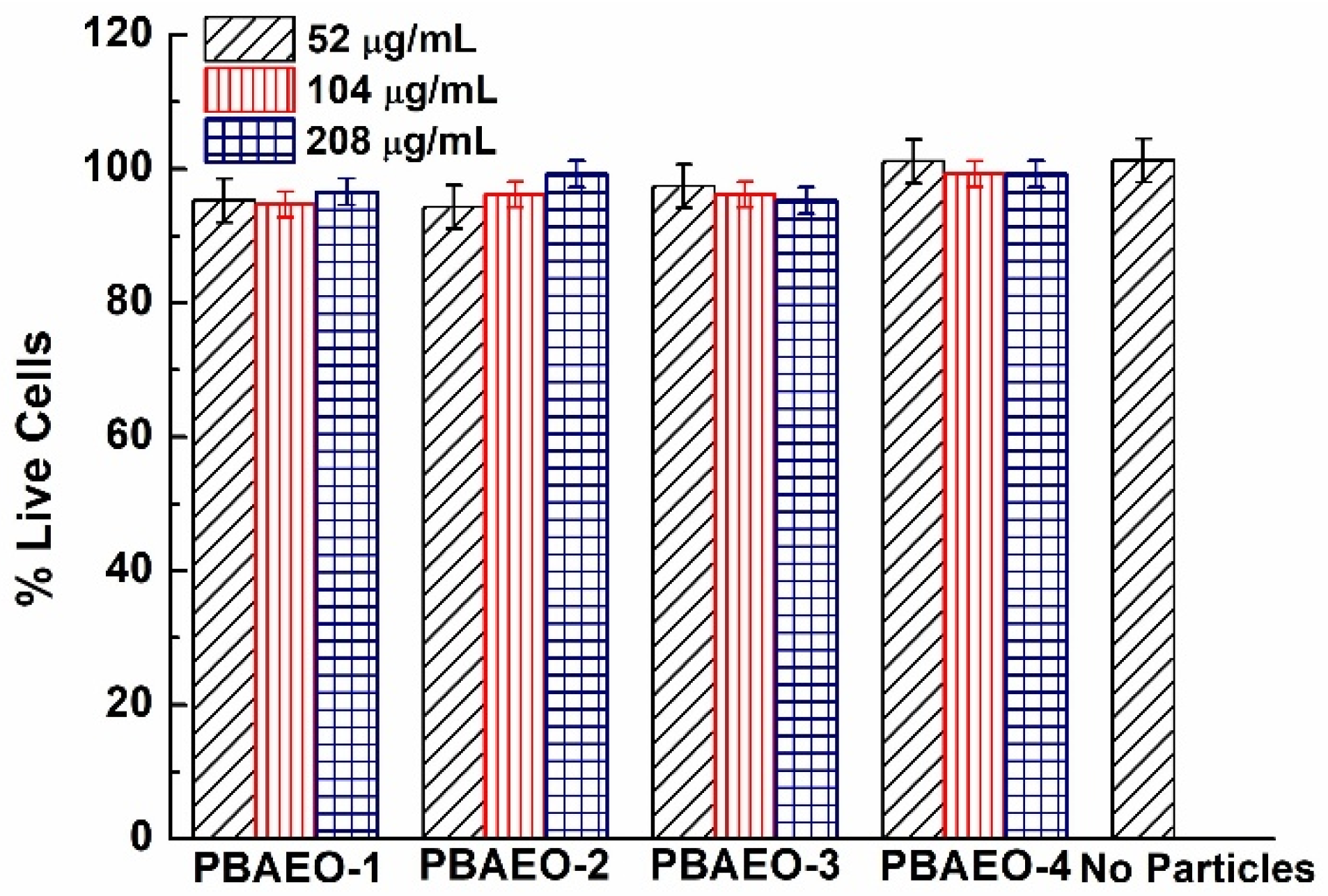
2.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of p(VPBA-DMAEA-MEO5MA) Microgels
3.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Studies
3.4. Insulin Loading and In Vitro Release
3.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies
3.6. Other Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, N.J.; Lockwood, G.P.; Heffernan, S.J.; Daymond, J.; Ngu, M.; Narayanan, R.K.; Westwood, L.J.; Mohanty, B.; Esser, L.; Williams, C.C.; et al. Oral nanotherapeutic formulation of insulin with reduced episodes of hypoglycaemia. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 19, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Su, B.; Liu, D.; Webber, M.J. Managing diabetes with hydrogel drug delivery. Adv. Therap. 2024, 7, 2300127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mukherjee, S.; Yi, J.; Banerjee, P.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, S. Biocompatible chitosan–carbon dot hybrid nanogels for NIR-imaging-guided synergistic photothermal–chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18639–18649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, R.; Randhawa, G.; Kim, D.; Simpson, M.; Hoare, T. Microgels and nanogels for the delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 1704–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Rudov, A.A.; Schroeder, R.; Portnov, I.; Richtering, W.; Potemkin, I.I.; Pich, A. Distribution of ionizable groups in polyampholyte microgels controls interactions with captured proteins: From blockade and “levitation” to accelerated release. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 1578–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, C.; Carvalho, W.S.P.; Gao, Y.; Serpe, M.J. Triggered small-molecule release from dual-stimuli responsive microgels. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preman, N.K.; Jain, S.; Johnson, R.P. “Smart” polymer nanogels as pharmaceutical carriers: A versatile platform for programmed delivery and diagnostics. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5075–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Kinetics of glucose-induced swelling of P(NIPAM-AAPBA) microgels. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4479–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, H.; Hu, J.; Liu, S. Glucose-regulated insulin release from acid-disintegrable microgels covalently immobilized with glucose oxidase and catalase. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1852–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Dang, T.T.; Ma, M.; Tang, B.C.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, S.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Anderson, D.G. Glucose-responsive microgels integrated with enzyme nanocapsules for closed-loop insulin delivery. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6758–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, F.; Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Lv, J.; Ma, R.; et al. Glucose and H2O2 dual-sensitive nanogels for enhanced glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 9163–9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpatti, L.R.; Facklam, A.L.; Cortinas, A.B.; Lu, Y.C.; Matranga, M.A.; MacIsaac, C.; Hill, M.C.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Microgel encapsulated nanoparticles for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Biomaterials 2021, 267, 120458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniewska, K.; Mackiewicz, M.; Smutok, O.; Gonchar, M.; Katz, E.; Karbarz, M. Enzymatically triggered drug release from microgels controlled by glucose concentration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 6415–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Wang, K.; Du, S.; Chen, L.; Nie, J.; Zhang, W. Design of genipin-crosslinked microgels from concanavalin A and glucosyloxyethyl acrylated chitosan for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; He, J.; Kang, L.; Nie, J.; Yin, R. Regulated basal and bolus insulin release from glucose-responsive core-shell microspheres based on concanavalin A-sugar affinity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Yan, S.; Hu, Y.; Ding, L.; Wu, W. Synthesis and volume phase transition of concanavalin A-based glucose-responsive nanogels. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhou, S. Synthesis and volume phase transitions of glucose-sensitive microgels. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3196–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapeyre, V.; Gosse, I.; Chevreux, S.; Ravaine, V. Monodispersed glucose-responsive microgels operating at physiological salinity. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3356–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancla, C.; Lapeyre, V.; Gosse, I.; Catargi, B.; Ravaine, V. Designed glucose-responsive microgels with selective shrinking behavior. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12693–12701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, T.; Pelton, R. Charge-switching, amphoteric glucose-responsive microgels with physiological swelling activity. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Contraction-type glucose-sensitive microgel functionalized with a 2-substituted phenylboronic acid ligand. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Lu, F.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Q.; Chang, A.; Wu, W. Switchable glucose-responsive volume phase transition behavior of poly(phenylboronic acid) microgels. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 8306–8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Du, X.; Chang, A.; Jiang, X.; Yan, X.; Cao, X.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Wu, W. Bioinspired Synthesis of Poly(phenylboronic acid) microgels with high glucose selectivity at physiological pH. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 6500–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, W.L.A.; Sumerlin, B.S. Synthesis and applications of boronic acid-containing polymers: From materials to medicine. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 1375–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiino, D.; Murata, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Koyama, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y. Preparation and characterization of a glucose-responsive insulin-releasing polymer device. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiino, D.; Murata, Y.; Kubo, A.; Kim, Y.J.; Kataoka, K.; Koyama, Y.; Kikuchi, A.; Yokoyama, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Okano, T. Amine containing phenylboronic acid gel for glucose-responsive insulin release under physiological pH. J. Control. Release 1995, 37, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Miyazaki, H.; Bunya, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y. Totally synthetic polymer gels responding to external glucose concentration: Their preparation and application to on–off regulation of insulin release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 12694–12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Ishii, T.; Nishida, J.; Matsumoto, H.; Kataoka, K.; Miyahara, Y. A synthetic approach toward a self-regulated insulin delivery system. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2124–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Ur-Rahman, K. Advances in phenylboronic acid-based closed-loop smart drug delivery system for diabetic therapy. J. Control. Release 2019, 305, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lin, B.; Zhu, H.; Bi, F.; Xiao, S.; Wang, L.; Gai, G.; Zhao, L. Recent advances in phenylboronic acid-based gels with potential for self-regulated drug delivery. Molecules 2019, 24, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Mitra, N.; Yan, E.C.Y.; Zhou, S. Multifunctional hybrid nanogel for integration of optical glucose sensing and self-regulated insulin release at physiological pH. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4831–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yi, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, S. NIR upconversion fluorescence glucose sensing and glucose-responsive insulin release of carbon dot-immobilized hybrid microgels at physiological pH. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; Wu, Z.; Xia, X.; Li, C. Glucose- and Temperature-Responsive Core–Shell Microgels for Controlled Insulin Release. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 9904–9913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Li, C.; Yu, D. An injectable and glucose-sensitive nanogel for controlled insulin release. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 22788–22796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, S.; Gao, C.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M. Highly stable and degradable multifunctional microgel for self-regulated insulin delivery under physiological conditions. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 6498–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, G.; Ma, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lv, J.; Shi, L. Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) and phenylboronic acid (PBA) functionalized nanogels for efficient encapsulation and controlled release of insulin. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 4, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Choe, K.; Jeong, Y.; Yoo, J.; Lee, S.M.; Park, J.; Kim, P.; Kim, Y. Establishment of a controlled insulin delivery system using a glucose-responsive double-layered nanogel. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 14482–14491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xiao, C.; Ding, J.; He, P.; Tang, Z.; Pang, X.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Facile one-pot synthesis of glucose-sensitive nanogel via thiol-ene click chemistry for self-regulated drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6535–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lin, A.; Yuan, X.; Li, H.; Ma, D.; Xue, W. Glucose-sensitive and blood-compatible nanogels for insulin-controlled release. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, S. A fluorescent responsive hybrid nanogel for closed loop control of glucose. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2012, 6, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Banerjee, P.; Zhou, S. Specific glucose-to-SPR signal transduction at physiological pH by molecularly imprinted responsive hybrid microgels. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7115–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yi, J.; Velado, D.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, S. Immobilization of carbon dots in molecularly imprinted microgels for optical sensing of glucose at physiological pH. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15735–15745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Kahkoska, A.R.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Glucose-responsive insulin and delivery systems: Innovation and Translation. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1902004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, A.; Tanaka, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Ochi, K.; Moro-oka, Y.; Kuwata, H.; Yamada, H.; Shirakawa, I.; Miyazawa, T.; Ishii, H.; et al. Synthetic “smart gel” provides glucose-responsive insulin delivery in diabetic mice. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, eaaq0723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk-Wozniak, A.; Brzozka, Z.; Dabrowski, M.; Madura, I.D.; Scheidsbach, R.; Tomecka, E.; Zukowski, K.; Sporzynski, A. Influence of the ortho-methoxyalkyl substituent on the properties of phenylboronic acids. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1035, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Springsteen, G.; Deeter, S.; Wang, B. The relationship among pKa, pH, and binding constants in the interactions between boronic acids and diols—It is not as simple as it appears. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 11205–11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, J.F.; Hoth, A. Preparation of ideal PEG analogues with a tunable thermosensitivity by controlled radical copolymerization of 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl methacrylate and oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kureha, T.; Hayashi, K.; Ohira, M.; Li, X.; Shibayama, M. Dynamic fluctuations of thermoresponsive poly(oligo-ethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate)-based hydrogels investigated by dynamic light scattering. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 8932–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgakiran, E.; Tatlipinar, H. The role of hydrophobic hydration in the LCST behaviour of POEGMA300 by all-atom molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 15389–15399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, C.; Gunther, E.; Hiebler, S.; Ensari, O.F.; Kahraman, D. Polyethylene glycol-sugar composites as shape stabilized phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Polym. Compos. 2012, 33, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, S.; Patidar, R.; Ray, D.; Aswal, V.K.; Shah, S.A.; Ranjan, N.; Bahadur, P.; Tiwari, S. Monosaccharide-induced Growth and Higher Order Transitions in TPGS Micelles. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 632, 127792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, K.; Shinkai, S. Phase separation in the mixture of schizophyllan and poly(ethylene oxide) in aqueous solution driven by a specific interaction between the glucose side chain and poly(ethylene oxide). Carbohydr. Res. 2000, 324, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjoberg, A.; Karlstrom, G.; Tjerneld, F. Effects on the Cloud Point of Aqueous Poly(ethylene glycol) Solutions upon Addition of Low Molecular Weight Saccharides. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 4512–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Yamaguchi, A.; Midorikawa, H.; Kamijo, T.; Ono, T.; Dairaku, T.; Sato, T.; Fujimura, T.; Kashiwagi, Y.; Sato, K. Adsorption and Release of Rose Bengal on Layer-by-Layer Films of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and Poly(Amidoamine) Dendrimers Bearing 4-Carboxyphenylboronic Acid. Polymers 2020, 12, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J. Intelligent Nano/Microgels for Cell Scaffold and Drug Delivery System. Doctoral Dissertation, City University of New York, New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, B. Laser Light Scattering, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 13–61. [Google Scholar]



| Sample | VPBA (mmol) | DMAEA (mmol) | MEO5MA (mmol) | Molar Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBAEO-0 | 1.63 | 0.329 | − | 10/2/0 |
| PBAEO-1 | 1.63 | 0.329 | 0.163 | 10/2/1 |
| PBAEO-2 | 1.63 | 0.329 | 0.326 | 10/2/2 |
| PBAEO-3 | 1.63 | 0.329 | 0.489 | 10/2/3 |
| PBAEO-4 | 1.63 | 0.329 | 0.652 | 10/2/4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roy, P.G.; Zhang, J.; Bhattacharya, K.; Banerjee, P.; Shen, J.; Zhou, S. One-Pot Synthesis of Phenylboronic Acid-Based Microgels for Tunable Gate of Glucose-Responsive Insulin Release at Physiological pH. Molecules 2025, 30, 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153059
Roy PG, Zhang J, Bhattacharya K, Banerjee P, Shen J, Zhou S. One-Pot Synthesis of Phenylboronic Acid-Based Microgels for Tunable Gate of Glucose-Responsive Insulin Release at Physiological pH. Molecules. 2025; 30(15):3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153059
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoy, Prashun G., Jiangtao Zhang, Koushik Bhattacharya, Probal Banerjee, Jing Shen, and Shuiqin Zhou. 2025. "One-Pot Synthesis of Phenylboronic Acid-Based Microgels for Tunable Gate of Glucose-Responsive Insulin Release at Physiological pH" Molecules 30, no. 15: 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153059
APA StyleRoy, P. G., Zhang, J., Bhattacharya, K., Banerjee, P., Shen, J., & Zhou, S. (2025). One-Pot Synthesis of Phenylboronic Acid-Based Microgels for Tunable Gate of Glucose-Responsive Insulin Release at Physiological pH. Molecules, 30(15), 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153059







