Crucian Carp-Derived ACE-Inhibitory Peptides with In Vivo Antihypertensive Activity: Insights into Bioactivity, Mechanism, and Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
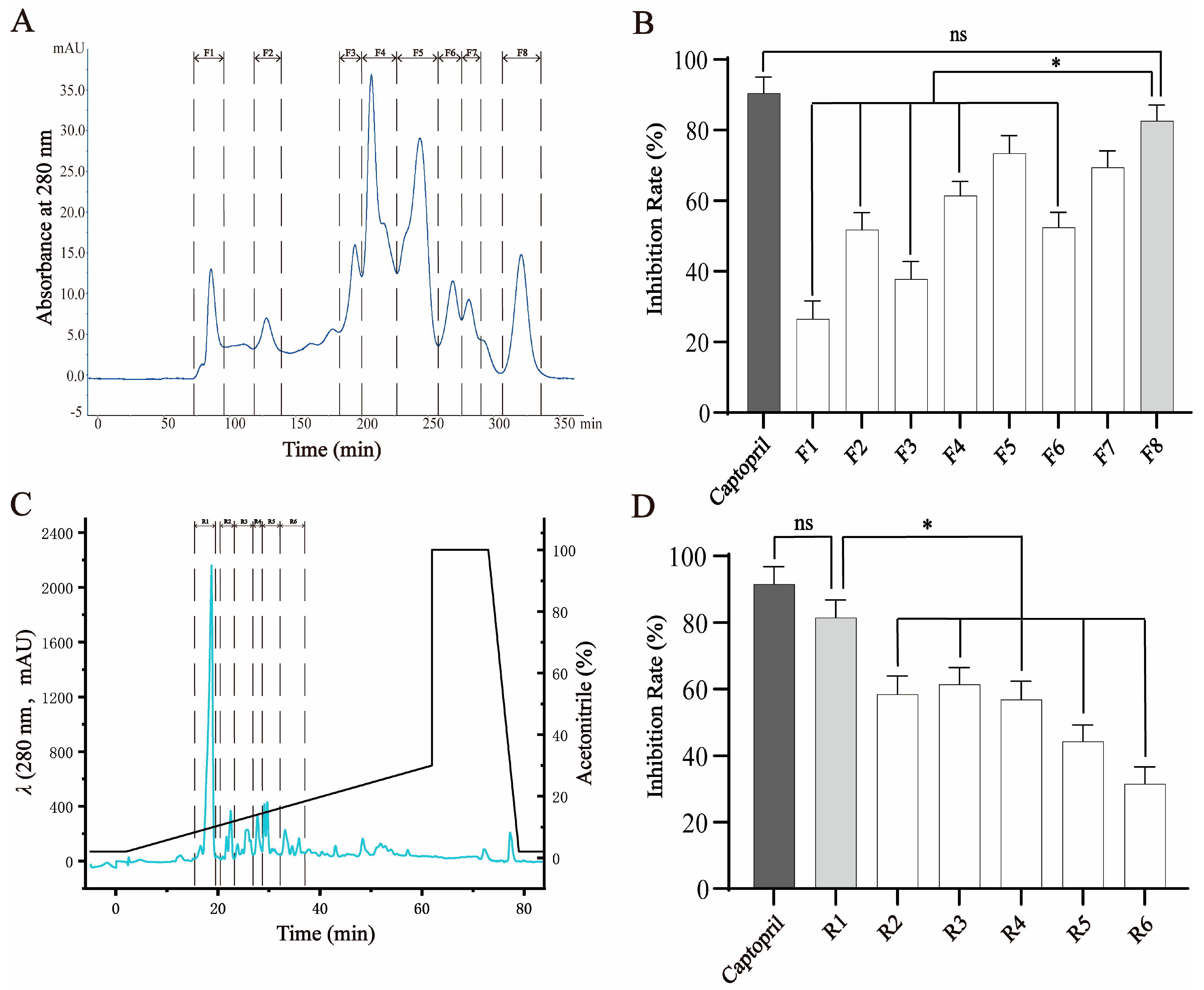
2.1. Isolation and Purification of ACE-Inhibitory Peptide
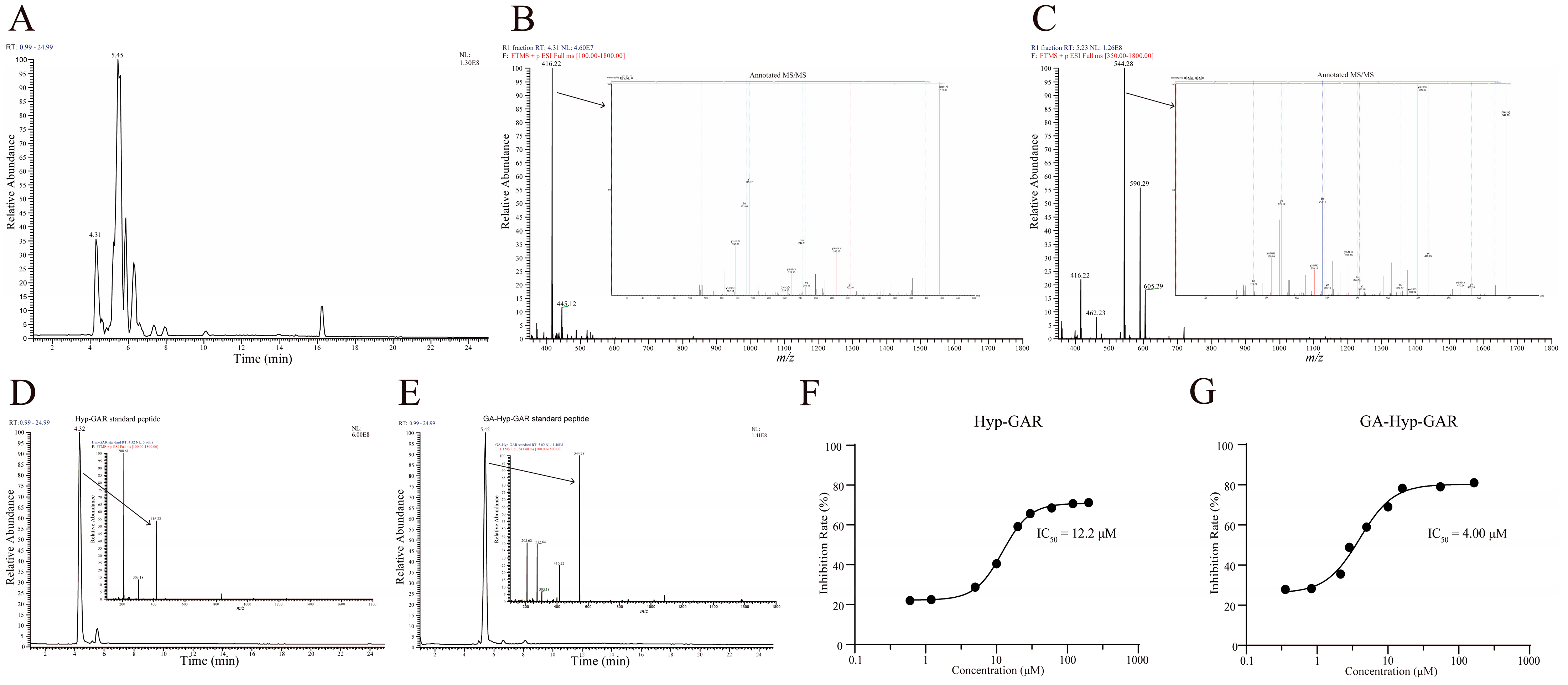
2.2. Identification and Validation of Peptides in R1 Fractions
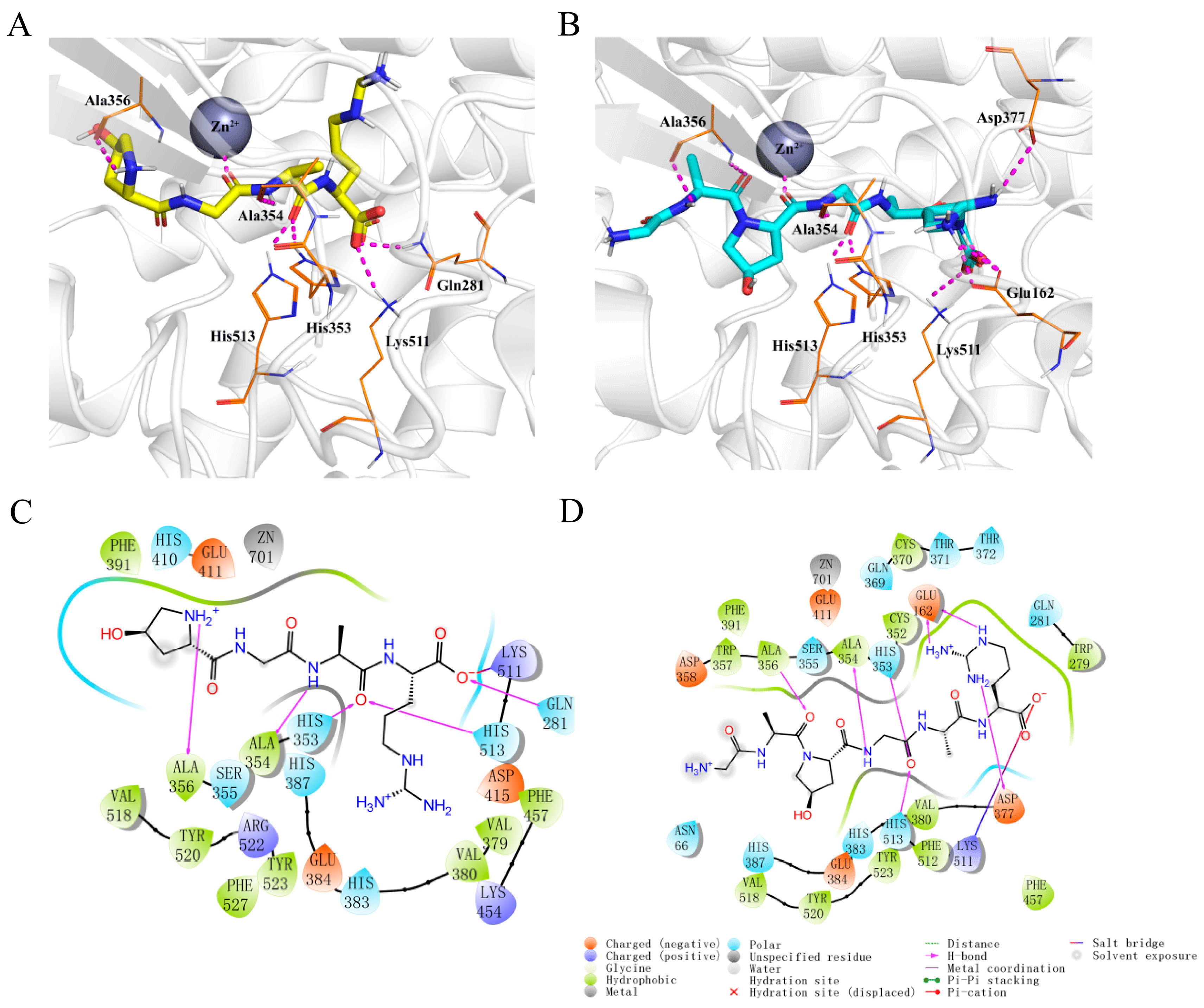
2.3. Molecular Docking of Hyp-GAR and GA-Hyp-GAR
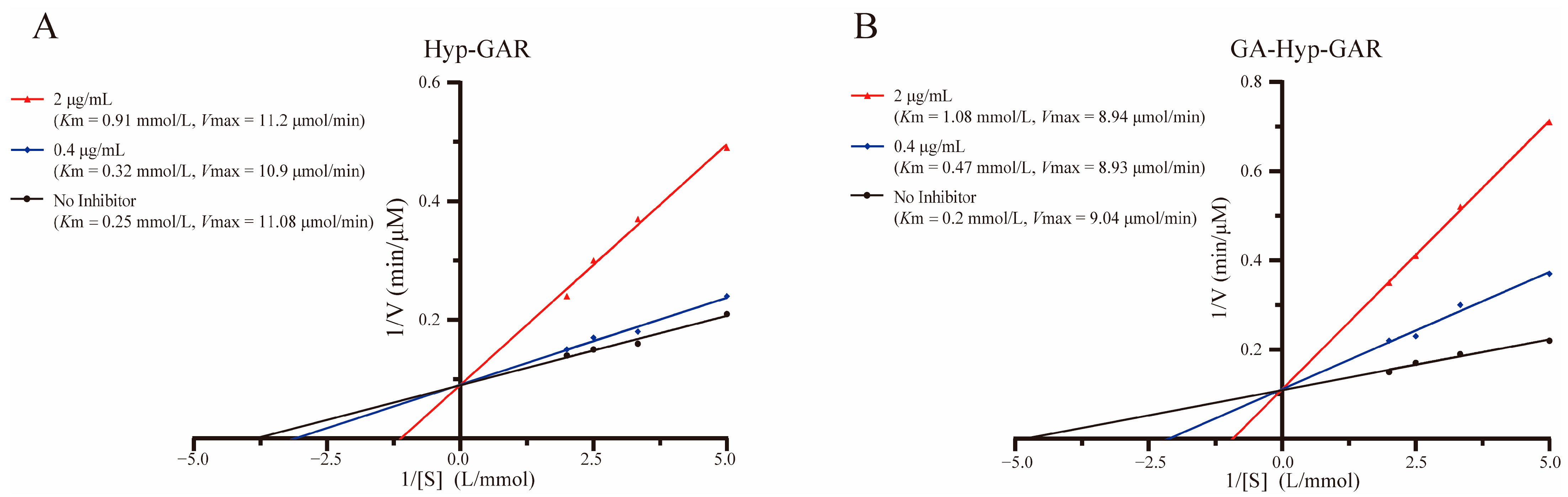
2.4. Inhibition Patterns of Hyp-GAR and GA-Hyp-GAR
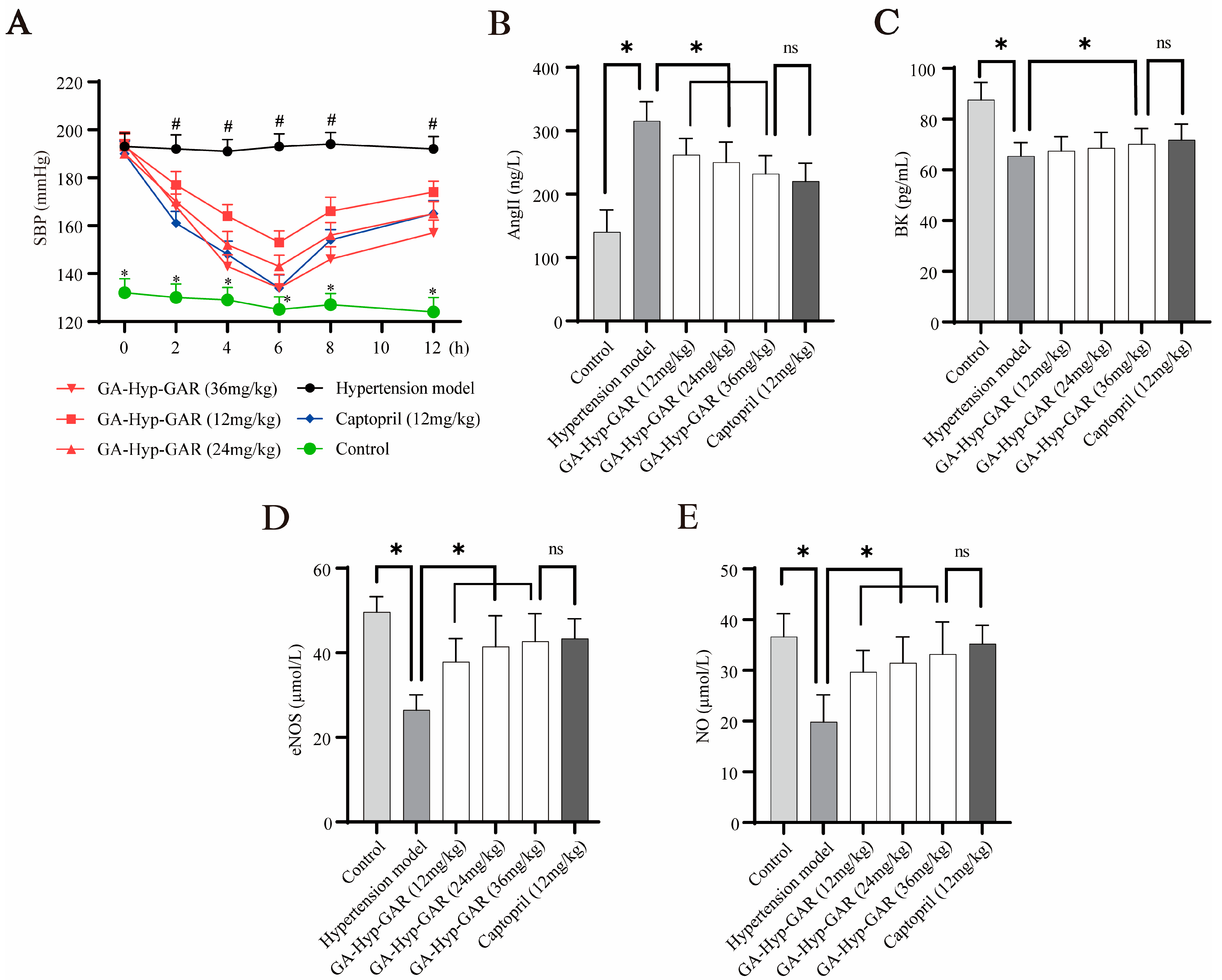
2.5. Antihypertensive Effect of GA-Hyp-GAR in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats and Its Impact on AngII, BK, eNOS, and NO
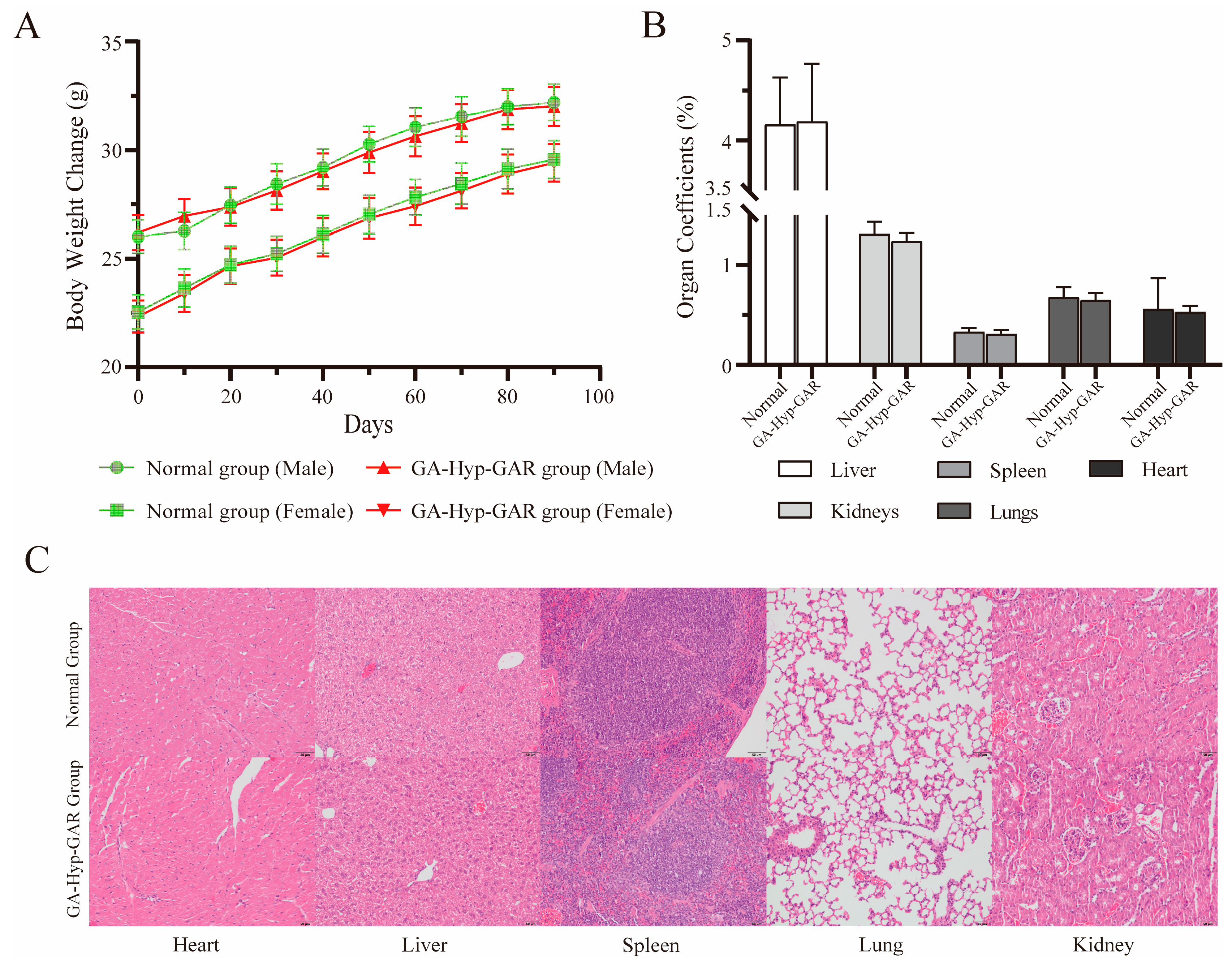
2.6. Long-Term Dosing Safety Evaluation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of Crucian Carp Swim Bladder Hydrolysate
4.3. ACE-Inhibitory Activity Assay
4.4. Purification of ACE Inhibitor Peptides by Chromatography
4.5. Peptide Identification and Synthesis
4.6. Molecular Docking
4.7. Determination of ACE Inhibition Pattern
4.8. Animal Experiment and Systolic Blood Pressure Measurement
4.9. Long-Term Dosing Safety Experiment
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin I-converting enzyme |
| AngII | Angiotensin II |
| BK | Bradykinin |
| HCSB | Hydrolysate of crucian carp swim bladder |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyethyl) piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid |
| FAPGG | N-[3-(2-Furyl) acryloyl]-Phe-Gly-Gly |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| RP-HPLC | Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography |
| UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap | Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with linear ion trap-Orbitrap tandem mass spectrometry |
| Hyp-GAR | Hydroxyproline-Gly-Ala-Arg |
| GA-Hyp-GAR | Gly-Ala-hydroxyproline-Gly-Ala-Arg |
| SHRs | Spontaneously hypertensive rats |
| WKY | Wistar-Kyoto |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| Vmax | Maximum reaction velocity |
| Km | Michaelis constant |
References
- Boateng, E.B.; Ampofo, A.G. A glimpse into the future: Modelling global prevalence of hypertension. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, E.B.; Ampofo, A.G. Adherence in hypertension: A review of prevalence, risk factors, impact, and management. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1124–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangid, M.K.; Doshi, G.M. Cross talk on therapeutic strategies: Natriuretic peptides and inhibiting neprilysin in hypertension management. Hypertens. Res. 2025, 48, 284–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, J.; Villarroel, C.; Asunción-Alvarez, D.; Cifuentes, F.; Paredes, A.; Nwokocha, C.R.; Castro-Álvarez, A.; Parra, C. Metabolites Isolated from Senecio nutans Sch. Bip and Their Synthesized Oximes Inhibit Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Activity in Vascular Smooth Muscle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.-W.; Chan, C.-K.; Lin, C.-H.; Lee, C.-F.; Lo, H.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Yeh, C.-F.; Chen, M.Y.-C.; Lai, T.-H.; Huang, K.-C.; et al. Evaluations of secondary hypertension and laboratory data in the elderly population. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.J. ACE inhibitor–induced angioedema: Current concepts in pathogenesis and treatment. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2017, 19, 912–917. [Google Scholar]
- Israili, Z.H.; Hall, W.D. Cough and angioneurotic edema associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy: A review of the literature and pathophysiology. Ann. Intern. Med. 1992, 117, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiuri, S.P.; Pierce, G.N. A review of the relative efficacy of dietary, nutritional supplements, lifestyle, and drug therapies in the management of hypertension. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3508–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Deussen, A. Effects of natural peptides from food proteins on angiotensin converting enzyme activity and hypertension. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1264–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-S.; Yang, W.-S.; Kim, C.-H. Beneficial effects of soybean-derived bioactive peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berselli, E.; Coccolini, C.; Tosi, G.; Gokce, E.H.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Fathi, F.; Krambeck, K.; Souto, E.B. Therapeutic Peptides and Proteins: Stabilization Challenges and Biomedical Applications by Means of Nanodelivery Systems. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2024, 30, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xiao, Z.; Ge, C.; Wu, Y. Animal by-products collagen and derived peptide, as important components of innovative sustainable food systems—A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 8703–8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Therkildsen, M.; Aluko, R.E.; Lametsch, R. Exploration of collagen recovered from animal by-products as a precursor of bioactive peptides: Successes and challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2011–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, G. Antihypertensive effects in vitro and in vivo of novel angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from bovine bone gelatin hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 68, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhan, F.; Hussain, Z.; Tauseef, I.; Shehzad, A.; Wahid, F. A review on recent advances and applications of fish collagen. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbi, Z.; Azmi, N.S.; Ming, L.C.; Hossain, M.S. A Concise Review of Extraction and Characterization of Chondroitin Sulphate from Fish and Fish Wastes for Pharmacological Application. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2022, 44, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Fishery Statistics Yearbook 2018; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Mo, W.Y.; Man, Y.B.; Wong, M.H. Use of food waste, fish waste and food processing waste for China’s aquaculture industry: Needs and challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Z. Collagen from Fish By-Products: Extraction and Characterization. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Dai, L.; Yu, F.-J.; Li, X.-N.; Wang, G.-X.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.-P. Chemical and Biological Characteristics of Hydrolysate of Crucian Carp Swim Bladder: Focus on Preventing Ulcerative Colitis. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 74, 104256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yu, F.; Wu, Y.; Dai, L.; Feng, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, G.; Ma, H.; Li, X.; Dai, C. Identification of a novel peptide that activates alcohol dehydrogenase from crucian carp swim bladder and how it protects against acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 207, 114426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehler, M.; Berard, M.; Feinstein, R.; Gallagher, A.; Illgen-Wilcke, B.; Pritchett-Corning, K.; Raspa, M.; Revision, F.W.G. FELASA recommendations for the health monitoring of mouse, rat, hamster, guinea pig and rabbit colonies in breeding and experimental units. Lab Anim. 2014, 48, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouse Phenome Database. The Jackson Laboratory. BALB/cByJ Strain Survey Data for Clinical Chemistry Traits. Available online: https://phenome.jax.org/ (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Okagu, I.U.; Ezeorba, T.P.C.; Aham, E.C.; Aguchem, R.N.; Nechi, R.N. Recent findings on the cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of novel food-derived antihypertensive peptides. Food Chem. 2022, 4, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Sun, X.; Udenigwe, C.C. Role of structural properties of bioactive peptides in their stability during simulated gastrointestinal digestion: A systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 120, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olalere, O.A.; Yap, P.-G.; Gan, C.-Y. Comprehensive review on some food-derived bioactive peptides with anti-hypertension therapeutic potential for angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition. J. Proteins Proteom. 2023, 14, 129–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huizen, N.A.; Ijzermans, J.N.M.; Burgers, P.C.; Luider, T.M. Collagen analysis with mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2020, 39, 309–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daskaya-Dikmen, C.; Yucetepe, A.; Karbancioglu-Guler, F.; Daskaya, H.; Ozcelik, B. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from plants. Nutrients 2017, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Hu, H.; Wang, Q.; Adhikari, B. Isolation, purification and molecular mechanism of a peanut protein-derived ACE-inhibitory peptide. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzihradszky, K.F.; Chalkley, R.J. Lessons in de novo peptide sequencing by tandem mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2015, 34, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.M.; Ibrahim, R.S.; Metwally, A.M.; Mahrous, R.S.R. In-depth in silico and in vitro screening of selected edible plants for identification of selective C-domain ACE-1 inhibitor and its synergistic effect with captopril. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiga, A.; Iwai, K.; Hayakawa, T.; Takahata, Y.; Kitamura, S.; Nishimura, T.; Morimatsu, F. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Peptides Obtained from Chicken Collagen Hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10211–10217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, S.J.; Booz, G.W.; Sigmund, C.D.; Coffman, T.M.; Kawai, T.; Rizzo, V.; Scalia, R.; Eguchi, S. Angiotensin II signal transduction: An update on mechanisms of physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1627–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancion, A.; Tridetti, J.; Nguyen Trung, M.-L.; Oury, C.; Lancellotti, P. A review of the role of bradykinin and nitric oxide in the cardioprotective action of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: Focus on perindopril. Cardiol. Ther. 2019, 8, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, S.; Bortolotto, L. Unraveling the pivotal role of bradykinin in ACE inhibitor activity. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2016, 16, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miralles, B.; Amigo, L.; Recio, I. Critical review and perspectives on food-derived antihypertensive peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9384–9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangsawad, P.; Roytrakul, S.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from the simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of cooked chicken breast. J. Funct. Foods. 2017, 29, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhang, K.; Hendrie, C.; Liang, C.; Li, M.; Doherty-Kirby, A.; Lajoie, G. PEAKS: Powerful software for peptide de novo sequencing by tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 2337–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesh, R.; Schwager, S.L.U.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal structure of the human angiotensin-converting enzyme–lisinopril complex. Nature 2003, 421, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory. Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zheng, L.; Huang, M.; Zhao, M. Collagen derived Gly-Pro-type DPP-IV inhibitory peptides: Structure-activity relationship, inhibition kinetics and inhibition mechanism. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Rivas-Serna, I.M.; Monirujjaman, M.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Mazurak, V.C.; Wu, J. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects of bioactive peptides IKW and RIY in spontaneously hypertensive rats and angiotensin II-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, I.; Maeda-Yamamoto, M.; Tachibana, H.; Kamei, M. Antihypertensive effect of Benifuuki tea containing O-methylated EGCG. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellagamba, O.; Guo, A.J.; Senthilkumar, S.; Lillevik, S.H.; De Biase, D.; Lai, K.; Balakrishnan, B. Assessment of Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Purple Sweet Potato Color (PSPC) and Myo-Inositol (MI) Treatment for Motor Related and Behavioral Phenotypes in a Mouse Model of Classic Galactosemia. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2025, 48, e70002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.L.; Li, H.; Li, X.X.; Cui, C.Y.; Wang, R.; Yu, N.X.; Chen, L.X. Acute and 30-day oral toxicity studies of administered carnosic acid. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 4348–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, M.; He, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, B.; Xu, W.; Yu, J.; Chen, S.; et al. The beneficial effects of Polygonatum sibiricum Red. superfine powder on metabolic hypertensive rats via gut-derived LPS/TLR4 pathway inhibition. Phytomedicine 2022, 106, 154404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Normal Group | GA-Hyp-GAR Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hematological Parameters | |||
| Red Blood Cells (×1012/L) | 10.71 ± 0.83 | 11.13 ± 0.73 | 0.2451 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width—SD (fL) | 32.81 ± 11.68 | 31.99 ± 7.11 | 0.8517 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width—CV (fL) | 26.58 ± 1.94 | 25.95 ± 1.49 | 0.4260 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 167.60 ± 13.10 | 174.70 ± 10.50 | 0.1978 |
| Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (pg) | 15.65 ± 0.32 | 15.70 ± 0.27 | 0.7101 |
| Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (g/L) | 341.80 ± 15.10 | 355.90 ± 5.50 | 0.7101 |
| White Blood Cells (×10⁹/L) | 4.28 ± 1.72 | 3.66 ± 1.19 | 0.3610 |
| Platelet Count (×10⁹/L) | 675.50 ± 200.50 | 683.40 ± 140.00 | 0.9198 |
| Mean Platelet Volume (fL) | 2.05 ± 3.45 | 2.09 ± 3.52 | 0.9798 |
| Platelet Distribution Width (fL) | 2.91 ± 4.95 | 3.09 ± 5.00 | 0.9364 |
| Plateletcrit (%) | 0.16 ± 0.27 | 0.16 ± 0.26 | >0.9999 |
| Platelet Large Cell Ratio (%) | 3.62 ± 6.29 | 3.65 ± 6.26 | 0.9916 |
| Serum Biochemical Parameters | |||
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (µkat/L) | 2.48 ± 1.03 | 2.44 ± 0.96 | 0.9294 |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (nkat/L) | 684.30 ± 288.39 | 701.81 ± 316.56 | 0.8986 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (µkat/L) | 3.32 ± 0.65 | 2.99 ± 0.46 | 0.2065 |
| Blood Urea Nitrogen (mmol/L) | 7.81 ± 1.53 | 8.13 ± 1.33 | 0.6237 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 14.70 ± 5.80 | 18.13 ± 6.76 | 0.2390 |
| Total Protein (g/L) | 58.21 ± 3.77 | 58.16 ± 2.09 | 0.9711 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 35.24 ± 1.32 | 35.60 ± 1.01 | 0.5021 |
| Total Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 2.47 ± 0.23 | 2.32 ± 0.25 | 0.1796 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.94 ± 0.40 | 2.35 ± 0.48 | 0.0526 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 5.69 ± 3.38 | 7.79 ± 3.11 | 0.1654 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, R.; Tian, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhou, G.; Dai, C.; Wang, C. Crucian Carp-Derived ACE-Inhibitory Peptides with In Vivo Antihypertensive Activity: Insights into Bioactivity, Mechanism, and Safety. Molecules 2025, 30, 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132812
Han R, Tian J, Han Y, Wang G, Zhou G, Dai C, Wang C. Crucian Carp-Derived ACE-Inhibitory Peptides with In Vivo Antihypertensive Activity: Insights into Bioactivity, Mechanism, and Safety. Molecules. 2025; 30(13):2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132812
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Runxi, Jingshan Tian, Yingge Han, Guoxiang Wang, Guanghong Zhou, Chen Dai, and Chong Wang. 2025. "Crucian Carp-Derived ACE-Inhibitory Peptides with In Vivo Antihypertensive Activity: Insights into Bioactivity, Mechanism, and Safety" Molecules 30, no. 13: 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132812
APA StyleHan, R., Tian, J., Han, Y., Wang, G., Zhou, G., Dai, C., & Wang, C. (2025). Crucian Carp-Derived ACE-Inhibitory Peptides with In Vivo Antihypertensive Activity: Insights into Bioactivity, Mechanism, and Safety. Molecules, 30(13), 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30132812






